Abstract
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is one of the progressive neurological disorders and the main cause of dementia all over the world. The multifactorial nature of Alzheimer’s disease is a reason for the lack of effective drugs as well as a basis for the development of new structural leads. In addition, the appalling side effects such as nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, muscle cramps, and headaches associated with the marketed treatment modalities and many failed clinical trials significantly limit the use of drugs and alarm for a detailed understanding of disease heterogeneity and the development of preventive and multifaceted remedial approach desperately. With this motivation, we herein report a diverse series of piperidinyl-quinoline acylhydrazone therapeutics as selective as well as potent inhibitors of cholinesterase enzymes. Ultrasound-assisted conjugation of 6/8-methyl-2-(piperidin-1-yl)quinoline-3-carbaldehydes (4a,b) and (un)substituted aromatic acid hydrazides (7a-m) provided facile access to target compounds (8a-m and 9a-j) in 4–6 min in excellent yields. The structures were fully established using spectroscopic techniques such as FTIR, 1H- and 13C NMR, and purity was estimated using elemental analysis. The synthesized compounds were investigated for their cholinesterase inhibitory potential. In vitro enzymatic studies revealed potent and selective inhibitors of AChE and BuChE. Compound 8c showed remarkable results and emerged as a lead candidate for the inhibition of AChE with an IC50 value of 5.3 ± 0.51 µM. The inhibitory strength of the optimal compound was 3-fold higher compared to neostigmine (IC50 = 16.3 ± 1.12 µM). Compound 8g exhibited the highest potency and inhibited the BuChE selectively with an IC50 value of 1.31 ± 0.05 µM. Several compounds, such as 8a-c, also displayed dual inhibitory strength, and acquired data were superior to the standard drugs. In vitro results were further supported by molecular docking analysis, where potent compounds revealed various important interactions with the key amino acid residues in the active site of both enzymes. Molecular dynamics simulation data, as well as physicochemical properties of the lead compounds, supported the identified class of hybrid compounds as a promising avenue for the discovery and development of new molecules for multifactorial diseases, such as Alzheimer’s disease (AD).
1. Introduction
In the current healthcare system, dementia has proven as a devastating health issue and a major societal challenge around the globe and continues to impact the global population with time. Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the paramount cause of vascular dementia, a prevalent, multifactorial, and neurological disorder identified at molecular level by proteopathies, mitochondrial aberrations, oxidative stress, and neuroinflammation [1,2]. The expected but alarming rise in number of patients affected by dementia with AD from 55 million to 139 million by 2050, 60% of them belonging to low- and middle-income countries, underscores the severity and continuous failure to produce anti-Alzheimer’s drugs [3].
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a severe and irreversible progressive neurodegenerative disorder with a complex pathophysiology and clinical symptoms that causes cognitive impairment, decreased thinking ability, and motor and executive functions. The distinctive brain changes associated with AD result from the decline of inter-neuronal connectivity and neuronic apoptosis, particularly in areas such as the limbic system [4]. Though the pathophysiology and etiology of AD remain ambiguous, cholinergic dysfunction has been predicted to play a vital role in the progress of AD [5]. The important parts of the brain, such as the hippocampus and cerebral cortex, become deficient in the neurotransmitter acetylcholine (ACh), which is closely linked with AD [6]. Currently, the strategies leading to enhanced levels of cholinergic neurotransmission with reduced hydrolysis of ACh are still considered the most effective treatment for AD. The hydrolysis of ACh is mediated by two well-known cholinesterases: acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and butyrylcholinesterase (BuChE) [7]. AChE is more vigorous than BuChE by 1013-fold up and is responsible for nearly 80% of ACh hydrolysis [8]. There are two binding sites in the enzymatic pocket of AChE; the catalytic active site (CAS) and the peripheral anionic site (PAS), which acts as an allosteric modulation site of enzymatic activity [9,10]. The involvement of AChE, through the PAS, in the aggregation of the Aβ peptide has given a new meaning to the therapeutic use of mixed or non-competitive acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (AChEIs), as they could act both by restoring the acetylcholine levels and interfering on the aggregation of the Aβ peptide [11,12]. BuChE, whose expression and activity increase in advanced AD states, is also responsible for the hydrolysis of acetylcholine and may have a supporting role when AChE activity is reduced [13,14].
The current treatment approaches give only symptomatic remedies to AD patients. The marketed drugs such as tacrine, donepezil, rivastigmine, and galantamine prove ineffective at halting or reversing the progression of AD [15,16,17,18], although they vary in structural features and pharmacokinetic profiles [17]. These drugs are hampered by their after-effects, including gastric disturbance, liver toxicity, and hypotension [19,20,21,22,23]. Among the FDA-approved drugs, only aducanumab is used as an etiological treatment, but poor efficacy in the phase III trials makes this drug controversial [18,24]. Therefore, the development of new and more effective drugs to treat multifaceted diseases remains a promising field of research.
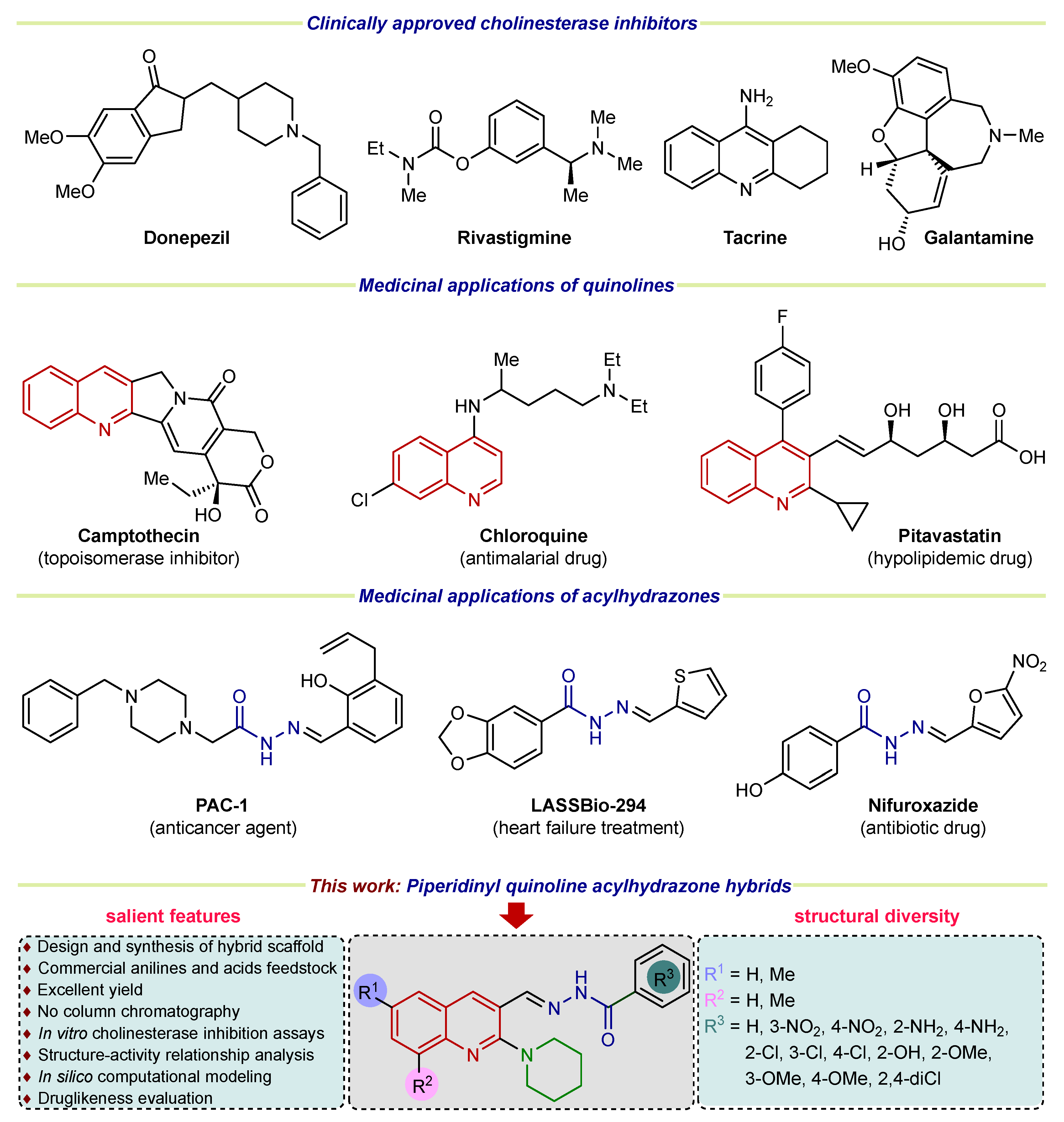
On the other hand, N-acyl hydrazones represent a class of organic compounds recognized for their various pharmacological applications [25]. Acyl hydrazone pharmacophore is widely distributed in numerous natural products, agrochemicals, and bioactive drug candidates [26]. The important medicinal applications including antiplatelet [27], antiproliferative [28], antitrypanosomal [29], antimicrobial [30], anti-inflammatory, anti-analgesic [31], antitumor [32], antioxidant, antihypertensive [33], inhibitory potential of alkaline phosphatase [34], and treatment of neurological disorders [26] have been reported. In parallel, the literature reports evidenced a well-established medicinal chemistry profile of nitrogen-containing heterocycles (quinoline and piperidine) [35,36,37,38,39,40]. Therefore, combining three biologically active pharmacophores into a single unit giving rise to a hybrid framework, could produce beneficial effects in treating neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease. Figure 1 demonstrates the representative examples of commercial cholinesterase inhibitors and hybridization strategies leading to the piperidinyl-quinoline substituted N-acylhydrazone scaffold investigated in this study.
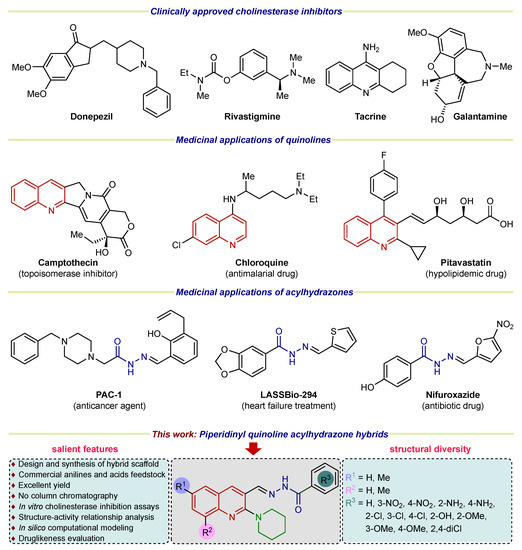
Figure 1.
Examples of clinically approved drugs for AD and rationale of current study.
Building on our previous track record in the exploration of anti-Alzheimer’s compounds [41,42,43,44] and the current lack of treatment modalities, possibly due to a large gap between basic research and translation to novel therapeutics and a very little success at the late-stage clinical trials inspire the drug discovery and medicinal chemists to explore the wider chemical space, thus delivering new and promising structural leads with potent anti-Alzheimer’s potential. Therefore, we herein established a hybrid scaffold incorporating quinoline, piperidine, and acyl hydrazone fragments as a favorable candidate for the generation of a distinct library of cholinesterase inhibitors. The concept of hybridization was used for the design of novel cholinesterase inhibitors, which is based on the assembly of two or more bioactive pharmacophores into a single unit. In vitro cholinesterase, inhibitory assays were performed against acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase enzymes, and the acquired potency was strengthened using computational modeling analysis. The investigation of druglikeness properties also revealed favorable data and a safer profile of the synthesized hybrid compounds.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthetic Chemistry
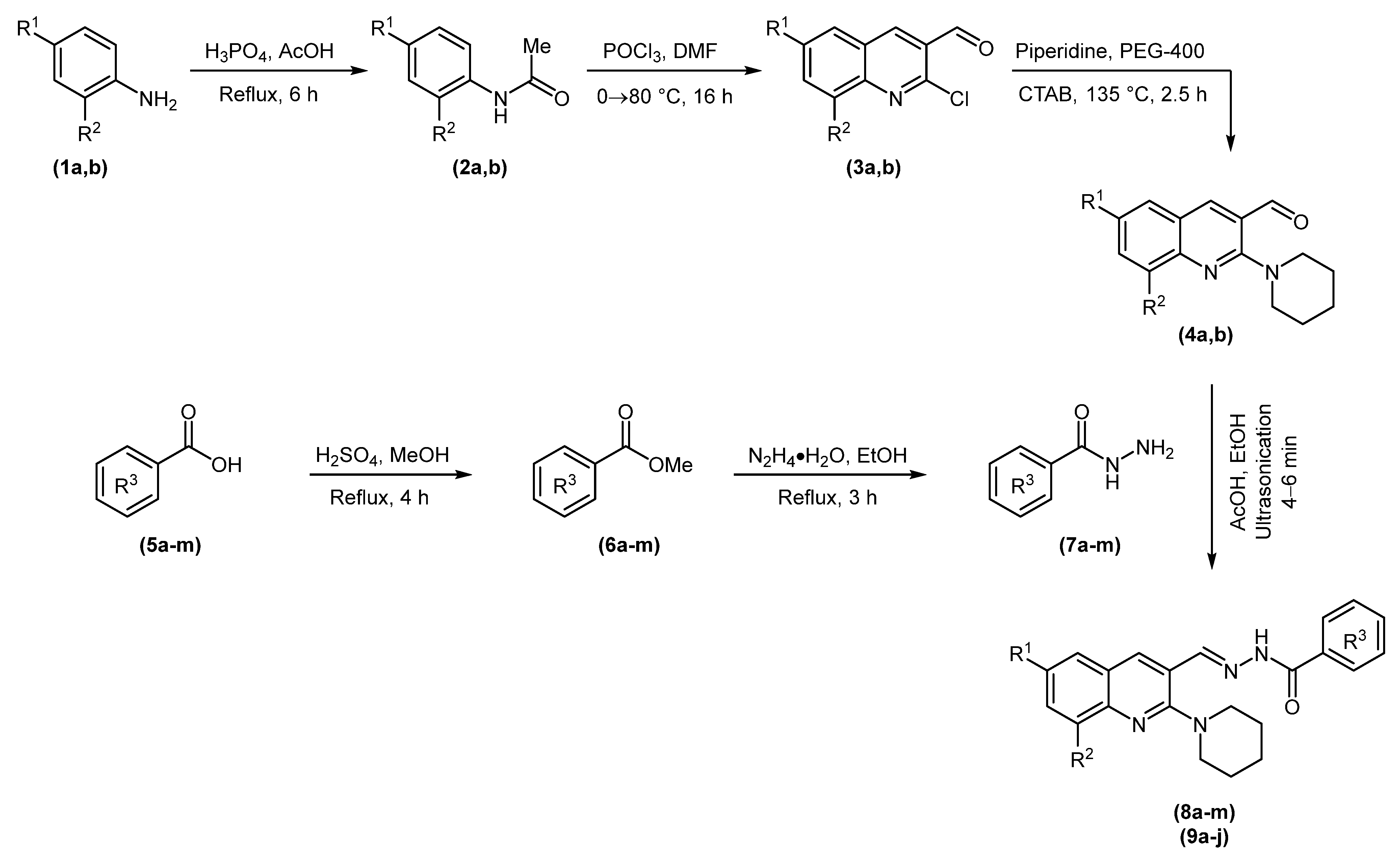
The target compounds were synthesized following the synthetic route illustrated in Scheme 1. N-Acetylation of o- and p-toluidine 1 followed by Vilsmeier–Haack formylation of 2 yielded 2-chloro-3-formylquinolines (3a and 3b). Nucleophilic aromatic substitution of 3a or 3b with piperidine produced 2-(piperidin-1-yl)quinoline-3-carbaldehydes (4a and 4b) [41,43,45]. In parallel, Fischer esterification of substituted benzoic acids (5a-m) gave their corresponding methyl esters (6a-m), which were treated with hydrazine monohydrate to obtain acid hydrazides (7a-m) [46,47]. The acid-catalyzed condensation of synthesized hydrazides (7a-m) and aldehydes (4a and 4b) delivered two sets of piperidinyl-quinoline N-acylhydrazones (8a-m and 9a-j) in 15–45 min in good yields. Another set of experiments was performed in an ultrasonic bath that reduced the reaction time to 4–6 min with slightly improved yields. The comparative results are presented in Table 1.
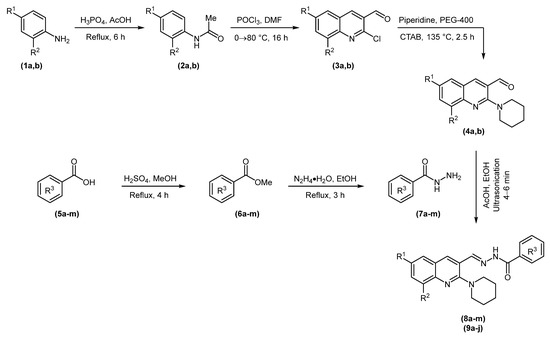
Scheme 1.
Synthetic route to piperidinyl-quinoline N-acylhydrazones (8a-m and 9a-j).

Table 1.
Comparative yields (conventional vs. ultrasonic-assisted synthesis) of piperidinyl-quinoline N-acylhydrazones (8a-m and 9a-j).
2.2. In Vitro Cholinesterase Inhibition and Structure–Activity Relationship Analyses
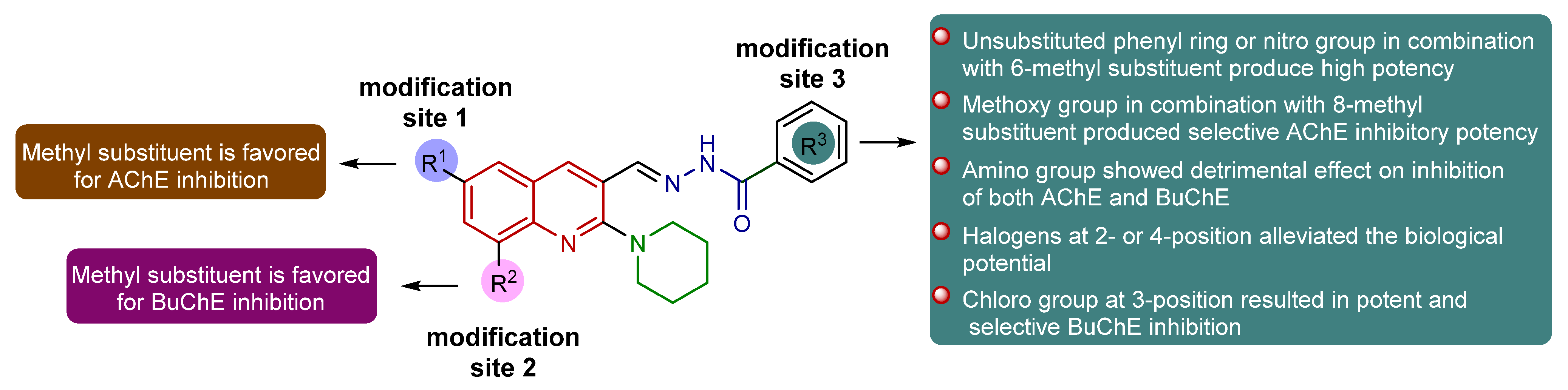
The newly designed and synthesized piperidinyl-quinoline acylhydrazone derivatives (8a-m and 9a-j) with diverse substitution patterns were evaluated for their in vitro inhibitory efficacy against cholinesterases (AChE and BuChE) using Ellman’s method [48,49]. In vitro inhibition results of tested compounds are presented in Table 2 and Table 3. The commercially available compounds neostigmine and donepezil were used as positive controls for AChE and BuChE, respectively. Various potencies of different orders of magnitude were achieved towards both targets. The designed scaffold comprised three modification sites (R1, R2, R3) for structural variations and three rigid motifs, including quinoline, piperidine, and acylhydrazone moieties. In particular, the benzohydrazide region served as a central motif in the formation of key interactions such as hydrogen bonding. Nitrogen atom of the hydrazone nucleus was found to establish hydrogen bonding and acts as a hydrogen bond donor, whereas carbonyl oxygen also interacted through H-bonding contacts. The introduction of a methyl group at the 6- or 8-position of the quinoline ring established alkyl linkages with various amino acid residues. The piperidine ring was involved in the formation of π-sigma bonds and π-alkyl linkages, whereas the quinoline core displayed π–π stacked interactions. Consequently, all the bioactive pharmacophoric regions and structurally stretchy sites are crucial for inhibitory potency due to their involvement in the formation of multiple significant interactions with several amino acid residues within the active pocket of both enzymes. The introduction of a substitution pattern in the form of electron-donating group (EDG) or electron-withdrawing group (EWG) not only provided the desired structural diversity but also contributed pharmacokinetically to attaining drug-like properties. As the in vitro cholinesterase inhibitory profiles presented herein depict a diverse picture, the structure–activity relationship analyses against both targets (AChE/BuChE) are worth investigating to propel the drug discovery endeavor to new avenues. Figure 2 illustrates a graphical representation of key pharmacophores alongside structural modification sites and crucial outcomes.

