Zaluzanin C Alleviates Inflammation and Lipid Accumulation in Kupffer Cells and Hepatocytes by Regulating Mitochondrial ROS
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
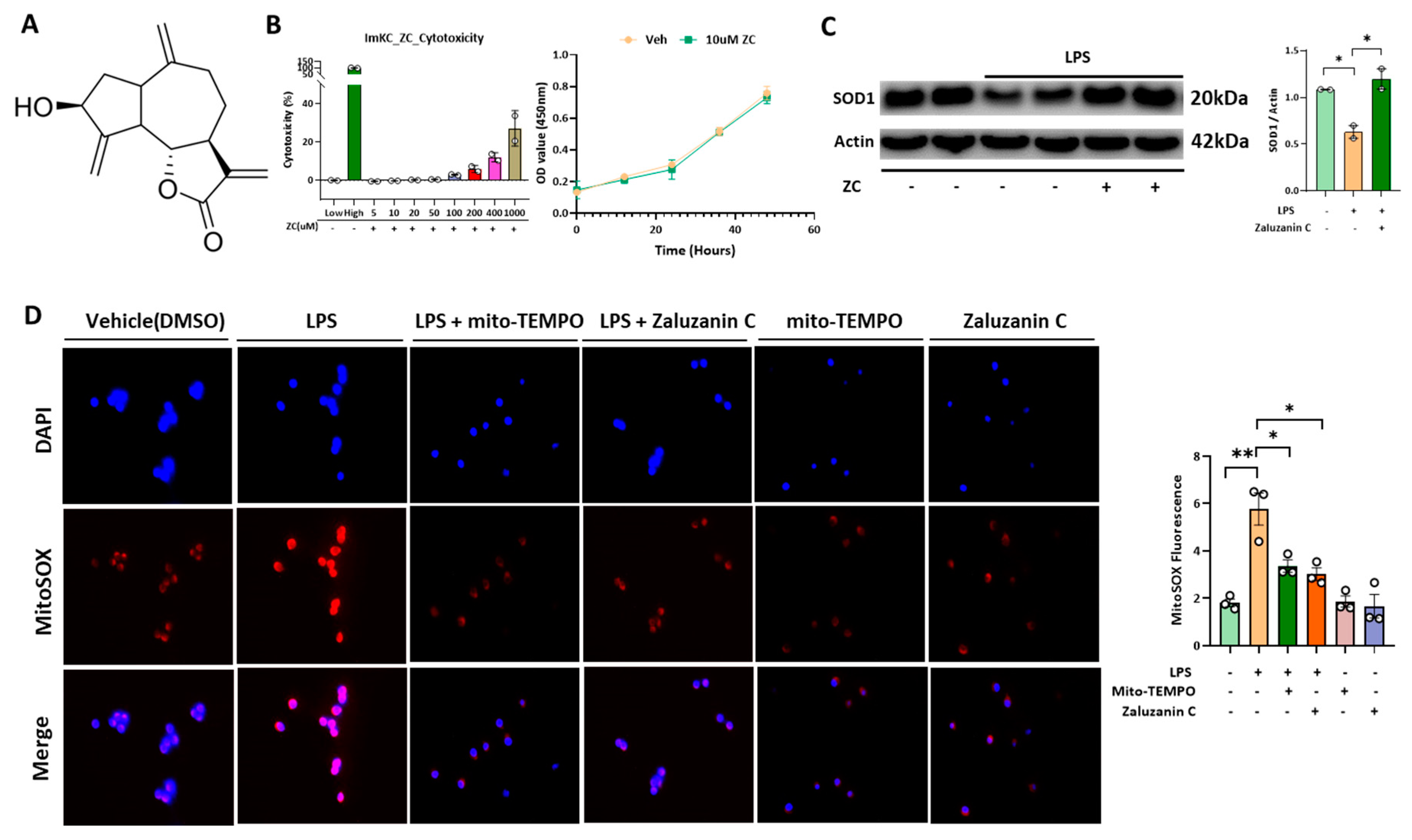
2.1. ZC Inhibits LPS-Induced ROS Production in Immortalized Mouse Kupffer Cells (ImKCs)
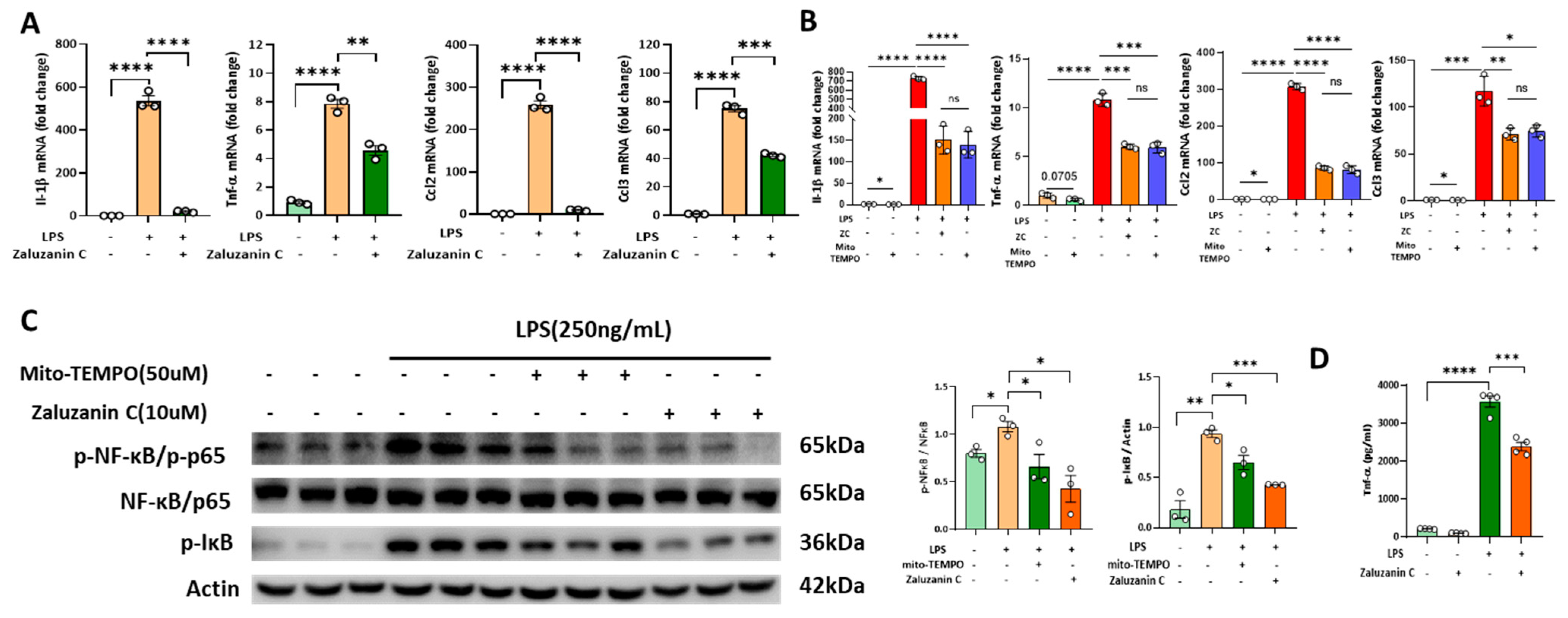
2.2. ZC Ameliorates Inflammation by Inhibiting ROS-Induced NF-κB Signaling in Kupffer Cells
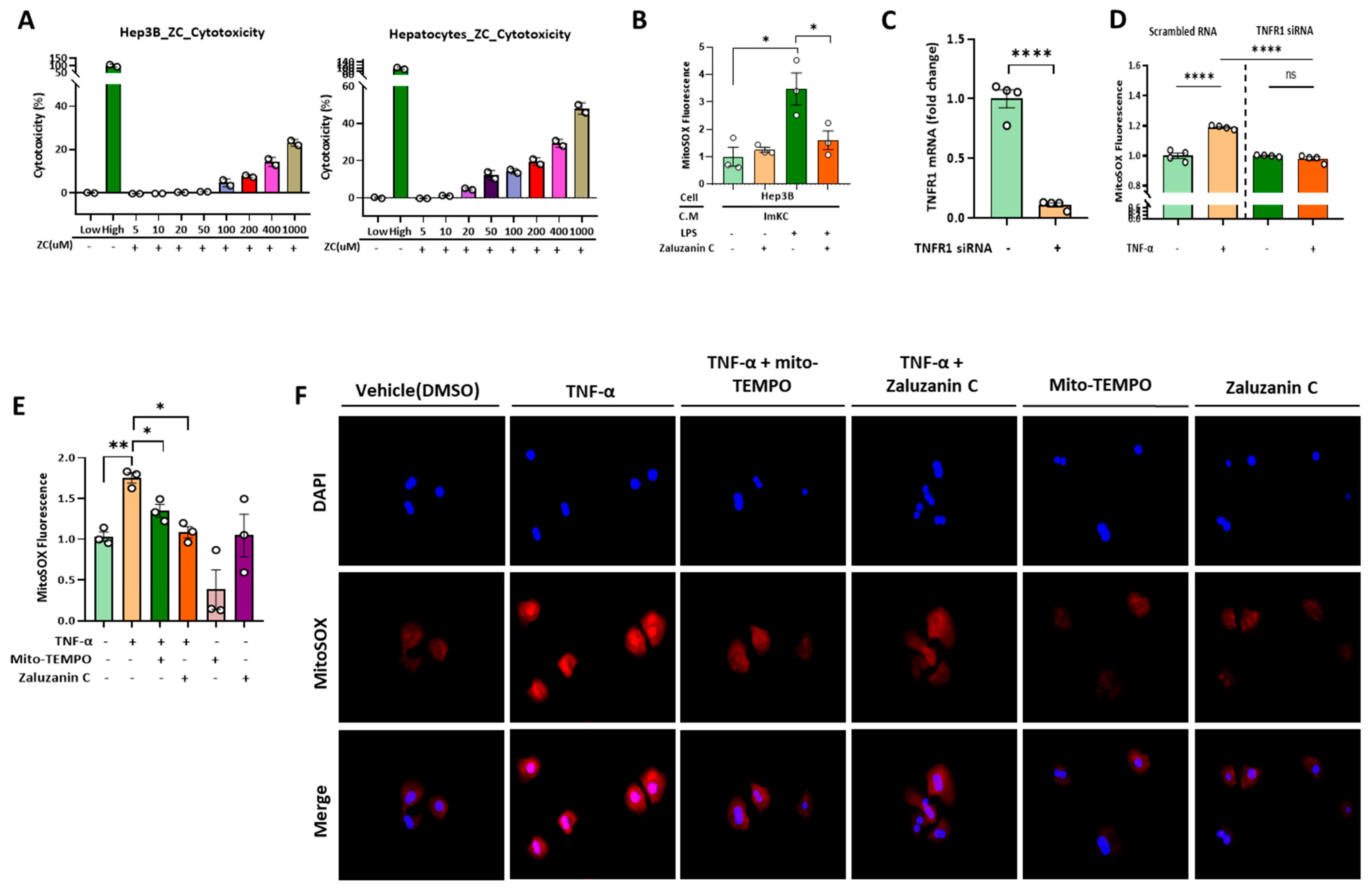
2.3. ZC Inhibits ROS Production in Hepatocytes Induced by TNF-α Secreted by ImKCs
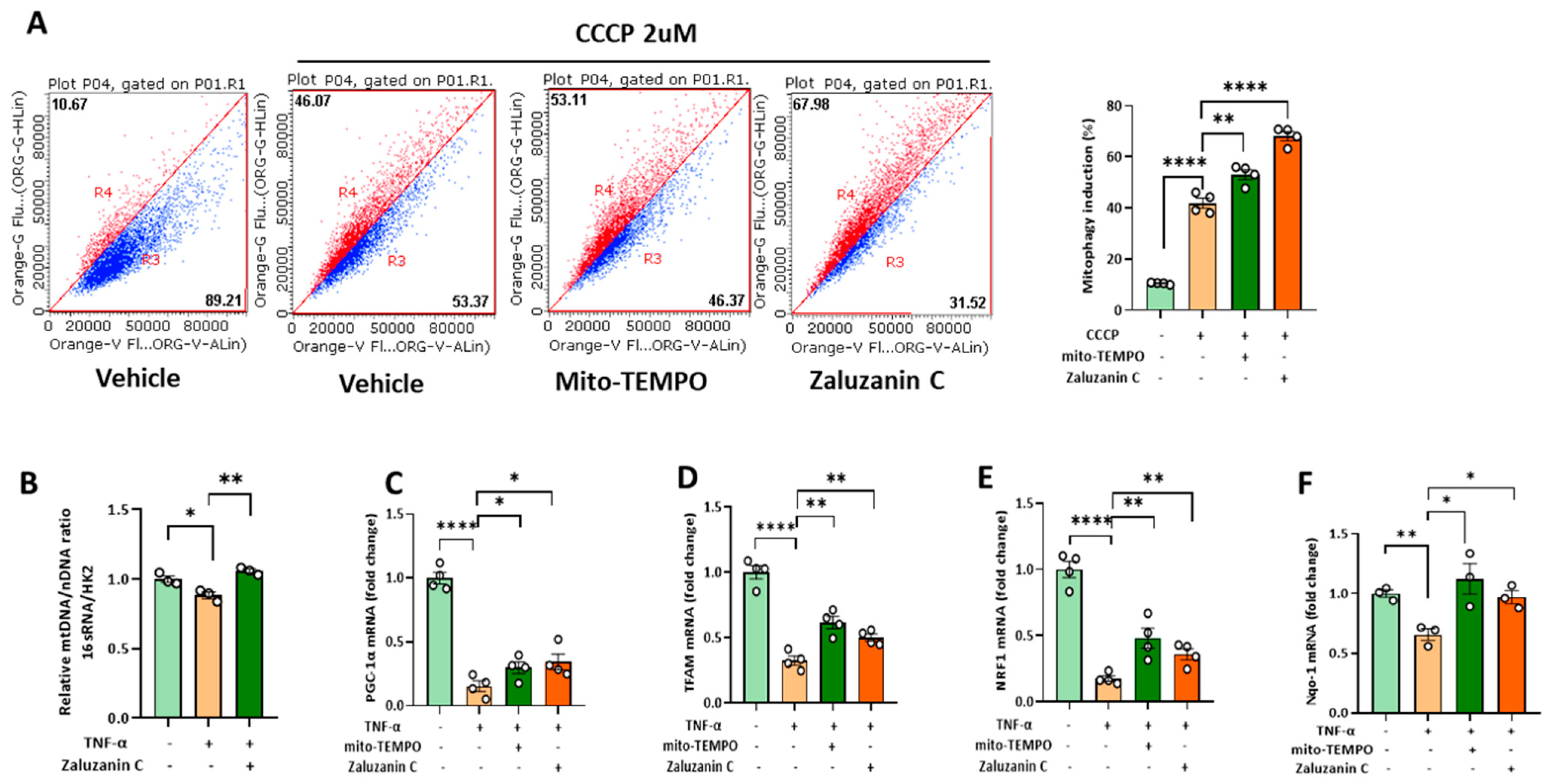
2.4. ZC Alleviates MtROS-Induced Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Hepatocytes
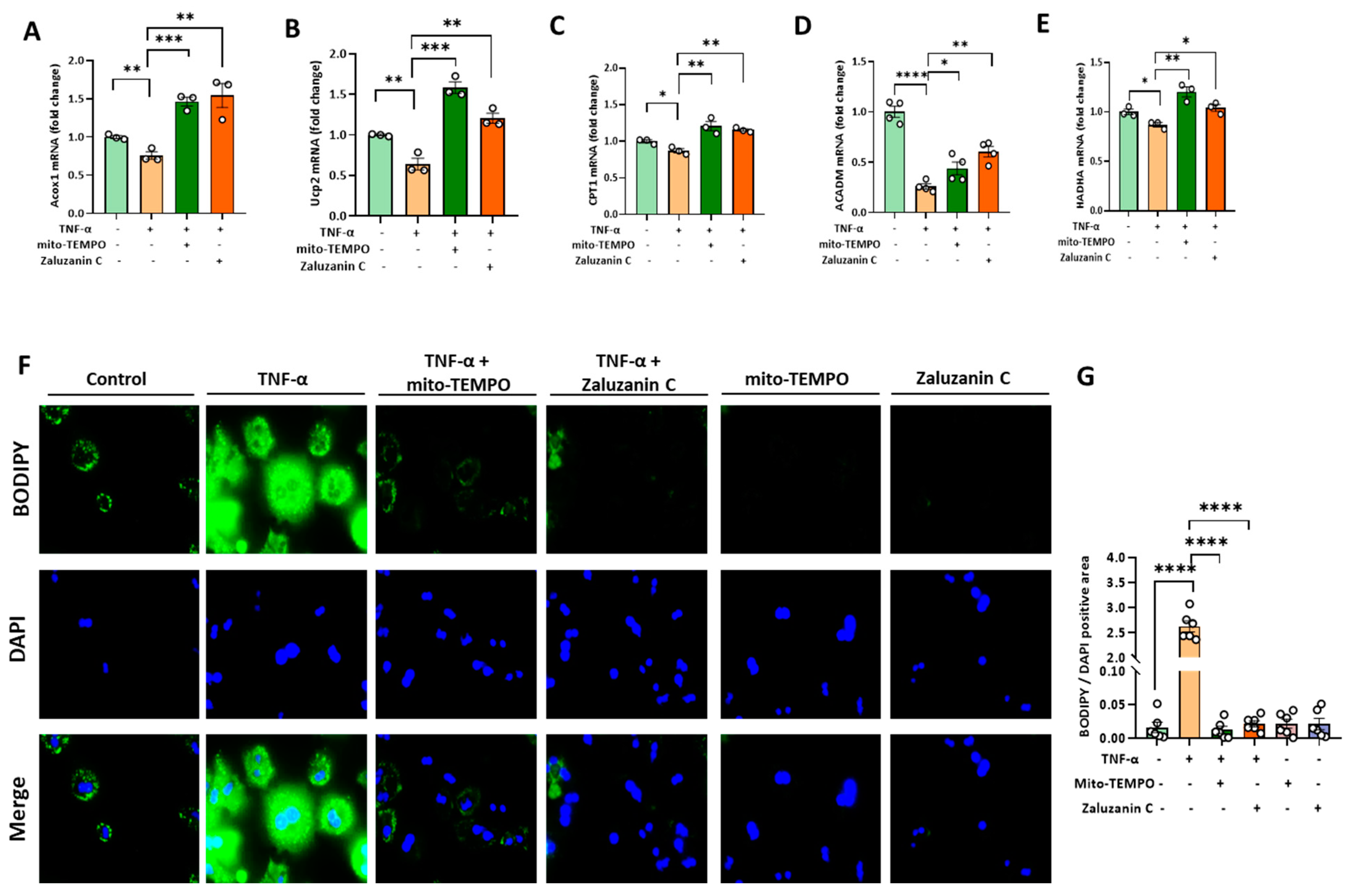
2.5. ZC Ameliorates ROS-Induced Lipid Accumulation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
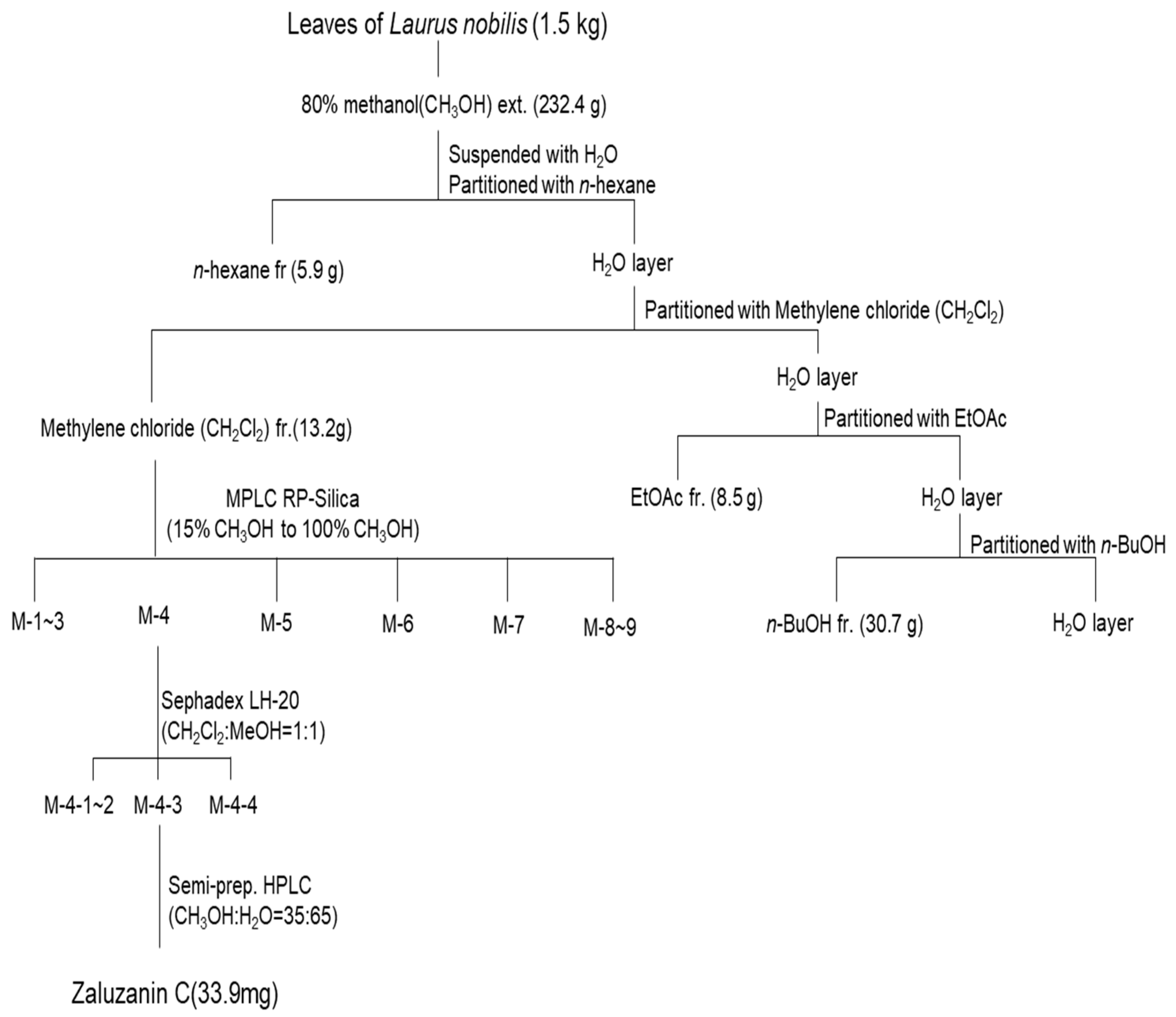
4.1. Isolation of ZC
4.2. Chemicals
4.3. Immortalized Mouse Kupffer Cells (ImKCs) and Hep3B Cell Culture
4.4. Primary Hepatocyte Cell Culture
4.5. Short Interfering RNA (siRNA) to Knock down Gene Expression
4.6. Cytotoxicity Assay
4.7. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
4.8. Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR) and Mitochondrial DNA Analysis
4.9. Western Blot Assay
4.10. Measurement and Staining of Mitochondrial Superoxide (MitoSOX)
4.11. Staining of Neutral Lipid Droplets for Microscopy
4.12. Flow Cytometry Analysis for Mitophagy
4.13. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NAFLD | Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease |
| KCs | Kupffer cells |
| mtROS | Mitochondrial ROS |
| ZC | Zaluzanin C |
| SOD | Superoxide dismutases |
| MitoSOX | Mitochondrial superoxides |
| ImKC | Immortalized mouse kupffer cells |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| TNF | Tumor necrosis factor |
| CCL | C-C motif ligand |
| CXCL | C-X-C motif ligand |
| CPT-1 | Carnitine palmitoyltransferase I |
| ACADM | Acyl-Coenzyme A dehydrogenase |
| HADHA | Hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase trifunctional multienzyme complex subunit alpha |
| PGC-1α | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha |
| TFAM | Mitochondrial transcription factor A |
| Nrf1 | Nuclear respiratory factor 1 |
| Nqo-1 | NAD(P)H quinone dehydrogenase 1 |
| Acox1 | Acyl-CoA oxidase 1 |
| Ucp2 | Uncoupling protein 2 |
References
