Molecularly Imprinted Nanomaterials with Stimuli Responsiveness for Applications in Biomedicine
Abstract
1. Introduction
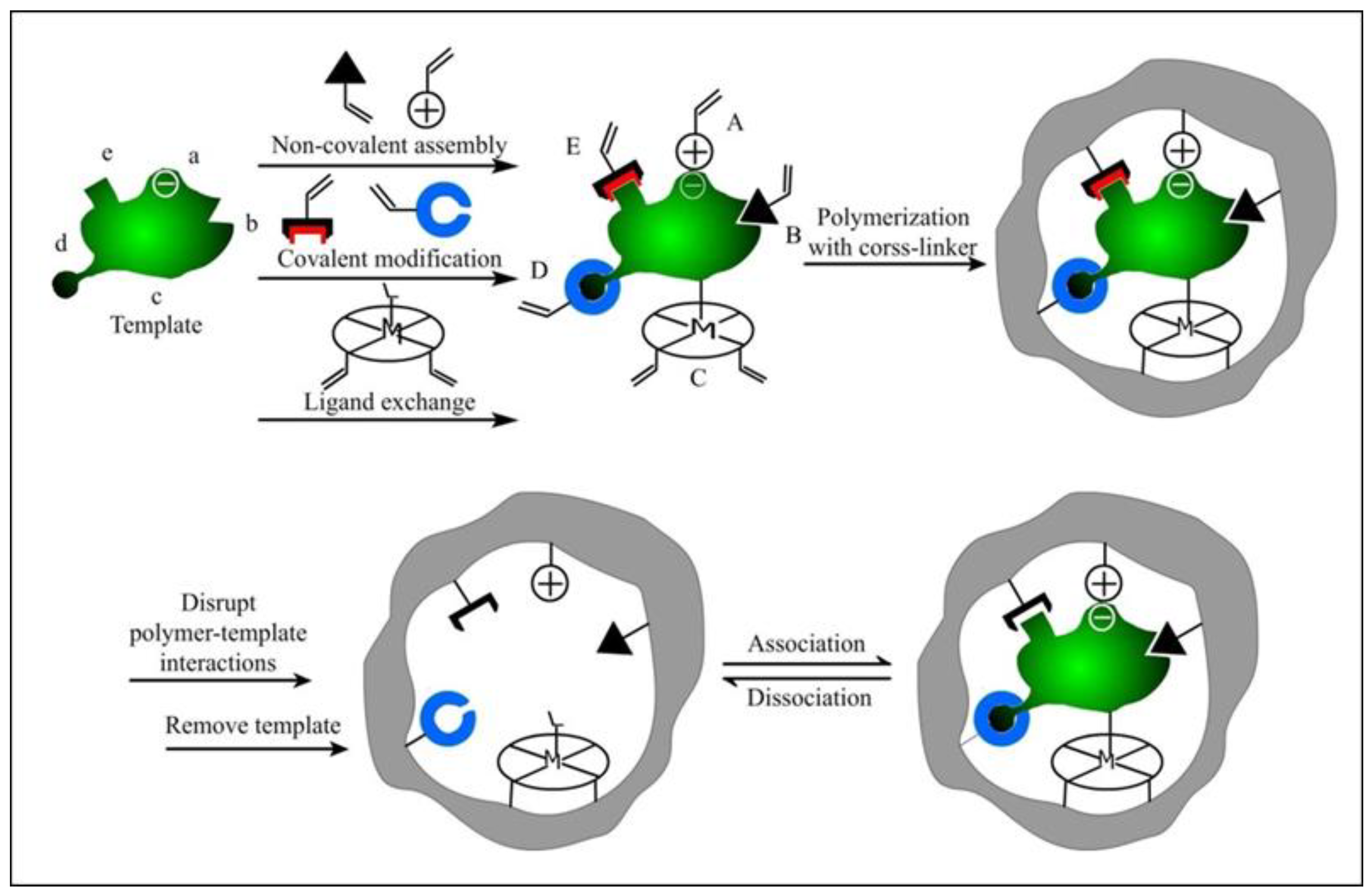
1.1. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers
1.2. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Nanomaterials (MIP-NMs)
1.2.1. Small-Molecule-Imprinted Nanomaterials
Drug Molecule Imprinting
Small-Biomolecule Imprinting
1.2.2. Biomacromolecule-Imprinted Nanomaterials
Polysaccharide Imprinting
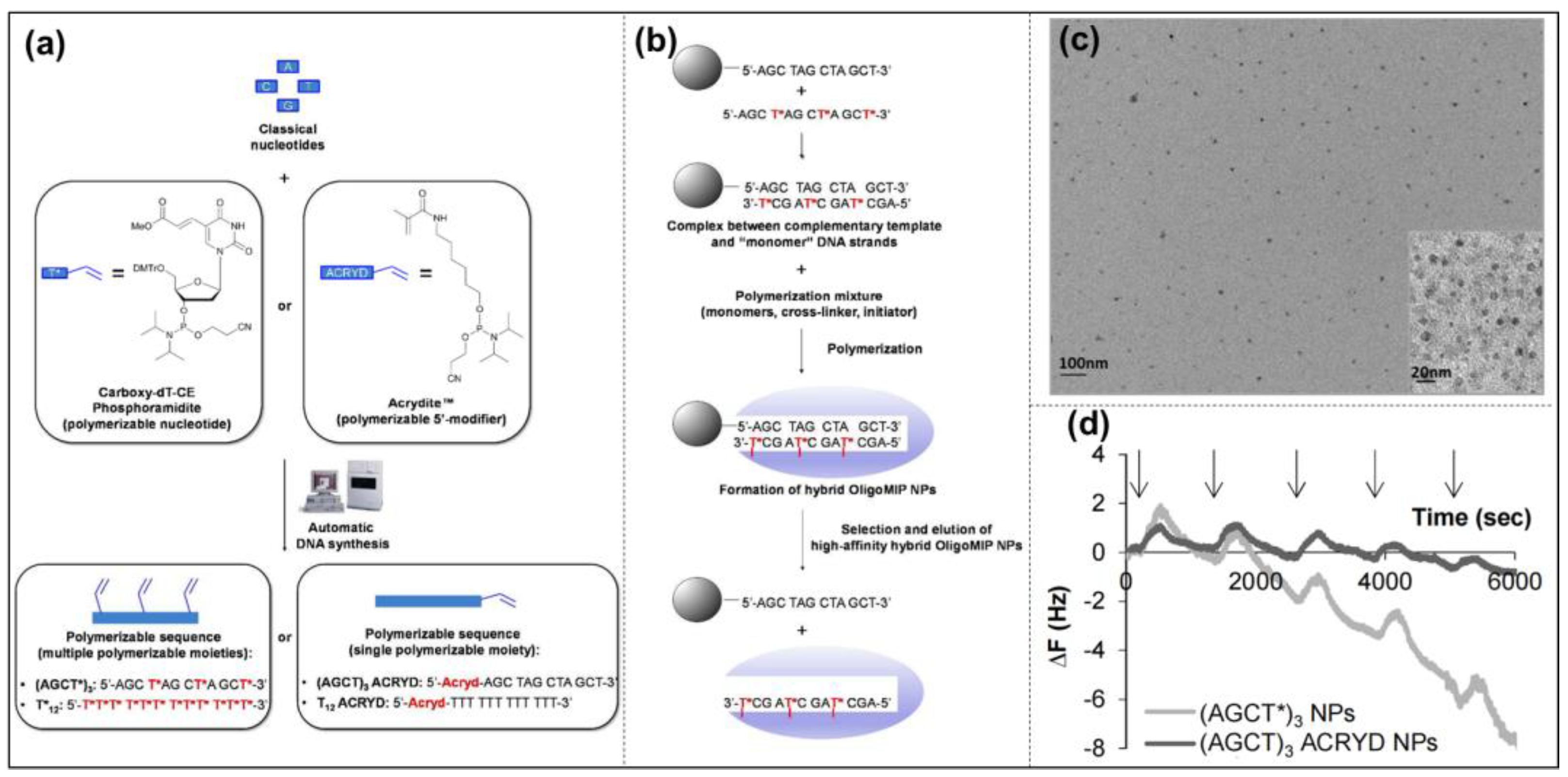
Nucleic Acid Imprinting
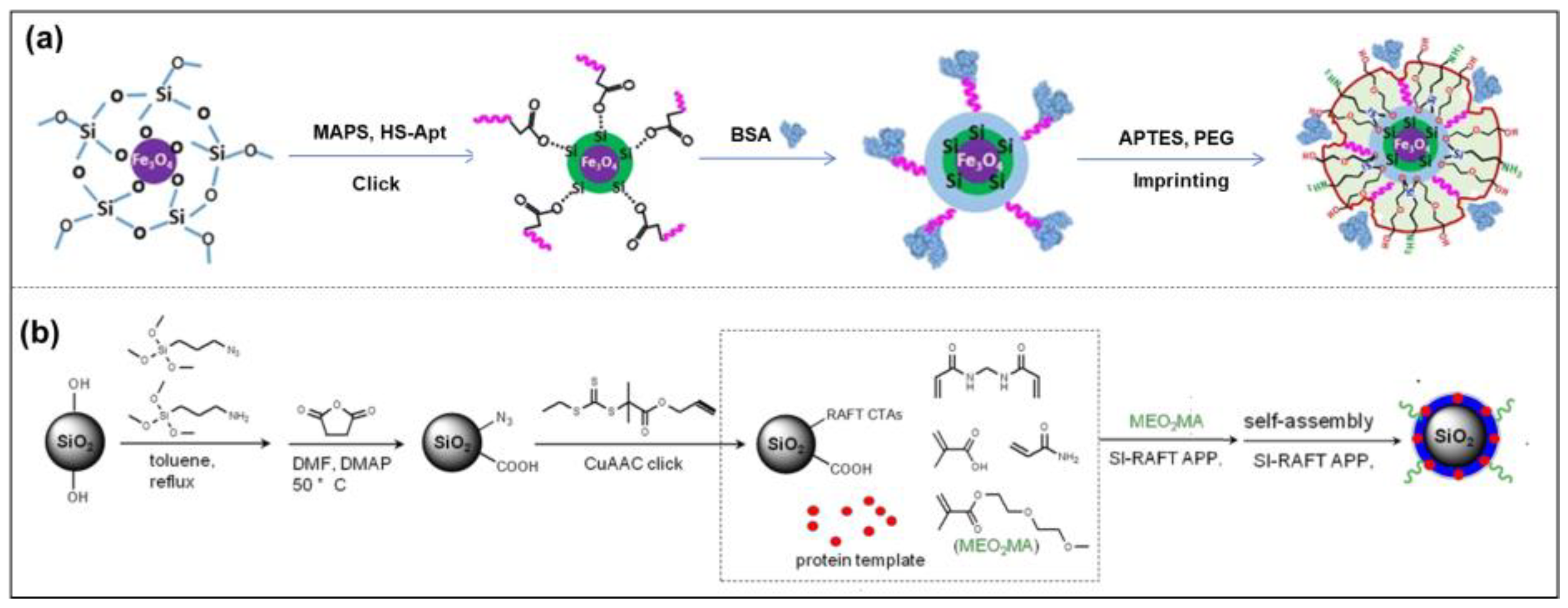
Protein Imprinting
Surface Imprinting
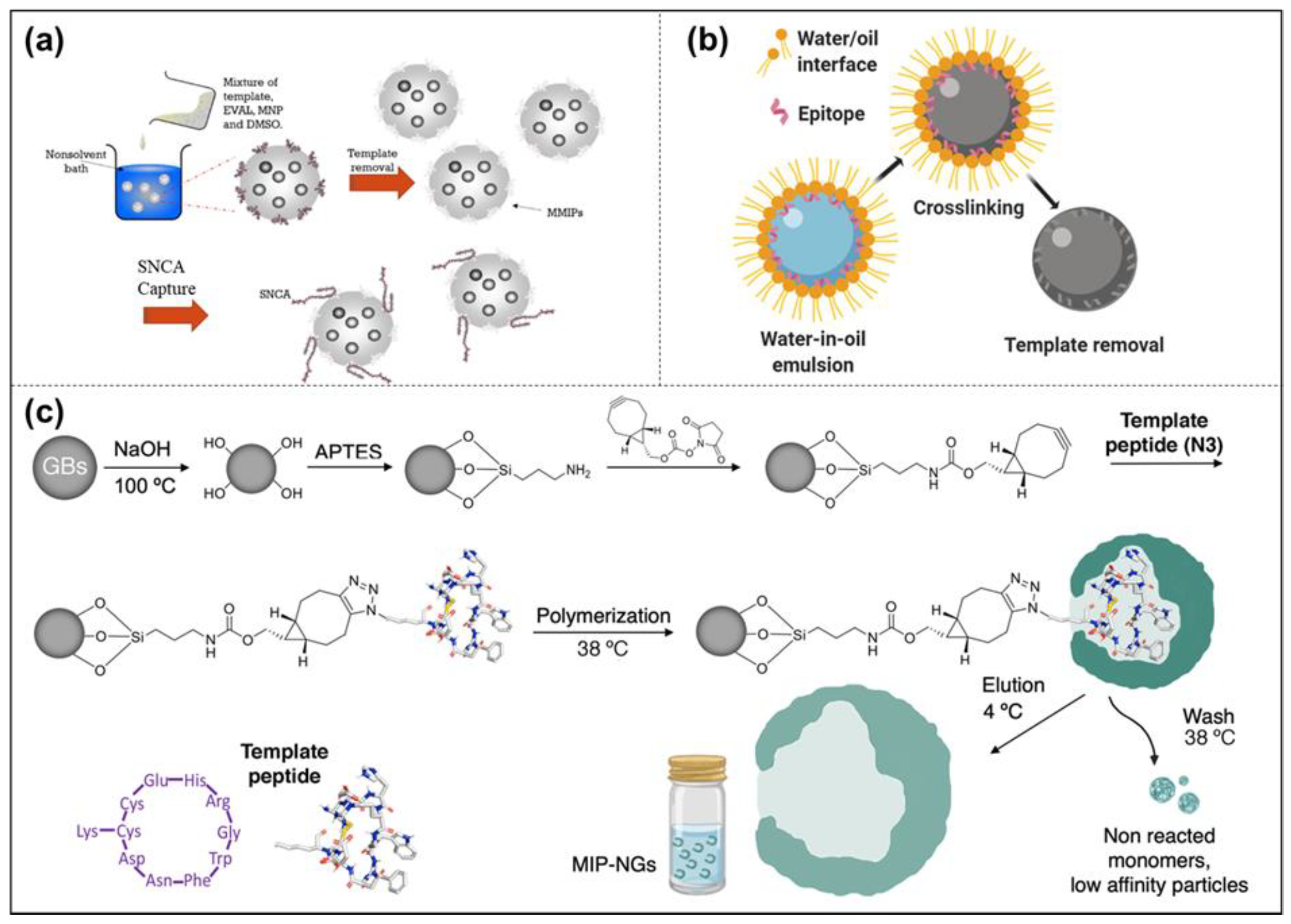
Epitope Peptide Imprinting
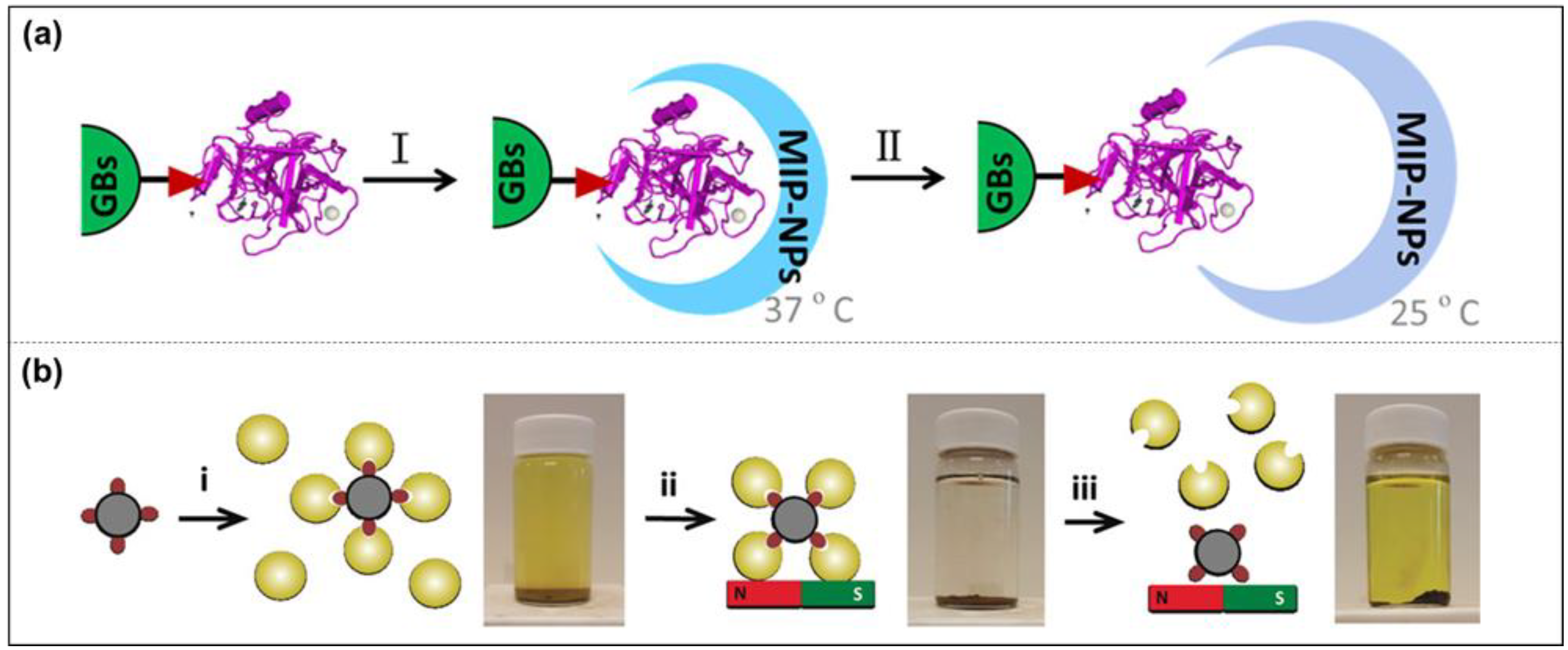
Solid-Phase Imprinting
1.2.3. Cell Imprinting
1.2.4. Others
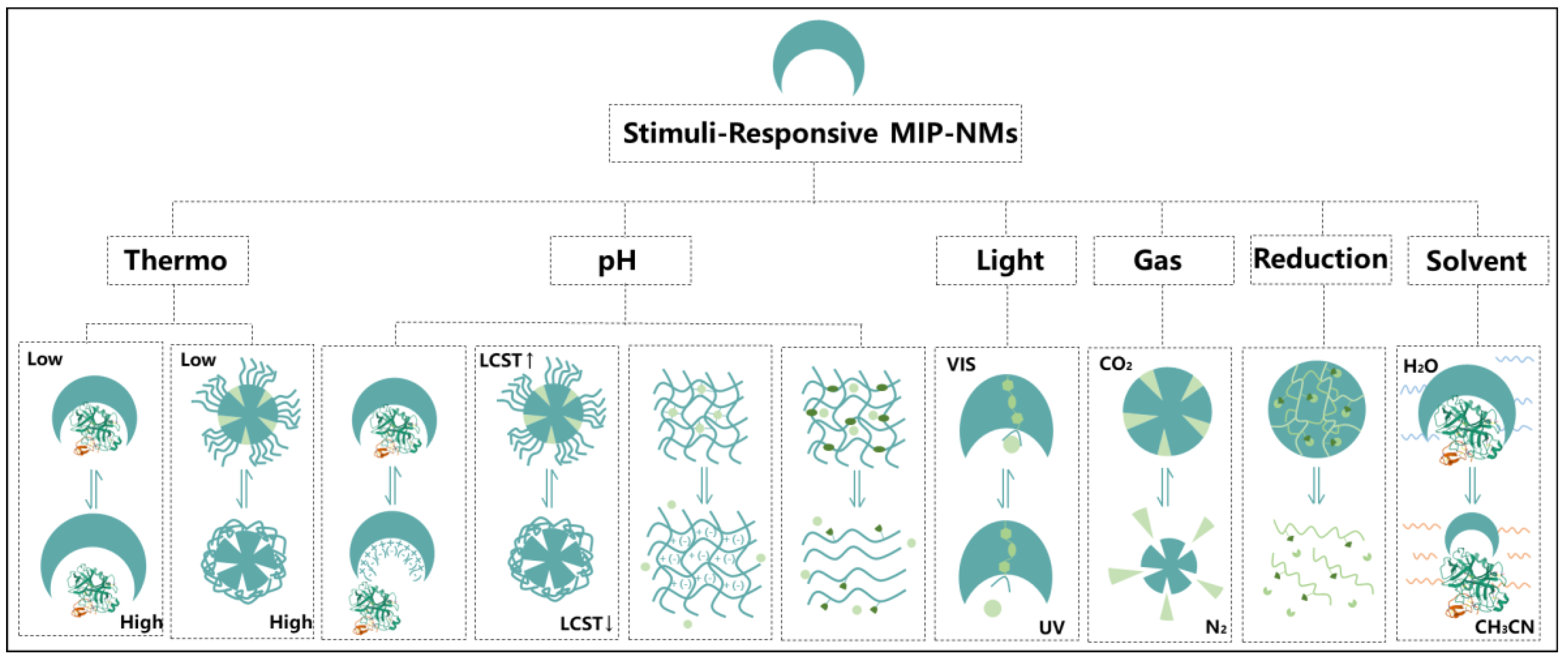
2. Stimuli-Responsive MIP-NMs
2.1. Thermal Responsiveness
2.2. PH Responsiveness
2.3. Light Responsiveness
2.4. Gas Responsiveness
2.5. Reduction Responsiveness
2.6. Solvent Responsiveness
2.7. Dual/Multiple Responsiveness
3. Biomedical Applications of Stimuli-Responsive MIP-NMs
3.1. Bioanalysis and Diagnosis
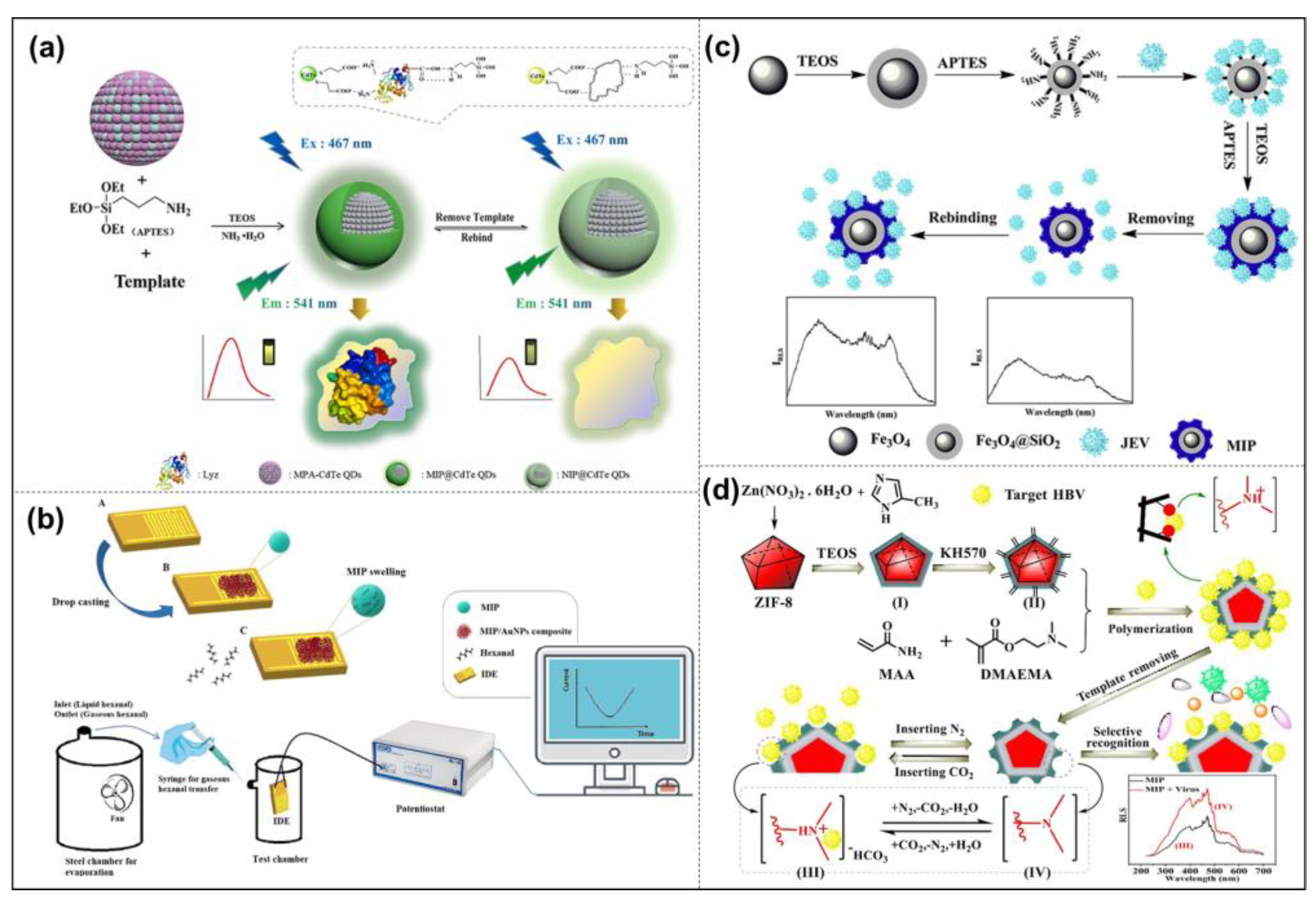
3.2. Bioimaging
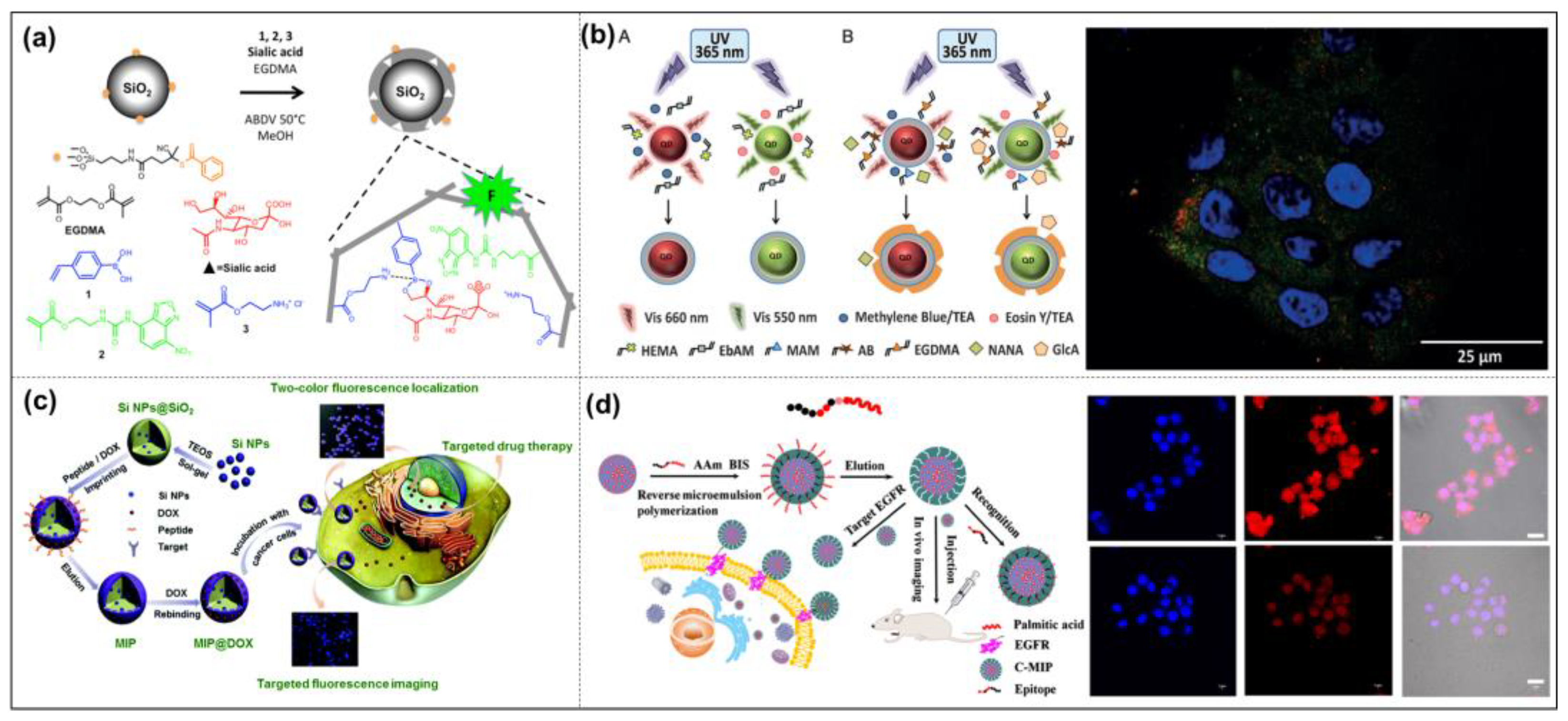
3.3. Drug Delivery
3.4. Disease Intervention
4. Conclusions and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pauling, L. A Theory of the Structure and Process of Formation of Antibodies. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1940, 62, 2643–2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickey, F.H. The preparation of specific absorbents. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1949, 35, 227–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulff, G.; Sarhan, A.; Zabrocki, K. Enzyme-analogue built polymers and their use for the resolution of racemates. Tetrahedron Lett. 1973, 14, 4329–4332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulff, G.; Oberkobusch, D.; Minárik, M. Enzyme-analogue built polymers, 18 chiral cavities in polymer layers coated on wide-pore silica. React. Polym. Ion Exch. Sorbents 1985, 3, 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlatakis, G.; Andersson, L.I.; Müller, R.; Mosbach, K. Drug assay using antibody mimics made by molecular imprinting. Nature 1993, 361, 645–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Li, X.; Miao, H.; Xu, J.; Pan, G. State of the art in development of molecularly imprinted biosensors. View 2022, 3, 20200170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J. Preparing Selective Nanozymes by Molecular Imprinting. Methods Mol. Biol. 2021, 2359, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanavicius, S.; Jagminas, A.; Ramanavicius, A. Advances in Molecularly Imprinted Polymers Based Affinity Sensors. Polymers 2021, 13, 974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wu, L.; Yan, H.; Lu, Z.; Yin, W.; Han, H. Enzyme induced molecularly imprinted polymer on SERS substrate for ultrasensitive detection of patulin. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1101, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H. Molecularly imprinted nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1806328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, S.A. Molecular imprinted polymers as drug delivery vehicles. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 2262–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haupt, K.; Rangel, P.X.M.; Bui, B.T.S. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers: Antibody Mimics for Bioimaging and Therapy. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 9554–9582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Ma, Y.; Pan, J.; Meng, Z.; Pan, G.; Sellergren, B. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers with Stimuli-Responsive Affinity: Progress and Perspectives. Polymers 2015, 7, 1689–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BelBruno, J.J. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 94–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Say, R.; Ersoz, A.; Sener, I.; Atilir, A.; Diltemiz, S.; Denizli, A. Comparison of adsorption and selectivity characteristics for 4-nitrophenol imprinted polymers prepared via bulk and suspension polymerization. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 3471–3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellens, E.; Bove, H.; Conradi, M.; D’Olieslaeger, L.; Wagner, P.; Landfester, K.; Junkers, T.; Ethirajan, A. Improved Molecular Imprinting Based on Colloidal Particles Made from Miniemulsion: A Case Study on Testosterone and Its Structural Analogues. Macromolecules 2016, 49, 2559–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.J.; Tong, Y.W. Molecularly imprinted beads by surface imprinting. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 389, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Heiden, P.A. Recent Developments in Molecularly Imprinted Nanoparticles by Surface Imprinting Techniques. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2014, 299, 268–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.H.; Wang, H.Y.; Li, S.; He, X.W.; Li, W.Y.; Zhang, Y.K. Preparation of glycan-oriented imprinted polymer coating Gd-doped silicon nanoparticles for targeting cancer Tn antigens and dual-modal cell imaging via boronate-affinity surface imprinting. Talanta 2021, 223, 121706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.T.; Ma, Y.J.; Feng, Y.S.; He, X.W.; Li, W.Y.; Zhang, Y.K. Targeted Mitochondrial Fluorescence Imaging-Guided Tumor Antimetabolic Therapy with the Imprinted Polymer Nanomedicine Capable of Specifically Recognizing Dihydrofolate Reductase. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 40332–40341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.J.; Chen, Y.J.; Fang, M.Y.; Tian, Y.B.; Bai, G.Y.; Zhuo, K.L. Silanized carbon dot-based thermo-sensitive molecularly imprinted fluorescent sensor for bovine hemoglobin detection. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 5811–5817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Qin, Y.; Tan, T.; Lv, Y. Targeted Live Cell Raman Imaging and Visualization of Cancer Biomarkers with Thermal-Stimuli Responsive Imprinted Nanoprobes. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2018, 35, 1800390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medlock, J.; Das, A.A.K.; Madden, L.A.; Allsup, D.J.; Paunov, V.N. Cancer bioimprinting and cell shape recognition for diagnosis and targeted treatment. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 5110–5127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, S.A. An Overview of Bio-Inspired Intelligent Imprinted Polymers for Virus Determination. Biosensors 2021, 11, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krstulja, A.; Lettieri, S.; Hall, A.J.; Roy, V.; Favetta, P.; Agrofoglio, L.A. Tailor-Made Molecularly Imprinted Polymer for Selective Recognition of the Urinary Tumor Marker Pseudouridine. Macromol. Biosci. 2017, 17, 1700250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodoki, A.E.; Iacob, B.C.; Bodoki, E. Perspectives of Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Drug Delivery Systems in Cancer Therapy. Polymers 2019, 11, 2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodoki, A.E.; Iacob, B.C.; Dinte, E.; Vostinaru, O.; Samoila, O.; Bodoki, E. Perspectives of Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Drug Delivery Systems in Ocular Therapy. Polymers 2021, 13, 3649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kioomars, S.; Heidari, S.; Malaekeh-Nikouei, B.; Rad, M.S.; Khameneh, B.; Mohajeri, S.A. Ciprofloxacin-imprinted hydrogels for drug sustained release in aqueous media. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2017, 22, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jantarat, C.; Attakitmongkol, K.; Nichsapa, S.; Sirathanarun, P.; Srivaro, S. Molecularly imprinted bacterial cellulose for sustained-release delivery of quercetin. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2020, 31, 1961–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.Z.; Chen, S.; Chen, J.L.; Ding, H.L.; Deng, D.W.; Xie, Z.Y. Self-Reporting Colorimetric Analysis of Drug Release by Molecular Imprinted Structural Color Contact Lens. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 34611–34617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neamtu, I.; Rusu, A.G.; Diaconu, A.; Nita, L.E.; Chiriac, A.P. Basic concepts and recent advances in nanogels as carriers for medical applications. Drug Deliv. 2017, 24, 539–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masumoto, S.; Nakamura, Y.; Haginaka, J. Molecularly imprinted polymers for arbutin and rutin by modified precipitation polymerization and their application for selective extraction of rutin in nutritional supplements. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 205, 114294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Ma, Q.; Wei, W.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, R.; Liu, X. Synthesis of Water-Dispersible Molecularly Imprinted Electroactive Nanoparticles for the Sensitive and Selective Paracetamol Detection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 21028–21038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Lu, W.; Meng, X. Using chiral magnetic surface molecularly imprinted polymers for chiral separation of Ofloxacin. J. Polym. Res. 2021, 28, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempe, H.; Kempe, M. Ouzo polymerization: A bottom-up green synthesis of polymer nanoparticles by free-radical polymerization of monomers spontaneously nucleated by the Ouzo effect; Application to molecular imprinting. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 616, 560–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffari-Bohlouli, P.; Zahedi, P.; Shahrousvand, M. Enhanced osteogenesis using poly (l-lactide-co-d, l-lactide)/poly (acrylic acid) nanofibrous scaffolds in presence of dexamethasone-loaded molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 165, 2363–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, J.; Wang, H.; Huang, C.; Bo, C.; Gong, B.; Ou, J. Progress of molecular imprinting technique for enantioseparation of chiral drugs in recent ten years. J. Chromatogr. A 2022, 1668, 462914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Jia, L. Research progress of molecularly imprinted polymers in separation of chiral drugs by capillary electrochromatography. Chin. J. Chromatogr. 2020, 38, 1046–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, A.K.; Gee, M.E.; Brown, J.N. Efficacy and safety of levetiracetam for migraine prophylaxis: A systematic review. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2018, 43, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi, E.; Farahzadi, R.; Javanmardi, S.; Vietor, I. L-carnitine extends the telomere length of the cardiac differentiated CD117+-expressing stem cells. Tissue Cell 2020, 67, 101429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, G.; Bhakta, S.; Mishra, P. Surface Molecularly Imprinted Biomimetic Magnetic Nanoparticles for Enantioseparation. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 6747–6756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Hoshino, Y.; Rodriguez, A.; Yoo, H.; Shea, K.J. Synthetic Polymer Nanoparticles with Antibody-like Affinity for a Hydrophilic Peptide. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cenci, L.; Tatti, R.; Tognato, R.; Ambrosi, E.; Piotto, C.; Bossi, A.M. Synthesis and characterization of peptide-imprinted nanogels of controllable size and affinity. Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 109, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yang, K.; Deng, N.; Min, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y. Thermoresponsive Epitope Surface-Imprinted Nanoparticles for Specific Capture and Release of Target Protein from Human Plasma. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 5747–5751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira, S.P.B.; Domingues, R.M.A.; Babo, P.S.; Berdecka, D.; Miranda, M.S.; Gomes, M.E.; Peppas, N.A.; Reis, R.L. Epitope-Imprinted Nanoparticles as Transforming Growth Factor-β3 Sequestering Ligands to Modulate Stem Cell Fate. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 31, 2003934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldara, M.; Lowdon, J.W.; Rogosic, R.; Arreguin-Campos, R.; Jimenez-Monroy, K.L.; Heidt, B.; Tschulik, K.; Cleij, T.J.; Dilien, H.; Eersels, K.; et al. Thermal Detection of Glucose in Urine Using a Molecularly Imprinted Polymer as a Recognition Element. ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 4515–4525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Guan, L.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Pan, J.; Peng, Y.; Pan, G. Sialic acid-imprinted mesoporous nanocarriers for tumor cell targeted drug delivery. Colloid Interface Sci. Commun. 2021, 42, 100421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Jiang, L.; Zhou, J.; Hu, L.; Feng, S. Epitope-imprinted mesoporous silica nanoparticles for specific recognition of tyrosine phosphorylation. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 9927–9930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabi, M.; Ostovan, A.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Choo, J.; Chen, L. Molecular imprinting: Green perspectives and strategies. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2100543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Zhang, N.; Xu, Y.; Li, Z.; Yan, C.; Mei, K.; Ding, M.; Ding, S.; Guan, P.; Qian, L. Molecularly imprinted materials for selective biological recognition. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2019, 40, 1900096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumano, O.; Akatsuchi, K.; Amiral, J. Updates on Anticoagulation and Laboratory Tools for Therapy Monitoring of Heparin, Vitamin K Antagonists and Direct Oral Anticoagulants. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawano, Y.; Patrulea, V.; Sublet, E.; Borchard, G.; Iyoda, T.; Kageyama, R.; Morita, A.; Seino, S.; Yoshida, H.; Jordan, O.; et al. Wound Healing Promotion by Hyaluronic Acid: Effect of Molecular Weight on Gene Expression and In Vivo Wound Closure. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Row, K.H. Magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers for recognition and enrichment of polysaccharides from seaweed. J. Sep. Sci. 2017, 40, 4765–4772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barclay, T.G.; Day, C.M.; Petrovsky, N.; Garg, S. Review of polysaccharide particle-based functional drug delivery. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 221, 94–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, J. Molecular Imprinting with Functional DNA. Small 2019, 15, e1805246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piletskiy, S.; Kukhar, V.; Fedoryak, D. Preparation of polymeric adsorbents selective for nucleic acid components. Ukr. Khim. Zh. 1989, 55, 872–875. [Google Scholar]
- Nawaz, N.; Abu Bakar, N.K.; Mahmud, H.N.M.E.; Jamaludin, N.S. Molecularly imprinted polymers-based DNA biosensors. Anal. Biochem. 2021, 630, 114328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slinchenko, O.; Rachkov, A.; Miyachi, H.; Ogiso, M.; Minoura, N. Imprinted polymer layer for recognizing double-stranded DNA. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2004, 20, 1091–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahmbhatt, H.; Poma, A.; Pendergraff, H.M.; Watts, J.K.; Turner, N.W. Improvement of DNA recognition through molecular imprinting: Hybrid oligomer imprinted polymeric nanoparticles (oligoMIP NPs). Biomater. Sci. 2016, 4, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjertén, S.; Liao, J.L.; Nakazato, K.; Wang, Y.; Zamaratskaia, G.; Zhang, H.X. Gels mimicking antibodies in their selective recognition of proteins. Chromatographia 1997, 44, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glad, M.; Norrlöw, O.; Sellergren, B.; Siegbahn, N.; Mosbach, K. Use of silane monomers for molecular imprinting and enzyme entrapment in polysiloxane-coated porous silica. J. Chromatogr. A 1985, 347, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Tsai, W.B.; Garrison, M.D.; Ferrari, S.; Ratner, B.D. Template-imprinted nanostructured surfaces for protein recognition. Nature 1999, 398, 593–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Tu, T.; Yang, M.; Xu, C. Efficient preparation of surface imprinted magnetic nanoparticles using poly (2-anilinoethanol) as imprinting coating for the selective recognition of glycoprotein. Talanta 2018, 184, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoghi, E.; Mirahmadi-Zare, S.Z.; Ghasemi, R.; Asghari, M.; Poorebrahim, M.; Nasr-Esfahani, M.-H. Nanosized aptameric cavities imprinted on the surface of magnetic nanoparticles for high-throughput protein recognition. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Han, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Li, Y.; Lu, J.; Chen, J.; Ou, L.; Fu, G. Facile modification of protein-imprinted polydopamine coatings over nanoparticles with enhanced binding selectivity. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 385, 123463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Sun, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Qiu, F.; Fu, G. Controlled synthesis of PEGylated surface protein-imprinted nanoparticles. Analyst 2019, 144, 5439–5448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Li, S.; Liu, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, W.; Pei, J.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y. Epitope Imprinting Technology: Progress, Applications, and Perspectives toward Artificial Antibodies. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, e1902048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Bi, Q.Y.; Long, Y.Y.; Li, Z.X.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Li, C. Inducible epitope imprinting: ‘generating’ the required binding site in membrane receptors for targeted drug delivery. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 5394–5397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachkov, A.; Minoura, N. Towards molecularly imprinted polymers selective to peptides and proteins. The epitope approach. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2001, 1544, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mier, A.; Maffucci, I.; Merlier, F.; Prost, E.; Montagna, V.; Ruiz-Esparza, G.U.; Bonventre, J.V.; Dhal, P.K.; Bui, B.T.S.; Sakhaii, P.; et al. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Nanogels for Protein Recognition: Direct Proof of Specific Binding Sites by Solution STD and WaterLOGSY NMR Spectroscopies. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 20849–20857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.H.; Jan, J.S.; Thomas, J.L.; Shih, Y.P.; Li, J.A.; Lin, C.Y.; Ooya, T.; Barna, L.; Mészáros, M.; Harazin, A. Cellular Therapy Using Epitope-Imprinted Composite Nanoparticles to Remove α-Synuclein from an In Vitro Model. Cells 2022, 11, 2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayakawa, N.; Kitayama, Y.; Igarashi, K.; Matsumoto, Y.; Takano, E.; Sunayama, H.; Takeuchi, T. Fc Domain-Imprinted Stealth Nanogels Capable of Orientational Control of Immunoglobulin G Adsorbed In Vivo. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 16074–16081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowen, T.; Stefanucci, E.; Piletska, E.; Marrazza, G.; Canfarotta, F.; Piletsky, S.A. Synthetic mechanism of molecular imprinting at the solid phase. Macromolecules 2020, 53, 1435–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canfarotta, F.; Poma, A.; Guerreiro, A.; Piletsky, S. Solid-phase synthesis of molecularly imprinted nanoparticles. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 443–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poma, A.; Guerreiro, A.; Whitcombe, M.J.; Piletska, E.V.; Turner, A.P.; Piletsky, S.A. Solid-Phase Synthesis of Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Nanoparticles with a Reusable Template—“Plastic Antibodies”. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 2821–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Ambrosini, S.; Tamahkar, E.; Rossi, C.; Haupt, K.; Bui, B.T.S. Toward a Universal Method for Preparing Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Nanoparticles with Antibody-like Affinity for Proteins. Biomacromolecules 2016, 17, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahajan, R.; Rouhi, M.; Shinde, S.; Bedwell, T.; Incel, A.; Mavliutova, L.; Piletsky, S.; Nicholls, I.A.; Sellergren, B. Highly efficient synthesis and assay of protein-imprinted nanogels by using magnetic templates. Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 737–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aherne, A.; Alexander, C.; Payne, M.; Perez, N.; Vulfson, E.N. Bacteria-mediated lithography of polymer surfaces. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 8771–8772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickert, F.L.; Hayden, O. Bioimprinting of Polymers and Sol-Gel Phases. Selective Detection of Yeasts with Imprinted Polymers. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 1302–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piletsky, S.; Canfarotta, F.; Poma, A.; Bossi, A.M.; Piletsky, S. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Cell Recognition. Trends Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 368–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.; Xu, S.; Guo, Z.; Zhao, M.; Liu, Z. Redox-Responsive Molecularly Imprinted Nanoparticles for Targeted Intracellular Delivery of Protein toward Cancer Therapy. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 18214–18225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piletsky, S.S.; Rabinowicz, S.; Yang, Z.; Zagar, C.; Piletska, E.V.; Guerreiro, A.; Piletsky, S.A. Development of molecularly imprinted polymers specific for blood antigens for application in antibody-free blood typing. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 1793–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.Y.; Cao, P.P.; He, Z.Y.; He, X.W.; Li, W.Y.; Li, Y.H.; Zhang, Y.K. Targeted imaging and targeted therapy of breast cancer cells via fluorescent double template-imprinted polymer coated silicon nanoparticles by an epitope approach. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 17018–17030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idil, N.; Bakhshpour, M.; Perçin, I.; Mattiasson, B.; Denizli, A. Molecular Imprinting-Based Sensing Platforms for Recognition of Microorganisms. In Molecular Imprinting for Nanosensors and Other Sensing Applications; Denizli, A., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 255–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, X.; Lu, W.; Wu, X.; Li, J. Molecular imprinting: Perspectives and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 2137–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morsi, S.M.; Abd El-Aziz, M.E.; Mohamed, H.A. Smart polymers as molecular imprinted polymers for recognition of target molecules. Int. J. Polym. Mater. 2022, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Z.; Yu, P.; Dong, Y.; Lu, Y.; Tan, Z.; Yu, X.; Zhao, R.; Yan, Y. Thermo-Responsive Molecularly Imprinted Hydrogels for Selective Adsorption and Controlled Release of Phenol From Aqueous Solution. Front. Chem. 2019, 6, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Jiang, Z.; Ma, R.; Yang, L.; Li, Q.; Tan, L.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Q. Magnetic temperature-sensitive molecularly imprinted materials for separation and enrichment of single component of formononetin in medicinal plants. CIESC J. 2020, 71, 4711–4719. [Google Scholar]