Table 2.
Anti-cholinesterase (AChE and BuChE) potential of synthesized compounds 8a–m.

Table 3.
Anti-cholinesterase (AChE and BuChE) potential of synthesized compounds 9a-j.
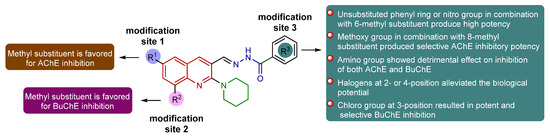
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of structural modifications and their effect on inhibition profile.
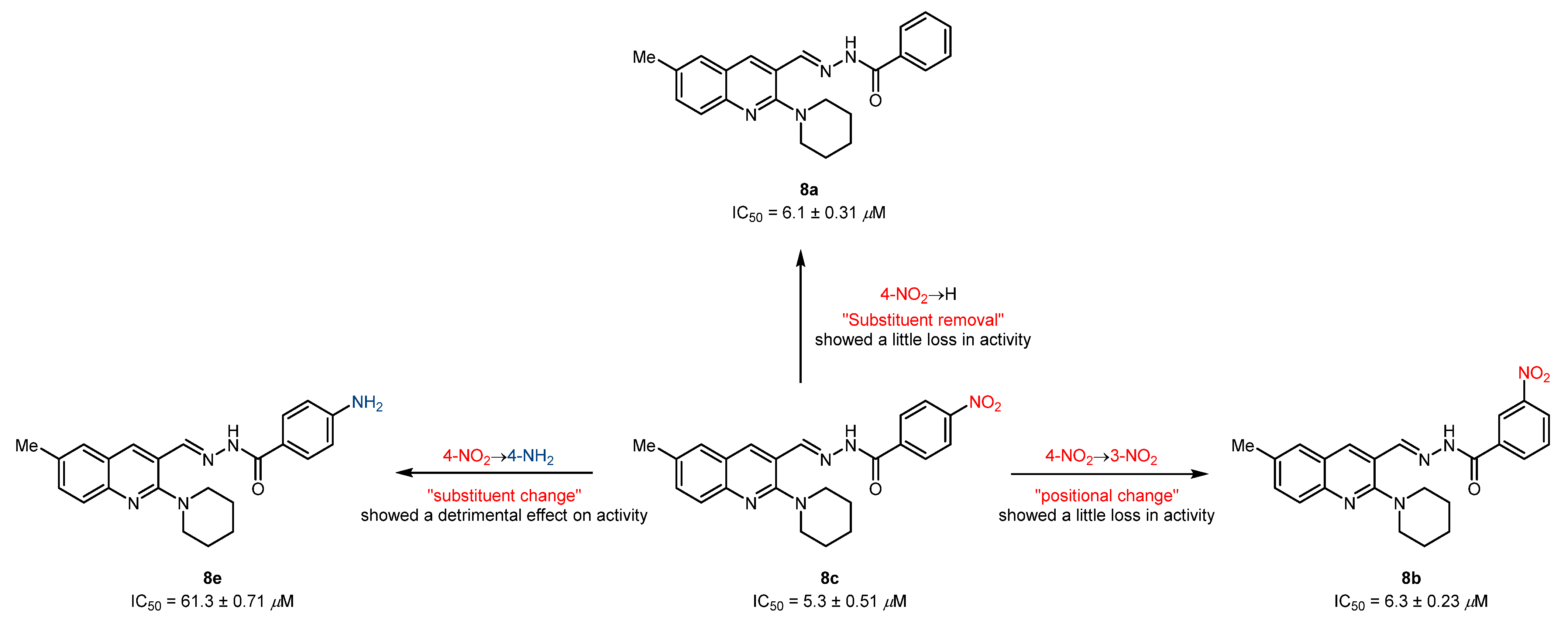
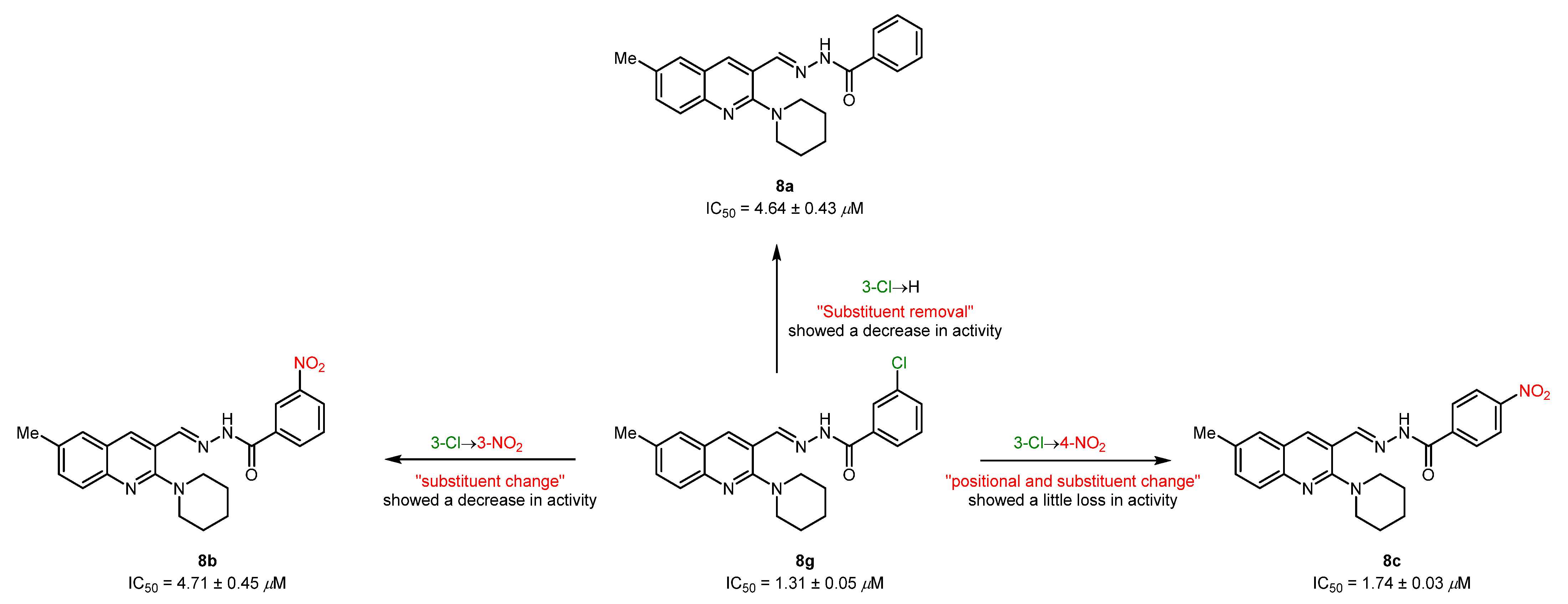
The striking feature of the present study is the exceptional role of various substituents/functional groups towards the inhibitory efficiency of cholinesterases, therefore leading to a distinct degree of biological inhibition potential. Keeping this in mind, we have divided the tested derivatives into two sets of compounds (8a-m and 9a-j) primarily based on the substitution pattern (R1 and R2) at the quinoline ring. In the first set of compounds, 8a-c were identified as potent and dual inhibitors of AChE and BuChE enzymes; however, 8c showed better results and remained as a lead candidate for the inhibition of AChE with an IC50 value of 5.3 ± 0.51 µM. This inhibitory strength was 3-fold higher compared to neostigmine (IC50 = 16.3 ± 1.12 µM). A slight loss in activity was noticed when the nitro group at the 3-position of the phenyl ring in compound 8c was moved to the 4-position (8b) or completely removed (8a). Both compounds exhibited similar inhibitory strength with IC50 values of 6.3 ± 0.23 and 6.1 ± 0.31 µM, respectively. Although the biological activities were slightly diminished, the positional change or substitution removal imparted beneficial effects, thus supporting the generation of compound libraries. However, a drastic effect on inhibition efficacy was realized when a highly polarizable electron-deficient (NO2) group was replaced with an electron-rich (NH2) group. This effect could possibly be attributed to the removal of a hydrogen bond acceptor and incorporation of a hydrogen bond donor, thus alleviating the explicit interaction formed by the former group (Figure 3). The remaining compounds in the first set showed <50% inhibitory efficacy (31–43%) against AChE.
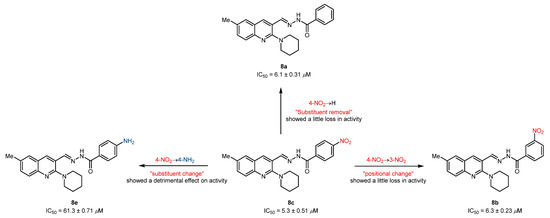
Figure 3.
Illustration of positional and substituent effect on the inhibitory efficacy against AChE.
In parallel, the synthesized piperidinyl-quinoline acylhydrazones (8a-m) were also tested against the butyrylcholinesterase enzyme. A similar inhibition profile was obtained, revealing compound 8g as the lead and selective candidate with an IC50 value of 1.31 ± 0.05 µM, a 5.5-fold stronger inhibition than donepezil (IC50 = 7.23 ± 0.12 µM). This derivative incorporates a chloro substituent at the 3-position of benzohydrazide, which fits well in the active pocket of BuChE. The exchange of an inductively electron-withdrawing group (Cl) with a stronger electron-withdrawing (NO2) group demonstrated a significant influence on the activity strength, thus reducing the inhibition ability to 3-folds (8b; IC50 = 4.71 ± 0.45 µM). The deletion of the chloro group also produced similar results to the substituent swapping approach (8a; IC50 = 4.64 ± 0.43 µM). However, the loss in inhibitory strength was compensated with the introduction of the nitro group at the 4-position of benzohydrazide (8c; IC50 = 1.74 ± 0.03 µM). This change contributes to the rehabilitation and retention of biological potency (Figure 4). Although these hybrid structures show a common trend with a decline in inhibitory potency in comparison to the lead structure 8g, they still represent potent inhibitors compared to standard drug (donepezil). The remaining compounds exhibited <50% inhibition in the range of 13–39%.
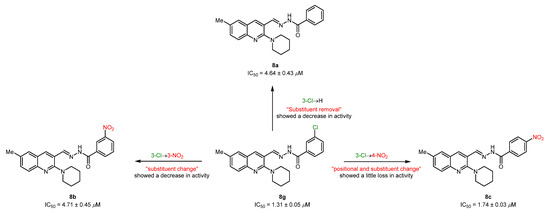
Figure 4.
Illustration of positional and substituent effect on the inhibitory efficacy against BuChE.
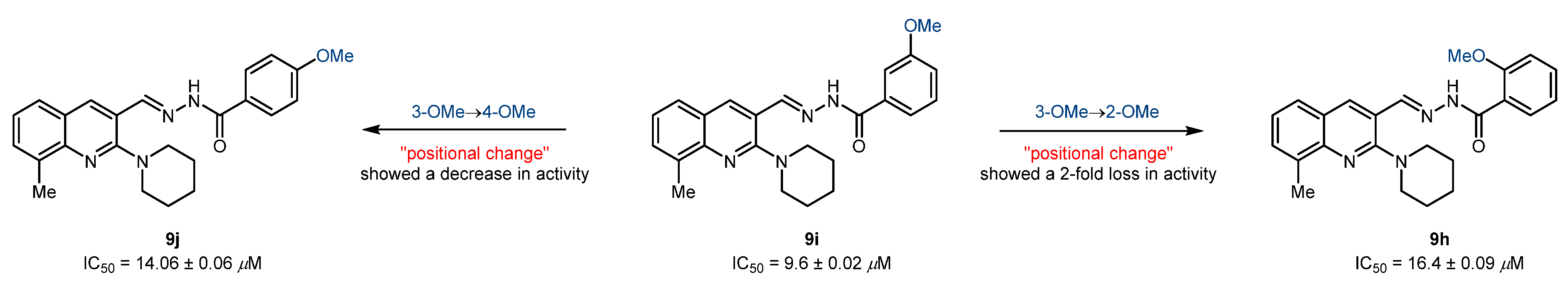
The second set of compounds (9a-j) bearing a methyl group at 8-position of the quinoline core showed a completely opposite trend for the inhibition of cholinesterases. The inhibitory potential of acylhydrazones against cholinesterase enzymes is reported in Table 3. Compounds 9h-j bearing an electron-donating (OMe) group at 2-, 3-, and 4-position of benzohydrazide moiety were found as the only potent but completely selective inhibitors with IC50 values in the range of 9.6–16.4 µM. Compound 9i bearing a 3-OMe substituent on benzohydrazide moiety displayed the highest inhibition with an IC50 value of 9.6 ± 0.02 µM. Subsequently, the effect of the positional change was investigated, and results revealed that the movement of the methoxy group to 2-, or 4-position showed a decline in inhibitory efficacy with IC50 values of 16.4 ± 0.09 (9h) and 14.06 ± 0.06 µM (9j), respectively (Figure 5). The remaining compounds of set 2 were poor inhibitors and showed <50% inhibition (27–41%). In comparison to the first set of compounds, 9a-j failed to produce any potent lead against BuChE, and mild inhibition potency (27–40%) was observed. These results clearly suggested that the tested compounds were not reasonably accommodated in the active site; therefore, no beneficial interactions and inhibition potential were noted.
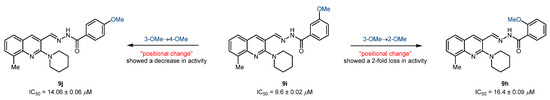
Figure 5.
Illustration of positional effect on the inhibitory efficacy against AChE.
To summarize, the first round of in vitro evaluation of AChE and BuChE inhibitory potency and diverse structure–activity relationships in both sets of compounds confirmed our design strategy and provided explicit guidance for further optimization of piperidinyl-quinoline acylhydrazones into potential drug candidates for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease.
2.3. Molecular Docking Studies
To justify the in vitro biological results, the most potent and selective compounds were docked within the active site of AChE and BuChE enzymes. In vitro results elucidated that several compounds show potent inhibitory efficacy against both enzymes, as reported previously [50]. Compound 9i showed complete selectivity towards AChE with two-fold inhibition, while 8g inhibited the BuChE enzyme exclusively. In parallel, 8a–c were significantly active and identified as dual inhibitors of AChE and BuChE. Therefore, both selective and potent inhibitors were docked within the active pocket of both cholinesterases. For the purpose of exploring the binding interactions of potent compounds, crystallographic structures were downloaded from the protein databank. For docking analysis, the crystallographic structure of human acetylcholinesterase (4BDT) [41,43] and butyrylcholinesterase (4BDS) [41,43] were selected.
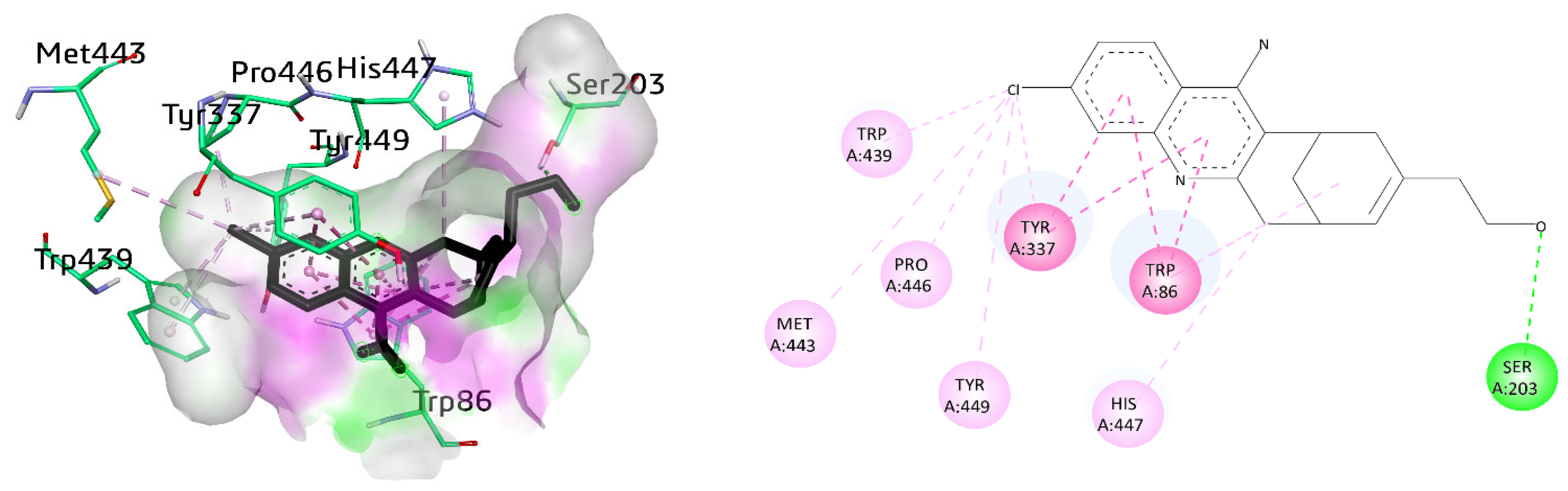
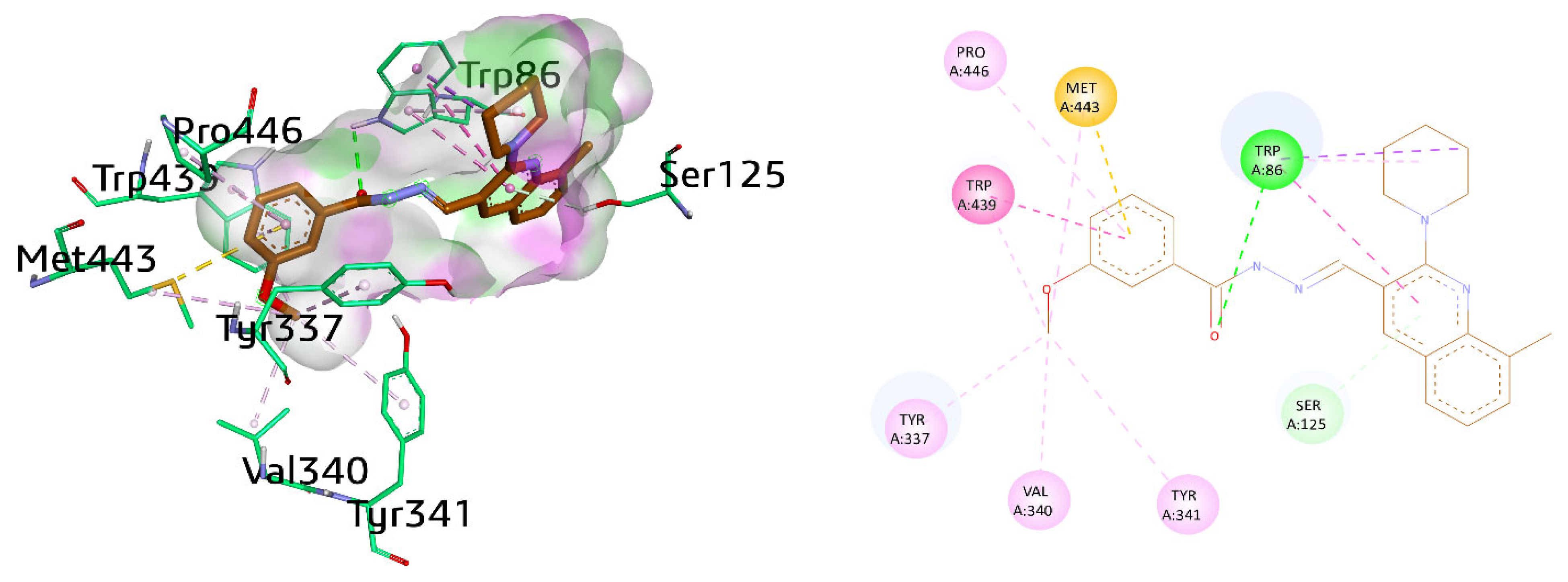
Various amino acid residues such as Leu76, Tyr124, Phe338, Gly122, Trp286, Tyr337, Val 340, Phe297, Leu289, Tyr72, Ser298, Ser125, Arg 296, Ser203, Tyr341, Ala204, and His447 surrounded the active pocket of AChE. The active compounds 8a, 9i, and cognate ligand huprine W exhibited hydrogen bonding and π–π interactions. The cognate ligand displayed conventional hydrogen bonding with Ser203 and stacked with two π–π stacking interactions against Trp86 and Tyr337. Additionally, π–alkyl interactions were also observed with Trp86, and multiple alkyl linkages with Trp439, Pro446, Tyr449, Met443, His447, and Tyr337 were also noticed (Figure 6).