- Benedict, M.; Zhang, X. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: An expanded review. World J. Hepatol. 2017, 9, 715–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrne, C.D.; Targher, G. NAFLD: A multisystem disease. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62 (Suppl. S1), S47–S64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heyens, L.J.M.; Busschots, D.; Koek, G.H.; Robaeys, G.; Francque, S. Liver Fibrosis in Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: From Liver Biopsy to Non-invasive Biomarkers in Diagnosis and Treatment. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 615978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pydyn, N.; Miękus, K.; Jura, J.; Kotlinowski, J. New therapeutic strategies in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A focus on promising drugs for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Pharmacol. Rep. 2020, 72, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-Y.; Yeh, M.M. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A review with clinical and pathological correlation. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2021, 120 Pt 1, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.F.; Wu, Y.K.; Mu, D.; Gong, J.P.; Wu, C.X.; Huang, C. Kupffer cells: Increasingly significant role in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Ann. Hepatol. 2014, 13, 489–495. [Google Scholar]
- Su, L.; Li, N.; Tang, H.; Lou, Z.; Chong, X.; Zhang, C.; Su, J.; Dong, X. Kupffer cell-derived TNF-α promotes hepatocytes to produce CXCL1 and mobilize neutrophils in response to necrotic cells. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Poulsen, K.L.; Wu, L.; Liu, S.; Miyata, T.; Song, Q.; Wei, Q.; Zhao, C.; Lin, C.; Yang, J. Targeted therapeutics and novel signaling pathways in non-alcohol-associated fatty liver/steatohepatitis (NAFL/NASH). Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzameli, I. The evolving role of mitochondria in metabolism. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 23, 417–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhowmick, S.; Singh, V.; Jash, S.; Lal, M.; Sinha Roy, S. Mitochondrial metabolism and calcium homeostasis in the development of NAFLD leading to hepatocellular carcinoma. Mitochondrion 2021, 58, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; He, F.; Barkema, H.W.; Xu, S.; Gao, J.; Liu, G.; Deng, Z.; Shahid, M.; Shi, Y.; Kastelic, J.P.; et