Abstract
Herein, ZIF-67-derived Co and N-doped carbon (Co/NC) particle-modified multilayer MXene (MXene@Co/NC) was developed as remarkable electrode material for carbendazim (CBZ) detection. MXene as a substrate provides an excellent conductive framework and plentiful accessibility sites. Co/NC particles embedding in MXene can not only prevent the interlayer stacking of MXene but also contribute a great deal of metal catalytic active sites and finally improve the adsorption and catalytic properties of the composite. Accordingly, the MXene@Co/NC electrode displays excellent electrocatalytic activity toward CBZ oxidation. Experimental parameters such as pH value, accumulation time, MXene@Co/NC modification volume and constituent materials’ mass ratios were optimized. Under optimal conditions, the as-prepared sensor based on MXene@Co/NC holds a broad linearity range from 0.01 μM to 45.0 μM with a low limit of detection (LOD) of 3.3 nM (S/N = 3, S means the detection signal, while N represents the noise of the instrument). Moreover, the proposed sensor displays excellent anti-interference ability, superior reproducibility, excellent stability, and successfully achieves actual applications for CBZ detection in a lettuce sample.
1. Introduction
Carbendazim (CBZ) is one of the systematic benzimidazole fungicides widely used in modern agricultural production, which is mainly used to prevent and control vegetable and fruit crops from being harmed by various fungi and pests [1,2]. However, CBZ accumulated in the environment and in fruits and vegetables can cause serious harm to ecosystems and the human nervous system [3]. To date, various methods have been explored for CBZ detection, such as surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy [4,5], liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry [6], fluorimetry [7], and electrochemical methods [8,9]. Among them, electrochemical sensors stand out for their fast analysis speed, low-cost production, and ability to continuously monitor in complex systems. In particular, these properties are further enhanced when nanomaterials are incorporated into the design of electrochemical sensors. Up to now, several kinds of functional nanomaterials, such as phosphorus-doped helical carbon nanofibers [10], metal nanoparticles [11], laser-induced graphene [12] and CoCu nanoparticles modified COF/SWCNT [13], have been used as electrode modifiers for CBZ detection. Unfortunately, with the poor electrochemical activity and low residual amount of CBZ, some major issues such as low sensitivity and narrow linearity range still remain. Therefore, it is necessary to explore better sensitizing materials for electrochemical detection of CBZ.
The novel 2D transition metal carbide or nitride MXene is a promising electrode material for electrochemical sensors due to its fascinating metallic conductivity, large surface area, and satisfactory hydrophilicity [14,15]. Hitherto, MXene-based electrodes have been developed as various sensors to detect chemical and biological molecules, such as adrenaline [16], 4-chlorophenol [17], and bisphenol A [18]. In these works, the self-accumulation phenomenon for MXene nanosheets induced by hydrogen bonds and van der Waals interactions has a serious negative impact on the accessibility of electrolyte ions and electrochemical stability. To overcome this weakness, currently, a variety of materials such as metal particles [19] and carbon tubes [20] have been loaded in MXene interlamination. Meanwhile, to obtain better electrochemical sensing performance, it is necessary to explore suitable spacers that meet the anti-collapse requirements of MXene and simultaneously improve the electrocatalytic ability of the formed composites.
Metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) composed of organic ligands bridging metal ions are a recently developed intercalation material with clear porosity, large specific surface area, and certain catalytic activity [21,22,23]. Zhang et al. developed a Cr-MOF/MXene composite as a sensing substrate for xanthine detection with an acceptable linearity of 1.5–7.3 µM and 73.0–133.0 µM [24]. Li et al. prepared a ZIF-67 MOF/MXene electrode material for determination of anticancer drug flutamide with good selectivity and a wide calibration range [25]. The introduction of MOFs in MXene improves porosity and contributes to specific surface area, which is conducive to the improvement of sensing performance. Regrettably, the limited conductivity of MOFs limits the further development of nanocomposites. Metal–organic framework (MOF)-derived carbon materials have recently become the focus of electro-catalyst research on account of their rich and controllable pore structures, intrinsic heteroatom doping, and improved conductivity of precursor MOFs [26]. Typically, imidazole acid zeolite-based Co-MOF (ZIF-67)-derived carbon materials have attracted much attention. For example, Hira et al. synthesized a heteroatom-doped hierarchical porous material via ZIF-67 as a high-performance electrode for catecholamine detection, which displays a wide linearity of 5–115 µM with a low LOD of 0.43 µM [27]. Zhou et al. designed ZIF-67-derived Co nanoparticles directly supported on N-doped carbon skeletons for the sensitive determination of hydrogen peroxide [28]. Wang et al. reported MOF-derived CoPx nanoparticles embedded in hairy nitrogen-doped porous carbon (CoPx@NCNTs) polyhedrons for the electrochemical detection of p-nitrophenol with a low LOD of 0.79 nM [29]. On the one hand, the outstanding electrochemical performance of the above ZIF-67-derived carbon materials comes from the fact that ZIF-67 can maintain the original polyhedral form after carbonization and build a stable three-dimensional carbon electron conduction structure. On the other hand, the adjustable porosity and nitrogen doping enable the target analyte to be effectively fixed by physical confinement or chemisorption. The Co core could also provide a rich metal active site, which accelerates the catalytic action of the target analyte.
