Plantainoside D Reduces Depolarization-Evoked Glutamate Release from Rat Cerebral Cortical Synaptosomes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
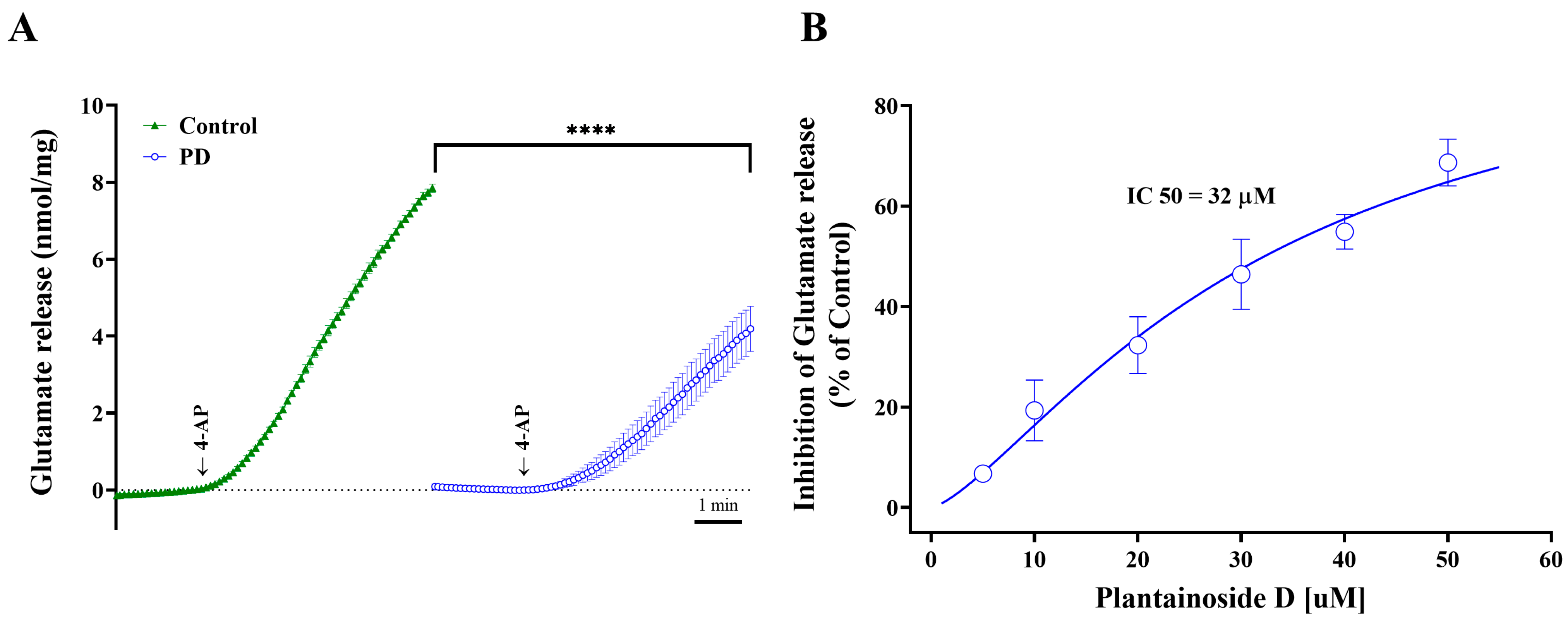
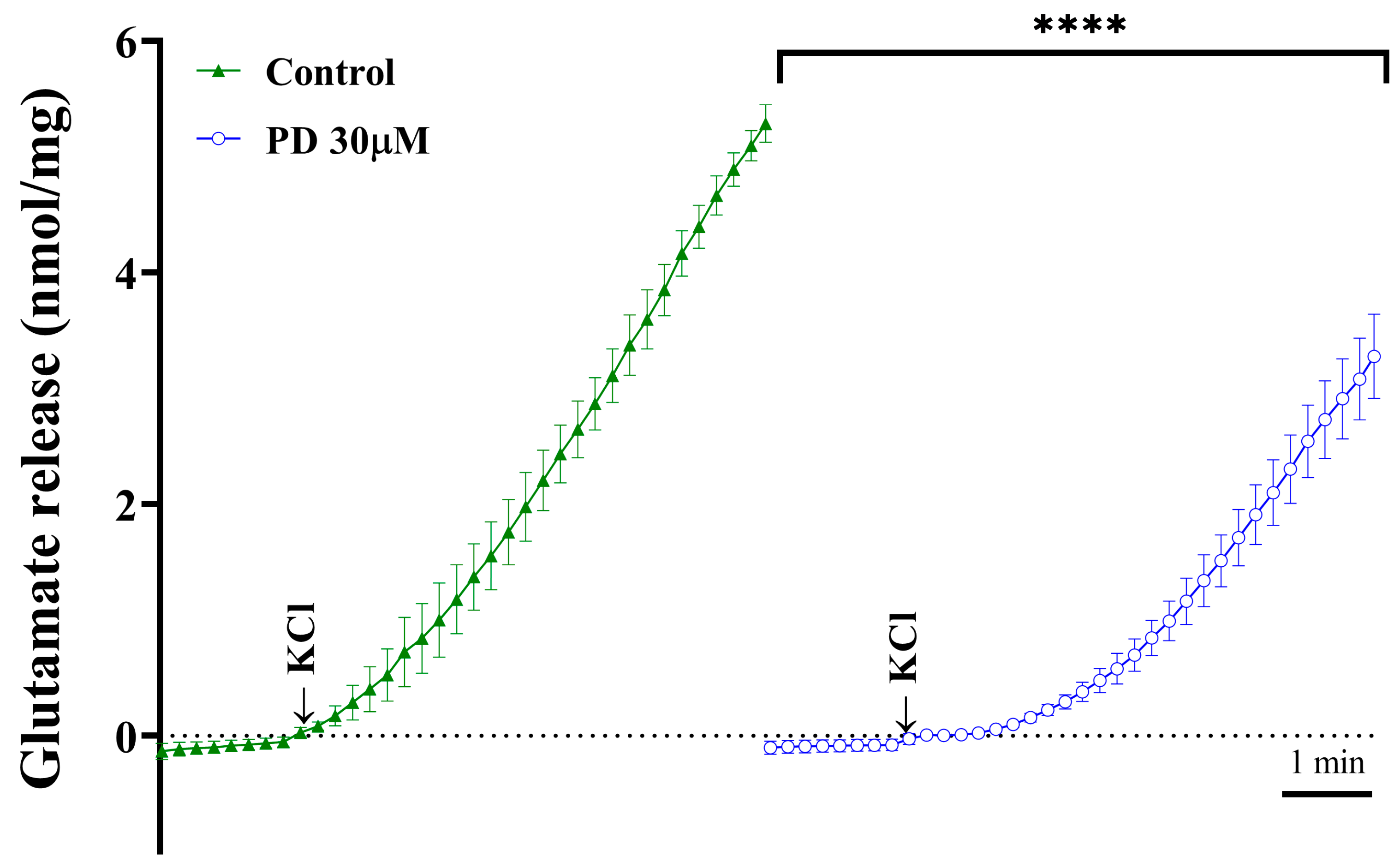
2.1. Inhibitory Effects of Plantainoside D on 4-AP-Induced Glutamate Release from Rat Cortical Synaptosomes
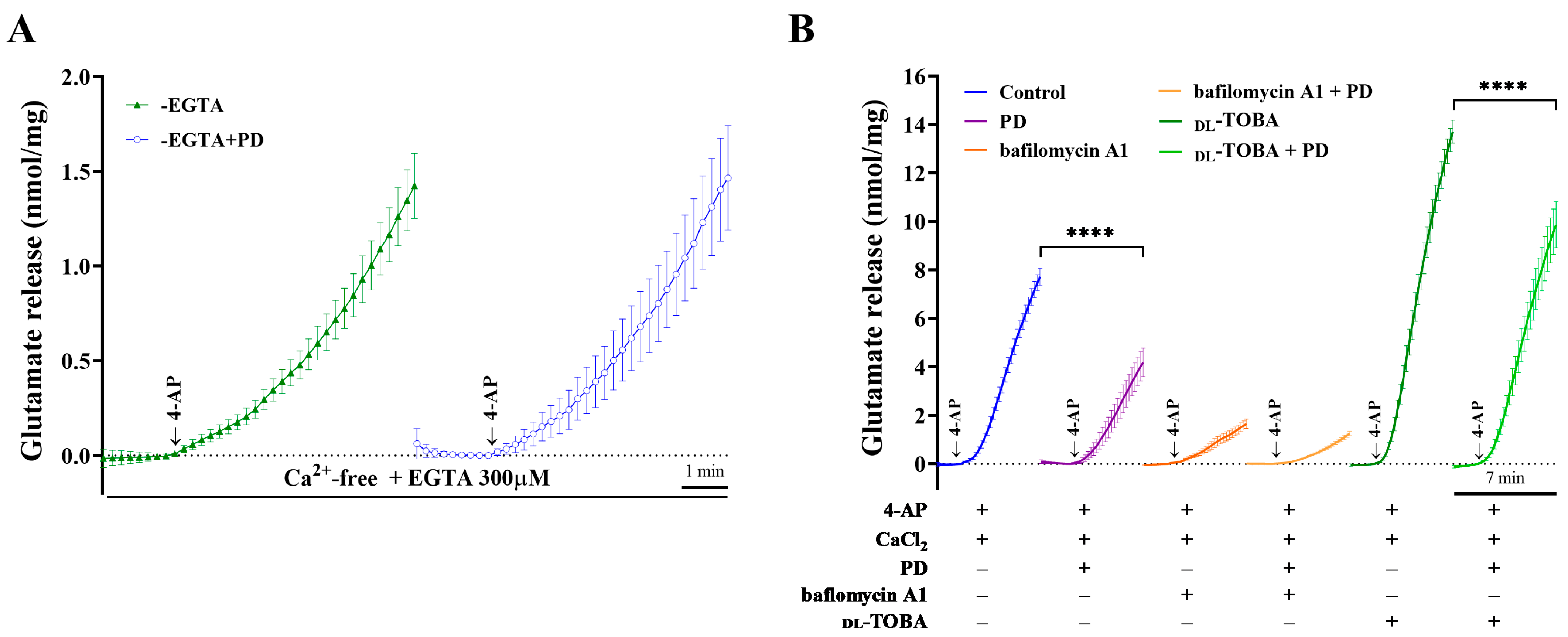
2.2. PD Inhibition of 4-AP-Induced Glutamate Release Is Mediated by an Exocytotic Mechanism
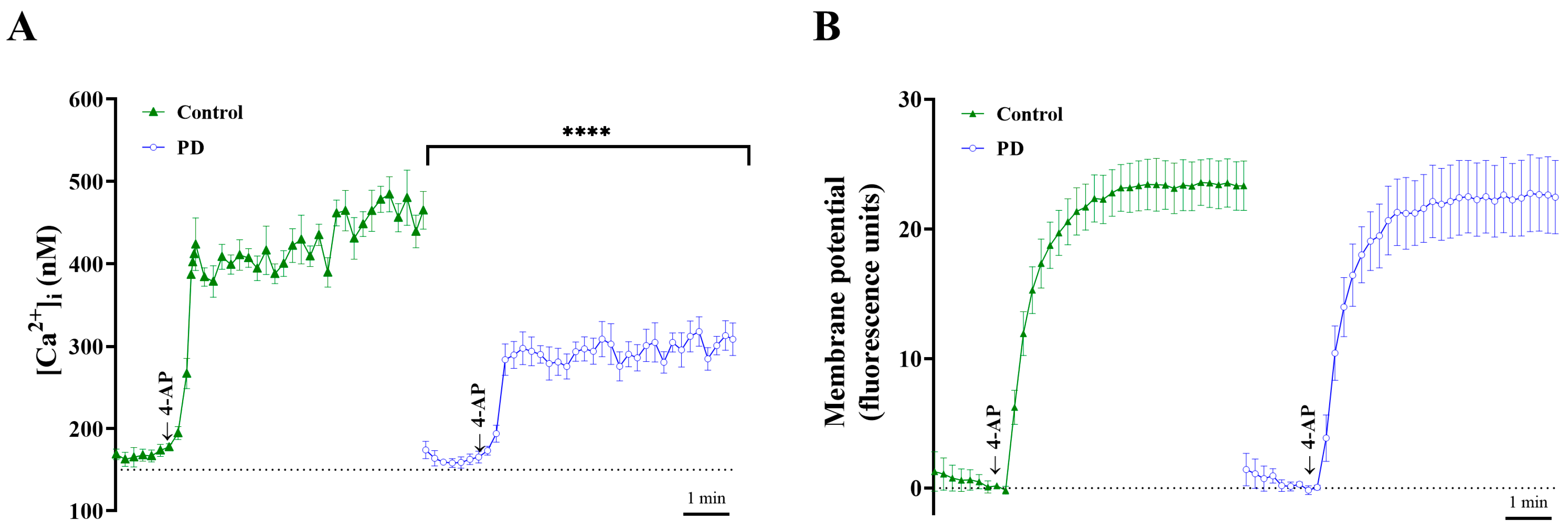
2.3. Effect of PD on Cytosolic [Ca2+] and Synaptosomal Membrane Potential
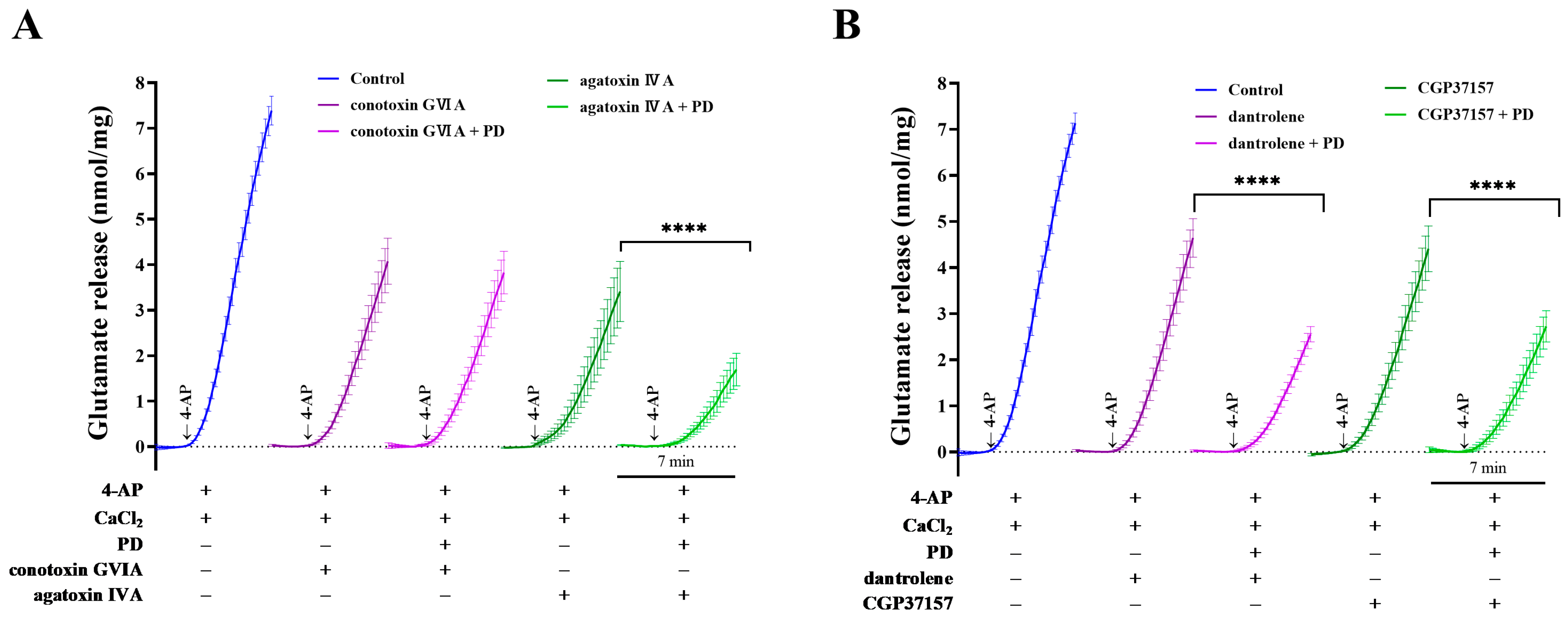
2.4. Effects of Ca2+-Channel Antagonists on PD-Mediated Inhibition of 4-AP-Induced Glutamate Release
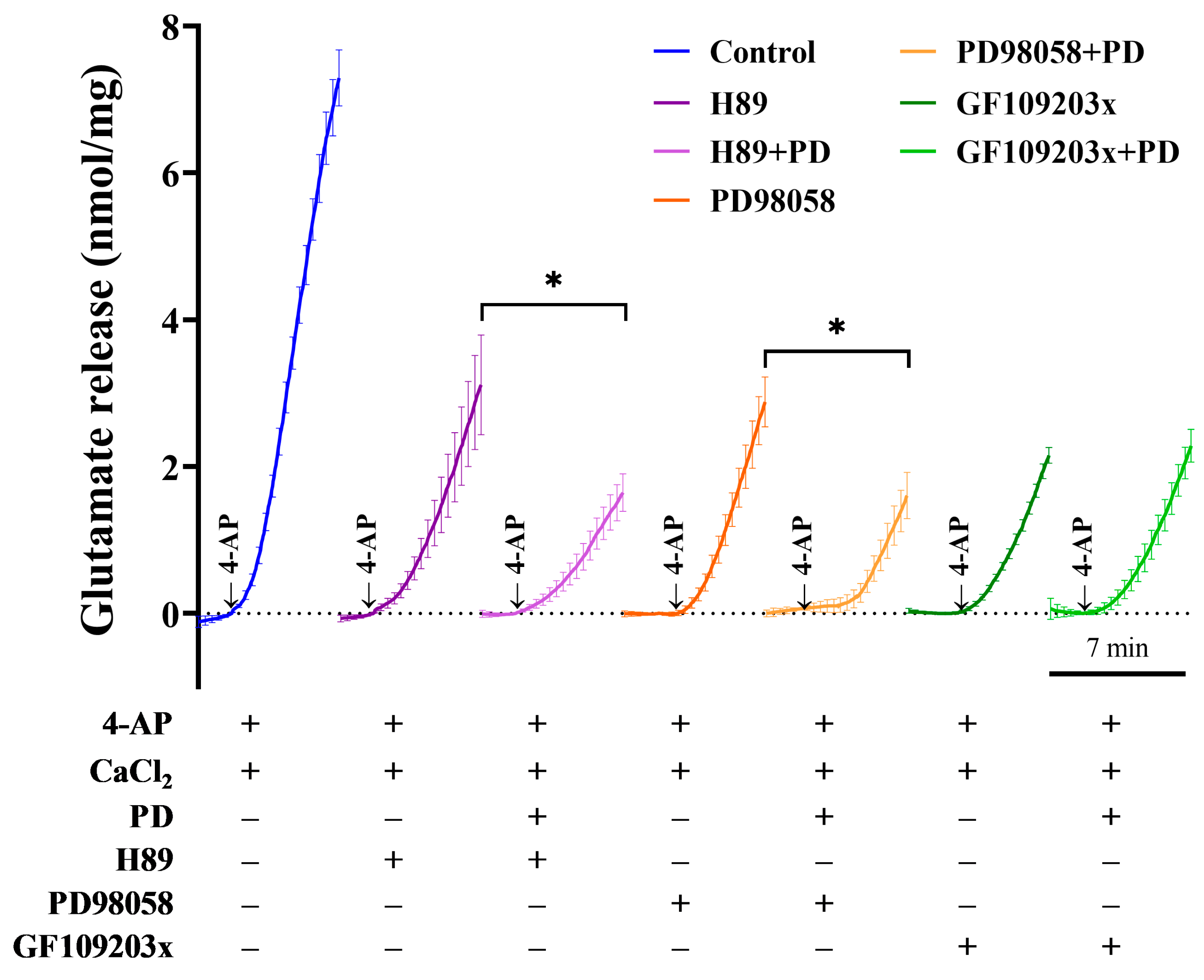
2.5. The Protein Kinase C (PKC) Pathway Is Responsible for the PD-Mediated Inhibition of Glutamate Release
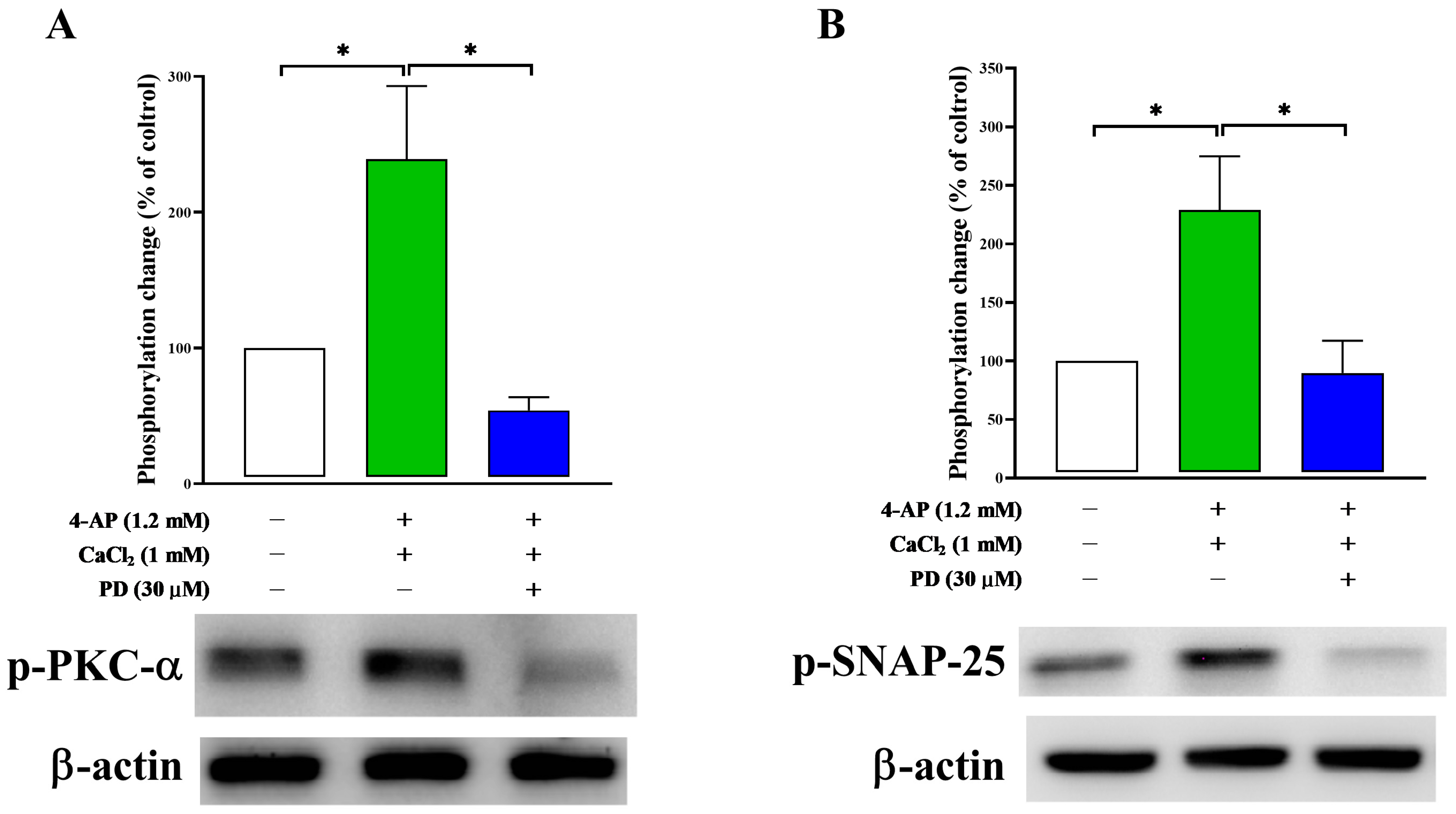
2.6. Effect of PD on Synaptosomal Protein Phosphorylation
3. Discussion
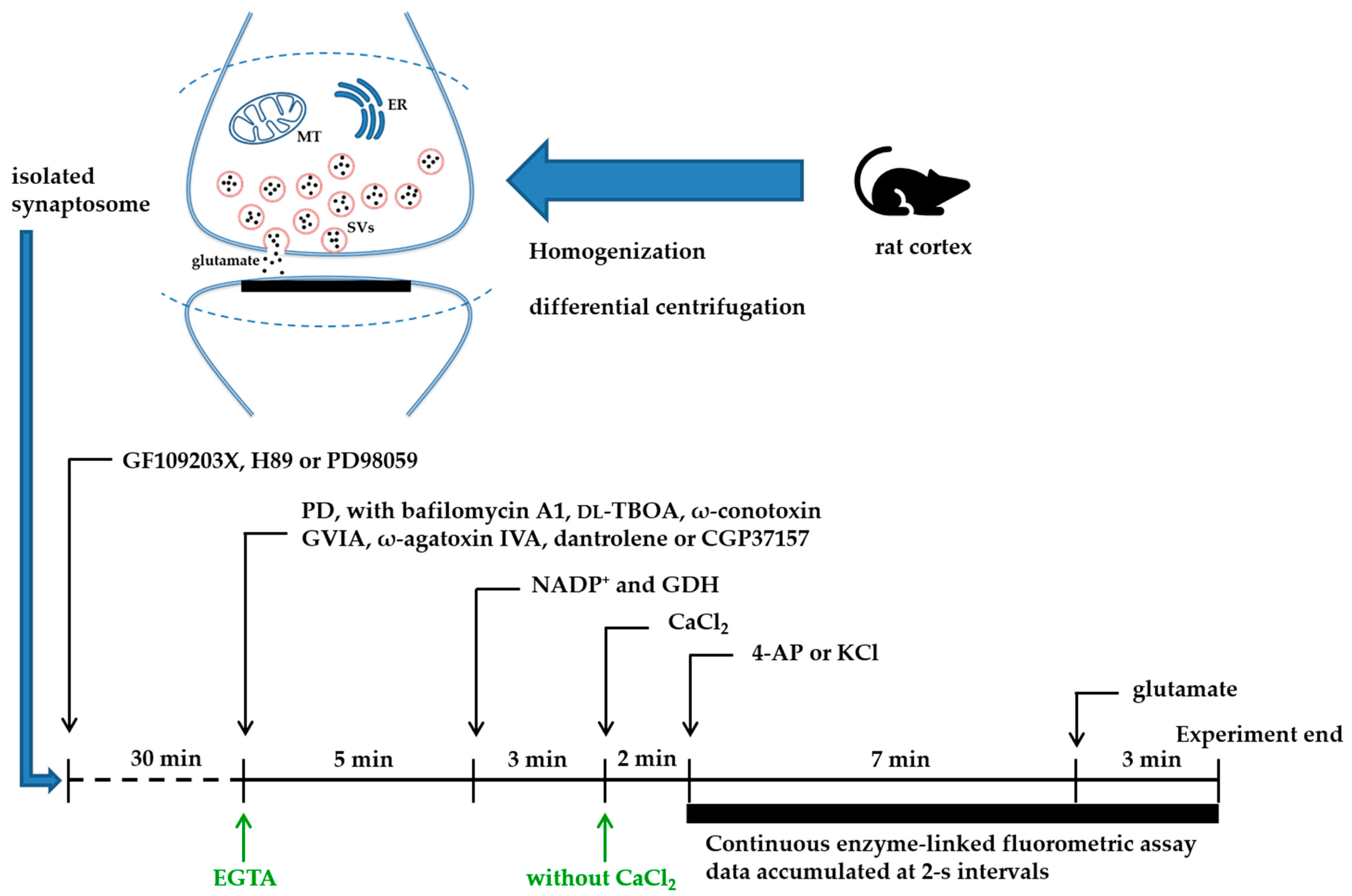
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals and Ethics Statement
4.2. Chemicals, Reagents and Buffers
4.3. Synaptosomal Preparation
4.4. Glutamate Release
4.5. Measurements of Fluorometric Cytosolic Ca2+ ([Ca2+]c) and Membrane Potential
4.6. Western Blotting
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Hackett, J.T.; Ueda, T. Glutamate release. Neurochem. Res. 2015, 40, 2443–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Danbolt, N.C. Glutamate as a neurotransmitter in the healthy brain. J. Neural. Transm. 2014, 121, 799–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meldrum, B.S. Glutamate as a neurotransmitter in the brain: Review of physiology and pathology. J. Nutr. 2000, 130, 1007s–1015s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.X.; Wang, Y.; Qin, Z.H. Molecular mechanisms of excitotoxicity and their relevance to pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2009, 30, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewerenz, J.; Maher, P. Chronic glutamate toxicity in neurodegenerative diseases-What is the evidence? Front. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, M.; Lizama, B.N.; Chu, C.T. Excitotoxicity, calcium and mitochondria: A triad in synaptic neurodegeneration. Transl. Neurodegener. 2022, 11, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, M.; Njapo, S.A.; Rastogi, V.; Hedna, V.S. Taming glutamate excitotoxicity: Strategic pathway modulation for neuroprotection. CNS Drugs 2015, 29, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Woo, E.; Kang, K.W. Screening of new chemopreventive compounds from Digitalis purpurea. Pharmazie 2006, 61, 356–358. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, L.C.; Zhu, T.F.; Xiang, H.; Yu, L.; Yan, Z.H.; Gan, S.C.; Wang, D.C.; Zeng, S.; Deng, X.M. New secoiridoid glycosides from the roots of Picrorhiza scrophulariiflora. Molecules 2008, 13, 2049–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, F.; Yang, L.; Chou, G.; Wang, Z. Bioguided isolation of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors from the seeds of Plantago asiatica L. Phytother. Res. 2010, 24, 1088–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Fu, S.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Gong, M.; Qiu, F. LC-ESI-MS/MS analysis and pharmacokinetics of plantainoside D isolated from Chirita longgangensis var. hongyao, a potential anti-hypertensive active component in rats. Molecules 2014, 19, 15103–15115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, C.; Liu, L.