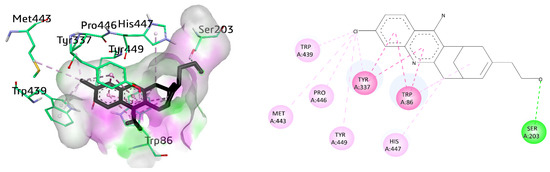
Figure 6.
Three-dimensional and two-dimensional visualization of huprine W, π–π stacking interactions exhibited as fuchsia, hydrogen bond as green, and alkyl interactions as light pink dashed lines.
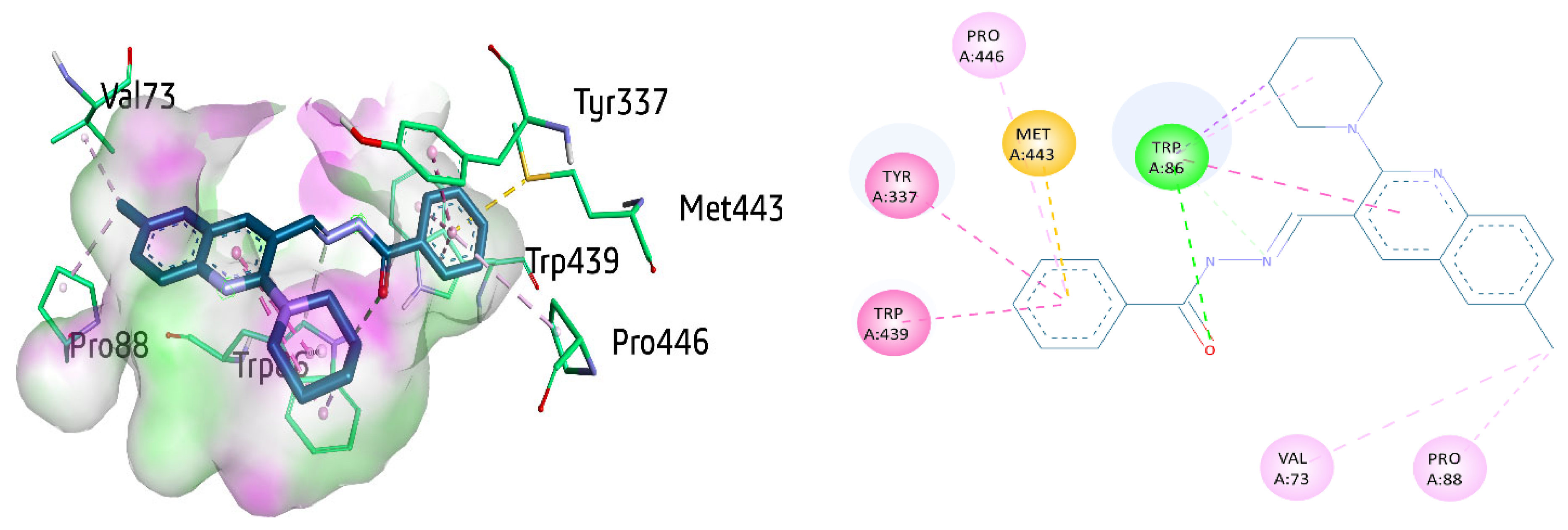
The active compound 8a showed multiple interactions with amino acid residues within the active site of AChE. These interactions include π–π stacking with Tyr337, Trp439, π-alkyl interaction with Pro446, and π-sulfur interaction with Met443 and benzohydrazide ring. Conventional hydrogen bonding was unveiled between the carbonyl oxygen atom and Trp86 (2.54 Å), the most significant residue present in the active site of AChE. Trp86 also depicted π–π stacked interaction (4.92 Å) against the 6-methyl quinoline ring of 8a as well as the π–sigma bond and π-alkyl linkage with piperidine ring. Trp86 also showed a carbon hydrogen bond with benzohydrazide. Moreover, Val73 and Pro88 exhibited alkyl linkage with methyl quinoline ring (Figure 7).
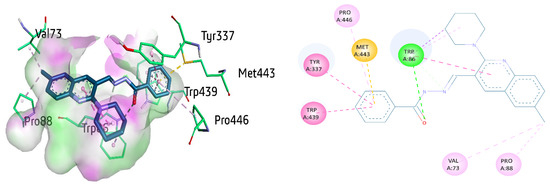
Figure 7.
Three-dimensional and two-dimensional visualization of compound 8a against AChE. π–π stacking interactions are shown as fuchsia, hydrogen bond as green, π-sulfur as yellow, π-sigma as purple, π-alkyl and alkyl interactions as light pink dotted lines.
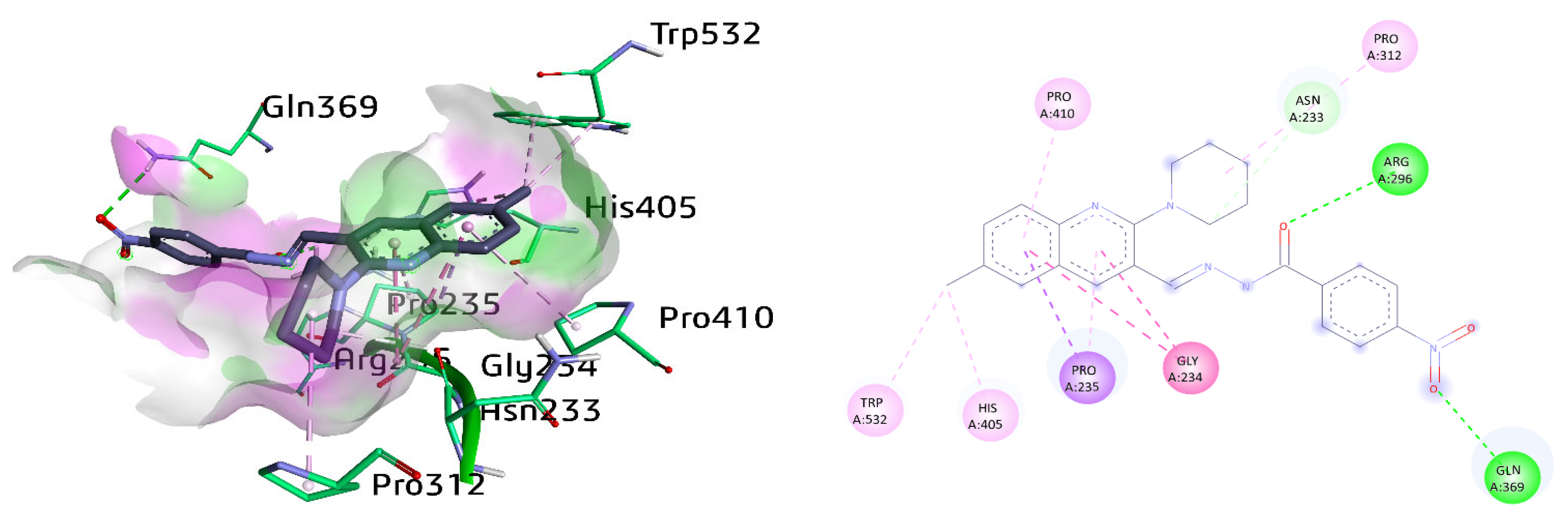
The most potent compound 8c against AChE exhibited different vital interactions with the amino acid residues of the active pocket of protein receptors. These include amide-π stacked against Gly234 and conventional hydrogen bonding between Arg296 and carbonyl oxygen atom as well as Gln369 and nitro group, respectively. Moreover, Pro235 also revealed π-sigma and π-alkyl interaction with the methyl quinoline ring with a distance of 3.92 Å and 4.07 Å, respectively. Subsequently, alkyl linkages were observed with amino acids Trp532, His405, and Pro312. Moreover, Asn233 also exhibited a carbon-hydrogen bond with a distance of 3.20 Å with the piperidine ring of compound 8c. π-Alkyl linkage was also realized between Pro410 and the quinoline ring, as shown in Figure 8.
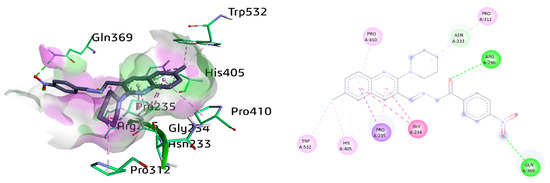
Figure 8.
Three-dimensional and two-dimensional visualization of compound 8c against AChE. Amide-π stacking interactions are shown as dark fuchsia, hydrogen bond as green, C-H bond as light green, π-alkyl and alkyl interactions as light pink, and π-sigma as dark purple dotted lines.
Similarly, another selective and active inhibitor 9i docked within the AChE pocket revealed multiple important interactions. Trp439 showed π–π stacked interactions against benzohydrazide ring of 9i and an alkyl linkage with a methyl substituent. Furthermore, Met443 and Pro446 showed π-sulfur and π-alkyl interactions, respectively, with the benzohydrazide ring. Trp86 exhibited conventional hydrogen bonding with a carbonyl oxygen atom in addition to π–π stacked interaction (5.26 Å) with an 8-methyl quinoline ring. Trp86 also showed π-sigma and π-alkyl linkage with the piperidine ring. Several alkyl bonds involving Tyr337 (4.28 Å), Val340, Tyr341, and Met443 were also present with the methoxy group present at benzohydrazide moiety. π-Donor hydrogen bond was also noticed between Ser125 and the quinoline ring, as shown in Figure 9.
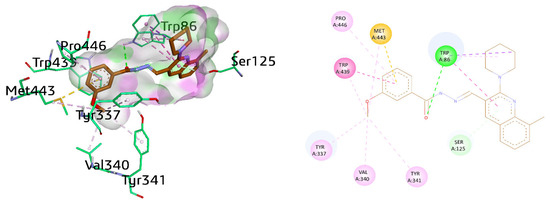
Figure 9.
Three-dimensional and two-dimensional visualization of compound 9i against AChE. π–π stacking interactions are shown as fuchsia, hydrogen bond as green, π-sulfur as yellow, π-alkyl and alkyl interactions as light pink, and C-H bond dotted lines.
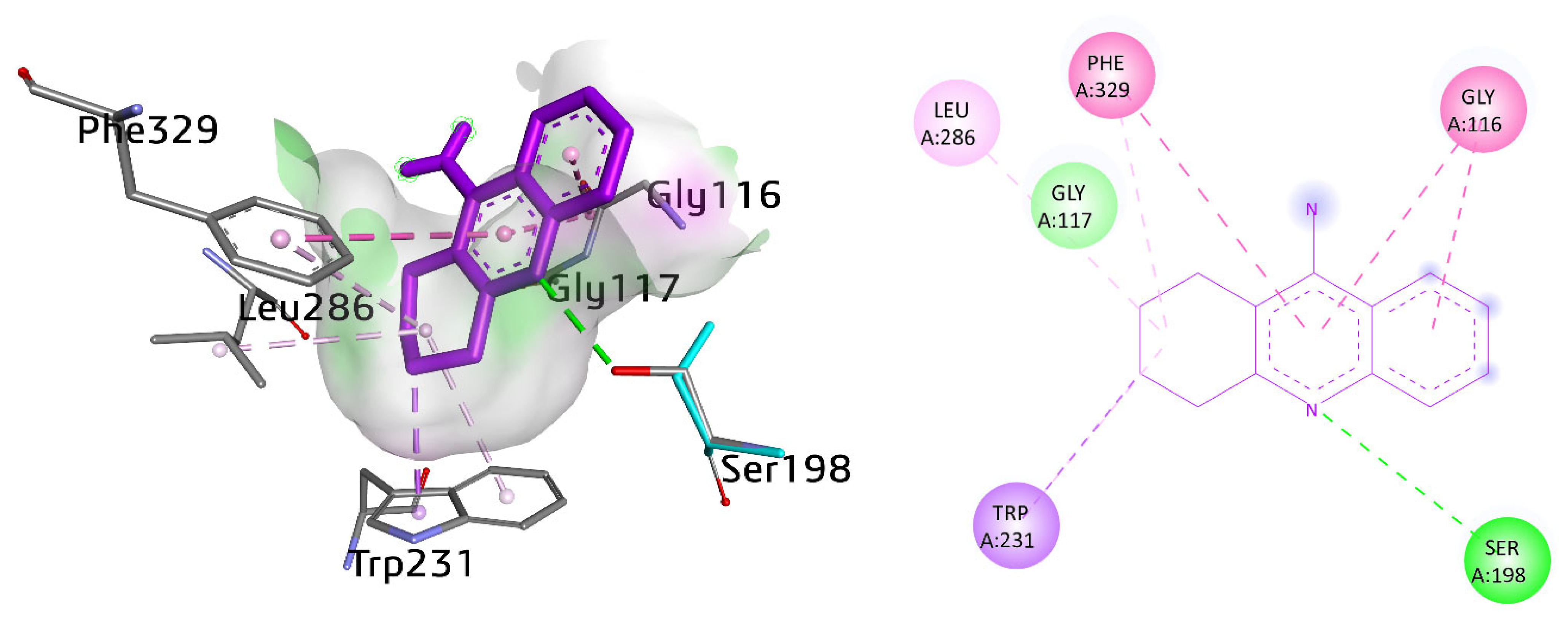
On the other hand, the active pocket of butyrylcholinesterase encompassed several amino acid residues such as Trp82, His438, Tyr332, Leu286, Val288, Phe398, Trp231, Gly116, Gly117, Ala328, Pro285, and Phe329. Several interactions were observed by selective as well as potent compounds with BuChE. The cognate ligand tacrine exhibited various interactions. For instance, π–π T-stacked interaction with Phe329 with a distance of 5.62 Å. Gly116 also showed amide-π stacked interactions (4.13, 4.37 Å). Conventional hydrogen bonding was also noticed between the nitrogen atom of the ring and the hydrogen atom of Ser198, with a distance of 2.80 Å. Additionally, Trp231 exhibited π-sigma and π-alkyl linkage with a distance of 3.57 and 4.63 Å, respectively. A π-linkage was also observed with Phe329 (5.48 Å) (Figure 10).
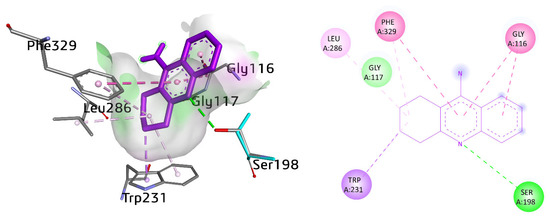
Figure 10.
Three-dimensional and two-dimensional visualization of tacrine. π–π T shaped interactions are shown as light fuchsia, amide-π stacked as dark fuchsia, hydrogen bond as green, alkyl interactions as light pink, C-H bond as light green, and π-sigma as purple dotted lines.
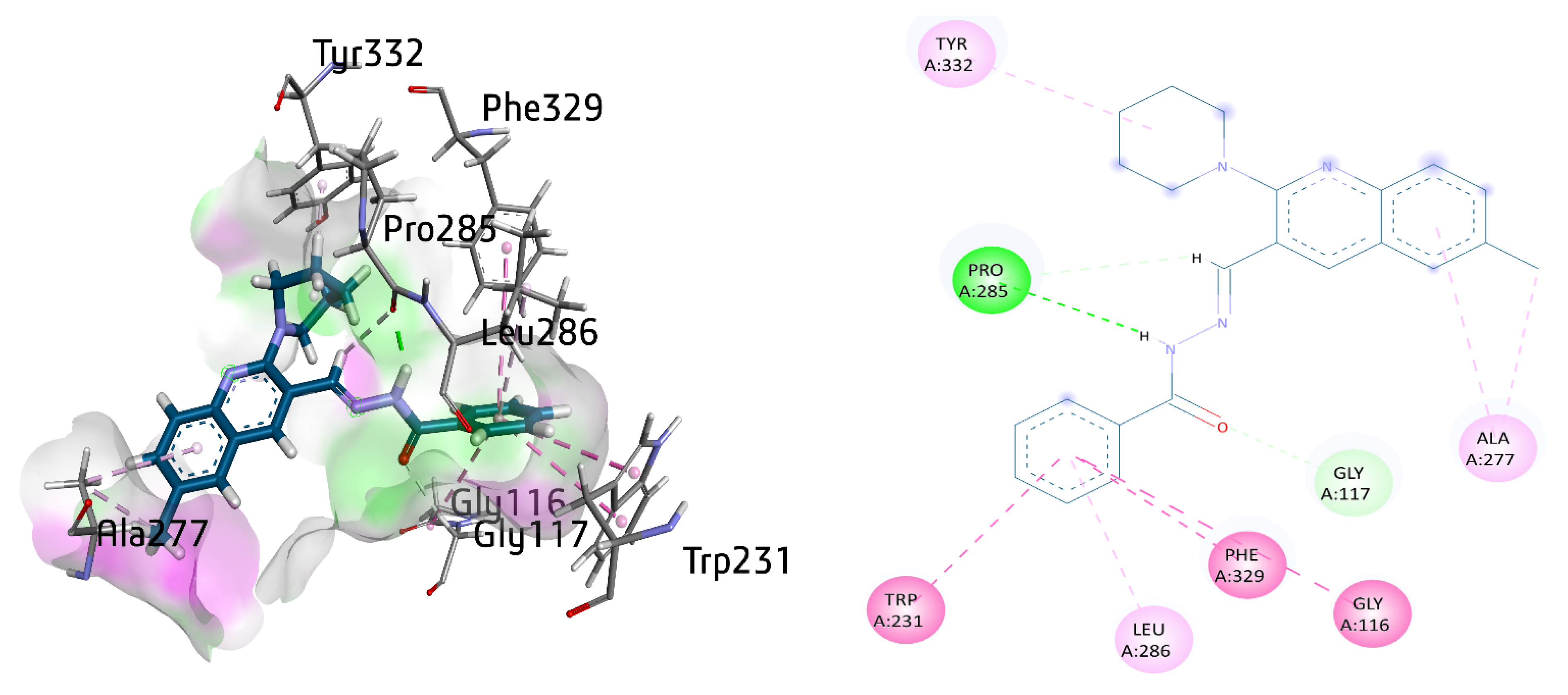
The active inhibitor 8a against BuChE exhibited several important interactions with the amino acid residues of the active site. Among them, π–π T-shaped interactions between Phe329 and Trp231, as well as amide-π stacked interaction between Gly116 and benzohydrazide moiety, were the most prominent. A π-alkyl linkage between the Leu286 aromatic ring was also observed, whereas conventional hydrogen bonding and carbon hydrogen bond were also noticed with amino acid residue Pro285 with distance of 1.93 and 3.08 Å, respectively. Gly117 also exhibited a hydrogen bond with carbonyl oxygen atom. Additionally, Ala277 showed π-alkyl and an alkyl linkage with the methyl quinoline ring of 8a. Finally, a π-alkyl linkage was also noticed between the piperidine ring and Tyr332 with a distance of 4.07 Å, as shown in Figure 11.
