Abstract
Malignant cardiac arrhythmias with high morbidity and mortality have posed a significant threat to our human health. Scutellarein, a metabolite of Scutellarin which is isolated from Scutellaria altissima L., presents excellent therapeutic effects on cardiovascular diseases and could further be metabolized into methylated forms. A series of 22 new scutellarein derivatives with hydroxyl-substitution based on the scutellarin metabolite in vivo was designed, synthesized via the conjugation of the scutellarein scaffold with pharmacophores of FDA-approved antiarrhythmic medications and evaluated for their antiarrhythmic activity through the analyzation of the rat number of arrhythmia recovery, corresponding to the recovery time and maintenance time in the rat model of barium chloride-induced arrhythmia, as well as the cumulative dosage of aconitine required to induce VP, VT, VF and CA in the rat model of aconitine-induced arrhythmia. All designed compounds could shorten the time of the arrhythmia continuum induced by barium chloride, indicating that 4′-hydroxy substituents of scutellarein had rapid-onset antiarrhythmic effects. In addition, nearly all of the compounds could normalize the HR, RR, QRS, QT and QTc interval, as well as the P/T waves’ amplitude. The most promising compound 10e showed the best antiarrhythmic activity with long-term efficacy and extremely low cytotoxicity, better than the positive control scutellarein. This result was also approved by the computational docking simulation. Most importantly, patch clamp measurements on Nav1.5 and Cav1.2 channels indicated that compound 10e was able to reduce the INa and ICa in a concentration-dependent manner and left-shifted the inactivation curve of Nav1.5. Taken together, all compounds were considered to be antiarrhythmic. Compound 10e even showed no proarrhythmic effect and could be classified as Ib Vaughan Williams antiarrhythmic agents. What is more, compound 10e did not block the hERG potassium channel which highly associated with cardiotoxicity.
1. Introduction
Sudden cardiac death caused by malignant cardiac arrhythmias including ventricular tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation and cardiac arrest with high morbidity and mortality over recent decades have posed a significant threat to our human health, accounting for 15–20% of all deaths [1]. One major cause for arrythmias is the aberrant sinus node firing of electrical signals mediated by the voltage-gated ion channels including Na, K and Ca, etc., and β-adrenergic stimulation [2]. Based on the different mechanisms of action, antiarrhythmic drugs could be classified into four classes such as Na channel blockers (category I), β-receptor blockers (category II), K channel blockers (category III) and Ca channel blockers (category IV) according to the Vaughan Williams’ classification [3]. At present, antiarrhythmic drugs were the predominant clinical treatments, but almost all of them had proarrhythmic effects at different degrees [4,5]. In traditional Chinese medicine, arrhythmia could be classified as “palpitations” [6]. Anti-arrhythmic Chinese medicine formulas had advantages of safety in the prevention and treatment of arrhythmias, for instance, Wen Xin Granules and Shensong Yangxin Capsules [7,8,9,10,11]. Therefore, screening from natural products in Chinese materia medica acting as antiarrhythmic drugs mediated by multiple ion channels seemed to be an approach of importance [12,13].
Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) has been widely used to treat cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases with unique clinical benefits including multi-target pharmacological functions and fewer side effects [14,15,16]. Particularly, a panel of dietary flavonoids have been reported [17,18,19]. Scutellarin isolated from Scutellaria altissima L. has been reported to present excellent therapeutic effects on cardiovascular diseases and inflammation [20,21]. Recent investigations also have provided evidence for its multiple pharmacological properties such as anti-cancer, anticonvulsive, antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, hepatoprotective, antibacterial, antiviral and neuroprotective activity [22,23,24,25]. Meanwhile, the long-term regimen of a high-dose scutellarin was also proved to be a sufficient margin of safety suggested by acute and subacute toxicity studies [26]. These investigations confirmed that scutellarin could be a promising drug candidate for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases.
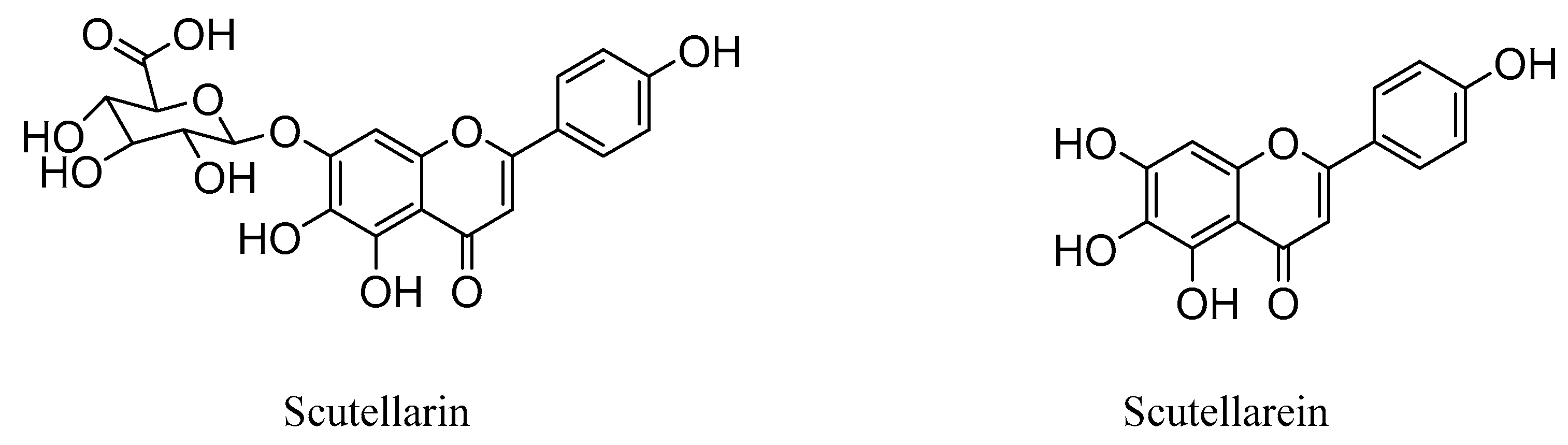
Interestingly, studies have revealed that the prodrug scutellarin transformed into scutellarein in vivo, which could further be metabolized into methylated forms, as shown in Figure 1 [27,28,29,30]. Therefore, scutellarein analogues bearing substitutes at the hydroxyl group could be more metabolic stable and have a much higher bioavailability in vivo, compared with scutellarin only with 0.4% oral bioavailability in a beagle dog [31,32].
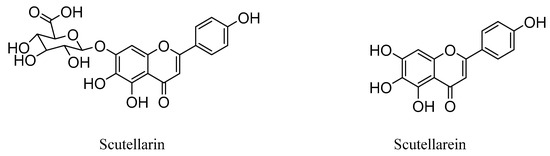
Figure 1.
Chemical structures of scutellarin and scutellarein.
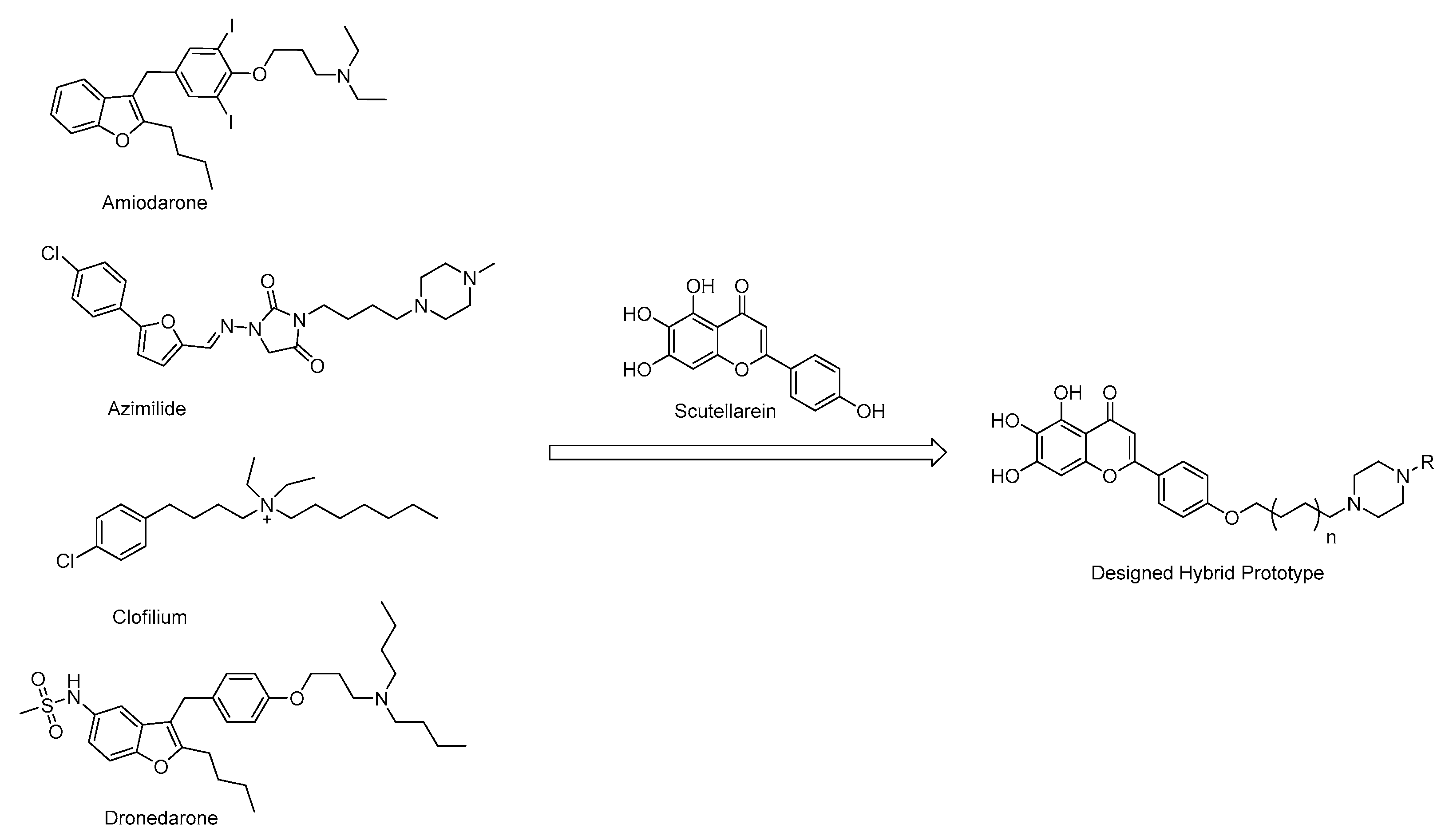
Based on the structural analysis results of antiarrhythmic drugs approved by the FDA, such as Amiodarone, Dronedarone, Azimilide, etc., it was found that they all have a nitrogen atom-containing group, which easily transforms to quaternary ammonium salts with an ability to bind to the peptide anion on the cardiomyocyte membrane (Figure 2).
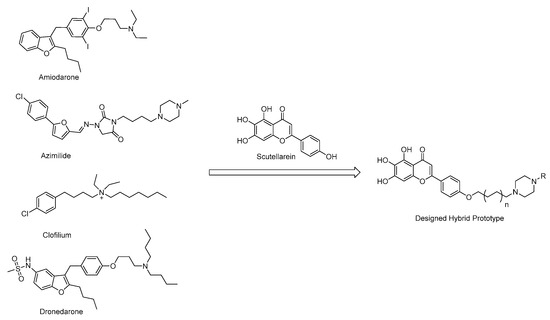
Figure 2.
Chemical structures of antiarrhythmic drugs approved by FDA and Design strategy of new scutellarein derivatives.
In order to find the Structure–Activity relationships (SAR) of scutellarein derivatives, herein we described the synthesis and in vivo antiarrhythmic evaluation of a novel series of scutellarein analogues via semi-synthetic methods. By adopting a hybrid prototype combining scutellarein and tertiary amines, 22 novel compounds were designed and synthesized. Then, the antiarrhythmic activities of these compounds were evaluated by the detection of the rat number of arrhythmia recovery, corresponding to the recovery time, maintenance time, as well as ECG parameters such as heart rate (HR), QT interval (QT), QRS interval, QTc interval (QTc) and the amplitude of P and T waves in the rat model of barium chloride-induced arrhythmia. Meanwhile, the cumulative dosage of aconitine required to induce ventricular premature beats (VP), ventricular tachycardia (VT), ventricular fibrillation (VF) and cardiac arrest (CA) in the rat model of aconitine-induced arrhythmia were also determined. Furthermore, to reveal the antiarrhythmic mechanism of these compounds, we examined their effects on voltage-gated ion channels including Nav1.5 and Cav1.2. Nav1.5 is the dominant voltage-gated sodium channel in the heart, responsible for type 3 long QT syndrome (LQT3) and Brugada syndrome (BrS). The dysfunction of the Nav channels is generally associated with multiple pathophysiological syndromes, exemplified by arrhythmias, seizures, epilepsy, autism and Parkinson’s disease [33]. We have also confirmed that regulation of the Nav channels could reverse peripheral neuropathic pain [34,35,36]. Among the Cav channels, the Cav1 family belonging to the L-type channels require strong depolarization for activation to form the dominant Ca2+ influx route in vascular cells. The drug-associated inhibition of hERG potassium channels could cause long QT syndrome and trigger fatal arrhythmias such as torsades de pointes (Tdp) [37]. In recent years, a variety of non-anti-arrhythmic drugs such as terfenadine, asimizole and astemizole have been removed by the FDA, mainly due to fatal arrhythmias caused by the inhibition of hERG potassium channels, also known as Kv11.1 [38]. Therefore, we also reported here the effects of these compounds on hERG potassium channels to illustrate whether it displayed cardiotoxicity or not.
2. Results
2.1. Chemistry
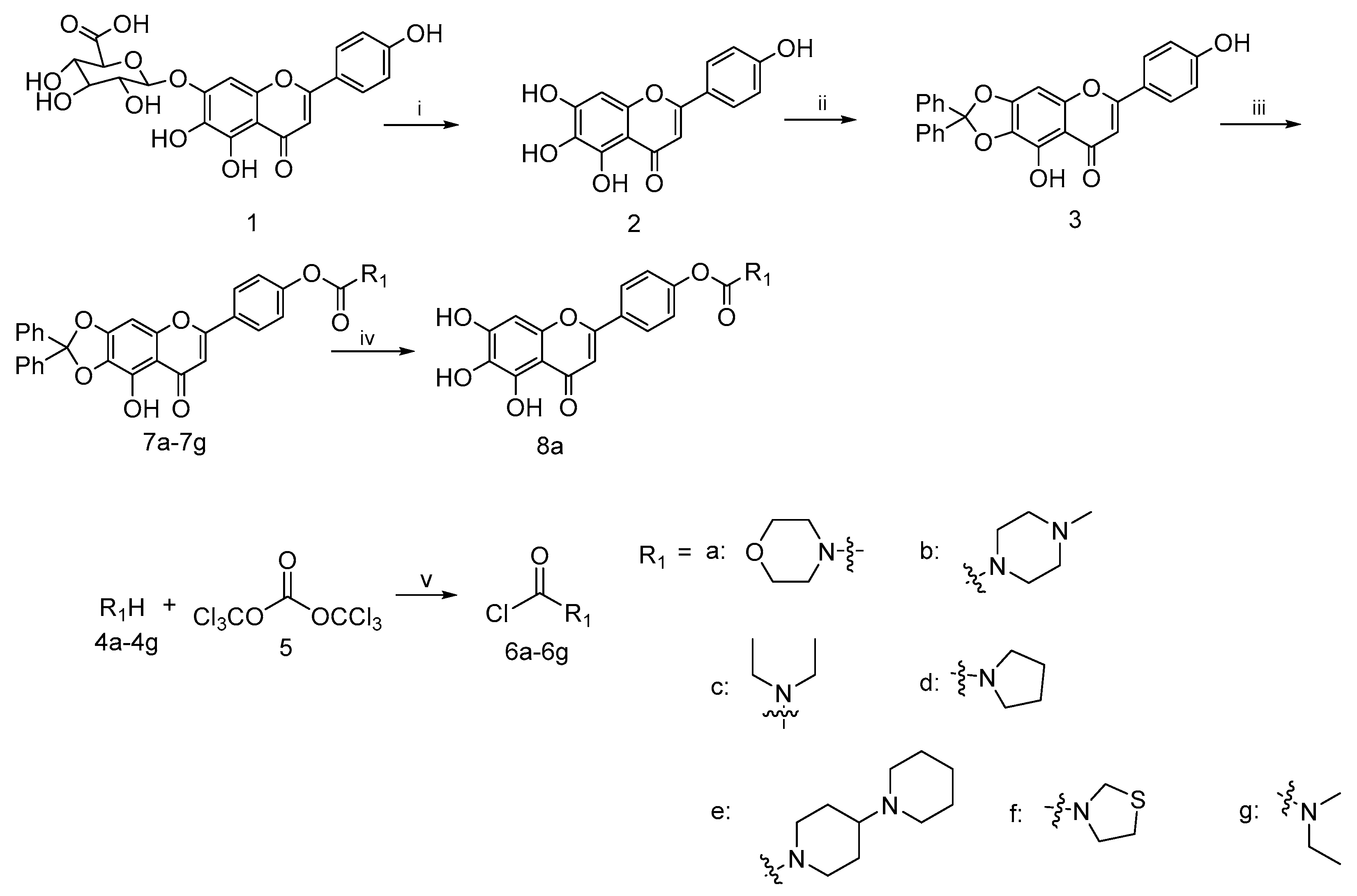
Based on the previous reports, a concise synthetic route for the preparation of an intermediate compound with good yields was depicted in Scheme 1. Starting from the commercially available scutellarin (1), the conversion to compound 2 by refluxing with 6N H2SO4 in alcohol followed by subsequent protection with dichlorodiphenylmethane using a diphenyl ether as the solvent and esterification with a wide range of fresh prepared acid chloride 6a–6h using K2CO3 and KI as the catalysts in N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF), we successfully afforded the target compounds 7a–7h in three steps with reasonably good yields. The deprotection of 7a in the presence of a catalytic amount of 10% palladium on carbon at the room temperature gave the compound 8a in good yield [39].
