Bioactive Peptides from Ruditapes philippinarum Attenuate Hypertension and Cardiorenal Damage in Deoxycorticosterone Acetate–Salt Hypertensive Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
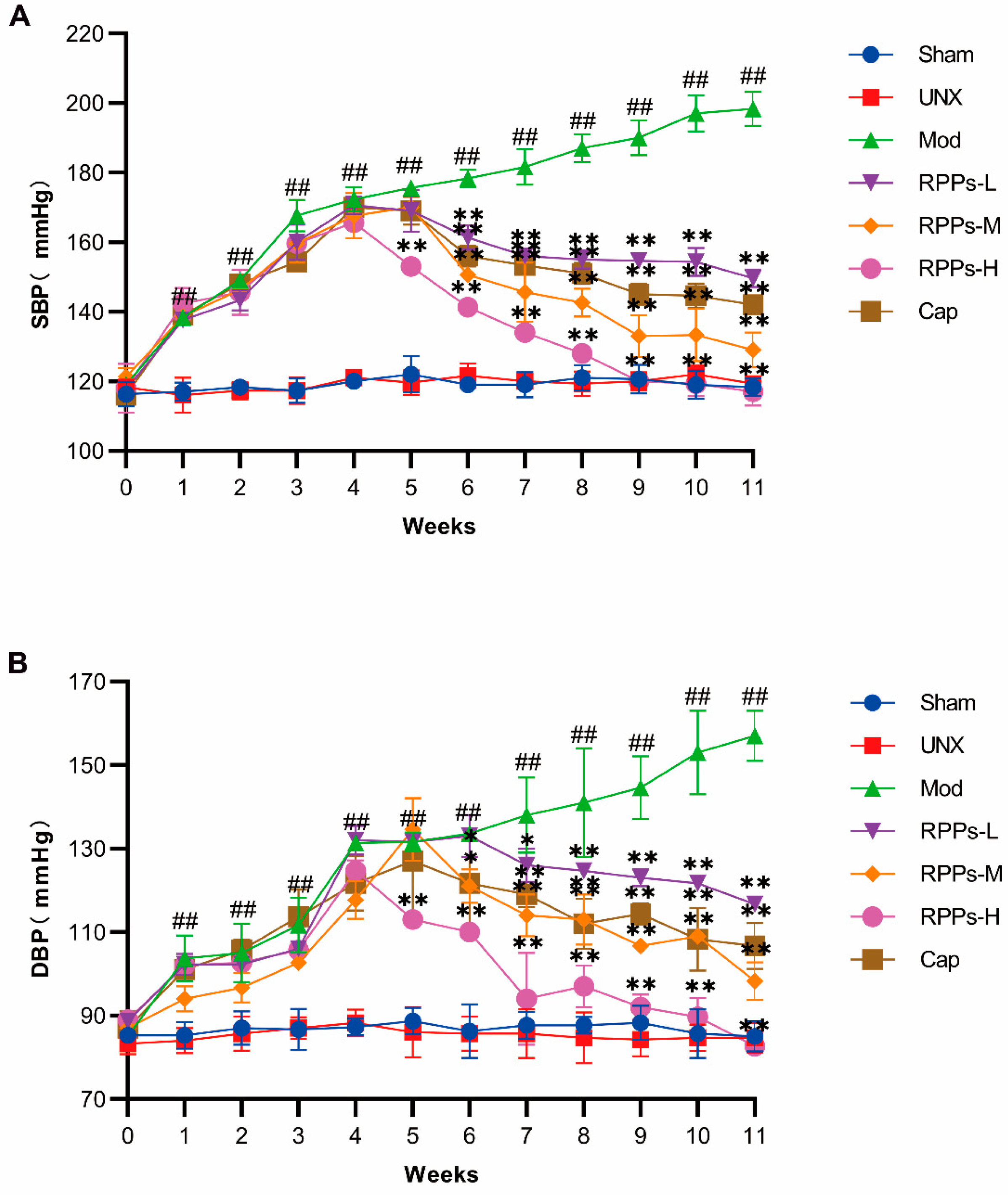
2.1. RPPs Significantly Reduced Blood Pressure in DOCA–Salt Hypertensive Rats
2.2. RPPs Improved Vascular Remodeling and Attenuated Vascular Fibrosis in DOCA–Salt Hypertensive Rats
2.3. RPPs Regulated Water–Sodium Balance in DOCA–Salt Hypertensive Rats
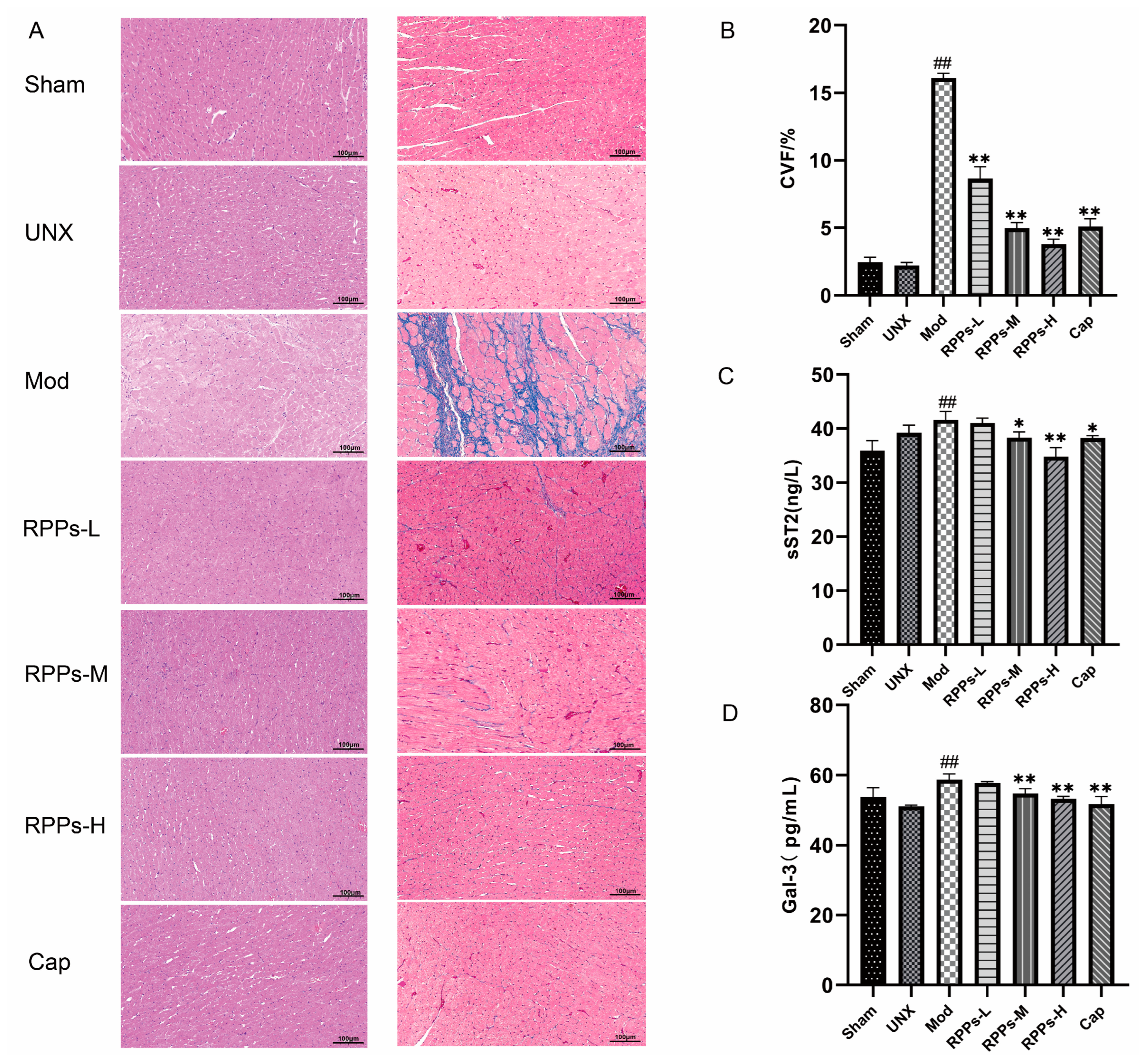
2.4. RPPs Exerted an Improving Effect on Heart Damage Caused by Hypertension
2.5. RPPs Ameliorated Hypertension-Induced Kidney Damage
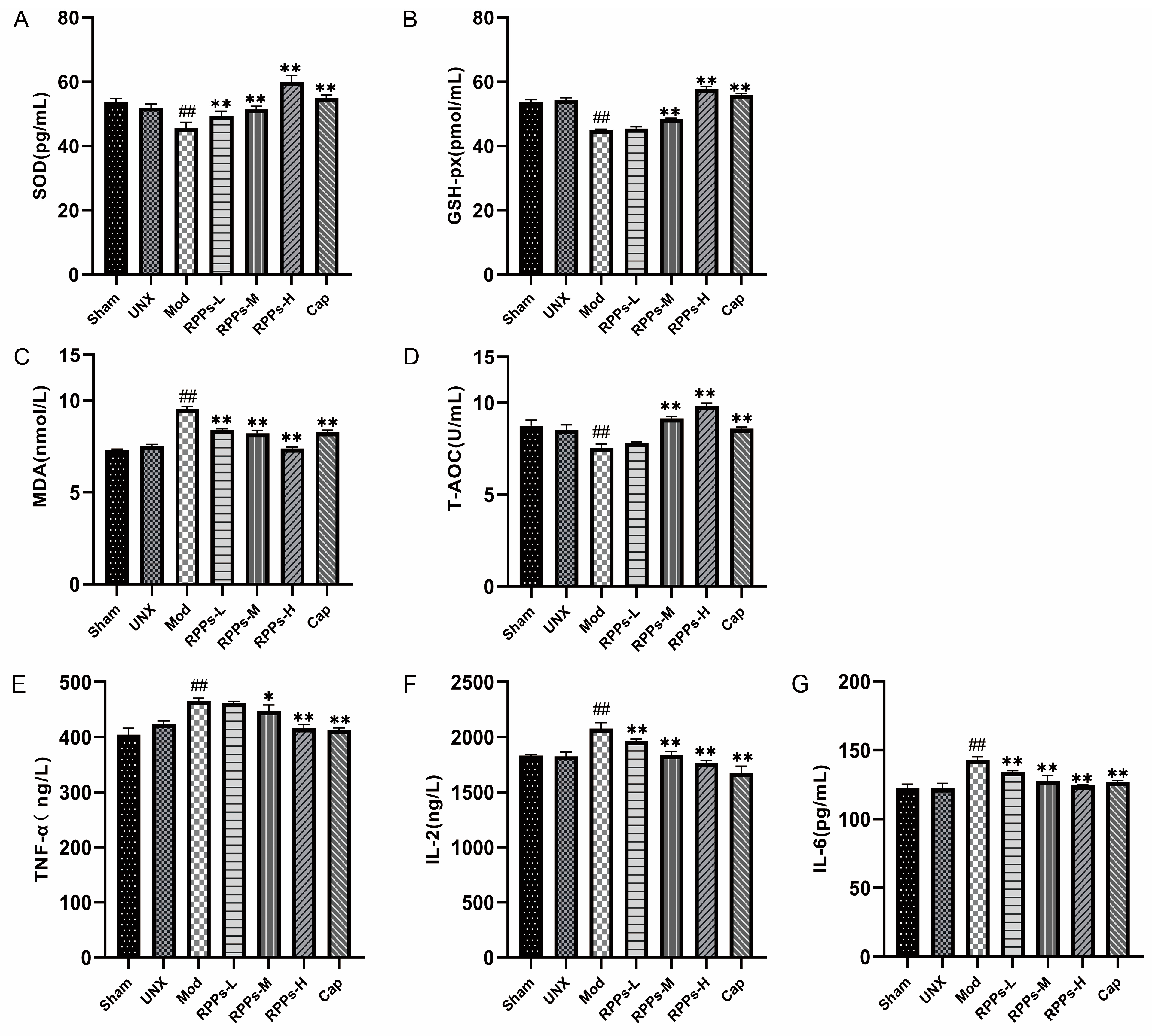
2.6. RPPs Reduced Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Responses in DOCA–Salt Hypertensive Rats
2.7. RPPs Had a Positive Regulatory Effect on the Gut Microbiota of DOCA–Salt Hypertensive Rats
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Animals and Experimental Design
4.3. Pathological Sections and Histopathological Analysis
4.4. Biochemical Analysis of Serum and Kidney Tissue
4.5. Analysis of Gut Microbial Diversity
4.6. Statistical Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Charles, L.; Triscott, J.; Dobbs, B. Secondary Hypertension: Discovering the Underlying Cause. Am. Fam. Physician 2017, 96, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Elijovich, F.; Laffer, C.L.; Sahinoz, M.; Pitzer, A.; Ferguson, J.F.; Kirabo, A. The Gut Microbiome, Inflammation, and Salt-Sensitive Hypertension. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2020, 22, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, A.T.; Edwards, D.G.; Farquhar, W.B. The Influence of Dietary Salt Beyond Blood Pressure. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2019, 21, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, D.A. Hypertensive Crisis: A Review of Pathophysiology and Treatment. Crit. Care Nurs. Clin. N. Am. 2015, 27, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ram, C.V. Antihypertensive Drugs: An Overview. Am. J. Cardiovasc. Drugs 2002, 2, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albasri, A.; Hattle, M.; Koshiaris, C.; Dunnigan, A.; Paxton, B.; Fox, S.E.; Smith, M.; Archer, L.; Levis, B.; Payne, R.A.; et al. Association between Antihypertensive Treatment and Adverse Events: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMJ 2021, 372, n189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aluko, R.E. Antihypertensive Peptides from Food Proteins. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 6, 235–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, N.; Chen, C.; Zhang, N.; Song, L.; Li, Y.; Guo, L.; Liu, R.; Zhang, W. Bitter Almond Albumin Ace-Inhibitory Peptides: Purification, Screening, and Characterization in Silico, Action Mechanisms, Antihypertensive Effect in Vivo, and Stability. Molecules 2023, 28, 6002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baskaran, R.; Balasubramanian, B.; Ho, J.H.; Wang, M.F.; Abomughaid, M.M.; Yang, H.S.; Lin, W.T. Vh-4-a Bioactive Peptide from Soybean and Exercise Training Constrict Hypertension in Rats through Activating Cell Survival and Ampkα1, Sirt1, Pgc1α, and Fox3α. Molecules 2022, 27, 7705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Nie, H.; Huo, Z.; Ding, J.; Li, Z.; Yan, L.; Jiang, L.; Mu, Z.; Wang, H.; Meng, X.; et al. Clam Genome Sequence Clarifies the Molecular Basis of Its Benthic Adaptation and Extraordinary Shell Color Diversity. iScience 2019, 19, 1225–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Yu, F.; Sun, S.; Liu, X.; Sun, Z.; Cao, W.; Liu, S.; Li, Z.; Xue, C. Evaluation indicators of Ruditapes philippinarum nutritional quality. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 58, 2943–2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Chen, L.; Liu, Y.; Cong, M.; Wu, H.; Li, F.; Ji, C.; Zhao, J. A Defensin-Like Antimicrobial Peptide from the Manila Clam Ruditapes Philippinarum: Investigation of the Antibacterial Activities and Mode of Action. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 80, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Cai, Q.; Wang, S.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Zou, S.; Gao, X.; Wei, Y. The Ameliorative Effect and Mechanisms of Ruditapes philippinarum Bioactive Peptides on Obesity and Hyperlipidemia Induced by a High-Fat Diet in Mice. Nutrients 2022, 14, 5066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, L.; Yu, J.; Wang, S.; Cao, T.; Gao, X.; Wei, Y. Identification and Antihypertension Study of Novel Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Peptides from the Skirt of Chlamys farreri Fermented with Bacillus natto. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, T.F.; Liu, J.L.; Fan, F.; Yin, D.C.; Zhou, S.C. Optimization of Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Hongdao Clam and Anti-Hypertensive Activity of the Resulted Products. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2021, 42, 216–222. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.-C.; Wang, X.-J.; Zhu, J.-H.; Huang, X.-Y.; Liu, M.; Qiao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Zhan, P.; et al. GPR97 deficiency ameliorates renal interstitial fibrosis in mouse hypertensive nephropathy. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2023, 44, 1206–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, H.C.; Lu, X.Y.; Xu, Y.P.; Wang, Y.H.; Wang, D.; Feng, Y.L.; Chi, Z.; Yan, X.Q.; Lu, C.S.; Wang, H.W. Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Attenuates Salt-Sensitive Hypertension-Induced Nephropathy through Anti-Inflammation and Anti-Oxidation Mechanism. Mol. Med. 2021, 27, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, K. The criteria for the selection of antihypertensive drugs by JSH2014 guidelines. Nihon Rinsho 2015, 73, 1841–1845. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Z.; Aoyagi, T.; Yang, T. mPGES-1 Protects Against DOCA-Salt Hypertension via Inhibition of Oxidative Stress or Stimulation of NO/cGMP. Hypertension 2010, 55, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, B.R.; Yerly, A.; van der Vorst, E.P.C.; Baumgartner, I.; Bernhard, S.M.; Schindewolf, M.; Döring, Y. Inflammatory Mediators in Atherosclerotic Vascular Remodeling. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 868934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Wang, S.; Shi, W.; Zhou, W.; Niu, Y.; Huang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, A.; Jia, Z. Roxadustat prevents Ang II hypertension by targeting angiotensin receptors and eNOS. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 6, e133690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palacios-Ramírez, R.; Hernanz, R.; Martín, A.; Pérez-Girón, J.V.; Barrús, M.T.; González-Carnicero, Z.; Aguado, A.; Jaisser, F.; Briones, A.M.; Salaices, M.; et al. Pioglitazone Modulates the Vascular Contractility in Hypertension by Interference with Et-1 Pathway. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Lam, T.Y.; Shum, T.F.; Tsai, T.Y.; Chiou, J. Hypotensive Effect of Captopril on Deoxycorticosterone Acetate-Salt-Induced Hypertensive Rat Is Associated with Gut Microbiota Alteration. Hypertens Res. 2022, 45, 270–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, M.; Kikuya, M.; Hara, A.; Ohkubo, T.; Mori, T.; Metoki, H.; Utsugi, M.T.; Hirose, T.; Obara, T.; Inoue, R.; et al. Aldosterone-to-renin ratio and home blood pressure in subjects with higher and lower sodium intake: The Ohasama Study. Hypertens. Res. 2011, 34, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banek, C.T.; Gauthier, M.M.; Van Helden, D.A.; Fink, G.D.; Osborn, J.W. Renal Inflammation in Doca-Salt Hypertension. Hypertension 2019, 73, 1079–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boesen, E.I.; Williams, D.L.; Pollock, J.S.; Pollock, D.M. Immunosuppression with mycophenolate mofetil attenuates the development of hypertension and albuminuria in deoxycorticosterone acetate-salt hypertensive rats. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2010, 37, 1016–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armaly, Z.; Assady, S.; Abassi, Z. Corin: A New Player in the Regulation of Salt-Water Balance and Blood Pressure. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2013, 22, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díez, J. Chronic heart failure as a state of reduced effectiveness of the natriuretic peptide system: Implications for therapy. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2017, 19, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokota, N.; Aburaya, M.; Yamamoto, Y.; Kato, J.; Kitamura, K.; Kida, O.; Eto, T.; Minamino, N.; Kangawa, K.; Matsuo, H.; et al. Increased plasma brain natriuretic peptide levels in DOCA-salt hypertensive rats: Relation to blood pressure and cardiac concentration. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1990, 173, 632–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reginauld, S.H.; Cannone, V.; Iyer, S.; Scott, C.; Bailey, K.; Schaefer, J.; Chen, Y.; Sangaralingham, S.J.; Burnett, J.C. Differential Regulation of ANP and BNP in Acute Decompensated Heart Failure: Deficiency of ANP. JACC Heart Fail. 2019, 7, 891–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwahara, K. The natriuretic peptide system in heart failure: Diagnostic and therapeutic implications. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 227, 107863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.Y.; Nithiyanantham, S.; Liao, J.Y.; Lin, W.T. Bioactive peptides attenuate cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis in spontaneously hypertensive rat hearts. J. Food Drug Anal. 2020, 28, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barutaut, M.; Fournier, P.; Peacock, W.F.; Evaristi, M.F.; Dambrin, C.; Caubère, C.; Koukoui, F.; Galinier, M.; Smih, F.; Rouet, P. Sst2 Adds to the Prognostic Value of Gal-3 and Bnp in Chronic Heart Failure. Acta Cardiol. 2020, 75, 739–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paoletti, E.; Bellino, D.; Amidone, M.; Rolla, D.; Cannella, G. Relationship between arterial hypertension and renal damage in chronic kidney disease: Insights from ABPM. J. Nephrol. 2006, 19, 778–782. [Google Scholar]
- Palm, F.; Nordquist, L. Renal Oxidative Stress, Oxygenation, and Hypertension. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2011, 301, R1229–R1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, S.; Xie, S.; Gao, Y.; Wang, Y. Triptolide attenuates renal damage by limiting inflammatory responses in DOCA-salt hypertension. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 89, 107035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Y.-M.; Diao, Z.-L.; Huang, H.-D.; Zheng, J.-F.; Zhang, Q.-D.; Wang, L.-Y.; Liu, W.-H. Bioactive peptide apelin rescues acute kidney injury by protecting the function of renal tubular mitochondria. Amino Acids 2021, 53, 1229–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daenen, K.; Andries, A.; Mekahli, D.; Van Schepdael, A.; Jouret, F.; Bammens, B. Oxidative stress in chronic kidney disease. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2019, 34, 975–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, L.; Chen, M.; Zheng, X.; Yang, P.; Zhao, X.; Tian, Z. Effects of almonds on ameliorating salt-induced hypertension in dahl salt-sensitive rats. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2022, 102, 2710–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattson, D.L.; Dasinger, J.H.; Abais-Battad, J.M. Gut-Immune-Kidney Axis: Influence of Dietary Protein in Salt-Sensitive Hypertension. Hypertension 2022, 79, 2397–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, R.; Hao, Y.