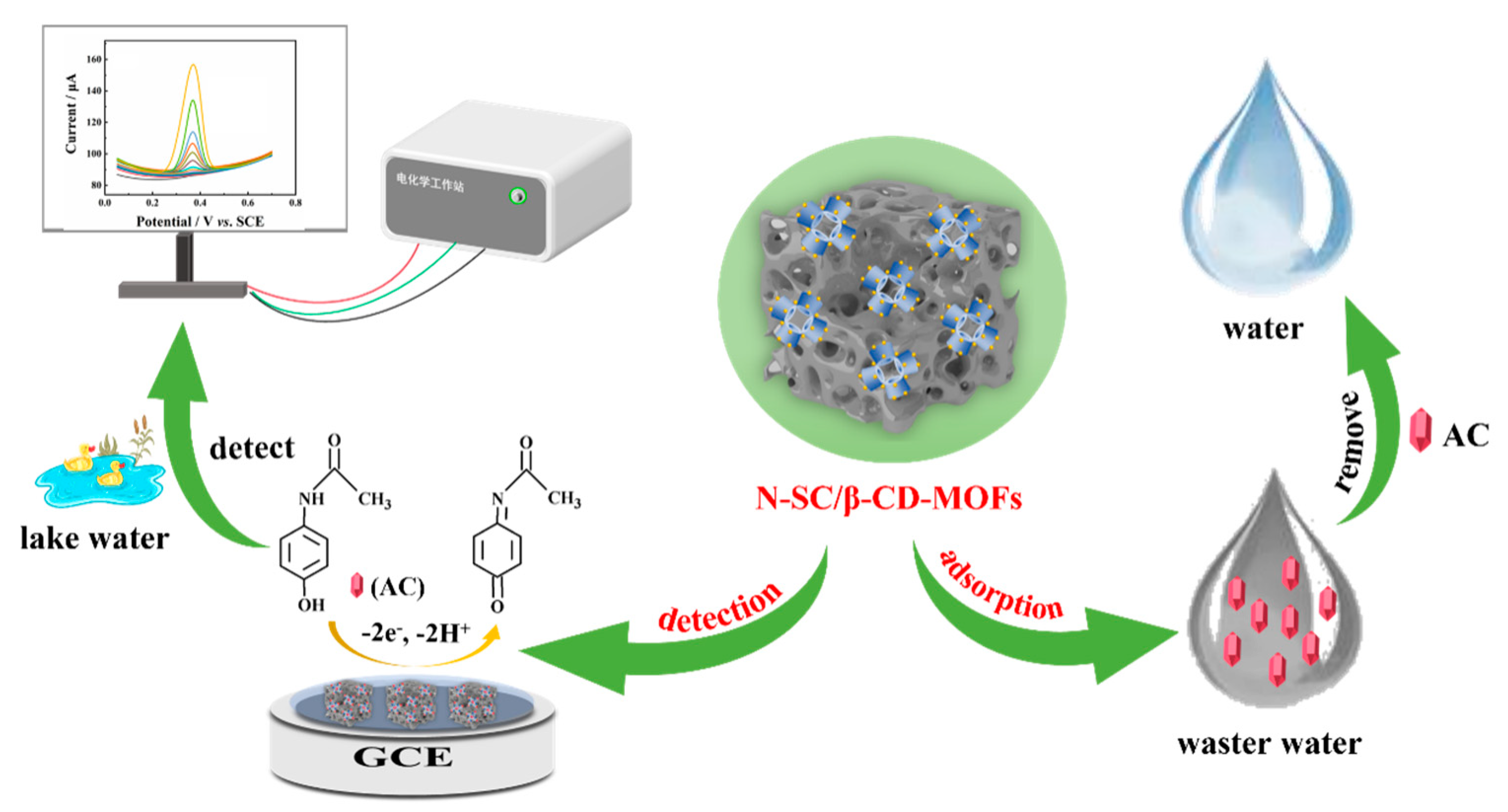
Nitrogen Doped Porous Biochar/β-CD-MOFs Heterostructures: Bi-Functional Material for Highly Sensitive Electrochemical Detection and Removal of Acetaminophen
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Result and Discussion
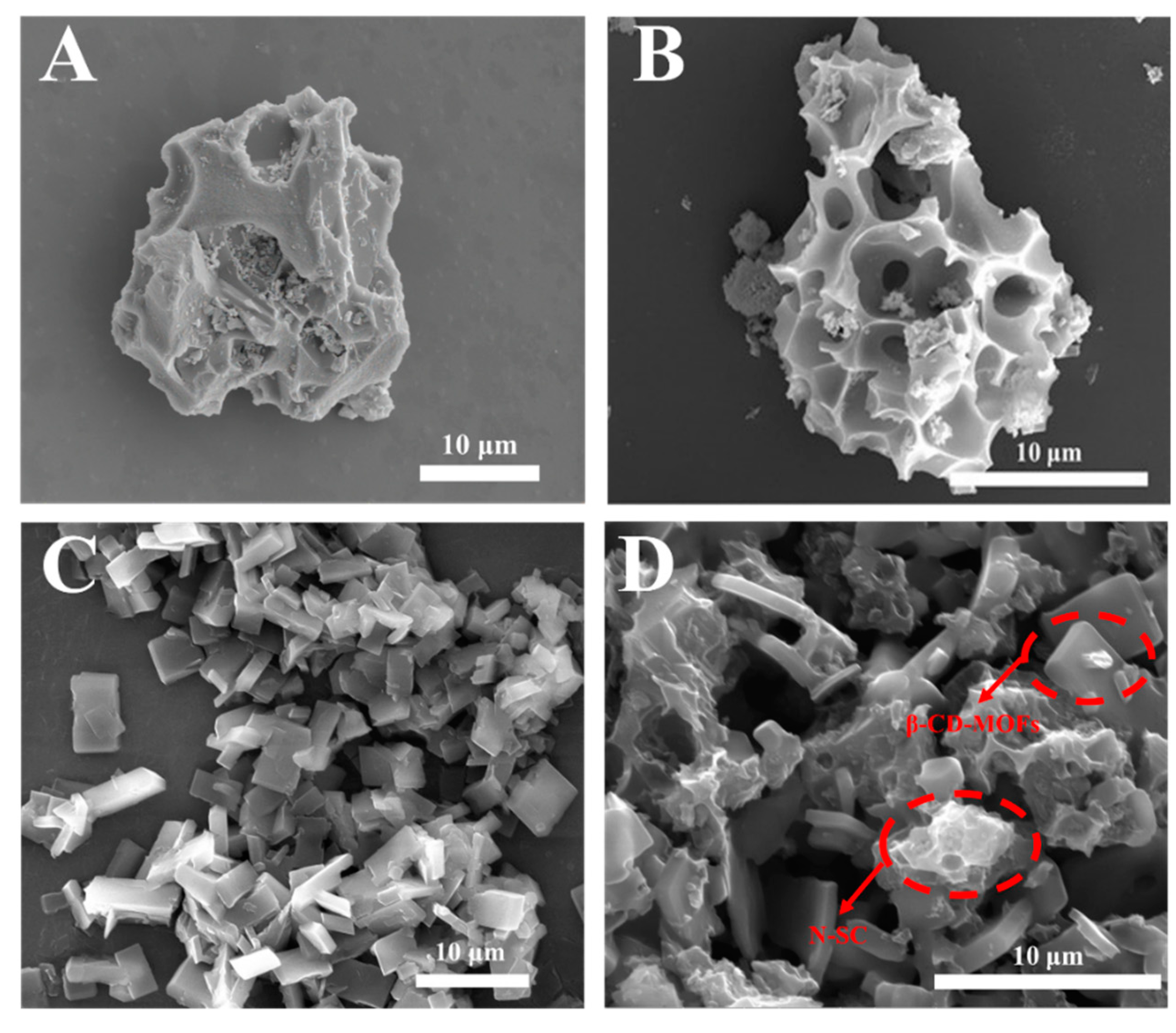
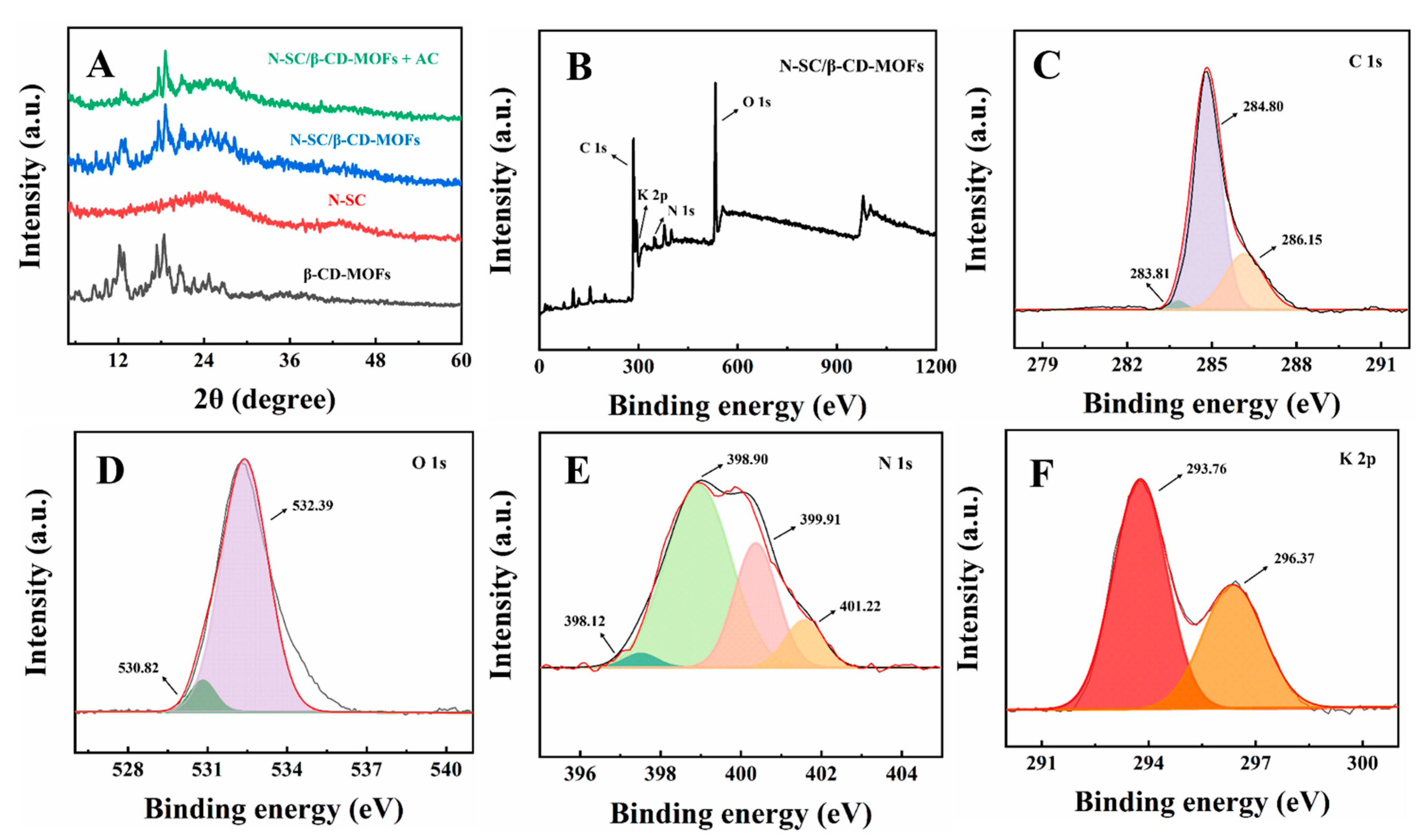
2.1. Material Characterization
2.2. Adsorption Studies
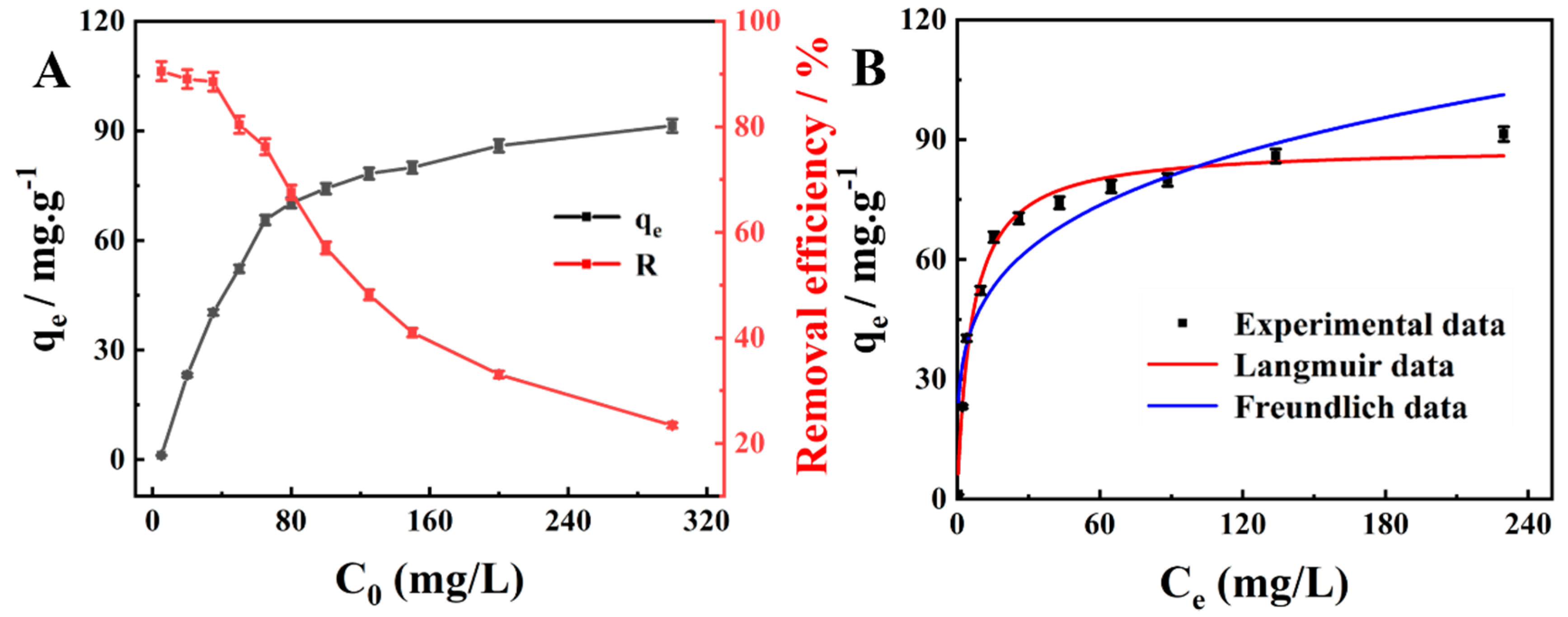
2.2.1. Effect of Adsorption Conditions
2.2.2. Adsorption Kinetics
2.2.3. Adsorption Isotherm Analysis
2.2.4. Adsorption Mechanism
2.2.5. Desorption Studies
2.3. Electrochemical Detection of AC Based on N-SC/β-CD-MOFs/GCE
2.3.1. Electrochemical Characterization of Various Modified Electrodes
2.3.2. Electrochemical Behaviors of AC on Various Electrodes
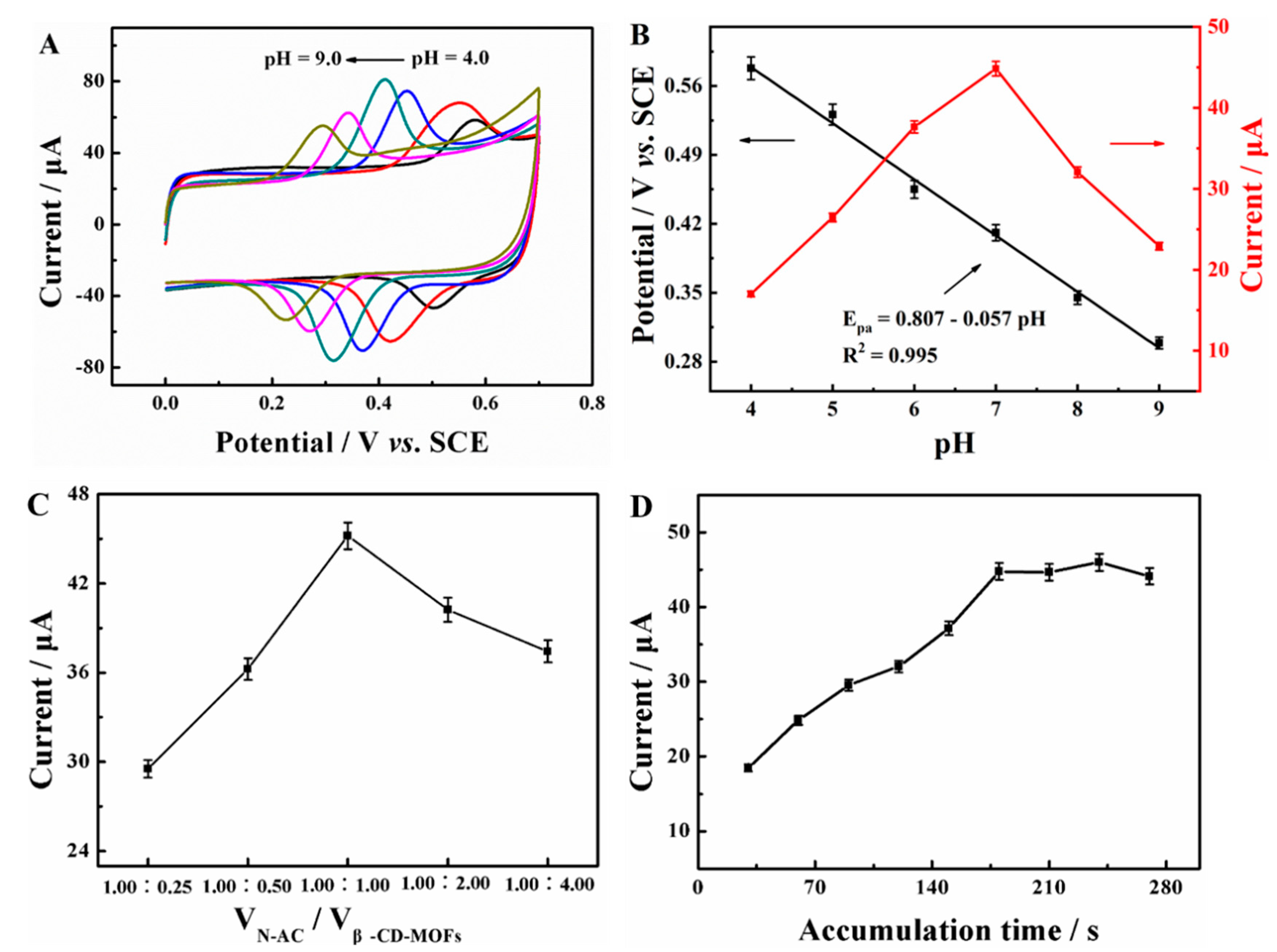
2.3.3. Optimization of Experiment Parameters
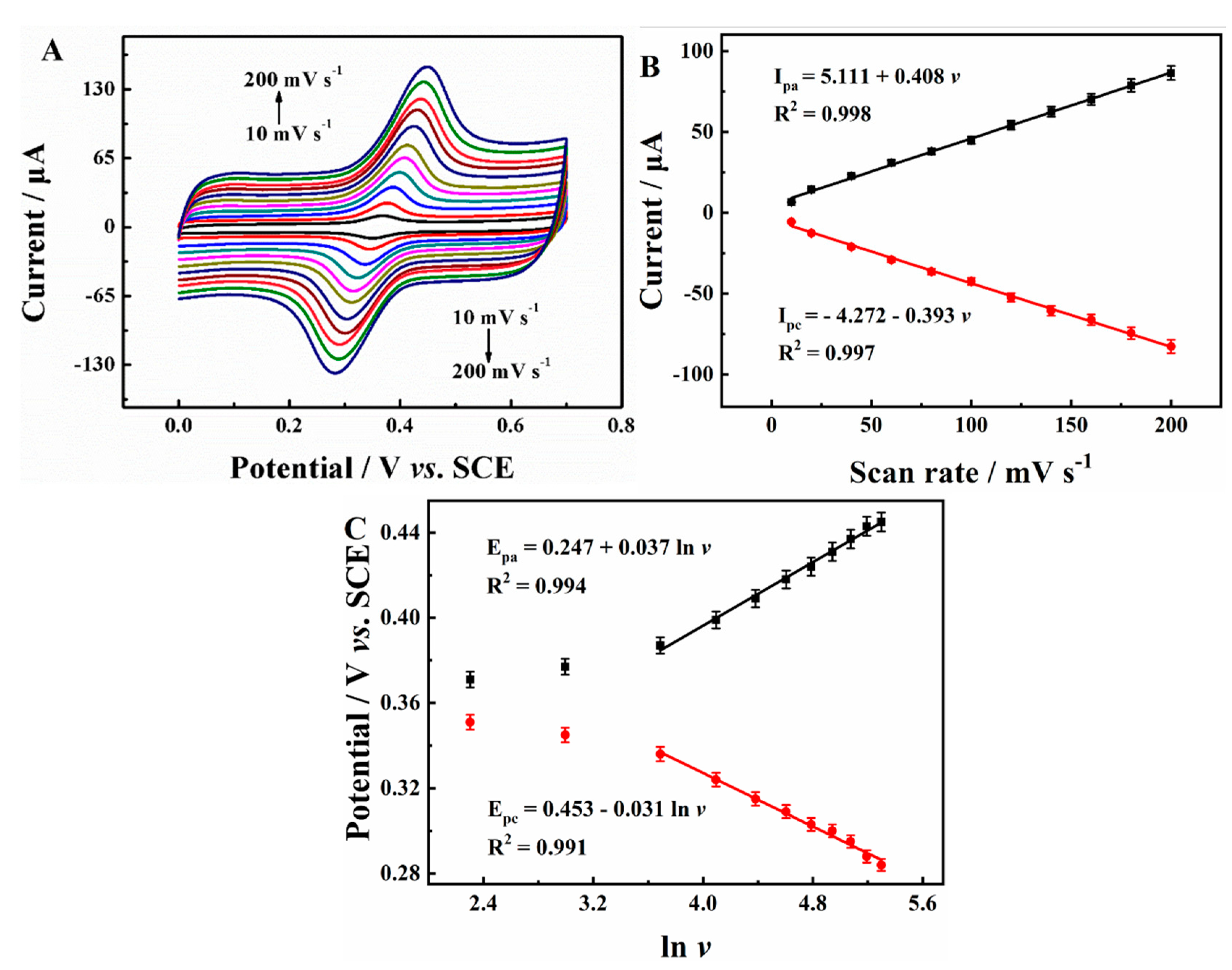
2.3.4. Electrocatalytic Mechanism of AC on N-SC/β-CD-MOFs/GCE
2.3.5. Electrochemical Detection of AC Based on N-SC/β-CD-MOFs/GCE
2.3.6. Reproducibility, Repeatability, Stability and Anti-Interference of N-SC/β-CD-MOFs/GCE
2.3.7. Real Samples Analysis
3. Experimental
3.1. Reagents
3.2. Apparatuses
3.3. Preparation of N-SC
3.4. Preparation of β-CD-MOFs
3.5. Preparation of N-SC/β-CD-MOFs
3.6. Adsorption Studies of AC
3.7. Desorption Studies of AC
3.8. Preparation of Modified Electrodes
3.9. Preparation of Real Samples
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pandey, J.; Ali, A.; Gupta, A.K. Synthesis and evaluation of some new 2-(5-(4-benzamidobenzylidene)-2,4-dioxothiazolidin-3-YL) acetic acid analogs as aldose reductase inhibitors. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2017, 10, 62–66. [Google Scholar]
- Badri, W.; Miladi, K.; Nazari, Q.A.; Greige-Gerges, H.; Fessi, H.; Elaissari, A. Encapsulation of NSAIDs for inflammation management: Overview, progress, challenges and prospects. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 515, 757–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, M.; Kumar, R.; Pittman, C.J.; Mohan, D. Ciprofloxacin and acetaminophen sorption onto banana peel biochars: Environmental and process parameter influences. Environ. Res. 2021, 201, 111218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Avilés, A.; Sellaoui, L.; Badawi, M.; Bonilla-Petriciolet, A.; Bedia, J.; Belver, C. Simultaneous adsorption of acetaminophen, diclofenac and tetracycline by organo-sepiolite: Experiments and statistical physics modelling. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 404, 126601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Kim, J.M.; Jeon, Y.; Lee, J.; Oh, J.; Hooch Antink, W.; Kim, D.; Piao, Y. Novel two-step activation of biomass-derived carbon for highly sensitive electrochemical determination of acetaminophen. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 259, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinke, C.; Zanicoski-Moscardi, A.P.; de Oliveira, P.R.; Mangrich, A.S.; Marcolino-Junior, L.H.; Bergamini, M.F. Simple and low-cost sensor based on activated biochar for the stripping voltammetric detection of caffeic acid. Microchem. J. 2020, 159, 105380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abay, İ.; Denizli, A.; Bişkin, E.; Salih, B. Removal and pre-concentration of phenolic species onto β-cyclodextrin modified poly(hydroxyethylmethacrylate–ethyleneglycoldimethacrylate) microbeads. Chemosphere 2005, 61, 1263–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, A.U.; Howlader, M.M.R.; Hu, N.; Deen, M.J. Electrochemical sensing of lead in drinking water using β-cyclodextrin-modified MWCNTs. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 296, 126632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, A.U.; Qin, Y.; Howlader, M.M.R.; Hu, N.; Deen, M.J. Electrochemical sensing of acetaminophen using multi-walled carbon nanotube and β-cyclodextrin. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 254, 896–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, P.; Liu, X.; Yi, X.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, D. Multifunctional β-Cyclodextrin MOF-Derived Porous Carbon as Efficient Herbicides Adsorbent and Potassium Fertilizer. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 14479–14489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, X.; Gao, F.; Ma, X.; Zou, J.; Yu, Y.; Li, M.; Qu, F.; Huang, X.; Lu, L. Mxene/carbon nanohorn/β-cyclodextrin-Metal-organic frameworks as high-performance electrochemical sensing platform for sensitive detection of carbendazim pesticide. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 396, 122776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vithanage, M.; Herath, I.; Joseph, S.; Bundschuh, J.; Bolan, N.; Ok, Y.S.; Kirkham, M.B.; Rinklebe, J. Interaction of arsenic with biochar in soil and water: A critical review. Carbon 2017, 113, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Hei, Y.; Liu, J.; Sun, M.; Sha, T.; Hassan, M.; Bo, X.; Guo, Y.; Zhou, M. Low-cost and environment-friendly synthesis of carbon nanorods assembled hierarchical meso-macroporous carbons networks aerogels from natural apples for the electrochemical determination of ascorbic acid and hydrogen peroxide. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1047, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Zang, Y.; Ruan, S.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, P.; Yin, W.; Hou, C.; Huo, D.; Yang, M.; Fa, H. A high efficiency N, P doped porous carbon nanoparticles derived from lotus leaves for simultaneous electrochemical determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine, and uric acid. Microchem. J. 2021, 165, 106152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Liu, J.; Yu, Q.; Gao, Y.; Chen, S.; Huang, X.; Hu, D.; Liu, S.; Lu, L. Facile Synthesis of Nitrogen Self-Doped Porous Carbon Derived from Cicada Shell via KOH Activation for Simultaneous Detection and Removal of Cu2+. Molecules 2022, 27, 4516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.X.; Du, S.M.; Cao, J.; Huang, W.S.; Zhang, X.R.; Qi, B.P.; Zhang, S.H. Simultaneous Determination of Hydroquinone and Catechol by N-doped Porous Biochar-modified Electrode. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2020, 41, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nourmoradi, H.; Moghadam, K.F.; Jafari, A.; Kamarehie, B. Removal of acetaminophen and ibuprofen from aqueous solutions by activated carbon derived from Quercus Brantii (Oak) acorn as a low-cost biosorbent. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 6807–6815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Zou, J.; Peng, G.; Gao, F.; Gao, Y.; Fan, G.; Chen, S.; Lu, L. A facile fabrication of ratiometric electrochemical sensor for sensitive detection of riboflavin based on hierarchical porous biochar derived from KOH-activated Soulangeana sepals. Nanotechnology 2022, 33, 445501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makul, N. Waste-derived activators for alkali-activated materials: A review. Cement Concrete Comp. 2021, 118, 103980. [Google Scholar]