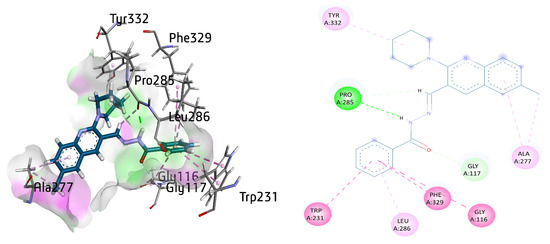
Figure 11.
Three-dimensional and two-dimensional visualization of compound 8a against BuChE. π–π stacking interactions are shown as light fuchsia, amide-π interaction as dark fuchsia, hydrogen bond as green, π-alkyl and alkyl interactions as light pink, and C-H bond as light green dotted lines.
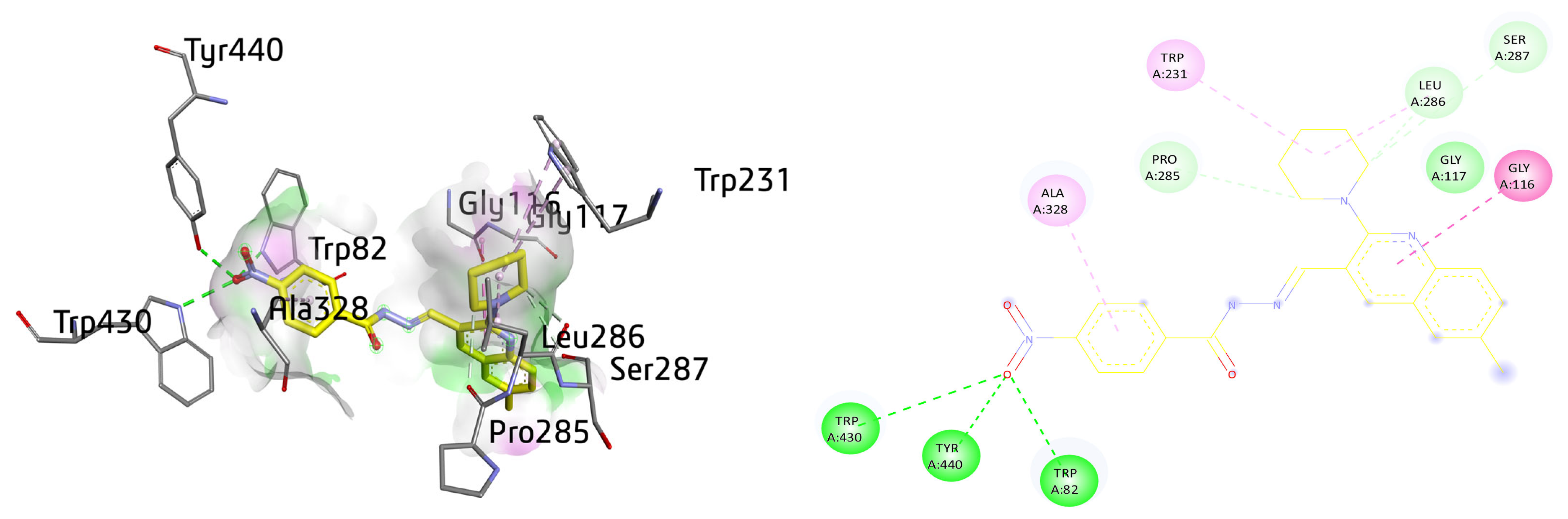
Compound 8c depicted multiple important interactions such as amide-π stacked, alkyl and π-alkyl, conventional hydrogen bond, C-H bond, and van der Waals interactions within the active pocket of BuChE. The oxygen of the -NO2 group present at benzene is making multiple hydrogen bonds with the amino acid residues such as TRP430, TYR440, and TRP82. The quinoline ring of compound 8c is amide-π stacked against GLY116, whereas van der Waals interactions were noticed with GLY117. The piperidine ring also revealed alkyl interactions with TRP231 (6.90 Å) and LEU286 (4.66 Å) and multiple C-H bonds with PRO285, SER287, and LEU286. The aromatic ring of the compound also exhibited π-alkyl linkage with the ALA328 with a distance of 4.36 Å, as shown in Figure 12.
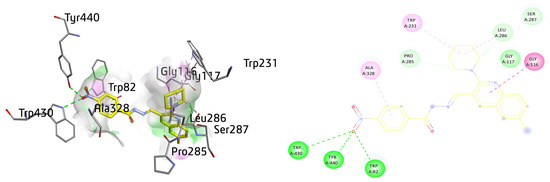
Figure 12.
Three-dimensional and two-dimensional visualization of compound 8c against BuChE. Amide-π stacking interactions are shown as dark fuchsia, hydrogen bond as green, π-alkyl and alkyl interactions as light pink, and C-H bond as light green dotted lines.
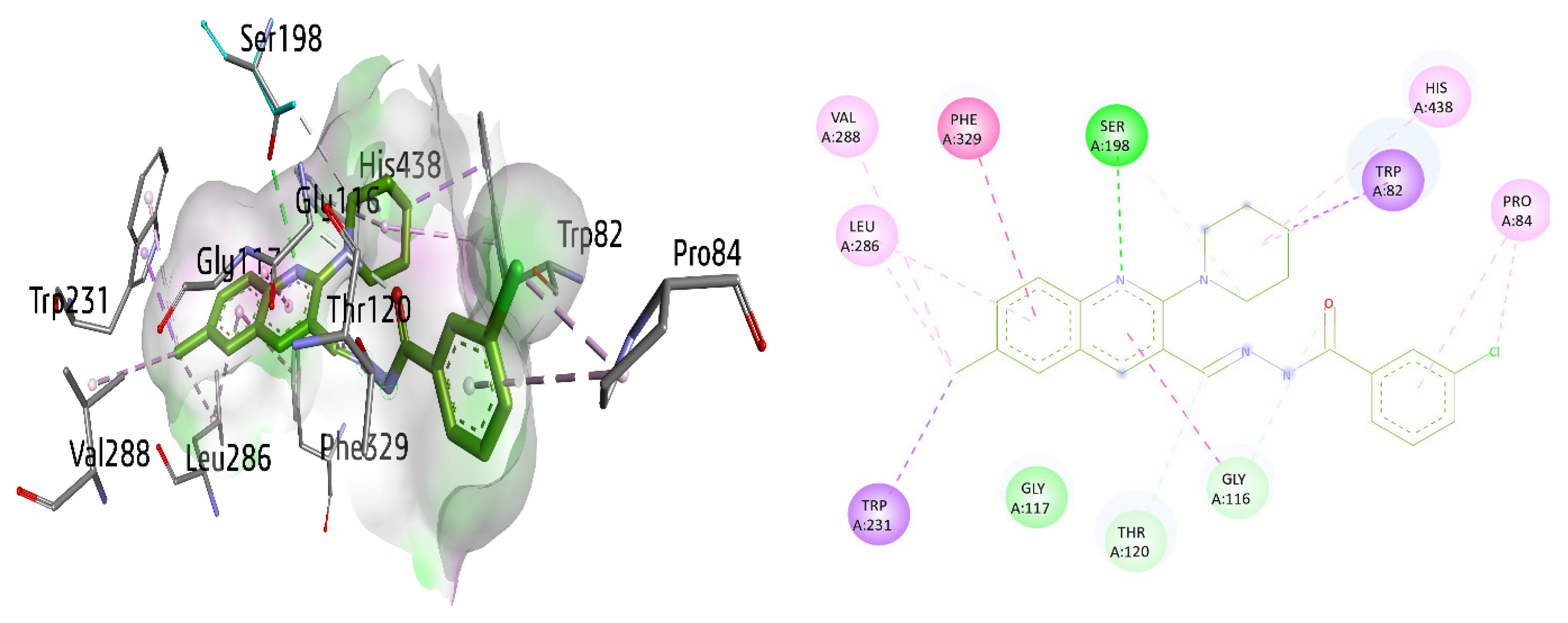
Finally, the potent and selective lead 8g against BuChE exhibited multiple interactions, including π–π T-shaped interactions with Phe329 and amide-π stacked interaction with Gly116 by the quinoline ring, π-sigma interaction with Trp231, conventional hydrogen bonding with Ser198, alkyl and π-alkyl linkage with Leu286 and alkyl bond with Val288 in the active pocket of the enzyme. Furthermore, the piperidine ring revealed a π-sigma linkage with Trp82, a carbon hydrogen bond with Ser198 as well as a π-alkyl linkage with His438. Pro84 exhibited an alkyl and a π-alkyl linkage with a 3-chlorophenyl ring. Gly116 and Thr120 also interacted through carbon hydrogen bonds, as shown in Figure 13.
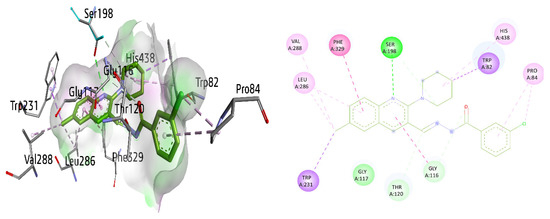
Figure 13.
Three-dimensional and two-dimensional visualization of compound 8g against BuChE. π–π stacking interactions are shown as light fuchsia, hydrogen bond as green, π-sigma as purple, π-alkyl and alkyl interactions as light pink, and C-H bond as light green dotted lines.
In summary, all the potent and selective compounds, as well as co-crystallized ligands, showed various crucial interactions against acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase enzymes. Some amino acid residues do not reveal the binding at a similar position but interact through other residues and are moderately aside from the active site.
Various types of interactions between compounds (8a, 8c, and 9i) and receptor (PDB; 4BDT), and compound (8a, 8c, and 8g) and receptor (PDB; 4BDS) with appropriate distances and atoms involved in the binding interactions are demonstrated in Figure 6, Figure 7, Figure 8, Figure 9, Figure 10, Figure 11, Figure 12 and Figure 13 and Tables S1 and S2.
2.4. SeeSAR Visual Drug Design
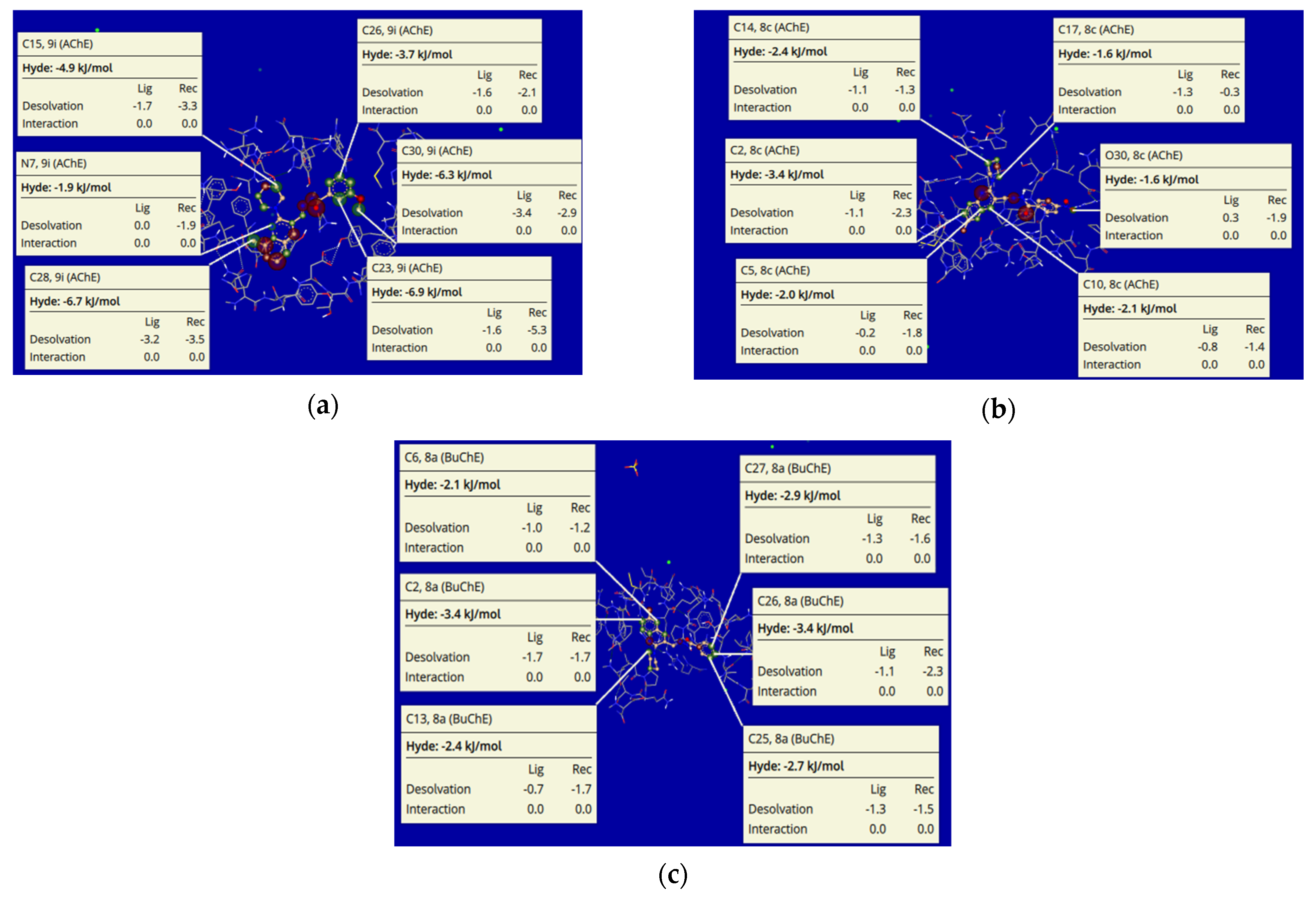
Among all the tested compounds, 8c and 9i showed exceptional Hyde energies against AChE, while 8a was identified with a similar profile against BuChE. The visual and explore modes of the docked poses of inhibitors 9i (a), 8c (b), and 8a (c) depicted expressible, inventive, and important conformations using the SeeSAR tool of LeadIT software [51,52]. Figure 14 shows the iterative and interactive optimization of leads exhibiting the binding and non-binding capacity of inhibitors. Different atoms exhibited Hyde energies in 9i (AChE), such as C15 (−4.9 kj/mol), C26 (−3.7 kj/mol), C30 (−6.3 kj/mol), C28 (−6.7 kj/mol), C23 (−6.9 kj/mol) and N (−1.9 kj/mol). In parallel, compound 8c also showed Hyde energies such as C14 (−2.4 kj/mol), C17 (−1.6 kj/mol), C2 (−3.4 kj/mol), C5 (−2.0 kj/mol), C10 (−2.1 kj/mol) and O30 (−1.6 kj/mol). Likewise, compound 8a (BuChE) also depicted Hyde energies such as C6 (−2.1 kj/mol), C2 (−3.4 kj/mol), C13 (−2.4 kj/mol), C27 (−2.9 kj/mol), C26 (−3.4 kj/mol) and C25 (−2.7 kj/mol) as shown in Figure 14. Desolvation and interactions for compounds 9i, 8c, and 8a are also shown in Figure 14. The approach predicts the visual and interpretable feedback for implicit hydrogen bonds and dehydration and confirms our molecular docking results obtained using FlexX default parameters.
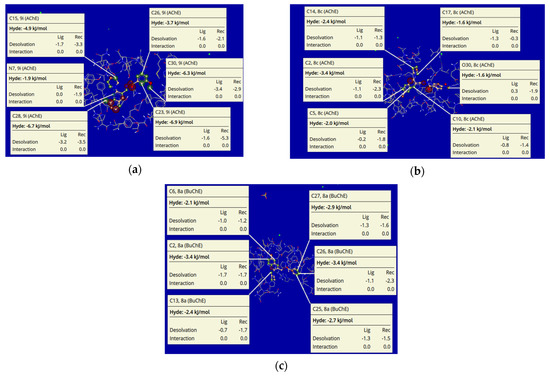
Figure 14.
Visualization and investigational modes of the docked pose of compounds 9i (a) 8c (b), and 8a (c) within the active pocket of AChE (pdb: 4BDT) and BuChE (pdb: 4BDS), respectively. The green color depicts the favorable and contributing atoms revealing interactions within the active site; subsequently, light green are chlorine atoms, red color are oxygen atoms, and blue are nitrogen atoms.