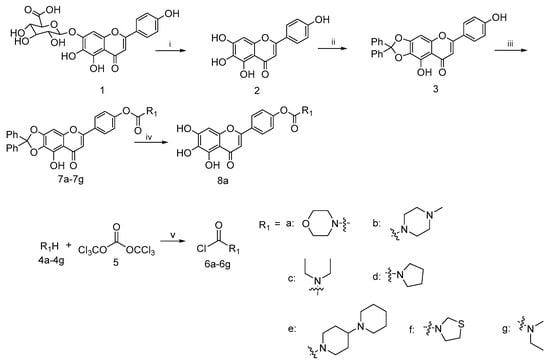
Scheme 1.
Reagents and conditions: (i) H2SO4, EtOH, N2, reflux, 8 h; (ii) dichlorodiphenylmethane, diphenyl ether, 175 °C, 30 min; (iii) 6a–6g, K2CO3, KI, DMF, 25 °C, 24 h; (iv) H2, 10%Pd/C, THF/EtOH, 12 h; (v) Et3N, DCM, N2, 0 °C, 5 h.
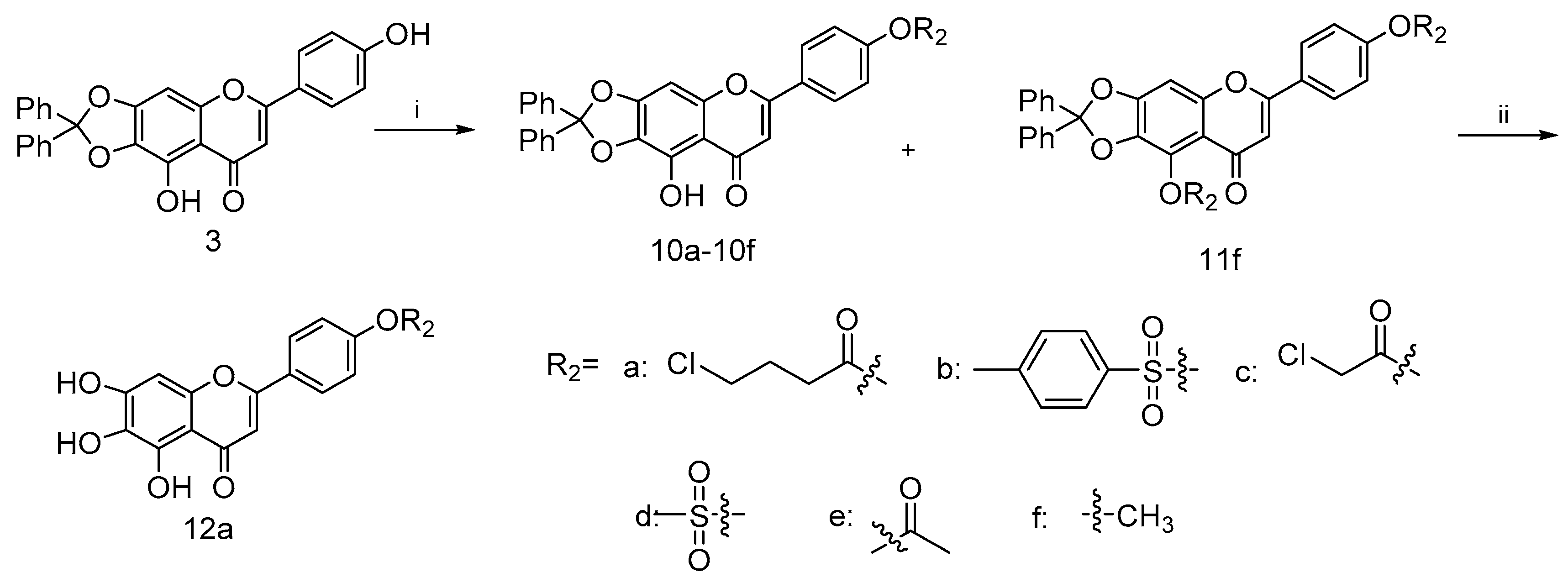
Similarly, the coupling of intermediate 3 with various acid chloride 9a–9e in the presence of Et3N gave 10a–10e, as shown in Scheme 2 [40,41]. Such efficient syntheses of 4′-substituted scutellarein derivatives allowed the rapid construction of target compounds for subsequent biological studies. In addition, scutellarein derivatives 10f and 11f were obtained in moderate yields as the consequences of the methylation of 3, respectively. Subsequently, the palladium-on-carbon-catalyzed facile hydrogenative deprotection of 10a in THF/EtOH solution with an H2 atmosphere at room temperature produced 12a.
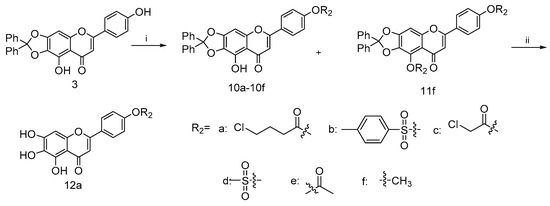
Scheme 2.
Reagents and conditions: (i) for 9a–9e, Et3N, DMF, 25 °C, 24 h; for 10f and 11f, K2CO3, KI, DMF, 25 °C, 24 h (ii) H2, 10%Pd/C, THF/EtOH, 12 h.
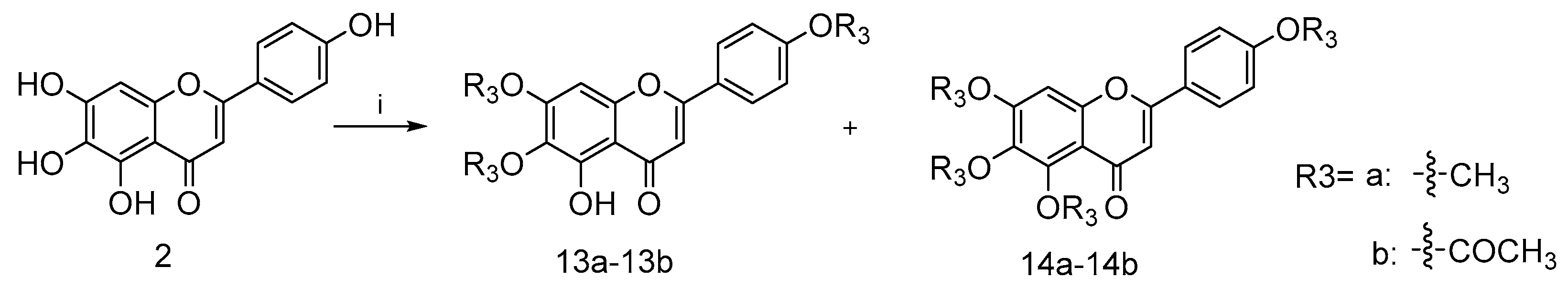
Furthermore, compounds 13a–13b with a methyl group and 14a–14b with a acetyl group were prepared as shown in Scheme 3 in order to explore the importance of the 1-phenolic hydroxyl group. The treatment of intermediate 2 with methyl iodide or acetic anhydride gave the desired compound 13a–13b and 14a–14b, respectively.
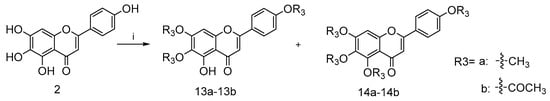
Scheme 3.
Reagents and conditions: (i) for 13a and 14a, NaH, pyridine, 25 °C, 12 h; for 13b and 14b, DMAP, pyridine, 25 °C, 12 h.
2.2. Biological Activity
According to the published method, the antiarrhythmic activity of the synthetic compounds was examined in a barium chloride- or aconitine-induced arrhythmia rat model [42]. Normal electrocardiogram (ECG) waves could be observed before intraperitoneal anesthesia with pentobarbital sodium (50 mg/kg) and before a sublingual vein injection of barium chloride (4 mg/kg). The aftermath of the administration of arrhythmogen including BaCl2 and aconitine was the occurrence of VP, followed by aggravating VT and VF, eventually with CA resulting in the cardiac mortality of the rat.
2.2.1. Antiarrhythmic Effects of Scutellarein Derivatives on BaCl2-Induced Arrhythmia in Rats
The criterion for antiarrhythmic activity was the gradual disappearance of arrhythmia and the restoration of the sinus rhythm. The observation was performed for 35 min. A total of 22 scutellarein derivatives administrated at a dose of 8 mg/kg were evaluated for antiarrhythmic activity by monitoring the recovery period from arrhythmia and the duration of recovery maintenance after treatments. BaCl2 (4 mg/kg) administered into the sublingual vein evokes heart rhythm irregularities including extrasystoles, conduction blocks and bradycardia which lead to long QT syndrome. The negative control group such as the NS or DMSO group receiving no treatment except for the administration of arrhythmogen showed arrhythmia, suggesting that the barium chloride-induced arrhythmia rat model was set up successfully. Both the lead compound scutellarein at a dose of 8 mg/kg and the FDA-approved antiarrhythmic drug Verapamil (Ver) at a dose of 2 mg/kg acted as positive controls for comparison.
These results shown in Table 1 suggest that nearly all of the scutellarein analogues exhibited better antiarrhythmic activity against barium chloride-induced arrhythmia than that of the positive control scutellarein, especially shortening the time of the arrhythmia continuum, indicating that 4′-hydroxy substituents of scutellarein had rapid-onset antiarrhythmic effects (p < 0.001; Table 1). Meanwhile, the onset time of our synthetic compounds showed no difference with that of Ver. Compounds 8a and 12a, without the diphenyl protecting group, even displayed weaker antiarrhythmic activity with a shorter duration of efficacy, compared with the corresponding compounds 7a and 10a. At the same time, the number of rats with a duration of efficacy larger than 20 min was decreased by 1–2, respectively. This might be ascribed to the steric hindrance of the diphenyl protecting group hampering the metabolism of the scutellarein analogues, which leads to an extension of the duration of efficacy, suggesting that the 6,7- and 4′-hydroxyl groups of scutellarein would not be beneficial for antiarrhythmic activity. In addition, it was worthy to notice that compounds 7b, 10a, 10e, 11f and 13b with the 4′-hydroxyl substituents and the diphenyl group exhibited better antiarrhythmic effects than that of the positive control scutellarein, subject to the speeding up of the onset of drugs. Compound 10e even had a longer duration of efficacy (p < 0.05) and a shorter time to onset (p < 0.001) than the lead compound scutellarein. In addition, the number of rats with a duration of efficacy larger than 20 min also increased, further proving the aforementioned conclusion. However, the methylated compounds 13a and 14a have a much shorter duration time than the acetylated compounds 13b and 14b. This is mainly due to the fact that acetylated compounds could be easier to metabolize.

Table 1.
Onset time and duration of efficacy of scutellarein derivatives on BaCl2-induced arrhythmia in rats.
Generally, arrhythmias could give rise to long QT syndrome. The results, as shown in the Table 2, further prove this situation. The administration of BaCl2 prior to the investigated compounds (pre-dose group) caused a significant extension in QT duration, whereas the injection of the tested compounds (post-dose group) could sharply reduce the duration of QT and even made no difference with the normal group, with the exception of the negative control groups (p < 0.001), as well as Ver, 10b, 11f and 12a (p < 0.05). Moreover, an injection of the tested compounds could all significantly alter the QT intervals compared with that of the NS group (p < 0.05, p < 0.01 or p < 0.001). Based on the conclusion that the synthesized compounds could restore the QT interval, it was suggested that the synthesized compounds may be targeted to treat sudden cardiac death caused by ventricular tachycardia.

Table 2.
Influence of the synthetic compounds on ECG intervals QT. Normal group referring to anesthesia group without any treatments, pre-dose group referring to BaCl2 treated group, post-dose group referring to compounds-treated group.
To diminish the influence of the heart rate on the QT interval, the QTc interval was also investigated. The QTc, shown in Figure 3, was calculated according to the formula of Bazzett: QTc = QT/√RR.
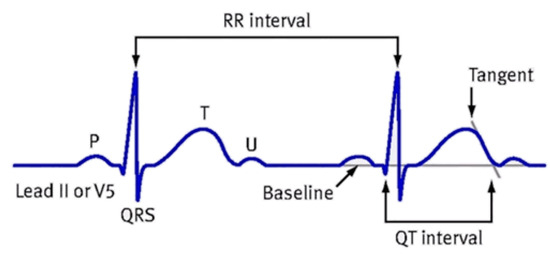
Figure 3.
Measurement diagram of QTc.
The results of the QTc are listed in Table 3. It was worth noting that an injection of BaCl2 (pre-dose) could alter the QTc interval, heart rate (HR) and QRS interval. However, after the administration of synthetic compounds, the QTc interval showed no difference with that of the Normal group, with the exception of compound 13a and 14a (p < 0.05), which suggests that our compound could restore the QTc value after the administration of BaCl2. Still worse, the positive control Ver and negative control NS could not restore the QTc. In addition, the results related to the HR, RR and QRS interval also suggested that nearly all of the compounds could normalize the HR, RR and QRS interval after the administration of BaCl2 (refer to S2–S4 in the Supporting Information).

Table 3.
Influence of the synthetic compounds on ECG intervals QTc. Normal group referring to anesthesia group without any treatments, pre-dose group referring to BaCl2-treated group and post-dose group referring to compounds-treated group.
Compared with the normal group, the pre-dose group, referring to the BaCl2-treated group, significantly decreased the P wave and T wave amplitude, as shown in Table 4 and Table 5. After one injection with our compounds, the P wave and T wave amplitude was nearly restored.

Table 4.
Influence of the synthetic compounds on ECG amplitude P wave. Normal group referring to anesthesia group without any treatments, pre-dose group referring to BaCl2-treated group and post-dose group referring to compounds-treated group.

Table 5.
Influence of the synthetic compounds on ECG amplitude T wave. Normal group referring to anesthesia group without any treatments, pre-dose group referring to BaCl2-treated group and post-dose group referring to compounds-treated group.
Next, by the analysis of the antiarrhythmic activity of a small library of scutellarein analogues that we constructed, the potent compound 10e was screened out and it was further determined whether it has dose-dependent effects on BaCl2-induced arrhythmia in rats. It was found that increasing the administration dose of 10e from 2 mg/kg to 8 mg/kg could diminished the onset time of efficacy and extended the duration efficacy. The results are summarized in Table 6, which displays that the number of rats with a duration of efficacy more than 20 min increased from 0 to 5, as well as that the number of rats with a duration of efficacy less than 10 min decreased from 3 to 1. However, the antiarrhythmic effects decreased when the administration dose of 10e was 16 mg/kg. Overall, compound 10e could sharply decrease the onset time in a dose-dependent manner.