- Dos Reis, G.S.; Guy, M.; Mathieu, M.; Jebrane, M.; Lima, E.C.; Thyrel, M.; Dotto, G.L.; Larsson, S.H. A comparative study of chemical treatment by MgCl2, ZnSO4, ZnCl2, and KOH on physicochemical properties and acetaminophen adsorption performance of biobased porous materials from tree bark residues. Colloid Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 642, 128626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, D.R.; Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A.; Thue, P.S.; Lima, E.C.; de Albuquerque, Y.R.T.; Dos Reis, G.S.; Umpierres, C.S.; Dias, S.L.P.; Tran, H.N. Efficient acetaminophen removal from water and hospital effluents treatment by activated carbons derived from Brazil nutshells. Colloid Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 583, 123966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, T.; Li, Y.; Dong, Z.; Lanju, S.; Shengliang, Z.; Wei, Z.; Xiao, W.; Wei, Q.D.; Hao, W. MXene-Derived Metal-Organic Framework@Mxene Heterostructures toward Electrochemical NO Sensing. Small 2022, 18, 2204942. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, S.; Liu, Y. Adsorption of CO2 from flue gas by novel seaweed-based KOH-activated porous biochars. Fuel 2020, 260, 116382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Wu, L.; Guo, T.; Wang, C.; Wu, W.; Tang, Y.; Xiong, T.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, J. Crystal Transformation of β-CD-MOF Facilitates Loading of Dimercaptosuccinic Acid. AAPS PharmSciTech 2019, 20, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Kim, I.Y.; Lakhi, K.S.; Srivastava, P.; Naidu, R.; Vinu, A. Single step synthesis of activated bio-carbons with a high surface area and their excellent CO2 adsorption capacity. Carbon 2017, 116, 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liang, X.; Chang, Z.; Ding, L.; Zhang, S.; Li, B. Effective Formaldehyde Capture by Green Cyclodextrin-Based Metal–Organic Framework. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Pei, F.; Feng, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, F.; Hao, Q.; Xia, M.; Lei, W. Simultaneous determination of riboflavin and chloramphenicol by MoS2 nanosheets decorated three-dimensional porous carbon: Reaction mechanism insights by computational simulation. Colloid Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 628, 127291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Y.; Hei, Y.; Wang, N.; Liu, J.; Ma, C. Synthesis of a clustered carbon aerogel interconnected by carbon balls from the biomass of taros for construction of a multi-functional electrochemical sensor. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1164, 338514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Lv, N.; Li, X.; Liu, B.; Feng, J.; Ren, X.; Guo, T.; Chen, D.; Fraser, S.J.; Gref, R.; et al. Composite CD-MOF nanocrystals-containing microspheres for sustained drug delivery. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 7454–7463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernal, V.; Erto, A.; Giraldo, L.; Moreno-Piraján, J. Effect of Solution pH on the Adsorption of Paracetamol on Chemically Modified Activated Carbons. Molecules 2017, 22, 1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, N.; Nasir, M. Effective removal of acetaminophen from aqueous solution using Ca (II)-doped chitosan/β-cyclodextrin composite. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 301, 112454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.; Lim, Y.; Ngadi, N.; Mat, R.; Hassan, O.; Inuwa, I.M.; Mohamed, N.B.; Low, J.H. Removal of acetaminophen by activated carbon synthesized from spent tea leaves: Equilibrium, kinetics and thermodynamics studies. Powder Technol. 2018, 338, 878–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem. 1999, 34, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Araújo, T.P.; Quesada, H.B.; Bergamasco, R.; Vareschini, D.T.; de Barros, M.A.S.D. Activated hydrochar produced from brewer’s spent grain and its application in the removal of acetaminophen. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 310, 123399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foo, K.Y.; Hameed, B.H. Insights into the modeling of adsorption isotherm systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 156, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Liao, B.; Lin, L.; Qiu, W.; Song, Z. Adsorption of Cu(II) and Cd(II) from aqueous solutions by ferromanganese binary oxide–biochar composites. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 615, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.T.; Tran, H.N.; Juang, R.; Dat, N.D.; Tomul, F.; Ivanets, A.; Woo, S.H.; Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A.; Nguyen, V.P.; Chao, H. Adsorption process and mechanism of acetaminophen onto commercial activated carbon. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Chu, M.; Xin, J.; Wang, X.; Halloran, K.P.O.; Ma, H.; Pang, H.; Tan, L.; Yang, G. Hierarchical and hollow boron/nitrogen co-doped yolk-shell mesoporous carbon nanospheres attached to reduced graphene oxide with high sensing performance for the simultaneous detection of xanthine and guanosine. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 343, 130068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nematollahi, D.; Shayani-Jam, H.; Alimoradi, M.; Niroomand, S. Electrochemical oxidation of acetaminophen in aqueous solutions: Kinetic evaluation of hydrolysis, hydroxylation and dimerization processes. Electrochim. Acta 2009, 54, 7407–7415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laviron, E. Adsorption, autoinhibition and autocatalysis in polarography and in linear potential sweep voltammetry. J. Electroanalyt. Chem. Interfacial Electrochem. 1974, 52, 355–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, A.; Taoufik, N.; García, A.M.; Korili, S.A. Comparative removal of emerging contaminants from aqueous solution by adsorption on an activated carbon. Environ Technol. 2019, 40, 3017–3030. [Google Scholar]
- Rakić, V.; Rac, V.; Krmar, M.; Otman, O.; Auroux, A. The adsorption of pharmaceutically active compounds from aqueous solutions onto activated carbons. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 282, 141–149. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Wei, X.; Zhang, R.; Wu, Y.; Farid, M.U.; Huang, H. Comparison of chemical, ultrasonic and thermal regeneration of carbon nanotubes for acetaminophen, ibuprofen, and triclosan adsorption. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 52719–52728. [Google Scholar]