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, F.; Zhu, J.; Mu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Wang, X.; et al. Effective materials and mechanisms study of Tibetan herbal medicine Lagotis integra W. W. Smith treating DSS-induced ulcerative colitis based on network pharmacology, molecular docking and experimental validation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 301, 115800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Sun, Y.; Ye, W.C.; Xiong, F.; Wu, J.J.; Yang, C.H.; Zhao, S.X. Antioxidative phenylethanoid and phenolic glycosides from Picrorhiza scrophulariiflora. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2004, 52, 615–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.S.; Woo, E.R.; Chae, S.W.; Ha, K.C.; Lee, G.H.; Hong, S.T.; Kwon, D.Y.; Kim, M.S.; Jung, Y.K.; Kim, H.M.; et al. Plantainoside D protects adriamycin-induced apoptosis in H9c2 cardiac muscle cells via the inhibition of ROS generation and NF-kappaB activation. Life Sci. 2007, 80, 314–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, R.C.; Qi, M.; Yang, Q.M.; Li, P.F.; Wang, D.D.; Lan, J.P.; Wang, Z.T.; Yang, L. Extract of Plantago asiatica L. seeds ameliorates hypertension in spontaneously hypertensive rats by inhibition of angiotensin converting enzyme. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Hua, F.; Wang, X.; Huang, J.L. Therapeutic potential of IKK-β inhibitors from natural phenolics for inflammation in cardiovascular diseases. Inflammopharmacology 2020, 28, 19–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, J.; Huang, L.; Bao, Y.; Wang, L.; Lyu, Q.; Kuang, H.; Wang, K.; Sang, X.; Yang, Q.; Shan, Q.; et al. A deep clustering-based mass spectral data visualization strategy for anti-renal fibrotic lead compound identification from natural products. Analyst 2022, 147, 4739–4751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coyle, J.T.; Puttfarcken, P. Oxidative stress, glutamate, and neurodegenerative disorders. Science 1993, 262, 689–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-Gutierrez, E.; Muñoz-Arenas, G.; Treviño, S.; Espinosa, B.; Chavez, R.; Rojas, K.; Flores, G.; Díaz, A.; Guevara, J. Alzheimer’s