Development and Application of Ruthenium(II) and Iridium(III) Based Complexes for Anion Sensing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Discussion
2.1. Ruthenium(II) Based Complexes for Sensing of Anion
2.1.1. Triazole/Iodo-Triazole-Based Ru(II) Complexes as Chemosensors
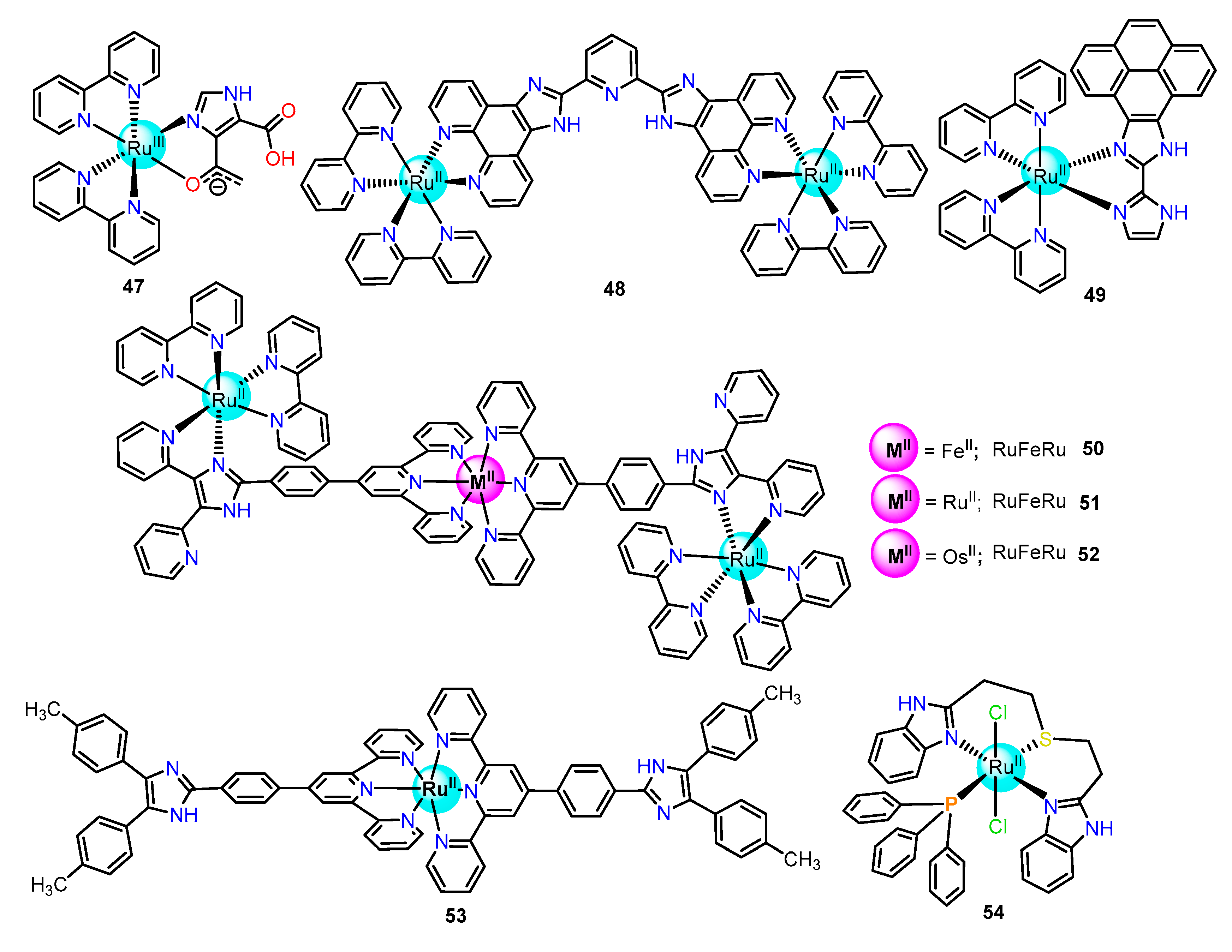
2.1.2. Imidazole/Benzimidazole-Based Ru(II) Complexes as Chemosensors
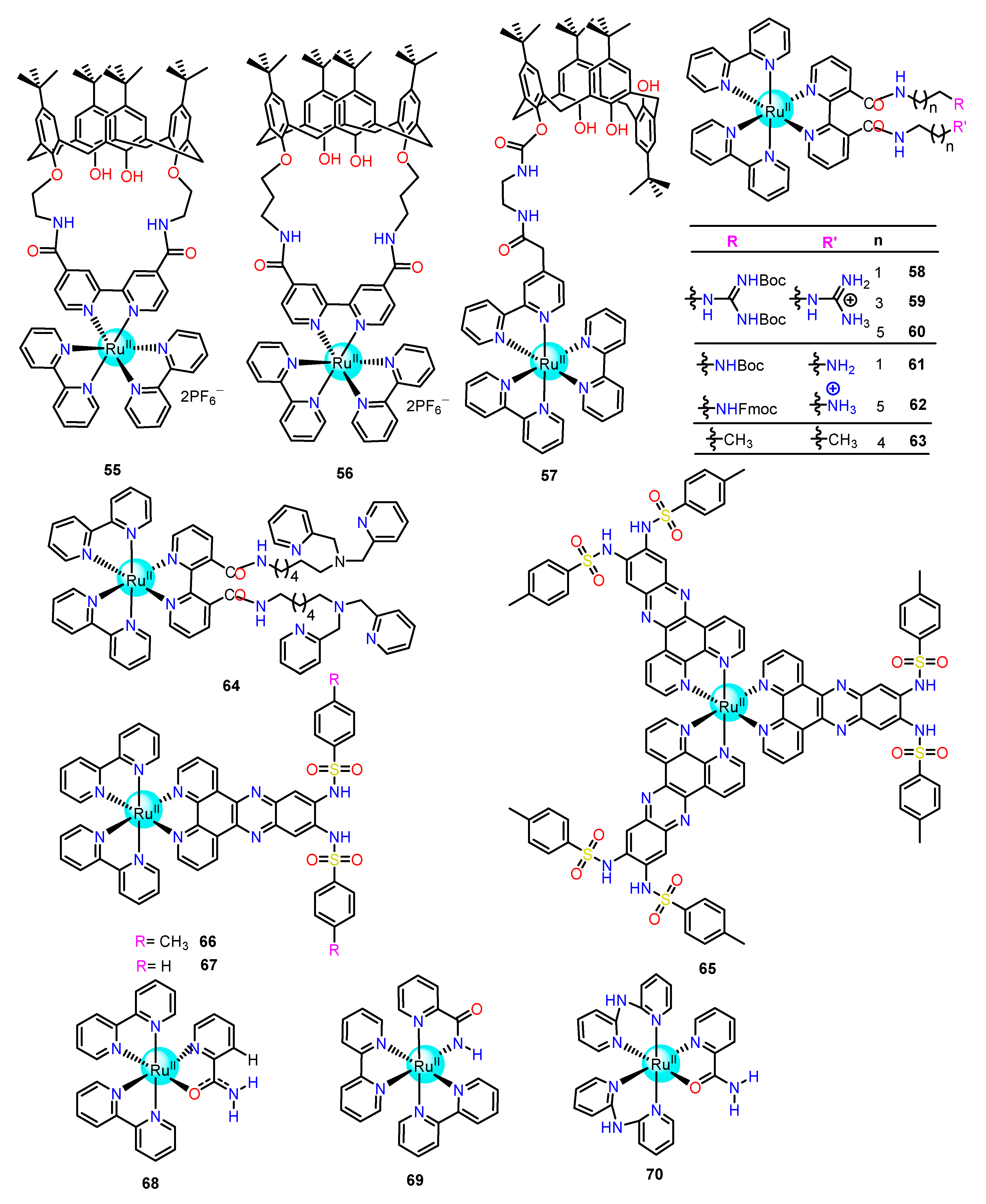
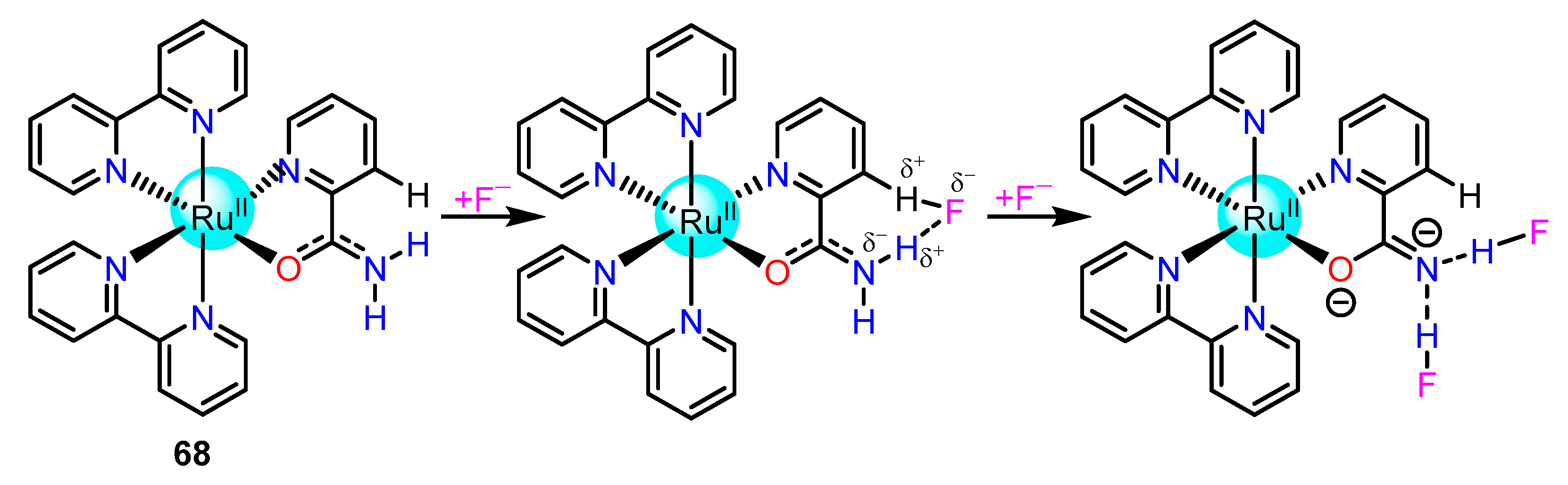
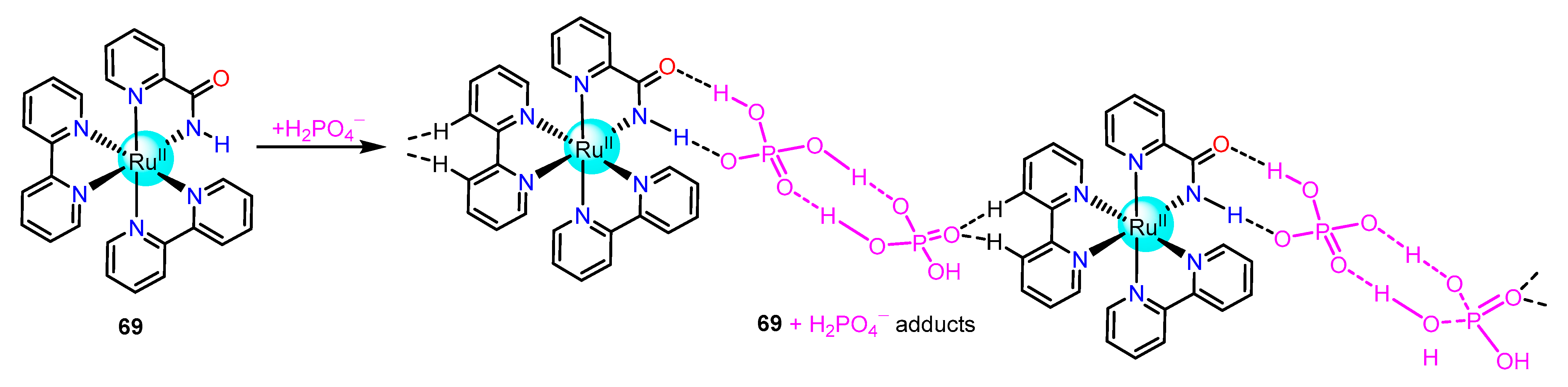
2.1.3. Amide/Sulphonamide/Picolinamide Based Ru(II) Complexes as Chemosensors
2.1.4. Pyrrol-Based Ru(II) Complexes as Chemosensors
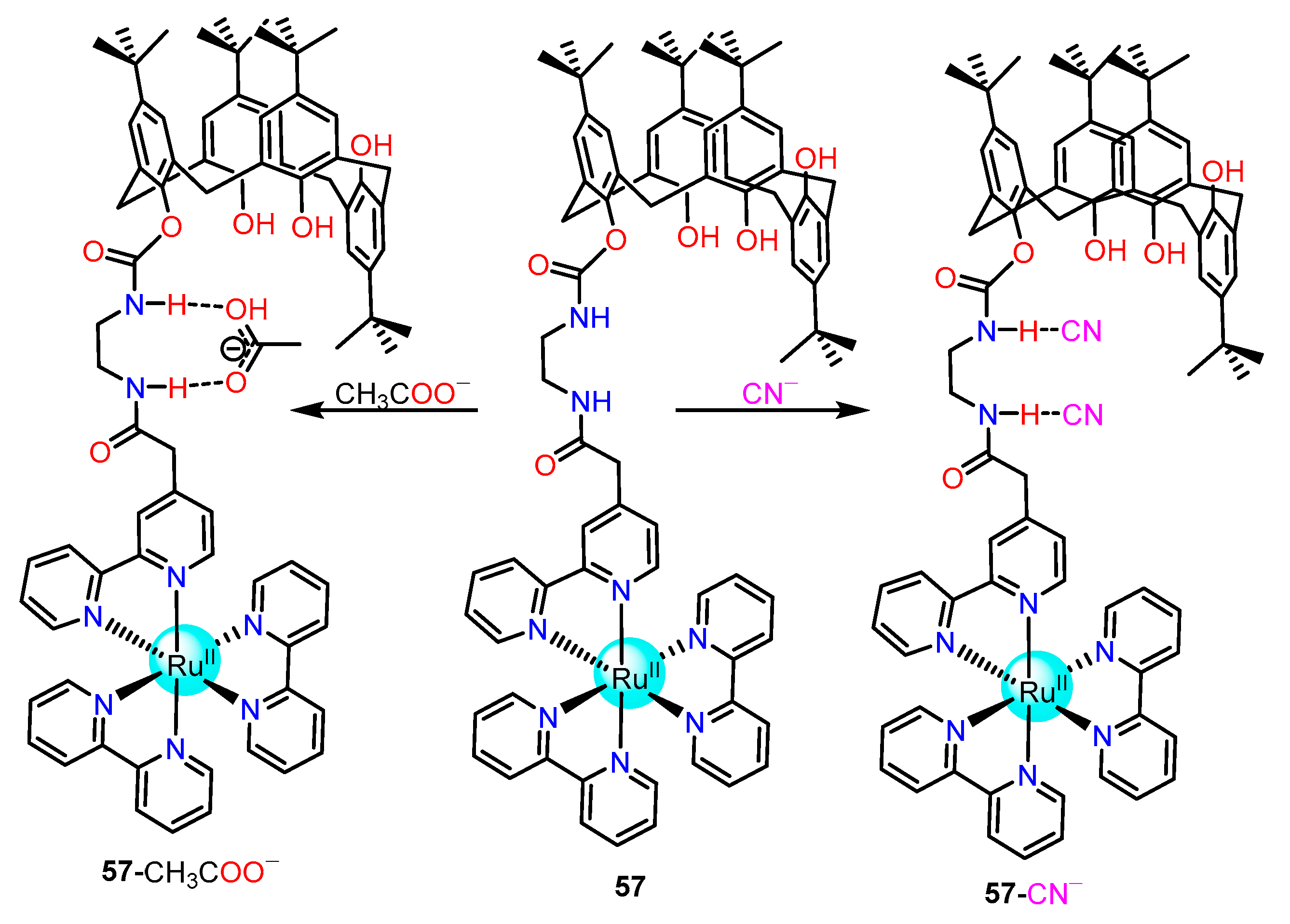
2.1.5. Urea-Based Ru(II) Complexes as Chemosensors
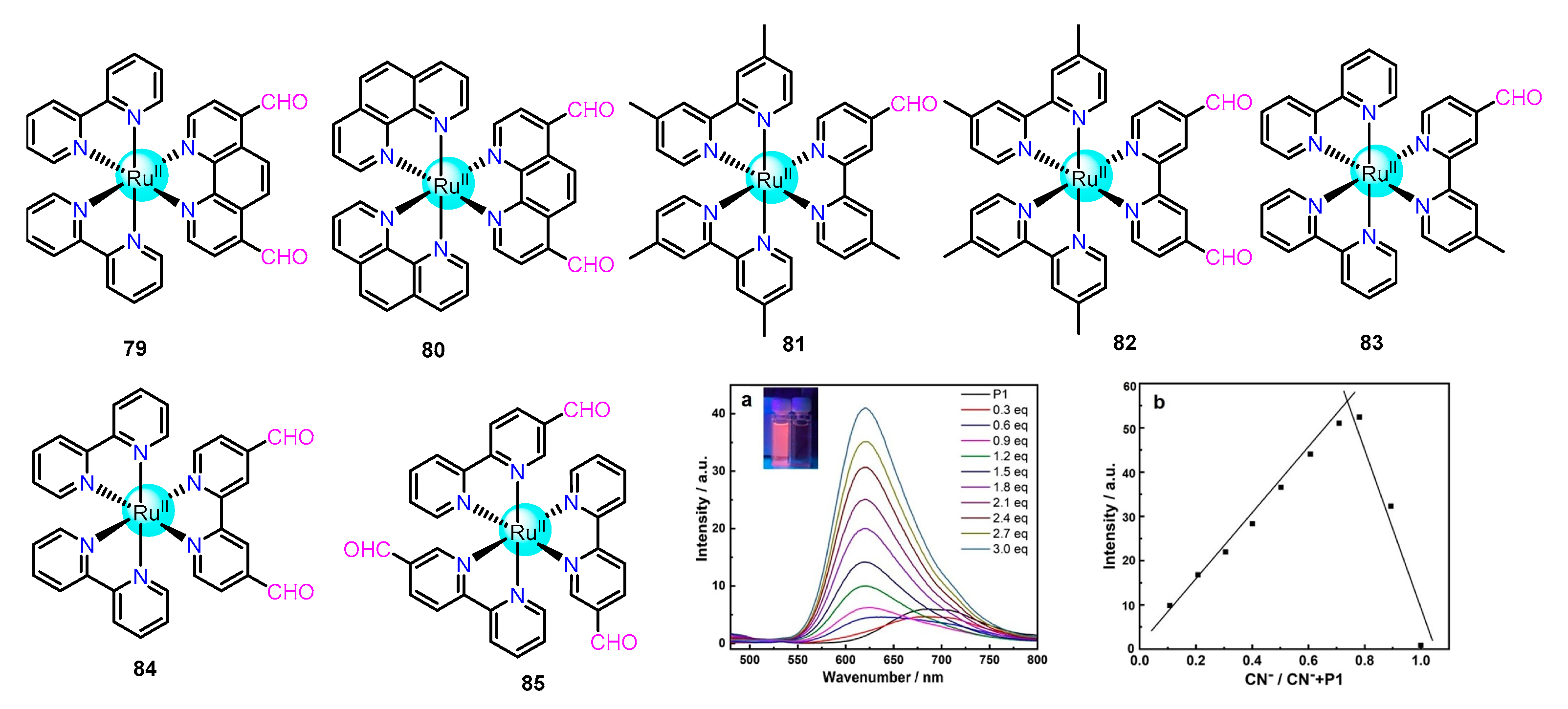
2.1.6. Aldehyde Incorporated Ru(II) Complexes as Chemodosimeters
2.1.7. Some Example of Bis-Heteroleptic Ru(II) Complexes as Chemosensor
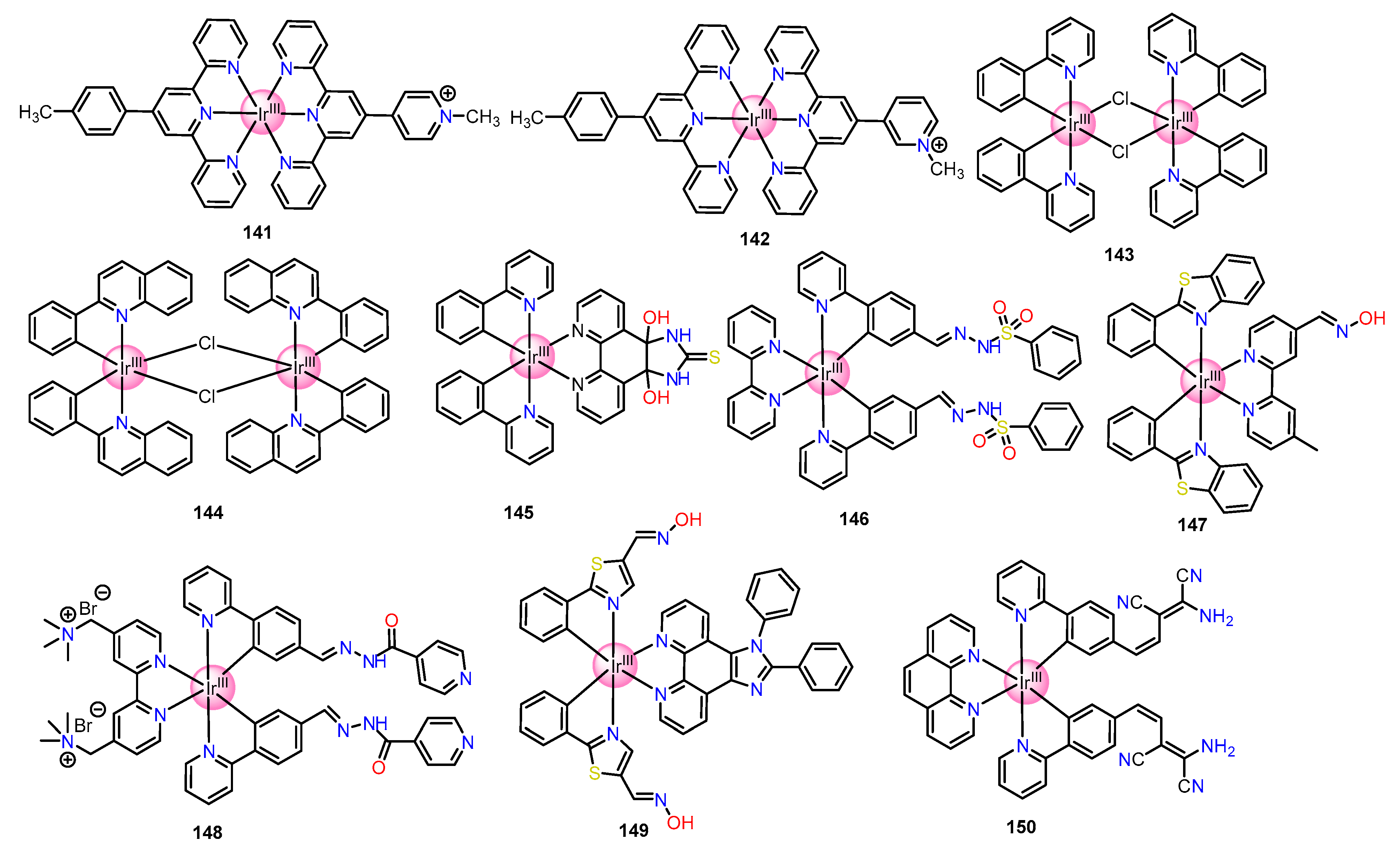
2.2. Cyclometalated Iridium(III)-Based Complexes for Sensing of Anions
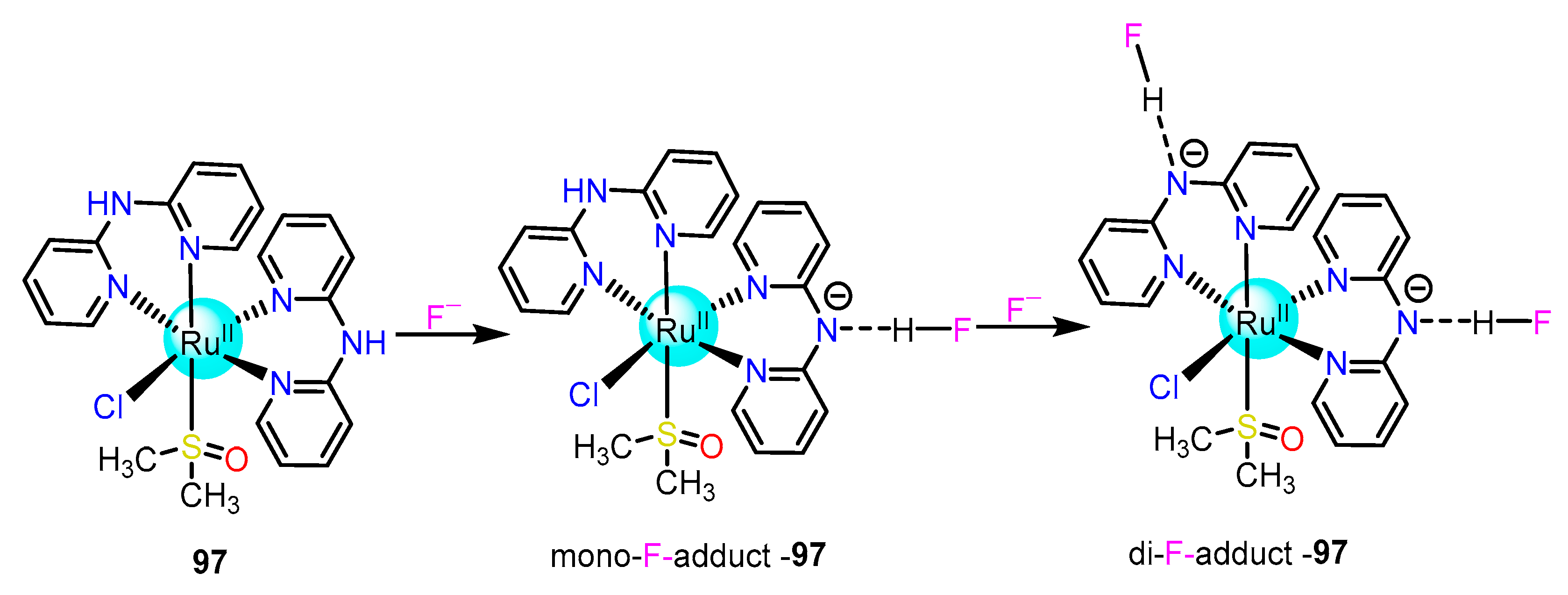
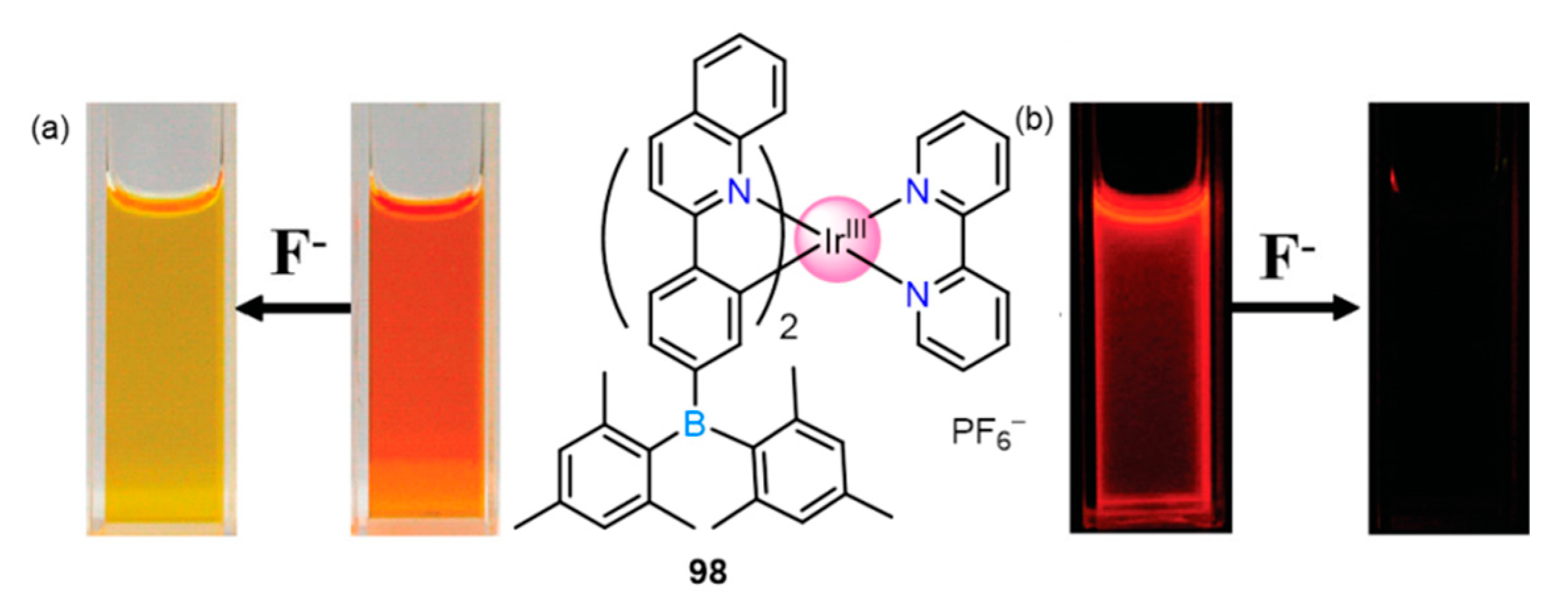
2.2.1. Fluoride Sensing
2.2.2. Sensing of Cyanide
2.2.3. Sensing of Phosphates
2.2.4. Sensing of Perchlorate
2.2.5. Sensing of Chloride
2.2.6. Sensing of Nitrite
2.2.7. Sensing of Carbonate/Bicarbonate
2.2.8. Sensing of Hypochlorite
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sessler, J.L.; Gale, P.A.; Cho, W.S. Anion Receptor Chemistry; Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Sessler, J.L.; Camiolo, S.; Gale, P.A. Pyrrolic and polypyrrolic anion binding agents. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2003, 240, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.O.; Hossain, M.A.; Bowman-James, K. Influence of dimensionality and charge on anion binding in amide-based macrocyclic receptors. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2006, 250, 3038–3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gale, P.A.; Quesada, R. Anion coordination and anion-templated assembly: Highlights from 2002 to 2004. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2006, 250, 3219–3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunnlaugsson, T.; Glynn, M.; Tocci, G.M.; Kruger, P.E.; Pfeffer, F.M. Anion recognition and sensing in organic and aqueous media using luminescent and colorimetric sensors. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2006, 250, 3094–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katayev, E.A.; Ustynyuk, Y.A.; Sessler, J.L. Receptors for tetrahedral oxyanions. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2006, 250, 3004–3037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gale, P.A.; Garcia-Garrido, S.E.; Garric, J. Anion receptors based on organic frameworks: Highlights from 2005 and 2006. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 151–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.N.; Lee, M.H.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, J.S.; Yoon, J. A new trend in rhodamine-based chemosensors: Application of spirolactam ring-opening to sensing ions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 1465–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caltagirone, C.; Gale, P.A. Anion receptor chemistry: Highlights from 2007. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 520–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Chen, X.; Kim, H.N.; Yoon, J. Sensors for the optical detection of cyanide ion. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beer, P.D.; Gale, P.A. Anion recognition and sensing: The state of the art and future perspectives. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2001, 40, 486–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubik, S. Anion recognition in water. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 3648–3663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gale, P.A.; Caltagirone, C. Anion sensing by small molecules and molecular ensembles. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 4212–4227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busschaert, N.; Caltagirone, C.; Rossom, W.V.; Gale, P.A. Applications of supramolecular anion recognition. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 8038–8155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langton, M.J.; Serpell, C.J.; Beer, P.D. Anion recognition in water: Recent advances from a supramolecular and macromolecular perspective. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 1974–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gale, P.A.; Caltagirone, C. Fluorescent and colorimetric sensors for anionic species. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2018, 354, 2–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hein, R.; Beer, P.D.; Davis, J.J. Electrochemical anion sensing: Supramolecular approaches. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 1888–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Li, F.; Huang, C. Phosphorescent chemosensors based on heavy-metal complexes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 3007–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Huang, C.; Li, F. Phosphorescent heavy-metal complexes for bioimaging. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 2508–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, K.K.-W.; Choi, A.W.-T.; Law, W.H.-T. Applications of luminescent inorganic and organometallic transition metal complexes as biomolecular and cellular probes. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 6021–6047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baggaley, E.; Weinstein, J.A.; Williams, J.A.G. Lighting the way to see inside the live cell with luminescent transition metal complexes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2012, 256, 1762–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, K.; Chen, Y.; Rees, T.W.; Ji, L.; Chao, H. Organelle-targeting metal complexes: From molecular design to bio-applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2019, 378, 66–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, L.C.-C.; Lo, K.K.-W. Luminescent and photofunctional transition metal complexes: From molecular design to diagnostic and therapeutic applications. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 14420–14440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yam, V.W.-W.; Wong, K.M.-C. Luminescent metal complexes of d6, d8 and d10 transition metal centres. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 11579–11592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, D.-L.; Lin, S.; Wang, W.; Yang, C.; Leung, C.-H. Luminescent chemosensors by using cyclometalated iridium(III) complexes and their applications. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 878–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, H.; Wang, Y.; Lin, S.; Lou, J.; Zhang, Q. Recent development and application of cyclometalated iridium(III) complexes as chemical and biological probes. Dalton Trans. 2021, 50, 6410–6417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arndtsen, B.A.; Bergman, R.G. Unusually mild and selective hydrocarbon CH bond activation with positively charged iridium (III) complexes. Science 1995, 270, 1970–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chepelin, O.; Ujma, J.; Wu, X.; Slawin, A.M.; Pitak, M.B.; Coles, S.J.; Michel, J.; Jones, A.C.; Barran, P.E.; Lusby, P.J. Luminescent, enantiopure, phenylatopyridine iridium-based coordination capsules. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 19334–19337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llinares, J.M.; Powell, D.; Bowman-James, K. Ammonium based anion receptors. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2003, 240, 57–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Espana, E.; Diaz, P.; Llinares, J.M.; Bianchi, A. Anion coordination chemistry in aqueous solution of polyammonium receptors. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2006, 250, 2952–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Wang, J.; Xie, B.; Liu, J.Q.; Yadav, R.; Singh, A.; Kumar, A. Fluorescence sensing of nitro-aromatics by Zn (II) and Cd (II) based coordination polymers having the 5-[bis (4 carboxybenzyl)-amino] isophthalic acid ligand. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 3537–3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Li, Y.; Liang, F.; Li, L.; Lan, Y.; Li, Z.; Lu, X.; Yang, M.; Ma, D. A microporous 2D cobalt-based MOF with pyridyl sites and open metal sites for selective adsorption of CO2. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2022, 341, 112098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Liang, F.; Li, Y.; Wu, J.; Guan, S.; Wu, M.; Xie, S.; Luo, M.; Ma, D. A 2D porous zinc-organic framework platform for loading of 5-fluorouracil. Inorganics 2022, 10, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desiraju, G.R. A bond by any other name. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, T. Unrolling the hydrogen bond properties of C–H•••O interactions. Chem. Commun. 1997, 8, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desiraju, G.R.; Ho, P.S.; Kloo, L.; Legon, A.C.; Marquardt, R.; Metrangolo, P.; Politzer, P.; Resnati, G.; Rissanen, K. Definition of the halogen bond (IUPAC Recommendations 2013). Pure Appl. Chem. 2013, 85, 1711–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilday, L.C.; Robinson, S.W.; Barendt, T.A.; Langton, M.J.; Mullaney, B.R.; Beer, P.D. Halogen bonding in supramolecular chemistry. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 7118–7195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallo, G.; Metrangolo, P.; Milani, R.; Pilati, T.; Priimagi, A.; Resnati, G.; Terraneo, G. The halogen bond. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 2478–2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beale, T.M.; Chudzinski, M.G.; Sarwar, M.G.; Taylor, M.S. Halogen bonding in solution: Thermodynamics and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 1667–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schottel, B.L.; Chifotides, H.T.; Dunbar, K.R. Anion-π interactions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 68–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, R.E.; Hennig, A.; Weimann, D.P.; Emery, D.; Ravikumar, V.; Montenegro, J.; Takeuchi, T.; Gabutti, S.; Mayor, M.; Mareda, J.; et al. Experimental evidence for the functional relevance of anion–π interactions. Nat. Chem. 2010, 2, 533–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frontera, A.; Gamez, P.; Mascal, M.; Mooibroek, T.J.; Reedijk, J. Putting anion–π interactions into perspective. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 9564–9583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chifotides, H.T.; Dunbar, K.R. Anion−π interactions in supramolecular architectures. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 894–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, A.; Pan, Y.; Liu, J.Q.; Kumar, A. Multicomponent isoreticular metal-organic frameworks: Principles, current status and challenges. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 445, 214074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Zhang, Z.; Yong, J.; Schenk, P.M.; Tian, D.; Xu, Z.P.; Zhang, R. Determination and imaging of small biomolecules and ions using ruthenium(II) complex-based chemosensors. Top. Curr. Chem. 2022, 380, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.-C.; Sun, S.-S.; Odago, M.O.; Lees, A.J. Anion recognition and sensing by transition-metal complexes with polarized N H recognition motifs. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2015, 284, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alreja, P.; Kaur, N. Recent advances in 1,10-phenanthroline ligands for chemosensing of cations and anions. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 23169–23217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Ghosh, T.K.; Ghosh, R.; Mondal, S.; Ghosh, P. Recent advances in recognition, sensing and extraction of phosphates: 2015 onwards. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2020, 405, 213128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Pachisia, S.; Gupta, R. Turn-on detection of assorted phosphates by luminescent chemosensors. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2021, 8, 3587–3607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juris, A.; Balzani, V.; Barigeletti, F.; Campagna, S.; Belser, P.; Zelewsky, A.V. Ru(II) polypyridine complexes: Photophysics, photochemistry, eletrochemistry, and chemiluminescence. Coord. Chem. Rev. 1988, 84, 85–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beer, P.D.; Dickson, C.A.P.; Fletcher, N.; Goulden, A.J.; Grieve, A.; Hodacova, J.; Wear, T. New classes of anion receptor containing charged and neutral transition metal Lewis acidic recognition sites. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1993, 10, 828–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, B.; Khatua, S.; Dutta, R.; Chakraborty, S.; Ghosh, P. Bis-heteroleptic ruthenium(II) complex of a triazole ligand as a selective probe for phosphates. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 53, 8061–8070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, B.; Dutta, R.; Khatua, S.; Ghosh, P. A cyanuric acid platform based tripodal bis-heteroleptic Ru(II) complex of click generated ligand for selective sensing of phosphates via C–H···anion interaction. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 55, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondal, S.; Sarkar, K.; Ghosh, P. Influence of triazole substituents of bis-heteroleptic Ru(II) probes toward selective sensing of dihydrogen phosphate. Inorg. Chem. 2021, 60, 9084–9096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, B.; Sinha, S.; Ghosh, P. Selective sensing of phosphates by a new bis-heteroleptic RuII complex through halogen bonding: A superior sensor over its hydrogen-bonding analogue. Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 18051–18059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; Rashid, A.; Ghosh, P. Apentafluorophenyl functionalized RuII-probe having halogen bond center toward recognition and sensing of perrhenate and dihydrogen phosphate. J. Organomet. Chem. 2021, 952, 122027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; Ghosh, T.K.; Chowdhury, B.; Ghosh, P. Supramolecular self-assembly driven selective sensing of phosphates. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 58, 15993–16003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, T.K.; Chakraborty, S.; Chowdhury, B.; Ghosh, P. Bis-heteroleptic ruthenium(II) complex of pendant urea functionalized pyridyl triazole and phenanthroline for recognition, sensing, and extraction of oxyanions. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 5371–5382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, T.K.; Ghosh, P. Balancing the acidity of the pendant urea arm of bis-heteroleptic ruthenium(II) complex containing pyridyl triazole for improved oxyanion recognition. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 7561–7570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, T.K.; Mondal, S.; Bej, S.; Nandi, M.; Ghosh, P. An integrated urea and halogen bond donor based receptor for superior and selective sensing of phosphates. Dalton Trans. 2019, 48, 4538–4546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, B.; Sinha, S.; Dutta, R.; Mondal, S.; Karmakar, S.; Ghosh, P. Discriminative behavior of a donor–acceptor–donor triad toward cyanide and fluoride: Insights into the mechanism of naphthalene diimide reduction by cyanide and fluoride. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 59, 13371–13382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheet, S.K.; Sen, B.; Thounaojam, R.; Aguan, K.; Khatua, S. Ruthenium(II) complex-based luminescent bifunctional probe for Ag+ and phosphate ions: Ag+-assisted detection and imaging of rRNA. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 1249–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, B.; Kumar, S.P.; Rabha, M.; Sheet, S.K.; Aguan, K.; Samanta, D.; Khatua, S. Luminescence detection of Ag+ and phosphate ions by a ruthenium(II) complex-based multianalyte probe: A combined spectroscopic, crystallographic, and theoretical approach. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2021, 35, 3549–3560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, M.; Anandan, S. Triazole appending ruthenium(II) polypyridine complex for selective sensing of phosphate anions through C–H–anion interaction and copper(II) ions via cancer cells. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 6186–6196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, M.; Syed, A.; Marraiki, N.; Anandan, S. The aqueous dependent sensing of hydrazine and phosphate anions using a bis-heteroleptic Ru(II) complex with a phthalimide–anchored pyridinetriazole ligand. Analyst 2021, 146, 1430–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, P.; Tárraga, A.; Otón, F. Imidazole derivatives: A comprehensive survey of their recognition properties. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2012, 10, 1711–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rommel, S.A.; Sorsche, D.; Fleischmann, M.; Rau, S. Optical sensing of anions via supramolecular recognition with biimidazole complexes. Chem. Eur. J. 2017, 23, 18101–18119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ion, L.; Morales, D.; Perez, J.; Riera, L.; Riera, V.; Kowenicki, R.; McPartlin, M. Ruthenium biimidazole complexes as anion receptors. Chem. Commun. 2006, 1, 91–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Mo, H.-J.; Chen, J.-C.; Niu, Y.-L.; Zhong, Y.-R.; Zheng, K.-C.; Ye, B.-H. Anion-selective interaction and colorimeter by an optical metalloreceptor based on ruthenium (ii) 2, 2 ′-biimidazole: Hydrogen bonding and proton transfer. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 46, 6427–6436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Niu, Y.-L.; Cao, M.-L.; Wang, K.; Mo, H.-J.; Zhong, Y.-R.; Ye, B.-H. Ruthenium (II) 2, 2′-bibenzimidazole complex as a second-sphere receptor for anions interaction and colorimeter. Inorg. Chem. 2008, 47, 5616–5624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, H.-J.; Niu, Y.-L.; Zhang, M.; Qiao, Z.-P.; Ye, B.-H. Photophysical, electrochemical and anion sensing properties of Ru(II) bipyridine complexes with 2,2′-biimidazole-like ligand. Dalton Trans. 2011, 40, 8218–8225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, H.-J.; Chao, H.-Y.; Ye, B.-H. A ruthenium biimidazole-like anion receptor with two chelating Nsingle bondH⋯O intramolecular hydrogen bonds. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2013, 35, 100–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorsche, D.; Rommel, A.S.; Rau, S. Functional dimming of pincer-shaped bibenzimidazole ruthenium(II) complexes with improved anion-sensitive luminescence. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 10, 1503–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, H.-J.; Shen, Y.; Ye, B.-H. Selective recognition of cyanide anion via formation of multipoint NH and phenyl CH hydrogen bonding with acyclic ruthenium bipyridine imidazole receptors in water. Inorg. Chem. 2012, 51, 7174–7184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.-B.; Huang, Q.-Y.; Han, Y.-F.; Zuo, J.; Ma, Y.-N. Ruthenium(II) complex-based chemosensors for highly sensitive and selective sequential recognition of copper ion and cyanide. Sens. Actuators B 2017, 253, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, T.; Mobin, S.M.; Lahiri, G. Paramagnetic ruthenium-biimidazole derivatives [(acac)2RuIII(LHn)]m, n/m = 2/+, 1/0, 0/-. Synthesis, structures, solution properties and anion receptor features in solution state. Dalton Trans. 2010, 39, 4232–4242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanmohammadi, H.; Rezaeian, K. A catalyst-free approach to a novel imidazo [4,5-f][1,10] phenanthroline ligand and its corresponding ruthenium(II) complex: Insights into their applications in colorimetric anion sensing. New J. Chem. 2014, 38, 5536–5543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapata, F.; Caballero, A.; Espinosa, A.; Tárraga, A.; Molina, P. Cation coordination induced modulation of the anion sensing properties of a ferrocene−imidazophenanthroline dyad: Multichannel recognition from phosphate-related to chloride anions. J. Org. Chem. 2008, 73, 4034–4044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.-X.; Liu, Y.-J.; Zhao, L.; Wang, K.-Z. Highly selective acetate optical sensing of a ruthenium(II) complex carrying imidazole and indole groups. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2010, 76, 146–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.-B.; Duan, Z.-M.; Ma, Y.-Y.; Wang, K.-Z. Highly sensitive and selective difunctional ruthenium(II) complexbased chemosensor for dihydrogen phosphate anion and ferrous cation. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 52, 2306–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.-B.; Wu, Y.-Q.; Wang, K.-Z.; Li, F. pH luminescence switching, dihydrogen phosphate sensing, and cellular uptake of a heterobimetallic ruthenium(II)–rhenium(I) complex. Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 3273–3284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, D.; Das, S.; Bhaumik, C.; Dutta, S.; Baitalik, S. Monometallic and bimetallic ruthenium(II) complexes derived from 4,5-bis(benzimidazol-2-yl)imidazole (H3Imbzim) and 2,20-bipyridine as colorimetric sensors for anions: Synthesis, characterization, and binding studies. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 49, 2334–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Saha, D.; Bhaumik, C.; Dutta, S.; Baitalik, S. Ru(II) and Os(II) mixed-chelates derived from imidazole-4,5-dicarboxylic acid and 2,2′-bipyridine as colorimetric sensors for anions: Synthesis, characterization and binding studies. Dalton Trans. 