- Al-rimawi, F.; Daana, M.; Khamis, M.; Karaman, R.; Khoury, H.; Qurie, M. Removal of Selected Pharmaceuticals from Aqueous Solutions Using Natural Jordanian Zeolite. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2019, 44, 209–215. [Google Scholar]
- Quesada, H.B.; Cusioli, L.F.; O Bezerra, C.; Baptista, A.T.; Nishi, L.; Gomes, R.G.; Bergamasco, R. Acetaminophen adsorption using a low‐cost adsorbent prepared from modified residues of Moringa oleifera Lam. seed husks. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2019, 94, 3147–3157. [Google Scholar]
- Coimbra, R.; Escapa, C.; Otero, M. Adsorption Separation of Analgesic Pharmaceuticals from Ultrapure and Waste Water: Batch Studies Using a Polymeric Resin and an Activated Carbon. Polymers 2018, 10, 958. [Google Scholar]
- Yanyan, L.; Kurniawan, T.A.; Zhu, M.; Ouyang, T.; Avtar, R.; Dzarfan Othman, M.H.; Mohammad, B.T.; Albadarin, A.B. Removal of acetaminophen from synthetic wastewater in a fixed-bed column adsorption using low-cost coconut shell waste pretreated with NaOH, HNO3, ozone, and/or chitosan. J. Environ. Manage. 2018, 226, 365–376. [Google Scholar]
- Venkatachalam, R.; Annadurai, T.; Nesakumar, N.; Vembu, S. Fortified electrochemical activity of Au@Fe3O4@rGO decorated GCE for sensing of acetaminophen. Mater. Today Commun. 2021, 27, 102236. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, W.; Liu, L.; Li, Y.; Ren, H.; Zhu, T.; Xu, Y.; Ye, B. Nitrogen-rich porous carbon modified electrochemical sensor for the detection of acetaminophen. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2019, 855, 113496. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, F.; Zou, J.; Zhong, W.; Tu, X.; Huang, X.; Yu, Y.; Wang, X.; Lu, L.; Bai, L. Prussian blue-carboxylated MWCNTs/ZIF-67 composite: A new electrochemical sensing platform for paracetamol detection with high sensitivity. Nanotechnology 2020, 32, 085501. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Lv, X.; Lei, W.; Ding, Y.; Chen, C.; Lv, J.; Feng, S.; Chen, S.; Hao, Q. A sensitive sensing platform for acetaminophen based on palladium and multi-walled carbon nanotube composites and electrochemical detection mechanism. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 239, 121977. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, K.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, L. Phosphorus-doped graphene-based electrochemical sensor for sensitive detection of acetaminophen. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2018, 1036, 26–32. [Google Scholar]

