Brief History, Preparation Method, and Biological Application of Mesoporous Silica Molecular Sieves: A Narrative Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. History of Mesoporous Silica Molecular Sieves
3. Preparation Methods
4. Biological Applications
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Mansour, F.; Al-Hindi, M.; Yahfoufi, R.; Ayoub, G.M.; Ahmad, M.N. The use of activated carbon for the removal of pharmaceuticals from aqueous solutions: A review. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2018, 17, 109–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raut, E.R.; Thakur, A.B.; Chaudhari, A.R. Review on toxic metal ions removal by using activated carbon prepared from natural biomaterials. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1913, 12091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalan, J.; Buthiyappan, A.; Abdul Raman, A.A. Insight into metal-impregnated biomass based activated carbon for enhanced carbon dioxide adsorption: A review. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2022, 113, 72–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.; Militky, J.; Venkataraman, M. 7-nanoporous materials. In Nanotechnology in Textiles; Mishra, R., Militky, J., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2019; pp. 311–353. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, G.Q.; Zhao, X.S. Nanoporous Materials: Science and Engineering; Imperial College Press: London, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Kianfar, E.; Sayadi, H. Recent advances in properties and applications of nanoporous materials and porous carbons. Carbon Lett. 2022, 32, 1645–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.P.; Wu, Q.S.; Cui, C.; Lu, G.S.; Zhang, C.S.; Yan, Z.Y. Preparation of TiO2/Al-MCM-41 mesoporous materials from coal-series kaolin and photodegradation of methyl orange. Mater. Sci. 2013, 31, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeelani, P.G.; Mulay, P.; Venkat, R.; Ramalingam, C. Multifaceted application of silica nanoparticles. A review. Silicon 2020, 12, 1337–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.H.; Sun, M.H.; Wang, Z.; Yang, W.M.; Xie, Z.K.; Su, B.L. Hierarchically structured zeolites: From design to application. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 11194–11294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettinari, C.; Marchetti, F.; Mosca, N.; Tosi, G.; Drozdov, A. Application of metal-organic frameworks. Polym. Int. 2017, 66, 731–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.P.; Sun, Q.; Aguila, B.; Ma, S.Q. Opportunities of covalent organic frameworks for advanced applications. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1801410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wickramaratne, N.P.; Qiao, S.Z.; Jaroniec, M. Molecular-based design and emerging applications of nanoporous carbon spheres. Nat. Mater. 2015, 14, 763–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzano, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for drug delivery. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1902634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.X.; Barnes, J.C.; Bosoy, A.; Stoddart, J.F.; Zink, J.I. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles in biomedical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2590–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.; Shen, Y.W.; Guan, Y.Y.; Jiang, Y.X.; Wu, Y.; Rahman, K.; Zhang, L.J.; Liu, H.J.; Luan, X. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles: Facile surface functionalization and versatile biomedical applications in oncology. Acta Biomater. 2020, 116, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Efsa, P.O.F.A.; Younes, M.; Aggett, P.; Aguilar, F.; Crebelli, R.; Dusemund, B.; Filipič, M.; Frutos, M.J.; Galtier, P.; Gott, D.; et al. Re-evaluation of silicon dioxide (e 551) as a food additive. EFSA J. 2018, 16, e5088. [Google Scholar]
