Effect of Protein-Glutaminase on Calcium Sulphate-Induced Gels of SPI with Different Thermal Treatments
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Degree of Deamidation
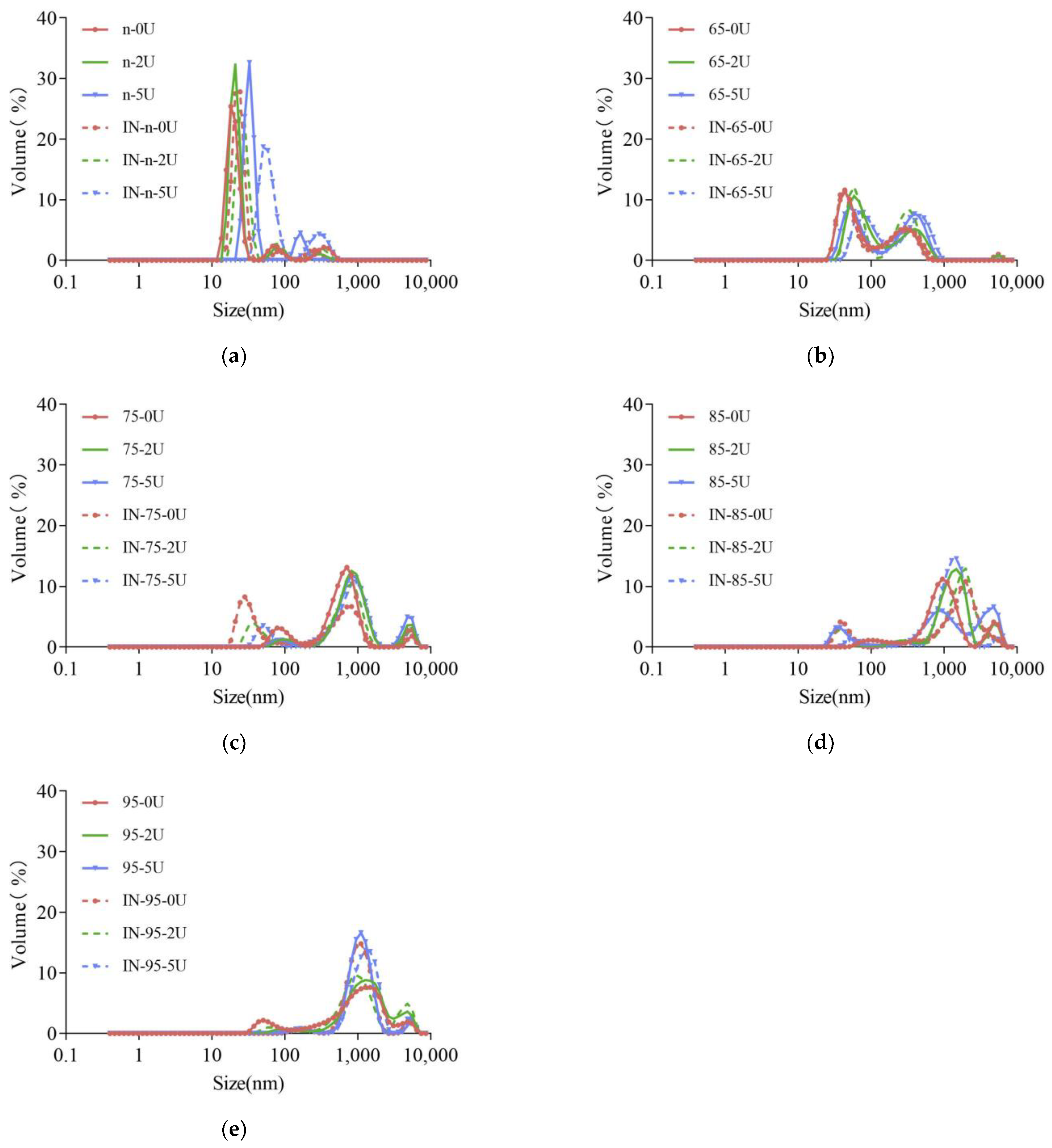
2.2. Particle Size Distribution
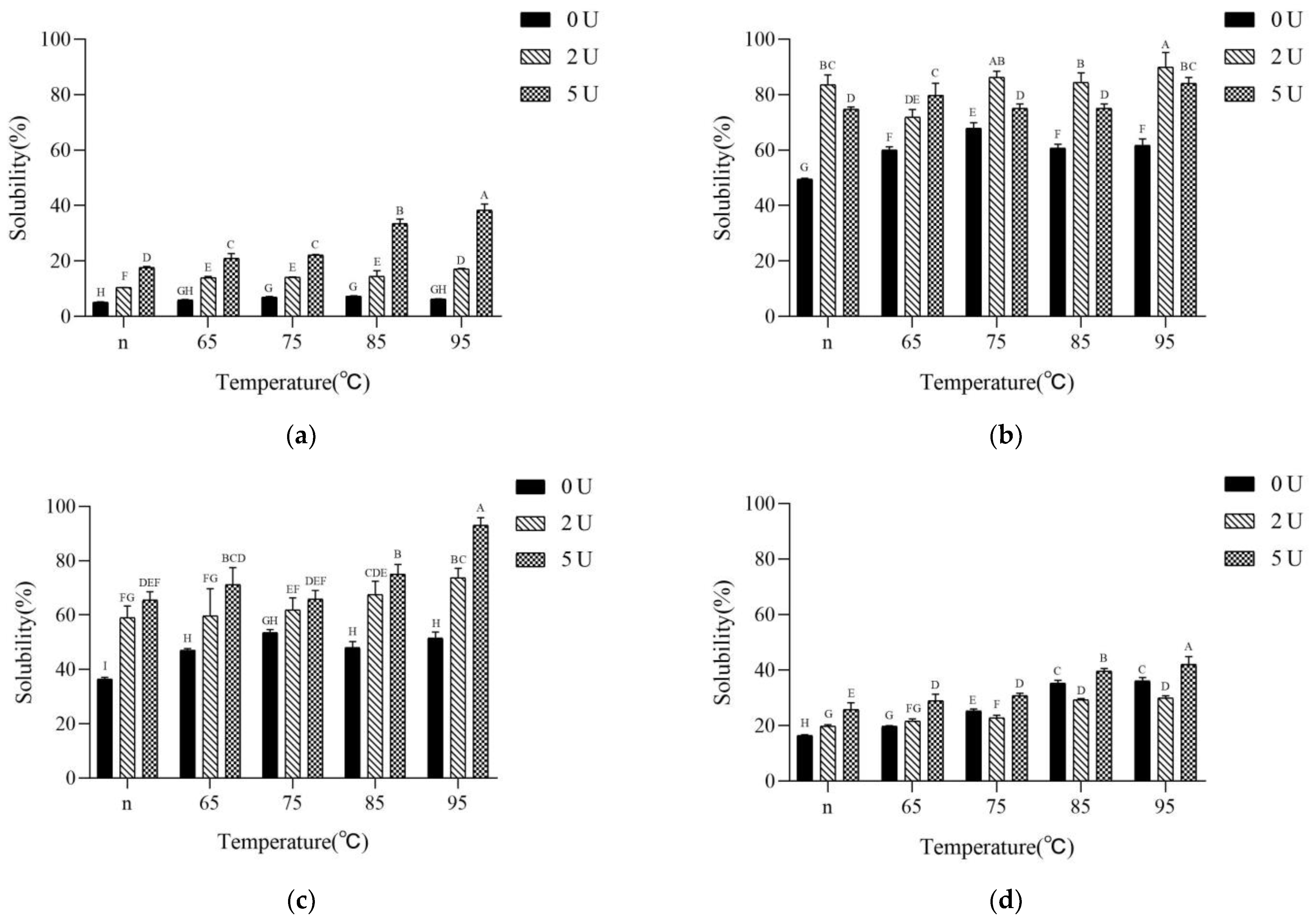
2.3. Surface Hydrophobicity
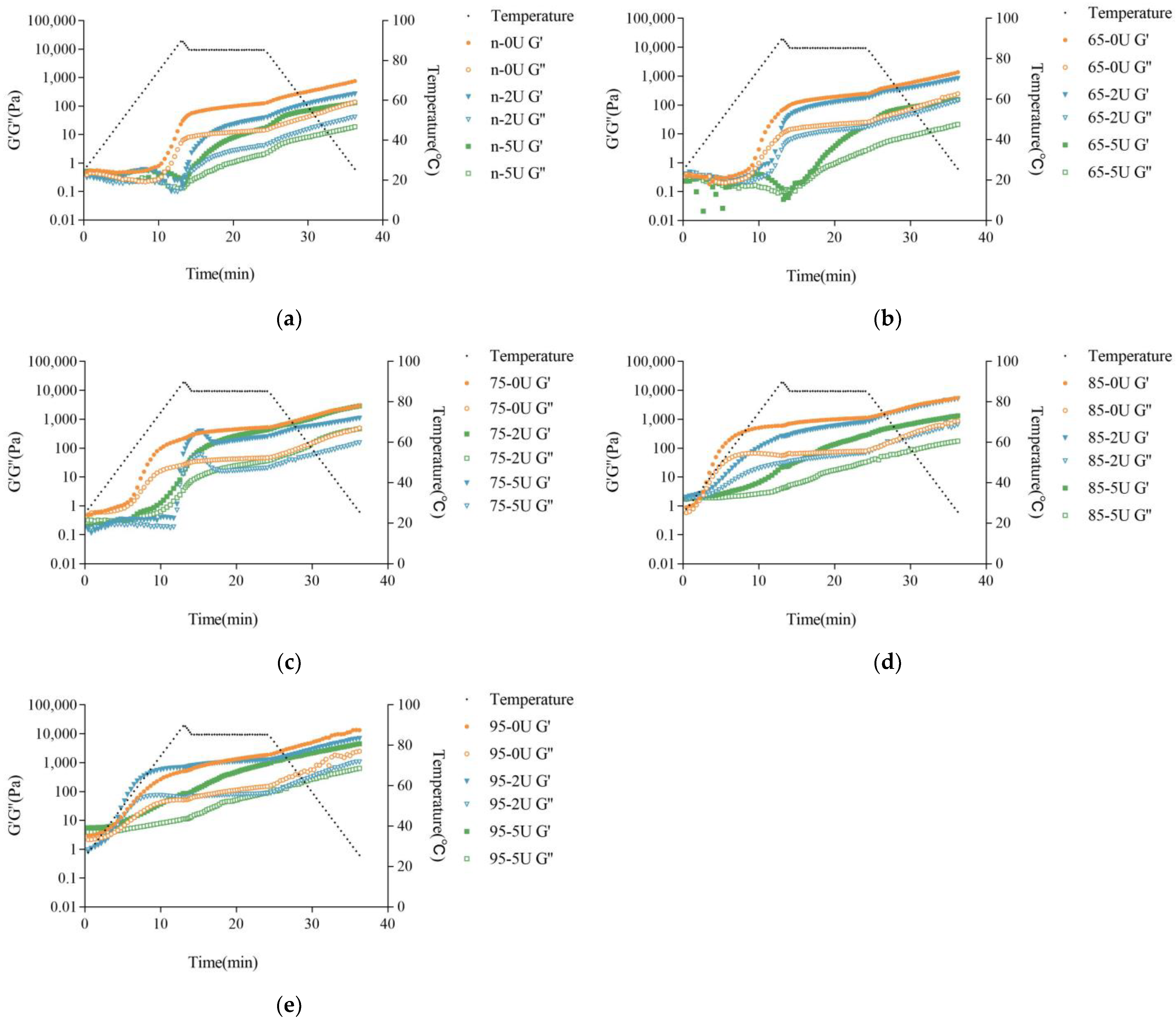
2.4. Rheological
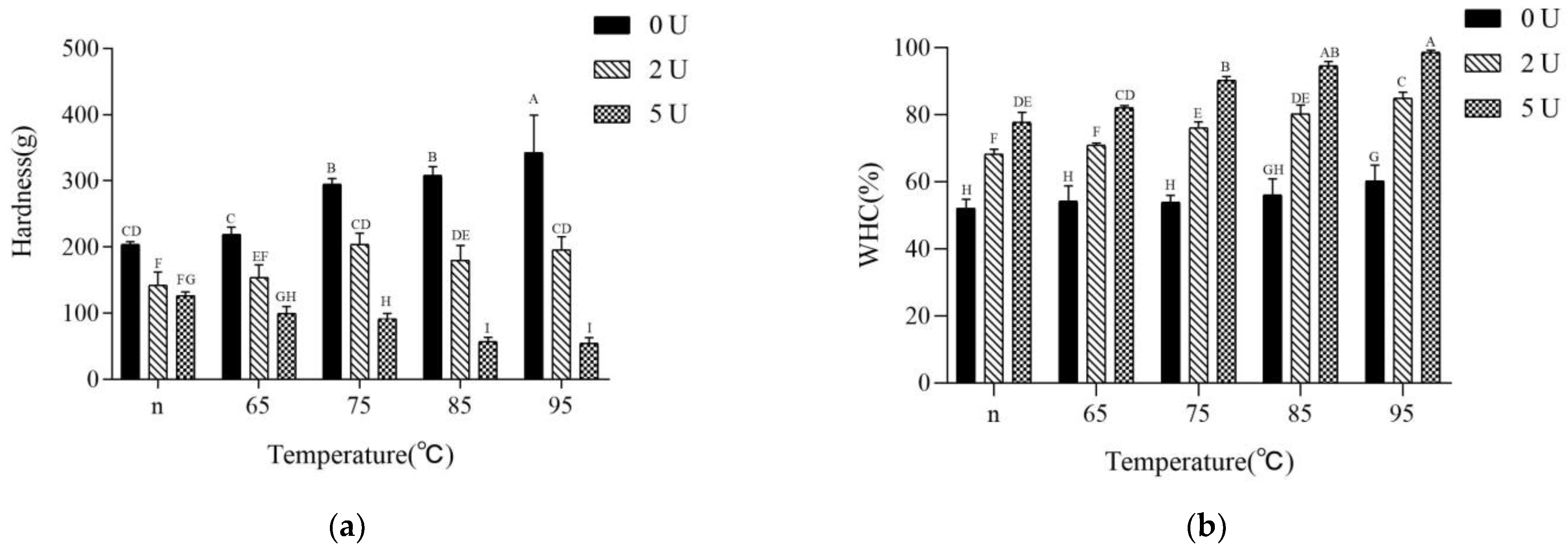
2.5. Gel Strength and Water-Holding Capacity (WHC)
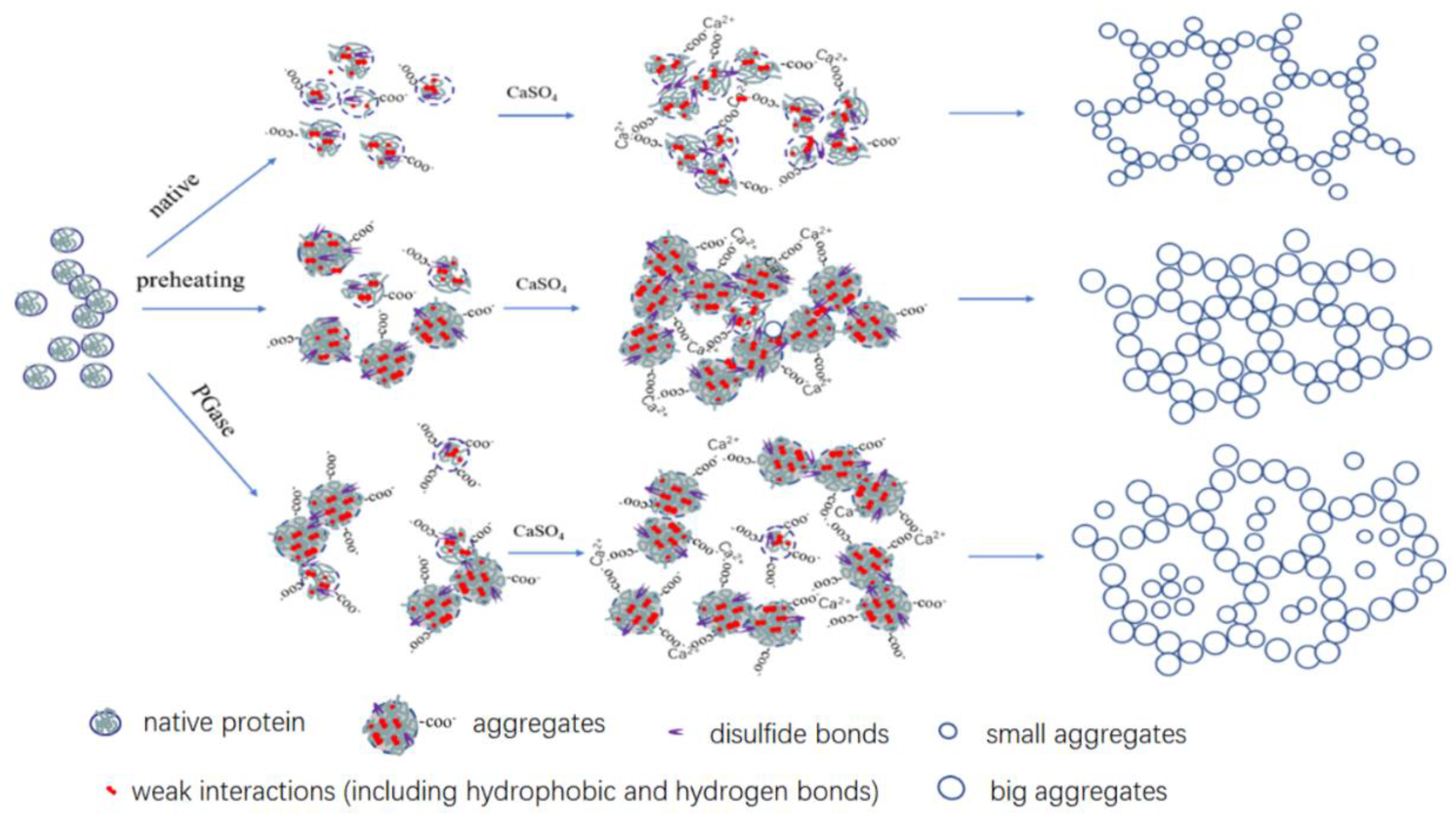
2.6. Molecular Forces in the Gels
2.7. SEM
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of Native Soy Protein Isolate
3.3. Preparation of Preheated SPI and Enzymatic Deamidation Products and Their CaSO4-Induced Gel Products
3.4. Determining the Degree of Deamidation
3.5. Particle Size Analysis
3.6. Surface Hydrophobicity (S0)
3.7. Measurement of Rheological Properties
3.8. Gel Strength and Water-Holding Capacity
3.9. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
3.10. Molecular Forces in the Gels
3.11. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Lu, X.; Lu, Z.; Yin, L.; Cheng, Y.; Li, L. Effect of Preheating Temperature and Calcium Ions on the Properties of Cold-Set Soybean Protein Gel. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 1673–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Vliet, T.; Martin, A.H.; Bos, M.A. Gelation and Interfacial Behaviour of Vegetable Proteins. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 7, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Suárez, J.C.; Xiong, Y.L. Effect of Transglutaminase-Induced Cross-Linking on Gelation of Myofibrillar/Soy Protein Mixtures. Meat Sci. 2003, 65, 899–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sha, L.; Xiong, Y.L. Trends in Food Science & Technology Plant Protein-Based Alternatives of Reconstructed Meat: Science, Technology, and Challenges. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 102, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Liu, Y.; En, Y.; Lee, J.; Chan, A.; Lee, P.; Yang, H. Effect of Starch Addition on the Physicochemical Properties, Molecular Interactions, Structures, and in Vitro Digestibility of the Plant-Based Egg Analogues. Food Chem. 2023, 403, 134390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Yin, L.; Qu, Y.; Yan, W.; Zhang, M.; Su, J.; Jia, X. Effect of Calcium Ions Concentration on the Properties and Microstructures of Doubly Induced Sorghum Arabinoxylan/Soy Protein Isolate Mixed Gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 133, 107997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.H.; Li, L.; Wang, J.L.; Yang, X.Q. Formation and Rheological Properties of “cold-Set” Tofu Induced by Microbial Transglutaminase. LWT 2007, 40, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Teng, F.; Wang, N.; Zhang, X.N.; Regenstein, J.M.; Liu, J.S.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.J. Addition of Salt Ions before Spraying Improves Heatand Cold-Induced Gel Properties of Soy Protein Isolate (SPI). Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alting, A.C.; De Jongh, H.H.J.; Visschers, R.W.; Simons, J.W.F.A. Physical and Chemical Interactions in Cold Gelation of Food Proteins. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 4682–4689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltais, A.; Remondetto, G.E.; Gonzalez, R.; Subirade, M. Formation of Soy Protein Isolate Cold-Set Gels: Protein and Salt Effects. J. Food Sci. 2005, 70, C67–C73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhakaran, M.P.; Perera, C.O.; Valiyaveettil, S. Effect of Different Coagulants on the Isoflavone Levels and Physical Properties of Prepared Firm Tofu. Food Chem. 2006, 99, 492–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skurray, G.; Cunich, J.; Carter, O. The Effect of Different Varieties of Soybean and Calcium Ion Concentration on the Quality of Tofu. Food Chem. 1980, 6, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Luo, K.; Liu, S.; Adhikari, B.; Chen, J. Improvement of Gelation Properties of Soy Protein Isolate Emulsion Induced by Calcium Cooperated with Magnesium. J. Food Eng. 2019, 244, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, S.; Yu, Y.; St. Martin, S. Effect of Soybean Varieties and Growing Locations on the Physical and Chemical Properties of Soymilk and Tofu. J. Food Sci. 2005, 70, C8–C21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Li, W.; Qin, F.; Chen, J. Calcium Sulphate-Induced Soya Bean Protein Tofu-Type Gels: Influence of Denaturation and Particle Size. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 731–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puppo, M.C.; Añón, M.C. Structural Properties of Heat-Induced Soy Protein Gels as Affected by Ionic Strength and PH. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 3583–3589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, H.; Qiao, F.; Yang, P.; Guo, F.; Huang, X.; Adhikari, B.; Chen, J. Roles of Soluble and Insoluble Aggregates Induced by Soy Protein Processing in the Gelation of Myofibrillar Protein. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Yin, H.; Yan, J.; Niu, X.; Qi, B.; Liu, J. Structure and Acid-Induced Gelation Properties of Soy Protein Isolate–Maltodextrin Glycation Conjugates with Ultrasonic Pretreatment. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 112, 106278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.H.; Yang, M.; Liu, F.; Chen, Z. Stirring Greatly Improves Transglutaminase-Induced Gelation of Soy Protein-Stabilized Emulsions. LWT 2013, 51, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Li-Chan, E.C.Y.; Wan, L.; Tian, M.; Pan, S. The Effect of High Intensity Ultrasonic Pre-Treatment on the Properties of Soybean Protein Isolate Gel Induced by Calcium Sulfate. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 32, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.T.; Ono, T. The Role of Composition and Content of Protein Particles in Soymilk on Tofu Curding by Glucono-δ-Lactone or Calcium Sulfate. J. Food Sci. 2005, 70, 258–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicole, M.; Caimeng, Z.; Joseph, H.; Eric, K.; Yufei, H. Soybean Oil Volume Fraction Effects on the Rheology Characteristics and Gelation Behavior of Glucono-δ-Lactone and Calcium Sulfate-Induced Tofu Gels. J. Texture Stud. 2016, 47, 112–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito-Oliveira, T.C.; Cavini, A.C.M.; Ferreira, L.S.; Moraes, I.C.F.; Pinho, S.C. Microstructural and Rheological Characterization of NaCl-Induced Gels of Soy Protein Isolate and the Effects of Incorporating Different Galactomannans. Food Struct. 2020, 26, 100158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Xiong, Y.L.; Chen, J.; Tang, X.; Zhou, G. Rheological and Microstructural Properties of Porcine Myofibrillar Protein-Lipid Emulsion Composite Gels. J. Food Sci. 2009, 74, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicole, M.; Caimeng, Z.; Eric, K.; Yufei, H. Salt and Acid-Induced Soft Tofu-Type Gels: Rheology, Structure and Fractal Analysis of Viscoelastic Properties as a Function of Coagulant Concentration. Int. J. Food Eng. 2014, 10, 595–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, F.J.; Su, N.W.; Lee, M.H. Effect of Calcium Sulfate Concentration in Soymilk on the Microstructure of Firm Tofu and the Protein Constitutions in Tofu Whey. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 6211–6216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, G.R. The Gelation of Proteins. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 1990, 34, 203–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbonaite, V.; de Jongh, H.H.J.; van der Linden, E.; Pouvreau, L. Water Holding of Soy Protein Gels Is Set by Coarseness, Modulated by Calcium Binding, Rather than Gel Stiffness. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 46, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; He, Z.; Zeng, M.; Qin, F.; Adhikari, B.; Chen, J. Effects of the Size and Content of Protein Aggregates on the Rheological and Structural Properties of Soy Protein Isolate Emulsion Gels Induced by CaSO4. Food Chem. 2017, 221, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.H.; Chen, L.; Foegeding, E.A. Mechanical and Water-Holding Properties and Microstructures of Soy Protein Isolate Emulsion Gels Induced by CaCl2, Glucono-δ-Lactone (GDL), and Transglutaminase: Influence of Thermal Treatments before and/or after Emulsification. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 4071–4077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miwa, N.; Yokoyama, K.; Wakabayashi, H.; Nio, N. Effect of Deamidation by Protein-Glutaminase on Physicochemical and Functional Properties of Skim Milk. Int. Dairy J. 2010, 20, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Wang, Z.; He, Z.; Zeng, M.; Qin, F.; Chen, J. Effect of Heat-Induced Aggregation of Soy Protein Isolate on Protein-Glutaminase Deamidation and the Emulsifying Properties of Deamidated Products. LWT 2022, 154, 112328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, S.; Yokoe, M. A Novel Protein-Deamidating Enzyme from Chryseobacterium Proteolyticum Sp. Nov., a Newly Isolated Bacterium from Soil. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 3337–3343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.Q.; Sontag-Strohm, T.; Salovaara, H.; Sibakov, J.; Kanerva, P.; Loponen, J. Oat Protein Solubility and Emulsion Properties Improved by Enzymatic Deamidation. J. Cereal Sci. 2015, 64, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suppavorasatit, I.; De Mejia, E.G.; Cadwallader, K.R. Optimization of the Enzymatic Deamidation of Soy Protein by Protein-Glutaminase and Its Effect on the Functional Properties of the Protein. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 11621–11628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorgentini, D.A.; Wagner, J.R.; Anon, M.C. Effects of Thermal Treatment of Soy Protein Isolate on the Characteristics and Structure-Function Relationship of Soluble and Insoluble Fractions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1995, 43, 2471–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T. Influence of Heating Temperature on Conformational Changes of Soybean Proteins. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1979, 43, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yie, H.Y.; Yamaguchi, S.; Yeun, S.G.; Mori, T.; Matsumura, Y. Effects of Enzymatic Deamidation by Protein-Glutaminase on Structure and Functional Properties of α-Zein. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 7094–7100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Tian, Z.; Chen, L. Effects of Deamidation on Aggregation and Emulsifying Properties of Barley Glutelin. Food Chem. 2011, 128, 1029–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, L.; Roos, Y.H.; Miao, S. Study on the Rheological Properties and Volatile Release of Cold-Set Emulsion-Filled Protein Gels. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 11420–11428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.Z.; Zhang, H.; Gao, L.; Wang, L.; Qian, H.F. Influence of PH and Ionic Strength on Heat-Induced Formation and Rheological Properties of Cottonseed Protein Gels. Food Bioprod. Process. 2015, 96, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saio, K.; Koyama, E.; Yamazaki, S.; Watanabe, T. Protein-Calcium-Phytic Acid Relationships in Soybean: Part III. Effect of Phytic Acid on Coagulative Reaction in Tofu-Making. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1969, 33, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Ma, S.; Liu, X.; Yin, X.; Liu, S.; Zhou, J.; Du, G. Protein-Glutaminase: Research Progress and Prospect in Food Manufacturing. Food Biosci. 2021, 43, 101314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Xie, L.; Guo, S. Effects of Small Molecular Compounds in Soymilk on the Protein Coagulation Process: Ca2+ as Coagulant. Food Res. Int. 2015, 77, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Xiong, Y.L. Interaction and Functionality of Mixed Myofibrillar and Enzyme-Hydrolyzed Soy Proteins. J. Food Sci. 2003, 68, 803–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Amount of Enzyme Addition | 0U | 2U | 5U | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G′ and Tgel | G′ (Pa) | Tgel (°C) | G′ (Pa) | Tgel (°C) | G′ (Pa) | Tgel (°C) |