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Huang, L.; Yao, Y.; Zhou, M.-S. Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha Deficiency Improves Endothelial Function and Cardiovascular Injury in Deoxycorticosterone Acetate/Salt-Hypertensive Mice. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 3921074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mell, B.; Jala, V.R.; Mathew, A.V.; Byun, J.; Waghulde, H.; Zhang, Y.; Haribabu, B.; Vijay-Kumar, M.; Pennathur, S.; Joe, B. Evidence for a link between gut microbiota and hypertension in the Dahl rat. Physiol. Genom. 2015, 47, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzatti, G.; Lopetuso, L.R.; Gibiino, G.; Binda, C.; Gasbarrini, A. Proteobacteria: A Common Factor in Human Diseases. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 9351507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilck, N.; Matus, M.G.; Kearney, S.M.; Olesen, S.W.; Forslund, K.; Bartolomaeus, H.; Haase, S.; Mähler, A.; Balogh, A.; Markó, L.; et al. Salt-Responsive Gut Commensal Modulates T(H)17 Axis and Disease. Nature 2017, 551, 585–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhaar, B.; Collard, D.; Prodan, A.; Levels, J.; Zwinderman, A.; Snijder, M.; Vogt, L.; Peters, M.; Muller, M.; Nieuwdorp, M.; et al. Associations between gut microbiome, short chain fatty acids and blood pressure across ethnic groups: The HELIUS study. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, ehaa946-2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henke, M.T.; Kenny, D.J.; Cassilly, C.D.; Vlamakis, H.; Xavier, R.J.; Clardy, J. Ruminococcus Gnavus, a Member of the Human Gut Microbiome Associated with Crohn’s Disease, Produces an Inflammatory Polysaccharide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 12672–12677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Contreras, A.; Franco-Ávila, T.; Miró, L.; Juan, M.E.; Moretó, M.; Planas, J.M. Dietary intake of table olives exerts antihypertensive effects in association with changes in gut microbiota in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 2793–2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, M.; Liu, M.; Zou, S.; Yin, D.; Lv, C.; Li, F.; Wei, Y. Immune Enhancement of Clam Peptides on Immunosuppressed Mice Induced by Hydrocortisone. Molecules 2023, 28, 5709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basting, T.; Lazartigues, E. DOCA-Salt Hypertension: An Update. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2017, 19, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Jiang, L.; Shum, T.-F.; Chiou, J. Elucidation of Anti-Hypertensive Mechanism by a Novel Lactobacillus rhamnosus AC1 Fermented Soymilk in the Deoxycorticosterone Acetate-Salt Hypertensive Rats. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panthiya, L.; Tocharus, J.; Onsa-Ard, A.; Chaichompoo, W.; Suksamrarn, A.; Tocharus, C. Hexahydrocurcumin Ameliorates Hypertensive and Vascular Remodeling in L-Name-Induced Rats. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2022, 1868, 166317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Dang, Y.; Li, Y.; Hao, Q.; Li, R.; Qi, X. Cardiac Contractility Modulation Attenuate Myocardial Fibrosis by Inhibiting Tgf-Β1/Smad3 Signaling Pathway in a Rabbit Model of Chronic Heart Failure. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 39, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, Z.; Wang, W.; Liu, J.; Zou, S.; Yin, D.; Lyu, C.; Yu, J.; Wei, Y. Bioactive Peptides from Ruditapes philippinarum Attenuate Hypertension and Cardiorenal Damage in Deoxycorticosterone Acetate–Salt Hypertensive Rats. Molecules 2023, 28, 7610. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28227610
Sun Z, Wang W, Liu J, Zou S, Yin D, Lyu C, Yu J, Wei Y. Bioactive Peptides from Ruditapes philippinarum Attenuate Hypertension and Cardiorenal Damage in Deoxycorticosterone Acetate–Salt Hypertensive Rats. Molecules. 2023; 28(22):7610. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28227610
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Zonghui, Weixia Wang, Jinli Liu, Shengcan Zou, Dongli Yin, Chenghan Lyu, Jia Yu, and Yuxi Wei. 2023. "Bioactive Peptides from Ruditapes philippinarum Attenuate Hypertension and Cardiorenal Damage in Deoxycorticosterone Acetate–Salt Hypertensive Rats" Molecules 28, no. 22: 7610. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28227610
APA StyleSun, Z., Wang, W., Liu, J., Zou, S., Yin, D., Lyu, C., Yu, J., & Wei, Y. (2023). Bioactive Peptides from Ruditapes philippinarum Attenuate Hypertension and Cardiorenal Damage in Deoxycorticosterone Acetate–Salt Hypertensive Rats. Molecules, 28(22), 7610. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28227610