Table 6.
Onset time and duration of efficacy of compounds on arrhythmia induced by BaCl2 in rats.
2.2.2. Antiarrhythmic Effects of Scutellarein Analogues on Aconitine-Induced Arrhythmia in Rats
VP were followed by VT and VF appearing in all treated rats with the administration of aconitine. The administration of compound 10e at a concentration of 8 mg/kg prior to aconitine caused a significant increase in the cumulative dosage of aconitine required to induce VF and CA compared with the NS and DMSO groups, respectively (p < 0.05 or p < 0.01; Table 7). In addition, an intraperitoneal injection of scutellarein gave rise to a notable improvement in the cumulative dosage of aconitine needed to evoke VP, VT and VF compared with the negative control groups and the Ver positive control group, whereas the pro-drug of scutellarein, named scutellarin, showed much weaker antiarrhythmic effects than scutellarein against VP, VT, VF as well as CA induced by aconitine, indicating that scutellarein was a promising lead compound for the investigation of an antiarrhythmic drug.

Table 7.
Effects of compounds on cardiac arrhythmia induced by aconitine in rats. VP: Ventricular premature, VT: ventricular tachycardia, VF: ventricular fibrillation, CA: cardiac arrest.
2.2.3. The Influence of the Compounds on Normal Rat ECG
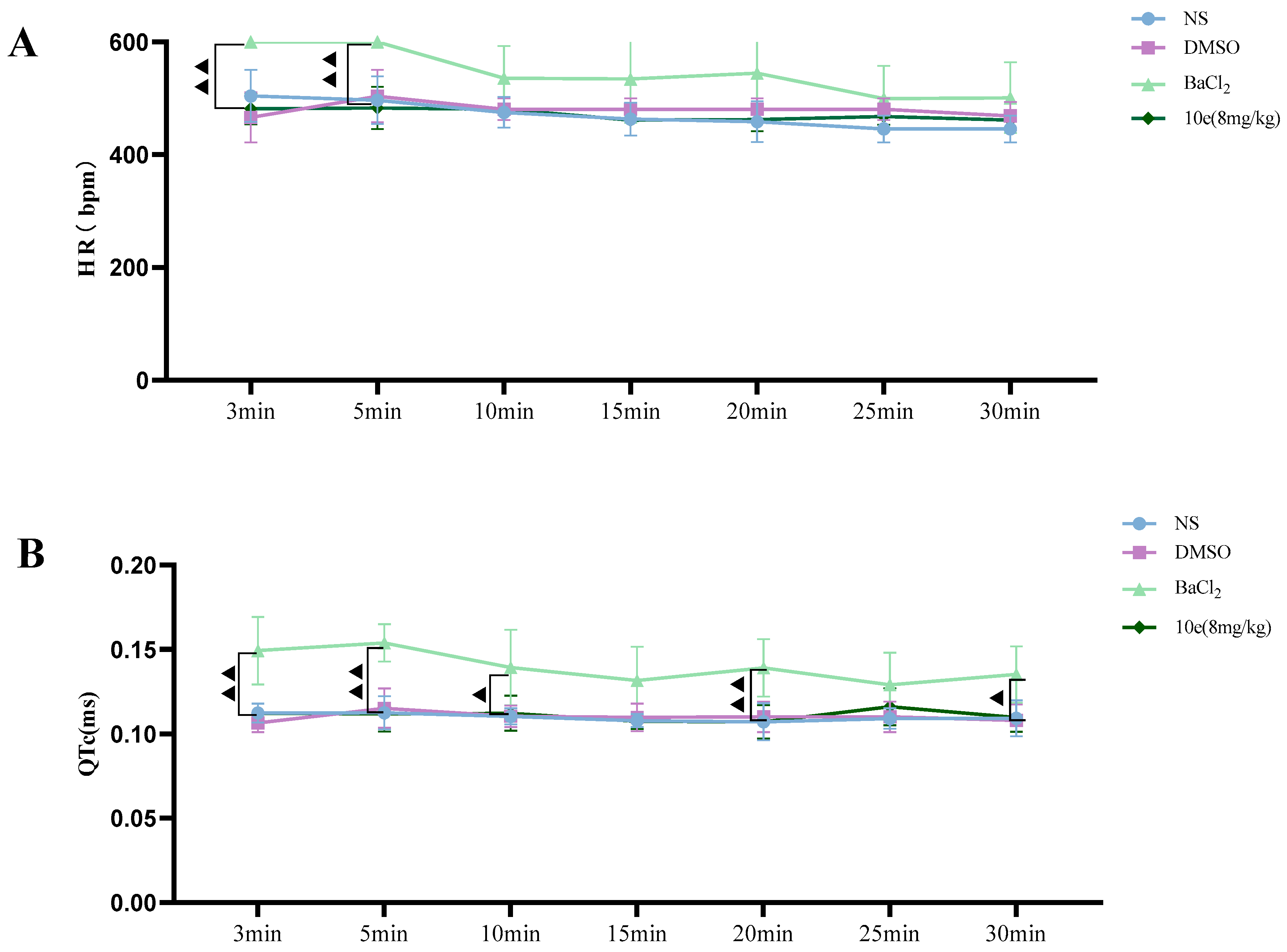
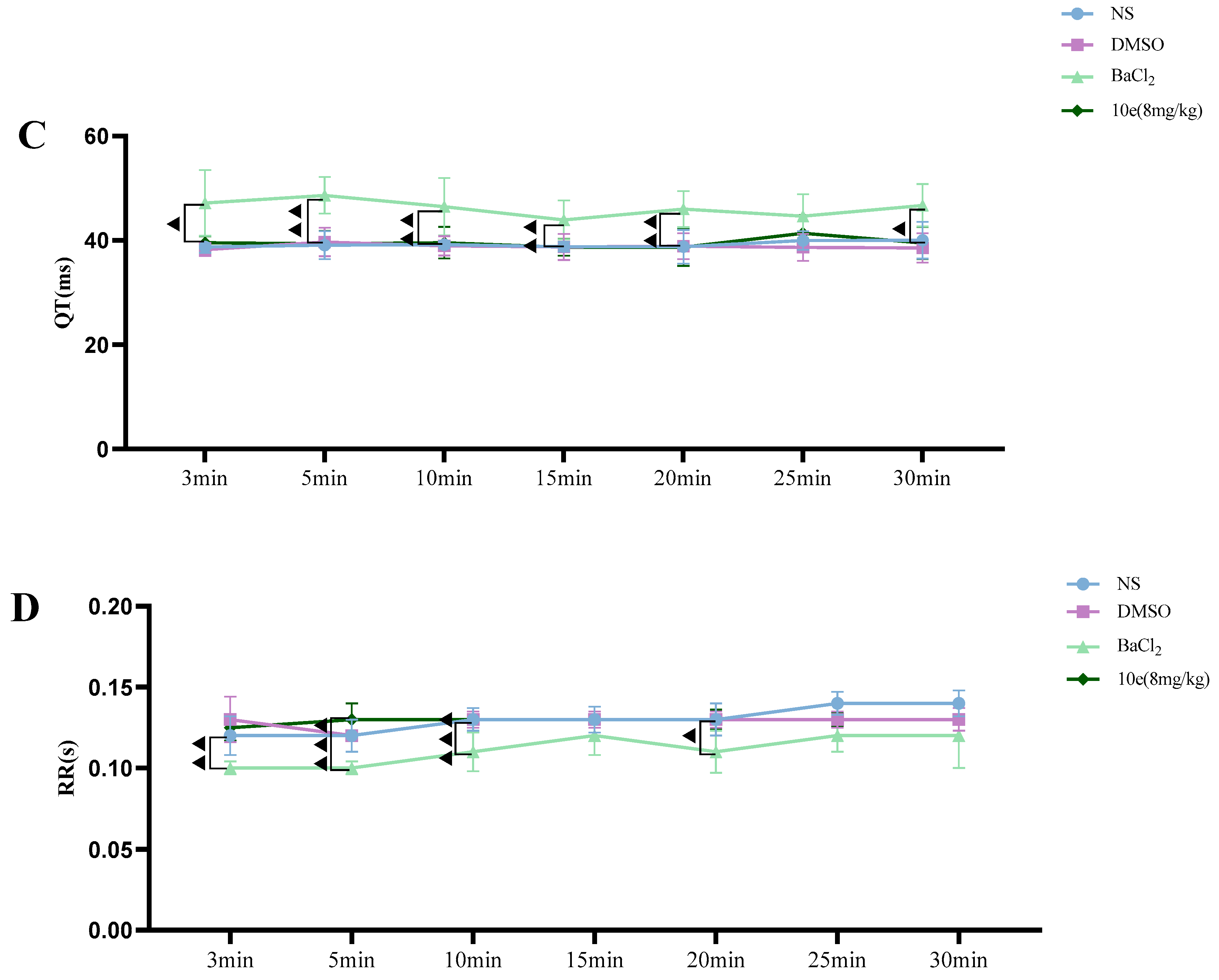
Compared with the NS and DMSO groups, compound 10e administered into the sublingual vein at a dose of 8 mg/kg did not show any significant difference in the HR, RR, QT and QTc interval, suggesting that this compound did not have any proarrhythmic effect and could be classified as Ib Vaughan Williams antiarrhythmic agents. In addition, after the administration of 10e, no statistically significant changes regarding QTc and QT were observed in 30 min. However, the injection of BaCl2 altered the QT, QTc intervals, HR and RR markedly in the 3rd and 5th min post-injection of anesthesia, as shown in Figure 4.
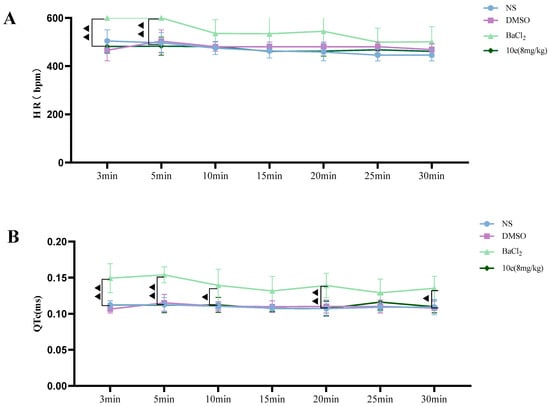
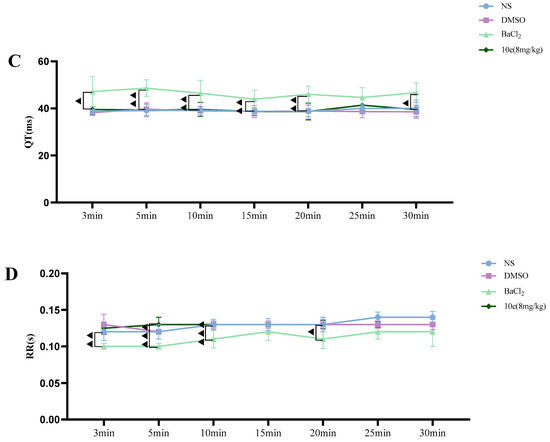
Figure 4.
Compound 10e-induced alterations of HR (A), QTc-Bazett’s (B), QT (C) and RR (D) in anesthetized rats. Significantly different between compound 10e group and BaCl2-treated group in QT and QTc value, ▲ p < 0.05, ▲▲ p < 0.01, ▲▲▲ p < 0.001.
2.2.4. Cytotoxicity Test of Compound 10e against Normal Cell
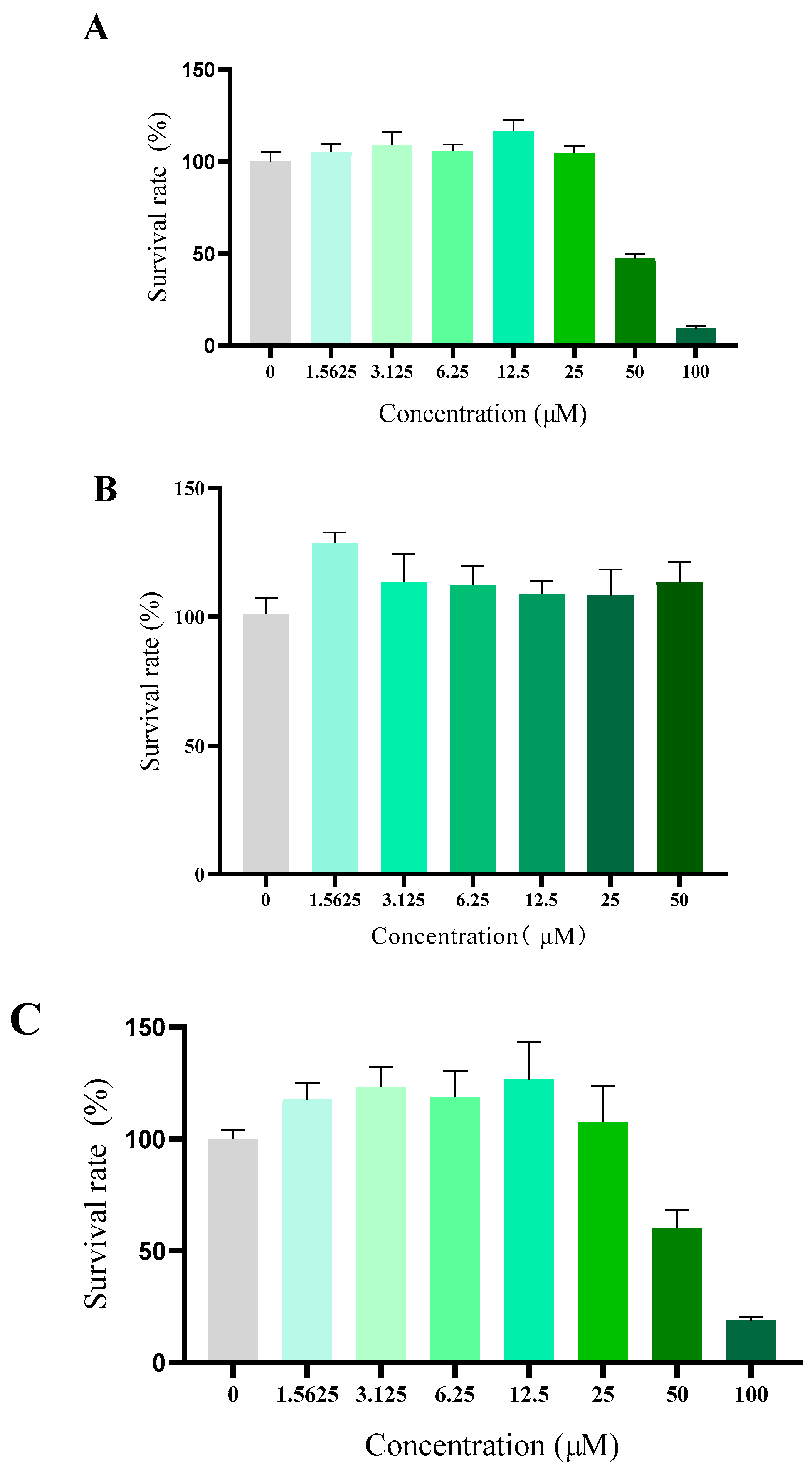
Compound toxicity has always been a great concern for the development of antiarrhythmic drug in clinic use. Although the daily oral treatment of scutellarin at a dose of 500 mg/kg for 30 days to rats was proved to be a sufficient margin of safety suggested by in vivo acute and subacute toxicity studies, whether scutellarin displayed high toxicity towards eukaryotic cells or not remained still unclear [26]. To verify the cytotoxicity of 10e in vitro, human fetal lung fibroblast I (HFL-I), HEK293 and H9c2 cells were used, respectively. As shown in Figure 5, compound 10e exhibited negligible cytotoxicity against HFL-I and H9c2 cells lines with a greater than 100% cell viability at a concentration of 25 μM, which is approximately the concentration in the patch clamp study. Microscopic investigations of H9c2 cell lines also indicated that there were no morphological changes after incubation with compound 10e at the concentration of 25 μM, displaying relatively low cytotoxicity. (Refer to Supplementary S8).