al. Prototheca spp. induce an inflammatory response via mtROS-mediated activation of NF-κB and NLRP3 inflammasome pathways in bovine mammary epithelial cell cultures. Vet. Res. 2021, 52, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwabe, R.F.; Brenner, D.A. Mechanisms of Liver Injury. I. TNF-alpha-induced liver injury: Role of IKK, JNK, and ROS pathways. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2006, 290, G583–G589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diehl, K.L.; Vorac, J.; Hofmann, K.; Meiser, P.; Unterweger, I.; Kuerschner, L.; Weighardt, H.; Förster, I.; Thiele, C. Kupffer Cells Sense Free Fatty Acids and Regulate Hepatic Lipid Metabolism in High-Fat Diet and Inflammation. Cells 2020, 9, 2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kastl, L.; Sauer, S.W.; Ruppert, T.; Beissbarth, T.; Becker, M.S.; Süss, D.; Krammer, P.H.; Gülow, K. TNF-α mediates mitochondrial uncoupling and enhances ROS-dependent cell migration via NF-κB activation in liver cells. FEBS Lett. 2014, 588, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, M.; Fontanesi, F.; Merscher, S.; Fornoni, A. The Vicious Cycle of Renal Lipotoxicity and Mitochondrial Dysfunction. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Lee, G.; Heo, S.-Y.; Roh, Y.-S. Oxidative Stress Is a Key Modulator in the Development of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, C.; Wong, V.K.W.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, W. Phytotherapy using blueberry leaf polyphenols to alleviate non-alcoholic fatty liver disease through improving mitochondrial function and oxidative defense. Phytomedicine 2020, 69, 153209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.G.; Kang, J.K.; Lee, K.R.; Lee, H.W.; Han, J.W.; Choi, W.S. Suppression of inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 expression in RAW 264.7 macrophages by sesquiterpene lactones. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2005, 68, 2119–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotina-Hennsen, B.; Bernal-Morales, E.; Roo De Vivar, A.; Perez, C.A.; Castro, R.A.; Aguilar-Martinez, M. Inhibition of oxygen evolution by zaluzanin C. J. Chem. Ecol. 1992, 18, 1891–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, S.H.; Kim, Y.H. Zaluzanin C Inhibits Differentiation of 3T3-L1 Preadipocytes into Mature Adipocytes. J. Obes. Metab. Syndr. 