- Jayaramudu, T.; Ko, H.-U.; Kim, H.C.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, J. Swelling behavior of polyacrylamide-cellulose nanocrystal hydrogels: Swelling kinetics, temperature, and pH effects. Materials 2019, 12, 2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tingji, D.; Ruihe, W.; Jiafang, X.; Jiayue, M.; Xiaohui, W.; Jiawen, X.; Xiaolong, Y. Synthesis and application of a temperature sensitive poly(N-vinylcaprolactam-co-N, N-diethyl acrylamide) for low-temperature rheology control of water-based drilling fluid. Colloids Surf. A 2022, 644, 128855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelton, R.H.; Chibante, P. Preparation of aqueous latices with N-isopropylacrylamide. Colloids Surf. 1986, 20, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.; Akahoshi, T.; Tabata, Y.; Nakayama, D. Molecular Specific Swelling Change of Hydrogels in Accordance with the Concentration of Guest Molecules. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 5577–5578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, M.; Guo, X.; Zhang, H. Efficient synthesis of narrowly dispersed molecularly imprinted polymer microspheres with multiple stimuli-responsive template binding properties in aqueous media. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 6217–6219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, T.; Lv, Y.; Qin, P.; Li, H.; Li, J.-p.; Tan, T. Selective binding of heparin oligosaccharides in a magnetic thermoresponsive molecularly imprinted polymer. Talanta 2019, 201, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javanbakht, S.; Saboury, A.; Shaabani, A.; Mohammadi, R.; Ghorbani, M. Doxorubicin imprinted photoluminescent polymer as a pH-responsive nanocarrier. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 4168–4178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikravan, G.; Haddadi-Asl, V.; Salami-Kalajahi, M. Stimuli-responsive DOX release behavior of cross-linked poly(acrylic acid) nanoparticles. e-Polymers 2019, 19, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saroj, S.; Rajput, S.J. Tailor-made pH-sensitive polyacrylic acid functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles for efficient and controlled delivery of anti-cancer drug Etoposide. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2018, 44, 1198–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.B.; Yuan, S.; Cai, X.; Xiang, G.; Zhang, Y.X.; Pehkonen, S.; Liu, X.Y. Magnetic nickel chrysotile nanotubes tethered with pH-sensitive poly(methacrylic acid) brushes for Cu (II) adsorption. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 276, 611–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.T.; Feng, Y.S.; Ma, Y.J.; He, X.W.; Li, W.Y.; Zhang, Y.K. Tumor-sensitive biodegradable nanoparticles of molecularly imprinted polymer-stabilized fluorescent zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 for targeted imaging and drug delivery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 24585–24598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, R.; Wang, S.; Bie, Z.; He, H.; Liu, Z. Preparation of molecularly imprinted polymers specific to glycoproteins, glycans and monosaccharides via boronate affinity controllable–oriented surface imprinting. Nat. Protoc. 2017, 12, 964–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Zhong, G.; Cai, C.; Chen, C.; Chen, X. Rapid and efficient separation of glycoprotein using pH double-responsive imprinted magnetic microsphere. Talanta 2017, 169, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhang, L.; Sun, Y.; Yu, H.; Fu, M. pH-Responsive molecularly imprinted hollow spheres for selective separation of ribavirin from water samples. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 450, 138064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Meng, J.; Wang, S. Photo-responsive polymer materials for biological applications. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2017, 28, 2085–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.B.; Zhang, S.; Qi, J.; Liang, X.J.; Yoon, J. Advances in application of azobenzene as a trigger in biomedicine: Molecular design and spontaneous assembly. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2007290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahoo, D.; Benny, R.; Ks, N.K.; De, S. Stimuli-Responsive Chiroptical Switching. ChemPlusChem 2022, 87, e202100322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Zhang, Z.T.; Young, D.J.; Chai, L.L.; Wu, Q.; Li, H.X. Visible-light mediated cross-coupling of aryl halides with sodium sulfinates via carbonyl-photoredox/nickel dual catalysis. Org. Chem. Front. 2022, 9, 1437–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.T.; Chen, M.J.; Yang, H.L.; Huang, Z.J.; Tang, Q.; Chow, C.F.; Gong, C.B.; Zu, M.H.; Xiao, B. An NIR-light-responsive surface molecularly imprinted polymer for photoregulated drug release in aqueous solution through porcine tissue. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 106, 110253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaei, H.S.; Tehrani, M.S.; Husain, S.W.; Panahi, H.A.; Mehramizi, A. Photo-regulated ultraselective extraction of Azatioprine using a novel photoresponsive molecularly imprinted polymer conjugated hyperbranched polymers based magnetic nano-particles. Polymer 2018, 148, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitayama, Y.; Isomura, M. Gas-stimuli-responsive molecularly imprinted polymer particles with switchable affinity for target protein. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 2538–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yang, J.; He, S.; Gong, H.; Chen, C.; Cai, C. A mild and safe gas-responsive molecularly imprinted sensor for highly specific recognition of hepatitis B virus. Sens. Actuators B 2022, 366, 131990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Wan, J.; Zhou, L.; Ma, W.; Yang, Y.; Luo, W.; Yu, Z.; Wang, H. Stimuli-responsive nanotherapeutics for precision drug delivery and cancer therapy. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2019, 11, e1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, P.F.; Travanut, A.; Conte, C.; Alexander, C. Reduction-responsive polymers for drug delivery in cancer therapy—Is there anything new to discover? Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 13, e1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Simon, C.; Attieh, M.D.; Haupt, K.; Falcimaigne-Cordin, A. Reduction-responsive molecularly imprinted nanogels for drug delivery applications. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 5978–5987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, S.; Lyu, Z.; Niu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, D.; Falahati, M.; Du, D.; Lin, Y. Integrating ionic liquids with molecular imprinting technology for biorecognition and biosensing: A review. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 149, 111830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; He, Z.; Xu, Y.; Su, Y.; Ding, L.; Li, Y. Fabrication of molecularly imprinted polymers with tunable adsorption capability based on solvent-responsive cross-linker. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 405, 126608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolla, M.; Cenci, L.; Anesi, A.; Ambrosi, E.; Tagliaro, F.; Vanzetti, L.; Guella, G.; Bossi, A.M. Solvent-Responsive Molecularly Imprinted Nanogels for Targeted Protein Analysis in MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 6908–6915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Guan, X.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H. A pH/glutathione double responsive drug delivery system using molecular imprint technique for drug loading. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 389, 1208–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Chen, J.; Lee, M.; Lin, B.; Wang, J. Multi-Responsive Ibuprofen-Imprinted Core–Shell Nanocarriers for Specific Drug Recognition and Controlled Release. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 3, 1147–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Hu, Q.; Ke, R.; Zhen, X.; Bu, Y.; Wang, S. Facile preparation of photonic and magnetic dual responsive protein imprinted nanomaterial for specific recognition of bovine hemoglobin. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 371, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.P.; Yu, J.X.; Yang, X.M.; Zhang, X.H.; Yuan, T.T.; Peng, H.L. Preparation, characterization, and application of multiple stimuli-responsive rattle-type magnetic hollow molecular imprinted poly (ionic liquids) nanospheres (Fe3O4@void@PILMIP) for specific recognition of protein. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 337, 722–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Song, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhao, L.; Sun, R. Dual responsive molecularly imprinted polymers based on UiO-66-DOX for selective targeting tumor cells and controlled drug release. Eur. Polym. J. 2022, 171, 111219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Ma, Y.; Niu, H.; Zhang, H. Hydrophilic hollow molecularly imprinted polymer microparticles with photo- and thermoresponsive template binding and release properties in aqueous media. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 27340–27350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.; Ma, Y.; Hou, C.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Q. Preparation of pH and temperature dual-sensitive molecularly imprinted polymers based on chitosan and N-isopropylacrylamide for recognition of bovine serum albumin. Polym. Int. 2019, 68, 955–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Hao, Y.; Tian, X.; Liang, Y.; He, X.; Gao, R.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y. Multi-stimuli responsive molecularly imprinted nanoparticles with tailorable affinity for modulated specific recognition of human serum albumin. J. Mater. Chem. B 2022, 10, 6634–6643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Wang, L.; Liu, Z. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Nanoparticles: An Emerging Versatile Platform for Cancer Therapy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 3858–3869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bui, B.T.S.; Haupt, K. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Hydrogel Nanoparticles: Synthetic Antibodies for Cancer Diagnosis and Therapy. Chembiochem 2022, 23, e202100598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.Q.; Dasgupta, P.; Baade, P. Quantifying the absolute number of cancer deaths that would be avoided if cancers were diagnosed prior to progressing to distant metastasis, New South Wales, Australia 1985–2014. Int. J. Cancer 2022, 150, 1760–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Li, Y.; Gao, S.; Lv, Y. Selective recognition of tumor cells by molecularly imprinted polymers. J. Sep. Sci. 2021, 44, 2483–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, P.; Zhang, H.; Huo, J.; Lin, X. An electrochemical sensor based on iron (II, III)@ graphene oxide@ molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles for interleukin-8 detection in saliva. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 7784–7791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Tang, X.; Zhao, L. Molecularly imprinted polymers-based novel optical biosensor for the detection of cancer marker lysozyme. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2022, 334, 113324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousazadeh, M.; Jahangiri-Manesh, A.; Nikkhah, M.; Abbasian, S.; Moshaii, A.; Masroor, M.J.; Norouzi, P. Detection of hexanal gas as a volatile organic compound cancer biomarker using a nanocomposite of gold nanoparticles and selective polymers. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2022, 905, 115962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushwaha, A.; Srivastava, J.; Singh, A.K.; Anand, R.; Raghuwanshi, R.; Rai, T.; Singh, M. Epitope imprinting of Mycobacterium leprae bacteria via molecularly imprinted nanoparticles using multiple monomers approach. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 145, 111698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Fan, T.; Xie, Z.; Zeng, Q.; Xue, P.; Zheng, T.; Chen, Y.; Luo, X.; Zhang, H. Advances in nanomaterials for photodynamic therapy applications: Status and challenges. Biomaterials 2020, 237, 119827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, L.; Yang, J.; Liang, K.; Chen, C.; Chen, X.; Cai, C. Fast and sensitive detection of Japanese encephalitis virus based on a magnetic molecular imprinted polymer–resonance light scattering sensor. Talanta 2019, 202, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Shen, T.; Hu, L.; Gong, H.; Chen, C.; Chen, X.; Cai, C. Development of a thermosensitive molecularly imprinted polymer resonance light scattering sensor for rapid and highly selective detection of hepatitis A virus in vitro. Sens. Actuators B 2017, 253, 1188–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Zhang, F.; Chen, C.; Cai, C. Molecular imprinting resonance light scattering nanoprobes based on pH-responsive metal-organic framework for determination of hepatitis A virus. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Liang, K.; Tang, L.; Gong, H.; Chen, C.; Cai, C. Photonic and Magnetic Dual-Responsive Molecularly Imprinted Sensor for Highly Specific Recognition of Enterovirus 71. ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 3715–3723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinde, S.; El-Schich, Z.; Malakpour, A.; Wan, W.; Dizeyi, N.; Mohammadi, R.; Rurack, K.; Wingren, A.G.; Sellergren, B. Sialic Acid-Imprinted Fluorescent Core—Shell Particles for Selective Labeling of Cell Surface Glycans. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 13908–13912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaneckova, T.; Bezdekova, J.; Han, G.; Adam, V.; Vaculovicova, M. Application of molecularly imprinted polymers as artificial receptors for imaging. Acta Biomater. 2020, 101, 444–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagiotopoulou, M.; Salinas, Y.; Beyazit, S.; Kunath, S.; Duma, L.; Prost, E.; Mayes, A.G.; Resmini, M.; Bui, B.T.S.; Haupt, K. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Coated Quantum Dots for Multiplexed Cell Targeting and Imaging. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 8244–8248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Deng, Z.; Bu, J.; Liu, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhong, S. Quantum dot based molecularly imprinted polymer test strips for fluorescence detection of ferritin. Sens. Actuators B 2022, 358, 131548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, L.L.; Song, X.J.; Niu, C.B.; Lv, Q.Y.; Li, C.L.; Cui, H.F.; Zhang, S.T. Red fluorescent nanoprobe based on Ag@Au nanoparticles and graphene quantum dots for H2O2 determination and living cell imaging. Microchim. Acta 2021, 188, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuerhong, M.; Yang, X.; Xue-Bo, Y. Review on carbon dots and their applications. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2017, 45, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yin, D.; Wang, W.; Shen, X.; Zhu, J.J.; Chen, H.Y.; Liu, Z. Targeting and imaging of cancer cells via monosaccharide-imprinted fluorescent nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beyer, S.; Kimani, M.; Zhang, Y.; Verhassel, A.; Sternbæk, L.; Wang, T.; Persson, J.L.; Härkönen, P.; Johansson, E.; Caraballo, R. Fluorescent Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Layers against Sialic Acid on Silica-Coated Polystyrene Cores—Assessment of the Binding Behavior to Cancer Cells. Cancers 2022, 14, 1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Cui, Q.; Wang, C.; Wang, X.; Yang, Y.; Li, L. Preparation of sialic acid-imprinted fluorescent conjugated nanoparticles and their application for targeted cancer cell imaging. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 3006–3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Li, S.; Jin, Y.; Qian, L.; Gao, N.; Yao, S.Q.; Huang, F.; Xu, Q.H.; Cao, Y. Red-emitting DPSB-based conjugated polymer nanoparticles with high two-photon brightness for cell membrane imaging. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 6754–6763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosserdt, M.; Erdőssy, J.; Lautner, G.; Witt, J.; Köhler, K.; Gajovic-Eichelmann, N.; Yarman, A.; Wittstock, G.; Scheller, F.W.; Gyurcsányi, R.E. Microelectrospotting as a new method for electrosynthesis of surface-imprinted polymer microarrays for protein recognition. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 73, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhammad, P.; Liu, J.; Xing, R.; Wen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z. Fast probing of glucose and fructose in plant tissues via plasmonic affinity sandwich assay with molecularly-imprinted extraction microprobes. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 995, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Tang, B.; Li, Y.; Liu, C.; Jiao, P.; Wei, Y. Molecularly Imprinted Magnetic Fluorescent Nanocomposite-Based Sensor for Selective Detection of Lysozyme. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, M.; Zhuo, K.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Bai, G.; Wang, J. Fluorescent probe based on carbon dots/silica/molecularly imprinted polymer for lysozyme detection and cell imaging. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 5799–5807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, B.; Lemberger, M.M.; Panagiotopoulou, M.; Rangel, P.X.M.; Timur, S.; Hirsch, T.; Bui, B.T.S.; Wegener, J.; Haupt, K. Tracking Hyaluronan: Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Coated Carbon Dots for Cancer Cell Targeting and Imaging. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 3305–3313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Ma, X.T.; He, X.W.; Li, W.Y.; Zhang, Y.K. Carbon dots-embedded epitope imprinted polymer for targeted fluorescence imaging of cervical cancer via recognition of epidermal growth factor receptor. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norell, M.C.; Andersson, H.S.; Nicholls, I.A. Theophylline molecularly imprinted polymer dissociation kinetics: A novel sustained release drug dosage mechanism. J. Mol. Recognit. 1998, 11, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canfarotta, F.; Lezina, L.; Guerreiro, A.; Czulak, J.; Petukhov, A.; Daks, A.; Smolinska-Kempisty, K.; Poma, A.; Piletsky, S.; Barlev, N.A. Specific Drug Delivery to Cancer Cells with Double-Imprinted Nanoparticles against Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor. Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 4641–4646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Z.; Dong, Y.; Xu, S.; Wang, L.; Liu, Z. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Smart Prodrug Delivery System for Specific Targeting, Prolonged Retention, and Tumor Microenvironment-Triggered Release. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 2663–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Deng, Z.; Bu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; He, Y.; Li, T.; Gao, P.; Yang, Y.; Zhong, S. Capsule-like molecular imprinted polymer nanoparticles for targeted and chemophotothermal synergistic cancer therapy. Colloids Surf. B 2021, 208, 112126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Li, W.; Gu, Z.; Xing, R.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Z. Inhibition of HER2-positive breast cancer growth by blocking the HER2 signaling pathway with HER2-glycan-imprinted nanoparticles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 10621–10625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Merlier, F.; Avalle, B.; Vieillard, V.; Debré, P.; Haupt, K.; Bui, B.T.S. Molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles as potential synthetic antibodies for immunoprotection against HIV. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 9824–9831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangel, P.X.M.; Moroni, E.; Merlier, F.; Gheber, L.A.; Vago, R.; Bui, B.T.S.; Haupt, K. Chemical Antibody Mimics Inhibit Cadherin-Mediated Cell–Cell Adhesion: A Promising Strategy for Cancer Therapy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 2816–2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangel, P.X.M.; Mier, A.; Moroni, E.; Merlier, F.; Gheber, L.A.; Vago, R.; Maffucci, I.; Bui, B.T.S.; Haupt, K. Molecularly imprinted polymer nanogels targeting the HAV motif in cadherins inhibit cell–cell adhesion and migration. J. Mater. Chem. B 2022, 10, 6688–6697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, Q.Y.; Low, S.C. Feasibility study on molecularly imprinted assays for biomedical diagnostics. Sens. Rev. 2019, 39, 862–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Schich, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Feith, M.; Beyer, S.; Sternbæk, L.; Ohlsson, L.; Stollenwerk, M.; Wingren, A.G. Molecularly imprinted polymers in biological applications. Biotechniques 2020, 69, 406–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


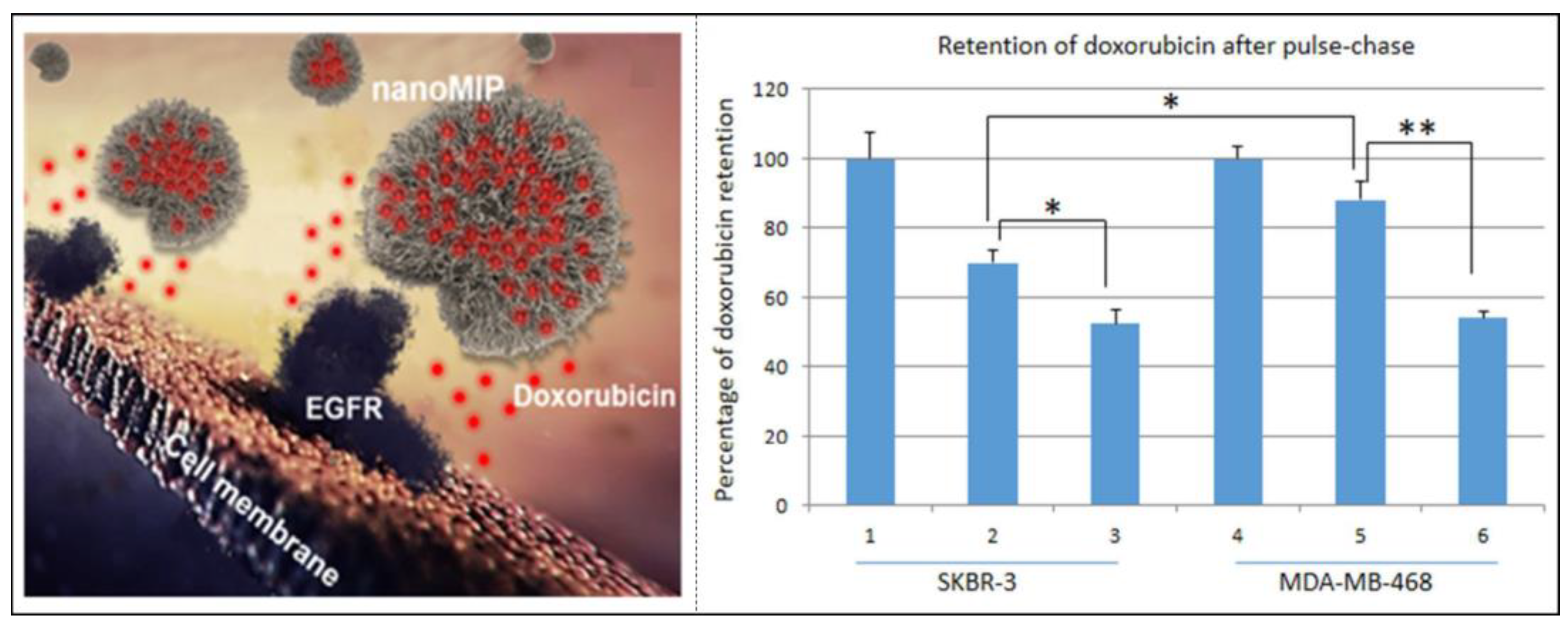
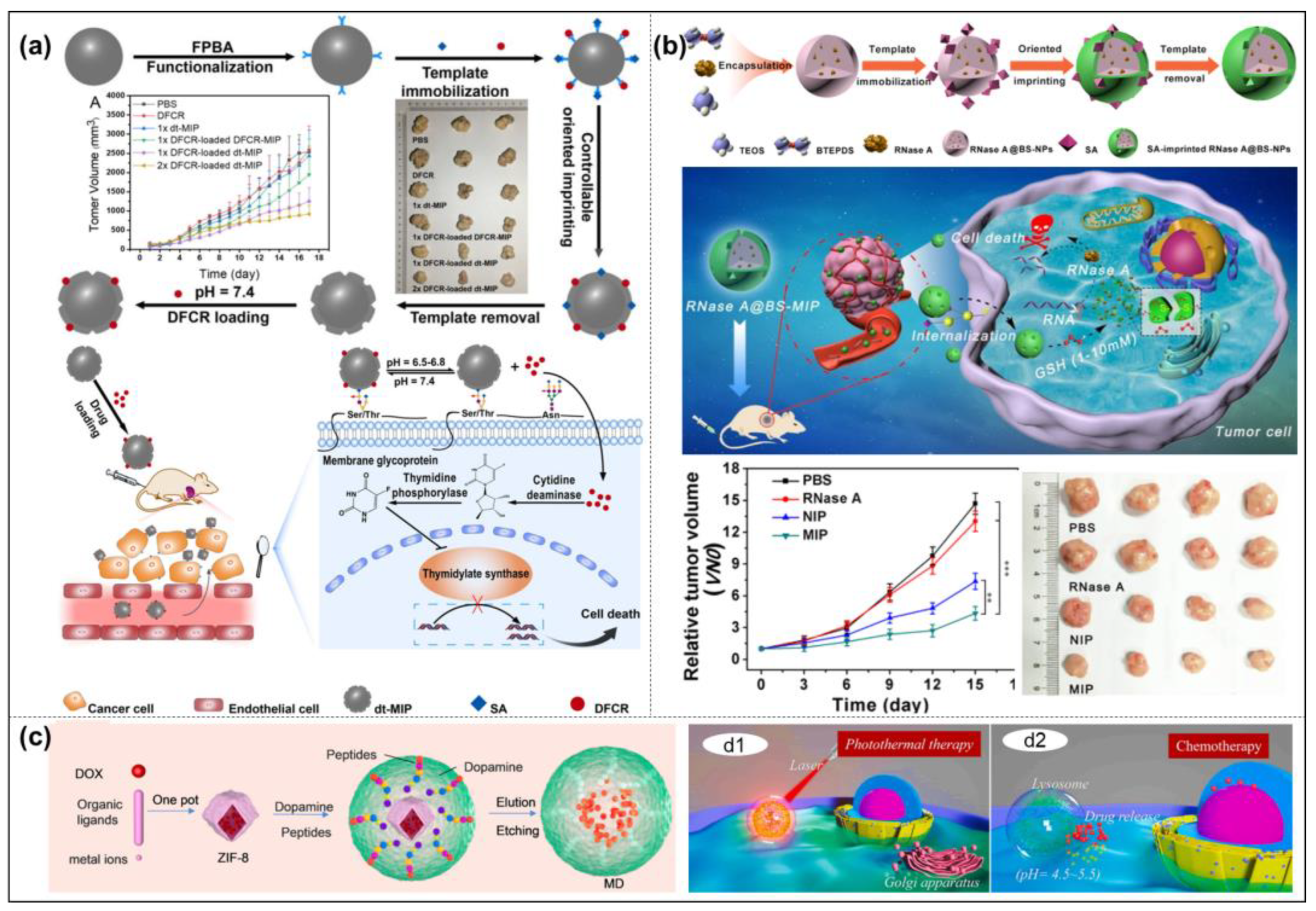
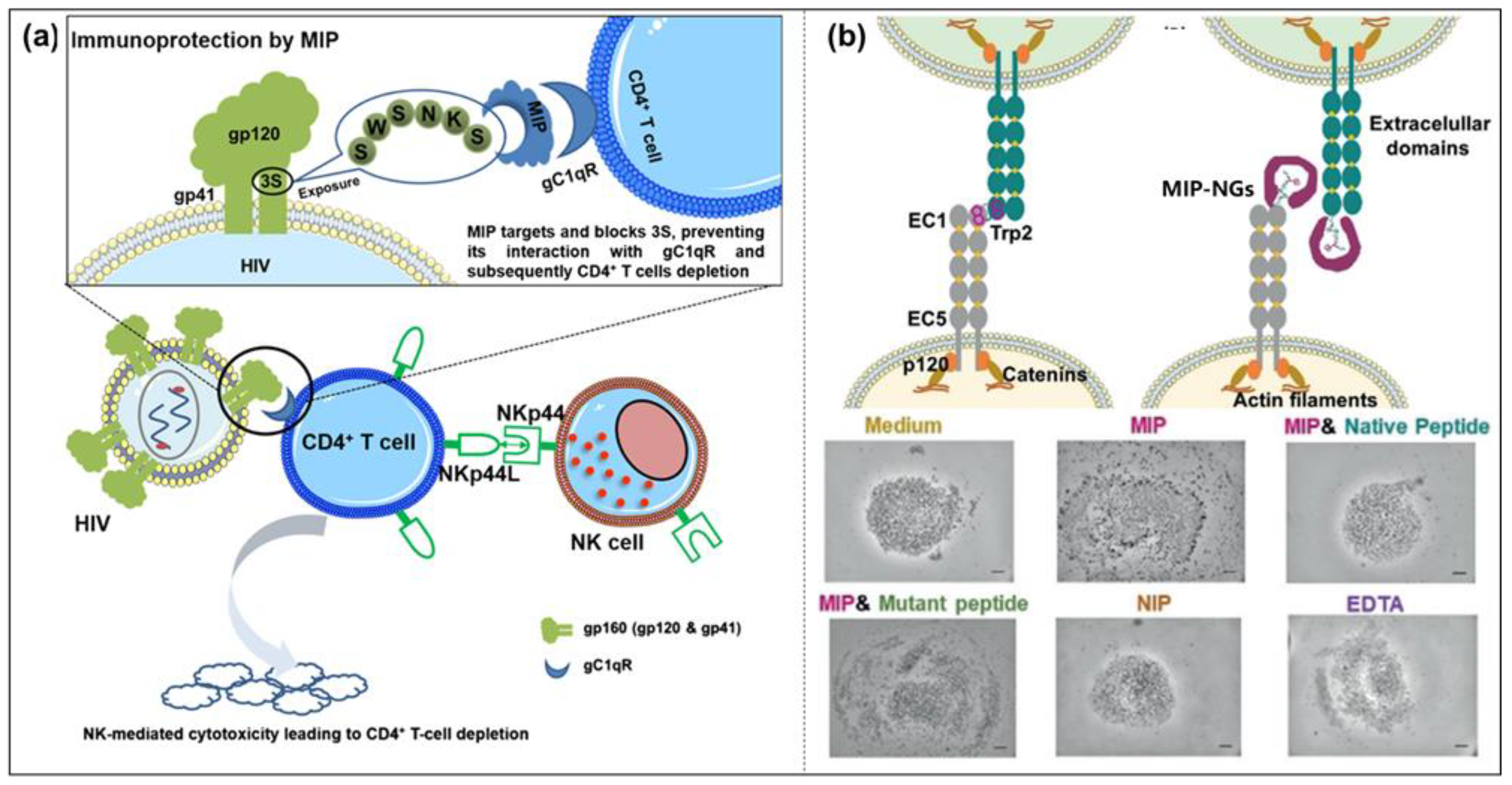
| The Template Molecules | References | Application | References | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Small Molecule Imprinting | Drug Molecules | paracetamol | [41,47,83,99,102,107,113,117,118,155,156,157] | separating and purifying target | [41,102,107] |
| (S)-naproxen | |||||
| doxorubicin | |||||
| ribavirin | drug delivery | [47,83,99,113,117,118,155,156,157] | |||
| S-propranolol | |||||
| ibuprofen | |||||
| Small Biomolecules | short peptide | [42,43,44,45,46,47,48,69,70,71,116] | identifying the target | [42,43,46,47] | |
| monosaccharide | recognizing proteins | [44,45,48,69,70,71,116] | |||
| Biomacromolecule Imprinting | Polysaccharide | heparin | [53,94] | separation of function | [53] |
| hyaluronic acid | |||||
| fucoidan | detection of function | [94] | |||
| Nucleic Acid | DNA or RNA | [58,59] | detection of genetic diseases | [58] | |
| identifying and detecting nucleic acid targets | [59] | ||||
| Protein | glycoproteins | [63,64,65,66,72,76,77,101,109,116,119,120,130] | separation and purification | [63,64,65,66,72,76,77,101,109,116,119,120,130] | |
| bovine hemoglobin | |||||
| lysozyme | |||||
| trypsin | |||||
| Cell Imprinting | Proteins and lipids on the surface of cell membranes | epidermal growth factor | [81,82,83,99,138,140,152,153,155,156,157,158,160,161] | identifying target cells | [81,82,160,161] |
| glycoprotein | biological imaging | [83,138,140,152,153] | |||
| Sugar structures on the surface of cell membranes | sialic acid | targeted cancer therapy | [83,99,155,156,157,158] | ||
| B-type blood trisaccharide | |||||
| Others | microorganisms | bacteria | [110,132,133,135,136,137,159] | microbial detection | [132] |
| fungi | |||||
| virus | HBV | virus detection | [110,133,135,136,137,159] | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, X.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, H.; Pan, G. Molecularly Imprinted Nanomaterials with Stimuli Responsiveness for Applications in Biomedicine. Molecules 2023, 28, 918. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28030918
Zhang Y, Wang Q, Zhao X, Ma Y, Zhang H, Pan G. Molecularly Imprinted Nanomaterials with Stimuli Responsiveness for Applications in Biomedicine. Molecules. 2023; 28(3):918. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28030918
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yan, Qinghe Wang, Xiao Zhao, Yue Ma, Hongbo Zhang, and Guoqing Pan. 2023. "Molecularly Imprinted Nanomaterials with Stimuli Responsiveness for Applications in Biomedicine" Molecules 28, no. 3: 918. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28030918
APA StyleZhang, Y., Wang, Q., Zhao, X., Ma, Y., Zhang, H., & Pan, G. (2023). Molecularly Imprinted Nanomaterials with Stimuli Responsiveness for Applications in Biomedicine. Molecules, 28(3), 918. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28030918