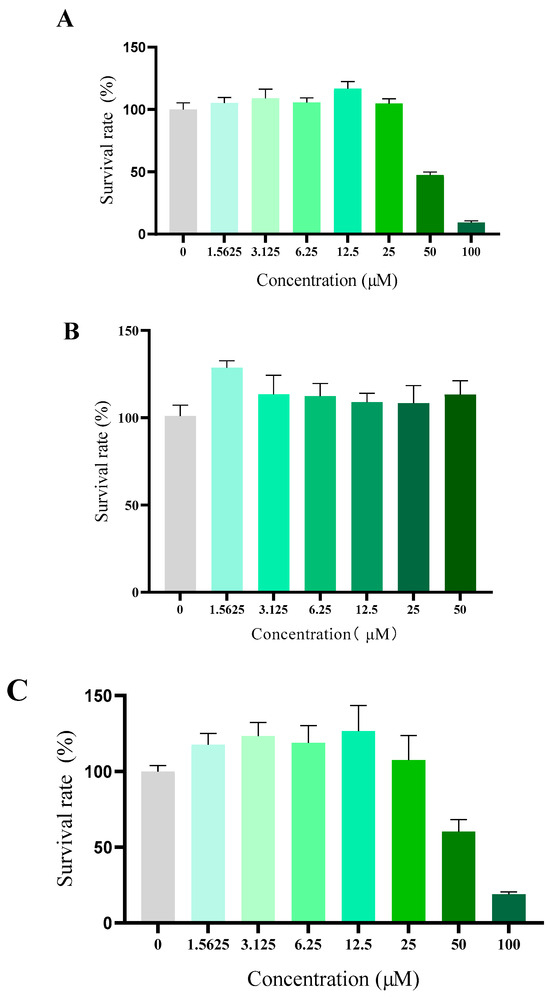
Figure 5.
Cytotoxicity of compound 10e towards HFLI cell lines (A), HEK293 cell lines (B) and H9c2 cell lines (C).
2.2.5. Molecular Docking with Nav1.5 and Cav1.2 Channels
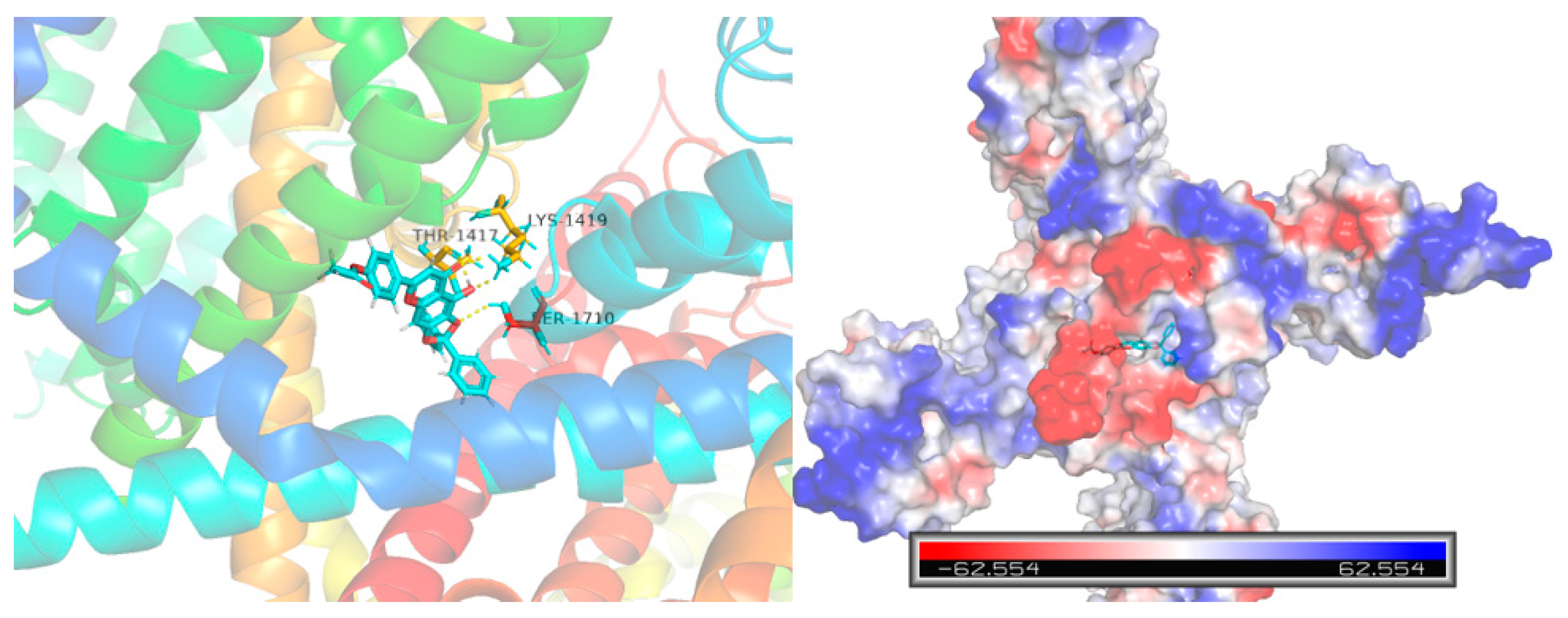
Computational molecular docking was conducted to gain more insights into the molecular interaction details between compound 10e and the Nav1.5 protein (ID: 6LQA) (Figure 6). The results revealed that the highest docking score positioned compound 10e into the substrate-binding site of the Nav1.5 protein (ID: 6LQA). The warheads of the 2,2-diphenyl protection group of compound 10e were well-situated in the central cavity of the pore domain of the ion channel of the Nav1.5 protein, interacting with the amino acid residues nearby. A conventional hydrogen-bonding interaction was predicted to occur between the amide group of THR-1417, LYS-1419 and the hydroxyl group of 10e, as well as between the amide group of SER-1710 and the hydroxyl group of 10e.
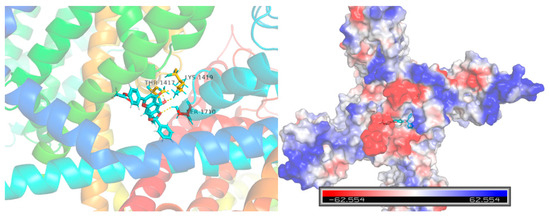
Figure 6.
Virtual molecular docking of compounds 10e with Nav1.5 protein.
Furthermore, the docking score of scutellarein and a Nav1.5 protein was 5.775, which was lower than that of compound 10e (6.8012), suggesting that compound 10e had better binding energy with the Nav1.5 protein in accordance with the aforementioned antiarrhythmic results. This indicated that 10e should be worthy of further study.
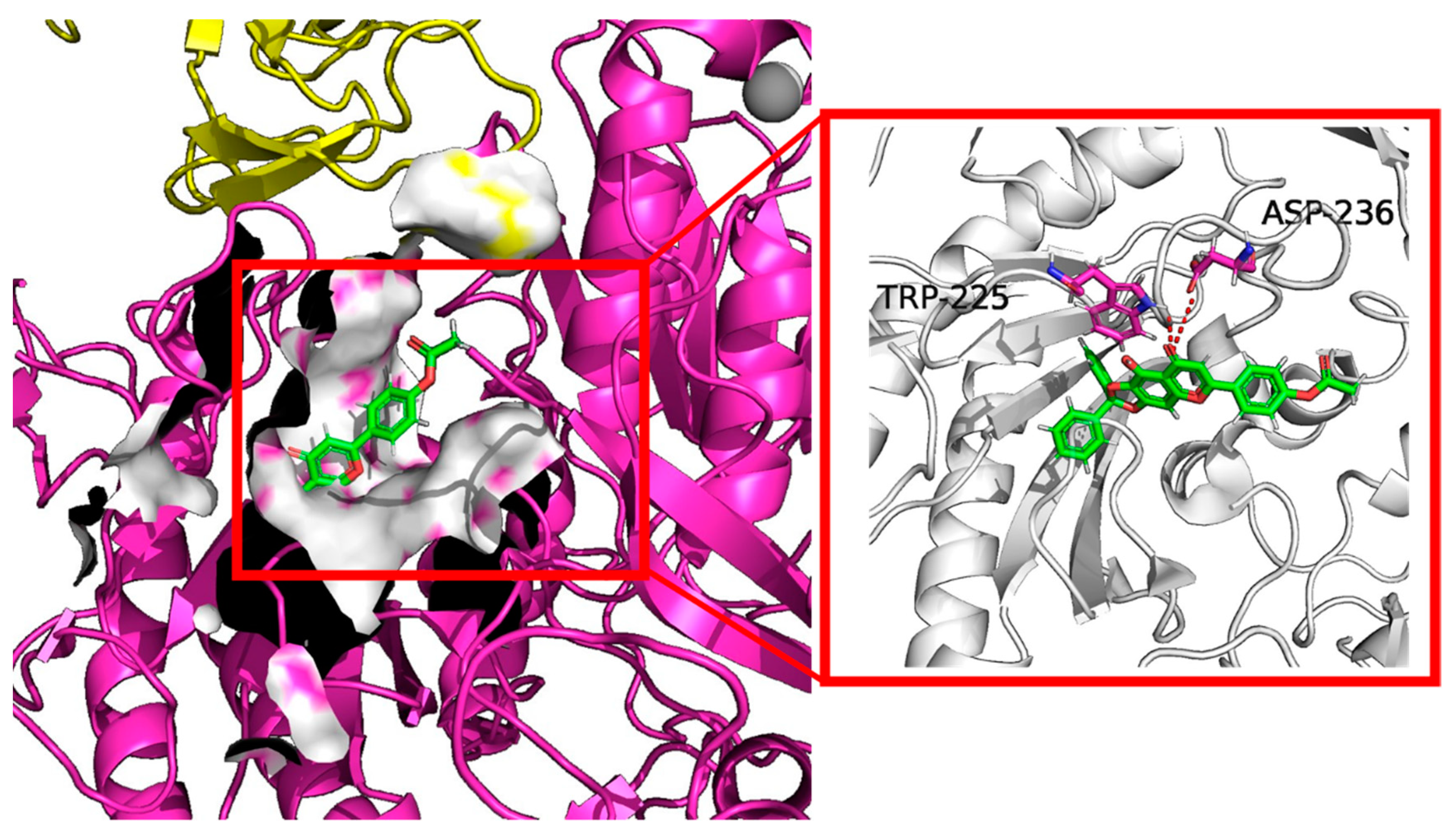
The docking results shown in Figure 7 also suggested that the highest docking score positioned compound 10e into the substrate-binding site of Cav1.2 (ID: 8FD7). A hydrogen-bonding interaction was predicted by the PLIP website to occur between residues TRP-225, ASP236 and the hydroxyl group of 10e. The length of the hydrogen bonds was less than 3 pm, showing a strong physicochemical force.
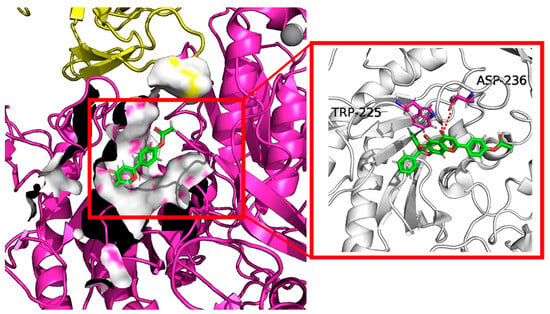
Figure 7.
Virtual molecular docking of compounds 10e with Cav1.2 protein.
2.2.6. Patch Clump Recordings
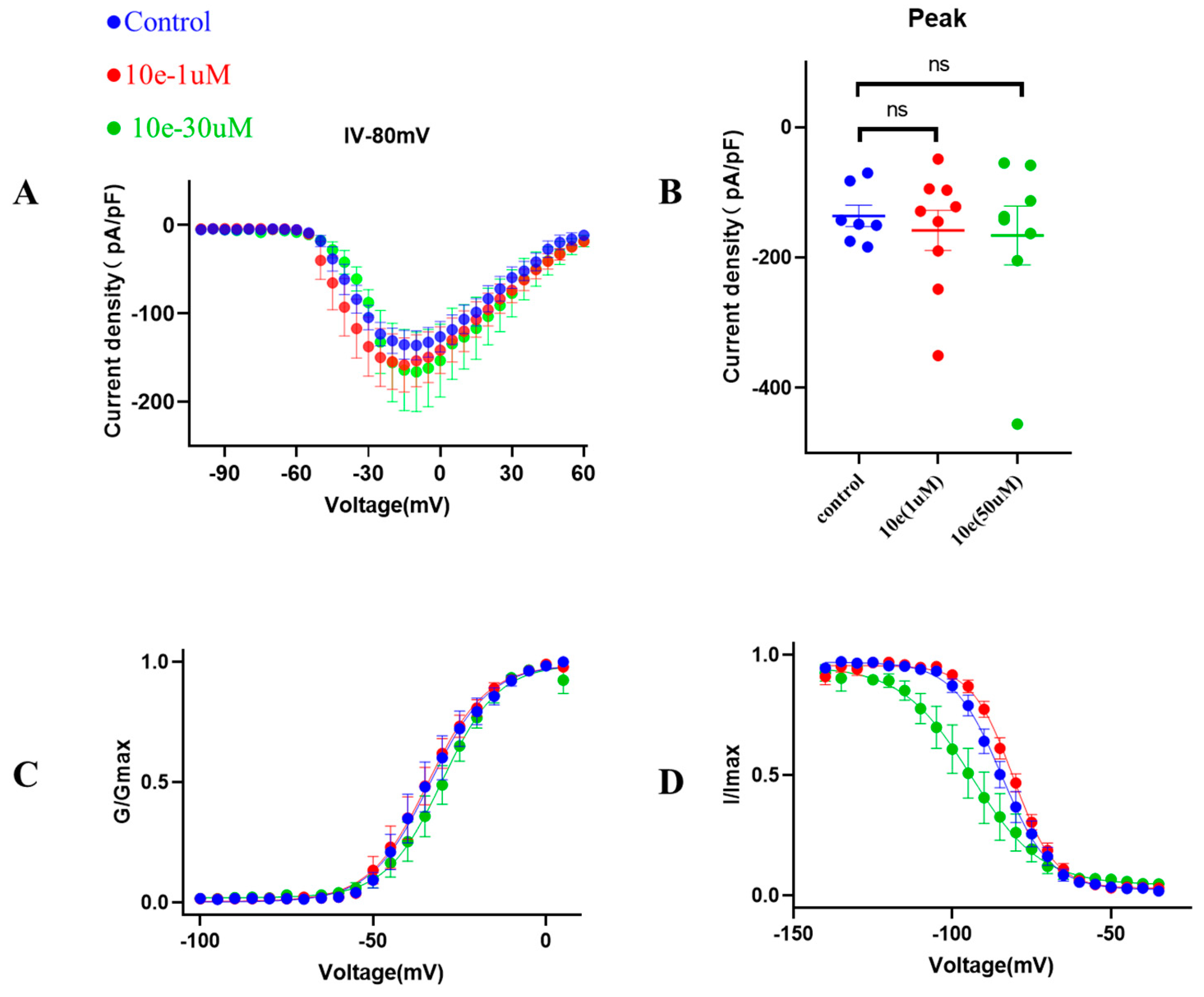
Next, to provide additional mechanistic insights into the effects of compound 10e on the biophysical properties of the INa, we investigated the voltage-dependent activation of the INa in the absence or presence of compound 10e (1 μM and 30 μM). It was clear that compound 10e did not alter the current density of the Nav1.5 channel and the voltage-dependency for INa activation (Figure 8). Figure 8C presents the comparable activation curves (G/GMAX, V1/2 = −33.6 ± 1.1 mV in control vs. −34.2 ± 0.9 mV in the presence of compound 10e at the concentration of 1 μmol vs. −30.1 ± 0.9 mV in the presence of compound 10e at the concentration of 30 μmol, n = 8, p > 0.05). However, the steady-state inactivation curve (Figure 8D) was left-shifted in the presence of compound 10e (I/IMAX, V1/2 = −84.4 ± 0.6 mV in control vs. −80.8 ± 0.4 mV in the presence of compound 10e at the concentration of 1 μmol vs. −94.1 ± 1.7 mV in the presence of compound 10e at the concentration of 30 μmol, n = 8, p < 0.05), indicating that compound 10e may enhance the inactivation of the Nav1.5 channel.