2.5. Molecular Dynamics Simulation
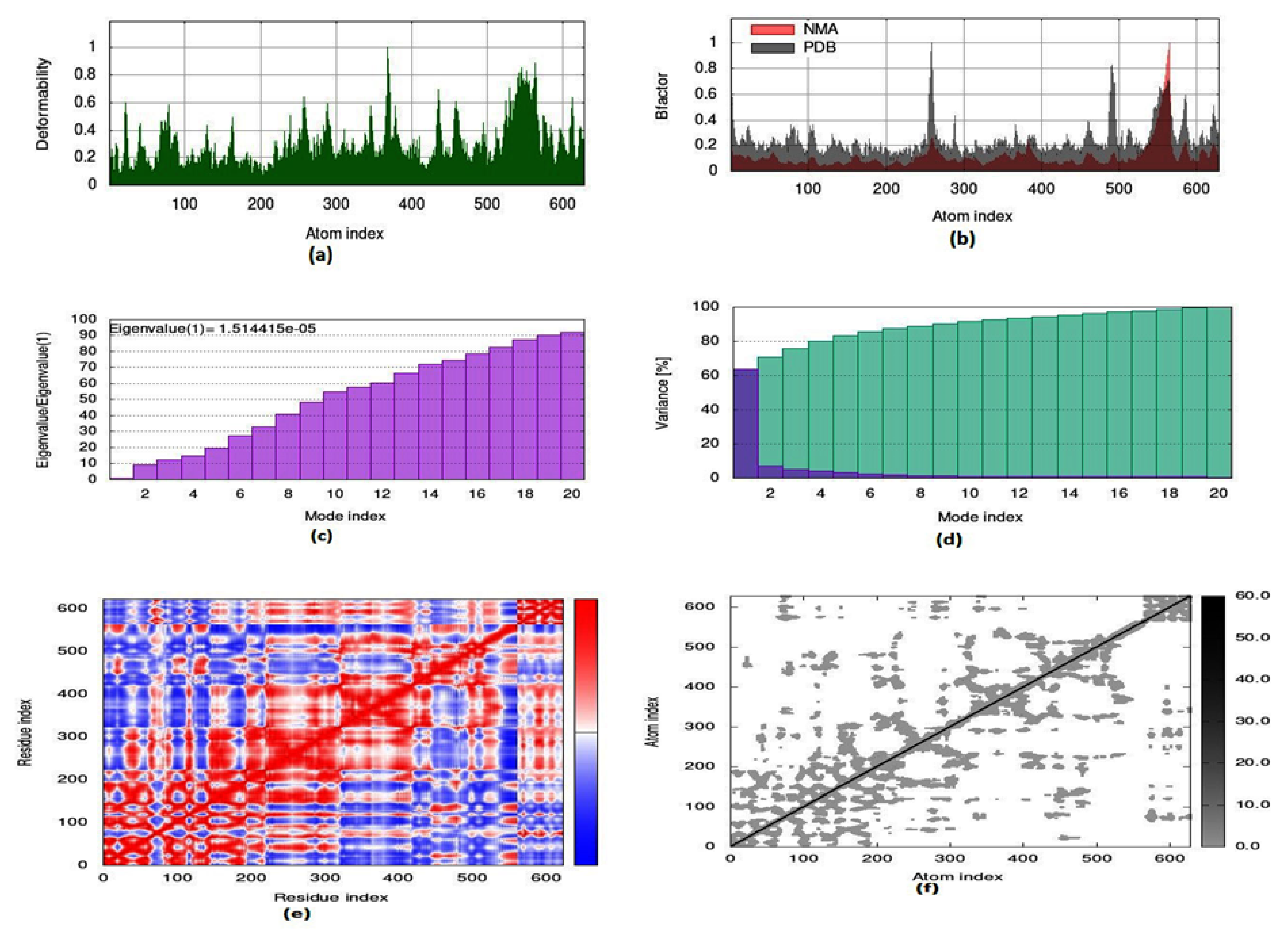
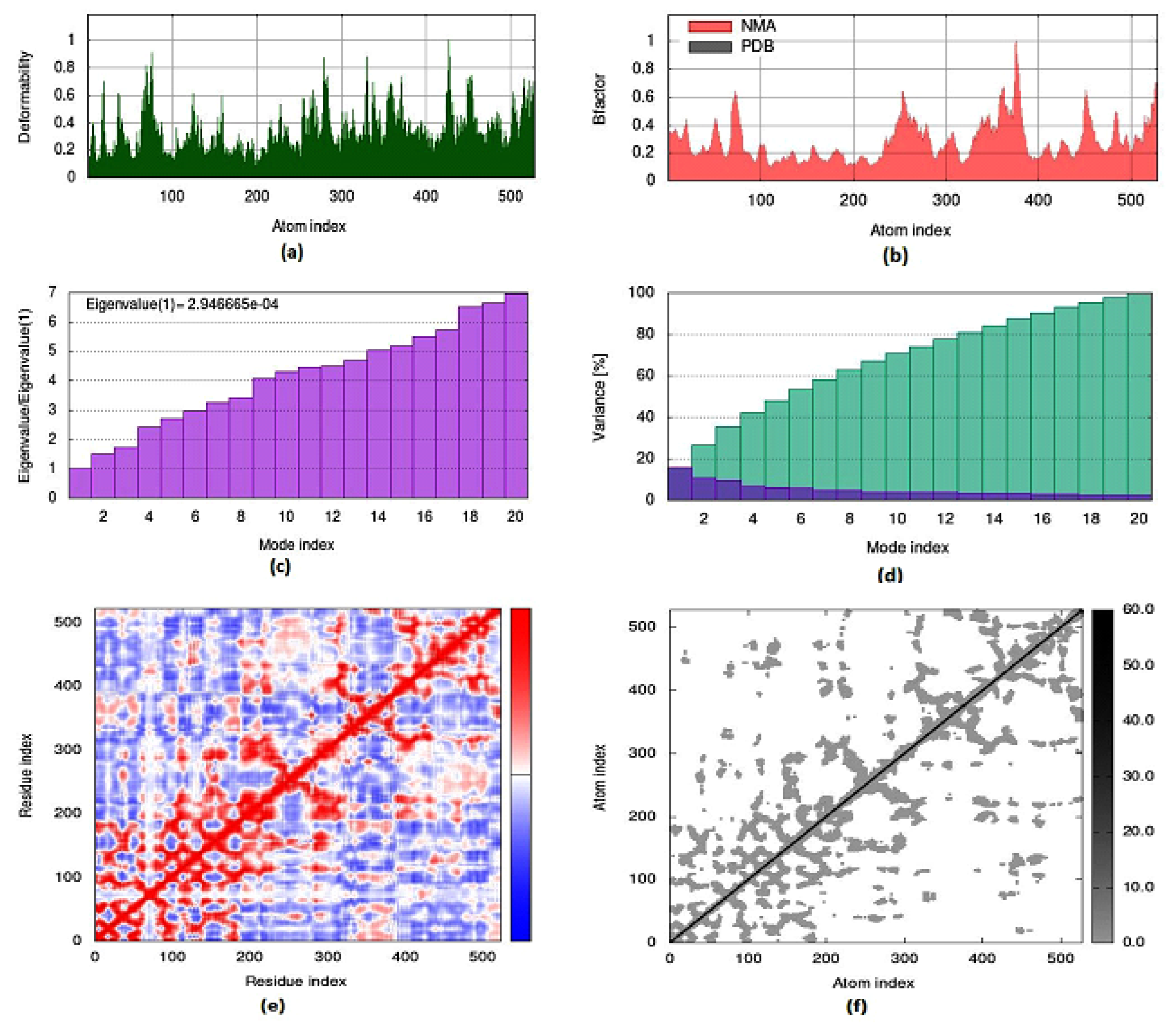
To evaluate the strength, movement of atoms and stiffness of the highest ranked docked pose of protein complex 8c (AChE) and 8a (BuChE), molecular dynamics simulation was carried out by employing the online web server iMODs (http://imods.chaconlab.org/ accessed on 20 October 2022) at a specific temperature (300 K), and constant pressure (1 atm). Molecular dynamics simulation was performed in normal mode analysis, and the results of docked complexes are displayed in Figure 15 and Figure 16. The deformability graphs of protein complexes are shown in Figure 15a and Figure 16a, with the location of different hinges (high and low) depicting the deformed region of residues in docked complexes. The experimental B-factor in Figure 15b and Figure 16b determines the value of root mean square (RMS) and reveals the unpredictability of atoms in the protein complexes. The eigenvalues of 8c and 8a were presented to be 1.514415 × 10−05 and 2.946665 × 10−04, respectively, as shown in Figure 15c and Figure 16c. Eigenvalue connected to normal mode exhibiting the motion inflexibility and proportional to the related binding energy to deform the globular structure of protein. Figure 15d and Figure 16d showed the variance graph of amino acid residues, which is inversely proportional to the eigenvalue. On the other hand, the covariance matrix shown in Figure 15e and Figure 16e stipulated the pairing between amino acid residues experience motions in different colors, such as red-color (correlated), white-color (uncorrelated), and blue-color (anti-correlated). The elastic model describes the coupling pair of atoms that are associated with springs. The different dots (grey color) present in the graph indicate one spring between interrelating atoms that define the inelastic springs, as shown in Figure 15f and Figure 16f.
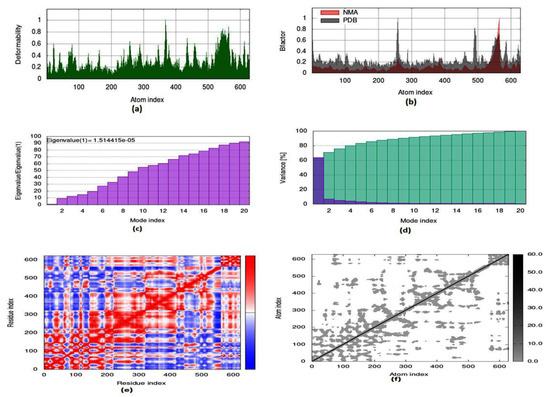
Figure 15.
Molecular dynamics simulation of 8c complex (AChE) by iMODS server. (a) Deformability, (b) B-factor values, (c) eigenvalue, (d) variance, (e) covariance, and (f) elastic network model.
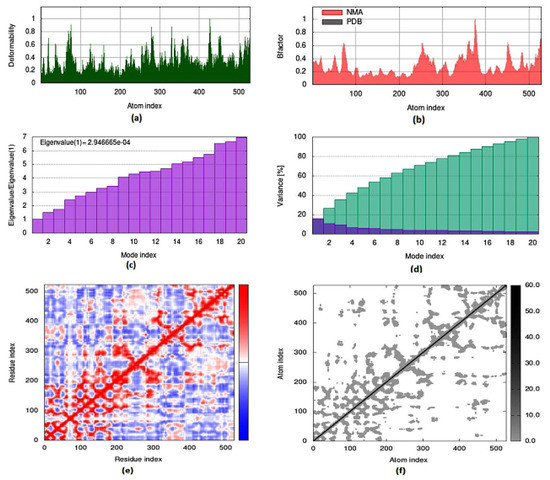
Figure 16.
Molecular dynamics simulation of 8a complex (BuChE) by iMODS server. (a) Deformability, (b) B-factor values, (c) eigenvalue, (d) variance, (e) covariance, and (f) elastic network model.
2.6. Physicochemical Properties
The pharmacokinetic properties of compounds 8a, 8c, 8g, and 9i were predicted to estimate the impact of various parameters using earlier published prediction tools [53,54,55]. These parameters include molecular weight, polar surface area, number of atom types (donor/acceptor), molecular refractivity and lipophilicity i-e., the partition coefficient such as log Po/w, n-octanol, MLOGP, WLOGP, and XLOGP3, etc. illustrating the binding energies of solvation and solvent accessible surface area. The most important parameters, such as molecular weight, are that small (<500 Da), hydrophobicity of the compounds (Log P values), and polar surface area (PSA) exhibited permeability of blood–brain barrier, whereas number of HBA and HBD showed as described in Table S2. Additionally, water solubility demonstrates the solubility of the compounds in water, such as Log S (ESOL) exhibited moderate solubility, and Log S (SILICOS-IT) depicted poor solubility. Pharmacokinetics also presented P-gp substrate, cytochrome inhibitors, and Log kp (skin permeation). These properties predict the drug-likeness and blood-brain barrier permeation of experimental compounds. All the selected compounds exhibit high gastrointestinal absorption, which makes them more feasible for the drug candidate. Compounds also showed up to mark efficacy with respective to drug likeliness followed by Lipinski, Ghose, Veber Egan, and Muegge rules with a bioavailability score of 0.55. The results presented in Table S3 reveal that synthetic derivatives could be developed as safe drugs.
2.7. Anticancer Activity
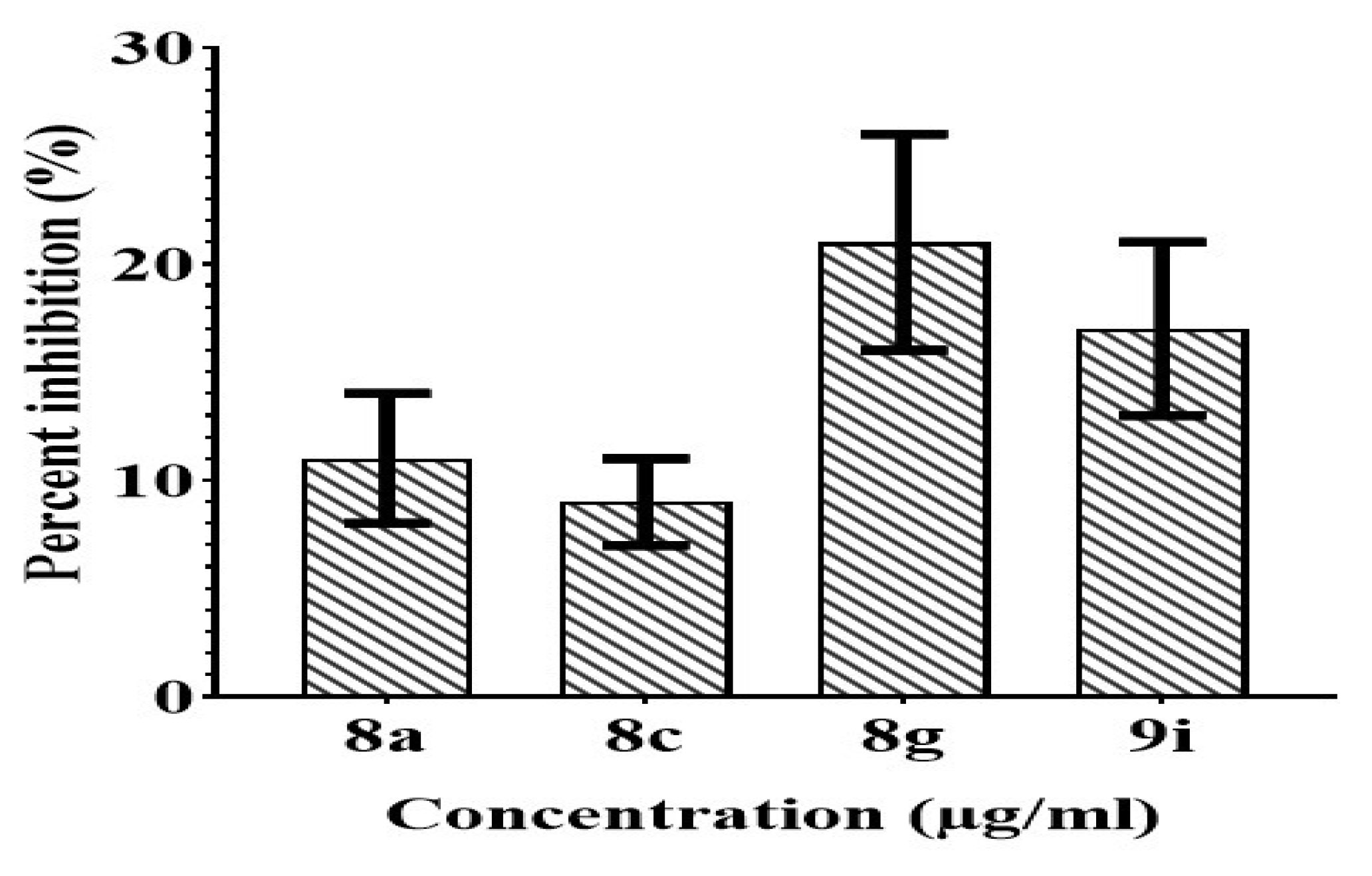
The initial screening revealed that potent compounds (8a, 8c, 8g, and 9i) exhibited less toxicity towards the normal kidney cells (Figure 17) which showed that our compounds are safe to be used as drugs. All the tested compounds displayed less than 22% inhibition.
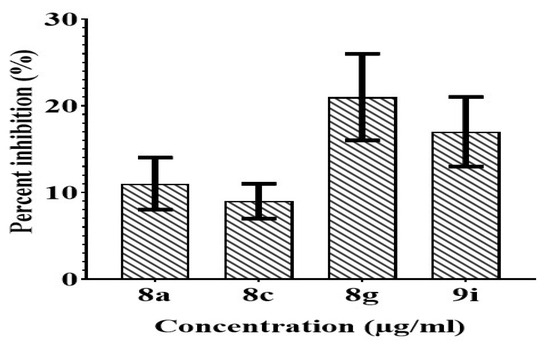
Figure 17.
Evaluation of anticancer potential of potent compounds against Vero cell line.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General
The chemicals and solvents were purchased from Scharlau, Merck, and Fluka and were used without further purification. Ultrasonic-mediated reactions were carried out in a Clifton Ultrasonic Bath (2 x T2A, 300W, DU-4). Thin layer chromatography (TLC) was carried out on aluminum plates coated with silica gel 60 F254 (Merck) in an appropriate eluent, while ultraviolet light was used for visualization. Melting points were noted on the Gallenkamp melting point apparatus in open capillaries and were uncorrected. 1H- and 13C NMR spectra were recorded in DMSO-d6 on the Brücker Avance NMR instrument at 300 and 75 MHz, respectively, using TMS as an internal standard. Chemical shifts are reported as δ values in parts per million (ppm), and coupling constants (J) are given in Hertz. FTIR spectra were recorded on Bruker FTIR Spectrophotometer. High-resolution mass spectra were recorded using the electron impact (EI) technique. Elemental analysis was recorded on LECO 630-200-200 TRUSPEC CHNS micro analyzer, and the values observed were within ± 0.4% of the calculated results. Compounds 2–4, 6, and 7 were synthesized using previously reported procedures [41,43,45,46].
3.2. General Procedure for the Synthesis of N′-((methyl-2-(piperidin-1-yl)quinolin-3-yl)methylene)benzohydrazides (8a-m and 9a-j)
3.2.1. Method A: Conventional Approach
To a stirred solution of 6/8-methyl-2-(piperidin-1-yl)quinoline-3-carbaldehyde 4a or 4b (1 mmol) in absolute ethanol (20 mL) was added aromatic acid hydrazide 7 (1 mmol) followed by a catalytic amount of glacial acetic acid. The resulting reaction mixture was heated at reflux temperature with continuous stirring until the product precipitated out. The precipitated product was filtered, washed with hot ethanol, and dried to afford compounds 8a-m and 9a-j.
3.2.2. Method B: Ultrasonic-Assisted Approach
The equimolar quantities of 6/8-methyl-2-(piperidin-1-yl)quinoline-3-carbaldehyde 4a or 4b (1 mmol) and aromatic acid hydrazide 7 (1 mmol) were dissolved in absolute ethanol (20 mL). A catalytic amount of glacial acetic acid was added to this reaction mixture and exposed to ultrasonic waves for 4–6 min at room temperature. The precipitated products were filtered, washed with hot ethanol, and dried to afford compounds 8a-m and 9a-j.
N′-((6-methyl-2-(piperidin-1-yl)quinolin-3-yl)methylene)benzohydrazide (8a): Yellow solid. Mp 260–262 °C. FTIR (ῡ, cm−1, neat): 3187 (NH), 3066 (CH-aromatic), 2960 (CH), 1641 (C=O), 1601 (C=N), 1070 (C-N); 1H NMR (DMSO-d6, 300 MHz) δ = 1.61–1.75 (m, 6H, piperidinyl-CH2), 2.45 (s, 3H, CH3), 3.19–3.22 (m, 4H, piperidinyl-N-CH2), 7.49–7.74 (m, 6H, ArH), 7.94 (d, J = 6.9 Hz, 2H, ArH), 8.52 (s, 1H, ArH), 8.61 (s, 1H, N=CH), 12.05 (s, 1H, NH); 13C NMR (DMSO-d6, 75 MHz) δ = 21.4 (CH3), 24.4 (piperidinyl-CH2), 25.9 (piperidinyl-CH2), 52.3 (piperidinyl-N-CH2), 122.0, 125.1, 127.3, 127.6, 128.2, 129.0, 132.3, 132.8, 134.0, 134.2, 135.0, 145.4, 145.8, 160.1, 163.8 (C=O); HRMS (EI) Exact mass calcd for C23H25N4O [M+H]+: 373.2025, found: 373.2021; Anal. Calcd. for C23H24N4O: C, 74.17; H, 6.49; N, 15.04%. Found: C, 74.25; H, 6.53; N, 15.10%.
