Construction of Ketoenamine-Based Covalent Organic Frameworks with Electron-Rich Sites for Efficient and Rapid Removal of Iodine from Solution
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
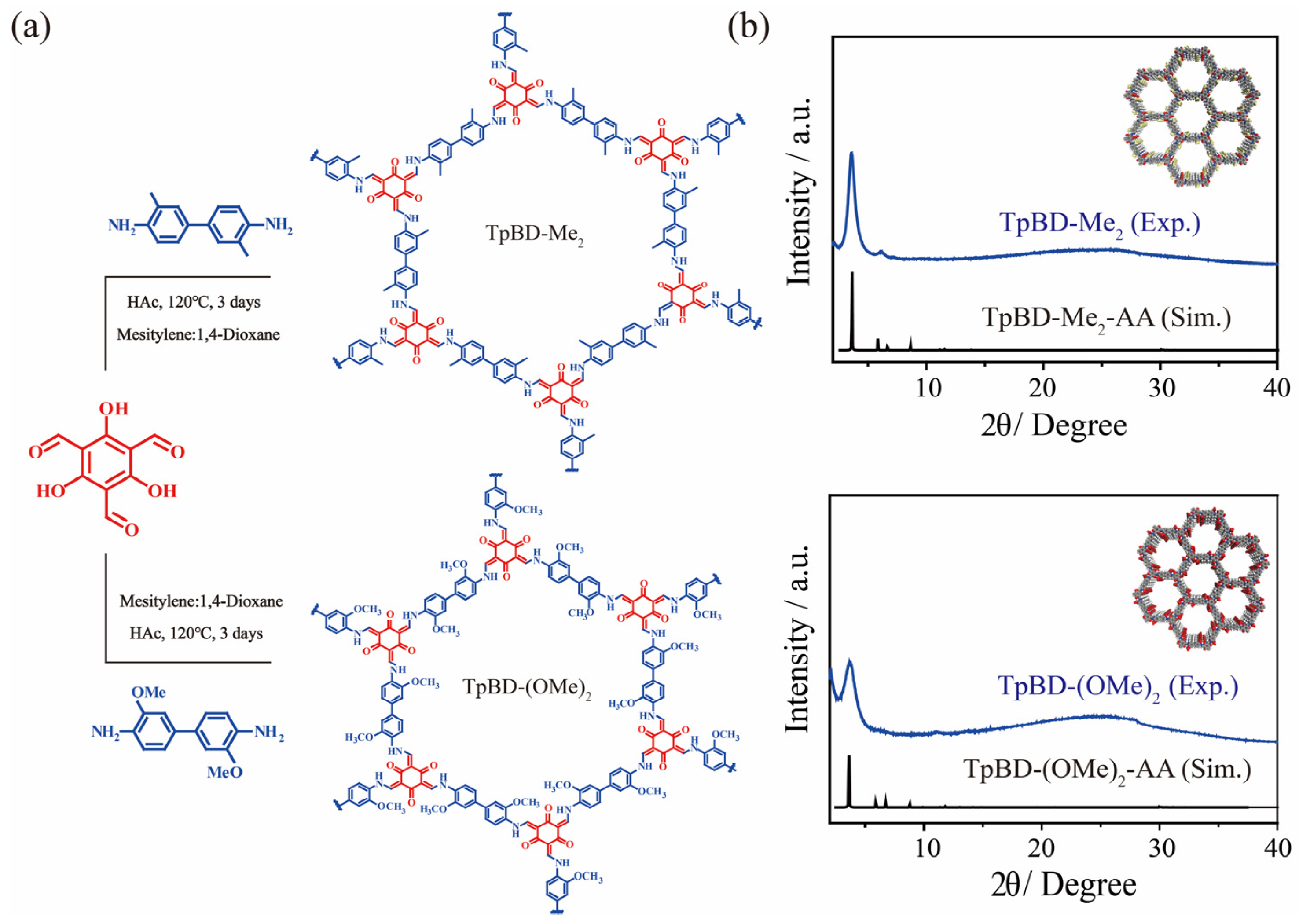
2.1. The Structure of TpBD-Me2 and TpBD-(OMe)2
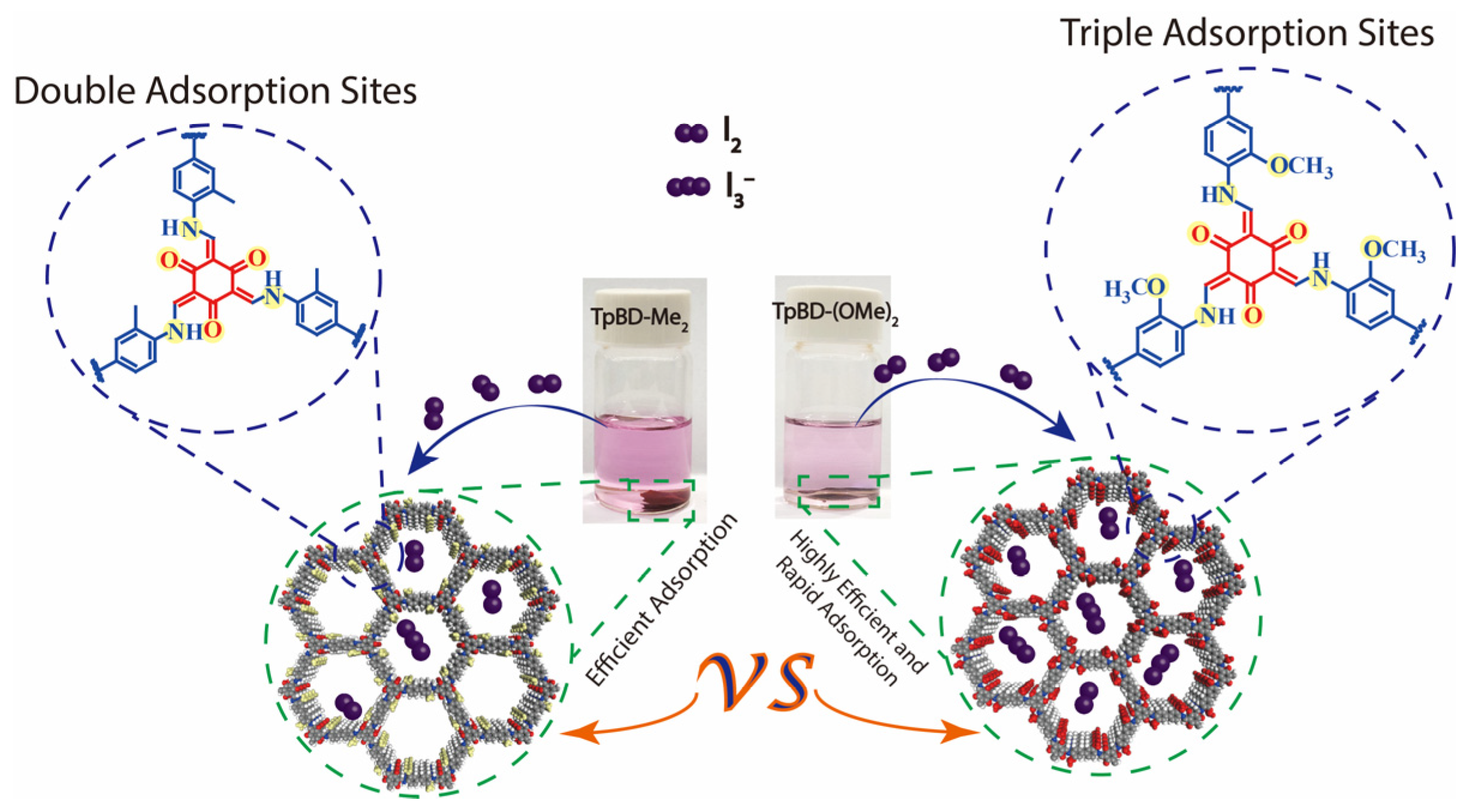
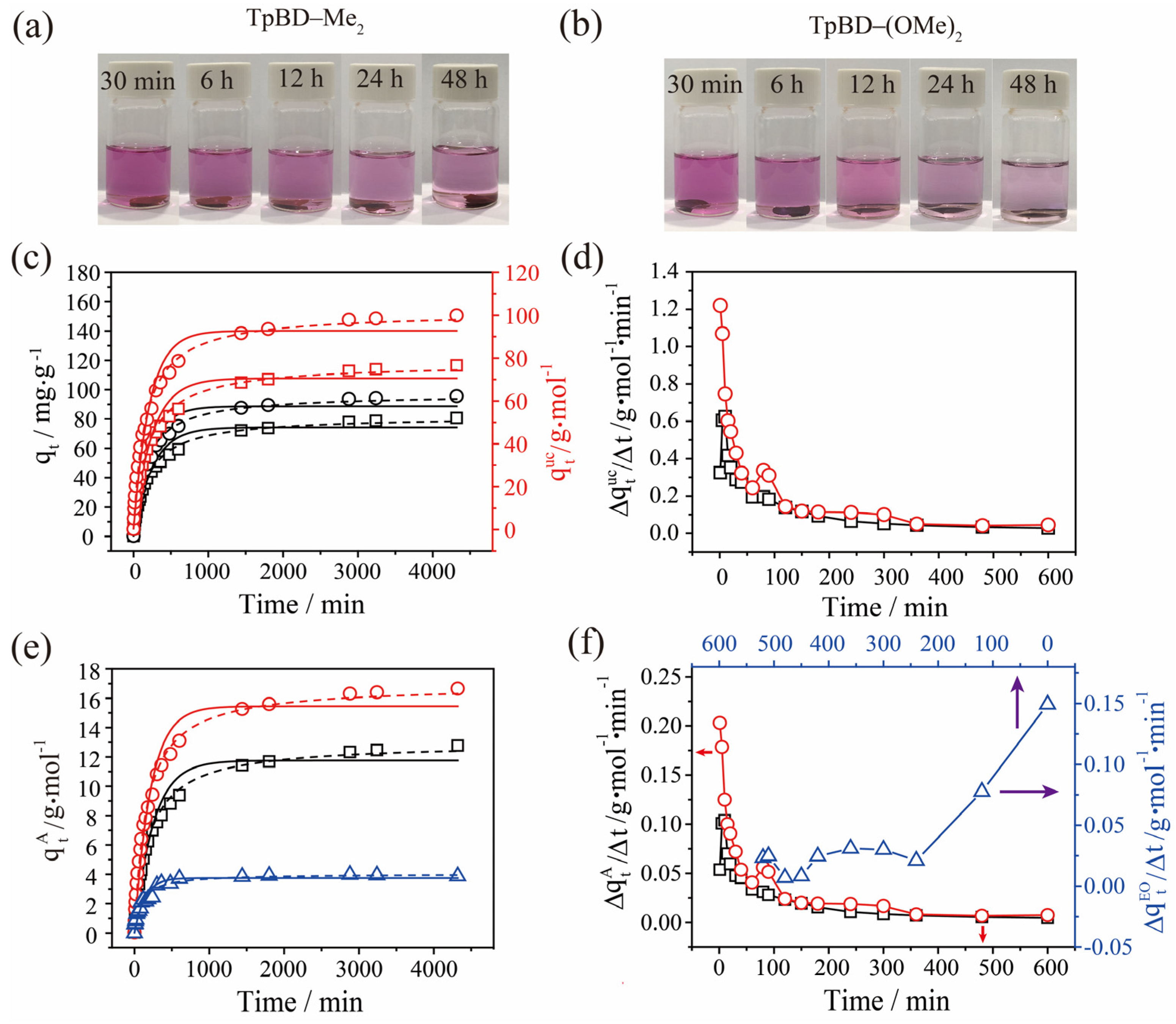
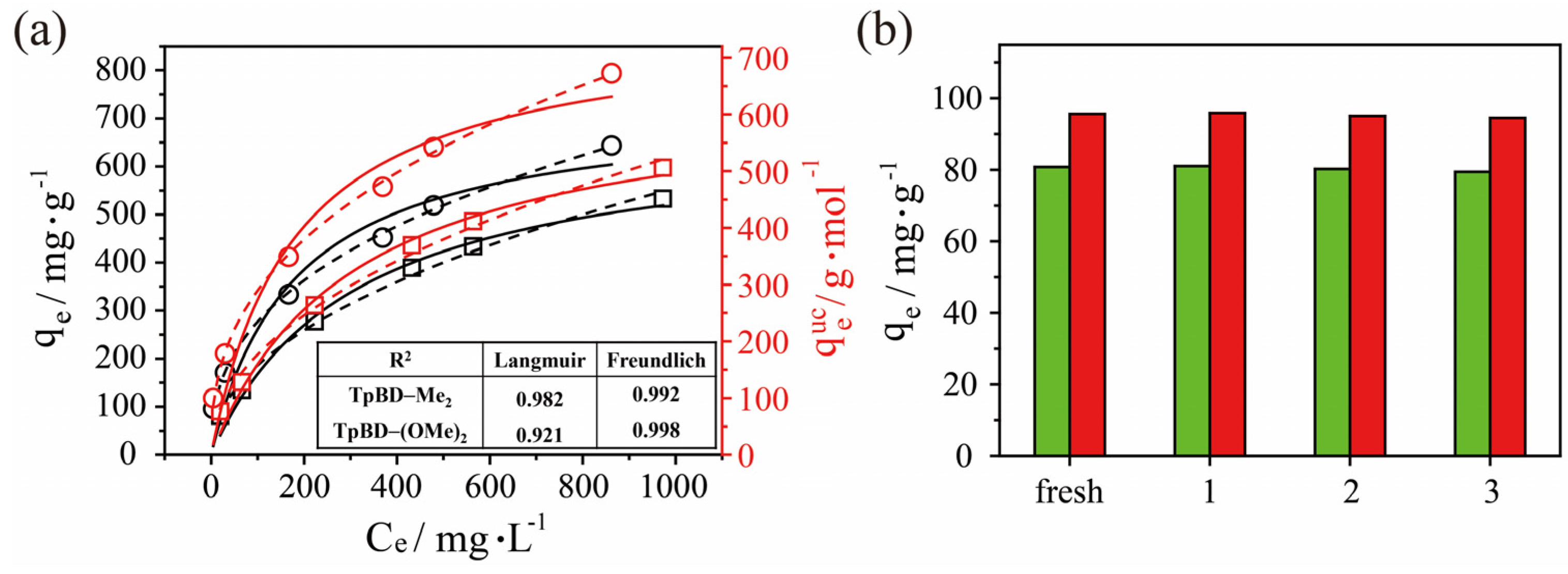
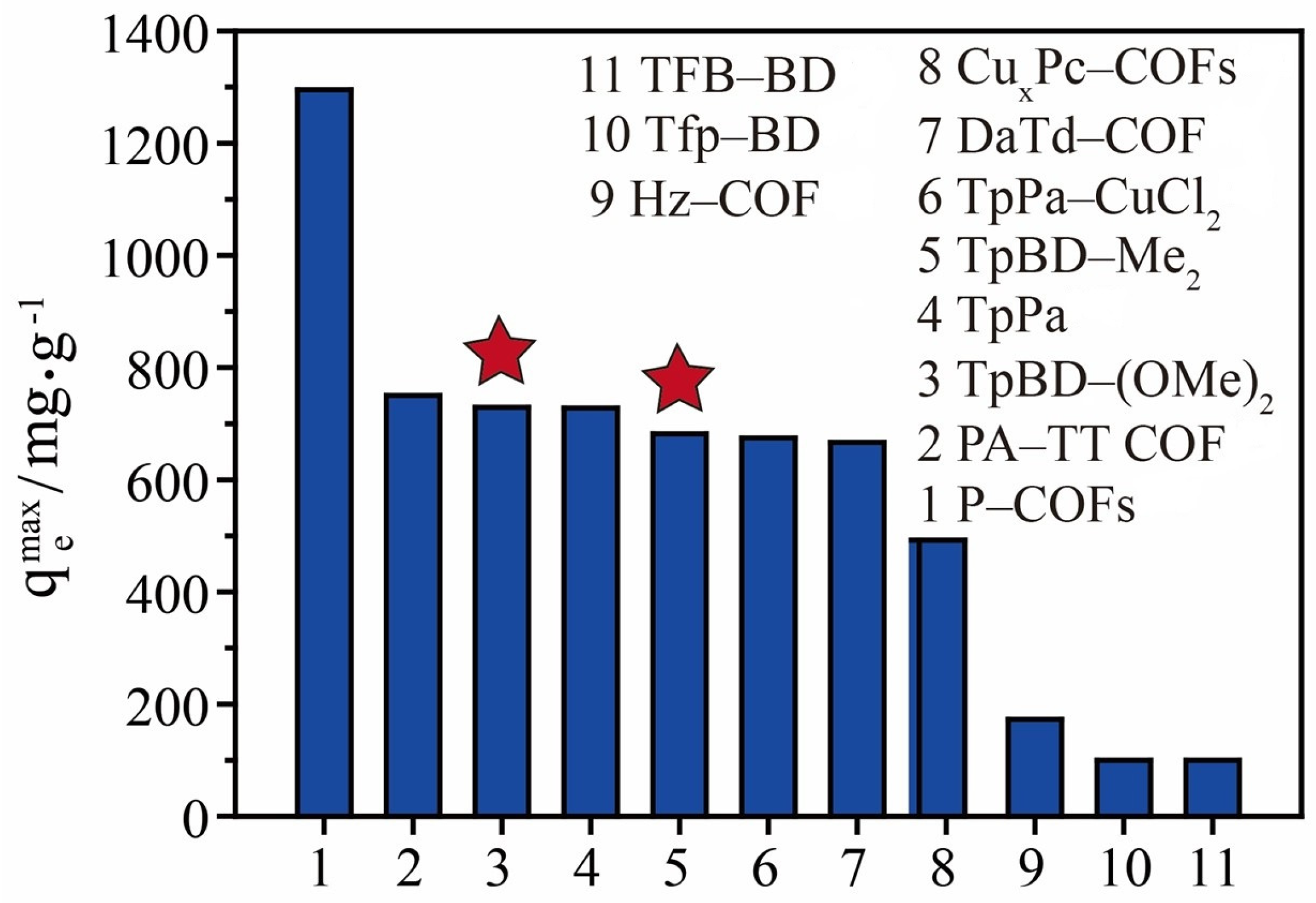
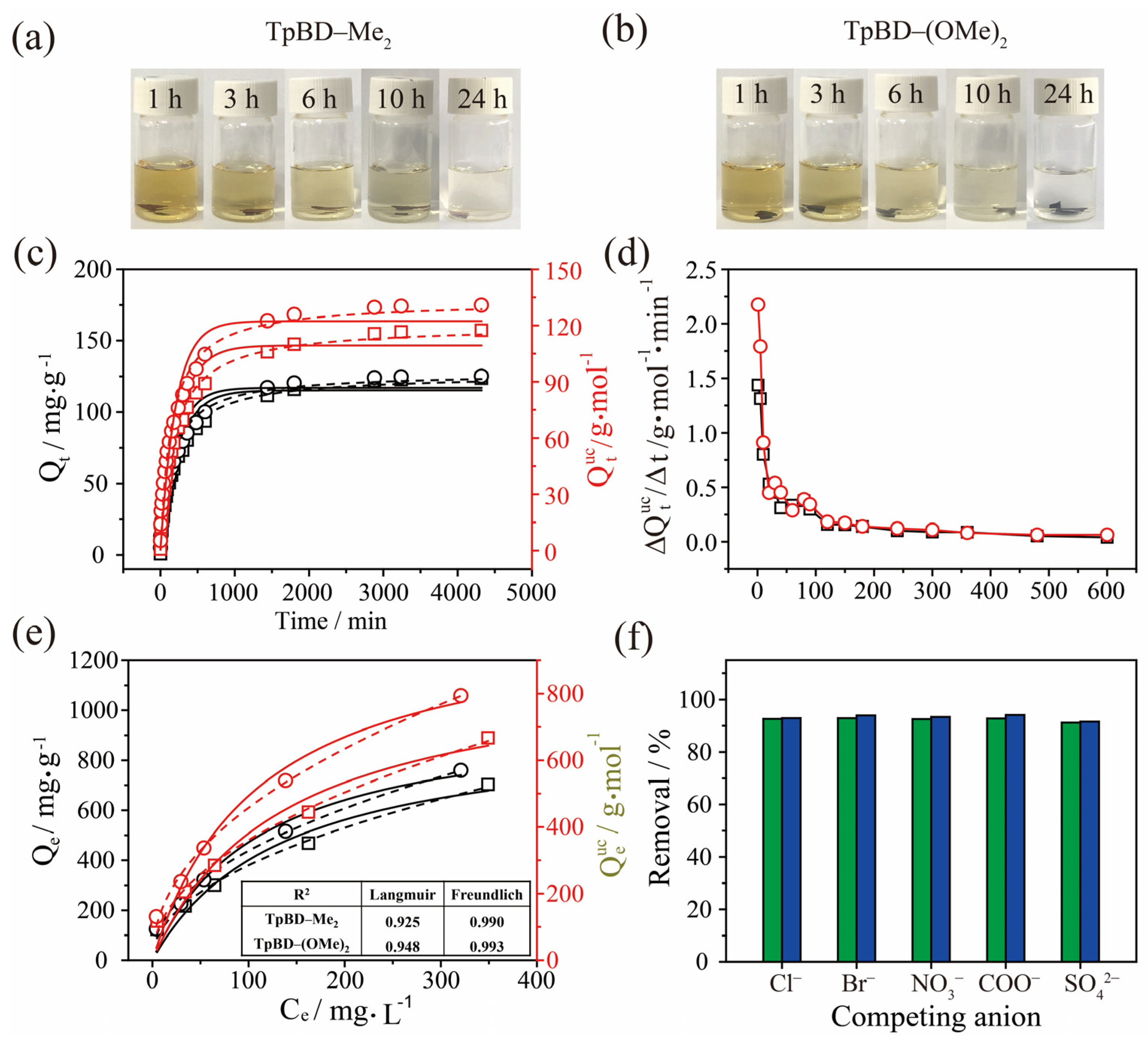
2.2. Adsorption of Iodine by TPBD-Me2 and TPBD-(OMe)2 in Cyclohexane
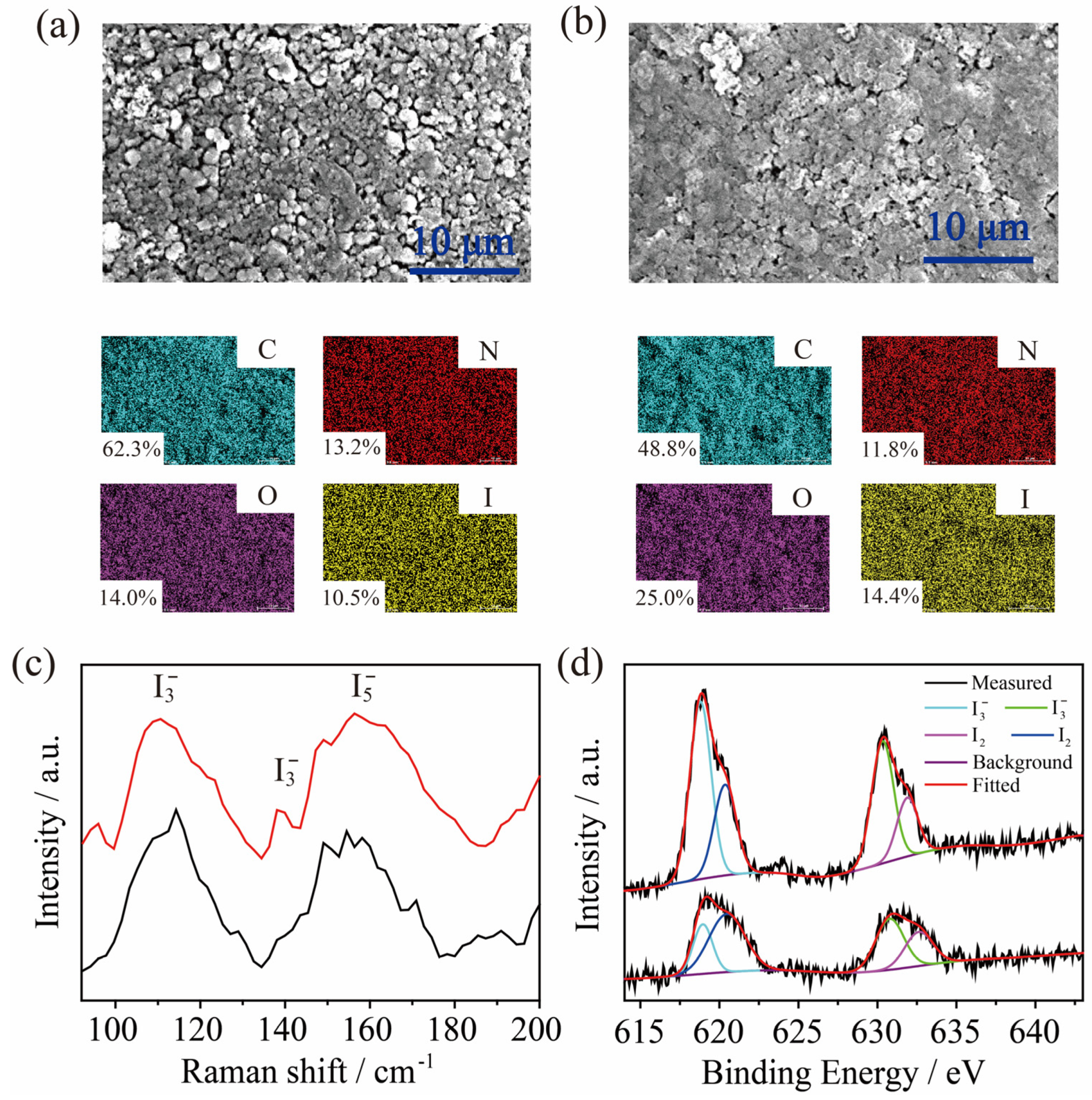
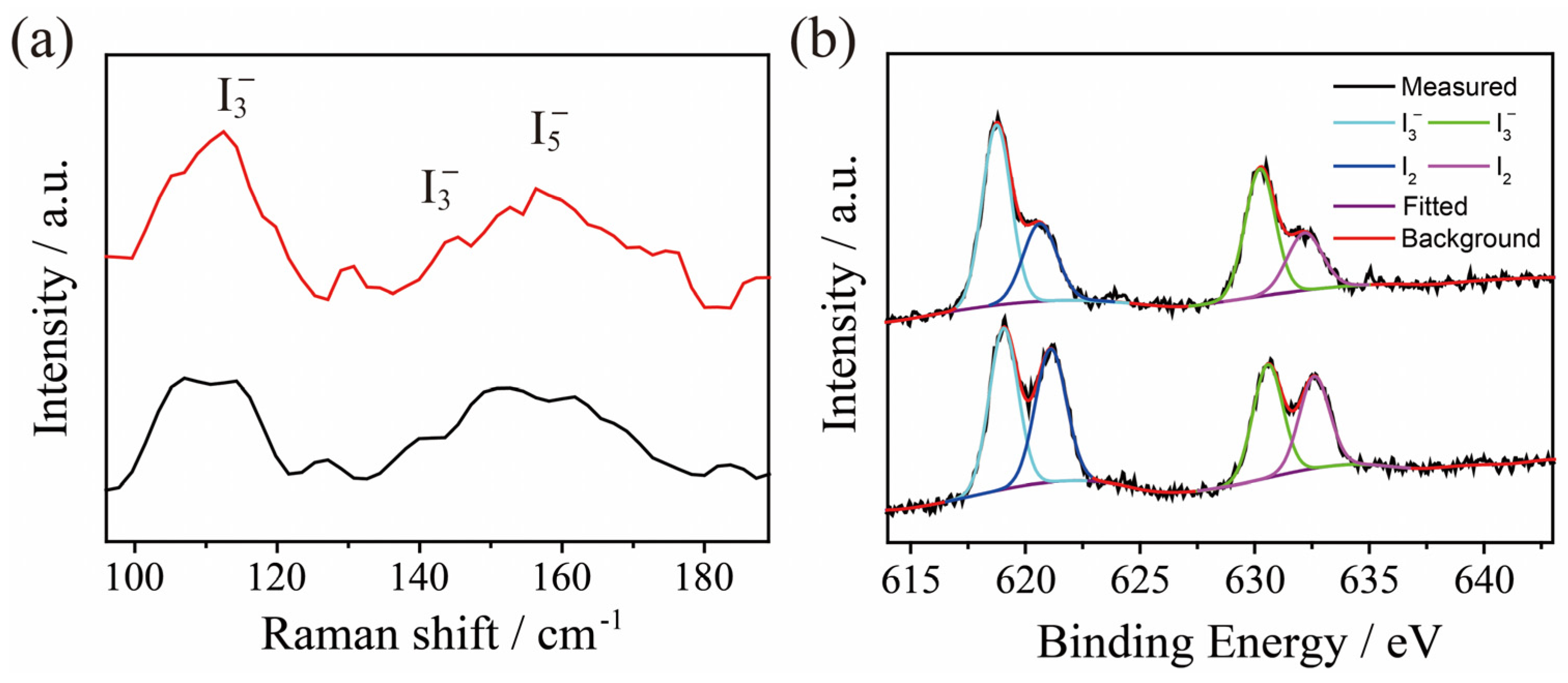
2.3. Adsorption of I3− by TPBD-Me2 and TPBD-(OMe)2 in Aqueous Solution
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Characterization
3.3. Synthesis of TpBD-Me2 and TpBD-(OMe)2 Powders
3.4. Study of Iodine Adsorption Property of TpBD-Me2 and TpBD-(OMe)2 in Cyclohexane
3.5. Study of Iodine Adsorption Property of TpBD-Me2 and TpBD-(OMe)2 in Aqueous Solution
3.6. Study of the Reusability of Iodine Uptake by TpBD-Me2 and TpBD-(OMe)2 in Cyclohexane
3.7. Evaluation of the Resistance to Anionic Interference on the Iodine Absorption Property in Aqueous Solutions
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bates, J.K.; Bradley, J.P.; Teetsov, A.; Bradley, C.R.; Buchholtz Ten Brink, M. Colloid Formation During Waste Form Reaction: Implications for Nuclear Waste Disposal. Science 1992, 256, 649–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Jiang, S.; Ma, W.; Liu, Z.; Liu, L.; Zou, Y.; Xu, B.; Tian, W. Polymorphic Covalent Organic Frameworks: Molecularly Defined Pore Structures and Iodine Adsorption Property. Molecules 2023, 28, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehner, G.; McBeth, M.K.; Moss, R.; Woerden, I. A Zero-Carbon Nuclear Energy Future? Lessons Learned from Perceptions of Climate Change and Nuclear Waste. Energies 2023, 16, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, H. Observation of Radioactive Iodine (I-131, I-129) in Cropland Soil after the Fukushima Nuclear Accident. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 566, 1432–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vienna, J.D. Nuclear Waste Vitrification in the United States: Recent Developments and Future Options. Int. J. Appl. Glass. Sci. 2010, 1, 309–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewing, R.C.; Hippel, F.N. Nuclear Waste Management in the United States-Starting Over. Science 2009, 325, 151–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teien, H.C.; Wada, T.; Kashparov, V.; Lopez-Gutierrez, J.M.; Garcia-Tenorio, R.; Hinton, T.G.; Salbu, B. Transfer of 129 I to Freshwater Fish Species within Fukushima and Chernobyl Exclusion Zones. J. Environ. Radioact. 2023, 207, 107269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Li, A.; Zhou, M.