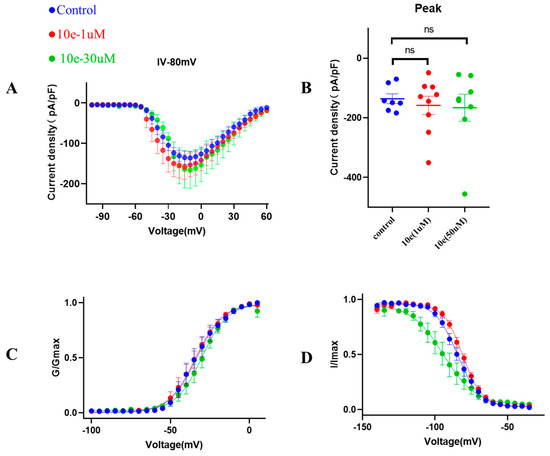
Figure 8.
Effect of compound 10e on voltage-dependent sodium current (INa) activation and inactivation. (A) Current density of Nav1.5 mediated by control (DMSO) and various concentration of compound 10e. (B) Scatter distribution plot of experimental data (C) Voltage-dependent activation (G/Gmax) and (D) inactivation (I/Imax) of the INa in the absence (blue circles) or presence of 1 μM compound 10e (red circles) or presence of 30 μM compound 10e (green circles).
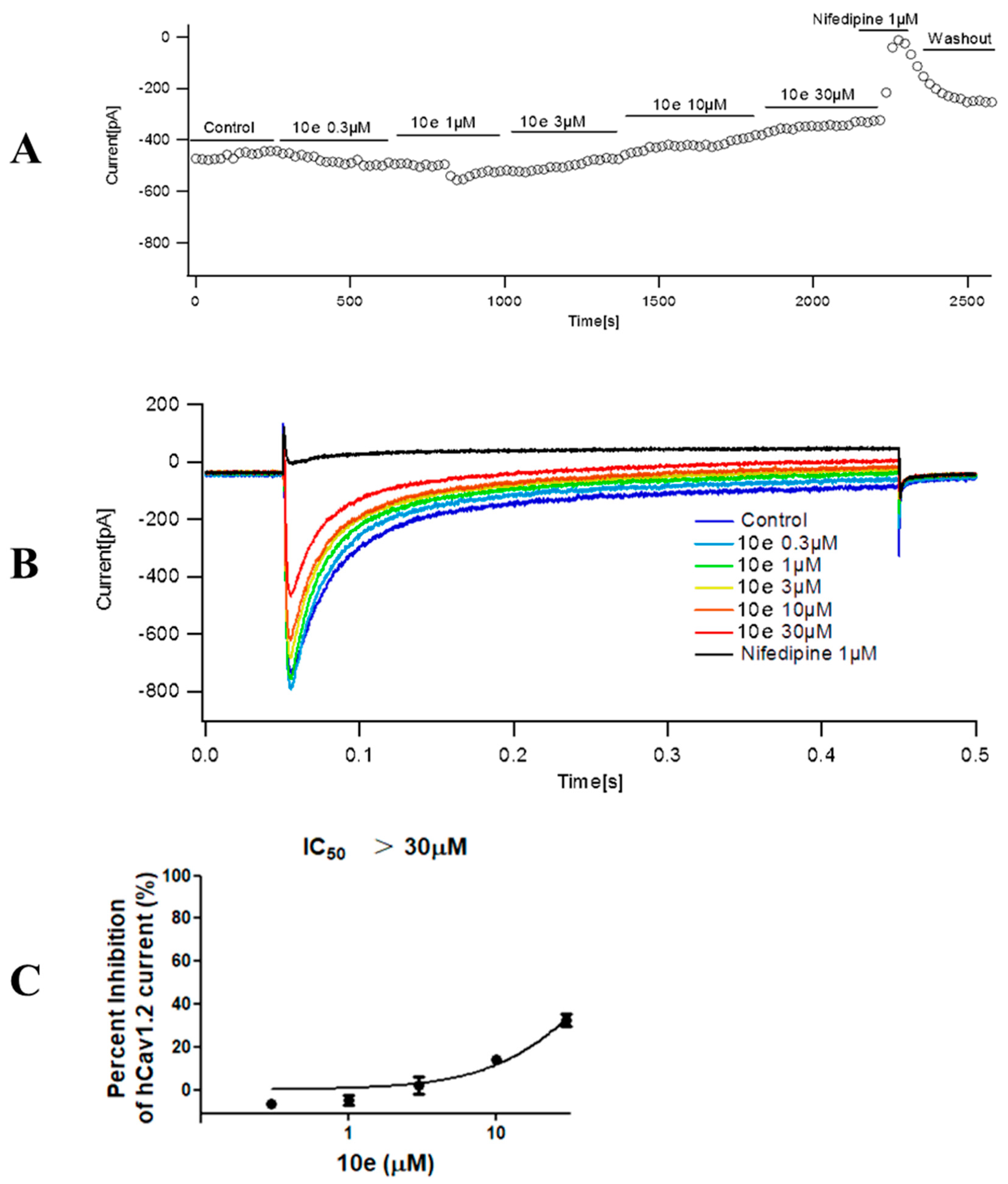
Compound 10e was found to reduce the ICa peak amplitude in a concentration-dependent manner. In addition, the maximum effect for each tested concentration was reached quickly, as is displayed in the time course effect of compound 10e (Figure 9). When cells were exposed to increasing concentrations of compound 10e (from 0.3 to 30 μM), a concentration–response curve of ICa peak inhibition was obtained. The interaction of drugs with the calcium channel depends on the channel state, for instance, closed, open and inactivated. Thus, we composed a concentration–response curve of compound 10e in cells expressing human Cav1.2 at a holding potential (VH) of −80 mV, which favor a partially inactivated state. We found that there was an evident dependency of the resting membrane potential in the potency of compound 10e to block ICa. Once the cell membrane was held at a VH of −80 mV, compound 10e (30 μM) reduced approximately 32.58 ± 5.16% of the ICa amplitude. This effect was partially reversible after washout. Interestingly, when the VH was set at −80 mV, Nifedipine (1 μM) attenuated almost 97.93 ± 0.96% of the ICa amplitude. The IC50 of compound 10e for ICa inhibition at a VH of −80 mV was undefined due to the solubility dilemma. These findings indicated that the compound 10e-dependent inhibition of the ICa preferentially targets the inactivated state of Cav 1.2 and may partially explain its antiarrhythmic activity.
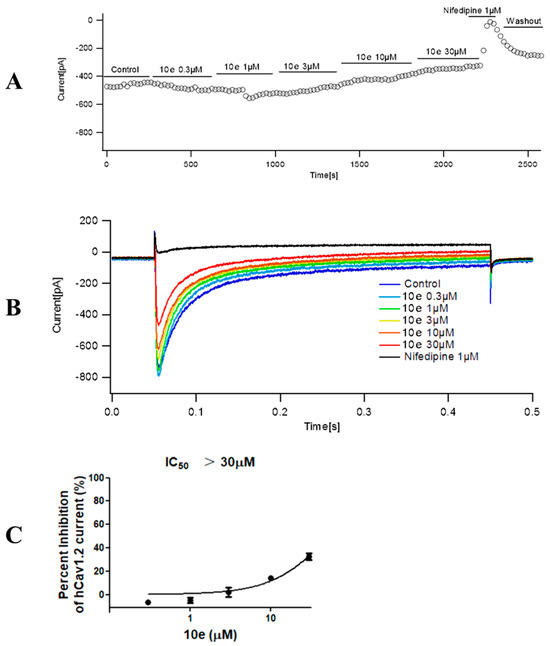
Figure 9.
Effect of compound 10e on the peak calcium current (ICa) amplitude. (A) Time course effect of different concentrations of compound 10e (0.3–30 μM) on the peak ICa at VH = −80 mV. (B) Representative ICa traces in the control group and in the presence of compound 10e at a holding potential (VH) = −80 mV. (C) Dose−response curve of compound 10e on the ICa amplitude when cells were maintained at VH = −80 mV. n = 3 cells.
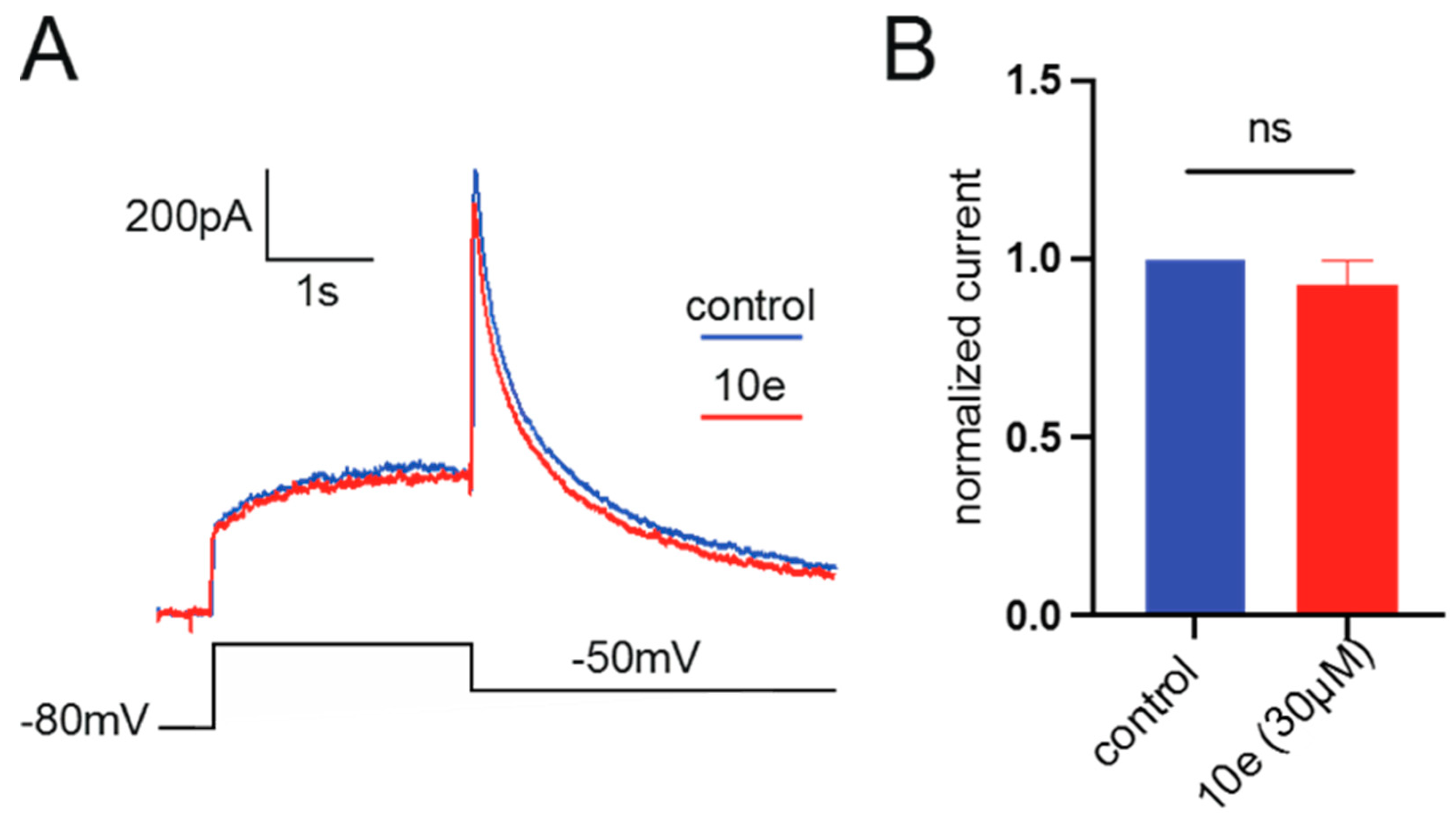
It was found that compound 10e at the concentration of 30 μM could not reduce the Ikr peak amplitude. This suggests that it did not block the hERG potassium channel, indicating that our compound in future drug development could avoid the cardiac side effects (Figure 10).
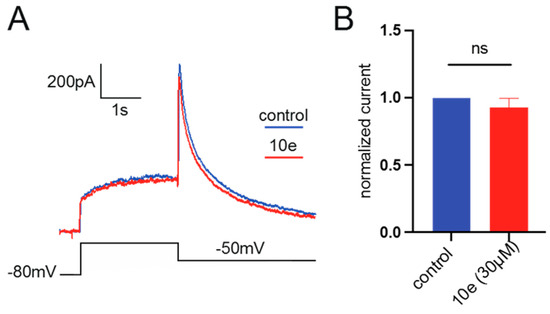
Figure 10.
(A). Representative traces of current recorded from HEK293 expressing hERG channel by patch clamp technique in the presence or absence of 10e (30 µM) perfusion. The current was recorded by depolarizing the voltage to +40 mV for 2.5 s from the holding potential at −80 mV, followed by a hyperpolarization step to −50 mV, lasting for 4 s, which elicited the peak tail current of hERG channel. (B). Normalized peak tail current of hERG channel, n = 4 for each group.
3. Discussion
In this work, based on the concept of a twin drug, a total of 22 novel scutellarein derivatives have been synthesized via the conjugation of the scutellarein scaffold with a pharmacophore of FDA-approved antiarrhythmic medication. The antiarrhythmic effects of these scutellarein derivatives were evaluated by the analyzation of the rat number of arrhythmia recovery, ECG parameters, corresponding recovery time and maintenance time in the rat model of barium chloride-induced arrhythmia, as well as the cumulative dosage of aconitine required to induce VP, VT, VF and CA in the rat model of aconitine-induced arrhythmia. Compounds with 4′-hydroxyl substituents had rapid-onset antiarrhythmic effects. Furthermore, an injection of our compounds could normalize the HR, RR, QRS, QT and QTc interval, as well as the P/T waves’ amplitude. The most promising compound, 10e, exhibited the best antiarrhythmic activity with long-term efficacy and extremely low cytotoxicity. What is more, compound 10e showed no proarrhythmic effects and it did not block the hERG potassium channel, which is highly associated with cardiotoxicity. Therefore, it could be classified as an Ib Vaughan Williams antiarrhythmic agent. Importantly, compound 10e could gently reduce the INa and ICa in a concentration-dependent manner and left-shifted the inactivation curve of Nav1.5. However, the IC50 of compound 10e could not be determined due to the poor solubility. At present, a variety of ion channels have been reported to be involved in the action potential of the myocardium, including the sodium, potassium and calcium channels, etc. Maybe compound 10e also interacts with other kinds of ion channels. However, in cardiomyocytes, which types of ion channels that compound 10e inhibits to exert such potent antiarrhythmic effects is unclear and needs to be further studied. Altogether, our work indicated that 10e represented an important scutellarein scaffold targeting voltage-gated ion channels including Nav1.5 and Cav1.2, providing a promising starting point to be further developed as a safe antiarrhythmic medication.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents, Solvents and Chemicals
Scutellarin (1) was purchased from Yuanye Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). All reagents and solvents were purchased from Aladdin Holdings Group Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China) and used without further purification unless otherwise stated. The anhydrous solvents were transferred via syringe. All reactions were monitored by TLC by using UV light of 254 nm as the detection wavelength. Chromatographic purifications were carried out on silica gel (160–200 mesh) by using gradient mixtures of petroleum ether and ethyl acetate as eluent. All activity tested compounds were determined by an Agilent 1260 series HPLC to have at least 95% purity. All 1H NMR and 13C NMR spectra were recorded on Bruker Avance spectrometer. High-resolution mass spectra (HRMS) were obtained on an Agilent 6545 by quadrupole time-of-flight (Q-TOF) mode.
4.2. Synthesis of Scutellarein Derivatives
4.2.1. 5,6,7-Trihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4H-chromen-4-one (2)
To a well-stirred mixture of scutellarin (1) (3.0 g, 6.4 mmol) in 95% ethanol (48 mL), solution of concentrated H2SO4 (18 mL) was added dropwise and the reaction was refluxed for 4 h under nitrogen. After that, excess water (50 mL) was added in portions to the reaction mixture. Meanwhile, the precipitates that appeared were filtered, washed with glacial acetic acid and dried in vacuo to afford scutellarein 2 (1.1 g, 59% yield) as a yellow solid; mp 324−335 °C; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 12.70 (s, 1H), 7.73–7.82 (m, 2H), 7.49–7.59 (m, 4H), 7.28–7.35 (m, 6H), 7.15–7.25 (m, 2H), 6.55 (s, 1H), 6.58 (s, 1H), 3.26–3.32 (m, 2H), 3.21 (q, J = 7.17 Hz, 2H) and 1.09–1.13 (m, 6H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 182.5, 164.0, 161.5, 153.8, 150.1, 147.5, 129.6, 128.8, 121.9, 116.4, 104.4, 102.7 and 94.3. HRMS(Q-TOF) m/z calculated for C15H10O6 [M + H]+: 287.0477 found: 287.0490.
