Engineered Graphene Quantum Dots as a Magnetic Resonance Signal Amplifier for Biomedical Imaging
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
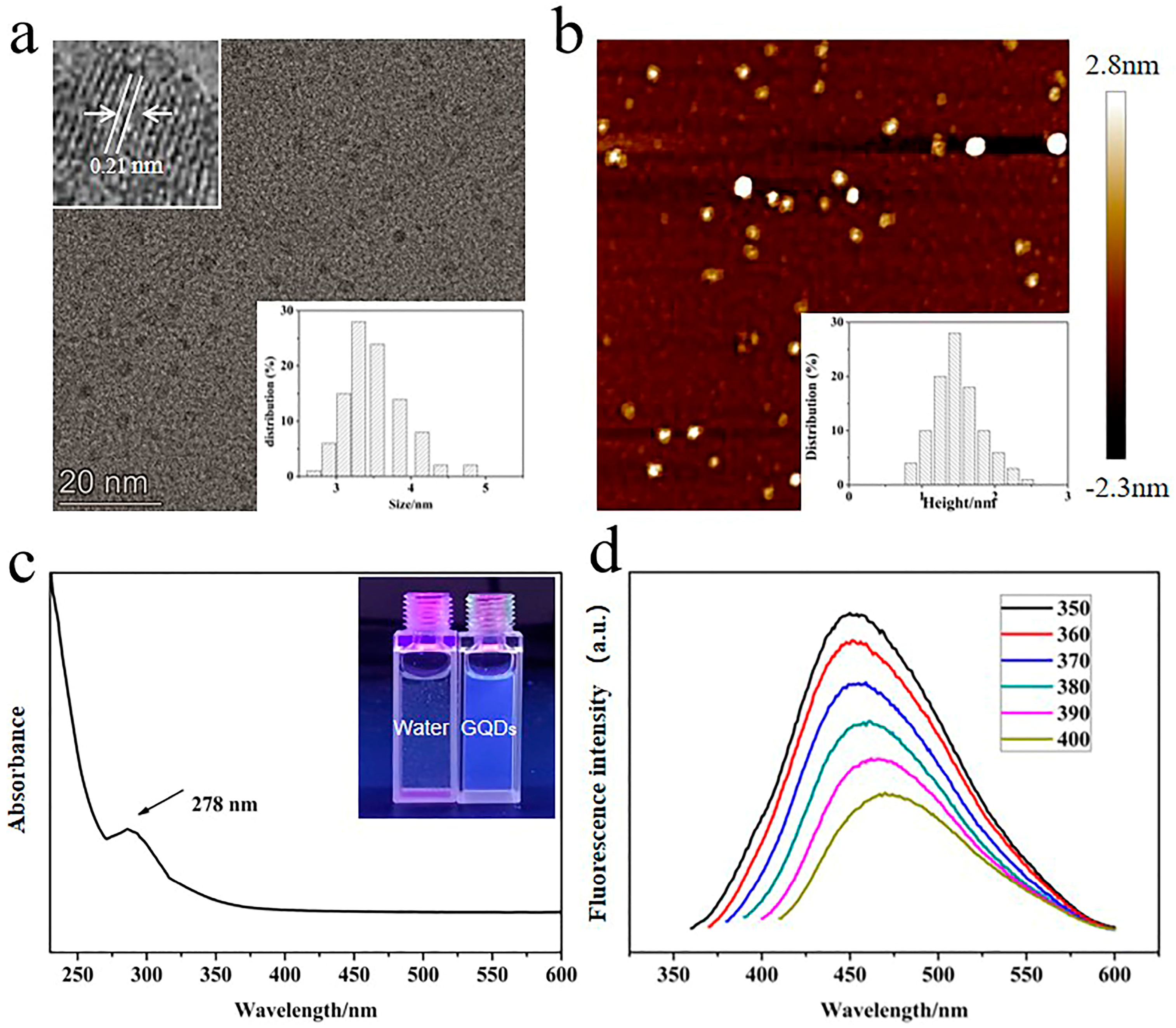
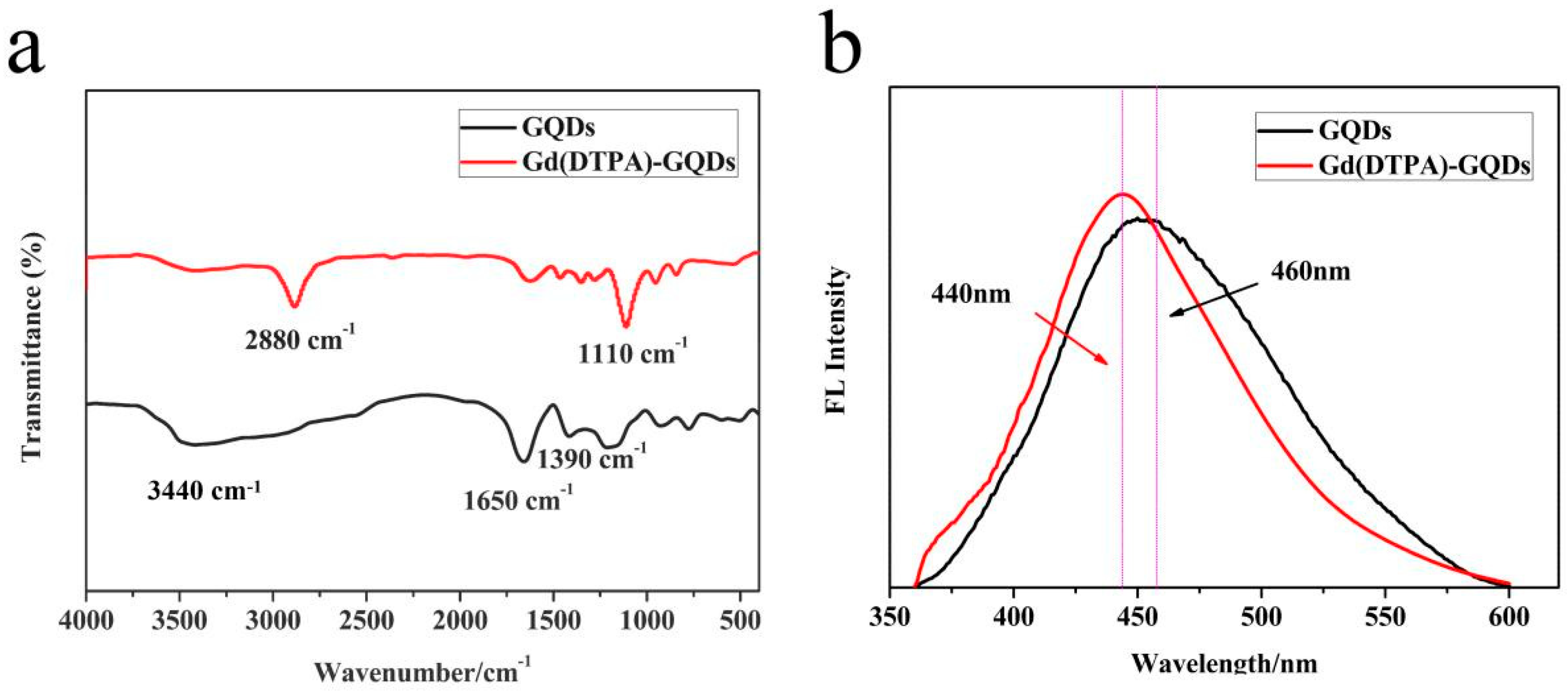
2.1. Synthesis and Structure of Gd(DTPA)−GQDs
2.2. Optical Properties
2.3. Assessment of the T1 Relaxivity
2.4. The Protein Adsorption and Stability of Gd(DTPA)−GQDs
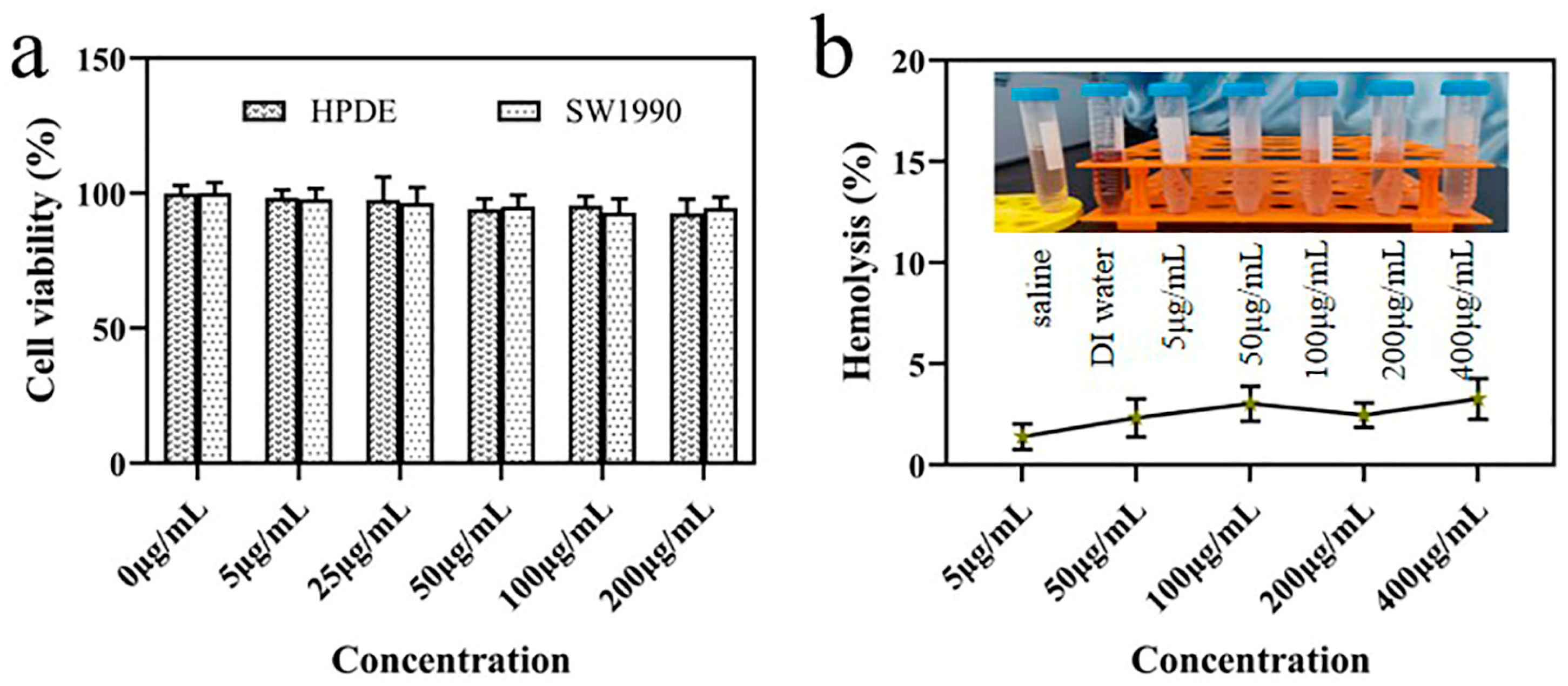
2.5. Biocompatibility and Cytotocivity
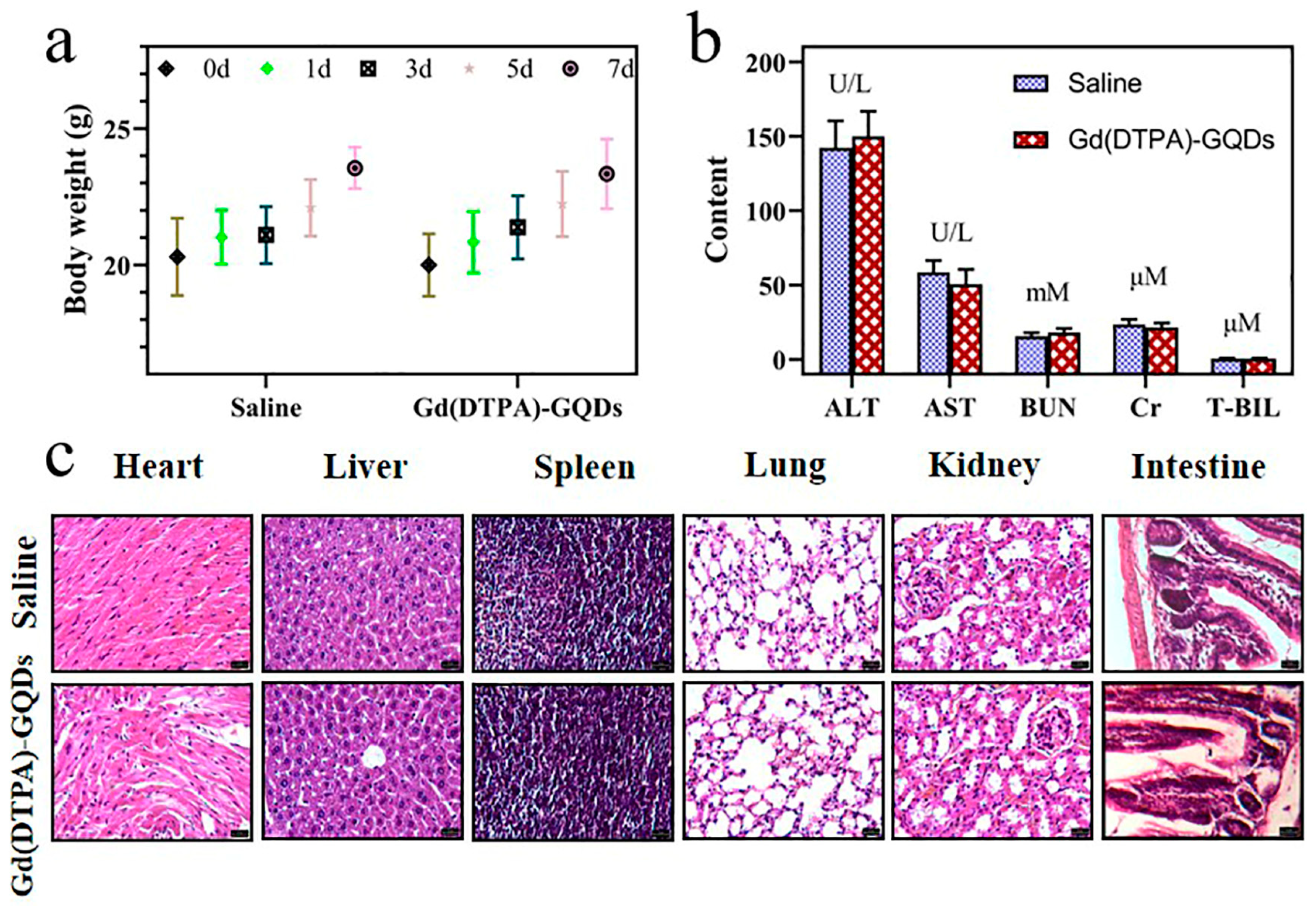
2.6. In Vivo Safety Evaluation
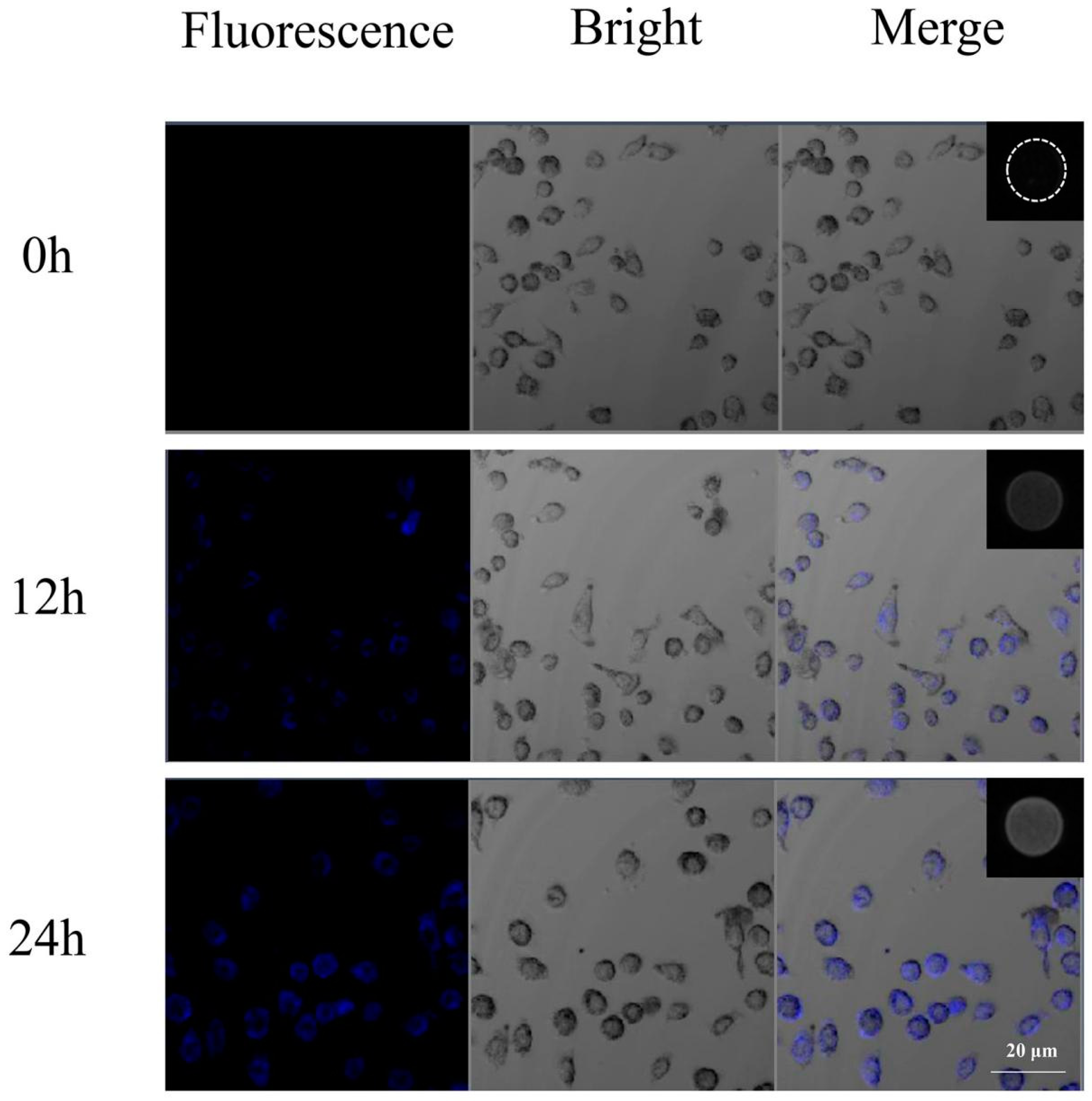
2.7. Cellular Uptake
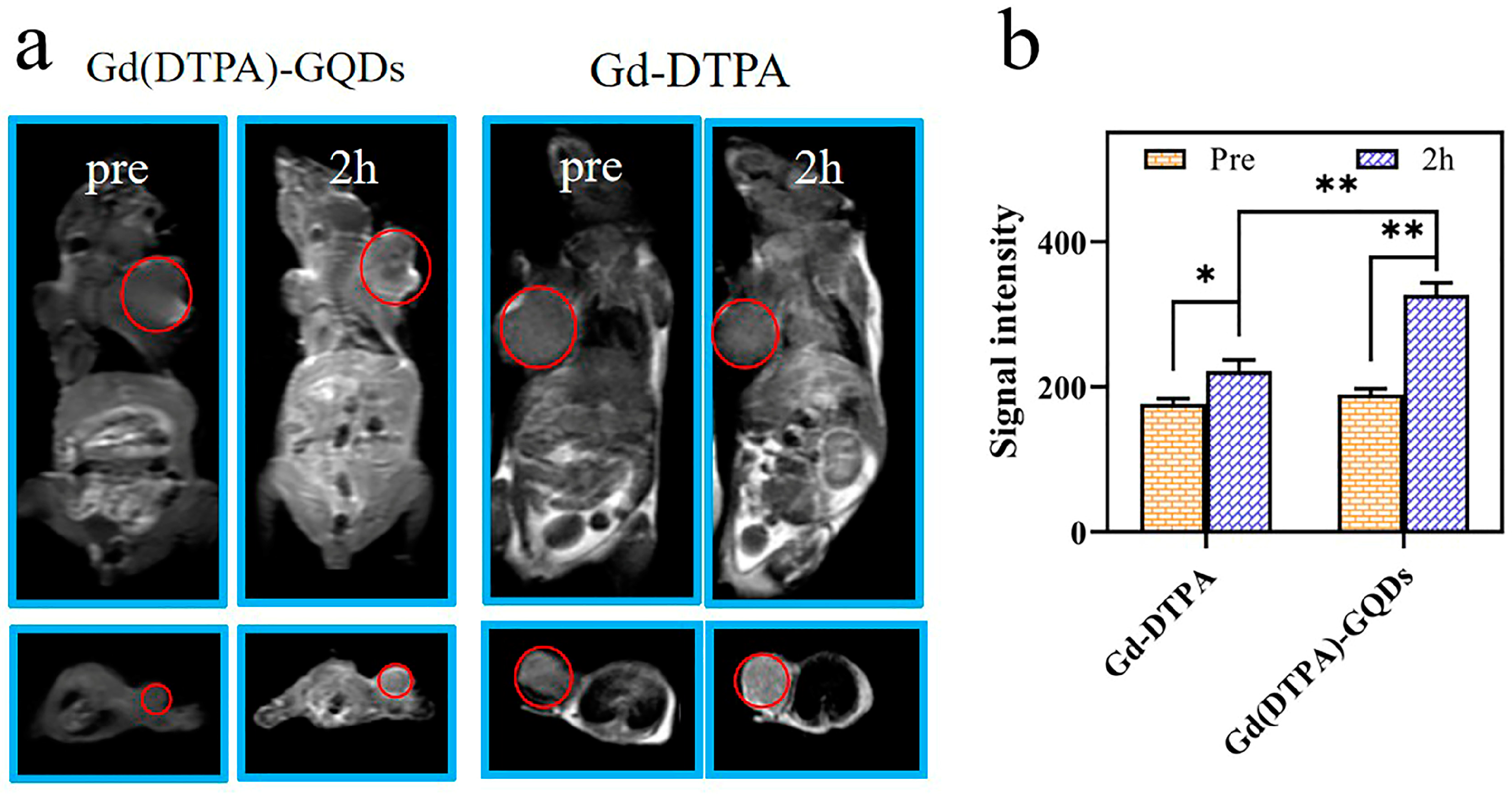
2.8. Imaging in Tumor−Bearing Mice
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Synthesis of GQDs
3.3. Synthesis of Gd(DTPA)−GQDs
3.4. Materials Characterization
3.5. Relaxivity Measurements
3.6. Cell Culture and Cellular Uptake Experiment
3.7. BSA Adsorption and Colloidal Stability
3.8. Biocompatibility
3.9. In Vivo Proof-of-Concept Study
3.10. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Bennett, K.M.; Jo, J.; Cabral, H.; Bakalova, R.; Aoki, I. MR imaging techniques for nano-pathophysiology and theranostics. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2014, 74, 75–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, Z.; Syrovets, T.; Genze, F.; Abaei, A.; Ma, G.; Simmet, T.; Rasche, V. High-resolution MRI analysis of breast cancer xenograft on the chick chorioallantoic membrane. NMR Biomed. 2015, 28, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caravan, P.; Ellison, J.J.; McMurry, T.J.; Lauffer, R.B. Gadolinium(III) Chelates as MRI Contrast Agents: Structure, Dynamics, and Applications. Chem. Rev. 1999, 99, 2293–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willke, P.; Yang, K.; Bae, Y.; Heinrich, A.J.; Lutz, C.P. Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Single Atoms on a Surface. Nat. Phys. 2019, 15, 1005–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Wang, X.; Dai, Y.; Dai, X.; Li, Z.; Luo, Q.; Zheng, X.; Gu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Gong, Q.; et al. Enhancing the Efficacy of Metal-Free MRI Contrast Agents via Conjugating Nitroxides onto PEGylated Cross-Linked Poly (Carboxylate Ester). Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 2000467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, S.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Kwak, B.K.; Lee, H.Y.; Seong, H.; Shin, B.C.; Yuk, S.H.; Hwang, S.J.; Cho, S.H. Biocompatible Polyhydroxyethylaspartamide-based Micelles with Gadolinium for MRI Contrast Agents. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2010, 5, 1970–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, D.; Bu, W.; Ehlerding, E.B.; Cai, W.; Shi, J. Engineering of inorganic nanoparticles as magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 7438–7468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulani, V.; Calamante, F.; Shellock, F.G.; Kanal, E.; Reeder, S.B. Gadolinium Deposition in the Brain: Summary of Evidence and Recommendations. Lancet Neurol. 2017, 16, 564–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, T.; Nakai, Y.; Oba, H.; Toyoda, K.; Kitajima, K.; Furui, S. Gadolinium deposition in the brain. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2016, 34, 1346–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraum, T.J.; Ludwig, D.R.; Bashir, M.R.; Fowler, K.J. Gadolinium-based contrast agents: A comprehensive risk assessment. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2017, 46, 338–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zu, G.; Kuang, Y.; Dong, J.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, T.; Liu, M.; Luo, L.; Pei, R. Gadolinium(III)-based Polymeric Magnetic Resonance Imaging Agents for Tumor Imaging. Curr. Med. Chem. 2018, 25, 2910–2937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Qiu, Y.; Ding, D.; Lin, H.; Sun, W.; Wang, G.D.; Huang, W.; Zhang, W.; Lee, D.; Liu, G.; et al. Gadolinium-Encapsulated Graphene Carbon Nanotheranostics for Imaging-Guided Photodynamic Therapy. Adv. Mater. 