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; He, Q. Nonporous Amorphous Superadsorbents for Highly Effective and Selective Adsorption of Iodine in Water. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 5388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandanwar, S.U.; Coldsnow, K.; Utgikar, V.; Sabharwall, P.; Aston, D.E. Capture of Harmful Radioactive Contaminants from Off-gas Stream Using Porous Solid Sorbents for Clean Environment—A Review. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 306, 369–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herdes, C.; Prosenjak, C.; Román, S.; Müller, E.A. Fundamental Studies of Methyl Iodide Adsorption in DABCO Impregnated Activated Carbons. Langmuir 2013, 29, 6849–6855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-García, C.M.; Román, S.; González, J.F.; Sabio, E.; Ledesma, B. Surface Free Energy Analysis of Adsorbents Used for Radioiodine Adsorption. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 282, 714–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huve, J.; Ryzhikov, A.; Nouali, H.; Lalia, V.; Auged, G.; Daou, T.J. Porous Sorbents for the Capture of Radioactive Iodine Compounds: A Review. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 29248–29273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabraoui, H.; Hessou, E.P.; Chibani, S.; Cantrel, L.; Lebegue, S.; Badawi, M. Adsorption of Volatile Organic and Iodine Compounds over Silver-Exchanged Mordenites: A Comparative Periodic DFT Study for Several Silver Loadings. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 485, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.; Chong, S.; Riley, B.J.; MoCloy, J.S.; Goel, A. Iodine Capture by Ag-Loaded Solid Sorbents Followed by Ag Recycling and Iodine Immobilization: An End-to-End Process. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2023, 62, 3635–3646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Sawada, J.A.; Kuznicki, D.B.; Kuznicki, T.; Kuznicki, S.M. Iodine Adsorption on Silver-Exchanged Titania-Derived Adsorbents. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2014, 302, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhire, C.; Reda, A.T.; Zhang, D.; Xu, Y.; Cui, C. An Overview on Metal Oxide-Based Materials for Iodine Capture and Storage. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 431, 133816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Kang, S.; Wang, H.; Wang, G.; Zhao, H.; Cai, W. Nanosheets-Built Flowerlike Micro/Nanostructured Bi2O2.33 and Its Highly Efficient Iodine Removal Performances. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 289, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, A.; Sarina, S.; Zheng, Z.; Yang, D.; Liu, H.; Zhu, H. Removal of Radioactive Iodine from Water Using Ag2O Grafted Titanate Nanolamina as Efficient Adsorbent. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 246, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmussen, R.M.; Matyas, J.; Qafoku, N.P.; Kruger, A.A. Silver-Functionalized Silica Aerogels and Their Application in the Removal of Iodine from Aqueous Environments. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 379, 119364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, S.; Choi, S.; Nan, Y.; Tavlarides, L.L. Adsorption of Methyl Iodide on Reduced Silver-Functionalized Silica Aerogel: Kinetics and Modeling. AIChE J. 2021, 67, e17137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buck, T.; Chibani, S.; Paul, J.-F.; Cantrel, L.; Badawi, M. Dissociative Iodomethane Adsorption on Ag-MOR and the Formation of Agl Clusters: An &ITab Initio&IT Molecular Dynamics Study. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 27530–27543. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Zhu, H.; Duan, T.; He, G.; Wei, Y.; Zhou, J. Multi-Layer Active Interface Construction with Polyphenols and Nano-Silver on Nano Collagen Fiber for Efficient Capturing Iodine Vapor. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 596, 153585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Cui, W.; Zhang, F.; Guo, Y.; Deng, T. Removal of Iodine from the Salt Water Used for Caustic Soda Production by Ion-Exchange Resin Adsorption. Desalination 2019, 458, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Ma, T.; Zhao, X.; Jing, X.; Zhao, R.; Zhu, G. Multi-Functionalization Integration into the Electrospun Nanofibers Exhibiting Effective Iodine Capture from Water. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 47126–47135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Fu, J.; Zhu, Q.; Yang, X.; Xu, X.; Qin, S.; He, L.; Tao, G. Efficient Enrichment of Iodine by Supported Ionic Liquid with Three Effective Adsorption Sites: Heteroatoms, Fused Aromatic Rings and Ionic Bond. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 456, 140979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Maddock, J.; Nenoff, T.M.; Denecke, M.A.; Yang, S.; Schroder, M. Adsorption of Iodine in Metal–Organic Framework Materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Li, Q.; Li, Z.; Wang, X.; Xia, L. Analysis of Radioactive Iodine Trapping Mechanism by Zinc-Based Metal−Organic Frameworks with Various N-Containing Carboxylate Ligands. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 35082–35091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cui, X.; Xing, H. Recent Advances in the Capture and Abatement of Toxic Gases and Vapors by Metal–Organic Frameworks. Mater. Chem. Front. 2021, 5, 5970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Ju, Y.; Yu, B.; Wu, X.; Lu, H.; Li, Y.; Zhou, J.; Guo, X.