Photocatalytic Degradation of Methyl Orange and Methylene Blue Dyes by Engineering the Surface Nano-Textures of TiO2 Thin Films Deposited at Different Temperatures via MOCVD
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Shan, A.Y.; Ghazi, T.I.M.; Rashid, S.A. Immobilisation of titanium dioxide onto supporting materials in heterogeneous photocatalysis: A review. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2010, 389, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Mao, S.S. Titanium Dioxide Nanomaterials: Synthesis, Properties, Modifications, and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcello, B.A.; Correa, O.V.; Bento, R.T.; Pillis, M.F. Effect of Growth Parameters on the Photocatalytic Performance of TiO2 Films Prepared by MOCVD. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2020, 31, 1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rico, V.; Romero, P.; Hueso, J.; Espinós, J.; González-Elipe, A. Wetting angles and photocatalytic activities of illuminated TiO2 thin films. Catal. Today 2009, 143, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharti, B.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, R. Superhydrophilic TiO2 thin film by nanometer scale surface roughness and dangling bonds. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 364, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Khan, S.A.; Shah, J.; Kotnala, R.K.; Mohapatra, S. Nanostructured TiO2 thin films prepared by RF magnetron sputtering for photocatalytic applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 422, 953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerbasi, R.; Bolzan, M.; el Habra, N.; Rossetto, G.; Schiavi, L.; Strini, A.; Barison, S. Photocatalytic Activity Dependence on the Structural Orientation of MOCVD TiO2 Anatase Films. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2009, 156, K233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miquelot, A.; Debieu, O.; Rouessac, V.; Villeneuve, C.; Prud’homme, N.; Cure, J.; Constantoudis, V.; Papavieros, G.; Roualdes, S.; Vahlas, C. TiO2 nanotree films for the production of green H2 by solar water splitting: From microstructural and optical characteristics to the photocatalytic properties. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 494, 1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krumdieck, S.; Gorthy, R.; Gardecka, A.J.; Lee, D.; Miya, S.S.; Talwar, S.D.; Polson, M.I.J.; Bishop, C. Surf Characterization of photocatalytic, wetting and optical properties of TiO2 thin films and demonstration of uniform coating on a 3-D surface in the mass transport. Coat. Technol. 2017, 326, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifa, Z.S.; Mahmoud, S.A. Photocatalytic and optical properties of titanium dioxide thin films prepared by metalorganic chemical vapor deposition. Physica E 2017, 91, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendieta-Reyes, N.E.; Cheuquepán, W.; Rodes, A.; Gómez, R. Spectroelectrochemical Study of CO2 Reduction on TiO2 Electrodes in Acetonitrile. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selloni, A. Anatase shows its reactive side. Nat. Mater. 2008, 7, 613–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzeri, M.; Vittadini, A.; Selloni, A. Structure and energetics of stoichiometric TiO2 anatase surfaces. Phys. Rev. B 2001, 63, 155409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diebold, U.; Ruzycki, N.; Herman, G.; Selloni, A. One step towards bridging the materials gap: Surface studies of TiO2 anatase. Catal. Today 2003, 85, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, P.M.; Watson, G.W.; Kelsey, E.T.; Parker, S.C. Atomistic simulation of the surface structure of the TiO2 polymorphs rutileand anatase. J. Mater. Chem. 1997, 7, 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Liu, G.; Lu, G.Q.; Cheng, H.-M. On the True Photoreactivity Order of {001}, {010}, and {101} Facets of Anatase TiO2 Crystals. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, N.; Sohn, Y.; Pradhan, D. Synergy of Low-Energy {101} and High-Energy {001} TiO2 Crystal Facets for Enhanced Photocatalysis. ASC Nano 2013, 7, 2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, T.; Sarukawa, K.; Matsumura, M. Crystal faces of rutile and anatase TiO2 particles and their roles in photocatalytic reactions. New J. Chem. 2002, 26, 1167–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taguchi, T.; Saito, Y.; Sarukawa, K.; Ohno, T.; Matsumura, M. Formation of new crystal faces on TiO2 particles by treatment with aqueous HF solution or hot sulfuric acid. New J. Chem. 2003, 27, 1304–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borras, A.; González-Elipe, A.R. Wetting Properties of Polycrystalline TiO2 Surfaces: A Scaling Approach to the Roughness Factors. Langmuir 2010, 26, 15875–15882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garlisi, C.; Scandura, G.; Palmisano, G.; Chiesa, M.; Lai, C.