- Ehlerding, E.B.; Chen, F.; Cai, W.B. Biodegradable and renal clearable inorganic nanoparticles. Adv. Sci. 2016, 3, 1500223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mebert, A.M.; Baglole, C.J.; Desimone, M.F.; Maysinger, D. Nanoengineered silica: Properties, applications and toxicity. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 109, 753–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Videira-Quintela, D.; Martin, O.; Montalvo, G. Emerging opportunities of silica-based materials within the food industry. Microchem. J. 2021, 167, 106318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watermann, A.; Brieger, J. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as drug delivery vehicles in cancer. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, B.G.; Kim, J. Functional mesoporous silica nanoparticles for bio-imaging applications. WIREs Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2019, 11, e1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanzadeh, M.; Shadjou, N.; de la Guardia, M.; Eskandani, M.; Sheikhzadeh, P. Mesoporous silica-based materials for use in biosensors. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2012, 33, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagisawa, T.; Shimizu, T.; Kuroda, K.; Kato, C. The preparation of alkyltrimethylammonium–kanemite complexes and their conversion to microporous materials. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1990, 63, 988–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresge, C.T.; Leonowicz, M.E.; Roth, W.J.; Vartuli, J.C.; Beck, J.S. Ordered mesoporous molecular sieves synthesized by a liquid-crystal template mechanism. Nature 1992, 359, 710–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, J.S.; Vartuli, J.C.; Roth, W.J.; Leonowicz, M.E.; Kresge, C.T.; Schmitt, K.D.; Chu, C.T.W.; Olson, D.H.; Sheppard, E.W.; Mccullen, S.B.; et al. A new family of mesoporous molecular sieves prepared with liquid crystal templates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 10834–10843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vartuli, J.C.; Roth, W.J.; Beck, J.S.; Mccullen, S.B.; Kresge, C.T. The synthesis and properties of m41s and related mesoporous materials. In Synthesis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1998; pp. 97–119. [Google Scholar]
- Vartuli, J.C.; Schmitt, K.D.; Kresge, C.T.; Roth, W.J.; Leonowicz, M.E.; Mccullen, S.B.; Hellring, S.D.; Beck, J.S.; Schlenker, J.L.; Olson, D.H.; et al. Development of a formation mechanism for m41s materials. In Studies in Surface Science and Catalysis; Weitkamp, J., Karge, H.G., Pfeifer, H., Hölderich, W., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1994; Volume 84, pp. 53–60. [Google Scholar]
- Vartuli, J.C.; Kresge, C.T.; Roth, W.J.; Mccullen, S.B.; Beck, J.S.; Schmitt, K.D.; Leonowicz, M.E.; Lutner, J.D.; Sheppard, E.W. Chapter 1-designed synthesis of mesoporous molecular sieve systems using surfactant-directing agents. In Advanced Catalysts and Nanostructured Materials; Moser, W.R., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1996; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Beck, J.S.; Vartuli, J.C.; Kennedy, G.J.; Kresge, C.T.; Roth, W.J.; Schramm, S.E. Molecular or supramolecular templating: Defining the role of surfactant chemistry in the formation of microporous and mesoporous molecular sieves. Chem. Mat. 1994, 6, 1816–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Jin, L.; Liu, B.; He, J. Templated growth of crystalline mesoporous materials: From soft/hard templates to colloidal templates. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhao, D. An overview of the synthesis of ordered mesoporous materials. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 943–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, N.; Bhaumik, A. Soft templating strategies for the synthesis of mesoporous materials: Inorganic, organic–inorganic hybrid and purely organic solids. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 189–190, 21–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.Y.; Feng, J.L.; Huo, Q.S.; Melosh, N.; Fredrickson, G.H.; Chmelka, B.F.; Stucky, G.D. Triblock copolymer syntheses of mesoporous silica with periodic 50 to 300 angstrom pores. Science 1998, 279, 548–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera-Muñoz, E.M.; Huirache-Acuña, R. Sol gel-derived SBA-16 mesoporous material. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, 3069–3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmat, N.; Abdullah, A.Z.; Mohamed, A.R. A review: Mesoporous santa barbara amorphous-15, types, synthesis and its applications towards biorefinery production. Am. J. Appl. Sci. 2010, 7, 1579–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, F.D.C.M.; Costa, M.J.D.S.; Da Silva, L.K.R.; Batista, A.M.; Da Luz, G.E. Functionalization methods of SBA-15 mesoporous molecular sieve: A brief overview. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, P.; Kuwahara, Y.; Mori, K.; Raja, R.; Yamashita, H. Functionalized mesoporous SBA-15 silica: Recent trends and catalytic applications. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 11333–11363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, J.A.S.; de Jesus, R.A.; Santos, D.O.; Neris, J.B.; Figueiredo, R.T.; Paranhos, C.M. Synthesis, functionalization, and environmental application of silica-based mesoporous materials of the M41s and SBA-n families: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanev, P.T.; Chibwe, M.; Pinnavaia, T.J. Titanium-containing mesoporous molecular sieves for catalytic oxidation of aromatic compounds. Nature 1994, 368, 321–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inagaki, S.; Fukushima, Y.; Kuroda, K. Synthesis and characterization of highly ordered mesoporous material; Fsm-16, from a layered polysilicate. In Studies in Surface Science and Catalysis; Weitkamp, J., Karge, H.G., Pfeifer, H., Hölderich, W., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1994; Volume 84, pp. 125–132. [Google Scholar]
- Bagshaw, S.A.; Prouzet, E.; Pinnavaia, T.J. Templating of mesoporous molecular sieves by nonionic polyethylene oxide surfactants. Science 1995, 269, 1242–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryoo, R.; Kim, J.M.; Ko, C.H.; Shin, C.H. Disordered molecular sieve with branched mesoporous channel network. J. Phys. Chem. 1996, 100, 17718–17721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.Z.; Yu, Y.H.; Zhao, D.Y. Highly ordered large caged cubic mesoporous silica structures templated by triblock PEO–PBO–PEO copolymer. Chem. Commun. 2000, 7, 575–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.L.; Du, H.B.; Xiao, F.S.; Zhu, G.S.; Pang, W.Q. Synthesis and characterization of a novel microporous titanosilicate JLU-1. Chem. Mat. 2000, 12, 665–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, J.C.; Shan, Z.; Marchese, L.; Zhou, W.; Puil, N.V.D.; Maschmeyer, T. A new templating method for three-dimensional mesopore networks. Chem. Commun. 2001, 8, 713–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jammaer, J.; Aerts, A.; D’Haen, J.; Seo, J.W.; Martens, J.A. Convenient synthesis of ordered mesoporous silica at room temperature and quasi-neutral ph. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 8290–8293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandiyanto, A.B.D.; Kim, S.; Iskandar, F.; Okuyama, K. Synthesis of spherical mesoporous silica nanoparticles with nanometer-size controllable pores and outer diameters. Microporous Mesoporous Mat. 2009, 120, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grün, M.; Lauer, I.; Unger, K.K. The synthesis of micrometer- and submicrometer-size spheres of ordered mesoporous oxide MCM-41. Adv. Mater. 1997, 9, 254–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Q.; Luo, Z.S.; Pang, W.Q.; Fan, Y.W.; Chen, X.H.; Cui, F.Z. Dilute solution routes to various controllable morphologies of MCM-41 silica with a basic medium. Chem. Mat. 2001, 13, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobler, J.; Möller, K.; Bein, T. Colloidal suspensions of functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2008, 2, 791–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möller, K.; Kobler, J.; Bein, T. Colloidal suspensions of mercapto-functionalized nanosized mesoporous silica. J. Mater. Chem. 2007, 17, 624–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möller, K.; Kobler, J.; Bein, T. Colloidal suspensions of nanometer-sized mesoporous silica. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2007, 17, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, P.P.; Ma, B.; Hung, C.T.; Li, W.; Zhao, D.Y. Spherical mesoporous materials from single to multilevel architectures. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 2928–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.P.; Cheng, Y.R.; Mou, C.Y. Hierarchical order in hollow spheres of mesoporous silicates. Chem. Mat. 1998, 10, 3772–3776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.S.; Shi, J.L.; Hua, Z.L.; Chen, H.R.; Ruan, M.L.; Yan, D.S. Hollow spheres of mesoporous aluminosilicate with a three-dimensional pore network and extraordinarily high hydrothermal stability. Nano Lett. 2003, 3, 609–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.F.; Shi, J.L.; Shen, W.H.; Chen, H.R.; Dong, X.P.; Ruan, M.L. Preparation of novel hollow mesoporous silica spheres and their sustained-release property. Nanotechnology 2005, 16, 2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, D.K.; Yang, J.P.; Li, X.M.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, R.Y.; Li, W.; Chen, L.; Wang, R.