2010, 39, 4162–4169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, D.; Das, S.; Mardanya, S.; Baitalik, S. Structural characterization and spectroelectrochemical, anion sensing and so vent dependence photophysical studies of a bimetallic Ru(II) complex derived from 1,3–di (1H-imidazo [4,5-f][1,10]phenanthroline-2-yl)benzene. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 8886–8898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, D.; Das, S.; Karmakar, S.; Dutta, S.; Baitalik, S. Synthesis, structural characterization and anion-, cation- and solvent-induced tuning of photophysical properties of a bimetallic Ru(II) complex: Combined experimental and DFT/TDDFT investigation. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 17314–17334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardanya, S.; Karmakar, S.; Bar, M.; Baitalik, S. Pyrene-biimidazole based Ru(II) and Os(II) complexes as highly efficient probes for the visible and near-infrared detection of cyanide in aqueous media. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 21053–21072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, A.; Bar, M.; Ahmed, T.; Baitalik, S. Anion-sensitive photophysics of luminescent trimetallic complexes of Fe(II), Ru(II), and Os(II) with polarized NH motifs. Polyhedron 2020, 190, 114772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, S.; Sahoo, A.; Pal, P.; Baitalik, S. Exploitation of the second coordination sphere to promote significant increase of room-temperature luminescence lifetime and anion sensing in ruthenium–terpyridine complexes. Inorg. Chem. 2021, 60, 6836–6851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pineda, L.H.; Flores, E.D.T.; Hernandez, J.G.; Thangarasu, P.; Ramos, J.M.V. Ruthenium complex of bis(benzimidazole-yl-ethyl)sulfide as chemo-sensor for selective recognition of chloride ion, and its application in real bacterial samples. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2021, 522, 120354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mareeswaran, P.M.; Babu, E.; Rajagopal, S. Optical recognition of anions by ruthenium(II)-bipyridine-calix [4]arene system. J Fluoresc. 2013, 23, 997–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maity, D.; Vyas, G.; Bhatt, M.; Paul, P. Detection of NaCN in aqueous media using a calixarene-based fluoroionophore containing ruthenium(II)-bipyridine as the fluorogenic unit. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 6151–6159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berni, E.; Henaff, L.L.; Jarrige, L.; Girard, E.; Jonusauskas, G.; Gosse, I.; Pinet, S. Functionalized ruthenium complexes: Selective “Turn-on” detection of biologically relevant anionic species. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 2017, 3620–3630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.-P.; Chen, C.-Y.; Wen, Y.-S.; Sun, S.-S. Synthesis, photophysical, and anion-sensing properties of quinoxalinebis(sulfonamide) functionalized receptors and their metal complexes. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 46, 9201–9212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, X.-F.; Li, J.; Lin, H.; Jiang, P.; Caia, Z.-S.; Lin, H.-K. Anion recognition and sensing of ruthenium(II) and cobalt(II) sulfonamido complexes. Dalton Trans. 2009, 12, 2096–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toyama, M.; Fujii, Y.; Endo, M. Bis-heteroleptic ruthenium(II) complex with 2-picolinamide: Synthesis, crystal structures, and spectroscopic study for anion recognition using the amide group. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2019, 486, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Z.-L.; Zhong, Y.-W. Spectroscopic and electrochemical recognition of H2PO4− based on a ruthenium complex with 2-picolinamide. J. Organomet. Chem. 2021, 931, 121612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyama, M.; Hasegaw, T.; Nagao, N. Colorimetric fluoride detection in dimethyl sulfoxide using a heteroleptic ruthenium (II) complex with amino and amide groups: X-ray crystallographic and spectroscopic analyses. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 25227–25239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, T.; Wei, W.-H.; Eller, L.R.; Sessler, J.L. Phenanthroline complexes bearing fused dipyrrolylquinoxaline anion recognition sites: Efficient fluoride anion receptors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 1134–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plitt, P.; Gross, D.E.; Lynch, V.M.; Sessler, J.L. Dipyrrolyl-functionalized bipyridine-based anion receptors for emission based selective detection of dihydrogen phosphate. Chem. Eur. J. 2007, 13, 1374–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anzenbacher, P., Jr.; Tyson, D.S.; Jursıkova, K.; Castellano, F.N. Luminescence lifetime-based sensor for cyanide and related anions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 6232–6233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.J.; Reddington, M.V.; Wilcox, C.S. Ion pair binding by a urea in chloroform solution. Tetrahedron Lett. 1992, 33, 6085–6088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, E.; van Arman, S.A.; Kincaid, S.; Hamilton, A.D. Molecular recognition: Hydrogen-bonding receptors that function in highly competitive solvents. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, 369–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.; Ganguly, B.; Das, A. Urea-based ruthenium(II)−polypyridyl complex as an optical sensor for anions: Synthesis, characterization, and binding studies. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 46, 9912–9918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitchen, J.A.; Boyle, E.M.; Gunnlaugsson, T. Synthesis, structural characterisation and luminescent anion sensing studies of a Ru(II)polypyridyl complex featuring an aryl urea derivatised 2,2’-bpy auxiliary ligand. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2012, 381, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baggi, G.; Boiocchi, M.; Ciarrocchi, C.; Fabbrizzi, L. Enhancing the anion affinity of urea-based receptors with a Ru(terpy)22+ chromophore. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 52, 5273–5283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Z.-L.; Deng, L.-Y.; Zhong, Y.-W.; Yao, J. Anion-regulated electronic communication in a cyclometalated diruthenium complex with a urea bridge. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 8902–8907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chae, M.Y.; Czarnik, A.W. Fluorometric chemodosimetry mercury (II) and silver (I) indication in water via enhanced fluorescence signaling. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 9704–9705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatua, S.; Samanta, D.; Bats, J.W.; Schmittel, M. Rapid and highly sensitive dual-channel detection of cyanide by bis-heteroleptic ruthenium (II) complexes. Inorg. Chem. 2012, 51, 7075–7086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.-W.; Ou, H.-D.; Xu, N.; Deng, W.; Yao, Z.-J. Ruthenium-based phosphorescent probe for selective and naked-eye detection of cyanide in aqueous media. Dyes Pigments 2020, 176, 108196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.-J.; Lin, Z.; Chena, X.; Chen, G. Colorimetric and luminescent bifunctional Ru(II) complexes for rapid and highly sensitive recognition of cyanide. Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 11745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose, D.A.; Kar, P.; Koley, D.; Ganguly, B.; Thiel, W.; Ghosh, H.N.; Das, A. Phenol- and catechol-based ruthenium(II) polypyridyl complexes as colorimetric sensors for fluoride ions. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 46, 5576–5584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, B.; Adak, P.; Naskar, S.; Pakhira, B.; Mitra, P.; Dinda, R.; Chattopadhyay, S.K. Ruthenium(II) complexes of thiosemicarbazones: Synthesis, X-ray crystal structures, spectroscopy, electrochemistry, DFT studies and fluoride sensing properties. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2017, 459, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.K.; Ghosh, R.; Kennedy, P.; Mobin, S.M.; Das, D. Potential anion sensing properties by a redox and substitution series of [Ru(bpy)3-n(Hdpa)n]2+, n ¼ 1–3; Hdpa = 2,2’-dipyridylamine: Selective recognition and stoichiometric binding with cyanide and fluoride ions. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 62310–62319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyama, M.; Mishima, D.; Suganoya, R.; Nagao, N. C1-symmetrical cis-bis(di-2-pyridylamine)chloro(dimethyl sulfoxide-S) ruthenium(II) complex: Synthesis, crystal structure, and anion recognition using the NH groups in the chelating ligands. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2018, 478, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everett, E.T. Fluoride’s effects on the formation of teeth and bones, and the influence of genetics. J. Dent. Res. 2011, 90, 552–560. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Q.; Li, F.; Liu, S.; Yu, M.; Liu, Z.; Yi, T.; Huang, C. Highly selective phosphorescent chemosensor for fluoride based on an iridium(III) complex containing arylborane units. Inorg. Chem. 2008, 47, 9256–9264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, Y.; Park, S.Y. A phosphorescent Ir(III) complex for selective fluoride ion sensing with a high signal-to-noise ratio. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 3820–3826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.-J.; Liu, S.-J.; Zhao, X.-Y.; Sun, S.; Cheng, S.; Ma, T.-C.; Sun, H.-B.; Zhao, Q.; Huang, W. Cationic iridium(III) complex containing both triarylboron and carbazole moieties as a ratiometric fluoride probe that utilizes a switchable triplet–singlet emission. Chem. Eur. J. 2010, 16, 7125–7133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Liu, S.; Zhao, Q.; Ma, T.C.; Sun, S.; Zhao, X.Y.; Huang, W. A near-infrared phosphorescent probe for F− based on a cationic iridium(III) complex with triarylboron moieties. Sci. China Chem. 2011, 54, 1750–1758. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; Liu, S.; Sun, H.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, Q.; Sun, S.; Cheng, S.; Ma, T.; Zhou, L.; Huang, W. FRET-based probe for fluoride based on a phosphorescent iridium(III) complex containing triarylboron groups. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 7572–7581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.-J.; Liu, S.-J.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, N.; Liu, Z.-Q.; Xu, H.; Liang, H.; Zhao, Q.; Yu, X.-Q.; Huang, W. Synthesis, one- and two-photon photophysical and excited-state properties, and sensing application of a new phosphorescent dinuclear cationic iridium(III) complex. Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadavi, R.S.; Kim, H.; Lee, K.M.; Kim, T.; Lee, J.; Lee, Y.S.; Lee, M.H. Turning On MLCT Phosphorescence of Iridium(III)−Borane Conjugates upon Fluoride Binding. Organometallics 2012, 31, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Huang, Z.; Ho, C.