-Y. Influence of oxygen partial pressure on wettability and photocatalytic properties of TiO2 films grown by RF magnetron sputtering. Langmuir 2016, 32, 11813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco, E.; Domínguez, M.; González-Leal, J.; Márquez, E.; Outón, J.; Ramírez-Del-Solar, M. Insights into the annealing process of sol-gel TiO2 films leading to anatase development: The interrelationship between microstructure and optical properties. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 439, 736–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifa, Z.S. EFFECT OF DEPOSITION TEMPERATURE ON THE PROPERTIES OF TIO2 THIN FILMS DEPOSITED BY MOCVD. Surf. Rev. Let. 2016, 23, 165001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifa, Z.; Lin, H.; Shah, S.I. Structural and electrochromic properties of TiO2 thin films prepared by metallorganic chemical vapor deposition. Thin Solid Films 2010, 518, 5457–5462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaban, M.; Almohammedi, A.; Saad, R.; El Sayed, A.M. Design of SnO2:Ni,Ir Nanoparticulate Photoelectrodes for Efficient Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dafinone, M.I.; Feng, G.; Brugarolas, T.; Tettey, K.E.; Lee, D. Mechanical Reinforcement of Nanoparticle Thin Films Using Atomic Layer Deposition. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 5078–5087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyauchi, M.; Kieda, N.; Hishita, S.; Mitsuhashi, T.; Nakajima, A.; Watanabe, T.; Hashimoto, K. Reversible wettability control of TiO2 surface by light irradiation. Surf. Sci. 2002, 511, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanov, B.I.; Niklasson, G.A.; Granqvist, C.G.; Österlund, L. Quantitative relation between photocatalytic activity and degree of <001> orientation for anatase TiO2 thin films, J. Mate. Chem. A 2015, 3, 1739. [Google Scholar]