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, D.Y. Biphase stratification approach to three-dimensional dendritic biodegradable mesoporous silica nanospheres. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malgras, V.; Ji, Q.M.; Kamachi, Y.; Mori, T.; Shieh, F.K.; Wu, K.C.W.; Ariga, K.; Yamauchi, Y. Templated synthesis for nanoarchitectured porous materials. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2015, 88, 1171–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Page, M.; Yu, E.; Li, J.; Rahman, M.; Dryden, D.M.; Vidu, R.; Stroeve, P. Template-based syntheses for shape controlled nanostructures. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 234, 51–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, A.; Bajaj, B.; Kaushik, A.; Saini, A.; Sud, D. A review on template assisted synthesis of multi-functional metal oxide nanostructures: Status and prospects. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2022, 286, 116005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, F.; Cornelius, M.; Morell, J.; Fröba, M. Silica-based mesoporous organic–inorganic hybrid materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 3216–3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, C.Y.; Lin, H.P. Control of morphology in synthesizing mesoporous silica. Pure Appl. Chem. 2000, 72, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayan, R.; Nayak, U.Y.; Raichur, A.M.; Garg, S. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles: A comprehensive review on synthesis and recent advances. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens, J.A.; Jammaer, J.; Bajpe, S.; Aerts, A.; Lorgouilloux, Y.; Kirschhock, C.E.A. Simple synthesis recipes of porous materials. Microporous Mesoporous Mat. 2011, 140, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, C.; Thielemans, W.; Mokaya, R. One step room temperature synthesis of ordered mesoporous silica SBA-15 mediated by cellulose nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matijasic, A.; Voegtlin, A.C.; Patarin, J.; Guth, J.L.; Huve, L. Room-temperature synthesis of silicate mesoporous materials. An in situ study of the lamellar to hexagonal phase transition. Chem. Commun. 1996, 10, 1123–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Q.S.; Margolese, D.I.; Ciesla, U.; Feng, P.Y.; Gier, T.E.; Sieger, P.; Leon, R.; Petroff, P.M.; Schüth, F.; Stucky, G.D. Generalized synthesis of periodic surfactant/inorganic composite materials. Nature 1994, 368, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.Y.; Hui, J.F.; Wang, P.P.; Xu, B.; Zhuang, J.; Wang, X. Hydrothermal synthesis of mesoporous silica spheres: Effect of the cooling process. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 7114–7120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, G.; Baskar, A.V.; El-Newehy, M.H.; Cha, W.S.; Al-Deyab, S.S.; Vinu, A. Quick high-temperature hydrothermal synthesis of mesoporous materials with 3d cubic structure for the adsorption of lysozyme. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2015, 16, 24806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, D.H.; Yuan, P.; Zhao, L.Z.; Liu, N.; Zhou, L.; Wei, G.F.; Zhang, J.; Ling, Y.C.; Fan, Y.; Wei, B.Y.; et al. New understanding and simple approach to synthesize highly hydrothermally stable and ordered mesoporous materials. Chem. Mat. 2009, 21, 5413–5425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Li, D.F.; Zhao, L.; Song, J.W.; Yang, X.Y.; Li, N.; Di, Y.; Li, C.J.; Wu, S.; Xu, X.Z.; et al. High-temperature generalized synthesis of stable ordered mesoporous silica-based materials by using fluorocarbon–hydrocarbon surfactant mixtures. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2003, 42, 3633–3637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.J.; Park, S.J. Conventional and microwave hydrothermal synthesis and application of functional materials: A review. Materials 2019, 12, 1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz De Greñu, B.; de Los Reyes, R.; Costero, A.M.; Amorós, P.; Ros-Lis, J.V. Recent progress of microwave-assisted synthesis of silica materials. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantini, M.C.A.; Matos, J.R.; Silva, L.C.C.D.; Mercuri, L.P.; Chiereci, G.O.; Celer, E.B.; Jaroniec, M. Ordered mesoporous silica: Microwave synthesis. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2004, 112, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tendeloo, G.V.; Lebedev, O.I.; Collart, O.; Cool, P.; Vansant, E.F. Structure of nanoscale mesoporous silica spheres? J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2003, 15, S3037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yano, K.; Fukushima, Y. Synthesis of mono-dispersed mesoporous silica spheres with highly ordered hexagonal regularity using conventional alkyltrimethylammonium halide as a surfactant. J. Mater. Chem. 2004, 14, 1579–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido, M.D.; El Haskouri, J.; Vie, D.; Beltrán, A.; Ros-Lis, J.V.; Marcos, M.D.; Moliner, N.; Amorós, P. Generalized “one-pot” preparative strategy to obtain highly functionalized silica-based mesoporous spherical particles. Microporous Mesoporous Mat. 2022, 337, 111942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.M.; He, Q.J.; Liu, J.N.; Chen, Y.; Ma, M.; Zhang, L.L.; Shi, J.L. Nuclear-targeted drug delivery of tat peptide-conjugated monodisperse mesoporous silica nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 5722–5725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.M.; Xu, Q.N.; Li, C.H.; Chen, Y.Q.; Zhang, Y.L.; Lu, B. Hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles as nanocarriers employed in cancer therapy: A review. Front. Mater. Sci. 2020, 14, 373–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunwoo, Y.; Karunakaran, G.; Cho, E.B. Hollow mesoporous silica nanospheres using pentablock copolymer micelle templates. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 13351–13362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Z.G.; Han, Y.D.; Li, J.; Yan, F.; Yang, W.S. Preparation of hollow mesoporous silica spheres by a sol–gel/emulsion approach. Microporous Mesoporous Mat. 2010, 127, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Gao, C.B.; Wu, X.W.; Chen, Q.R.; Shu, P.; Ding, Z.G.; Che, S.A. Anionic surfactants templating route for synthesizing silica hollow spheres with different shell porosity. Solid State Sci. 2011, 13, 721–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoeini, M.; Najafi, A.; Rastegar, H.; Amani, M. Improvement of hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles synthesis by hard-templating method via ctab surfactant. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 12700–12707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.L.; Chen, C.; Liu, Z.H.; Liu, P.X.; Zheng, N.F. A cationic surfactant assisted selective etching strategy to hollow mesoporous silica spheres. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 1632–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, Z.U.; Wei, N.; Li, Z.X.; Sun, W.X.; Wang, D.A. Preparation of hollow mesoporous silica nanospheres: Controllable template synthesis and their application in drug delivery. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 14122–14129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.X.; Li, X.Y.; Cai, X.J.; Du, Y.Y.; Zhang, L.L.; Shi, J.L. A salt-assisted acid etching strategy for hollow mesoporous silica/organosilica for ph-responsive drug and gene co-delivery. J. Mat. Chem. B 2015, 3, 766–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Dun, C.C.; Chen, J.J.; Rao, S.; Shah, M.; Wei, J.L.; Chen, K.W.; Xuan, Z.X.; Kyriakidou, E.A.; Urban, J.J.; et al. A general route to flame aerosol synthesis and in situ functionalization of mesoporous silica. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202206870. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.C.; Wang, X.D.; Wang, P.Y.; Liu, R.; Hou, X.M.; Cao, W.; Zhong, R.; Liu, X.L.; Zhang, Y. One-pot synthesis of biodegradable polydopamine-doped mesoporous silica nanocomposites (PMSNs) as ph-sensitive targeting drug nanocarriers for synergistic chemo-photothermal therapy. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 37433–37440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, A.L.; Ma, X.Y. Composite particles with dendritic mesoporous-silica cores and nano-sized CeO2 shells and their application to abrasives in chemical mechanical polishing. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 240, 122279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.Q.; Feng, J.J.; Loussala, H.M.; Han, S.; Ji, X.P.; Li, C.Y.; Sun, H.L.; Sun, M. Dendritic mesoporous silica nanospheres@porous carbon for in-tube solid-phase microextraction to detect polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in tea beverages. Food Chem. 2021, 364, 130379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yue, Q.; Zagho, M.M.; Zhang, J.; Elzatahry, A.A.; Jiang, Y.J.; Deng, Y.H. Core–shell magnetic mesoporous silica microspheres with large mesopores for enzyme immobilization in biocatalysis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 10356–10363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dogra, A.R.; Sharma, V.; Gahrotra, R.; Kumar, P. Evaporation induced self-assembly of silica nanoparticles on ito substrates in a confined cell for vertical alignment of liquid crystals and performance analysis. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 642, 128712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora-Raimundo, P.; Lozano, D.; Benito, M.; Mulero, F.; Manzano, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Osteoporosis remission and new bone formation with mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2101107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Guo, Y.D.; Wei, C.Y.; Hu, P.; Shi, J.L. Nanocatalytic innate immunity activation by mitochondrial DNA oxidative damage for tumor-specific therapy. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2008065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koohi Moftakhari Esfahani, M.; Alavi, S.E.; Cabot, P.J.; Islam, N.; Izake, E.L. Application of mesoporous silica nanoparticles in cancer therapy and delivery of repurposed anthelmintics for cancer therapy. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.N.; Du, Z.Q.; Bao, G.C.; Fang, G.C.; Cappadona, M.; Mcclements, L.; Tuch, B.E.; Lu, H.X.; Xu, X.X. Smart drug-delivery system of upconversion nanoparticles coated with mesoporous silica for controlled release. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, S.; Derakhshankhah, H.; Alaei, L.; Fattahi, A.; Varnamkhasti, B.S.; Saboury, A.A. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for therapeutic/diagnostic applications. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 109, 1100–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, H.; Mao, J.Q.; Liu, C.S.; Wei, J. Application of mesoporous molecular sieves in medicine. J. Pharm. Pract. Serv. 2012, 30, 262–265. [Google Scholar]
- Asefa, T.; Tao, Z. Biocompatibility of mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2012, 25, 2265–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallet-Regi, M.; Rámila, A.; Del Real, R.P.; Pérez-Pariente, J. A new property of MCM-41: Drug delivery system. Chem. Mat. 2001, 13, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poostforooshan, J.; Belbekhouche, S.; Shaban, M.; Alphonse, V.; Habert, D.; Bousserrhine, N.; Courty, J.; Weber, A.P. Aerosol-assisted synthesis of tailor-made hollow mesoporous silica microspheres for controlled release of antibacterial and anticancer agents. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 6885–6898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.F.; Shi, J.L.; Chen, H.R.; Shen, W.H.; Dong, X.P. A facile method to synthesize novel hollow mesoporous silica spheres and advanced storage property. Microporous Mesoporous Mat. 2005, 84, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhshian Nik, A.; Zare, H.; Razavi, S.; Mohammadi, H.; Torab Ahmadi, P.; Yazdani, N.; Bayandori, M.; Rabiee, N.; Izadi Mobarakeh, J. Smart drug delivery: Capping strategies for mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Microporous Mesoporous Mat. 2020, 299, 110115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alyassin, Y.; Sayed, E.G.; Mehta, P.; Ruparelia, K.; Arshad, M.S.; Rasekh, M.; Shepherd, J.; Kucuk, I.; Wilson, P.B.; Singh, N.; et al. Application of mesoporous silica nanoparticles as drug delivery carriers for chemotherapeutic agents. Drug Discov. Today 2020, 25, 1513–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.H.; Li, N.; Pan, W.; Yu, Z.Z.; Yang, L.M.; Tang, B. Hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles with tunable structures for controlled drug delivery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 2123–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzari, M.T.; Shamay, Y.; Kiguchi, H.; Rosen, N.; Scaltriti, M.; Heller, D.A. Targeted drug delivery strategies for precision medicines. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2021, 6, 351–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharti, C.; Nagaich, U.; Pal, A.K.; Gulati, N. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles in target drug delivery system: A review. Int. J. Pharm. Investig. 2015, 5, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, P.; Ghosh, B.; Biswas, S. Nanocarriers for cancer-targeted drug delivery. J. Drug Target. 2016, 24, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Hong, H.; Shi, S.X.; Goel, S.; Valdovinos, H.F.; Hernandez, R.; Theuer, C.P.; Barnhart, T.E.; Cai, W.B. Engineering of hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles for remarkably enhanced tumor active targeting efficacy. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, J.; Wunder, A.; Licha, K. Optical imaging. In Molecular Imaging in Oncology; Schober, O., Riemann, B., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 221–246. [Google Scholar]