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, J.; et al. Modulated Synthesis and Isoreticular Expansion of Th-MOFs with Record High Pore Volume and Surface Area for Iodine Adsorption. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 6715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, W.; Qin, Y.; Ni, C.; Dai, W.; Zou, J. Efficient Capture of Volatile Iodine by Thiophene-Containing Porous Organic Polymers. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2020, 2, 5121–5128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurisingal, J.F.; Yun, H.; Hong, C.S. Porous Organic Materials for Iodine Adsorption. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 458, 131835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Qiu, N.; Kong, X.; Hu, Z.; Zhong, F.; Li, Y.; Tan, H. Novel Carbazole-Based Porous Organic Polymer for Efficient Iodine Capture and Rhodamine B Adsorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 14846–14853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhu, G. Highly Efficient Enrichment of Volatile Iodine by Charged Porous Aromatic Frameworks with Three Sorption Sites. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 12733–12737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra, S.; Kandambeth, S.; Biswal, B.P.; Lukose, B.; Kunjir, S.M.; Chaudhary, M.; Babarao, R.; Heine, T.; Banerjee, R. Chemically Stable Multilayered Covalent Organic Nanosheets from Covalent Organic Frameworks via Mechanical Delamination. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 17853–17861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhao, Y.; Song, M.; Pang, X.; Shi, X.; Jia, J.; Chi, L.; Lu, G. Ordered Macro−Microporous Single Crystals of Covalent Organic Frameworks with Efficient Sorption of Iodine. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 2544–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, S.; Shi, Y.; Liu, N.; Liu, F. Theoretical Screening and Experimental Synthesis of Ultrahigh-Iodine Capture Covalent Organic Frameworks. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 10513–10523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Dong, X.; Yin, J.; Li, Z.; Li, X.; Zhang, D.; Pan, T.; Lei, Q.; Liu, X.; Xie, Y.; et al. Chemically Stable Guanidinium Covalent Organic Framework for the Efficient Capture of Low-Concentration Iodine at High Temperatures. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 6821–6829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Pan, T.; Lei, Q.; Chen, C.; Dong, X.; Yuan, Y.; Shen, J.; Cai, Y.; Zhou, C.; Pinnau, I.; et al. Ionic Functionalization of Multivariate Covalent Organic Frameworks to Achieve an Exceptionally High Iodine-Capture Capacity. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 22432–22440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Liu, W.; Cheng, G.; Ke, H. Phosphine-Based Covalent Organic Framework for Highly Efficient Iodine Capture. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2021, 325, 111351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Yang, Y.; Li, G.; Zhang, J.; He, Y.; Wang, R.; Lin, Z.; Cai, Z. Thiophene-Based Covalent Organic Frameworks for Highly Efficient Iodine Capture. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2023, 34, 107201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Song, S.; Xiao, D.; Gan, L.; Wang, Y. Easily Constructed Imine-Bonded COFs for Iodine Capture at Ambient Temperature. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 24262–24271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, S.; Gao, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Song, W.; Su, C.; Wang, W. Construction of Covalent Organic Framework for Catalysis: Pd/COF-LZU1 in Suzuki-Miyaura Coupling Reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 19816–19822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, L.; Cheng, C.; Wang, B.; Wang, S.; Xie, R.; Xia, H.; Wang, D. Controlled Iodine Phase Transfer of Covalent Organic Framework Membranes for Instant but Sustained Disinfection. Langmuir 2023, 39, 597–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Wei, W.; Ma, J.; Luo, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, S. Adsorption of Iodine on Adamantane-Based Covalent Organic Frameworks. Chem. Select 2021, 6, 10141–10148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, A.; Ma, R.; Wu, B.; Wen, T.; Ai, Y.; Sun, M.; Jin, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, X. Experimental and Theoretical Insights into Copper Phthalocyanine-Based Covalent Organic Frameworks for Highly Efficient Radioactive Iodine Capture. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2022, 33, 3549–3555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtari, N.; Dinari, M. Developing Novel Amine-Linked Covalent Organic Frameworks towards Reversible Iodine Capture. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 301, 121948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Shi, Y.; Liu, N.; Liu, F. C=N Linked Covalent Organic Framework for the Efficient Adsorption of Iodine in Vapor and Solution. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 10512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Yang, J.; Li, Y.; Zhuang, Q.; Gu, J. The Water-Based Synthesis of Chemically Stable Zr-Based MOFsUsing Pyridine-Containing Ligands and Their Exceptionally High Adsorption Capacity for Iodine. Dalton Trans. 2017, 46, 7412–7420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Li, J.; Jia, M.; Li, G.; Liu, Y. Contiguous Layer Based Metal–Organic Framework with Conjugated π-Electron Ligand for High Iodine Capture. Dalton Trans. 2021, 50, 13096–13102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, Y.; Li, Z.; Qiu, J.; Li, X.