- Stefanov, B.I.; Niklasson, G.A.; Granqvist, C.G.; Österlund, L. Gas-phase photocatalytic activity of sputter-deposited anatase TiO2 films: Effect of< 0 0 1> preferential orientation, surface temperature and humidity. J. Catal. 2016, 335, 187. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Nie, X.; Chen, J.; Wong, P.K.; An, T.; Yamashita, H.; Zhao, H. Enhanced simultaneous PEC eradication of bacteria and antibiotics by facilely fabricated high-activity {001} facets TiO2 mounted onto TiO2 nanotubular photoanode. Water Res. 2016, 101, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Yu, J.; Cheng, B. Facile preparation of Na-free anatase TiO2 film with highly photocatalytic activity on soda-lime glass. Catal. Commun. 2006, 7, 1000–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, Y.-H.; Chang, T.-F.; Chen, C.-Y.; Sone, M.; Hsu, Y.-J. Mechanistic Insights into Photodegradation of Organic Dyes Using Heterostructure Photocatalysts. Catalysts 2019, 9, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khataeea, A.R.; Kasiri, M.B. Impact of Powdered Activated Carbon and Anion Exchange Resin on Photocatalytic Treatment of Textile Wastewater. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2010, 328, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Guillard, C.; Lachheb, H.; Houas, A.; Ksibi, M.; Elaloui, E.; Herrmann, J.-M. Influence of chemical structure of dyes, of pH and of inorganic salts on their photocatalytic degradation by TiO2 comparison of the efficiency of powder and supported TiO2. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2003, 158, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, C.H.; Fu, C.-C.; Juang, R.-S. Degradation of methylene blue and methyl orange by palladium-doped TiO2 photocatalysis for water reuse: Efficiency and degradation pathways. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 202, 413–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trandafilović, L.V.; Jovanović, D.J.; Zhang, X.; Ptasińska, S.; Dramićanin, M.D. Enhanced photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue 524 and methyl orange by ZnO:Eu nanoparticles. Appl. Catal. B 2017, 203, 740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salah, D.; Hamd, A.; Soliman, N.K.; Elzanaty, A.M.; Alanazi, A.M.; Shaban, M.; El-Sayed, R.; Ahmed, S.A. Polyaniline/Glauconite Nanocomposite Adsorbent for Congo Red Dye from Textile Wastewater. Separations 2022, 9, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, F.; Hassaballa, S.; Shaban, M.; Ahmed, A.M. Highly Efficient Photocatalyst Fabricated from the Chemical Recycling of Iron Waste and Natural Zeolite for Super Dye Degradation. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaban, M.; Mustafa, M.; El Sayed, A. Structural, optical, and photocatalytic properties of the spray deposited nanoporous CdS thin films; influence of copper doping, annealing, and deposition parameters. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process 2016, 56, 329–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupa, A.V.; Manikandan, D.; Divakar, D.; Sivakumar, T. Effect of deposition of Ag on TiO2 nanoparticles on the photodegradation of Reactive Yellow-17. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 147, 906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaban, M.; Ahmed, A.M.; Shehata, N.; Betiha, M.A.; Rabie, A.M. Ni-doped and Ni/Cr co-doped TiO2 nanotubes for enhancement of photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2019, 555, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaban, M.; Elwahab, F.A.; Ghitas, A.E.; Zayat, M.Y. Efficient and recyclable photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue dye in aqueous solutions using nanostructured Cd1 − xCoxS films of different doping levels. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2020, 95, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zayed, M.; Ahmed, A.M.; Shaban, M. Synthesis and characterization of nanoporous ZnO and Pt/ZnO thin films for dye degradation and water splitting applications. Inter. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 17630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojviroon, T.; Rojviroon, O.; Sirivithayapakorn, S.; Angthong, S. Application of TiO2 nanotubes as photocatalysts for decolorization of synthetic dye wastewater. Water Resour. Ind. 2021, 26, 100163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhaya, D.; Kumar, P.; Purkayastha, D.D. Superhydrophobic ZnO/TiO2 heterostructure with significantly enhanced photocatalytic activity. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 10399–10407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, B.; Guo, J.; Zhang, L.; Ma, H. Magnetron sputtered TiO2/CuO heterojunction thin films for efficient photocatalysis of Rhodamine B. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 903, 163851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanguino, A.; Diaz-Uribe, C.; Duran, F.; Vallejo, W.; Guzman, L.; Ruiz, D.; Puello, E.; Quiñones, C.; Schott, E.; Zarate, X. Photocatalytic Degradation of Methylene Blue under Visible Light Using TiO2 Thin Films Impregnated with Porphyrin and Anderson-Type Polyoxometalates (Cu and Zn). Catalysts 2022, 12, 1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Uribe, C.; Duran, F.; Vallejo, W.; Puello, E.; Zarate, X.; Schott, E. Photocatalytic study of TiO2 thin films modified with Anderson-type polyoxometalates (Cr, Co and Ni): Experimental and DFT study. Polyhedron 2023, 231, 116253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safiay, N.M.; Khusaimi, Z.; Asib, N.A.M.; Rani, R.A.; Azhar, N.E.A.; Hamzah, F.; Rusop, M. Visible-Light Photocatalysis Using Nb-doped TiO2 Nanoparticles Synthesized Via Facile Sol-gel Method. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Regional Symposium on Micro and Nanoelectronics (RSM), Putrajaya, Malaysia, 21–23 August 2019; pp. 57–60. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.-F.; Wang, C.-W. Photocatalysis and characterization of the gel-derived TiO2 and P–TiO2 transparent thin films. Thin Solid Films 2011, 519, 6453–6458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensouici, F.; Bououdina, M.; Dakhel, A.; Tala-Ighil, R.; Tounane, M.; Iratni, A.; Souier, T.; Liu, S.; Cai, W. Optical, structural and photocatalysis properties of Cu-doped TiO2 thin films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 395, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-González, M.; Tomás, S.; Santoyo-Salazar, J.; Gallardo-Hernández, S.; Tellez-Cruz, M.; Solorza-Feria, O. Sol-gel synthesis of Ag-loaded TiO2-ZnO thin films with enhanced photocatalytic activity. J. Alloy. Compd. 2018, 779, 908–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radić, N.; Grbić, B.; Petrović, S.; Stojadinović, S.; Stefanov, P. Effect of cerium oxide doping on the photocatalytic properties of rutile TiO2 films prepared by spray pyrolysis. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2020, 599, 412544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marathe, S.D.; Shrivastava, V.S. Photocatalytic removal of hazardous Ponceau S dye using Nano structured Ni-doped TiO2 thin film prepared by chemical method. Appl. Nanosci. 2014, 5, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