2018, 23, e1802748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Xie, W.; Xu, Z.; Si, Y.; Li, Q.; Qi, X.; Gan, Y.; Wu, Z.; Tian, G. CuO dot-decorated Cu@Gd2O3 core-shell hierarchical structure for Cu(i) self-supplying chemodynamic therapy in combination with MRI-guided photothermal synergistic therapy. Mater. Horiz. 2021, 8, 1017–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aryal, M.; Papademetriou, I.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Power, C.; McDannold, N.; Porter, T. MRI Monitoring and Quantification of Ultrasound-Mediated Delivery of Liposomes Dually Labeled with Gadolinium and Fluorophore through the Blood-Brain Barrier. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2019, 45, 1733–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, J. Growing a Nucleotide/Lanthanide Coordination Polymer Shell on Liposomes. Langmuir 2019, 35, 11217–11224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, S.; Li, Z.; Hsu, C.H.; Hwang, L.P.; Lin, Y.C.; Chou, P.T.; Lin, Y.Y. Dendrimer-and copolymer-based nanoparticles for magnetic resonance cancer theranostics. Theranostics 2018, 8, 6322–6349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Guo, S.; Li, Z.; Xiao, X.; Gu, L.; Luo, Q.; Zhang, H.; Gong, Q.; Luo, K. Safe and Potent MRI Contrast Agents by Complexing Gadolinium with Enzyme/reduction Dual-sensitive Branched Polymers. Appl. Mater. Today 2019, 17, 92–103. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, S.; Xiao, X.; Wang, X.; Luo, Q.