| native | 757.69 | 81.15 | 267.71 | 85.33 | 132.50 | 89.60 |
| 65 | 1360.15 | 72.26 | 831.85 | 83.03 | 155.48 | 89.54 |
| 75 | 2944.65 | 57.18 | 2897.44 | 80.74 | 1090.23 | 85.23 |
| 85 | 8550.76 | 26.89 | 5180.77 | 44.12 | 1313.29 | 78.73 |
| 95 | 13,503.27 | 42.24 | 6960.80 | 40.02 | 4512.01 | 50.71 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Fu, L.; He, Z.; Zeng, M.; Chen, Q.; Qin, F.; Wang, Z.; Chen, J. Effect of Protein-Glutaminase on Calcium Sulphate-Induced Gels of SPI with Different Thermal Treatments. Molecules 2023, 28, 1752. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041752
Li X, Fu L, He Z, Zeng M, Chen Q, Qin F, Wang Z, Chen J. Effect of Protein-Glutaminase on Calcium Sulphate-Induced Gels of SPI with Different Thermal Treatments. Molecules. 2023; 28(4):1752. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041752
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xin, Liwei Fu, Zhiyong He, Maomao Zeng, Qiuming Chen, Fang Qin, Zhaojun Wang, and Jie Chen. 2023. "Effect of Protein-Glutaminase on Calcium Sulphate-Induced Gels of SPI with Different Thermal Treatments" Molecules 28, no. 4: 1752. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041752
APA StyleLi, X., Fu, L., He, Z., Zeng, M., Chen, Q., Qin, F., Wang, Z., & Chen, J. (2023). Effect of Protein-Glutaminase on Calcium Sulphate-Induced Gels of SPI with Different Thermal Treatments. Molecules, 28(4), 1752. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041752