-L.; Zhou, G.; Whang, D.R.; Yao, C.; Xu, X.; Park, S.Y.; Chuid, C.-H.; Wong, W.-Y. Dynamic dual stage phosphorescence chromatic change in a diborylated iridium phosphor for fluoride ion sensing with concentration discriminating capability. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 6553–6563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Kim, H.; Lee, Y.H.; Kim, T.; Lee, Y.S.; Lee, M.H. Heteroleptic cyclometalated iridium(III) complexes supported by triarylborylpicolinate ligand: Ratiometric turn-on phosphorescence response upon fluoride binding. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 53, 8672–8680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Tan, Q.; Liang, H.; Zhang, K.Y.; Liu, S.; Jiang, R.; Hu, R.; Xu, W.; Zhao, Q.; Huang, W. Phosphorescence switch and logic gate of iridium(III) complexes containing a triarylboron moiety triggered by fluoride and an electric field. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 1883–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.H.; Kim, S.; So, H.; Lee, J.H.; Hwang, H.; Lee, K.M. Intriguing ‘Turn-on’ phosphorescent response in the near infrared region upon fluoride binding: Dipyrromethene chelating-based triarylboryl-iridium(III) conjugates. Dyes Pigments 2020, 183, 108706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Liu, S.J.; Shi, M.; Li, F.Y.; Jing, H.; Yi, T.; Huang, C.H. Tuning photophysical and electrochemical properties of cationic iridium(III) complex salts with imidazolyl substituents by proton and anions. Organometallics 2007, 26, 5922–5930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayabharathi, J.; Sathishkumar, R.; Thanikachalam, V.; Jayamoorthy, K. Tuning photophysical and electrochemical properties of phosphorescent heteroleptic iridium complex salts–as chemosensors. J. Fluoresc. 2014, 24, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chena, K.; Schmittel, M. A triple-channel lab-on-a-molecule for triple-anion quantification using an iridium(III)–imidazolium conjugate. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 5756–5759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rommel, S.A.; Sorschea, D.; Rau, S. A supramolecular H-bond driven light switch sensor for small anions. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 74–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rommel, S.A.; Sorsche, D.; Dixit, A.; Rau, S. Interaction of an iridium(III)–bibenzimidazole complex with anions—Implications for luminescent sensing. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 2016, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Zhang, C.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, K.Y.; Zhou, X.; Jiang, J.; Xu, W.; Yang, T.; Huang, W. Dual-emissive polymer dots for rapid detection of fluoride in pure water and biological systems with improved reliability and accuracy. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.-B.; Wang, W.; Li, G.; Wang, R.-X.; Leung, C.-H.; Ma, D.-L. Luminescent iridium(III) chemosensor for tandem detection of F− and Al3+. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 9150–9155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nghia, N.V.; Oh, J.; Jung, J.; Lee, M.H. Deboronation-induced turn-on phosphorescent sensing of fluorides by iridium(III) cyclometalates with o-carborane. Organometallics 2017, 36, 2573–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bejoymohandas, K.S.; Kumar, A.; Sreenadh, S.; Varathan, E.; Varughese, S.; Subramanian, V.; Reddy, M.L.P. A highly selective chemosensor for cyanide derived from a formylfunctionalized phosphorescent iridium(III) complex. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 55, 3448–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, N.; Ou, H.-D.; Xu, Q.; Jin, Y.; Deng, W.; Yao, Z.-J. An efficient probe of cyclometallated phosphorescent iridium complex for selective detection of cyanide. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 4636–4645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Kim, H.J.; Shin, I.-S.; Hong, J.-I. Potential-dependent electrochemiluminescence for selective molecular sensing of cyanide. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 6019–6025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, Y.i.; Liu, Q.; Li, C.; Sun, L.; Li, F. Iridium(III) complex-coated nanosystem for ratiometric upconversion luminescence bioimaging of cyanide anions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 15276–15279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, Y. A simple empirical model describing the thermodynamics of hydration of ions of widely varying charges, sizes, and shapes. Biophys. Chem. 1994, 51, 111–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Yang, D.; Yang, X.-J.; Wu, B. Anion coordination chemistry: From recognition to supramolecular assembly. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2019, 378, 415–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, A.; Mondal, S.; Mondal, S.; Ghosh, P. A bis-heteroleptic imidazolium-bipyridine functionalized iridium(III)complex for fluorescence lifetime-based recognition and sensing of phosphates. Chem. Asian J. 2022, 17, e202200393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabha, M.; Sen, B.; Sheet, S.K.; Aguan, K.; Khatua, S. Cyclometalated iridium(III) complex of a 1,2,3- triazole-based ligand for highly selective sensing of pyrophosphate ion. Dalton Trans. 