4.2.2. 9-Hydroxy-6-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2,2-diphenyl-8H-[1,3]dioxolo[4,5-g]chromen-8-one (3)
A mixture of scutellarein (2) (10.0 g, 34.94 mmol) and dichlorodiphenylmethane (10.0 g, 42.17 mmol) in diphenyl ether (200 mL) was stirred at 180 °C under nitrogen protection for 1.5 h. Then, the resulting dilution was allowed to slowly cool to room temperature. Petroleum ether (400 mL) was added dropwise to the solution to remove the diphenyl ether from the solid that appeared. Then, the filtered solid was purified by column chromatography on silica gel with 25% ethyl acetate in petroleum ether as eluent to afford 3 (10.7 g, 68%) as a yellow solid; mp 357−364 °C; 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 7.81–7.93 (m, 2H), 7.46–7.55 (m, 4H), 7.36–7.46 (m, 6H), 6.99 (s, 1H), 6.89 (d, J = 8.80 Hz, 2H) and 6.79 (s, 1H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 182.9, 164.7, 162.8, 162.2, 153.2, 152.9, 139.3, 130.2, 129.2, 129.2, 129.0, 126.3, 121.1, 118.7, 116.5, 107.4, 103.1, 36.3 and 31.2. HRMS(Q-TOF) m/z calculated for C28H18O6 [M + H]+: 451.1103 found: 451.1179.
4.2.3. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Compounds 7a–7g
To a well-stirred mixture of compound 4a–4g (10.3 mmol) in dichlorodiphenylmethane (10 mL) a solution of triphosgene (3.0 g, 10.1 mmol) in DCM (15 mL) was added dropwise at 0 °C and the reaction mixture was stirred for 6–8 h. Then it was allowed to warm slowly to room temperature. After the disappearance of starting material, as indicated by TLC, the reaction mixture was blown by nitrogen and filtered to afford the filtrate 6a–6g, respectively, which could be used directly in the next step.
To a well-stirred solution of compound 3 (3 g, 6.6 mmol) in anhydrous DMF (30 mL) at rt. the aforementioned fresh prepared carbamoyl chloride 6a–6g in the presence of K2CO3 (1.0 g, 7.2 mmol) and KI (1.0 g, 6.0 mmol) was added. The resulting solution was diluted with ethyl acetate, washed with brine, dried over anhydrous Na2SO4, filtered and evaporated under reduced pressure. The crude residue was purified by flash column chromatography on silica gel using 50% ethyl acetate in petroleum ether as eluent to afford 7a–7g.
4-(9-Hydroxy-8-oxo-2,2-diphenyl-8H-[1,3]dioxolo[4,5-g]chromen-6-yl)phenyl morpholine-4-carboxylate (7a)
This compound (2.2 g, yield 54.0%) was prepared from important immediate compound 3 (3.0 g, 6.6 mmol), DMF (30 mL) and 4-morpholinylcarbonyl chloride 6a (1.2 g, 8 mmol) according to the general procedure described above. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 12.94 (s, 1H), 7.97–8.19 (m, J = 8.80 Hz, 2H), 7.47–7.55 (m, 5H), 7.39–7.45 (m, 6H), 7.28–7.34 (m, J = 8.80 Hz, 2H), 7.08 (s, 1H), 7.01 (s, 1H), 3.57–3.64 (m, 4H), 3.45–3.57 (m, 2H) and 3.38 (br. s., 2H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 183.2, 163.5, 154.5, 153.2, 139.2, 130.3, 129.2, 128.3, 126.3, 123.0, 107.6, 22.6 and 19.4. HRMS(Q-TOF) m/z calculated for C33H25NO8 [M + H]+: 564.1580 found: 564.1654.
4-(9-Hydroxy-8-oxo-2,2-diphenyl-8H-[1,3]dioxolo[4,5-g]chromen-6-yl)phenyl 4-methylpiperazine-1-carboxylate (7b)
This compound (0.4 g, yield 62.6%) was prepared from important immediate compound 3 (0.5 g, 1.1 mmol), DMF (10 mL) and 4-methylpiperazine-1-carbonyl chloride 6b (0.18 g, 1.3 mmol) according to the general procedure described above. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 13.00 (br. s., 1H), 8.12 (d, J = 8.07 Hz, 2H), 7.53–7.62 (m, 4H), 7.48 (d, J = 5.62 Hz, 6H), 7.36 (d, J = 7.58 Hz, 2H), 7.14 (s, 1H), 7.07 (s, 1H), 3.62 (br. s., 2H), 3.45 (br. s., 2H), 2.41 (br. s., 4H) and 2.25 (s, 3H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, METHANOL-d4) δ 166.6, 152.1, 98.3, 94.2, 77.1, 76.5, 76.1, 73.0, 70.3, 50.3, 50.1 and 12.5. HRMS(Q-TOF) m/z calculated for C34H28N2O7 [M + H]+: 577.1897 found: 577.1964.
4-(9-Hydroxy-8-oxo-2,2-diphenyl-8H-[1,3]dioxolo[4,5-g]chromen-6-yl)phenyl diethylcarbamate (7c)
This compound (0.32 g, yield 52.5%) was prepared from important immediate compound 3 (0.5 g, 1.1 mmol), DMF (10 mL) and diethylcarbamic chloride 6c (0.18 g, 1.3 mmol) according to the general procedure described above. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 12.70 (s, 1H), 7.73–7.82 (m, 2H), 7.49–7.59 (m, 4H), 7.28–7.35 (m, 6H), 7.15–7.25 (m, 2H), 6.55 (s, 1H), 6.58 (s, 1H), 3.26–3.32 (m, 2H), 3.21 (q, J = 7.17 Hz, 2H) and 1.09–1.13 (m, 6H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, CHLOROFORM-d) δ 182.99, 163.42,154.44, 153.50, 153.27, 142.30, 139.25, 130.04, 129.48, 128.38, 127.86, 127.43, 126.33, 122.45, 119.22, 107.77, 105.23, 89.56, 42.44, 42.37, 14.22 and 13.11. HRMS(Q-TOF) m/z calculated for C33H27NO7 [M + H]+: 550.1788 found: 550.1859.
4-(9-Hydroxy-8-oxo-2,2-diphenyl-8H-[1,3]dioxolo[4,5-g]chromen-6-yl)phenyl pyrrolidine-1-carboxylate (7d)
This compound (0.19 g, yield 79.2%) was prepared from important immediate compound 3 (0.2 g, 0.4 mmol), DMF (10 mL) and pyrrolidine-1-carbonyl chloride 6d (0.13 g, 0.97 mmol) according to the general procedure described above. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CHLOROFORM-d) δ 12.69 (s, 1H), 7.70–7.88 (m, 2H), 7.46–7.59 (m, 4H), 7.27–7.37 (m, 6H), 7.20–7.23 (m, 2H), 6.55 (s, 1H), 6.58 (s, 1H), 3.28–3.44 (m, 4H) and 1.17–1.22 (m, 4H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 183.0, 163.4, 142.3, 139.3, 130.1, 129.5, 128.4, 127.9, 127.4, 126.3, 122.4 and 89.5. HRMS(Q-TOF) m/z calculated for C33H25NO7 [M + Na]+: 570.1631 found: 572.1684.
4-(9-Hydroxy-8-oxo-2,2-diphenyl-8H-[1,3]dioxolo[4,5-g]chromen-6-yl)phenyl [1,4′-bipiperidine]-1′-carboxylate (7e)
This compound (0.18 g, yield 64.3%) was prepared from important immediate compound 3 (0.2 g, 0.4 mmol), DMF (10 mL) and [1,4′-bipiperidine]-1′-carbonyl chloride 6e (0.23 g,0.99 mmol) according to the general procedure described above. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm 1.12–1.26 (m, 2 H), 1.33–1.42 (m, 2 H), 1.49–1.56 (m, 5 H), 1.82 (d, J = 12.72 Hz, 2 H), 2.35–2.42 (m, 1 H), 2.42–2.50 (m, 4 H), 2.77 (t, J = 12.23 Hz, 1 H), 2.91 (t, J = 12.23 Hz, 1 H), 4.14–4.40 (m, 2 H), 6.48–6.60 (m, 2 H), 7.14–7.23 (m, 2 H), 7.25–7.38 (m, 6 H), 7.45–7.61 (m, 4 H) and 7.69–7.84 (m, 2 H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 183.0, 163.3, 153.5, 153.3, 142.3, 139.3, 129.5, 128.4, 128.1, 127.5, 126.3, 122.4, 119.2, 107.8, 105.3, 89.5, 62.5, 50.3, 26.0 and 24.5. HRMS(Q-TOF) m/z calculated for C39H36N2O7 [M + H]+: 645.2523 found: 645.2678.
4-(9-Hydroxy-8-oxo-2,2-diphenyl-8H-[1,3]dioxolo[4,5-g]chromen-6-yl)phenyl thiazolidine-3-carboxylate (7f)
This compound (0.05 g, yield 71.4%) was prepared from important immediate compound 3 (0.06 g, 0.1 mmol), DMF (10 mL) and thiazolidine-3-carbonyl chloride 6f (0.04 g, 0.2 mmol) according to the general procedure described above. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm 3.05–3.19 (m, 2 H), 3.84–3.97 (m, 2 H), 4.61 (s, 1 H), 4.68 (s, 1 H), 6.62–6.65 (m, 1 H), 6.66 (s, 1 H), 7.31 (m, J = 8.80 Hz, 2 H), 7.38–7.43 (m, 6 H), 7.58–7.66 (m, 4 H), 7.81–7.93 (m, 2 H) and 12.75 (s, 1 H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm 182.95, 163.17, 153.55, 153.28, 142.31, 139.24, 130.09, 129.48, 128.38, 127.55, 126.34, 122.35, 119.26, 107.79, 105.42 and 89.53. HRMS(Q-TOF) m/z calculated for C32H23NO7S [M + H]+:566.5925 found: 566.1265.
4-(9-Hydroxy-8-oxo-2,2-diphenyl-8H-[1,3]dioxolo[4,5-g]chromen-6-yl)phenyl ethyl(methyl)carbamate (7g)
This compound (0.16 g, yield 71.4%) was prepared from important immediate compound 3 (0.2 g, 0.4 mmol), DMF (10 mL) and ethyl(methyl)carbamic chloride 6g (0.12 g, 0.9 mmol) according to the general procedure described above. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 12.67 (s, 1H), 7.77–7.84 (m, 2H), 7.52–7.59 (m, 4H), 7.31–7.36 (m, 6H), 7.21–7.27 (m, J = 8.80 Hz, 2H), 6.52–6.60 (m, 2H), 4.60 (s, 1H), 4.52 (s, 1H), 3.76–3.89 (m, 2H) and 2.99–3.09 (m, 2H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 183.0, 164.0, 162.6, 153.3, 153.2, 142.4, 139.3, 129.4, 128.4, 128.0, 126.3, 114.5, 107.7, 104.0 and 89.4. HRMS(Q-TOF) m/z calculated for C32H25NO7 [M + H]+: 536.1631 found: 536.1702.
4.2.4. Synthesis of 4-(5,6,7-Trihydroxy-4-oxo-4H-chromen-2-yl) phenyl morpholine-4-carboxylate (8a)
Compound 7a (0.3 g, 0.5 mmol) was stirred with 10% Pd/C catalyst (0.03 g, 0.2 mmol) in a mixture solution of EtOH (10 mL) and THF (10 mL) for 12 h under hydrogen atmosphere, followed by filtration over celite for removal of catalyst. Then the filtrate was evaporated in vacuo and the resulting residue was purified by column chromatography on silica gel using 20% ethyl acetate in petroleum ether as eluent to afford 8a (0.15 g, 75.0% yield). 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ ppm 3.59–3.77 (m, 8 H), 6.58 (s, 1 H), 6.86 (s, 1 H), 7.24–7.41 (m, 2 H) and 7.97–8.16 (m, 2 H). HRMS(Q-TOF) m/z calculated for C20H17NO8 [M + H]+: 400.1184 found: 400.1215.
4.2.5. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Compounds 10a–10e
To a mixture solution of compound 3 and Et3N in anhydrous DCM (20 mL) at 0 °C, commercially available carbonyl chlorides 9a–9e (0.29 mmol) were added dropwise, stirring well over 12 h. Then, the reaction was diluted with water (20 mL). The collected organic phase was dried over anhydrous Na2SO4, filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure. Purification of the crude residue was performed by flash column chromatography on silica gel using 25% ethyl acetate in petroleum ether as eluent to afford the desired compound 10a–10f.
4-(9-Hydroxy-8-oxo-2,2-diphenyl-8H-[1,3]dioxolo[4,5-g]chromen-6-yl)phenyl 4-chlorobutanoate (10a)
This compound (0.34 g, yield 34.7%) was prepared from important immediate compound 3 (0.8 g, 1.7 mmol), Et3N (0.35 g, 3.4 mmol) and 4-chlorobutyrylchloride 9a (0.3 g, 2.1 mmol) according to the general procedure described above. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 12.98 (s, 1H), 8.08–8.23 (m, 2H), 7.54–7.60 (m, 4H), 7.46–7.52 (m, 6H), 7.36–7.42 (m, 2H), 7.15 (s, 1H), 7.09 (s, 1H), 3.76 (t, J = 6.48 Hz, 2H), 2.79 (t, J = 7.34 Hz, 2H) and 2.11 (t, J = 7.09 Hz, 2H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 183.2, 171.3, 163.4, 153.8, 153.4, 141.8, 139.2, 130.3, 129.4, 129.2, 128.6, 128.5, 126.3, 123.2, 118.9, 107.6, 90.8, 44.9, 31.4, 27.8 and 19.4. HRMS(Q-TOF) m/z calculated for C32H23ClO7 [M + H]+: 555.1132 found: 555.1964.
4-(9-Hydroxy-8-oxo-2,2-diphenyl-8H-[1,3]dioxolo[4,5-g]chromen-6-yl)phenyl 4-methylbenzenesulfonate (10b)
This compound (0.3 g, yield 75.0%) was prepared from important immediate compound 3 (0.3 g, 0.6 mmol), Et3N (0.88 g, 8.6 mmol) and tosyl chloride 9b (0.19 g, 0.99 mmol) according to the general procedure described above. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 12.90 (s, 1H), 8.06–8.16 (m, 2H), 7.66–7.85 (m, 2H), 7.53–7.62 (m, 4H), 7.41–7.53 (m, 9H), 7.19–7.29 (m, 2H), 7.06 (s, 1H), 7.10 (s, 1H) and 2.42 (s, 3H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 183.1, 162.7, 153.3, 153.3, 151.9, 146.6, 141.8, 139.2, 131.5, 130.8, 130.3, 130.1, 129.4, 129.2, 128.9, 128.8, 126.3, 123.3, 107.7, 90.7 and 21.7. HRMS(Q-TOF) m/z calculated for C35H24O8S [M + H]+: 605.1192 found: 605.1261.
4-(9-Hydroxy-8-oxo-2,2-diphenyl-8H-[1,3]dioxolo[4,5-g]chromen-6-yl)phenyl 2-chloroacetate (10c)
This compound (0.37 g, yield 46.3%) was prepared from important immediate compound 3 (0.5 g, 1.1 mmol), Et3N (0.28 g, 2.7 mmol) and chloroacetyl chloride 9c (0.15 g, 1.3 mmol) according to the general procedure described above. With 46.3% yield, 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 12.96 (s, 1H), 8.07–8.32 (m, J = 8.80 Hz, 2H), 7.53–7.62 (m, 4H), 7.46–7.53 (m, 7H), 7.40–7.46 (m, J = 8.80 Hz, 2H), 7.14 (s, 1H) and 7.09 (s, 1H), 4.75 (s, 2H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 183.2, 166.6, 163.3, 153.4, 153.4, 153.2, 141.8, 139.2, 130.3, 129.4, 129.2, 128.6, 126.3, 122.9, 118.9, 107.7, 105.6, 90.7 and 41.9. HRMS(Q-TOF) m/z calculated for C30H19ClO7 [M + H]+: 527.0819 found: 527.0889.