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Z.; He, M.; Wang, J.; Lin, J. Adsorption and Detection of Iodine Species by a Thorium-Based Metal−Organic Framework. Inorg. Chem. 2023, 62, 8158–8165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, N.; Wang, Y.; Bai, F.; Xing, Y.; Sun, L. Ln-MOFs with Window-Shaped Channels Based on Triazine Tricarboxylic Acid as a Linker for the Highly Efficient Capture of Cationic Dyes and Iodine. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2021, 8, 1736–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zheng, Q.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Jiang, J.; Qiu, J. A Pillared Double-Wall Metal-Organic Framework Adsorption Membrane for the Efficient Removal of Iodine from Solution. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 274, 118436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Sun, L.; Xing, Y.; Bai, F. A Double-Walled Thorium-Based Metal−Organic Framework as a Promising Dual-Function Absorbent for Efficiently Capturing Iodine and Dyes. Cryst. Growth Des. 2019, 19, 5686–5695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Zeng, G.; You, Z.; Wang, C.; Sun, L.; Bai, F.; Xing, Y. Cu(II) and Zn(II) Frameworks Constructed by Directional Tuning of Diverse Substituted Groups on a Triazine Skeleton and Supermassive Adsorption Behavior for Iodine and Dyes. Dalton Trans. 2022, 51, 5457–5470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Sun, L.; Bai, F.; Xing, Y. Thorium-Organic Framework Constructed with a Semirigid Triazine Hexacarboxylic Acid Ligand: Unique Structure with Thorium Oxide Wheel Clusters and Iodine Adsorption Behavior. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 59, 3964–3973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Cai, H.; Jiang, S.; Xing, Y.; Bai, F. Construction of a Triazine Polycarboxylate Co-MOF with Flexible and Rigid Coordination Arms as well as Excellent Catalytic Reduction and Adsorption Properties. Dalton Trans. 2023, 52, 6773–6781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yue, Z.; Ju, Y.; Wu, X.; Ren, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, X.; Lin, J. Ultrastable Thorium Metal−Organic Frameworks for Efficient Iodine Adsorption. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 59, 4435–4442. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Hu, H.; Deng, S.; Cai, S.; Fan, J.; Zhang, W.; Zheng, S. A Ni(II) metal–organic framework with helical channels for the capture of iodine via guest exchange induced amorphization. New J Chem. 2022, 46, 7144–7152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Chen, F.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, D.; Liang, Y.; Chen, Z. Heterometallic Metal-Organic Framework Based on [Cu4I4] and [Hf6O8] Clusters for Adsorption of Iodine. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 864131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falaise, C.; Volkringer, C.; Facqueur, J.; Bousquet, T.; Gasnot, L.; Loiseau, T. Capture of Iodine in Highly Stable Metal–Organic Frameworks: A Systematic Study. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 10320–10322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Ju, Y.; Lu, H.; Wu, X.; Yu, X.; Li, Y.; Wu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, J.; Qian, Y. Boosting the Iodine Adsorption and Radioresistance of Th-UiO-66 MOFs via Aromatic Substitution. Chem. Eur. J. 2020, 27, 1286–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Huang, J.; Huang, X.; Deng, S.; Zheng, S.; Cai, S.; Fan, J.; Zhang, W. A Hydrolytically Stable Cage-Based Metal–Organic Framework Containing two Types of Building Blocks for the Adsorption of Iodine and Dyes. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2021, 8, 1083–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Fan, L.; Zhang, X.; Ma, L. Robust Heterometallic TbIII/MnII−Organic Framework for CO2/CH4 Separation and I2 Adsorption. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 2680–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Li, Q.; Zhang, T.; Li, Z.; Xia, L. Zn, O Co-Adsorption Based on MOF-5 for Efficient Capture of Radioactive Iodine. Process Saf. Environ. 2023, 174, 770–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Tu, C.; Shi, J.; Zhao, T.; Liu, Z.; Cheng, F.; Luo, F. Highly Stable Cd(II)-MOFs Based on 2,6-Naphthanlenedisulfonate and Bisimidazole Ligands: A New Platform for Selective Detection of Cu2+ and Efficient Removal of Iodine. J. Solid State Chem. 2021, 302, 122439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Xing, Y.; Bai, F. A Uranyl-Organic Framework Featuring Two-Dimensional Graphene-like Layered Topology for Efficient Iodine and Dyes Capture. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 58, 6866–6876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Yuan, G.; Zeng, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liao, J.; Yang, J.; Liu, N. Flexible surface-supported MOF membrane via a convenient approach for efficient iodine adsorption. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Ch. 2020, 324, 1167–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Lafi, A.G.; Assfour, B.; Assaad, T. Metal Organic Framework MIL-101(Cr): Spectroscopic Investigations to Reveal Iodine Capture Mechanism. J. Inorg. Organomet. P. 2020, 30, 1218–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Sun, Z.; Yang, A.