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, H.; Li, H.; Gong, Q.; Luo, K. Reductive Microenvironment Responsive Gadolinium-Based Polymers as Potential Safe MRI Contrast Agents. Biomater. Sci. 2019, 7, 1919–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Li, H.; Li, Z.; Luo, Q.; Zhu, H.; Gu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Gong, Q.; Luo, K. Engineered Gadolinium-Based Nanomaterials as Cancer Imaging Agents. Appl. Mater. Today 2020, 20, 100686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Dai, X.; Wang, X.; Tan, P.; Gu, L.; Luo, Q.; Zheng, X.; Li, Z.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, H.; et al. A Nanostrategy for Efficient Imaging-Guided Antitumor Therapy through a Stimuli-Responsive Branched Polymeric Prodrug. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 1903243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younis, M.R.; He, G.; Lin, J.; Huang, P. Recent Advances on Graphene Quantum Dots for Bioimaging Applications. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.H.; Bae, K.; Huang, Z.W.; Xue, J.M. Two-photon graphene quantum dot modified Gd2O3 nanocomposites as a dual-mode MRI contrast agent and cell labelling agent. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 5642–5649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.H.; Hasan, M.T.; Lichthardt, D.; Gonzalez-Rodriguez, R.; Naumov, A.V. Manganese-nitrogen and gadolinium-nitrogen Co-doped graphene quantum dots as bimodal magnetic resonance and fluorescence imaging nanoprobes. Nanotechnology 2021, 32, 095103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gautam, A.; Pal, K. Gefitinib conjugated PEG passivated graphene quantum dots incorporated PLA microspheres for targeted anticancer drug delivery. Heliyon 2022, 8, e12512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, W.; Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; Zhou, M.; Xu, R.; Zhang, X. Smart surface coating of drug nanoparticles with cross-linkable polyethylene glycol for bio-responsive and highly efficient drug delivery. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 8118–8125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suk, J.S.; Xu, Q.; Kim, N.; Hanes, J.; Ensign, L.M. PEGylation as a strategy for improving nanoparticle-based drug and gene delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 99, 28–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Y.; Li, Y.M.; Seo, J.G.; Jang, T.S.; Knowles, J.C.; Song, S.H.; Lee, J.H. Biological Potential of Polyethylene Glycol (PEG)-Functionalized Graphene Quantum Dots in In Vitro Neural Stem/Progenitor Cells. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Liu, Z.; Guo, Z.; Ji, Y.; Jin, M.; Wang, X. Cellular distribution and cytotoxicity of graphene quantum dots with different functional groups. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becheru, D.F.; Vlăsceanu, G.M.; Banciu, A.; Vasile, E.; Ioniţă, M.; Burns, J.S. Optical Graphene-Based Biosensor for Nucleic Acid Detection; Influence of Graphene Functionalization and Ionic Strength. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Pan, T.; Lin, D.; Xia, W.; Shan, J.; Cheng, R.; Yang, M.; Hu, X.; Nan, K.; Qi, L. Biocompatible tumor-targeted GQDs nanocatalyst for chemodynamic tumor therapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2022, 10, 3567–3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, Z.; Yang, L.; Yan, X.; Wang, D.; Hua, Y.; Shi, W.; Lin, J.; Meng, Z. Effect and Mechanism of the Lenvatinib@H-MnO2-FA Drug Delivery System in Targeting Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2022, 28, 743–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotfollahzadeh, S.; Hosseini, E.S.; Mahmoudi Aznaveh, H.; Nikkhah, M.; Hosseinkhani, S. TRAIL/S-layer/graphene quantum dot nanohybrid enhanced stability and anticancer activity of TRAIL on colon cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Hnayn, R.; Canabady-Rochelle, L.; Desmarets, C.; Balan, L.; Rinnert, H.; Joubert, O.; Medjahdi, G.; Ben Ouada, H.; Schneider, R. One-Step Synthesis of Diamine-Functionalized Graphene Quantum Dots from Graphene Oxide and Their Chelating and Antioxidant Activities. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habiba, K.; Makarov, V.I.; Avalos, J.; Guinel, M.J.F.; Weiner, B.R.; Morell, G. Luminescent graphene quantum dots fabricated by pulsed laser synthesis. Carbon 2013, 64, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, H.; Wang, D.; Sadat, A.; Li, Z.; Hu, X.; Xu, M.; Morais, P.C.; Ge, B.; Sun, S.; Ge, J.; et al. Single-Atom Gadolinium Anchored on Graphene Quantum Dots as a Magnetic Resonance Signal Amplifier. ACS Appl. Bio. Mater. 2021, 4, 2798–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.; Ai, P.; Shao, C.; Wang, T.; Yan, C.; Ye, L.; Gu, W. Manganese-Doped Carbon Dots for Magnetic Resonance/Optical Dual-Modal Imaging of Tiny Brain Glioma. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 4, 2089–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Deng, H.; Yang, W.; Wang, Z.; Lin, L.; Munasinghe, J.; Jacobson, O.; Liu, Y.; Tang, L.; Ni, Q.; et al. Early stratification of radiotherapy response by activatable inflammation magnetic resonance imaging. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, Y.; Ge, C.; Yang, Z.; Garate, J.A.; Gu, Z.; Weber, J.K.; Liu, J.; Zhou, R. Reduced Cytotoxicity of Graphene Nanosheets Mediated by Blood-Protein Coating. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 5713–5724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Q.; Wang, Z.; An, Y.; Tian, J.; Li, Z.; Yang, Y.; Dong, Y.; Chen, M.; Liu, T. Chitosan-functionalized graphene oxide as adjuvant in HEV P239 vaccine. Vaccine 2022, 40, 7613–7621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Fang, H.; Liu, F.; Zhou, X.; Zhao, H.; He, X.; Guo, D. PEG-coated and Gd-loaded fluorescent silica nanoparticles for targeted prostate cancer magnetic resonance imaging and fluorescence imaging. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 5611–5622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Zhang, H.; Huang, D.; Feng, S.; Fujita, M.; Gao, X.D. Chitosan-Functionalized Graphene Oxide as a Potential Immunoadjuvant. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Qiu, H.; Lu, S.; Zhu, F.; Xiao, Q. Study on the molecular interaction of graphene quantum dots with human serum albumin: Combined spectroscopic and electrochemical approaches. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 285, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.Q.; Hao, L.Y.; Shao, X.R.; Zhang, Q.; Jia, X.Q.; Zhang, Z.R.; Lin, Y.F.; Peng, Q. Insight into the Interaction of Graphene Oxide with Serum Proteins and the Impact of the Degree of Reduction and Concentration. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 13367–13374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Liu, J.; Li, C.; Li, W.; Wang, W.; Liu, J. Ultrasound-Aided Targeting Nanoparticles Loaded with miR-181b for Anti-Inflammatory Treatment of TNF-α-Stimulated Endothelial Cells. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 17102–17110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martíne, N.M.; Russo, D.; Prévost, S.; Teixeira, J.; Morsbach, S.; Landfester, K. Poly(ethylene glycol)-Based Surfactant Reduces the Conformational Change of Adsorbed Proteins on Nanoparticles. Biomacromolecules 2022, 23, 4282–4288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Ding, X.; Qi, Y.; Yu, B.; Xu, F.J. Reduction-responsive multifunctional hyperbranched polyaminoglycosides with excellent antibacterial activity, biocompatibility and gene transfection capability. Biomaterials 2016, 106, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Kong, S.; Ouyang, Q.; Li, C.; Hou, T.; Chen, Y.; Li, S. Chitosan-Gentamicin Conjugate Hydrogel Promoting Skin Scald Repair. Mar. Drugs. 2020, 18, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, Y.; Ma, Y.; Shen, H.; Tu, X.; Zhou, X.; Xu, J.; Dai, J.; Fan, S.; Zhang, Z. The in vitro and in vivo toxicity of graphene quantum dots. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 5041–5048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, D.; Han, C.; Liu, C.; Ma, X.; Qian, J.; Zhou, J.; Li, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, W. Chitosan-capped enzyme-responsive hollow mesoporous silica nanoplatforms for colon-specific drug delivery. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zhao, H.; Jiao, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, C.; Li, F.; Wang, Y.; Gu, Z.; Yang, D. Biosynthetic molecular imaging probe for tumor-targeted dual-modal fluorescence/magnetic resonance imaging. Biomaterials 2020, 256, 120220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, H.; Zeng, D.; Tian, Y.; Chen, F.; Feng, J.; Shi, J. Core/shell structured hollow mesoporous nanocapsules: A potential platform for simultaneous cell imaging and anticancer drug delivery. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 6001–6013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Qi, G.; Shi, G.; Zhang, M.; Hu, H.; Hao, L. Engineered Graphene Quantum Dots as a Magnetic Resonance Signal Amplifier for Biomedical Imaging. Molecules 2023, 28, 2363. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28052363
Li Z, Qi G, Shi G, Zhang M, Hu H, Hao L. Engineered Graphene Quantum Dots as a Magnetic Resonance Signal Amplifier for Biomedical Imaging. Molecules. 2023; 28(5):2363. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28052363
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zhongtao, Guiqiang Qi, Guangyue Shi, Meng Zhang, Haifeng Hu, and Liguo Hao. 2023. "Engineered Graphene Quantum Dots as a Magnetic Resonance Signal Amplifier for Biomedical Imaging" Molecules 28, no. 5: 2363. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28052363
APA StyleLi, Z., Qi, G., Shi, G., Zhang, M., Hu, H., & Hao, L. (2023). Engineered Graphene Quantum Dots as a Magnetic Resonance Signal Amplifier for Biomedical Imaging. Molecules, 28(5), 2363. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28052363