4-(9-Hydroxy-8-oxo-2,2-diphenyl-8H-[1,3]dioxolo[4,5-g]chromen-6-yl)phenyl methanesulfonate (10d)
This compound (41 mg, yield 70.6%) was prepared from important immediate compound 3 (50 mg, 0.1 mmol), Et3N (20 mg, 0.1 mmol) and methanesulfonyl chloride 9d (10 mg, 0.08 mmol) according to the general procedure described above. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 12.87 (s, 1H), 8.15 (d, J = 8.80 Hz, 2H), 7.47–7.56 (m, 6H), 7.35–7.47 (m, 6H), 7.08 (d, J = 7.34 Hz, 2H) and 3.42 (s, 3H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ ppm 183.18, 162.94, 153.39, 152.04, 141.80, 139.16, 130.25, 130.05, 129.19, 129.16, 129.06, 126.31, 118.98, 107.70, 106.01, 90.77, 38.20 and 19.34. HRMS(Q-TOF) m/z calculated for C29H20O8S [M + H]+: 529.0879 found: 529.0951.
4-(9-Hydroxy-8-oxo-2,2-diphenyl-8H-[1,3]dioxolo[4,5-g]chromen-6-yl)phenyl acetate (10e)
This compound (0.02 g, yield 40.6%) was prepared from important immediate compound 3 (0.15 g, 0.1 mmol), Et3N (0.08 g, 0.7 mmol) and acetyl chloride 9e (0.07 g, 0.9 mmol) according to the general procedure described above. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 12.93–13.22 (m, 1H), 8.19 (d, J = 7.82 Hz, 2H), 7.59–7.68 (m, 4H), 7.49–7.59 (m, 6H), 7.41 (d, J = 7.83 Hz, 2H), 7.15–7.20 (m, 1H), 7.11 (s, 1H) and 2.36 (s, 3H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 183.2, 169.4, 163.4, 153.8, 153.3, 141.8, 139.2, 130.2, 129.4, 129.2, 128.5, 128.4, 126.3, 123.2, 107.6, 105.5, 90.7 and 21.4. HRMS(Q-TOF) m/z calculated for C30H20O7 [M + H]+: 493.1209 found: 493.1279.
4.2.6. 9-Hydroxy-6-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2,2-diphenyl-8H-[1,3]dioxolo[4,5-g]chromen-8-one (10f) and 9-methoxy-6-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2,2-diphenyl-8H-[1,3]dioxolo[4,5-g]chromen-8-one (11f)
A mixture of compound 3 (0.2 g, 0.4 mmol), methyl iodide (0.14 g, 0.9 mmol) and excess potassium carbonate (0.25 g, 1.8 mmol) in dry DMF (20 mL) was stirred in ice bath under nitrogen atmosphere for 30 min in the presence of catalytic amount of KI. The solution was allowed to slowly warm to room temperature with stirring overnight. Then, the reaction was diluted with brine (20 mL). The collected organic phase was dried over anhydrous Na2SO4, filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure. Subsequent purification of the crude mixture was performed using the flash column chromatography on silica gel with gradient elution (EA/PE, 50% to 60%) to afford the target compound 10f (0.03 g, 50.1% yield) and a side product compound 11f (0.1 g, 49.8% yield). For 10f: 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 12.79 (s, 1H), 7.65–7.85 (m, 2H), 7.49–7.63 (m, 4H), 7.25–7.43 (m, 6H), 6.86–6.98 (m, 2H), 6.55 (s, 1H), 6.49 (s, 1H) and 3.80 (s, 3H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) d 183.0, 164.0, 162.6, 153.3, 153.2, 142.4, 139.3, 129.4, 128.4, 128.0, 126.3, 114.5, 107.7, 104.0, 89.4 and 55.5. HRMS(Q-TOF) m/z calculated for C29H20O6 [M + H]+: 465.1260 found: 465.1529. For 11f: 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.67–7.76 (m, 2H), 7.47–7.56 (m, 4H), 7.24–7.39 (m, 6H), 6.87–6.97 (m, 2H), 6.70 (s, 1H), 6.47 (s, 1H), 4.13 (s, 3H) and 3.79 (s, 3H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) d 162.1, 160.8, 154.7, 139.2, 129.6, 128.4, 127.6, 126.3, 123.8, 118.6, 114.4, 107.1, 93.3, 61.2 and 55.5. HRMS(Q-TOF) m/z calculated for C30H22O6 [M + H]+: 479.1416 found: 479.1498.
4.2.7. 4-(5,6,7-Trihydroxy-4-oxo-4H-chromen-2-yl)phenyl 4-chlorobutanoate (12a)
Compound 10a (0.3 g) was stirred with 10% Pd/C catalyst (0.02 g, 0.1 mmol) in EtOH (10 mL) and THF (10 mL) for 12 h under hydrogen at atmospheric pressure, then the Pd/C catalyst was removed by filtration over celite. After the filtrate was evaporated, the crude material was purified by column chromatography on silica gel using 50% ethyl acetate in petroleum ether as eluent to afford 12a. With 90% yield, 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.03–8.29 (m, 2H), 7.29–7.44 (m, 2H), 6.84–7.05 (m, 1H), 6.54–6.74 (m, 1H), 3.76 (t, J = 6.48 Hz, 2H), 2.79 (t, J = 7.21 Hz, 2H) and 2.12 (t, J = 7.09 Hz, 2H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 182.3, 171.3, 162.4, 153.5, 150.3, 147.5, 129.8, 129.2, 128.3, 128.3, 123.1, 104.7, 44.9, 31.5 and 27.8. HRMS(Q-TOF) m/z calculated for C19H15ClO7 [M − H]+: 389.0506 found: 389.6161.
4.2.8. 5-Hydroxy-6,7-dimethoxy-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-4H-chromen-4-one (13a) and 5,6,7-trimethoxy-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-4H-chromen-4-one (14a)
To a mixture solution of compound 2 (0.2 g, 0.7 mmol) and NaH (0.17 g, 7.1 mmol) in anhydrous DMF (15 mL) at 170 ℃ under nitrogen atmosphere commercially available methyl iodide (0.69 g, 4.8 mmol) was added dropwise, stirring well over 12 h. After the disappearance of starting material, as indicated by TLC, the reaction mixture was diluted with EA and water. The collected organic phase was dried over anhydrous Na2SO4, filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure. Purification of the crude residue was performed by flash column chromatography on silica gel using 50% ethyl acetate in petroleum ether as eluent to afford the desired compound 13a (0.19 g, 82.9% yield) and a side product 14a (0.18 g, 80.1% yield). For 13a: 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm 3.90 (s, 3 H) 3.93 (s, 3 H), 3.97 (s, 3 H), 6.59 (s, 1 H), 6.55 (s, 1 H), 7.02 (m, J = 9.05 Hz, 2 H), 7.85 (m, J = 9.05 Hz, 2 H) and 12.78 (s, 1 H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm 182.68, 164.02, 162.62, 158.73, 153.23, 153.09, 128.00, 123.58, 114.53, 106.16, 104.15, 90.57, 60.86, 56.32 and 55.55. HRMS(Q-TOF) m/z calculated for 328.32 [M + Na]+: 351.3160 found: 351.0843. For 14a: 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm 3.87 (s, 3 H), 3.91 (s, 3 H), 3.97 (s, 3 H), 3.98 (s, 3 H), 6.57 (s, 1 H), 6.79 (s, 1 H), 6.95–7.03 (m, 2 H) and 7.75–7.87 (m, 2 H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm 177.18, 162.13, 161.14, 157.61, 154.49, 152.57, 127.63, 123.86, 114.39, 112.87, 107.05, 96.26, 62.19, 61.53, 56.28 and 55.48. HRMS(Q-TOF) m/z calculated for C19H18O6 [M + Na]+: 365.3426 found: 365.0996.
4.2.9. 2-(4-Acetoxyphenyl)-5-hydroxy-4-oxo-4H-chromene-6,7-diyl diacetate (13b) and 2-(4-acetoxyphenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromene-5,6,7-triyl triacetate (14b)
Compound 2 (0.2 g, 0.6 mmol) was dissolved in pyridine (15 mL) and mixed with acetic anhydride (0.32 g, 3.1 mmol) and a small amount of DMAP as catalyst under nitrogen atmosphere. The reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature overnight. After the disappearance of starting material, as indicated by TLC, the reaction mixture was diluted with DCM and brine. The collected organic phase was dried over anhydrous Na2SO4, filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure. Purification of the crude residue was performed by flash column chromatography on silica gel using 50% ethyl acetate in petroleum ether as eluent to afford the desired compound 13b (1.78 g, 56.2% yield) and a side product 14b (0.26 g, 57.1% yield). For 13b: 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm 2.28 (s, 6 H), 2.30 (s, 3 H), 6.63 (s, 1 H), 6.89 (s, 1 H), 7.13–7.31 (m, 3 H), 7.84 (d, J = 8.80 Hz, 2 H) and 12.83 (s, 1 H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm 182.68, 164.02, 162.62, 158.73, 153.23, 153.09, 128.00, 123.58, 114.53, 106.16, 104.15, 90.57, 60.86, 56.32 and 55.55. HRMS(Q-TOF) m/z calculated for C21H16O9 [M + Na]+: 435.3463 found: 435.0687. For 14b: 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm 2.25–2.30 (m, 10 H), 2.37 (s, 3 H), 6.55 (s, 1 H), 7.19 (t, J = 4.40 Hz, 3 H), 7.42 (s, 1 H) and 7.81 (d, J = 9.05 Hz, 2 H). 13CNMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm 176.08, 168.89, 168.30, 167.25, 166.99, 161.93, 154.18, 153.42, 146.95, 142.19, 132.80, 128.54, 127.63, 122.44, 115.56, 110.27, 108.25, 21.15, 20.82 and 20.09. HRMS(Q-TOF) m/z calculated for C23H18O10 [M + H]+: 455.0900 found: 455.0976.
4.3. Antiarrhythmic Assay
4.3.1. Antiarrhythmic Effects of Compounds on BaCl2-Induced Arrhythmia in Rats
SD rats (200–220 g) were purchased from Beijing Sibefu Biotechnology Co., LTD (Beijing, China) (SCXK(JING)2019-0010). They were kept in plastic cages at 22 ± 2 °C with free access to pellet food and water on a 12 h light/dark cycle. All of animal experimental procedures were carried out in accordance with the guide for the care and use of laboratory animals (National Research Council of USA, 1996) and related ethical regulations of Yunnan University of Chinese Medicine. As shown in Figure 11, rats were anesthetized with pentobarbital sodium (50 mg/kg), then a normal electrocardiogram was recorded in lead II and barium chloride (4 mg/kg) was injected through sublingual vein. After 3 min of duration of arrhythmia, the rats were randomly divided into negative control groups (NS and DMSO), positive control groups (scutellarein and Ver) and drug administration groups (n = 6, respectively). DMSO solution lacking any compounds was used as a negative control as all of tested compounds were dissolved in DMSO. Saline (0.27 mL/kg), DMSO (0.27 mL/kg), Scutellarein (8 mg/kg), Ver (2 mg/kg) and the synthesized compounds (8 mg/kg) were immediately injected into the sublingual vein of each group of rats, respectively. ECG recordings were conducted for 35 min following anesthesia. ECG data recorded for 10 s prior to administration of BaCl2 were served as the Normal group. Stable ECG data documented 3 min following administration of BaCl2 were acted as the pre-dose group. Stable ECG recovery data posted to administration of investigated compound acted as the post-dose group. The rat number of arrhythmia recovery, corresponding recovery onset time and maintenance time were recorded for antiarrhythmic activity evaluation. The ECG parameters including the HR, RR, QRS and QT intervals were recorded. The QTc interval was also established through using Bazett’s formula: QTc = QT/√RR. All of these aforementioned parameters derived from normal, pre-dose and post-dose groups were compared. In addition, the following parameters including R wave amplitude and T wave amplitude were also measured.

Figure 11.
The experimental setup for investigating antiarrhythmic activity of tested compounds in rat models of arrhythmia induced by BaCl2.
4.3.2. Effects of Compounds on Cardiac Arrhythmia Induced by Aconitine in Rats
As shown in Figure 12, rats were anesthetized with pentobarbital sodium (50 mg/kg), then a normal electrocardiogram was recorded in lead II. Saline (0.8 mL/kg), Ver (2 mg/kg) and the synthesized compounds (8 mg/kg) were injected into the sublingual vein. After 2 min, one side of the femoral vein was separated and aconitine (0.01 mg/mL) was injected into the femoral vein at a constant rate of 100 μL/min using an infusion pump to induce ventricular arrhythmia. The time required for onset of VP, VT, VF and CA were recorded and then converted into the cumulative aconitine dosage required to induce VP, VT, VF and CA.

Figure 12.
The experimental setup for investigating antiarrhythmic activity of tested compounds in rat models of arrhythmia induced by aconitine.
4.3.3. The Effect of Investigated Compounds on Normal Electrocardiogram in Rats
As shown in Figure 13, in vivo electrocardiographic investigations were carried out using an BL-420 multiple physiological signal acquisition and analysis system with a standard lead II mode. The tested compounds were administered through sublingual vein at a dose of 8 mg/kg after 3 min following general anesthesia with pentobarbital sodium (50 mg/kg), while the BaCl2 as the positive control was given into sublingual vein at a dose of 4 mg/kg, so as to NS and DMSO as the negative control. The ECG was recorded just 3, 5, 10, 15, 20, 25 and 30 min following general anesthesia, since the rat would be awake after 35 min following general anesthesia.

Figure 13.
The experimental setup for investigating proarrhythmic effect of tested compounds in normal rat.
4.4. Cytotoxicity Assay
The cell proliferation assay was based on the reduction of (2-(2-Methoxy-4-nitrophenyl)-3-(4-nitrophenyl)-5-(2,4-disulfophenyl)-2H-tetrazolium Sodium Salt (WST-8) to yellow formazan dye by succinate dehydrogenase in living cells. Cells in 100 μL of culture media were seeded into 96-well plate at a density of 5000 cells per well and incubated for 4 h at 37 °C. Then, the cells were exposed to various concentrations of compound 10e in DMSO for 48 h before CCK-8 assay. Medium containing 0.5% DMSO was used as a negative control. Medium without cells was used as blank control. After treatment, CCK-8 reagent (HB-CCK8-1, Hanbio Biotechnology, China) in PBS was added to each well and the cells were further incubated for 1 h at 37 °C according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The optical density was measured at 450 nm using a Microplate Reader (Clariostar, BMG, Ortenberg, Germany). The percentage of surviving cells was calculated using the following formula: (corrected reading from the test well/corrected reading from the blank well)/(corrected reading from negative well-corrected reading from the blank well) × 100%.
4.5. Patch Clamp Assay for Nav1.5, Cav1.2 and hERK
4.5.1. Cell Culture
Human embryonic kidney cells (HEK293) that showed no macroscopic sodium currents were used for patch clamp assay and purchased from the Shanghai Institute of Biological Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences (Shanghai, China). HEK293 cells were cultured in medium consisting of 90% DMEM, 10% fetal bovine serum, 1% penicillin and streptomycin at 37 °C and 5% CO2 atmosphere.
4.5.2. Cell Transfection
The Nav1.5 (SCN5A) plasmid was purchased from Addgene and the GFP plasmid was purchased from Shenzhen Yanming Biotechnology. According to the manufacturer’s instructions, HEK293 cells were transfected with GFP plasmids using pCDNA3.1hSCN5A for 6–8 h. Subsequently, patch clamp assays were carried out in whole-cell mode after about 24 h transfection.
The Cav1.2 (CACNA2D) plasmid was purchased from Youbio and the GFP plasmid was purchased from Beijing Bozhiyuan Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China). According to the manufacturer’s instructions, HEK293 cells were transfected with GFP plasmids using pCDNA3.1hCACNA2D for 6–8 h. Subsequently, patch clamp assays were carried out in whole-cell mode after about 24 h transfection.
The HEK293 cell lines were transfected with pcmv-kcnh2-egfp-neo plasmid purchased from Shenzhen Dingke Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Shenzhen, China) using jetPRIME (polyplus, 101000046) when cell confluence reached 60–80%. Electrophysiological experiments were performed 24–48 h after cell transfection.