- Balas, C. Review of biomedical optical imaging—A powerful, non-invasive, non-ionizing technology for improving in vivo diagnosis. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2009, 20, 104020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocklitz, T.; Silge, A.; Bae, H.; Rodewald, M.; Legesse, F.B.; Meyer, T.; Popp, J. Non-invasive imaging techniques: From histology to in vivo imaging. In Molecular Imaging in Oncology; Schober, O., Kiessling, F., Debus, J., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 795–812. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, J.H.; Moon, B.S.; Kim, D.H. Upconversion nanoparticles coated with mesoporous silica nanoshells loaded with dyes for fine-tuned multicolor emission in bioimaging applications. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 3541–3547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.H.; Ellis, C.M.; Davis, J.J. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles in bioimaging. Materials 2020, 13, 3795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, X.; Li, X.Y.; Xiong, L.; Zhang, X.J.; Kleitz, F.; Qiao, S.Z. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles with organo-bridged silsesquioxane framework as innovative platforms for bioimaging and therapeutic agent delivery. Biomaterials 2016, 91, 90–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gu, H.C. Core–shell-type magnetic mesoporous silica nanocomposites for bioimaging and therapeutic agent delivery. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 576–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Rao, B.A.; Jeong, J.; Angupillai, S.; Choi, J.S.; Nam, J.O.; Lee, C.S.; Son, Y.A. A rhodamine scaffold immobilized onto mesoporous silica as a fluorescent probe for the detection of Fe (III) and applications in bio-imaging and microfluidic chips. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 224, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.X.; Zhang, D.L.; Hu, X.X.; Peng, R.Z.; Li, J.B.; Zhang, X.B.; Tan, W.H. Multicolor two-photon nanosystem for multiplexed intracellular imaging and targeted cancer therapy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 12569–12576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; He, X.W.; Li, W.Y.; Zhang, Y.K. Multifunctional mesoporous silica nanoplatform based on silicon nanoparticles for targeted two-photon-excited fluorescence imaging-guided chemo/photodynamic synergetic therapy in vitro. Talanta 2020, 209, 120552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.W.; Zhang, L.; Yuan, X.A.; Liu, X.C.; Diao, X.L.; Zhao, Q.; Tian, Z.Z.; Sun, J.; Liu, Z.; You, J.M. Multifunctional fluorescent pegylated fluorinated graphene for targeted drug delivery: An experiment and dft study. Dyes Pigment. 2019, 162, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhong, S.L.; Xu, L.F.; He, S.H.; Dou, Y.M.; Zhao, S.N.; Chen, P.; Cui, X.J. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles capped with graphene quantum dots as multifunctional drug carriers for photo-thermal and redox-responsive release. Microporous Mesoporous Mat. 2019, 278, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
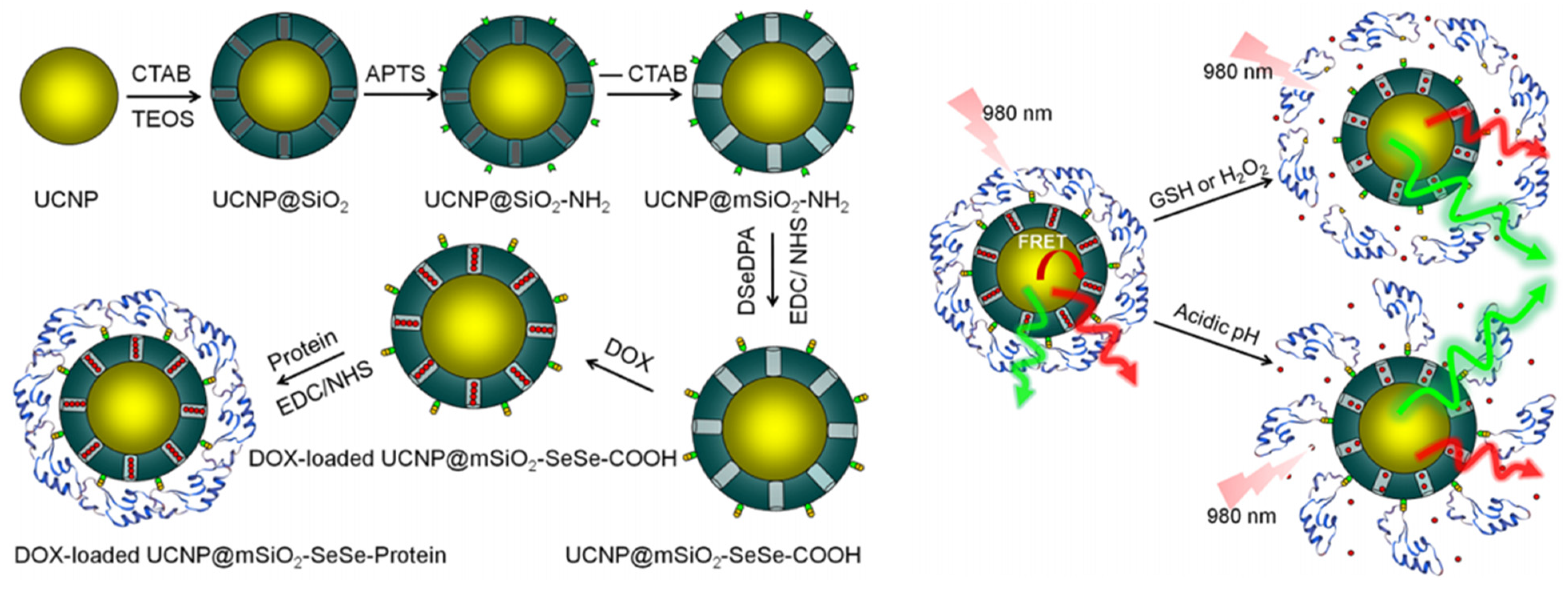
- Yan, H.; Dong, J.T.; Huang, X.; Du, X.Z. Protein-gated upconversion nanoparticle-embedded mesoporous silica nanovehicles via diselenide linkages for drug release tracking in real time and tumor chemotherapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 29070–29082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
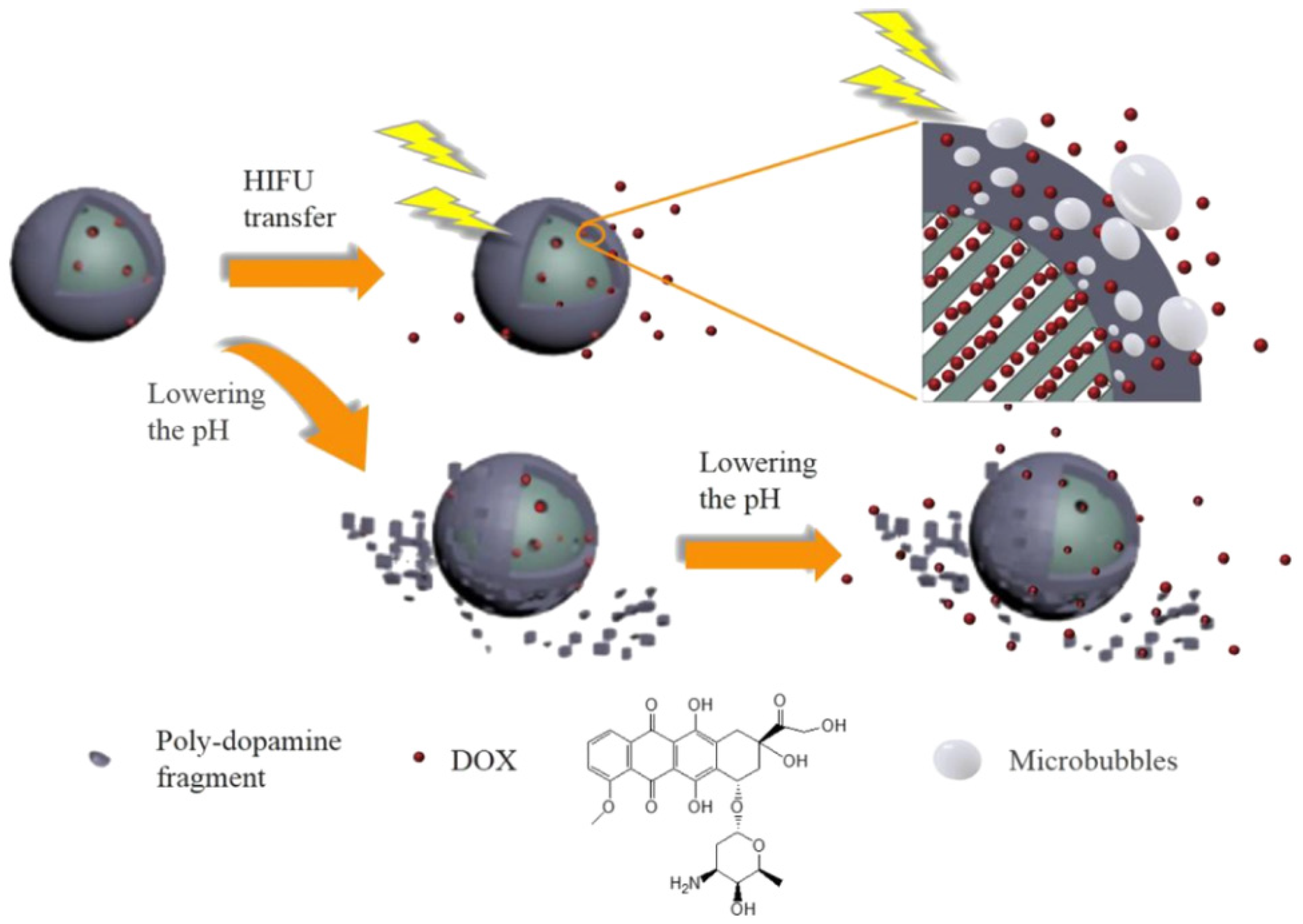