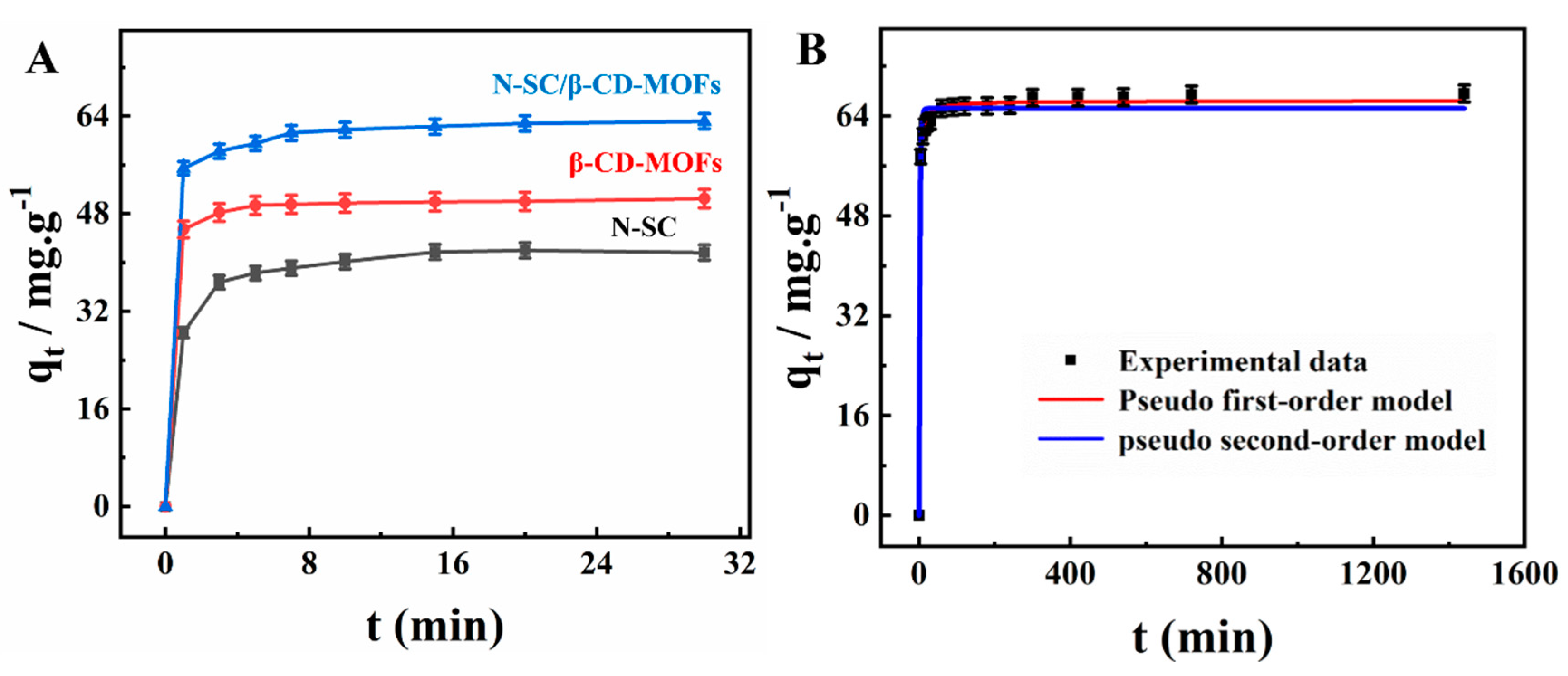


| Pseudo First-Order Model | Pseudo Second-Order Model | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qe,exp (mg⋅g−1) | k1 (min−1) | R2 | qe (mg⋅g−1) | k2 (g/mg⋅min) | R2 | qe (mg⋅g−1) |
| 67.61 | 0.4020 | 0.9864 | 65.19 | 0.0169 | 0.9975 | 66.41 |
| Langmuir | Freundlich | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qe (mg/g) | KL (L/mg) | R2 | 1/n | KF (mg/g) | R2 |
| 66.43 | 0.1658 | 0.9851 | 0.2376 | 27.82 | 0.8717 |
| Desorbing Agents | Desorption Efficiency (%) |
|---|---|
| NaOH (0.2 M) | 29.3 |
| HCl (0.2 M) | 9.72 |
| NaCl (0.2 M) | 5.33 |
| Ethanol | 62.1 |
| Methanol | 58.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, Q.; Zou, J.; Yu, C.; Peng, G.; Fan, G.; Wang, L.; Chen, S.; Lu, L.; Wang, Z. Nitrogen Doped Porous Biochar/β-CD-MOFs Heterostructures: Bi-Functional Material for Highly Sensitive Electrochemical Detection and Removal of Acetaminophen. Molecules 2023, 28, 2437. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062437
Yu Q, Zou J, Yu C, Peng G, Fan G, Wang L, Chen S, Lu L, Wang Z. Nitrogen Doped Porous Biochar/β-CD-MOFs Heterostructures: Bi-Functional Material for Highly Sensitive Electrochemical Detection and Removal of Acetaminophen. Molecules. 2023; 28(6):2437. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062437
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Qi, Jin Zou, Chenxiao Yu, Guanwei Peng, Guorong Fan, Linyu Wang, Shangxing Chen, Limin Lu, and Zongde Wang. 2023. "Nitrogen Doped Porous Biochar/β-CD-MOFs Heterostructures: Bi-Functional Material for Highly Sensitive Electrochemical Detection and Removal of Acetaminophen" Molecules 28, no. 6: 2437. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062437
APA StyleYu, Q., Zou, J., Yu, C., Peng, G., Fan, G., Wang, L., Chen, S., Lu, L., & Wang, Z. (2023). Nitrogen Doped Porous Biochar/β-CD-MOFs Heterostructures: Bi-Functional Material for Highly Sensitive Electrochemical Detection and Removal of Acetaminophen. Molecules, 28(6), 2437. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062437