2019, 28, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranneh, Y.; Akim, A.M.; Hamid, H.A.; Khazaai, H.; Fadel, A.; Mahmoud, A.M. Stingless bee honey protects against lipopolysaccharide induced-chronic subclinical systemic inflammation and oxidative stress by modulating Nrf2, NF-κB and p38 MAPK. Nutr. Metab. 2019, 16, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, S.; Nakagawa, Y.; Tsuji, A.; Kitagishi, Y.; Nakanishi, A.; Murai, T. Implications of PI3K/AKT/PTEN Signaling on Superoxide Dismutases Expression and in the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s Disease. Diseases 2018, 6, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minatel, I.O.; Francisqueti, F.; Correa, C.; Lima, G. Antioxidant Activity of γ-Oryzanol: A Complex Network of Interactions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Min, J.-S.; Kim, B.; Chae, U.-B.; Yun, J.W.; Choi, M.-S.; Kong, I.-K.; Chang, K.-T.; Lee, D.-S. Mitochondrial ROS govern the LPS-induced pro-inflammatory response in microglia cells by regulating MAPK and NF-κB pathways. Neurosci. Lett. 2015, 584, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Liu, S.; Wang, C.; Yuan, Y.; Yang, G.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, J.; Lu, Y.; et al. Mitochondrial ROS promote mitochondrial dysfunction and inflammation in ischemic acute kidney injury by disrupting TFAM-mediated mtDNA maintenance. Theranostics 2021, 11, 1845–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashrafi, G.; Schwarz, T.L. The pathways of mitophagy for quality control and clearance of mitochondria. Cell Death Differ. 2013, 20, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.; Malide, D.; Liu, J.; Rovira, I.I.; Combs, C.A.; Finkel, T. A fluorescence-based imaging method to measure in vitro and in vivo mitophagy using mt-Keima. Nat. Protoc. 2017, 12, 1576–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, Y.; Xin, Y.; Tian, G.; Zhou, J.; Liu, X. Mitochondrial ROS-Modulated mtDNA: A Potential Target for Cardiac Aging. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 9423593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Lang, H.; Chen, K.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Ran, L.; Yi, L.; Mi, M.; Zhang, Q. Resveratrol protects against nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by improving lipid metabolism and redox homeostasis via the PPARα pathway. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2020, 45, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlov, A.; Lancaster, J.; Meszaros, A.; Weidinger, A. Mitochondria-meditated pathways of organ failure upon inflammation. Redox Biol. 2017, 13, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Metlakunta, A.; Dedousis, N.; Zhang, P.; Sipula, I.; Dube, J.J.; Scott, D.K.; O’Doherty, R.M. Depletion of Liver Kupffer Cells Prevents the Development of Diet-Induced Hepatic Steatosis and Insulin Resistance. Diabetes 2009, 59, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, L.; Ye, S.; Jiang, R.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, J.; Meng, S. Liensinine alleviates high fat diet (HFD)-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) through suppressing oxidative stress and inflammation via regulating TAK1/AMPK signaling. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 104, 108306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, H.; Wang, L.; Xue, T.; Li, J.; Pei, L.; Zheng, M. Plant sterol ester of α-linolenic acid improves NAFLD through modulating gut microbiota and attenuating lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation via regulating TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway. J. Funct. Foods 2022, 94, 105137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Maciá, M.; Simón, J.; González-Rellan, M.J.; Azkargorta, M.; Goikoetxea-Usandizaga, N.; Lopitz-Otsoa, F.; De Urturi, D.S.; Rodríguez-Agudo, R.; Lachiondo-Ortega, S.; Mercado-Gomez, M.; et al. Neddylation inhibition ameliorates steatosis in NAFLD by boosting hepatic fatty acid oxidation via the DEPTOR-mTOR axis. Mol. Metab. 2021, 53, 101275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Deng, X.; Zhu, X.; Yan, Q.; Zhou, N.; Du, S.; Li, X. HtrA2/Omi mitigates NAFLD in high-fat-fed mice by ameliorating mitochondrial dysfunction and restoring autophagic flux. Cell Death Discov. 2022, 8, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.-J.; Zhang, G.-F.; Zheng, J.-Y.; Sun, J.-H.; Ding, S.-B. Targeting Mitochondrial ROS-Mediated Ferroptosis by Quercetin Alleviates High-Fat Diet-Induced Hepatic Lipotoxicity. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 876550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Ruan, S.; Shen, H.; Guan, Q.; Zhai, L.; Yang, Y. Oridonin regulates the polarized state of Kupffer cells to alleviate nonalcoholic fatty liver disease through ROS-NF-κB. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 101, 108290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xu, T.; Chen, J.; Shao, Z.; Wang, K.; Yan, Y.; Wu, C.; Lin, J.; Wang, H.; Gao, W.; et al. Parkin-mediated mitophagy as a potential therapeutic target for intervertebral disc degeneration. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suematsu, N.; Tsutsui, H.; Wen, J.; Kang, D.; Ikeuchi, M.; Ide, T.; Hayashidani, S.; Shiomi, T.; Kubota, T.; Hamasaki, N.; et al. Oxidative stress mediates tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced mitochondrial DNA damage and dysfunction in cardiac myocytes. Circulation 2003, 107, 1418–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dongiovanni, P.; Anstee, Q.; Valenti, L. Genetic Predisposition in NAFLD and NASH: Impact on Severity of Liver Disease and Response to Treatment. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2013, 19, 5219–5238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Lv, W.-H.; Hogstrand, C.; Zhang, D.-G.; Xu, Y.-C.; Xu, Y.-H.; Luo, Z. Sirt3-Sod2-mROS-Mediated Manganese Triggered Hepatic Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Lipotoxicity in a Freshwater Teleost. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 8020–8033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Gao, J.; Hou, H.; Qi, Z.; Chen, H.; Zhang, X.-X. Inhibition of Mitochondrial Fatty Acid Oxidation Contributes to Development of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Induced by Environmental Cadmium Exposure. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 13992–14000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berlanga, A.; Guiu-Jurado, E.; Porras, J.; Auguet, T. Molecular pathways in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin. Exp. Gastroenterol. 2014, 7, 221–239. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Auger, C.; Alhasawi, A.; Contavadoo, M.; Appanna, V. Dysfunctional mitochondrial bioenergetics and the pathogenesis of hepatic disorders. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2015, 3, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.-C.; Qu, J.; Xie, S.-Y.; Yang, S.; Yao, H.-W. Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Chronic Respiratory Diseases: Implications for the Pathogenesis and Potential Therapeutics. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 5188306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soret, P.-A.; Magusto, J.; Housset, C.; Gautheron, J. In Vitro and In Vivo Models of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Critical Appraisal. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bettaieb, A.; Jiang, J.X.; Sasaki, Y.; Chao, T.I.; Kiss, Z.; Chen, X.; Tian, J.; Katsuyama, M.; Yabe-Nishimura, C.; Xi, Y.; et al. Hepatocyte Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate Reduced Oxidase 4 Regulates Stress Signaling, Fibrosis, and Insulin Sensitivity During Development of Steatohepatitis in Mice. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 468–480.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oniciu, D.; Hashiguchi, T.; Shibazaki, Y.; Bisgaier, C. Gemcabene downregulates inflammatory, lipid-altering and cell-signaling genes in the STAM™ model of NASH. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, K.; Itoh, Y.; Yokomizo, C.; Nishimura, T.; Niimi, T.; Umemura, A.; Fujii, H.; Okanoue, T.; Yoshikawa, T. Blockade of IL-6 signaling exacerbates liver injury and suppresses antiapoptotic gene expression in methionine choline-deficient diet-Fed db/db mice. Lab. Investig. 2011, 91, 609–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, Y.-C.; Lee, K.-C.; Wu, P.-S.; Huo, T.-I.; Huang, Y.-H.; Hou, M.-C.; Lin, H.-C. Eritoran Attenuates Hepatic Inflammation and Fibrosis in Mice with Chronic Liver Injury. Cells 2021, 10, 1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turk, A.; Ahn, J.; Jo, Y.; Song, J.Y.; Khalife, H.; Gali-Muhtasib, H.; Kim, Y.I.; Hwang, B.Y.; Lee, M.K. NF-κB inhibitory sesquiterpene lactones from Lebanese Laurus nobilis. Phytochem. Lett. 2019, 30, 120–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiros, P.M.; Goyal, A.; Jha, P.; Auwerx, J. Analysis of mtDNA/nDNA ratio in mice. Curr. Protoc. Mouse Biol. 2017, 7, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Gene. | Forward (5′ to 3′) | Reverse (5′ to 3′) |
|---|---|---|
| Mouse | ||
| GAPDH | ACGGCAAATTCAACGGCACAG | AGACTCCACGACATACTCAGCAC |
| IL-1β | CTCGCAGCAGCACATCAACAAG | CCACGGGAAAGACACAGGTAGC |
| TNF-α | AGGGTCTGGGCCATAGAACT | CCACCACGCTCTTCTGTCTA |
| CCL2 | ATTGGGATCATCTTGCTGGT | CCTGCTGTTCACAGTTGCC |
| CCL3 | TCCCAGCCAGGTGTCATTTTCC | CAGTTCCAGGTCAGTGATGTATTCTTG |