4.5.3. Patch Clamp Measurements for Nav1.5
Patch clamp experiments were conducted by using an EPC-10.2 patch-clamp amplifier (HEKA Elektronik, Reutlingen, Germany) and patchmaster v2x91 acquisition software in transfected HEK293 cells with heterologous expression of human Nav1.5 channels. Before membrane Nav1.5 currents recorded, cells were replated on glass coverslips and mounted on a recording chamber. The extracellular recording solution for recording sodium current consisted of (in mM) 140 NaCl, 30 tetraethylammonium chloride, 10 D-glucose, 3 KCl, 1 CaCl2, 0.5 CdCl2, 1 MgCl2 and 10 HEPES. The pH of the solution was adjusted to 7.3 by using NaOH, meanwhile the osmolality was maintained at 310–315 mOsm/L. The composition of the intracellular recording solution was (in mM) 140 CsF, 10 NaCl, 15 HEPES and 1.1 Cs-EGTA, in which pH was adjusted to 7.3 with CsOH. HEK293 cells were used for all records. The current voltage (I-V) measurement was recorded by 50 ms square pulses ranging from −100 to +60 mV, with 5 mV increment from a holding potential of −120 mV. The corresponding current density was obtained. Voltage dependency for sodium current activation was recorded by 50 ms square pulses ranging from −100 to +40 mV, with 5 mV increment from a holding potential of −120 mV. Data were fitted with the modified Boltzman function , where V1/2 was the voltage in which half of the current is activated. Em was the membrane potential and K was the slope factor. Voltage-dependent inactivation was measured in a 50 ms duration test pulse to −30 mV amplitude immediately after 5000 ms conditioning pulse ranging from −140 mV to −35 mV, with 5 mV increment from a holding potential of −120 mV. Peak currents from the test pulse were normalized by maximum current (I/IMAX) and also fitted with the modified Boltzman function to calculate the potential Vh related to the half of inactivation and slope factor kh.
4.5.4. Patch Clamp Measurements for Cav1.2
The extracellular recording solution for recording calcium current consisted of (in mM) 140 TEA-Cl, 1 MgCl2•6H2O, 4 KCl, 10 CaCl2•2H2O, 10 D-Glucose and 5 mM HEPES. The pH of the solution was adjusted to 7.4 using TEA-OH. The composition of the intracellular recording solution was (in mM) 110 CsCl, 10 EGTA, 5 HEPES and 5 Mg-ATP, in which pH was adjusted to 7.2 with CsOH. Cav1.2 cells were used for all records. The stimulation procedure is shown below. The clamping voltage was set to −80 mV, then depolarized to 10 mV over a time range of 400 ms, then repolarized to −80 mV. The current was recorded every 20 s. The original data Cav1.2 current peak was extracted from the PatchMaster v2x91 software, and the current inhibition rate was calculated as follows: peak calcium current inhibition rate = 1 − (Peak current compound/Peak current vehicle). The mean and standard error were calculated for each concentration and the concentration–effect relationship was obtained. The analysis statistics were completed using Graphpad Prism 5.0 software.
4.5.5. Patch Clamp Measurements for hERG
The extracellular recording solution for recording calcium current consisted of (in mM) 140 NaCl, 3.5 KCl, 1 MgCl2•6H2O, 2 CaCl2•2H2O, 10 D-Glucose, 10 HEPES and 1.25 NaH2PO4•2H2O. The pH of the solution was adjusted to 7.4 using NaOH. The composition of the intracellular recording solution was (in mM) 10 NaCl, 50 CsCl, 60 CsF, 10 HEPES and 20 EGTA, in which pH was adjusted to 7.2 with CsOH. The current was recorded by depolarizing the voltage to +40 mV for 2.5 s from the holding potential at −80 mV, followed by a hyperpolarization step to −50 mV lasting for 4 s, which elicited the peak tail current of hERG channel. The analysis statistics were completed by using Graphpad Prism 5.0 software.
4.6. Computational Docking Studies
Autodock vina software was used for docking study. The 3D structure of compound 10e were generated from ChemDraw 22.0 software and imported into the Autodock vina software. The X-ray crystal structure of the human-derived protein Nav1.5 (PDB ID:6LQA) and Cav1.2 (PDB ID 8FD7) obtained from the Protein Data Bank were used for docking after removal of the water molecules and ions or small molecule compounds bound to the surface of protein. The position of the self-matched antibody single-chain variable fragment in the crystal was identified as the substrate-binding site of Nav1.5 or Cav1.2 protein. Compound 10e performed energy optimization before docking. The potential binding result positioned compound 10e into the substrate-binding site of Nav1.5 and Cav1.2 with hydrogen bonding interactions, respectively.
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Results were presented as either means ± SD. In our analysis, statistical analyses were performed using single-factor ANOVA test or non-parametric test followed by Welch test or Kruskal–Wallis test.
Supplementary Materials
Supporting information including NMR spectrum, ECG and morphological changes can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/molecules28217417/s1.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.J.; Data curation, W.W.; Investigation, W.Y., S.C., P.L., D.Z., J.N., J.K., A.H. and L.C.; Project administration, W.J.; Resources, W.J. and Y.M.; Supervision, W.J. and Y.M.; Writing—original draft, W.J.; Writing—review and editing, W.J. and Y.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 82104067), the Bioactive Ethnopharmacol Molecules Chemical Conversion and Application Innovation Team of the Department of Education of the Yunnan Province, the Yunnan Provincial Key Laboratory of Molecular Biology for Sinomedicine (2019DG016), the Yunnan Provincial Joint Project of Traditional Chinese Medicine (202001AZ070001-091) and the Natural Science Foundation of Yunnan (202001AU070133).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the animal research ethics committee of the Yunnan University of Chinese Medicine (Approval ID: R-062019S021, 14 August 2019).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data will be provided upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Srinivasan, N.T.; Schilling, R.J. Sudden Cardiac Death and Arrhythmias. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. Rev. 2018, 7, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lubberding, A.F.; Pereira, L.; Xue, J.; Gottlieb, L.A.; Matchkov, V.V.; Gomez, A.M.; Thomsen, M.B. Aberrant sinus node firing during β-adrenergic stimulation leads to cardiac arrhythmias in diabetic mice. Acta Physiol. 2020, 229, e13444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholz, H. Classification and mechanism of action of antiarrhythmic drugs. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 1994, 8, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, D.L.; Cooper, M.J.; Koo, C.C.; Skinner, M.P.; Davis, L.M.; Richards, D.A.; Uther, J.B. Proarrhythmic effects of antiarrhythmic drugs. Med. J. Aust. 1990, 153, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, M.; Wu, L.; Terrar, D.A.; Huang, C.L. Modernized Classification of Cardiac Antiarrhythmic Drugs. Circulation 2018, 138, 1879–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zheng, M.; Guo, Q.; Lan, H.; Wu, S.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Y. Dominant diseases of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM). Integr. Med. Res. 2022, 11, 100872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Tian, G.; Xu, L.; Sun, L.; Tao, R.; Zhang, S.; Cong, Z.; Deng, F.; Chen, J.; Yu, Y.; et al. Wenxin Keli for the Treatment of Arrhythmia-Systems Pharmacology and In Vivo Pharmacological Assessment. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 704622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heart Rhythm Society of the Chinese Society of Biomedical Engineering; Nao Xin Tong Zhi Committee of the Chinese Association of Integrative Medicine. Expert Consensus on Wenxin Granule for Treatment of Cardiac Arrhythmias. Chin. Med. J. 2017, 130, 203–210. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Gao, F.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhu, J.; Chang, L.; Du, Z.; Zhang, Y. Shensong Yangxin capsules prevent ischemic arrhythmias by prolonging action potentials and alleviating Ca2+ overload. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 13, 5185–5192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Tian, G.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X.; Wu, A.; Li, M.; Sun, Y.; Liu, B.; Xing, Y.; Shang, H. Traditional Chinese Medicine for Bradyarrhythmia: Evidence and Potential Mechanisms. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Q.; Xiao, G.; Wang, T.; Zhang, L.; Yu, M.; Peng, L.; Han, L.; Du, X.; Han, W.; He, S.; et al. Identification of linoleic acid as an antithrombotic component of Wenxin Keli via selective inhibition of p-selectin-mediated platelet activation. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 153, 113453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryzgalov, A.O.; Tolstikova, T.G.; Shults, E.E.; Petrova, K.O. Natural Products as a Source of Antiarrhythmic Drugs. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2018, 18, 345–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.A.N.; Zhang, X.F.; Wan-Sheng, W.E.I.; Zhang, J.; Zhen-Zhen, L.I. The cardiovascular protective effect and mechanism of calycosin and its derivatives. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2020, 18, 907–915. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Fu, J.L.; Hao, H.F.; Jiao, Y.N.; Li, P.P.; Han, S.Y. Metabolic reprogramming by traditional Chinese medicine and its role in effective cancer therapy. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 170, 105728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Ma, Q. Clinical benefits and pharmacology of scutellarin: A comprehensive review. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 190, 105–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Gao, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, R. Pharmacological mechanism of natural drugs and their active ingredients in the treatment of arrhythmia via calcium channel regulation. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 160, 114413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carullo, G.; Falbo, F.; Ahmed, A.; Trezza, A.; Gianibbi, B.; Nicolotti, O.; Campiani, G.; Aiello, F.; Saponara, S.; Fusi, F. Artificial intelligence-driven identification of morin analogues acting as CaV1.2 channel blockers: Synthesis and biological evaluation. Bioorganic Chem. 2023, 131, 106326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carullo, G.; Ahmed, A.; Trezza, A.; Spiga, O.; Brizzi, A.; Saponara, S.; Fusi, F.; Aiello, F. Design, synthesis and pharmacological evaluation of ester-based quercetin derivatives as selective vascular KCa1.1 channel stimulators. Bioorganic Chem. 2020, 105, 104404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carullo, G.; Ahmed, A.; Trezza, A.; Spiga, O.; Brizzi, A.; Saponara, S.; Fusi, F.; Aiello, F. A multitarget semi-synthetic derivative of the flavonoid morin with improved in vitro vasorelaxant activity: Role of CaV1.2 and KCa1.1 channels. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2021, 185, 114429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Chen, X.-Y.; Martin, C. Scutellaria baicalensis, the golden herb from the garden of Chinese medicinal plants. Sci. Bull. 2016, 61, 1391–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.-y.; Li, M.; Zhang, C.-l.; Liu, D. Pharmacological properties of baicalin on liver diseases: A narrative review. Pharmacol. Rep. 2021, 73, 1230–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, C.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, D.; Cong, X.; Cao, R.; Li, H.; Tian, W. Cytotoxic and chemosensitization effects of Scutellarin from traditional Chinese herb Scutellaria altissima L. in human prostate cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 38, 1491–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, Z.-M.; Ge, G.-B.; Dou, T.-Y.; Wang, P.; Liu, P.-K.; Tian, X.-H.; Qiao, N.; Yu, Y.; Zou, L.-W.; Zhou, Q.; et al. Characterization and structure-activity relationship studies of flavonoids as inhibitors against human carboxylesterase 2. Bioorganic Chem. 2018, 77, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, T.; Wang, Y.; Wang, M.; Li, X.; Cheng, K.; Gao, X.; Li, Z.; Bai, J.; Hua, H.; Li, D. Synthesis of scutellarein derivatives with antiproliferative activity and selectivity through the intrinsic pathway. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 158, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Nian, M.; Qiao, H.; Yang, X.; Wu, S.; Zheng, X. Review of bioactivity and structure-activity relationship on baicalein (5,6,7-trihydroxyflavone) and wogonin (5,7-dihydroxy-8-methoxyflavone) derivatives: Structural modifications inspired from flavonoids in Scutellaria baicalensis. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 243, 114733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Bai, L.; Xue, M. Acute and subacute toxicological evaluation of scutellarin in rodents. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2011, 60, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Ping, Q.N.; Guo, J.X.; Cao, F. Pharmacokinetics of breviscapine and its beta-cyclodextrin complex in rats. Yao Xue Xue Bao = Acta Pharm. Sin. 2005, 40, 563–567. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, J.F.; You, H.S.; Dong, Y.L.; Lu, J.; Chen, S.Y.; Zhu, H.F.; Dong, Q.; Wang, M.Y.; Dong, W.H. Metabolic and pharmacokinetic studies of scutellarin in rat plasma, urine, and feces. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2011, 32, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Zhang, W.; Dong, Z.X.; Gu, T.; Li, N.G.; Shi, Z.H.; Kai, J.; Qu, C.; Shang, G.X.; Tang, Y.P.; et al. A new and practical synthetic method for the synthesis of 6-O-methyl-scutellarein: One metabolite of scutellarin in vivo. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 7587–7594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.H.; Li, N.G.; Wang, Z.J.; Tang, Y.P.; Dong, Z.X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, P.X.; Gu, T.; Wu, W.Y.; Yang, J.P.; et al. Synthesis and biological evaluation of methylated scutellarein analogs based on metabolic mechanism of scutellarin in vivo. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 106, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, W.L.; Guo, J.X.; Ping, Q.N.; Li, J.; Zhao, C.W.; Zhang, L. Pharmacokinetics of breviscapine liposomes following intravenous injection in Beagle dogs. Yao Xue Xue Bao = Acta Pharm. Sin. 2006, 41, 24–29. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, R.; Liang, Y.; Xu, M.; Fu, K.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, L.; Wang, Z. Advances in Chemical Constituents, Clinical Applications, Pharmacology, Pharmacokinetics and Toxicology of Erigeron breviscapus. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 656335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Jin, X.; Wu, T.; Zhao, X.; Wang, W.; Lei, J.; Pan, X.; Yan, N. Structure of human Nav1.5 reveals the fast inactivation-related segments as a mutational hotspot for the long QT syndrome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2100069118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, S.; Tuohy, P.; Ma, C.; Kitamura, N.; Gomez, K.; Zhou, Y.; Ran, D.; Bellampalli, S.S.; Yu, J.; Luo, S.; et al. A modulator of the low-voltage-activated T-type calcium channel that reverses HIV glycoprotein 120-, paclitaxel-, and spinal nerve ligation-induced peripheral neuropathies. Pain 2020, 161, 2551–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Z.; Cai, S.; Yu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Vallecillo, T.G.M.; Serafini, M.J.; Thomas, A.M.; Pham, N.Y.N.; Bellampalli, S.S.; Moutal, A.; et al. Reversal of Peripheral Neuropathic Pain by the Small-Molecule Natural Product Physalin F via Block of CaV2.3 (R-Type) and CaV2.2 (N-Type) Voltage-Gated Calcium Channels. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2019, 10, 2939–2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moutal, A.; Cai, S.; Yu, J.; Stratton, H.J.; Chefdeville, A.; Gomez, K.; Ran, D.; Madura, C.L.; Boinon, L.; Soto, M.; et al. Studies on CRMP2 SUMOylation-deficient transgenic mice identify sex-specific Nav1.7 regulation in the pathogenesis of chronic neuropathic pain. Pain 2020, 161, 2629–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido, A.; Lepailleur, A.; Mignani, S.M.; Dallemagne, P.; Rochais, C. hERG toxicity assessment: Useful guidelines for drug design. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 195, 112290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, P.B. Drug safety sciences and the bottleneck in drug development. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 89, 788–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.B.; Xu, C.; Cheung, Q.; Gao, W.; Zeng, P.; Liu, J.; Chan, E.W.C.; Leung, Y.-C.; Chan, T.H.; Wong, K.-Y.; et al. Bioisosteric investigation of ebselen: Synthesis and in vitro characterization of 1,2-benzisothiazol-3(2H)-one derivatives as potent New Delhi metallo-β-lactamase inhibitors. Bioorganic Chem. 2020, 100, 103873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.B.; Xu, C.; Qi, X.L.; Zeng, P.; Gao, W.; Lai, K.H.; Chiou, J.; Chan, E.W.C.; Leung, Y.-C.; Chan, T.H.; et al. Synthesis of 1,3,4-trisubstituted pyrrolidines as meropenem adjuvants targeting New Delhi metallo-β-lactamase. New J. Chem. 2021, 45, 3515–3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.B.; Wang, Z.; Yang, W.; Zhang, D.; Ning, J.H.; Ke, J.; Hou, A.G.; Chen, L.Y.; Ma, Y.S. Selective [3 + 2] cycloaddition reaction of isothiazol-3(2h)-ones with in situ formed azomethine ylide to thiazolidines and oxazolidines. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 2023, 60, 1383–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapacz, A.; Sapa, J.; Bednarski, M.; Filipek, B.; Szkaradek, N.; Marona, H. Antiarrhythmic activity of some xanthone derivatives with β1-adrenoceptor affinities in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 738, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).