2022, 51, 11372–11380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewandowski, T.A.; Peterson, M.K.; Charnley, G. Iodine supplementation and drinking–water perchlorate mitigation. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 80, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucharzyk, K.H.; Crawford, R.L.; Cosens, B.; Hess, T. Development of drinking water standards for perchlorate in the United States. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 91, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Guan, W.; Du, S.; Zhu, D.; Shan, G.; Zhu, X.; Yan, L.; Su, Z.; Bryce, M.R.; Monkman, A.P. Anion-specific aggregation induced phosphorescence emission (AIPE) in an ionic iridium complex in aqueous media. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 16924–16927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, D.; Ni, S. Highly selective sensing of ClO4− in water with a simple cationic iridium(III) complex and its application in bioimaging. J. Photochem. Photobiol. 2016, 324, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, D.; Zhang, Y.; Chao, D.; Zhang, Y. A water–soluble cationic Ir(III) complex for turn–on sensing of ClO4− based on aggregation–induced emission. Sens. Actuators B 2017, 245, 599–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodall, W.; Williams, J.A.G. Iridium(III) bis-terpyridine complexes incorporating pendent N-methylpyridinium groups: Luminescent sensors for chloride ions. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 2000, 17, 2893–2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qinghai, S.; Bats, J.W.; Schmittel, M. Two closely related iridium(III) complexes as colorimetric and fluorometric chemodosimeters for nitrite in aqueous solution operating along different modes of action. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 50, 10531–10533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Fan, C.; Pu, S. A cyclometalated iridium(III) complex-based luminescent probe for HCO3− and CO32− detection and its application by test strips. Microchem. J. 2020, 158, 105166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Shangguan, M.; Zeng, X.; Guo, Y.; Wang, T.; Hou, L. Phosphorescent iridium(III) complex for efficient sensing of hypochlorite and imaging in living cells. Anal. Biochem. 2020, 592, 113573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Z.X.; Su, Z.S.; Chai, L.; Li, C.H.; Liu, R.; Lv, Y. Multimodal imaging iridium (III) complex for hypochlorous acid in living systems. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 8285–8291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, S.; Lu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Wang, J.; Qiao, Z.; Shen, R.; Zhang, J.; Hou, L. A novel mitochondria-targeted phosphorescence probe for hypochlorite ions detection in living cells. Talanta 2020, 209, 120516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, Z.X.; Zhang, K.X.; Zhang, L.C.; Li, Q.Y.; Lv, Y. Development of iridium(III) phosphorescent probe for hypochlorous acid detection in macrophages cells and cancer cells co-culture system and application in inflamed mouse model. Sens. Actuators B 2020, 303, 127016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Shangguan, M.; Lu, Z.; Yi, S.; Jiang, X.; Jiang, H. A cyclometalated iridium (III) complex-based fluorescence probe for hypochlorite detection and its application by test strips. Anal. Biochem. 2019, 566, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

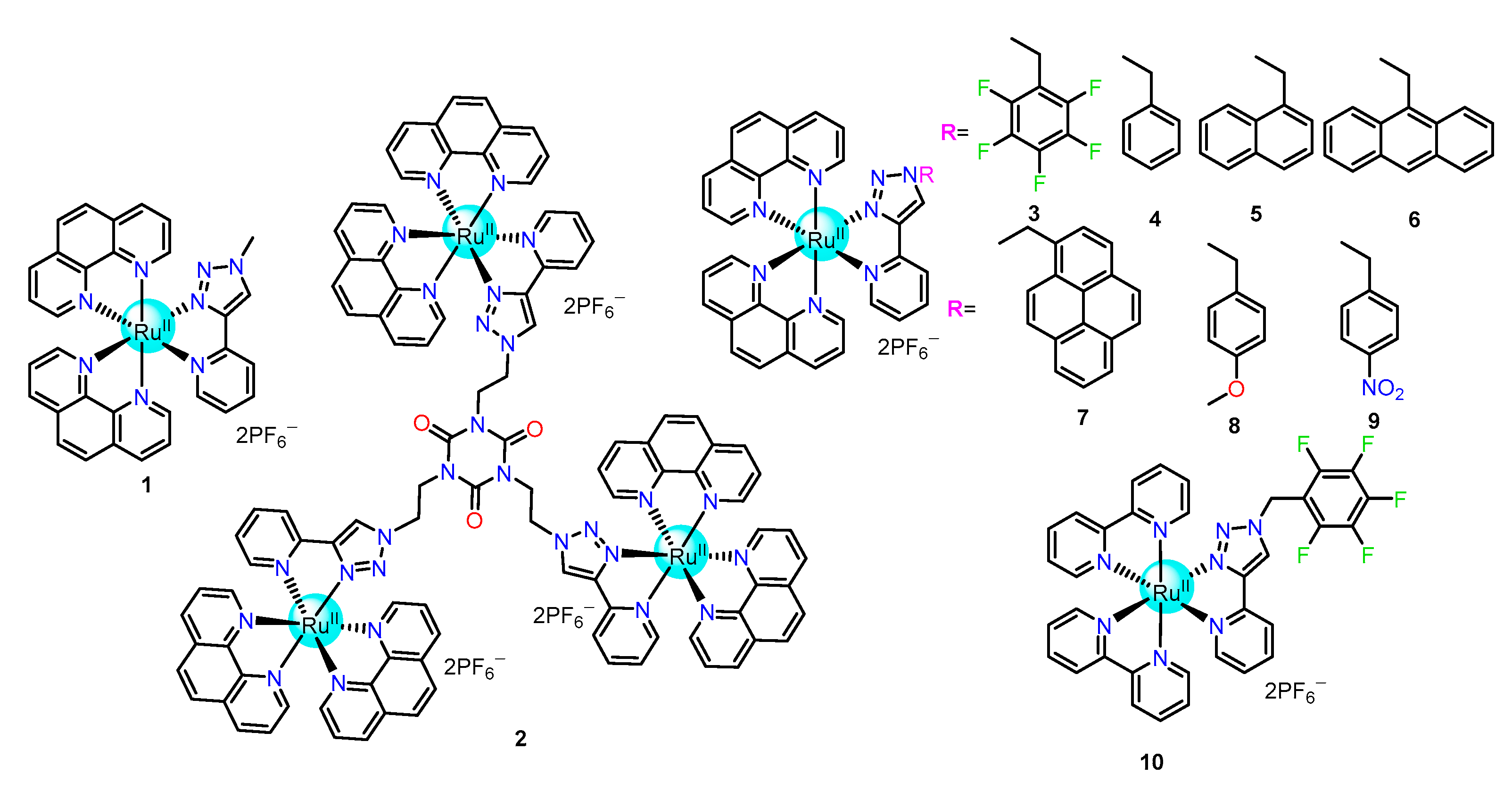
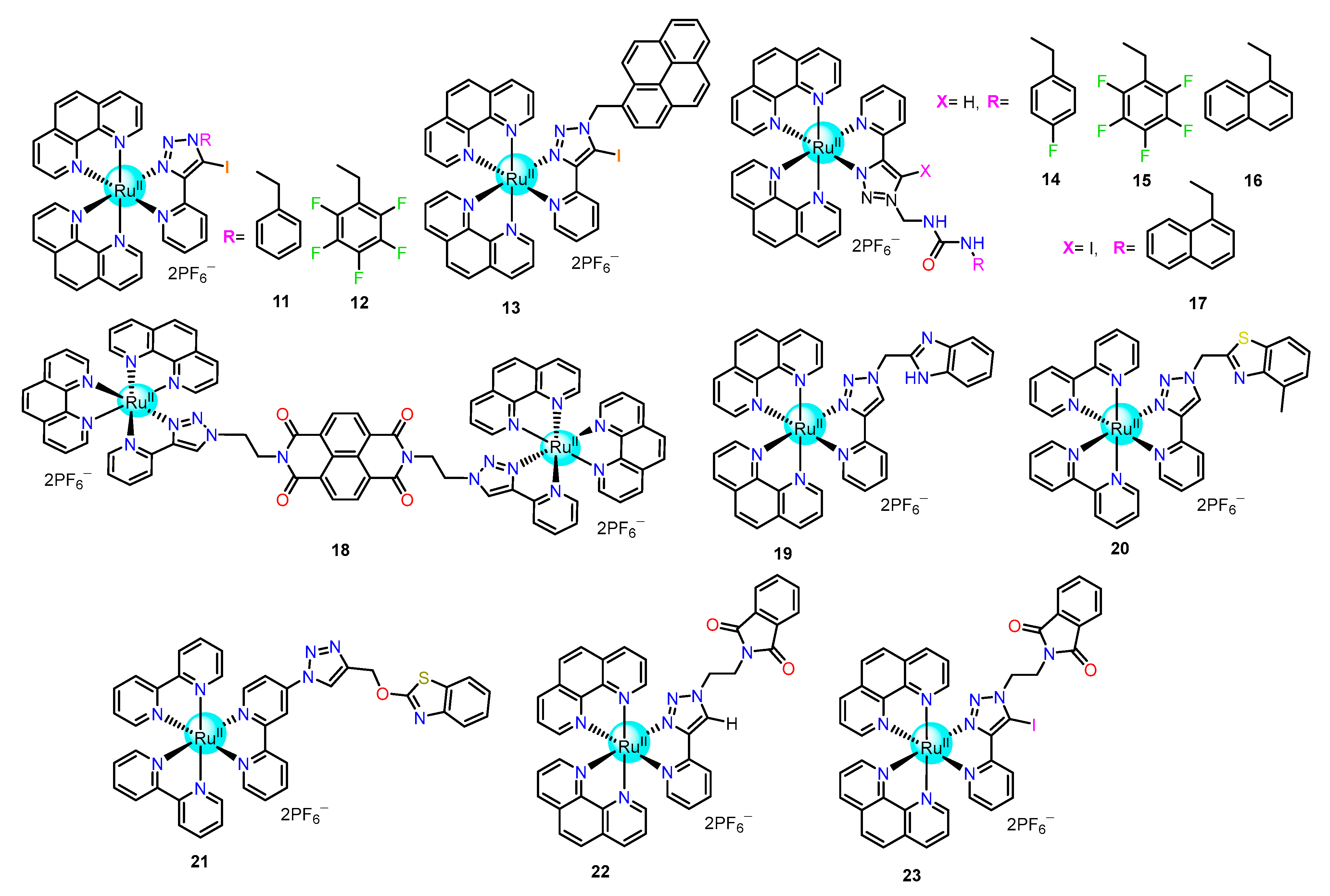

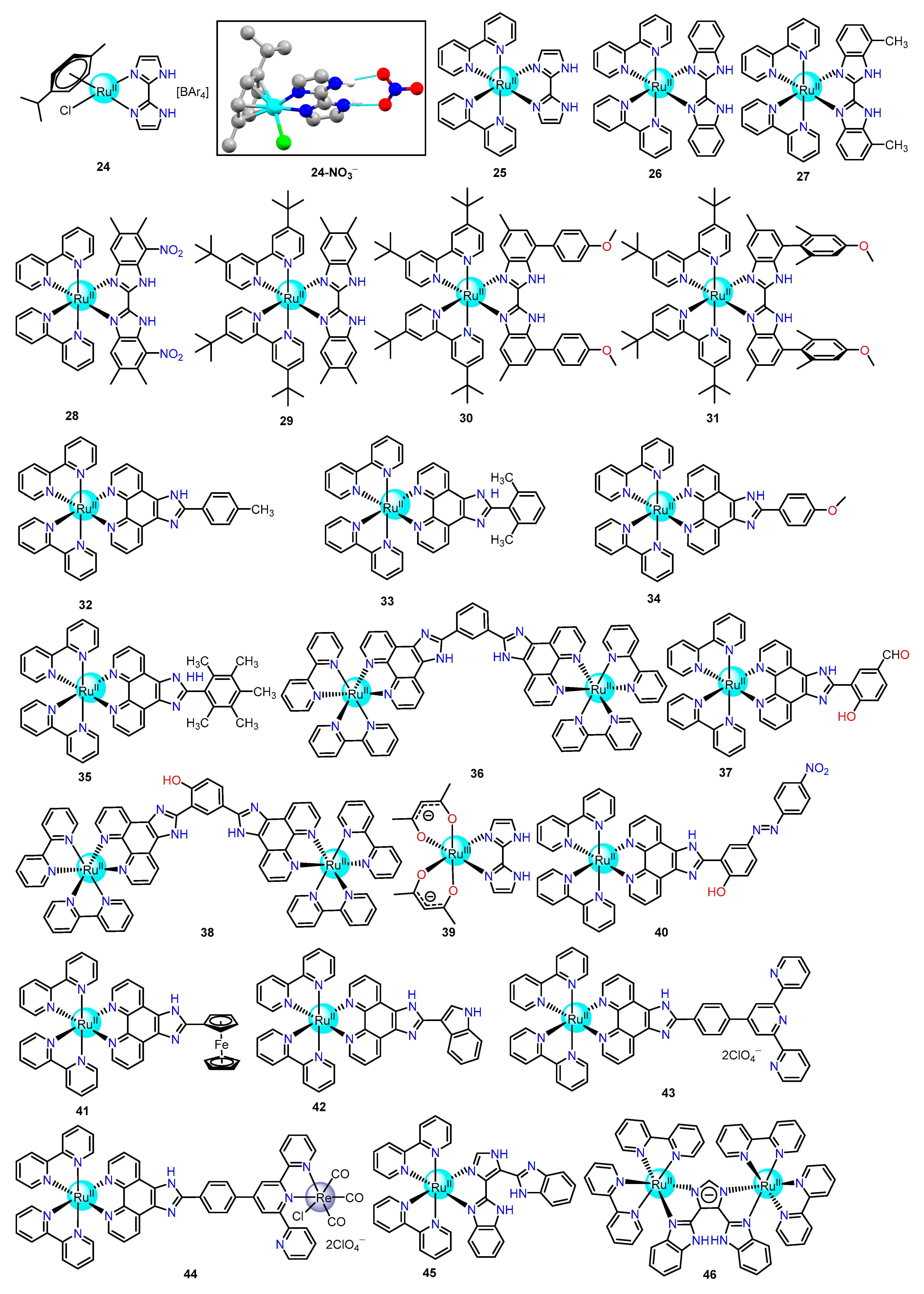

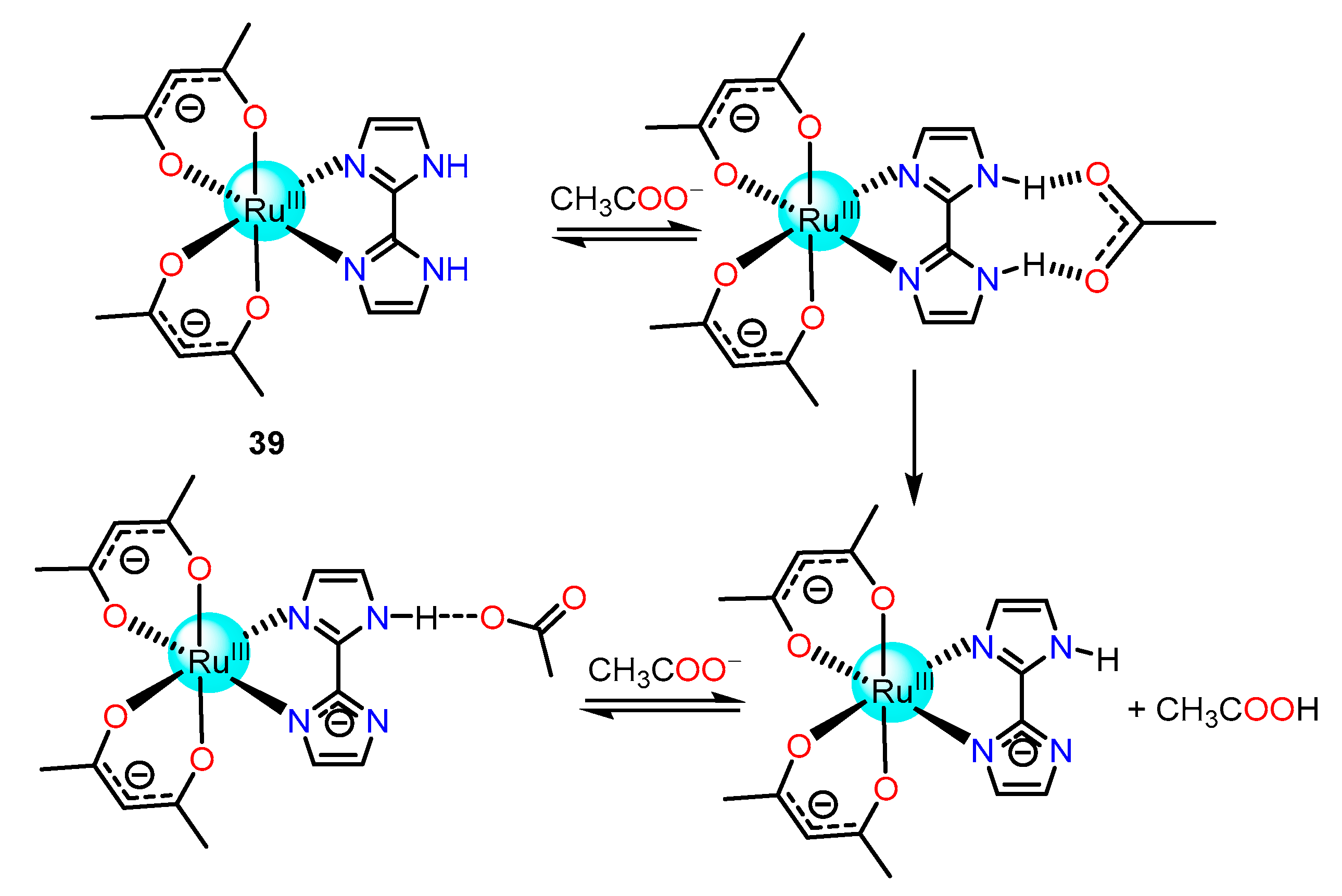







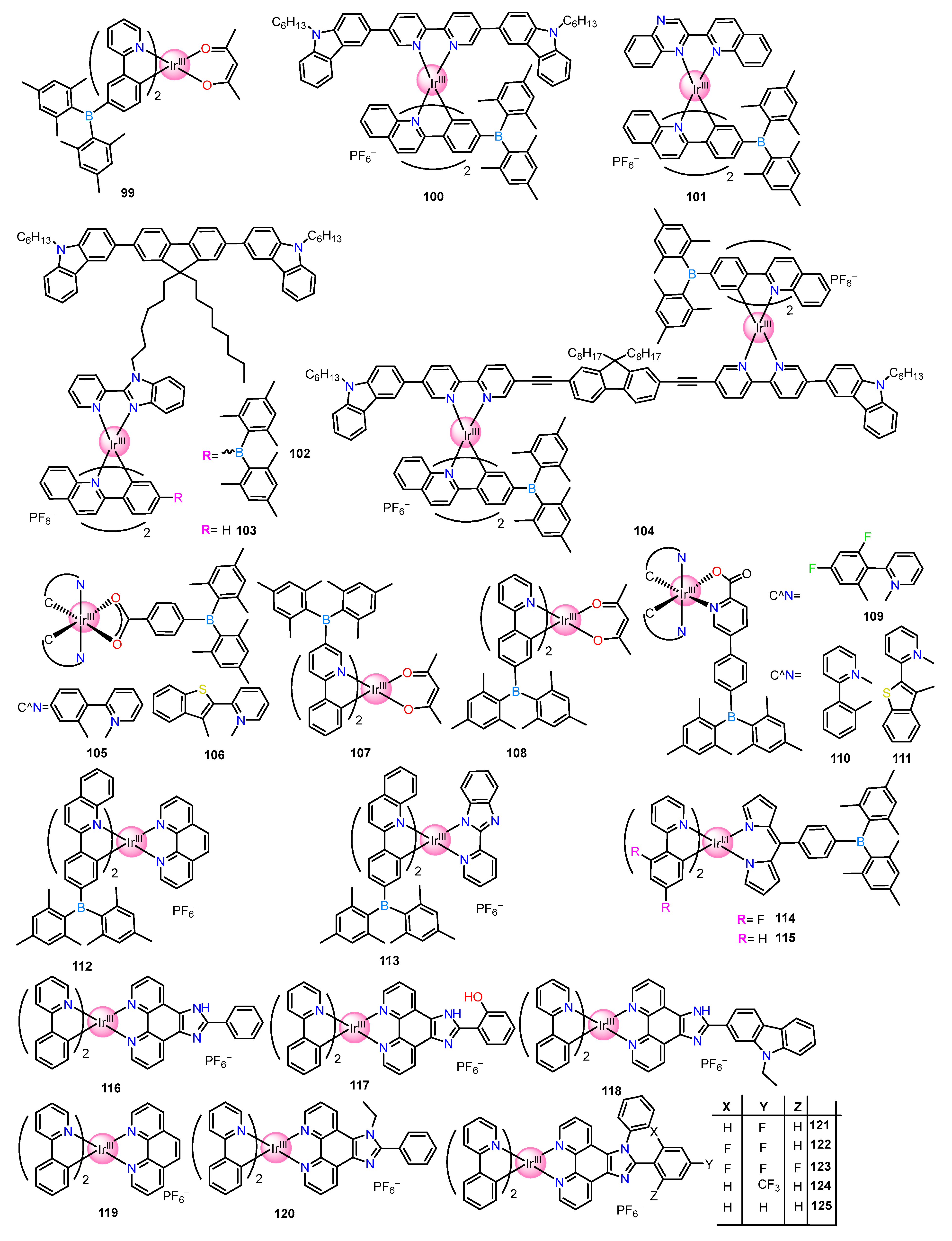

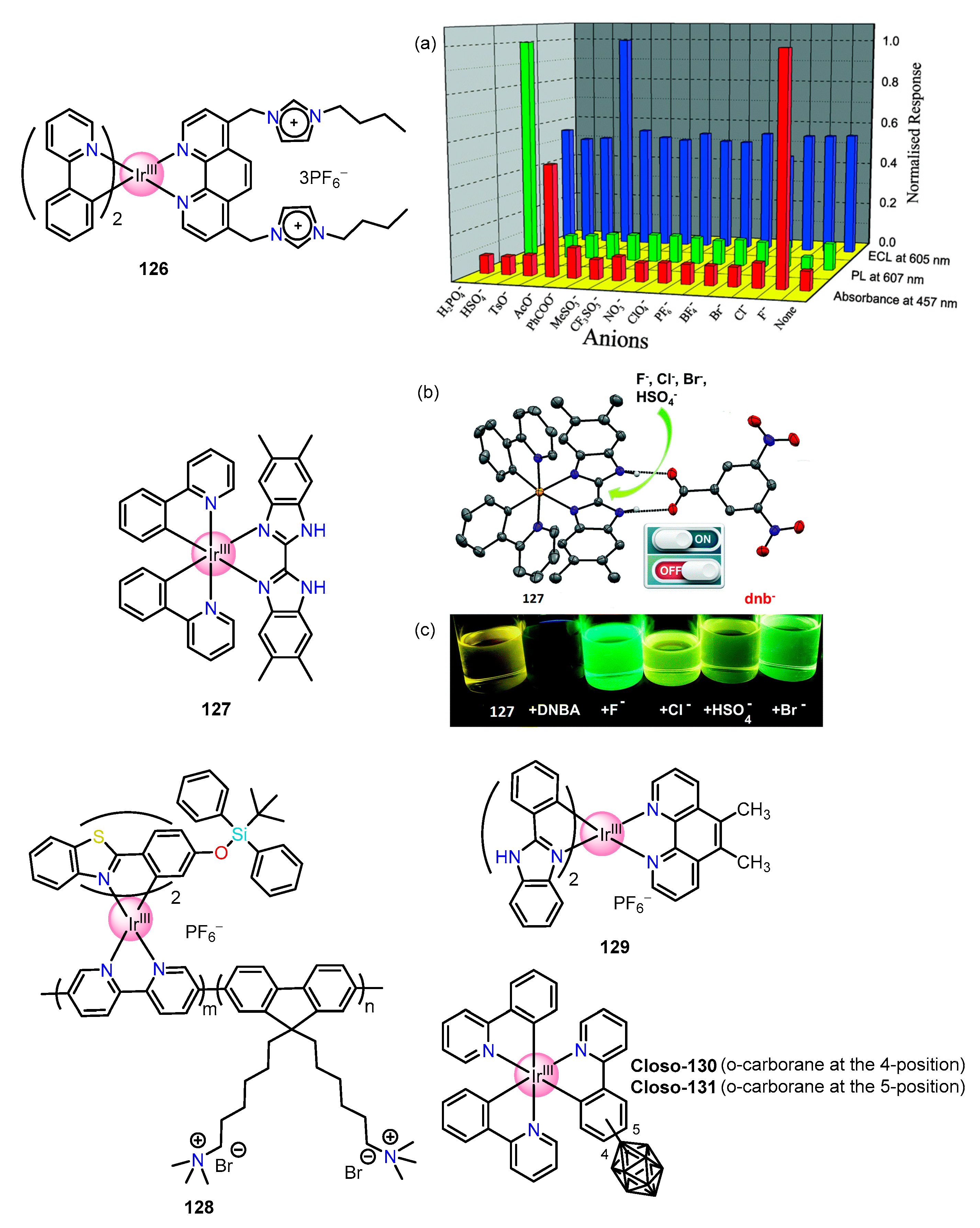
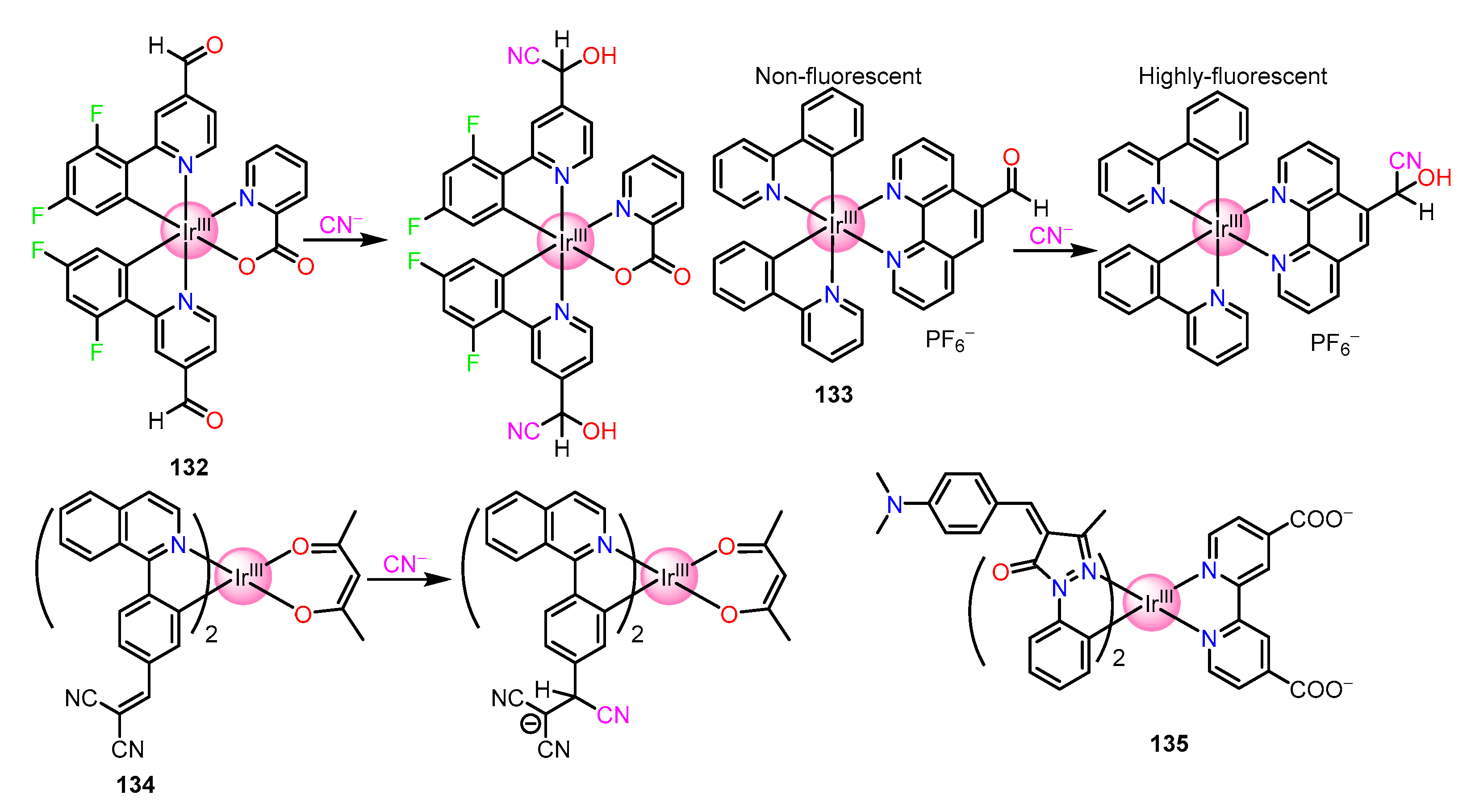

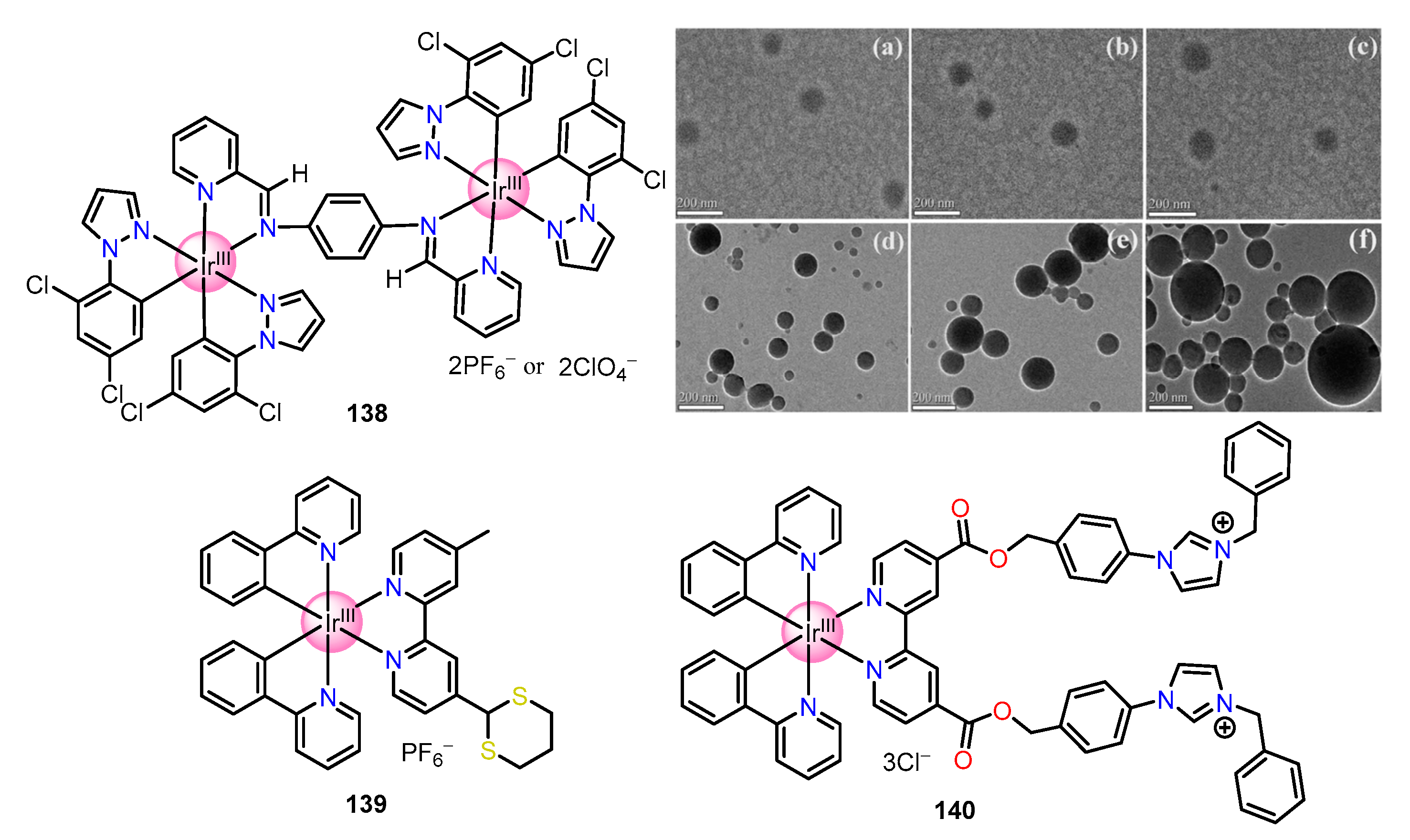
| Recognition/Sensing Units | Authors and References |
|---|---|
| Triazole/iodo-triazole | Ghosh [52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61], Khatua [62,63], Anandan [64,65] |
| Imidazole/benzimidazole Amide/Sulphonamide/Picolinamide Pyrrol Urea Aldehyde phenol and catechol thiosemicarbazones dimesityboryl dicyanovinyl | Ye [69,70,71,72,74], Rau [73,131],Wang [79,80,81], Baitalik [82,83,84,85,86,87], Huang [127], Ghosh [141], Khatua [142], Chao [147] Rajagopal [90], Pinet [92], Sun [93], Lin [94], Zhong [96] Sessler [98,99], Anzenbacher [100] Das [103], Gunnlaugsson [104], Fabbrizzi [105], Yao [106] Schmittel [108], Yao [109,136], Reddy [135] Das [111] Chattopadhyay [112] Huang [116,121,125], Park [117], Huan [118,119,120], Lee [124,126] Hong [137] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rashid, A.; Mondal, S.; Ghosh, P. Development and Application of Ruthenium(II) and Iridium(III) Based Complexes for Anion Sensing. Molecules 2023, 28, 1231. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031231
Rashid A, Mondal S, Ghosh P. Development and Application of Ruthenium(II) and Iridium(III) Based Complexes for Anion Sensing. Molecules. 2023; 28(3):1231. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031231
Chicago/Turabian StyleRashid, Ambreen, Sahidul Mondal, and Pradyut Ghosh. 2023. "Development and Application of Ruthenium(II) and Iridium(III) Based Complexes for Anion Sensing" Molecules 28, no. 3: 1231. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031231
APA StyleRashid, A., Mondal, S., & Ghosh, P. (2023). Development and Application of Ruthenium(II) and Iridium(III) Based Complexes for Anion Sensing. Molecules, 28(3), 1231. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031231