N′-((6-methyl-2-(piperidin-1-yl)quinolin-3-yl)methylene)-3-nitrobenzohydrazide (8b): Yellow solid. Mp 228–230 °C. FTIR (ῡ, cm−1, neat): 3186 (NH), 3034 (CH-aromatic), 2940 (CH), 1654 (C=O), 1608 (C=N), 1077 (C-N); 1H NMR (DMSO-d6, 300 MHz) δ = 1.59–1.75 (m, 6H, piperidinyl-CH2), 2.45 (s, 3H, CH3), 3.19–3.22 (m, 4H, piperidinyl-N-CH2), 7.50 (dd, J = 8.7, 1.5 Hz, 1H, ArH), 7.53 (d, J = 6.9 Hz, 1H, ArH), 7.81 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H, ArH), 7.87 (t, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H, ArH), 8.40 (d, J =7.8 Hz, 1H, ArH), 8.47 (dd, J = 8.1, 1.5 Hz, 1H, ArH), 8.59 (s, 1H, ArH), 8.62 (s, 1H, N=CH), 8.76 (t, J = 1.5 Hz, 1H, ArH), 12.32 (s, 1H, NH); 13C NMR (DMSO-d6, 75 MHz) δ = 21.4 (CH3), 24.4 (piperidinyl-CH2), 25.9 (piperidinyl-CH2), 52.3 (piperidinyl-N-CH2), 121.1, 122.8, 124.6, 124.7, 126.8, 126.9, 130.8, 134.7, 134.9, 135.3, 136.2, 146.1, 146.4, 148.3, 159.3, 161.6 (C=O); HRMS (EI) Exact mass calcd for C23H24N5O3 [M+H]+: 418.1877, found: 418.1875; Anal. Calcd. for C23H23N5O3: C, 66.17; H, 5.55; N, 16.78%. Found: C, 66.31; H, 5.69; N, 16.92%.
N′-((6-methyl-2-(piperidin-1-yl)quinolin-3-yl)methylene)-4-nitrobenzohydrazide (8c): Yellow solid. Mp 242–244 °C. FTIR (ῡ, cm−1, neat): 3210 (NH), 3047 (CH-aromatic), 2940 (CH), 1629 (C=O), 1604 (C=N), 1071 (C-N); 1H NMR (DMSO-d6, 300 MHz) δ = 1.61–1.75 (m, 6H, piperidinyl-CH2), 2.45 (s, 3H, CH3), 3.18–3.21 (m, 4H, piperidinyl-N-CH2), 7.50 (dd, J = 8.7, 1.5 Hz, 1H, ArH), 7.65–7.76 (m, 2H, ArH), 8.40 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H, ArH), 8.56 (s, 1H, ArH), 8.61 (s, 1H, N=CH), 8.71 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 2H, ArH), 12.31 (s, 1H, NH); 13C NMR (DMSO-d6, 75 MHz) δ = 21.4 (CH3), 24.4 (piperidinyl-CH2), 25.9 (piperidinyl-CH2), 52.3 (piperidinyl-N-CH2), 121.1, 122.8, 124.6, 124.7, 126.8, 126.9, 130.8, 134.7, 134.9, 135.3, 136.2, 146.4, 148.3, 159.3, 161.6 (C=O); HRMS (EI) Exact mass calcd for C23H24N5O3 [M+H]+: 418.1876, found: 418.1870; Anal. Calcd. for C23H23N5O3: C, 66.17; H, 5.55; N, 16.78%. Found: C, 66.29; H, 5.71; N, 16.84%.
2-Amino-N′-((6-methyl-2-(piperidin-1-yl)quinolin-3-yl)methylene)benzohydrazide (8d): Greenish yellow solid. Mp 260–262 °C. FTIR (ῡ, cm−1, neat): 3493, 3381 (NH2), 3202 (NH), 3057 (CH-aromatic), 2949 (CH), 1635 (C=O), 1587 (C=N), 1067 (C-N); 1H NMR (DMSO-d6, 300 MHz) δ = 1.60–1.75 (m, 6H, piperidinyl-CH2), 2.45 (s, 3H, CH3), 3.18–3.21 (m, 4H, piperidinyl-N-CH2), 6.40 (s, 2H, NH2), 6.61 (t, J = 7.5 Hz, 1H, ArH), 6.78 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H, ArH), 7.23 (td, J = 7.8, 1.5 Hz, 1H, ArH), 7.48 (dd, J = 8.7, 1.8 Hz, 1H, ArH), 7.59 (dd, J = 7.8, 1.2 Hz, 1H, ArH), 7.66 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H, ArH), 7.71 (s, 1H, ArH), 8.49 (s, 1H, ArH), 8.54 (s, 1H, N=CH), 11.85 (s, 1H, NH); 13C NMR (DMSO-d6, 75 MHz) δ = 21.4 (CH3), 24.4 (piperidinyl-CH2), 25.9 (piperidinyl-CH2), 52.3 (piperidinyl-N-CH2), 114.0, 115.1, 116.8, 122.2, 125.1, 127.3, 127.6, 128.9, 132.7, 132.8, 134.2, 134.7, 144.3, 145.7, 150.5, 160.1, 165.9 (C=O); HRMS (EI) Exact mass calcd for C23H26N5O [M+H]+: 388.2130, found: 388.2124; Anal. Calcd. for C23H25N5O: C, 71.29; H, 6.50; N, 18.07%. Found: C, C, 71.43; H, 6.62; N, 18.15%.
4-Amino-N′-((6-methyl-2-(piperidin-1-yl)quinolin-3-yl)methylene)benzohydrazide (8e): Greenish Yellow solid. Mp 252–254 °C. FTIR (ῡ, cm−1, neat): 3480, 3386 (NH2), 3212 (NH), 3047 (CH-aromatic), 2939 (CH), 1629 (C=O), 1605 (C=N), 1072 (C-N); 1H NMR (DMSO-d6, 300 MHz) δ = 1.61–1.75 (m, 6H, piperidinyl-CH2), 2.44 (s, 3H, CH3), 3.18–3.21 (m, 4H, piperidinyl-N-CH2), 5.83 (s, 2H, NH2), 6.62 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H, ArH), 7.48 (dd, J = 8.7, 1.8 Hz, 1H, ArH), 7.63–7.71 (m, 4H, ArH), 8.46 (s, 1H, ArH), 8.54 (s, 1H, N=CH), 11.68 (s, 1H, NH); 13C NMR (DMSO-d6, 75 MHz) δ = 21.4 (CH3), 24.4 (piperidinyl-CH2), 25.9 (piperidinyl-CH2), 52.2 (piperidinyl-N-CH2), 113.0, 119.9, 122.4, 125.1, 127.3, 127.5, 129.9, 130.0, 132.6, 134.2, 134.5, 143.4, 145.6, 152.9, 160.1 (C=O); HRMS (EI) Exact mass calcd for C23H26N5O [M+H]+: 388.2131, found: 388.2127; Anal. Calcd. for C23H25N5O: C, 71.29; H, 6.50; N, 18.07%. Found: C, 71.17; H, 6.32; N, 18.01%.
2-Chloro-N′-((6-methyl-2-(piperidin-1-yl)quinolin-3-yl)methylene)benzohydrazide (8f): Light yellow solid. Mp 244–246 °C. FTIR (ῡ, cm−1, neat): 3186 (NH), 3060 (CH-aromatic), 2918 (CH), 1658 (C=O), 1575 (C=N), 1050 (C-N); 1H NMR (DMSO-d6, 300 MHz) δ = 1.59–1.72 (m, 6H, piperidinyl-CH2), 2.45 (s, 3H, CH3), 3.16–3.19 (m, 4H, piperidinyl-N-CH2), 7.49–7.65 (m, 6H, ArH), 7.75 (s, 1H, ArH), 8.44 (s, 1H, ArH), 8.55 (s, 1H, N=CH), 12.14 (s, 1H, NH); 13C NMR (DMSO-d6, 75 MHz) δ = 21.4 (CH3), 24.4 (piperidinyl-CH2), 25.9 (piperidinyl-CH2), 52.3 (piperidinyl-N-CH2), 121.6, 125.1, 127.3, 127.8, 129.9, 130.3, 130.9, 132.0, 132.9, 134.3, 135.0, 135.6, 145.6, 145.9, 160.1, 162.9, 169.0 (C=O); HRMS (EI) Exact mass calcd for C23H24ClN4O [M+H]+: 407.1638, found: 407.1629; Anal. Calcd. for C23H23ClN4O: C, 67.89; H, 5.70; N, 13.77%. Found: C, 68.01; H, 5.84; N, 13.91%.
3-Chloro-N′-((6-methyl-2-(piperidin-1-yl)quinolin-3-yl)methylene)benzohydrazide (8g): Yellow solid. Mp 216–218 °C. FTIR (ῡ, cm−1, neat): 3178 (NH), 3066 (CH-aromatic), 2921 (CH), 1655 (C=O), 1589 (C=N), 1049 (C-N); 1H NMR (DMSO-d6, 300 MHz) δ = 1.59–1.75 (m, 6H, piperidinyl-CH2), 2.45 (s, 3H, CH3), 3.19–3.22 (m, 4H, piperidinyl-N-CH2), 7.50 (dd, J = 8.7, 1.5 Hz, 1H, ArH), 7.60 (t, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H, ArH), 7.65–7.74 (m, 3H, ArH), 7.91 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H, ArH), 7.98 (t, J = 1.5 Hz, 1H, ArH), 8.52 (s, 1H, ArH), 8.60 (s, 1H, N=CH), 12.13 (s, 1H, NH); 13C NMR (DMSO-d6, 75 MHz) δ = 21.4 (CH3), 24.4 (piperidinyl-CH2), 25.9 (piperidinyl-CH2), 52.3 (piperidinyl-N-CH2), 121.8, 125.1, 127.0, 127.3, 127.7, 127.8, 131.1, 132.1, 132.9, 133.8, 134.3, 135.1, 135.9, 145.8, 145.9, 160.1, 162.4 (C=O); HRMS (EI) Exact mass calcd for C23H24ClN4O [M+H]+: 407.1632, found: 407.1630; Anal. Calcd. for C23H23ClN4O: C, 67.89; H, 5.70; N, 13.77%. Found: C, 67.95; H, 5.74; N, 13.89%.
4-Chloro-N′-((6-methyl-2-(piperidin-1-yl)quinolin-3-yl)methylene)benzohydrazide (8h): Yellow solid. Mp 250–252 °C. FTIR (ῡ, cm−1, neat): 3200 (NH), 3069 (CH-aromatic), 2939 (CH), 1644 (C=O), 1593 (C=N), 1065 (C-N); 1H NMR (DMSO-d6, 300 MHz) δ = 1.59–1.75 (m, 6H, piperidinyl-CH2), 2.45 (s, 3H, CH3), 3.19–3.22 (m, 4H, piperidinyl-N-CH2), 7.50 (dd, J = 8.7, 1.5 Hz, 1H, ArH), 7.64 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 2H, ArH), 7.66–7.74 (m, 2H, ArH), 7.97 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H, ArH), 8.52 (s, 1H, ArH), 8.60 (s, 1H, N=CH), 12.11 (s, 1H, NH); 13C NMR (DMSO-d6, 75 MHz) δ = 21.4 (CH3), 24.4 (piperidinyl-CH2), 25.9 (piperidinyl-CH2), 52.3 (piperidinyl-N-CH2), 121.9, 125.1, 127.3, 127.6, 129.1, 130.1, 132.6, 132.8, 134.3, 135.1, 137.1, 145.7, 145.8, 160.1, 162.7 (C=O); HRMS (EI) Exact mass calcd for C23H24ClN4O [M+H]+: 407.1631, found: 407.1633; Anal. Calcd. for C23H23ClN4O: C, 67.89; H, 5.70; N, 13.77%. Found: C, 67.75; H, 5.56; N, 13.59%.
2,4-Dichloro-N′-((6-methyl-2-(piperidin-1-yl)quinolin-3-yl)methylene)benzohydrazide (8i): Light yellow solid. Mp 240–242 °C. FTIR (ῡ, cm−1, neat): 3184 (NH), 3055 (CH-aromatic), 2944 (CH), 1662 (C=O), 1590 (C=N), 1073 (C-N); 1H NMR (DMSO-d6, 300 MHz) δ = 1.59–1.72 (m, 6H, piperidinyl-CH2), 2.45 (s, 3H, CH3), 3.16–3.19 (m, 4H, piperidinyl-N-CH2), 7.50 (dd, J = 8.7, 1.5 Hz, 1H, ArH), 7.57–7.77 (m, 4H, ArH), 7.82 (d, J = 1.8 Hz, 1H, ArH), 8.44 (s, 1H, ArH), 8.55 (s, 1H, N=CH), 12.16 (s, 1H, NH); 13C NMR (DMSO-d6, 75 MHz) δ = 21.4 (CH3), 24.4 (piperidinyl-CH2), 25.9 (piperidinyl-CH2), 52.4 (piperidinyl-N-CH2), 121.5, 125.1, 127.3, 127.7, 128.1, 129.9, 131.0, 131.3, 132.3, 133.0, 134.3, 134.4, 135.8, 142.9, 145.9, 160.1, 162.0 (C=O); HRMS (EI) Exact mass calcd for C23H23Cl2N4O [M+H]+: 441.1245, found: 441.1240; Anal. Calcd. for C23H22Cl2N4O: C, 62.59; H, 5.02; N, 12.69%. Found: C, 62.81; H, 5.28; N, 12.85%.
2-Methoxy-N′-((6-methyl-2-(piperidin-1-yl)quinolin-3-yl)methylene)benzohydrazide (8j): Yellow solid. Mp 228–230 °C. FTIR (ῡ, cm−1, neat): 3182 (NH), 3051 (CH-aromatic), 2930 (CH), 1636 (C=O), 1596 (C=N), 1246 (C-O), 1070 (C-N); 1H NMR (DMSO-d6, 300 MHz) δ = 1.60–1.74 (m, 6H, piperidinyl-CH2), 2.44 (s, 3H, CH3), 3.18–3.21 (m, 4H, piperidinyl-N-CH2), 3.85 (s, 3H, OCH3), 7.19 (ddd, J = 7.2, 2.4, 1.2 Hz, 1H, ArH), 7.45–7.53 (m, 4H, ArH), 7.66 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H, ArH), 7.72 (s, 1H, ArH), 8.51 (s, 1H, ArH), 8.61 (s, 1H, N=CH), 12.03 (s, 1H, NH); 13C NMR (DMSO-d6, 75 MHz) δ = 21.4 (CH3), 24.4 (piperidinyl-CH2), 25.9 (piperidinyl-CH2), 52.3 (piperidinyl-N-CH2), 55.8, 113.5, 117.9, 120.3, 122.0, 125.1, 127.3, 127.6, 130.2, 132.8, 134.2, 135.0, 135.3, 145.5, 145.8, 159.7, 160.1, 163.6 (C=O); HRMS (EI) Exact mass calcd for C24H27N4O2 [M+H]+: 403.2134, found: 403.2125; Anal. Calcd. for C24H26N4O2: C, 71.62; H, 6.51; N, 13.92%. Found: C, 71.78; H, 6.67; N, 14.08%.
3-Methoxy-N′-((6-methyl-2-(piperidin-1-yl)quinolin-3-yl)methylene)benzohydrazide (8k): Yellow solid. Mp 190–192 °C. FTIR (ῡ, cm−1, neat): 3181 (NH), 3051 (CH-aromatic), 2931 (CH), 1635 (C=O), 1595 (C=N), 1245 (C-O), 1071 (C-N); 1H NMR (DMSO-d6, 300 MHz) δ = 1.58–1.73 (m, 6H, piperidinyl-CH2), 2.45 (s, 3H, CH3), 3.17–3.21 (m, 4H, piperidinyl-N-CH2), 3.87 (s, 3H, OCH3), 7.07 (t, J = 7.5 Hz, 1H, ArH), 7.17 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H, ArH), 7.48–7.58 (m, 3H, ArH), 7.66 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H, ArH), 7.73 (s, 1H, ArH), 8.45 (s, 1H, ArH), 8.51 (s, 1H, N=CH), 11.75 (s, 1H, NH); 13C NMR (DMSO-d6, 75 MHz) δ = 21.4 (CH3), 24.4 (piperidinyl-CH2), 25.9 (piperidinyl -CH2), 52.3 (piperidinyl-N-CH2), 56.2, 112.4, 120.9, 121.9, 124.6, 125.1, 127.3, 127.6, 130.1, 132.5, 132.8, 134.2, 134.9, 144.7, 145.8, 157.1, 160.1, 163.1 (C=O); HRMS (EI) Exact mass calcd for C24H27N4O2 [M+H]+: 403.2128, found: 403.2131; Anal. Calcd. for C24H26N4O2: C, 71.62; H, 6.51; N, 13.92%. Found: C, 71.44; H, 6.39; N, 13.80%.
4-Methoxy-N′-((6-methyl-2-(piperidin-1-yl)quinolin-3-yl)methylene)benzohydrazide (8l): Greenish yellow solid. Mp 248–250 °C. FTIR (ῡ, cm−1, neat): 3209 (NH), 3051 (CH-aromatic), 2955 (CH), 1640 (C=O), 1601 (C=N), 1247 (C-O), 1068 (C-N); 1H NMR (DMSO-d6, 300 MHz) δ = 1.62–1.76 (m, 6H, piperidinyl-CH2), 2.46 (s, 3H, CH3), 3.20–3.23 (m, 4H, piperidinyl-N-CH2), 3.86 (s, 3H, OCH3), 7.10 (d, J = 9.0 Hz, 2H, ArH), 7.50 (dd, J = 8.4, 1.5 Hz, 1H, ArH), 7.67 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H, ArH), 7.74 (d, J = 0.9 Hz, 1H, ArH), 7.94 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 2H, ArH), 8.51 (s, 1H, ArH), 8.60 (s, 1H, N=CH), 11.94 (s, 1H, NH); 13C NMR (DMSO-d6, 75 MHz) δ = 21.4 (CH3), 24.4 (piperidinyl-CH2), 25.9 (piperidinyl-CH2), 52.3 (piperidinyl-N-CH2), 55.9, 114.2, 122.1, 125.1, 125.9, 127.3, 127.6, 130.1, 132.7, 134.2, 134.8, 144.7, 145.7, 160.1, 162.5, 163.2 (C=O); HRMS (EI) Exact mass calcd for C24H27N4O2 [M+H]+: 403.2132, found: 403.2126; Anal. Calcd. for C24H26N4O2: C, 71.62; H, 6.51; N, 13.92%. Found: C, 71.60; H, 6.45; N, 13.86%.
2-Hydroxy-N′-((6-methyl-2-(piperidin-1-yl)quinolin-3-yl)methylene)benzohydrazide (8m): Yellow solid. Mp 210–212 °C. FT-IR (ῡ cm−1; neat): 3405 (OH), 3209 (NH), 3047 (CH-Aromatic), 2939 (CH), 1629 (C=O), 1604 (C=N), 1070 (C-N); 1H NMR (DMSO-d6, 300 MHz) δ = 1.59–1.75 (m, 6H, Piperidinyl -CH2-), 2.45 (s, 3H, -CH3), 3.20–3.23 (m, 4H, Piperidinyl N-CH2-), 6.96–7.01 (m, 2H, ArH), 7.46 (dd, J = 8.1 Hz, 1.5 Hz, 1H, ArH), 7.51 (dd, J = 8.4 Hz, 1.8 Hz, 1H, ArH), 7.67 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H, ArH), 7.74 (s, 1H, ArH), 7.89 (dd, J = 8.1 Hz, 2.1 Hz, 1H, ArH), 8.53 (s, 1H, ArH), 8.60 (s, 1H, -N=CH-), 11.81 (s, 1H, -OH), 12.07 (s, 1H, -NH-) ppm. 13C NMR (DMSO-d6, 75 MHz) δ = 21.4 (-CH3), 24.4 (Piperidinyl -CH2), 25.9 (2C; Piperidinyl -CH2), 52.3 (2C; Piperidinyl-N-CH2), 116.5, 117.8, 119.4, 121.8, 125.1, 127.3, 127.7, 128.9, 132.9, 134.2, 134.3, 135.2, 145.9, 146.3, 159.6, 160.1, 165.6 (C=O) ppm; HRMS (EI) Exact mass calcd for C23H25N4O2 [M+H]+: 389.1975, found: 389.1980; Anal. Calcd. for C23H24N4O2: C, 71.11; H, 6.23; N, 14.42%. Found: C, 71.33; H, 6.49; N, 14.60%.