| CCL4 | CTCTGCGTGTCTGCCCTCTC | TGGTCTCATAGTAATCCATCAC |
| CXCL2 | GCCAAGGGTTGACTTCAAGAACA | AGGCTCCTCCTTTCCAGGTCA |
| CXCL9 | GGAACCCTAGTGATAAGGAATGCA | TGAGGTCTTTGAGGGATTTGTAGTG |
| TNFR1 | GCTGGAGATGCAGAACGGGC | ACGAGGGGGCGGGATTTCTC |
| 16sRNA | CCGCAAGGGAAAGATGAAAGAC | TCGTTTGGTTTCGGGGTTTC |
| HK2 | GCCAGCCTCTCCTGATTTTAGTGT | GGGAACACAAAAGACCTCTTCTGG |
| Human | ||
| β-Actin | AGAGCTACGAGCTGCCTGAC | AGCACTGTGTTGGCGTACAG |
| CPT1 | TCCAGTTGGCTTATCGTGGTG | TCCAGAGTCCGATTGATTTTTGC |
| ACADM | GCCTGCTTGTTGCTGTAGACTCC | ATTGCTGCCTGATTGTTCCTCTGG |
| HADHA | TTACCAGGAGCAGGAGGCACAC | GAGGCAGGAGAATCGCTTGAACC |
| PGC-1α | TTTGTTCCTTGCTTCTTTGGCTTCTTG | TGCTTGGCTACGGTAATCATCACTATG |
| TFAM | CTCGCTTCTCCCATCCCTCCTC | GTATCCAACGCCTTCAACAAGAATGC |
| Nrf1 | CCAGACGACGCAAGCATCAGAG | CTGTTCCAATGTCACCACCTCCAC |
| Nqo-1 | GCTGGAGTGCAGTGGTGTGATC | ACTTTGGGAGGCTGAGGTAGGC |
| Acox1 | GGCGAGACCTCCCTCCTTTCC | CAGGGTCAGCGATGCCAAACTC |
| Ucp2 | GGCTGGAGGTGGTCGGAGATAC | GGCAGAAGTGAAGTGGCAAGGG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jung, J.-W.; Wang, F.; Turk, A.; Park, J.-S.; Ma, H.; Ma, Y.; Noh, H.-R.; Sui, G.; Shin, D.-S.; Lee, M.-K.; et al. Zaluzanin C Alleviates Inflammation and Lipid Accumulation in Kupffer Cells and Hepatocytes by Regulating Mitochondrial ROS. Molecules 2023, 28, 7484. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28227484
Jung J-W, Wang F, Turk A, Park J-S, Ma H, Ma Y, Noh H-R, Sui G, Shin D-S, Lee M-K, et al. Zaluzanin C Alleviates Inflammation and Lipid Accumulation in Kupffer Cells and Hepatocytes by Regulating Mitochondrial ROS. Molecules. 2023; 28(22):7484. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28227484
Chicago/Turabian StyleJung, Ji-Won, Feng Wang, Ayman Turk, Jeong-Su Park, Hwan Ma, Yuanqiang Ma, Hye-Rin Noh, Guoyan Sui, Dong-Su Shin, Mi-Kyeong Lee, and et al. 2023. "Zaluzanin C Alleviates Inflammation and Lipid Accumulation in Kupffer Cells and Hepatocytes by Regulating Mitochondrial ROS" Molecules 28, no. 22: 7484. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28227484
APA StyleJung, J.-W., Wang, F., Turk, A., Park, J.-S., Ma, H., Ma, Y., Noh, H.-R., Sui, G., Shin, D.-S., Lee, M.-K., & Roh, Y. S. (2023). Zaluzanin C Alleviates Inflammation and Lipid Accumulation in Kupffer Cells and Hepatocytes by Regulating Mitochondrial ROS. Molecules, 28(22), 7484. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28227484