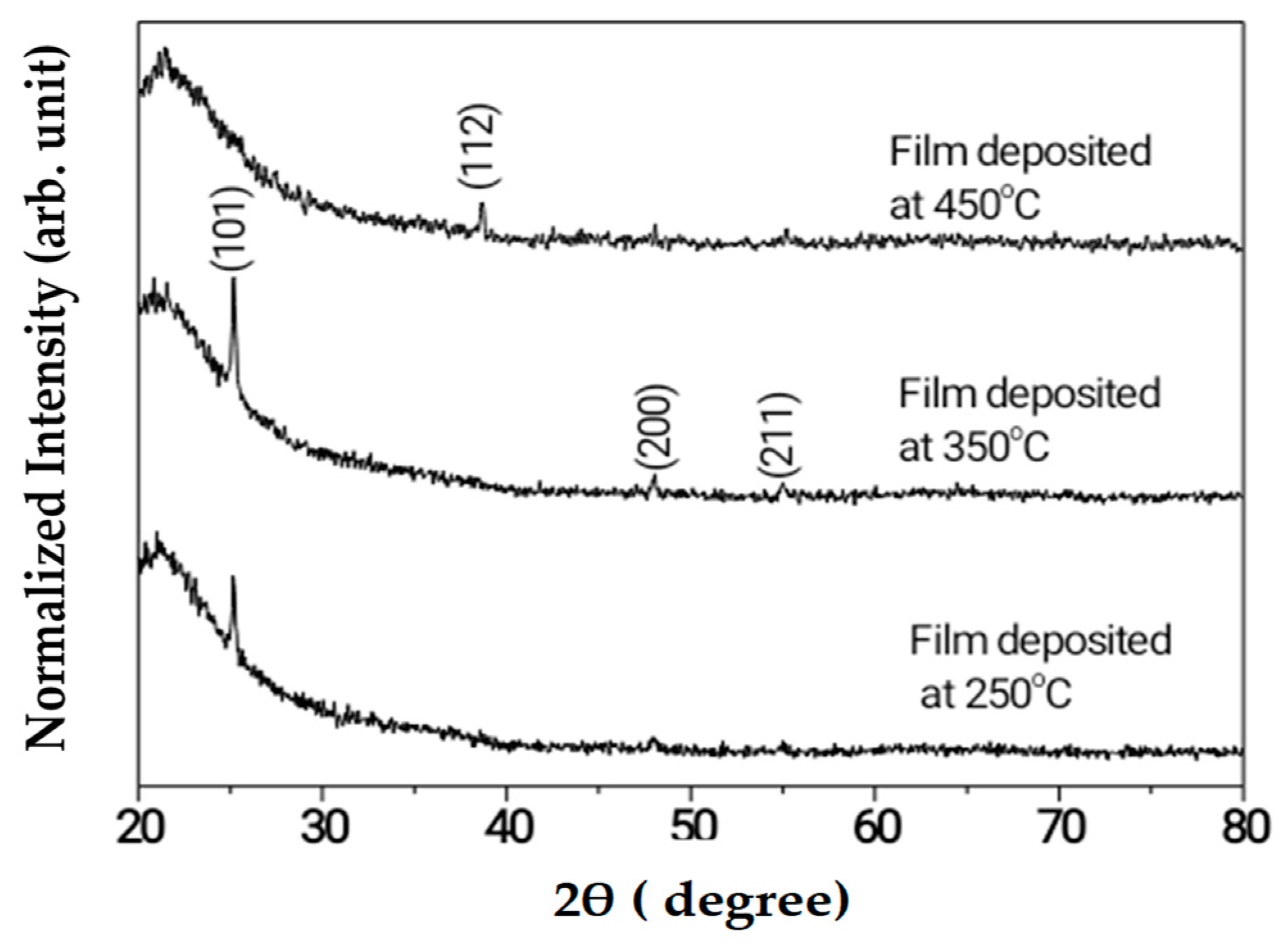
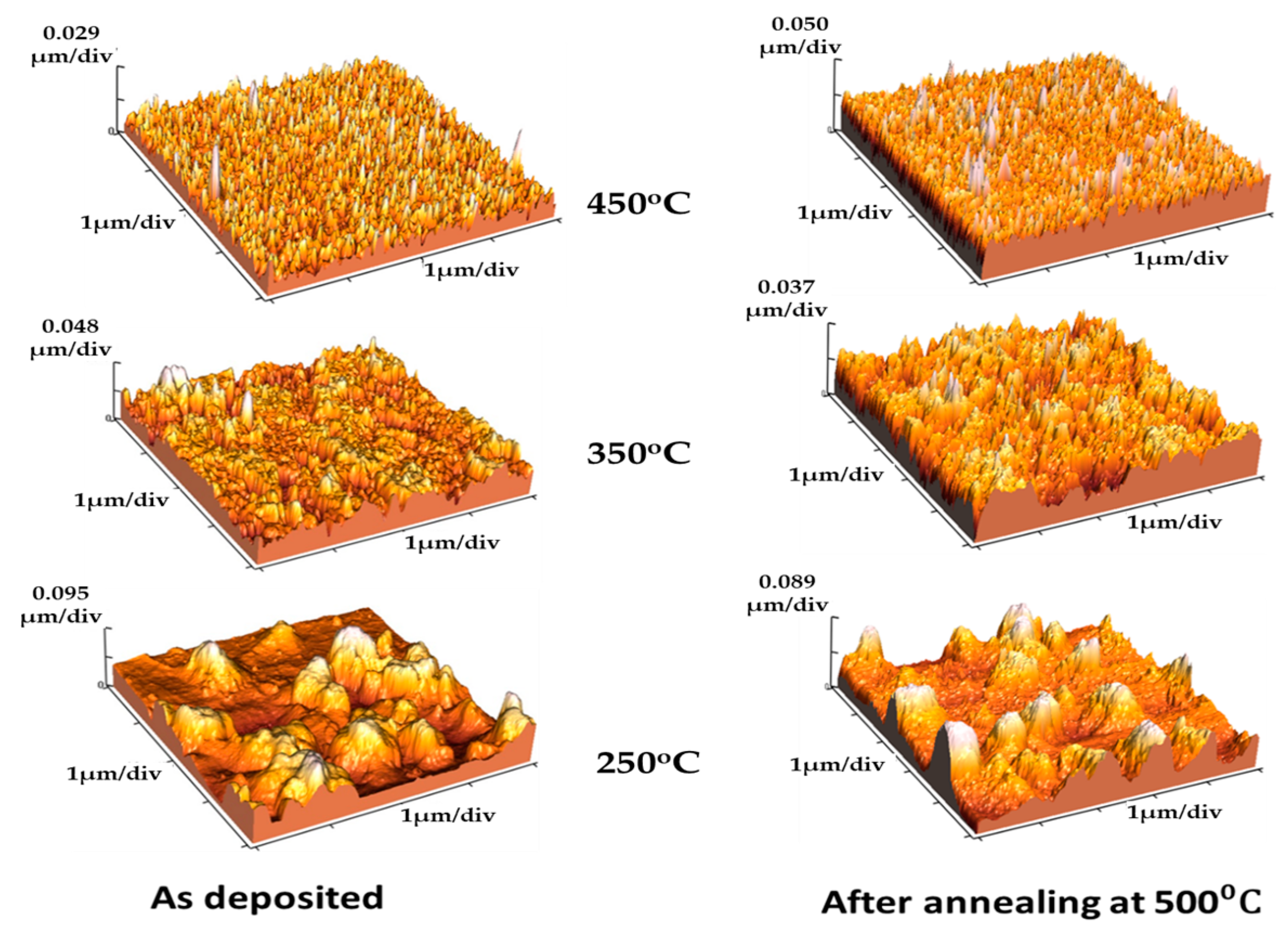


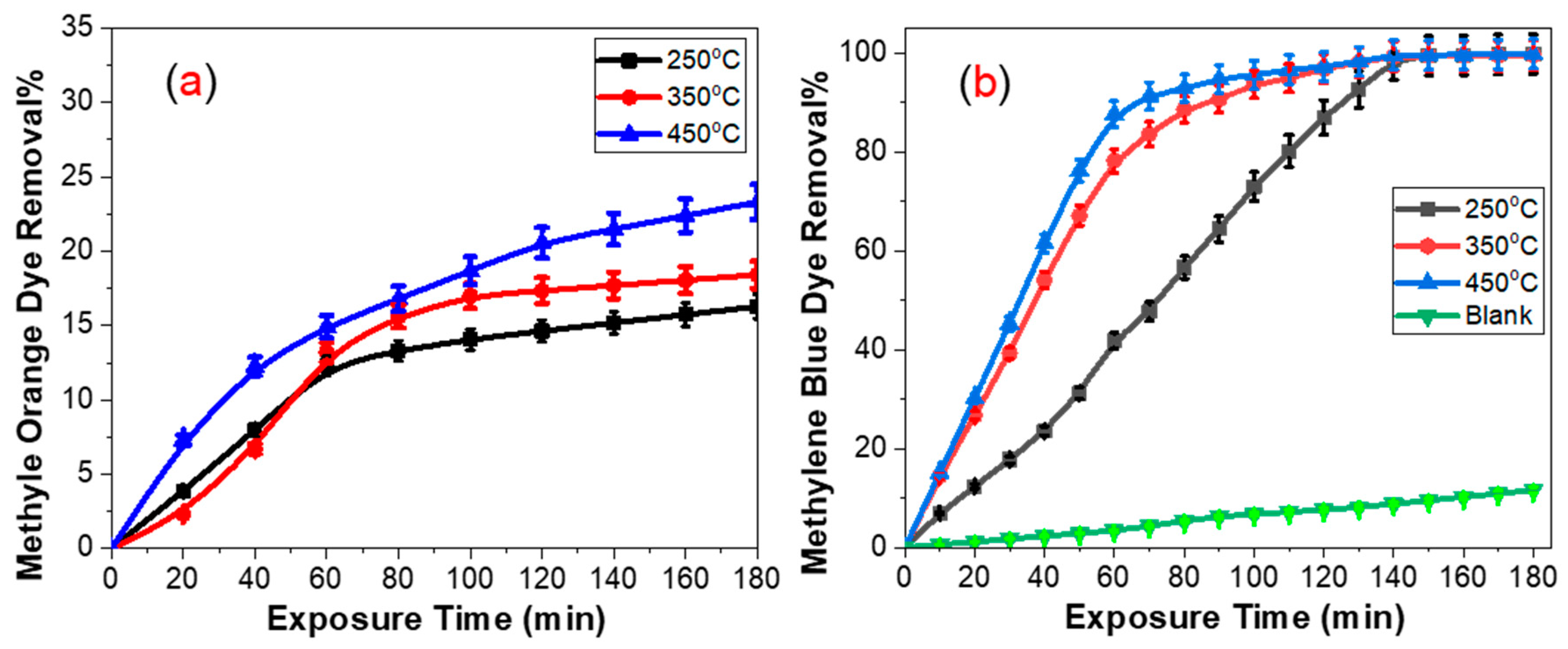

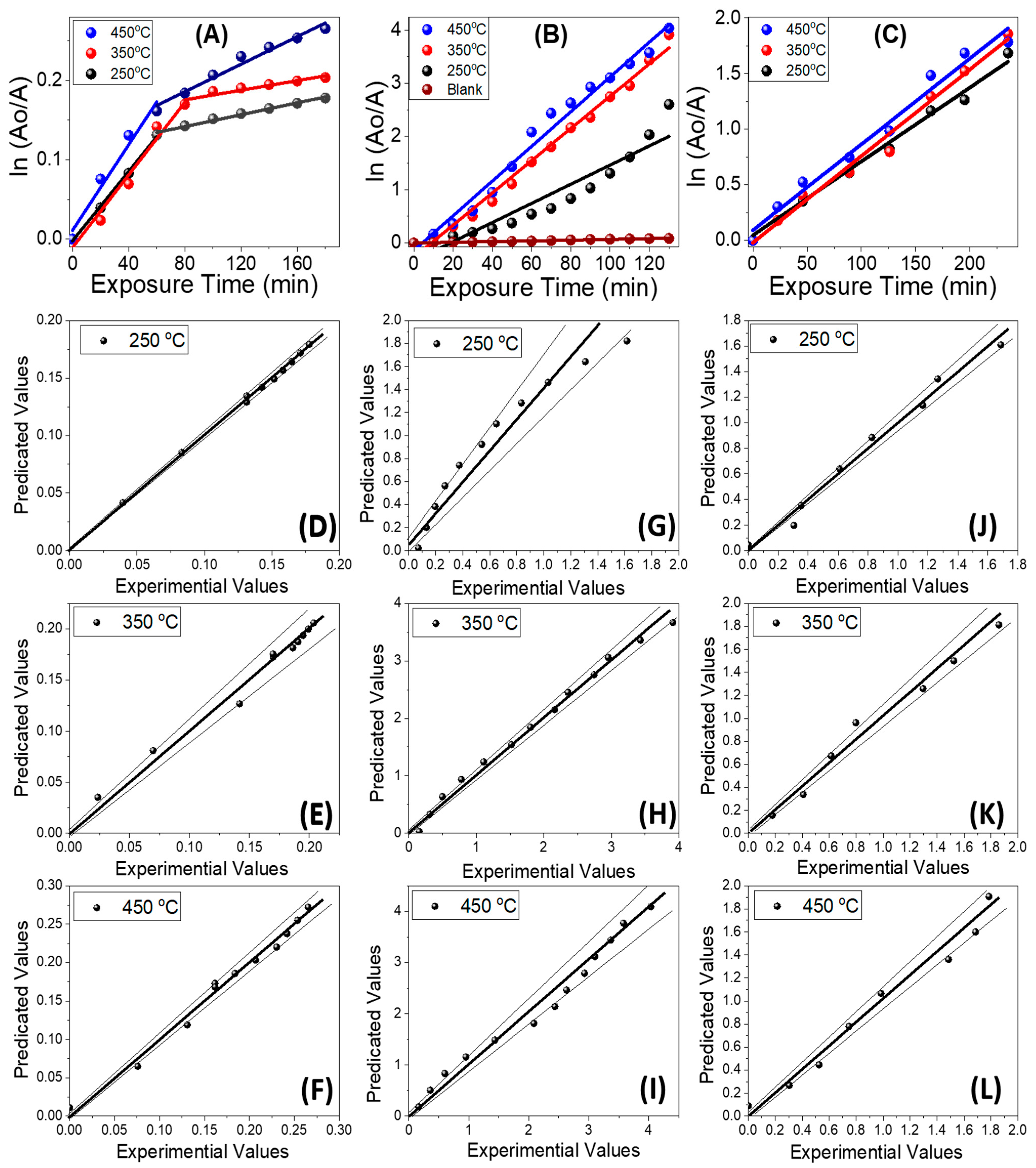
| Projected Area (μm2) | Average Roughness (Ra) (nm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 250 °C | 350 °C | 450 °C | ||
| As deposited | 16 | 27.15 | 8.94 | 3.92 |
| Annealed at 500 °C | 25 | 26.11 | 9.54 | 6.59 |
| Contact angle measurements For as-deposited films | 39° ± 5° | 41° ± 5° | 51° ± 5° | |
| Sample | MO Before Annealing | MB | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before Annealing | After Annealing | |||||
| Parameters | kR (min−1) | R2 | kR (min−1) | R2 | kR (min−1) | R2 |
| 250 °C | (220 ± 7) × 10−5 | 0.9990 | (18 ± 2) × 10−3 | 0.9437 | (67 ± 3) × 10−4 | 0.9933 |
| (37 ± 2) × 10−5 | 0.9934 | |||||
| 350 °C | (23 ± 2) × 10−4 | 0.9900 | (303 ± 9) × 10−4 | 0.9943 | (78 ± 4) × 10−4 | 0.9940 |
| (30 ± 5) × 10−5 | 0.9495 | |||||
| 450 °C | (27 ± 4) × 10−4 | 0.9831 | (33 ± 1) × 10−3 | 0.9919 | (77 ± 5) × 10−4 | 0.9901 |
| (87± 6) × 10−5 | 0.9901 | |||||
| Catalyst | Morphology | Synthesize Technique | Dye/Light Source | Removal% | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TiO2 sheets | TiO2 nanotubes | Electrochemical anodization | 180 min UVA irradiation and 4 μM initial dye concentration | 74.14% (indigo carmine) 65.71% reactive black 5 (RB5) | [44] |
| ZnO/TiO2 TiO2/ZnO TiO2 | Nanostructured thin film of agglomerated nanoparticles (20 nm) | Sol–gel spin-coating technique | methylene blue (MB) and octadecanoic acid; UV light (6 W) | 0.012 min−1 (94%) 0.008 min−1 (87%) 0.007 min−1 (82%) | [45] |
| TiO2/CuO (120 nm/90 nm) | Heterojunction nano-thin films | Magnetron sputtering technology | Rhodamine B (RhB) within 120 min 300 W high-pressure mercury lamp | 92.94% | [46] |
| Tetra(4-carboxyphenyl)porphyrin /Cu Polyoxometalate/TiO2 | Thin films | Doctor blade technique | 100 mL of a 10 mg/L MB, two tubular visible-light lamps, 5 h | 49% | [47] |
| CrMo6/TiO2. | Thin films | Doctor blade technique | MB dye UV tubular lamp (7 W, 15 µW/cm2), 5 h | 83% | [48] |