- Du, M.; Chen, Y.H.; Tu, J.W.; Liufu, C.; Yu, J.S.; Yuan, Z.; Gong, X.J.; Chen, Z.Y. Ultrasound responsive magnetic mesoporous silica nanoparticle-loaded microbubbles for efficient gene delivery. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 6, 2904–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mura, S.; Nicolas, J.; Couvreur, P. Stimuli-responsive nanocarriers for drug delivery. Nat. Mater. 2013, 12, 991–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, F.C.; Xie, Y.J.; Deng, T.; Zink, J.I. Magnetism, ultrasound, and light-stimulated mesoporous silica nanocarriers for theranostics and beyond. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 6025–6036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.C.; Xie, C.; Xia, H.S.; Wang, Z.H. Ph and ultrasound dual-responsive polydopamine-coated mesoporous silica nanoparticles for controlled drug delivery. Langmuir 2018, 34, 9974–9981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourshahrestani, S.; Kadri, N.A.; Zeimaran, E.; Towler, M.R. Well-ordered mesoporous silica and bioactive glasses: Promise for improved hemostasis. Biomater. Sci. 2019, 7, 31–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, Y.K.; Lee, D.R.; Chung, D.J. Advances in the development of hemostatic biomaterials for medical application. Biomater. Res. 2021, 25, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.F.; Yin, M.L.; Zheng, X.H.; Li, W.; Ren, X.H. Chitosan/mesoporous silica hybrid aerogel with bactericidal properties as hemostatic material. Eur. Polym. J. 2021, 142, 110132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, S.S.Y.; Gambino, A.; Banchero, M.; Ronchetti, S.; Manna, L.; Cavalli, R.; Onida, B. Tranexamic acid-loaded mesoporous silica microspheres as a hemostatic material. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 34, 105198. [Google Scholar]
- Hooshmand, S.; Mollazadeh, S.; Akrami, N.; Ghanad, M.; El-Fiqi, A.; Baino, F.; Nazarnezhad, S.; Kargozar, S. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles and mesoporous bioactive glasses for wound management: From skin regeneration to cancer therapy. Materials 2021, 14, 3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.R.; Liu, T.; Qi, Z.H.; Li, F.; Yang, K.; Ding, S.; Lin, S.; Tian, F. Fabrication of effective mesoporous silica materials for emergency hemostasis application. Silicon 2022, 14, 10521–10534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
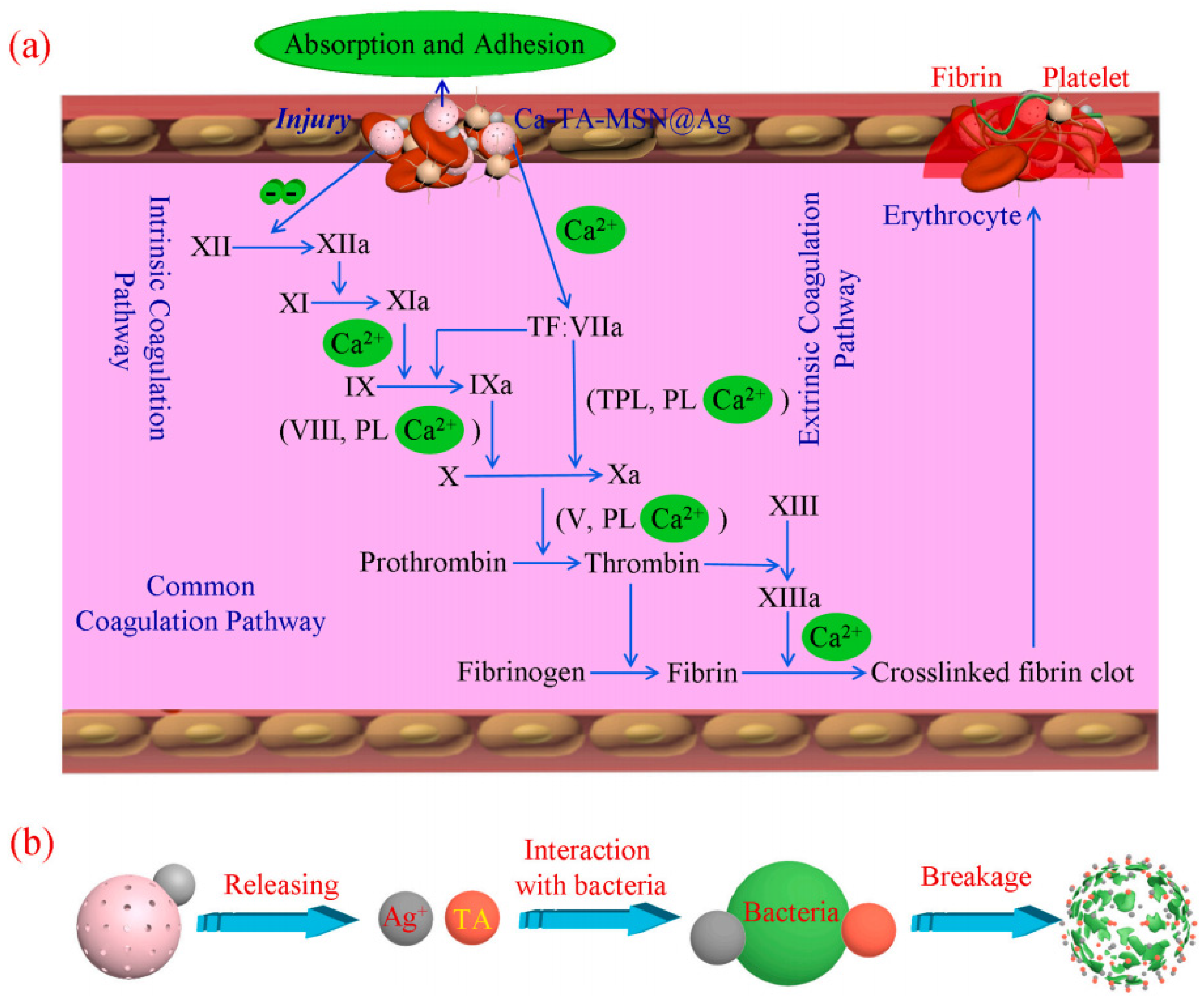
- Chen, J.W.; Qiu, L.P.; Li, Q.L.; Ai, J.; Liu, H.Q.; Chen, Q.H. Rapid hemostasis accompanied by antibacterial action of calcium crosslinking tannic acid-coated mesoporous silica/silver janus nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 123, 111958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
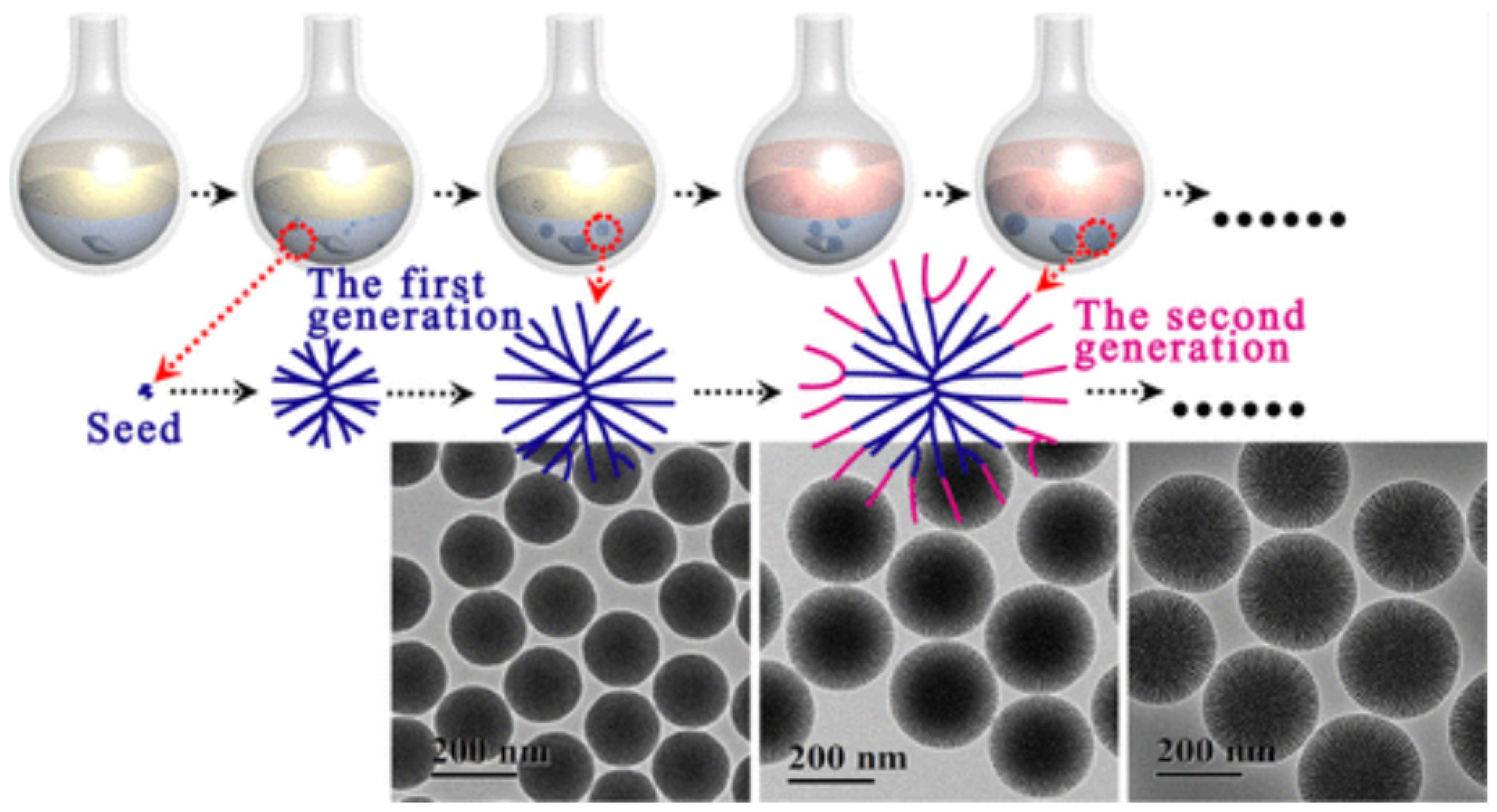
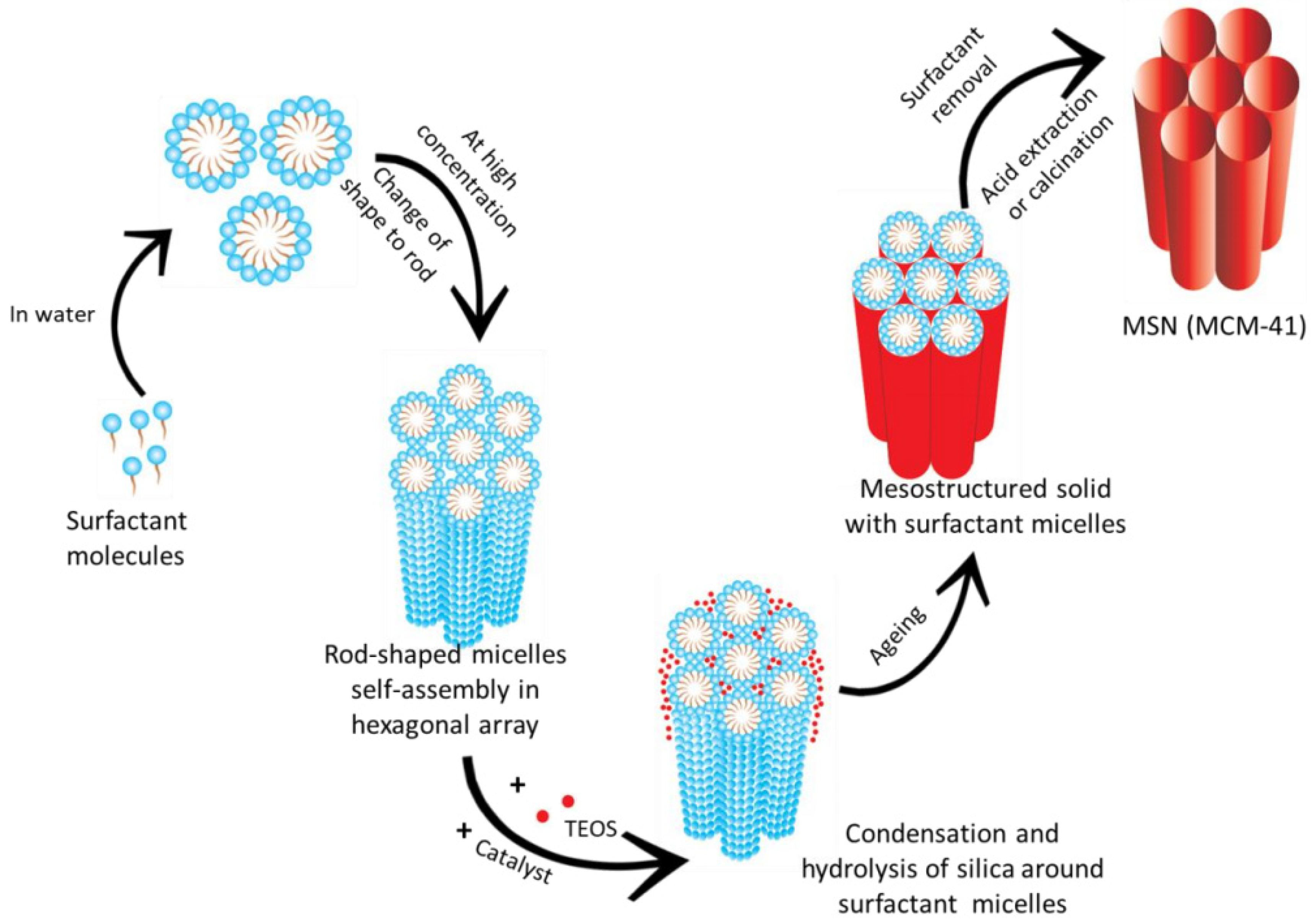
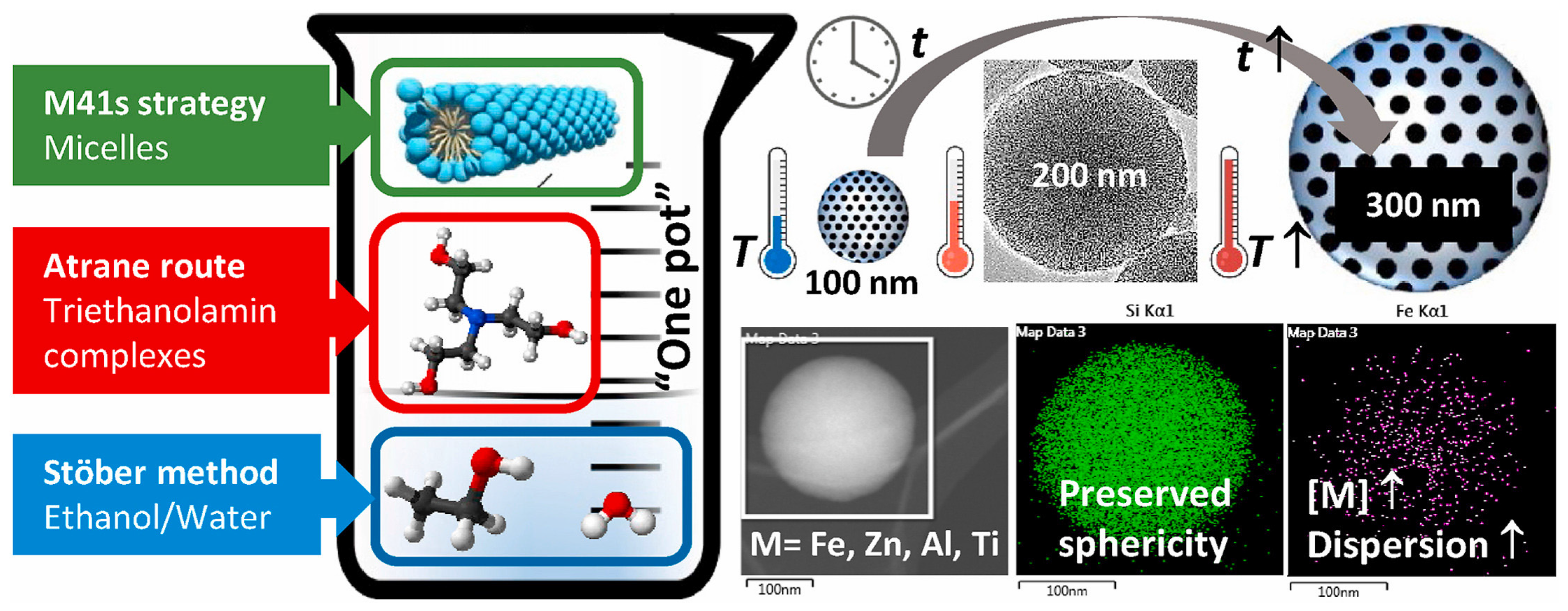
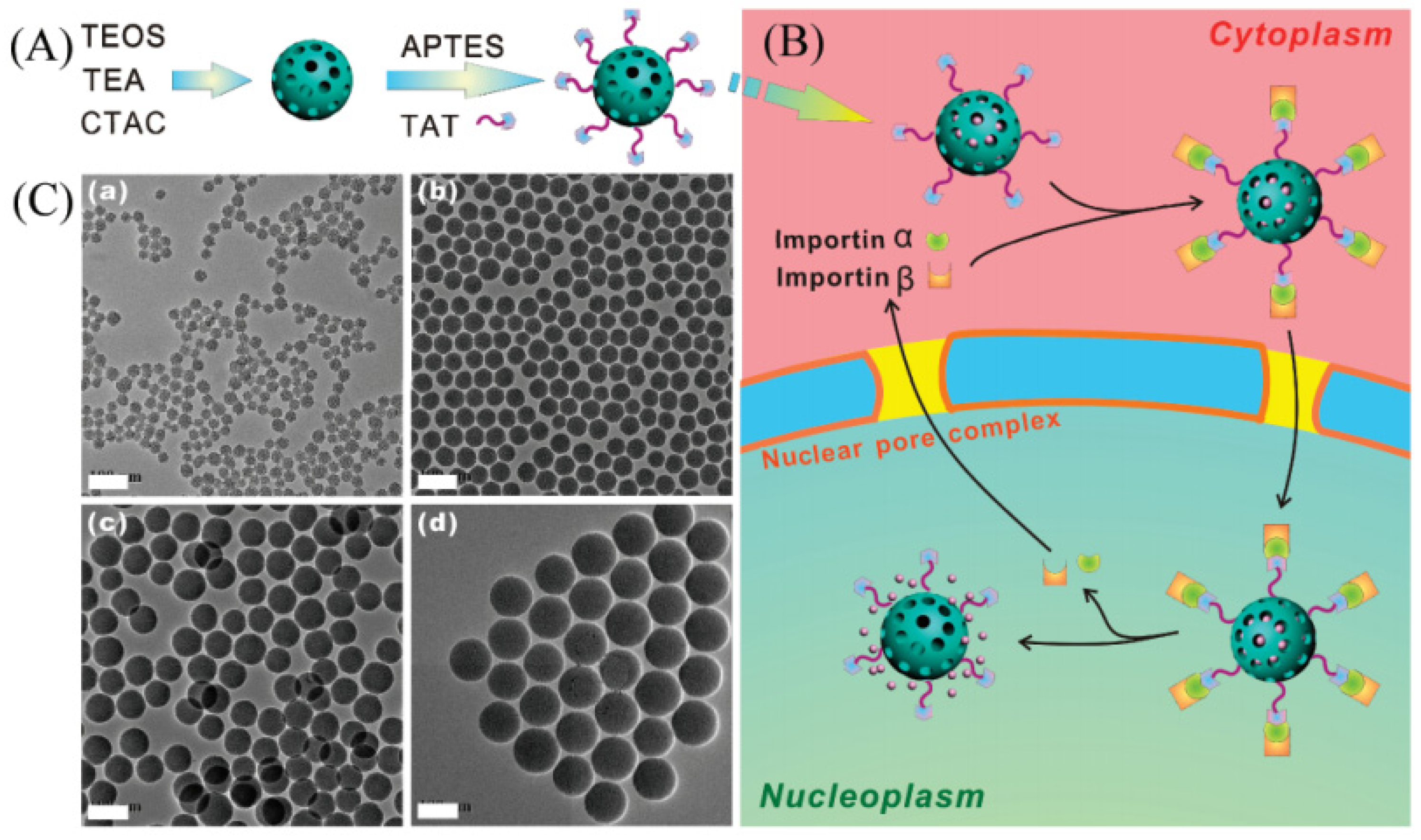
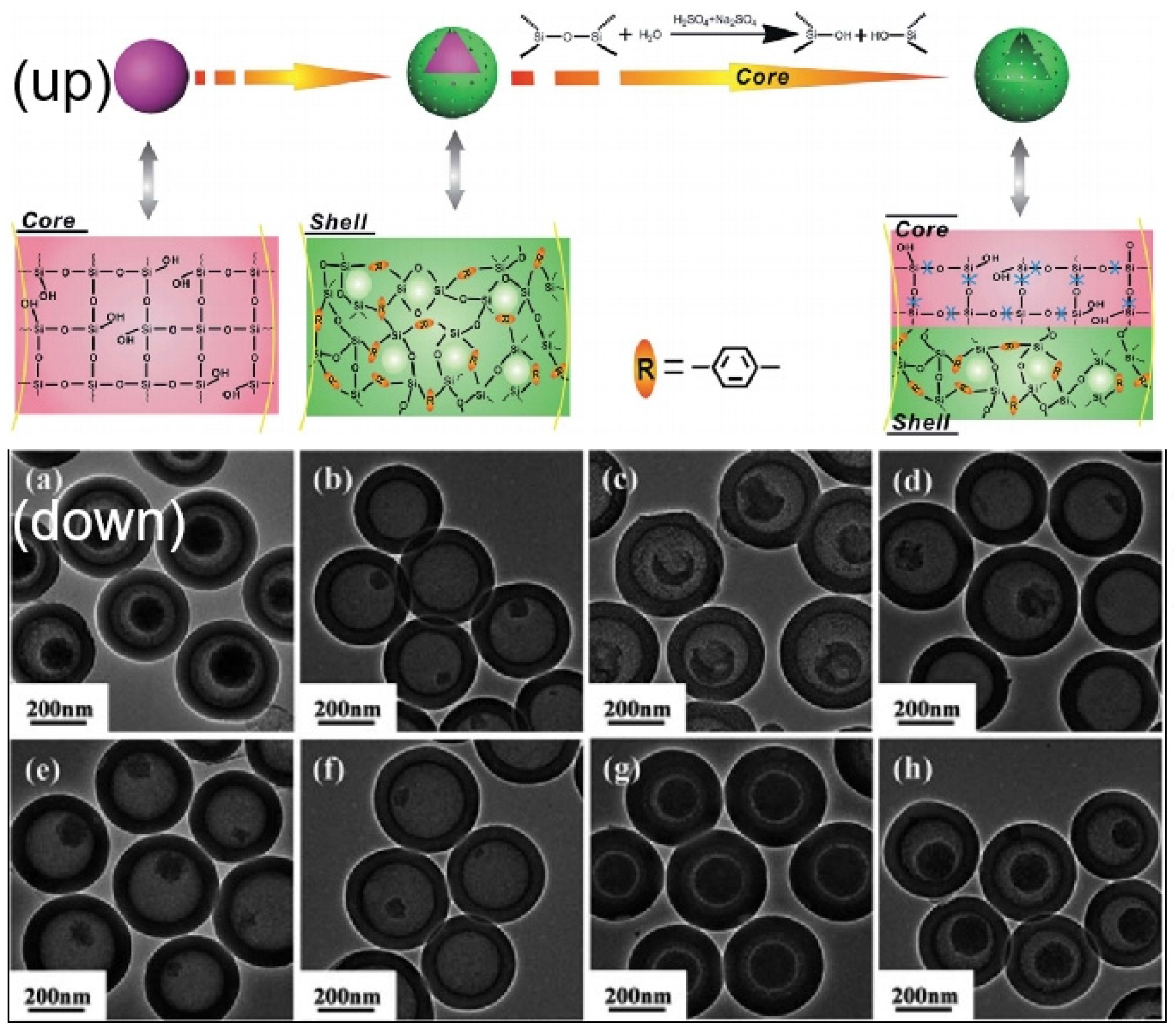
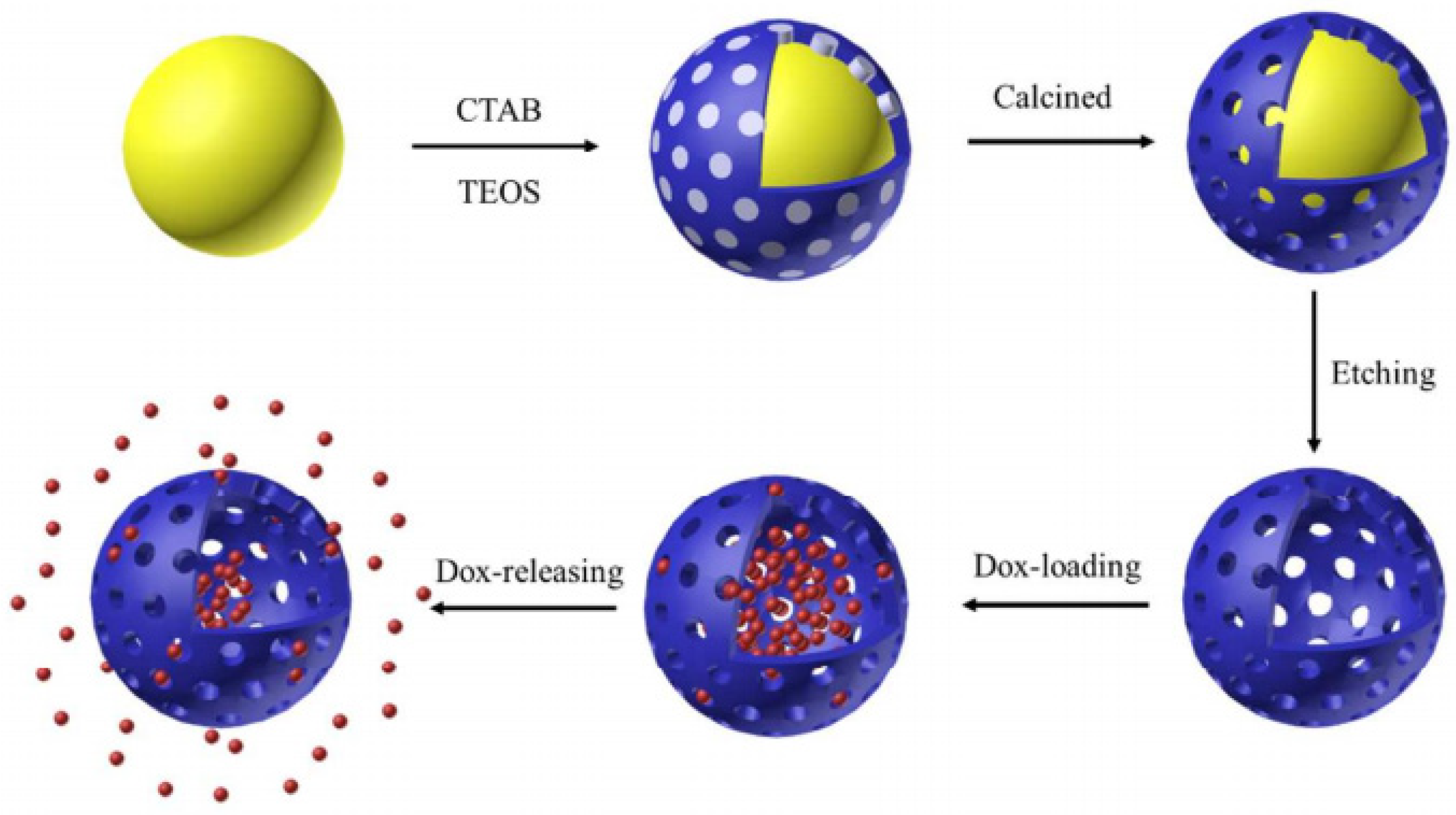
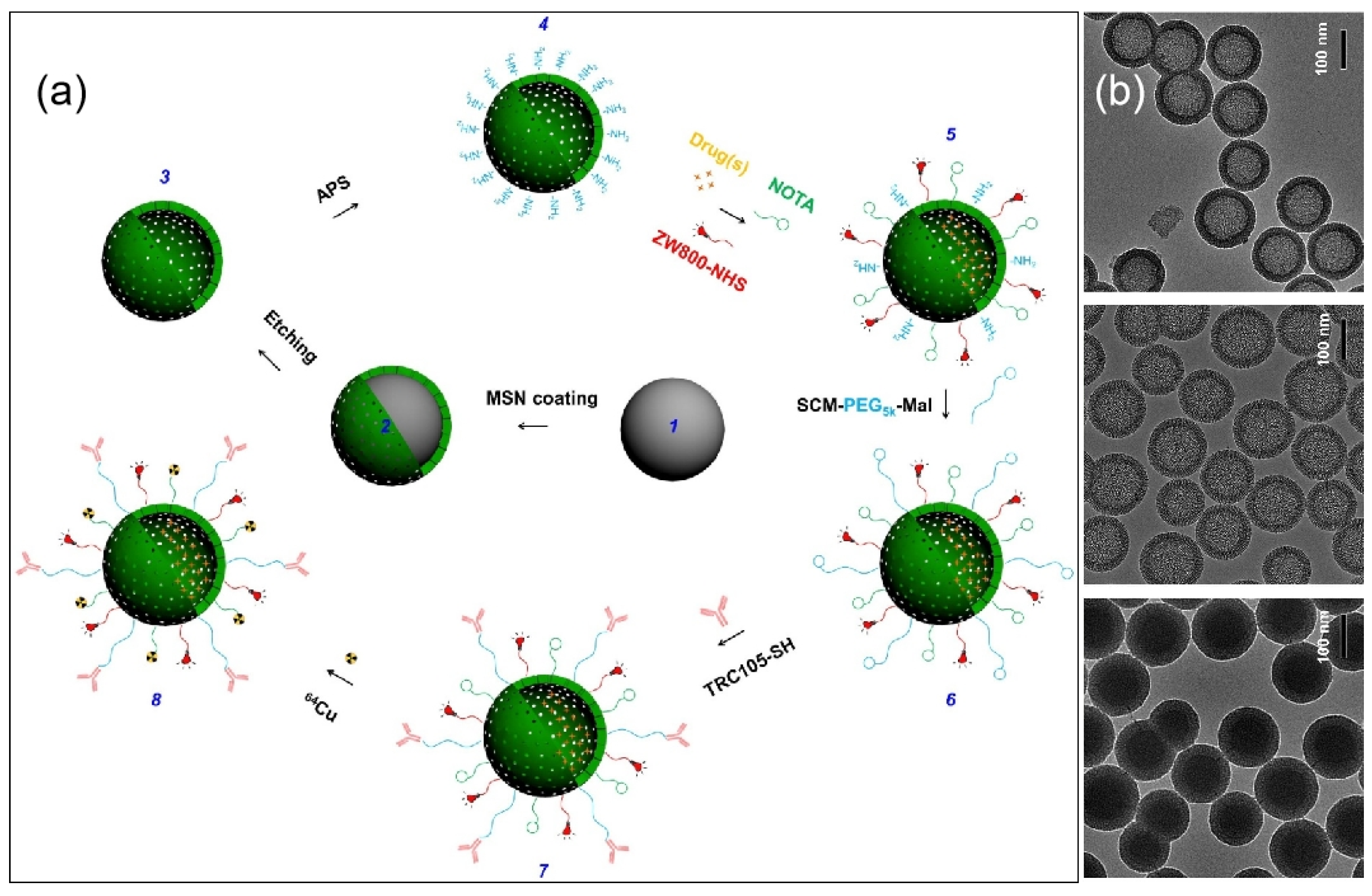
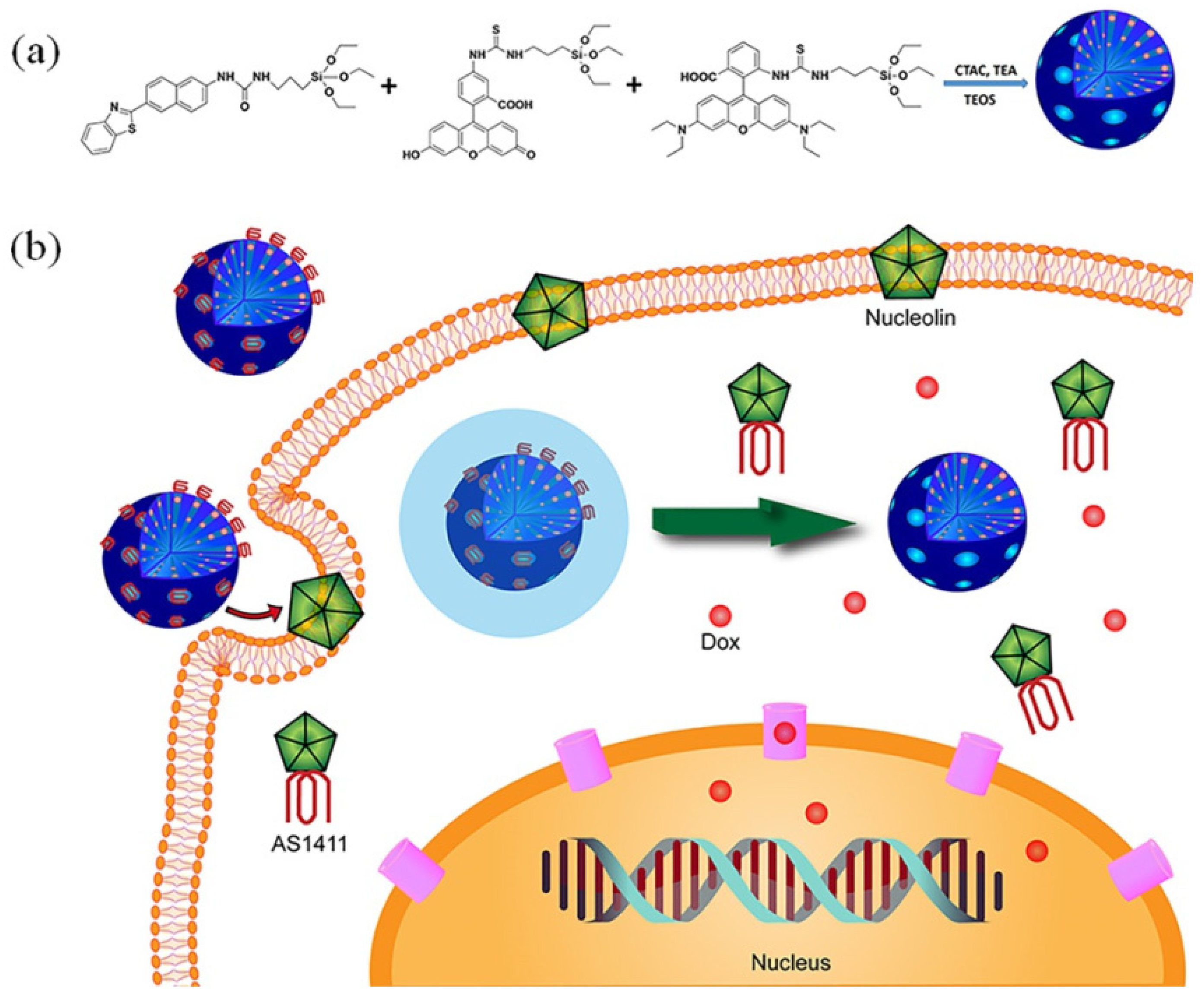
| Name | Origin of Name | First Report | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| M41S | Mobil Composition of Matter No. 41 | Kresge et al./1992 | [24,25] |
| HMS | Hexagonal Mesoporous Silica | Tanev et al./1994 | [39] |
| FSM | Folded Sheets Mesoporous Materials | Inagaki et al./1994 | [40] |
| MSU | Michigan State University | Bagshaw et al./1995 | [41] |
| KIT | Korea AdvancedInstitute of Science and Technology | Ryoo et al./1996 | [42] |
| SBA | Santa Barbara Amorphous | Zhao et al./1998 | [33] |
| FDU | Fudan University | Yu et al./2000 | [43] |
| JLU | JiLin University | Liu et al./2000 | [44] |
| TUD | Technische Universiteit Delft | Jansen et al./2001 | [45] |
| COK | Centrum voor Oppervlaktechemie en Katalyse | Jammaer et al./2008 | [46] |
| HMM | Hiroshima Mesoporous Material | Nandiyanto et al./2009 | [47] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Q.; Zhou, Y. Brief History, Preparation Method, and Biological Application of Mesoporous Silica Molecular Sieves: A Narrative Review. Molecules 2023, 28, 2013. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28052013
Li Q, Zhou Y. Brief History, Preparation Method, and Biological Application of Mesoporous Silica Molecular Sieves: A Narrative Review. Molecules. 2023; 28(5):2013. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28052013
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Qiuping, and You Zhou. 2023. "Brief History, Preparation Method, and Biological Application of Mesoporous Silica Molecular Sieves: A Narrative Review" Molecules 28, no. 5: 2013. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28052013
APA StyleLi, Q., & Zhou, Y. (2023). Brief History, Preparation Method, and Biological Application of Mesoporous Silica Molecular Sieves: A Narrative Review. Molecules, 28(5), 2013. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28052013