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, X.; Li, W.; Liu, Y.; Luan, J. A Novel Azo-Linked Polymer Bearing Trifluoromethyl Groups for I2 Capture. Macromol. Rapid Comm. 2023, 44, 2200982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thurakkal, L.; Cheekatla, S.; Porel, M. Superfast Capture of Iodine from Air, Water, and Organic Solvent by Potential Dithiocarbamate-Based Organic Polymer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.; Ding, C.; Zhang, Z.; Ke, H.; Cheng, G. Functional Porous Organic Polymer with High S and N for Reversible Iodine Capture. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2020, 300, 110161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Duan, L.; Ran, X.; Ran, B.; Yi, S. Two Nitrogen-Rich Conjugated Microporous Polymers for Efficient Iodine Sequestration and Removal. J. Polym. Res. 2022, 29, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigen, A.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Xia, H.; Xue, M.; Liu, X.; Mu, Y. Highly Efficient and Reversible Iodine Capture Using a Metalloporphyrin-Based Conjugated Microporous Polymer. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 8495–8498. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Song, C.; Kong, A. Nitrogen and Sulfur-Enriched Porous Bithiophene-Melamine Covalent Organic Polymers for Effective Capture of CO2 and Iodine. Mater. Lett. 2020, 277, 128291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, A.; Al-Sayah, M.H.; Ahmed, A.; El-Kadri, O.M. Triazine-Based Porous Organic Polymers for Reversible Capture of Iodine and Utilization in Antibacterial Application. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Shi, W.; Liu, S.; Xu, K. Multifunctional Diphenyl Ether-Based, Cross-Linked Polyisocyanide for Efficient Iodine Capture and NO2-/SO32- Electrochemical Probing. Colloid Surface A 2022, 642, 128680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tao, Q.; Zhang, X.; Jing, L.; Sun, L.; Dang, P. Construction of Ketoenamine-Based Covalent Organic Frameworks with Electron-Rich Sites for Efficient and Rapid Removal of Iodine from Solution. Molecules 2023, 28, 8151. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28248151
Tao Q, Zhang X, Jing L, Sun L, Dang P. Construction of Ketoenamine-Based Covalent Organic Frameworks with Electron-Rich Sites for Efficient and Rapid Removal of Iodine from Solution. Molecules. 2023; 28(24):8151. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28248151
Chicago/Turabian StyleTao, Qi, Xiao Zhang, Liping Jing, Lu Sun, and Peipei Dang. 2023. "Construction of Ketoenamine-Based Covalent Organic Frameworks with Electron-Rich Sites for Efficient and Rapid Removal of Iodine from Solution" Molecules 28, no. 24: 8151. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28248151
APA StyleTao, Q., Zhang, X., Jing, L., Sun, L., & Dang, P. (2023). Construction of Ketoenamine-Based Covalent Organic Frameworks with Electron-Rich Sites for Efficient and Rapid Removal of Iodine from Solution. Molecules, 28(24), 8151. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28248151