| Nb-doped TiO2 | Thin films of nanoparticles | Sol–gel spin-coating | 3 h of visible-light irradiation, 10 ppm of MB | 76% | [49] |
| undoped and P-doped TiO2 | Films | Spin-coating technique | degradation of MB dye in aqueous solution under UV light (365 nm), 7.1 h | 84% | [50] |
| Pure and TiO2, 10%Cu2+-doped TiO2 | Granular structure thin films | Sol–gel dip-coating technique | MB, 180 min, UV-light exposure | 92% (0.015 min−1) 16% (0.001 min−1) | [51] |
| Ag-loaded TiO2-ZnO | Thin films (aggregated nanoparticles of size 20–25 nm) | Dip-coating sol–gel process | methylene blue | 80% after 2 h | [52] |
| cerium oxide-doped rutile TiO2 | Films | Spray pyrolysis | methyl orange (MO) | 0.006 min−1 | [53] |
| Ni-doped TiO2 | Nano-structured thin films (particle size ~92 nm) | Chemical bath deposition method | Ponceau S dye, UV light, and sunlight | ~85% | [54] |
| Pure TiO2 | Nanotextures of TiO2 thin films | MOCVD at 450 °C | Sunlight | 97.5% after 2 h | Current work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khalifa, Z.S.; Shaban, M.; Ahmed, I.A. Photocatalytic Degradation of Methyl Orange and Methylene Blue Dyes by Engineering the Surface Nano-Textures of TiO2 Thin Films Deposited at Different Temperatures via MOCVD. Molecules 2023, 28, 1160. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031160
Khalifa ZS, Shaban M, Ahmed IA. Photocatalytic Degradation of Methyl Orange and Methylene Blue Dyes by Engineering the Surface Nano-Textures of TiO2 Thin Films Deposited at Different Temperatures via MOCVD. Molecules. 2023; 28(3):1160. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031160
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhalifa, Zaki S., Mohamed Shaban, and Inas A. Ahmed. 2023. "Photocatalytic Degradation of Methyl Orange and Methylene Blue Dyes by Engineering the Surface Nano-Textures of TiO2 Thin Films Deposited at Different Temperatures via MOCVD" Molecules 28, no. 3: 1160. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031160
APA StyleKhalifa, Z. S., Shaban, M., & Ahmed, I. A. (2023). Photocatalytic Degradation of Methyl Orange and Methylene Blue Dyes by Engineering the Surface Nano-Textures of TiO2 Thin Films Deposited at Different Temperatures via MOCVD. Molecules, 28(3), 1160. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031160