N′-((8-methyl-2-(piperidin-1-yl)quinolin-3-yl)methylene)benzohydrazide (9a): Yellow solid. Mp 254–256 °C. FTIR (ῡ, cm−1, neat): 3186 (NH), 3065 (CH-aromatic), 2960 (CH), 1642 (C=O), 1553 (C=N), 1070 (C-N); 1H NMR (CDCl3, 300 MHz) δ = 1.66–1.83 (m, 6H, piperidinyl-CH2), 2.72 (s, 3H, CH3), 3.34–3.37 (m, 4H, piperidinyl-N-CH2), 7.25–7.30 (m, 1H, ArH), 7.49–7.64 (m, 5H, ArH), 7.91–7.95 (m, 2H, ArH), 8.46 (s, 1H, ArH), 8.70 (s, 1H, N=CH), 9.27 (s, 1H, NH); 13C NMR (DMSO-d6, 75 MHz) δ = 17.8 (CH3), 24.5 (piperidinyl-CH2), 25.8 (piperidinyl-CH2), 52.1 (piperidinyl-N-CH2), 114.5, 114.2, 121.5, 124.6, 124.8, 125.9, 126.6, 130.1, 130.6, 134.9, 135.8, 144.7, 145.9, 159.3, 162.5 (C=O); HRMS (EI) Exact mass calcd for C23H25N4O [M+H]+: 373.2028, found: 373.2024; Anal. Calcd. for C23H24N4O: C, 74.17; H, 6.49; N, 15.04%. Found: C, 74.21; H, 6.57; N, 15.16%.
N′-((8-methyl-2-(piperidin-1-yl)quinolin-3-yl)methylene)-3-nitrobenzohydrazide (9b): Yellow solid. Mp 226–228 °C. FTIR (ῡ, cm−1, neat): 3186 (NH), 3033 (CH-aromatic), 2939 (CH), 1654 (C=O), 1609 (C=N), 1078 (C-N); 1H NMR (DMSO-d6, 300 MHz) δ = 1.64–1.77 (m, 6H, piperidinyl-CH2), 2.63 (s, 3H, CH3), 3.28–3.31 (m, 4H, piperidinyl-N-CH2), 7.31 (t, J = 7.5 Hz, 1H, ArH), 7.53 (d, J = 6.9 Hz, 1H, ArH), 7.81 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H, ArH), 7.87 (t, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H, ArH), 8.40 (d, J =7.8 Hz, 1H, ArH), 8.47 (dd, J = 8.1, 1.5 Hz, 1H, ArH), 8.59 (s, 1H, ArH), 8.63 (s, 1H, N=CH), 8.77 (t, J = 1.5 Hz, 1H, ArH), 12.33 (s, 1H, NH); 13C NMR (DMSO-d6, 75 MHz) δ = 17.8 (CH3), 24.5 (piperidinyl-CH2), 25.8 (piperidinyl-CH2), 52.2 (piperidinyl-N-CH2), 121.1, 122.8, 124.6, 124.7, 126.8, 126.9, 130.8, 134.7, 134.9, 135.3, 136.2, 146.1, 146.4, 148.3, 159.3, 161.6 (C=O); HRMS (EI) Exact mass calcd for C23H24N5O3 [M+H]+: 418.1870, found: 418.1864; Anal. Calcd. for C23H23N5O3: C, 66.17; H, 5.55; N, 16.78%. Found: C, 66.25; H, 5.59; N, 16.86%.
N′-((8-methyl-2-(piperidin-1-yl)quinolin-3-yl)methylene)-4-nitrobenzohydrazide (9c): Yellow solid. Mp 248–250 °C. FTIR (ῡ, cm−1, neat): 3209 (NH), 3047 (CH-aromatic), 2939 (CH), 1630 (C=O), 1604 (C=N), 1071 (C-N); 1H NMR (DMSO-d6, 300 MHz) δ = 1.61–1.76 (m, 6H, piperidinyl-CH2), 2.62 (s, 3H, CH3), 3.25–3.29 (m, 4H, piperidinyl-N-CH2), 7.31 (t, J = 7.5 Hz, 1H, ArH), 7.53 (d, J = 6.9 Hz, 1H, ArH), 7.81 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H, ArH), 8.40 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 2H, ArH), 8.54 (s, 1H, ArH), 8.60 (s, 1H, N=CH), 8.75 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H, ArH), 12.30 (s, 1H, NH); 13C NMR (DMSO-d6, 75 MHz) δ = 17.8 (CH3), 24.5 (piperidinyl-CH2), 25.8 (piperidinyl-CH2), 52.2 (piperidinyl-N-CH2), 121.1, 122.8, 124.6, 124.7, 126.8, 126.9, 130.8, 134.7, 134.9, 135.3, 136.2, 146.4, 148.3, 159.3, 163.6 (C=O); HRMS (EI) Exact mass calcd for C23H24N5O3 [M+H]+: 418.1873, found: 418.1871; Anal. Calcd. for C23H23N5O3: C, 66.17; H, 5.55; N, 16.78%. Found: C, 66.43; H, 5.79; N, 16.90%.
2-Chloro-N′-((8-methyl-2-(piperidin-1-yl)quinolin-3-yl)methylene)benzohydrazide (9d): Yellow solid. Mp 248–250 °C. FTIR (ῡ, cm−1, neat): 3187 (NH), 3061 (CH-aromatic), 2918 (CH), 1659 (C=O), 1560 (C=N), 1050 (C-N); 1H NMR (DMSO-d6, 300 MHz) δ = 1.59–1.73 (m, 6H, piperidinyl-CH2), 2.62 (s, 3H, CH3), 3.23–3.26 (m, 4H, piperidinyl-N-CH2), 7.31 (t, J = 7.5 Hz, 1H, ArH), 7.47–7.65 (m, 5H, ArH), 7.82 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H, ArH), 8.44 (s, 1H, ArH), 8.62 (s, 1H, N=CH), 12.14 (s, 1H, NH); 13C NMR (DMSO-d6, 75 MHz) δ = 17.8 (CH3), 24.5 (piperidinyl-CH2), 25.8 (piperidinyl-CH2), 52.2 (piperidinyl-N-CH2), 121.0, 124.6, 124.8, 126.8, 127.8, 129.5, 129.9, 130.3, 130.9, 132.0, 134.9, 135.6, 136.0, 145.6, 146.1, 159.4, 162.9 (C=O); HRMS (EI) Exact mass calcd for C23H24ClN4O [M+H]+: 407.1630, found: 407.1633; Anal. Calcd. for C23H23ClN4O: C, 67.89; H, 5.70; N, 13.77%. Found: C, 68.07; H, 5.94; N, 13.91%.
3-Chloro-N′-((8-methyl-2-(piperidin-1-yl)quinolin-3-yl)methylene)benzohydrazide (9e): Yellow solid. Mp 220–222 °C. FTIR (ῡ, cm−1, neat): 3200 (NH), 3068 (CH-aromatic), 2940 (CH), 1645 (C=O), 1600 (C=N), 1066 (C-N); 1H NMR (DMSO-d6, 300 MHz) δ = 1.60–1.75 (m, 6H, piperidinyl-CH2), 2.62 (s, 3H, CH3), 3.26–3.29 (m, 4H, piperidinyl-N-CH2), 7.30 (t, J = 7.5 Hz, 1H, ArH), 7.52 (d, J = 6.9 Hz, 1H, ArH), 7.58 (t, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H, ArH), 7.68 (t, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H, ArH), 7.78 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H, ArH), 7.92 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H, ArH), 8.00 (t, J = 1.5 Hz, 1H, ArH), 8.56 (s, 1H, ArH), 8.59 (s, 1H, N=CH), 12.20 (s, 1H, NH); 13C NMR (DMSO-d6, 75 MHz) δ = 17.8 (CH3), 24.5 (piperidinyl-CH2), 25.8 (piperidinyl-CH2), 52.1 (piperidinyl-N-CH2), 121.3, 124.6, 124.8, 126.7, 127.0, 127.9, 130.7, 131.0, 132.0, 133.7, 134.9, 136.0, 145.8, 146.0, 162.5 (C=O); HRMS (EI) Exact mass calcd for C23H24ClN4O [M+H]+: 407.1635, found: 407.1628; Anal. Calcd. for C23H23ClN4O: C, 67.89; H, 5.70; N, 13.77%. Found: C, 67.93; H, 5.82; N, 13.83%.
4-Chloro-N′-((8-methyl-2-(piperidin-1-yl)quinolin-3-yl)methylene)benzohydrazide (9f): Yellow solid. Mp 198–200 °C. FTIR (ῡ, cm−1, neat): 3201 (NH), 3068 (CH-aromatic), 2939 (CH), 1644 (C=O), 1594 (C=N), 1065 (C-N); 1H NMR (DMSO-d6, 300 MHz) δ = 1.65–1.76 (m, 6H, piperidinyl-CH2), 2.63 (s, 3H, CH3), 3.27–3.30 (m, 4H, piperidinyl-N-CH2), 7.31 (t, J = 7.5 Hz, 1H, ArH), 7.53 (d, J = 6.6 Hz, 1H, ArH), 7.64 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H, ArH), 7.81 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H, ArH), 7.97 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H, ArH), 8.58 (s, 1H, ArH), 8.61 (s, 1H, N=CH), 12.12 (s, 1H, NH); 13C NMR (DMSO-d6, 75 MHz) δ = 17.8 (CH3), 24.5 (piperidinyl-CH2), 25.8 (piperidinyl-CH2), 52.1 (piperidinyl-N-CH2), 121.3, 124.6, 124.8, 126.7, 129.1, 130.1, 130.8, 132.6, 134.9, 136.0, 137.1, 145.6, 146.0, 159.4, 162.7 (C=O); HRMS (EI) Exact mass calcd for C23H24ClN4O [M+H]+: 407.1632, found: 407.1631; Anal. Calcd. for C23H23ClN4O: C, 67.89; H, 5.70; N, 13.77%. Found: C, 67.98; H, 5.74; N, 13.91%.
2,4-Dichloro-N′-((8-methyl-2-(piperidin-1-yl)quinolin-3-yl)methylene)benzohydrazide (9g): Yellow solid. Mp 232–234 °C. FTIR (ῡ, cm−1, neat): 3187 (NH), 3055 (CH-aromatic), 2944 (CH), 1663 (C=O), 1589 (C=N), 1072 (C-N); 1H NMR (DMSO-d6, 300 MHz) δ = 1.61–1.73 (m, 6H, piperidinyl-CH2), 2.62 (s, 3H, CH3), 3.23–3.26 (m, 4H, piperidinyl-N-CH2), 7.31 (t, J = 7.5 Hz, 1H, ArH), 7.52–7.61 (m, 2H, ArH), 7.68 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H, ArH), 7.80–7.82 (m, 1H, ArH), 7.98 (s, 1H, ArH), 8.43 (s, 1H, ArH), 8.61 (s, 1H, N=CH), 12.15 (s, 1H, NH); 13C NMR (DMSO-d6, 75 MHz) δ = 17.8 (CH3), 24.5 (piperidinyl-CH2), 25.8 (piperidinyl-CH2), 52.2 (piperidinyl-N-CH2), 120.9, 124.6, 124.8, 126.8, 128.0, 129.9, 131.3, 132.3, 134.4, 135.0, 135.8, 136.0, 145.9, 159.4, 162.0 (C=O); HRMS (EI) Exact mass calcd for C23H23Cl2N4O [M+H]+: 441.1247, found: 441.1243; Anal. Calcd. for C23H22Cl2N4O: C, 62.59; H, 5.02; N, 12.69%. Found: C, 62.81; H, 5.34; N, 12.87%.
2-Methoxy-N′-((8-methyl-2-(piperidin-1-yl)quinolin-3-yl)methylene)benzohydrazide (9h): Light yellow solid. Mp 198–200 °C. FTIR (ῡ, cm−1, neat): 3119 (NH), 3050 (CH-aromatic), 2930 (CH), 1635 (C=O), 1595 (C=N), 1245 (C-O), 1070 (C-N); 1H NMR (DMSO-d6, 300 MHz) δ = 1.50–1.76 (m, 6H, piperidinyl-CH2), 2.63 (s, 3H, CH3), 3.27–3.30 (m, 4H, piperidinyl-N-CH2), 3.85 (s, 3H, OCH3), 7.19 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H, ArH), 7.31 (t, J = 7.5 Hz, 1H, ArH), 7.46–7.54 (m, 4H, ArH), 7.81 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H, ArH), 8.57 (s, 1H, ArH), 8.61 (s, 1H, N=CH), 12.02 (s, 1H, NH); 13C NMR (DMSO-d6, 75 MHz) δ = 17.8 (CH3), 24.5 (piperidinyl-CH2), 25.8 (piperidinyl-CH2), 52.1 (piperidinyl-N-CH2), 55.9, 113.5, 117.9, 120.3, 121.3, 124.6, 124.8, 126.7, 130.2, 130.7, 134.9, 135.4, 136.0, 145.4, 146.0, 159.3, 159.7, 163.5 (C=O); HRMS (EI) Exact mass calcd for C24H27N4O2 [M+H]+: 403.2130, found: 403.2127; Anal. Calcd. for C24H26N4O2: C, 71.62; H, 6.51; N, 13.92%. Found: C, 71.50; H, 6.29; N, 13.77%.
3-Methoxy-N′-((8-methyl-2-(piperidin-1-yl)quinolin-3-yl)methylene)benzohydrazide (9i): Yellow solid. Mp 194–196 °C. FTIR (ῡ, cm−1, neat): 3255 (NH), 3004 (CH-aromatic), 2931 (CH), 1650 (C=O), 1605 (C=N), 1224 (C-O), 1045 (C-N); 1H NMR (DMSO-d6, 300 MHz) δ = 1.61–1.74 (m, 6H, piperidinyl-CH2), 2.62 (s, 3H, CH3), 3.25–3.28 (m, 4H, piperidinyl-N-CH2), 3.87 (s, 3H, OCH3), 7.07 (t, J = 7.5 Hz, 1H, ArH), 7.18 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H, ArH), 7.30 (t, J = 7.5 Hz, 1H, ArH), 7.46–7.59 (m, 3H, ArH), 7.80 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H, ArH), 8.45 (s, 1H, ArH), 8.57 (s, 1H, N=CH), 11.74 (s, 1H, NH); 13C NMR (DMSO-d6, 75 MHz) δ = 17.8 (CH3), 24.5 (piperidinyl-CH2), 25.8 (piperidinyl-CH2), 52.1 (piperidinyl-N-CH2), 56.2, 112.4, 120.9, 121.3, 124.6, 124.8, 126.7, 130.1, 130.7, 132.5, 134.9, 135.9, 144.7, 146.0, 157.1, 159.3, 163.1 (C=O); HRMS (EI) Exact mass calcd for C24H27N4O2 [M+H]+: 403.2135, found: 403.2125; Anal. Calcd. for C24H26N4O2: C, 71.62; H, 6.51; N, 13.92%. Found: C, 71.70; H, 6.65; N, 14.10%.
4-Methoxy-N′-((8-methyl-2-(piperidin-1-yl)quinolin-3-yl)methylene)benzohydrazide (9j): Yellow solid. Mp 242–244 °C. FTIR (ῡ, cm−1, neat): 3251 (NH), 3049 (CH-aromatic), 2930 (CH), 1636 (C=O), 1596 (C=N), 1245 (C-O), 1071 (C-N); 1H NMR (DMSO-d6, 300 MHz) δ = 1.61–1.77 (m, 6H, piperidinyl-CH2-), 2.63 (s, 3H, CH3), 3.27–3.30 (m, 4H, piperidinyl-N-CH2), 3.85 (s, 3H, OCH3), 7.09 (d, J = 9.0 Hz, 2H, ArH), 7.30 (t, J = 7.5 Hz, 1H, ArH), 7.52 (d, J = 6.9 Hz, 1H, ArH), 7.79 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H, ArH), 7.94 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 2H, ArH), 8.56 (s, 1H, ArH), 8.60 (s, 1H, N=CH), 11.93 (s, 1H, NH); 13C NMR (DMSO-d6, 75 MHz) δ = 17.8 (CH3), 24.5 (piperidinyl-CH2), 25.8 (piperidinyl-CH2), 52.1 (piperidinyl-N-CH2), 55.9, 114.2, 114.5, 121.5, 124.6, 124.8, 125.9, 126.7, 130.1, 130.6, 134.9, 135.8, 144.7, 145.9, 159.3, 162.5 (C=O); HRMS (EI) Exact mass calcd for C24H27N4O2 [M+H]+: 403.2131, found: 403.2130; Anal. Calcd. for C24H26N4O2: C, 71.62; H, 6.51; N, 13.92%. Found: C, 71.88; H, 6.73; N, 14.14%.
3.3. In Vitro Cholinesterase Inhibition Assays
The inhibitory activity of synthesized compounds against acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase was determined by Ellman spectrophotometric method with slight modification [48,49]. The reaction contents contained 60 µL KH2PO4 or KOH buffers, pH (7.7), 10 µL of synthesized compounds solvated in 2% DMSO, and 10 µL of enzyme (AChE, 0.5 U/mg, and BuChE, 3.4 U/mg). The reaction mixture was mixed completely and pre-incubated for 10 min at 37 °C. To start the reaction, 10 µL of 1 mM substrate, acetylthiocholine chloride, and butyrylthiocholine chloride were added to AChE and BuChE enzyme solution. A coloring reagent (DTNB 10 µL, 0.5 mM) was also added to the reaction mixture. Absorbance was determined at wavelength (405 nm) by a 96-well microplate reader after the incubation for 25 min at 37 °C. All experiments were performed in triplicate. To estimate the inhibitory activity of enzyme, the following formula was used, and percent inhibition was calculated.
Inhibition (%) = 100 − (Ac/As) × 100
Ac and As are absorbance estimated for AChE and BuChE enzymes in the presence or absence of inhibitors. IC50 value was calculated for tested compounds exhibiting more than 50% inhibition against AChE and BuChE through non-linear Prism 5.0 (GraphPad, San Diego, CA, USA).
3.4. Molecular Docking Protocols
3.4.1. Structure Selection and Preparation
To investigate the possible interactions of the potent compounds forming complex with AChE or BuChE, molecular docking was performed. RCBS PDB database [56] was used to obtain the crystallographic structure of electric eel AChE (PDB ID:4BDT) and hBuChE (PDB ID:4BDS) to perform docking studies. Before the experiments, respective structures of enzymes and potent compounds were prepared. Protonate3D [57] utility within the modeling tool MOE [58] was used to protonate the enzyme structure. The structural energy of the enzyme was minimized by using the Amber99 force field, which includes all solvent molecules. During energy calculations, structurally important atoms were confined with mini force to avoid subsiding of the binding pockets. Then, co-crystallized ligands and crystallographic water molecules (solvent) were removed. Subsequently, polar hydrogen atoms were added to the stranded structure of protein with the MOE.
3.4.2. Compounds Preparation
MOE was used to generate the coordinates of compounds, followed by the pH adjustment of ionization and protonation states within a specific range by the wash module. Subsequently, the minimization of the energies of compounds was achieved by the software MMFF94x force field.