disease and metabolic syndrome: A link from oxidative stress and inflammation to neurodegeneration. Synapse 2017, 71, e21990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.K.; Bahler, B.D.; Hofmann, G.A.; Mattern, M.R.; Johnson, R.K.; Kingston, D.G. Isolation and structure elucidation of new PKCα inhibitors from Pinus flexilis. J. Nat. Prod. 1998, 61, 1407–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.N.; Bahler, B.D.; Hofmann, G.A.; Mattern, M.R.; Johnson, R.K.; Kingston, D.G. Phenylethanoid glycosides from Digitalis purpurea and Penstemon linarioides with PKCalpha-inhibitory activity. J. Nat. Prod. 1998, 61, 1410–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.W.; Yeh, K.C.; Chiu, K.M.; Lee, M.Y.; Lin, T.Y.; Wang, S.J. The effect of Isosaponarin derived from Wasabi leaves on glutamate release in rat synaptosomes and its underlying mechanism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magi, S.; Piccirillo, S.; Amoroso, S.; Lariccia, V. Excitatory amino acid transporters (EAATs): Glutamate transport and beyond. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, A.R.; Willnow, T.E. Excitatory amino acid transporters in physiology and disorders of the central nervous system. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, Y.C.; Kuo, Y.H.; Hsieh, P.W.; Hsieh, T.Y.; Kuo, J.R.; Wang, S.J. Chlorogenic acid decreases glutamate release from rat cortical nerve terminals by P/Q-type Ca2+ channel suppression: A possible neuroprotective mechanism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulido, C.; Ryan, T.A. Synaptic vesicle pools are a major hidden resting metabolic burden of nerve terminals. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabi9027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozdnyakova, N.; Krisanova, N.; Dudarenko, M.; Vavers, E.; Zvejniece, L.; Dambrova, M.; Borisova, T. Inhibition of sigma-1 receptors substantially modulates GABA and glutamate transport in presynaptic nerve terminals. Exp. Neurol. 2020, 333, 113434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Vázquez, H.; Gonzalez-Sandoval, C.; Vega, A.V.; Arias-Montaño, J.A.; Barral, J. Histamine H3 receptor activation modulates glutamate release in the corticostriatal synapse by acting at CaV2.1 (P/Q-Type) calcium channels and GIRK (KIR3) potassium channels. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2022, 42, 817–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.W.; Lin, T.Y.; Chiu, K.M.; Lee, M.Y.; Huang, J.H.; Wang, S.J. Silymarin inhibits glutamate release and prevents against kainic acid-induced excitotoxic injury in rats. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Hirata, M.; Mizokami, A.; Zhao, J.; Takahashi, I.; Takeuchi, H.; Hirata, M. Differential role of SNAP-25 phosphorylation by protein kinases A and C in the regulation of SNARE complex formation and exocytosis in PC12 cells. Cell. Signal. 2016, 28, 425–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, C.G.; Takayasu, Y.; Rodenas-Ruano, A.; Paternain, A.V.; Lerma, J.; Bennett, M.V.; Zukin, R.S. SNAP-25 is a target of protein kinase C phosphorylation critical to NMDA receptor trafficking. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanivel, V.; Gupta, V.; Mirshahvaladi, S.S.O.; Sharma, S.; Gupta, V.; Chitranshi, N.; Mirzaei, M.; Graham, S.L.; Basavarajappa, D. Neuroprotective effects of neuropeptide Y on human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells in glutamate excitotoxicity and ER stress conditions. Cells 2022, 11, 3665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pap, R.; Pandur, E.; Jánosa, G.; Sipos, K.; Nagy, T.; Agócs, A.; Deli, J. Lutein decreases inflammation and oxidative stress and prevents iron accumulation and lipid peroxidation at glutamate-induced neurotoxicity. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meldrum, B.; Garthwaite, J. Excitatory amino acid neurotoxicity and neurodegenerative disease. Trends. Pharmacol. Sci. 1990, 11, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, J.C.; Egea, J.; Del Carmen Godino, M.; Fernandez-Gomez, F.J.; Sánchez-Prieto, J.; Gandía, L.; García, A.G.; Jordán, J.; Hernández-Guijo, J.M. Neuroprotectant minocycline depresses glutamatergic neurotransmission and Ca2+ signalling in hippocampal neurons. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2007, 26, 2481–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuñez-Figueredo, Y.; Pardo Andreu, G.L.; Oliveira Loureiro, S.; Ganzella, M.; Ramírez-Sánchez, J.; Ochoa-Rodríguez, E.; Verdecia-Reyes, Y.; Delgado-Hernández, R.; Souza, D.O. The effects of JM-20 on the glutamatergic system in synaptic vesicles, synaptosomes and neural cells cultured from rat brain. Neurochem. Int. 2015, 81, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.W.; Huang, Y.C.; Chiu, K.M.; Lee, M.Y.; Lin, T.Y.; Wang, S.J. Enmein decreases synaptic glutamate release and protects against kainic acid-induced brain injury in rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millán, C.; Torres, M.; Sánchez-Prieto, J. Co-activation of PKA and PKC in cerebrocortical nerve terminals synergistically facilitates glutamate release. J. Neurochem. 2003, 87, 1101–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, S.; Gharagozloo, M.; Simard, C.; Gris, D. Astrocytes maintain glutamate hmeostasis in the CNS by controlling the balance between glutamate uptake and release. Cells 2019, 8, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, R.R.; Bernardino, T.C.; da Silva, M.C.M.; de Oliveira, A.C.P.; Drumond, L.E.; Rosa, D.V.; Massensini, A.R.; Moraes, M.F.D.; Doretto, M.C.; Romano-Silva, M.A.; et