3.4.3. Molecular Docking Studies
Molecular docking was performed using specific software LeadIT from BioSolveIT, GmbH Germany [59]. Compounds were docked using the FlexX receptor utility of LeadIT. The active site of the receptor (9.0 Å) was used for the docking analysis, designed derivatives, and related ligands. Binding energies were determined from the complex of ligand and receptor conformations. The maximal docked poses were selected for analysis (LeadIT). Such poses having low binding free energy were considered strong showing promising interactions with the receptor. The ligand and protein complex containing low binding energy for interaction was evaluated, and three-dimensional interaction modes were envisaged using discovery studio and PyMOL [51,60].
3.4.4. Molecular Dynamics Simulation
A molecular dynamics simulation was performed to analyze the stiffness, wide-ranging mobility, and sub-cellular functions of proteins. Based upon docking analysis, we carried out molecular dynamics simulation studies on the least binding energy value and highest docked pose complex. MD simulations were performed using online software, iMODS [61]. This software gives an appropriate association for this magnified normal mode analysis method within their coordinates. The web server is very unprompted and flexible to all important browsers and modern appliances. iMODs server also gives different parameters such as deformability of protein structure, B-factor values, computing the eigenvalues, variance, covariance map, and elastic network models. Keeping all the parameters by default, the PDB file of the docked complex was uploaded to an online server as an input file, and the results were observed within a few minutes.3.5. Anticancer Activity (SRB Dye Assay).
To investigate the cytotoxicity of potent compounds (8a, 8c, 8g, and 9i), an SRB assay was performed against Vero cell lines (normal kidney epithelial cells). The total protein generated when cells were treated with putative anticancer drugs was assessed using a very precise calorimetric technique. A negative charge fluorescent dye, sulforhodamine B (SRB), a water-soluble luminous dye that electrostatically binds to proteins when the pH of the medium is significantly lowered, was applied. It can readily connect with cells that have been fixed with trichloroacetic acid (TCA) [62]. A bright color is produced by the SRB dye when it binds solely to intracellular proteins, and the color is proportional to the quantity of protein present in the cell.
4. Conclusions
In summary, a library of new piperidinyl-quinoline acylhydrazones was designed and synthesized using a hybridization strategy. The robust multistep synthetic route was established where the final step involves an ultrasound-assisted condensation of 6/8-methyl-2-(piperidin-1-yl)quinoline-3-carbaldehydes and (un)substituted aromatic acid hydrazides. The target compounds were obtained in 4–6 min in 80–97% yield. The estimation of inhibitory potential against cholinesterases exhibited the discovery of various potent and therapeutically effective inhibitors, specifically compound 8c with an IC50 value of 5.3 ± 0.51 μM against AChE and compound 8g and with an IC50 value of 1.31 ± 0.05 μM against BuChE. Compound 8g was identified as a selective inhibitor of BuChE, whereas compounds 9h-j were selective inhibitors of AChE. Compounds 8a-c showed promising dual inhibition. The diverse structural variations on the hybrid scaffold offered ample opportunity to explore the in vitro results further and draw structural-activity relationships considering the important role of various substitutions on the inhibitory activity profile. Molecular docking and dynamics simulation data, as well as physicochemical properties results, also favored the development of piperidinyl-quinoline acylhydrazones hybrids as promising compounds for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/molecules28052131/s1, Table S1. Types of binding interactions, distance of bonds and atoms involved in interactions (AChE). Table S2. Types of binding interactions, distance of bonds and atoms involved in interactions (BuChE). Table S3. ADMET prediction scores for the potent compounds. 1H- and 13C-NMR spectra of all the synthesized compounds.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.M.; methodology, R.M.; software, S.Z.; validation, S.Z.; formal analysis, I.K., N.J., N.H., F.T.Z., A.A.D. and H.A.O.; investigation, R.M. and F.C. (synthesis); M.T.Y., Z.T. and S.Z. (bioactivity, cytotoxicity); M.T.Y., Z.T. and S.Z. (molecular docking, ADME properties); resources, R.M., S.Z. and H.A.O.; data curation, R.M., S.Z. and N.H.; writing—original draft preparation, I.K., R.M. and S.Z.; writing—review and editing, I.K. and A.A.D.; visualization, S.Z.; supervision, M.Z.-u.-R. and S.Z.; project administration, M.Z.-u.-R., S.Z. and I.K.; funding acquisition, H.A.O. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors extend their appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research (DSR) at King Khalid University, Abha, Saudi Arabia, for funding this work under grant number RGP.1/282/43.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in supplementary material.
Acknowledgments
The authors extend their appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research (DSR) at King Khalid University, Abha, Saudi Arabia, for funding this work under grant number RGP.1/282/43.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Sample Availability
Samples of the synthetic compounds are available from the authors upon reasonable request.
References
- Goedert, M.; Spillantini, M.G. A century of Alzheimer’s disease. Science 2006, 314, 777–781. Available online: https://www.science.org/doi/abs/10.1126/science.1132814 (accessed on 15 October 2022). [CrossRef]
- Bolognesi, M.L.; Cavalli, A.; Valgimigli, L.; Bartolini, M.; Rosini, M.; Andrisano, V.; Recanatini, M.; Melchiorre, C. Multi-target-directed drug design strategy: From a dual binding site acetylcholinesterase inhibitor to a trifunctional compound against Alzheimer’s disease. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 6446–6449. Available online: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jm701225u (accessed on 15 October 2022). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzheimer’s Disease International. Available online: https://www.alzint.org/about/dementia-facts-figures/dementia-statistics (accessed on 4 December 2022).
- Viegas, C., Jr.; Bolzani, V.D.S.; Barreiro, E.J.; Manssour Fraga, C.A. New anti-Alzheimer drugs from biodiversity: The role of the natural acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2005, 5, 915–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, Z.L.; Fu, T.M.; Li, W.; Xu, X.L.; Sun, H.P. Discovery of new acetylcholinesterase inhibitors with small core structures through shape-based virtual screening. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 3442–3446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, E.; Blessed, G.; Tomlinson, B.; Perry, R.; Crow, T.; Cross, A.; Dockray, G.; Dimaline, R.; Arregui, A. Neurochemical activities in human temporal lobe related to aging and Alzheimer-type changes. Neurobiol. Aging 1981, 2, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, P.; Singh, B. A review on cholinesterase inhibitors for Alzheimer’s disease. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2013, 36, 375–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, B.; Li, X.; Xia, J.; Wu, S. Discovery of novel isoflavone derivatives as AChE/BuChE dual-targeted inhibitors: Synthesis, biological evaluation and molecular modelling. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2017, 32, 968–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brus, B.; Kosak, U.; Turk, S.; Pislar, A.; Coquelle, N.; Kos, J.; Stojan, J.; Colletier, J.P.; Gobec, S. Discovery, biological evaluation, and crystal structure of a novel nanomolar selective butyrylcholinesterase inhibitor. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 8167–8179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, J.; Rudolph, M.J.; Burshteyn, F.; Cassidy, M.S.; Gary, E.N.; Love, J.; Franklin, M.C.; Height, J.J. Structures of human acetylcholinesterase in complex with pharmacologically important ligands. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 10282–10286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rees, T.; Hammond, P.I.; Soreq, H.; Younkin, S.; Brimijoin, S. Acetylcholinesterase promotes beta-amyloid plaques in cerebral cortex. Neurobiol. Aging 2003, 24, 777–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolini, M.; Bertucci, C.; Cavrini, V.; Andrisano, V. β-Amyloid aggregation induced by human acetylcholinesterase: Inhibition studies. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2003, 65, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greig, N.H.; Utsuki, T.; Yu, Q.S.; Zhu, X.; Holloway, H.W.; Perry, T.; Lee, B.; Ingram, D.K.; Lahiri, D.K. A new therapeutic target in Alzheimer’s disease treatment: Attention to butyrylcholinesterase. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2001, 17, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesulam, M.M.; Guillozet, A.; Shaw, P.; Levey, A.; Duysen, E.G.; Lockridge, O. Acetylcholinesterase knockouts establish central cholinergic pathways and can use butyrylcholinesterase to hydrolyze acetylcholine. Neuroscience 2002, 110, 627–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claassen, J.A.; Jansen, R.W. Cholinergically Mediated Augmentation of Cerebral Perfusion in Alzheimer’s Disease and Related Cognitive Disorders: The Cholinergic-Vascular Hypothesis. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2006, 61, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coulthard, E.; Singh-Curry, V.; Husain, M. Treatment of attention deficits in neurological disorders. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2006, 19, 613–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klafki, H.-W.; Staufenbiel, M.; Kornhuber, J.; Wiltfang, J. Therapeutic approaches to Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 2006, 129, 2840–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villarroya, M.; García, A.G.; Marco-Contelles, J.; López, M.G. An update on the pharmacology of galantamine. Exp. Opin. Investig. Drugs 2007, 16, 1987–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogan, D.B.; Patterson, C. Progress in clinical neurosciences: Treatment of Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias-review and comparison of the cholinesterase inhibitors. Canad. J. Neurol. Sci. 2002, 29, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geldmacher, D.S. Long-term cholinesterase inhibitor therapy for Alzheimer’s disease: Practical considerations for the primary care physician. Prim. Care Compan. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2003, 5, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selkoe, D.J.; Schenk, D. Alzheimer’s disease: Molecular understanding predicts amyloid-based therapeutics. Ann. Rev. Pharm. Toxicol. 2003, 43, 545–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguglia, E.; Onor, M.; Saina, M.; Maso, E. An open-label, comparative study of rivastigmine, donepezil and galantamine in a real-world setting. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2004, 20, 1747–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onor, M.L.; Trevisiol, M.; Aguglia, E. Rivastigmine in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease: An update. Clin. Interv. Aging 2007, 2, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behl, T.; Kaur, I.; Sehgal, A.; Singh, S.; Sharma, N.; Makeen, H.A.; Albratty, M.; Alhazmi, H.A.; Felemban, S.G.; Alsubayiel, A.M.; et al. “Aducanumab” making a comeback in Alzheimer’s disease: An old wine in a new bottle. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 148, 112746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, R.; Javid, N.; Zia-ur-Rehman, M.; Zaheer, M.; Huma, R.; Roohi, A.; Athar, M.M. Synthesis of novel N-acylhydrazones and their CN/NN bond conformational characterization by NMR spectroscopy. Molecules 2021, 26, 4908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Freitas Silva, M.; Tardelli Lima, E.; Pruccoli, L.; Castro, N.G.; Guimarães, M.J.R.; da Silva, F.M.R.; Viegas, C. Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Novel Triazole N-acylhydrazone Hybrids for Alzheimer’s Disease. Molecules 2020, 25, 3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, A.P.C.; Costa, L.M.; Santos, B.L.; Maia, R.C.; Miranda, A.L.; Barreiro, E.J.; Fraga, C.A. Novel furfurylidene N-acylhydrazones derived from natural safrole: Discovery of LASSBio-1215, a new potent antiplatelet prototype. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2012, 27, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Ma, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.P. Synthesis of sulfonylhydrazone- and acylhydrazone-Substituted 8-ethoxy-3-nitro-2H-chromenes as potent antiproliferative and apoptosis inducing agents. Arch. Pharm. 2014, 347, 576–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, S.A.; Feitosa, L.O.; Soares, M.; Costa, T.E.; Henriques, M.G.; Salomão, K.; de Castro, S.L.; Kaiser, M.; Brun, R.; Wardell, J.L.; et al. Design and synthesis of new (E)-cinnamic N-acylhydrazones as potent antitrypanosomal agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 54, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.B.; Feng, L.L.; Li, J.; Tao, R.J.; Ren, Y.L.; Wan, J.; He, H.W. Design, synthesis and molecular modeling of novel N-acylhydrazone derivatives as pyruvate dehydrogenase complex E1 inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2014, 22, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, P.; Cabrera, M.; Lavaggi, M.L.; Celano, L.; Tiscornia, I.; da Costa, T.R.; Thomson, L.; Bollati-Fogolín, M.; Miranda, A.L.P.; Lima, L.M.; et al. Discovery of new orally effective analgesic and anti-inflammatory hybrid furoxanyl N-acylhydrazone derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2012, 20, 2158–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, X.; Huang, Q.; Jiang, N.; Wu, D.; Zhou, H.; Gong, P. Discovery of hybrid dual N-acylhydrazone and diaryl urea derivatives as potent antitumor agents: Design, synthesis and cytotoxicity evaluation. Molecules 2013, 18, 2904–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leal, C.M.; Pereira, S.L.; Kümmerle, A.E.; Leal, D.M.; Tesch, R.; de Sant’Anna, C.M.; Fraga, C.A.M.; Barreiro, E.J.; Sudo, R.T.; Zapata-Sudo, G. Antihypertensive profile of 2-thienyl-3, 4-methylenedioxybenzoylhydrazone is mediated by activation of the A2A adenosine receptor. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziz, H.; Mahmood, A.; Zaib, S.; Saeed, A.; El-Seedi, H.R.; Pelletier, J.; Sévigny, J.; Iqbal, J. Synthesis, characterization, alkaline phosphatase inhibition assay and molecular modeling studies of 1-benzylidene-2-(4-tert-butylthiazol-2-yl) hydrazines. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2021, 39, 6140–6153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, R.; Kumar, K. Synthetic and medicinal perspective of quinolines as antiviral agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 215, 113220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Shah, S.J.A.; Ejaz, S.A.; Ibrar, A.; Hameed, S.; Lecka, J.; Mill’an, J.L.; Sévigny, J.; Iqbal, J. Investigation of quinoline-4-carboxylic acid as a highly potent scaffold for the development of alkaline phosphatase inhibitors: Synthesis, SAR analysis and molecular modelling studies. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 64404–64413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorito, J.; Saeed, F.; Zhang, H.; Staniszewski, A.; Feng, Y.; Francis, Y.I.; Rao, S.; Thakkar, D.M.; Deng, S.X.; Landry, D.W.; et al. Synthesis of quinoline derivatives: Discovery of a potent and selective phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitor for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 60, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, P.; Alam, O.; Naim, M.J.; Nawaz, F.; Iqbal, M.; Alam, M.I. Recent advancement of piperidine moiety in treatment of cancer-A review. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 157, 480–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, K.; Tao, Z.; Liu, Q.; Yang, L.; Wang, B.; Wu, S.; Wang, A.; Huang, M.; Liu, M.; Lu, Y. Design, synthesis and antitubercular evaluation of benzothiazinones containing a piperidine moiety. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 151, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Zhou, H.; Ma, L.; Dong, B.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, G.; Wang, M.; Wang, J.; Cen, S.; Wang, Y. Design and evaluation of novel piperidine HIV-1 protease inhibitors with potency against DRV-resistant variants. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 220, 113450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaib, S.; Munir, R.; Younas, M.T.; Kausar, N.; Ibrar, A.; Aqsa, S.; Shahid, N.; Asif, T.T.; Alsaab, H.O.; Khan, I. Hybrid Quinoline-Thiosemicarbazone Therapeutics as a New Treatment Opportunity for Alzheimer’s Disease-Synthesis, In Vitro Cholinesterase Inhibitory Potential and Computational Modeling Analysis. Molecules 2021, 26, 6573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alia, M.Y.; Zaib, S.; Jannat, S.; Khan, I. Discovery of potent and selective dual cholinesterases and β-secretase inhibitors in pomegranate as a treatment for Alzheimer’s disease. Bioorg. Chem. 2022, 129, 106137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, R.; Zia-ur-Rehman, M.; Murtaza, S.; Zaib, S.; Javid, N.; Awan, S.J.; Iftikhar, K.; Athar, M.M.; Khan, I. Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of (Piperidin-1-yl)quinolin-3-yl)methylene)hydrazinecarbothioamides as Potent Inhibitors of Cholinesterases: A Biochemical and In Silico Approach. Molecules 2021, 26, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, I.; Bakht, S.M.; Ibrar, A.; Abbas, S.; Hameed, S.; White, J.M.; Rana, U.A.; Zaib, S.; Shahid, M.; Iqbal, J. Exploration of a library of triazolothiadiazole and triazolothiadiazine compounds as a highly potent and selective family of cholinesterase and monoamine oxidase inhibitors: Design, synthesis, X-ray diffraction analysis and molecular docking studies. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 21249–21267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meth-Cohn, O.; Narine, B.; Tarnowski, B. A versatile new synthesis of quinolines and related fused pyridines, Part 5. The synthesis of 2-chloroquinoline-3-carbaldehydes. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1981, 1, 1520–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reilly, M.K.; King, R.P.; Wagner, A.J.; King, S.M. Microwave-assisted esterification: A discovery-based microscale laboratory experiment. J. Chem. Educ. 2014, 91, 1706–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, S.D.; Vagdevi, H.M.; Vaidya, V.P.; Gadaginamath, G.S. Synthesis of new 4-pyrrol-1-yl benzoic acid hydrazide analogs and some derived oxadiazole, triazole and pyrrole ring systems: A novel class of potential antibacterial and antitubercular agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 43, 1989–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellman, G.L.; Courtney, K.; Andres, V.; Featherstone, R.M. A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1961, 7, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumtaz, A.; Shoaib, M.; Zaib, S.; Shah, M.S.; Bhatti, H.A.; Saeed, A.; Hussain, I.; Iqbal, J. Synthesis, molecular modelling and biological evaluation of tetrasubstituted thiazoles towards cholinesterase enzymes and cytotoxicity studies. Bioorg. Chem. 2018, 78, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachon, F.; Carletti, E.; Ronco, C.; Trovaslet, M.; Nicolet, Y.; Jean, L.; Renard, P.Y. Crystal structures of human cholinesterases in complex with huprine W and tacrine: Elements of specificity for anti-Alzheimer’s drugs targeting acetyl- and butyrylcholinesterase. Biochem. J. 2013, 453, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, N.; Lange, G.; Hindle, S.; Klein, R.; Rarey, M. A consistent description of HYdrogen bond and DEhydration energies in protein–ligand complexes: Methods behind the HYDE scoring function. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2013, 27, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reulecke, I.; Lange, G.; Albrecht, J.; Klein, R.; Rarey, M. Towards an integrated description of hydrogen bonding and dehydration: Decreasing false positives in virtual screening with the HYDE scoring function. ChemMedChem 2008, 3, 885–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissADME: A free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. iLOGP: A simple, robust, and efficient description of n-octanol/water partition coefficient fordrug design using the GB/SA approach. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2014, 54, 3284–3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daina, A.; Zoete, V. A BOILED-Egg to predict gastrointestinal absorption and brain penetration of small molecules. ChemMedChem 2016, 11, 1117–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- RCSB Protein Data Bank. Available online: http://www.rcsb.org (accessed on 20 October 2022).
- Labute, P. Protonate 3D, Chemical Computing Group. 2007. Available online: http://www.chemcomp.com/journal/proton.htm (accessed on 20 October 2022).
- Chemical Computing Group’s Molecular Operating Environment (MOE). MOE 2019. Available online: http://www.chemcomp.com/MOEMolecular_Operating_Environment.htm (accessed on 20 October 2022).
- LeadIT, version 2.3.2; BioSolveIT GmbH: Sankt Augustin, Germany, 2017. Available online: www.biosolveit.de/LeadIT (accessed on 2 February 2023).
- BIOVIA. Discovery Studio Client v19.1.0.18287. In Accelrys Discovery Studio; Accelrys Software Inc.: San Diego, CA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- López-Blanco, J.R.; Aliaga, J.I.; Quintana-Ortí, E.S.; Chacón, P. iMODS: Internal coordinates normal mode analysis server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, H.S.; Nasrullah, U.; Zaib, S.; Usman, F.; Khan, A.; Gohar, U.F.; Uddin, J.; Khan, I.; Al-Harrasi, A. Preparation, characterization, and pharmacological investigation of withaferin-A loaded nanosponges for cancer therapy; in vitro, in vivo and molecular docking studies. Molecules 2021, 26, 6990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).