al. Neurochemical abnormalities in the hippocampus of male rats displaying audiogenic seizures, a genetic model of epilepsy. Neurosci. Lett. 2021, 761, 136123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, K.M.; Lin, T.Y.; Lee, M.Y.; Lu, C.W.; Wang, M.J.; Wang, S.J. Typhaneoside suppresses glutamate release through inhibition of voltage-dependent calcium entry in rat cerebrocortical nerve terminals. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2021, 34, 1286–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.K.; Hung, C.F.; Weng, J.R.; Hsieh, T.Y.; Wang, S.J. Kaempferol 3-Rhamnoside on glutamate release from rat cerebrocortical nerve terminals involves P/Q-type Ca2+ channel and Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II-dependent pathway suppression. Molecules 2022, 27, 1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvis, S.E.; Zamponi, G.W. Interactions between presynaptic Ca2+ channels, cytoplasmic messengers and proteins of the synaptic vesicle release complex. Trends. Pharmacol. Sci. 2001, 22, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, D.B.; Carvalho, A.P.; Duarte, C.B. Non-specific effects of the MEK inhibitors PD098,059 and U0126 on glutamate release from hippocampal synaptosomes. Neuropharmacology 2002, 42, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naik, M.U.; Benedikz, E.; Hernandez, I.; Libien, J.; Hrabe, J.; Valsamis, M.; Dow-Edwards, D.; Osman, M.; Sacktor, T.C. Distribution of protein kinase Mzeta and the complete protein kinase C isoform family in rat brain. J. Comp. Neurol. 2000, 426, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanuza, M.A.; Santafe, M.M.; Garcia, N.; Besalduch, N.; Tomàs, M.; Obis, T.; Priego, M.; Nelson, P.G.; Tomàs, J. Protein kinase C isoforms at the neuromuscular junction: Localization and specific roles in neurotransmission and development. J. Anat. 2014, 224, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katayama, N.; Yamamori, S.; Fukaya, M.; Kobayashi, S.; Watanabe, M.; Takahashi, M.; Manabe, T. SNAP-25 phosphorylation at Ser187 regulates synaptic facilitation and short-term plasticity in an age-dependent manner. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Y.; Liu, X.; Yang, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Gillis, K.D. Phosphorylation of SNAP-25 at Ser187 mediates enhancement of exocytosis by a phorbol ester in INS-1 cells. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.Y.; Chen, I.Y.; Lee, M.Y.; Lu, C.W.; Chiu, K.M.; Wang, S.J. Inhibition of glutamate release from rat cortical nerve terminals by dehydrocorydaline, an alkaloid from Corydalis yanhusuo. Molecules 2022, 27, 960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chiu, K.-M.; Lee, M.-Y.; Lu, C.-W.; Lin, T.-Y.; Wang, S.-J. Plantainoside D Reduces Depolarization-Evoked Glutamate Release from Rat Cerebral Cortical Synaptosomes. Molecules 2023, 28, 1313. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031313
Chiu K-M, Lee M-Y, Lu C-W, Lin T-Y, Wang S-J. Plantainoside D Reduces Depolarization-Evoked Glutamate Release from Rat Cerebral Cortical Synaptosomes. Molecules. 2023; 28(3):1313. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031313
Chicago/Turabian StyleChiu, Kuan-Ming, Ming-Yi Lee, Cheng-Wei Lu, Tzu-Yu Lin, and Su-Jane Wang. 2023. "Plantainoside D Reduces Depolarization-Evoked Glutamate Release from Rat Cerebral Cortical Synaptosomes" Molecules 28, no. 3: 1313. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031313
APA StyleChiu, K.-M., Lee, M.-Y., Lu, C.-W., Lin, T.-Y., & Wang, S.-J. (2023). Plantainoside D Reduces Depolarization-Evoked Glutamate Release from Rat Cerebral Cortical Synaptosomes. Molecules, 28(3), 1313. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031313