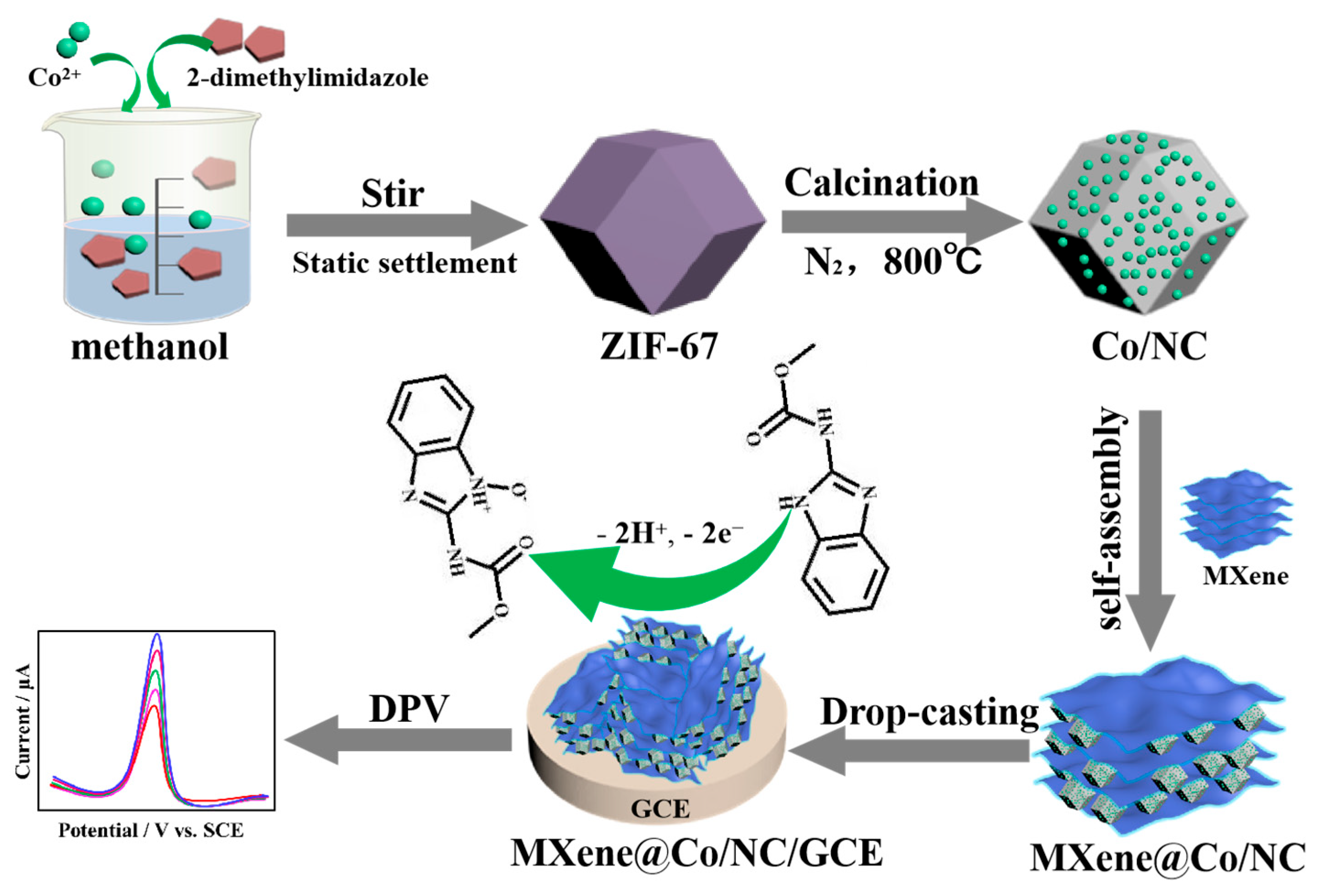
Herein, Co/CN derived from ZIF-67 was inserted into the interlayer of MXene as an interlayer spacer by a simple ultrasonic method, and an efficient electrochemical CBZ sensor was constructed based on the MXene@Co/NC composite. This strategy not only prevented the accumulation of MXene nanosheets, which effectively promotes electron transport, but also provided a large surface area for the distribution of Co/CN, effectively avoiding their accumulation, enabling the catalytic active site to be fully exposed and have high accessibility. Based on the synergistic effect between MXene and Co/NC, the electrochemical CBZ sensor displayed excellent analytical performance with high sensitivity, splendid stability, and good reproducibility for CBZ detection.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization
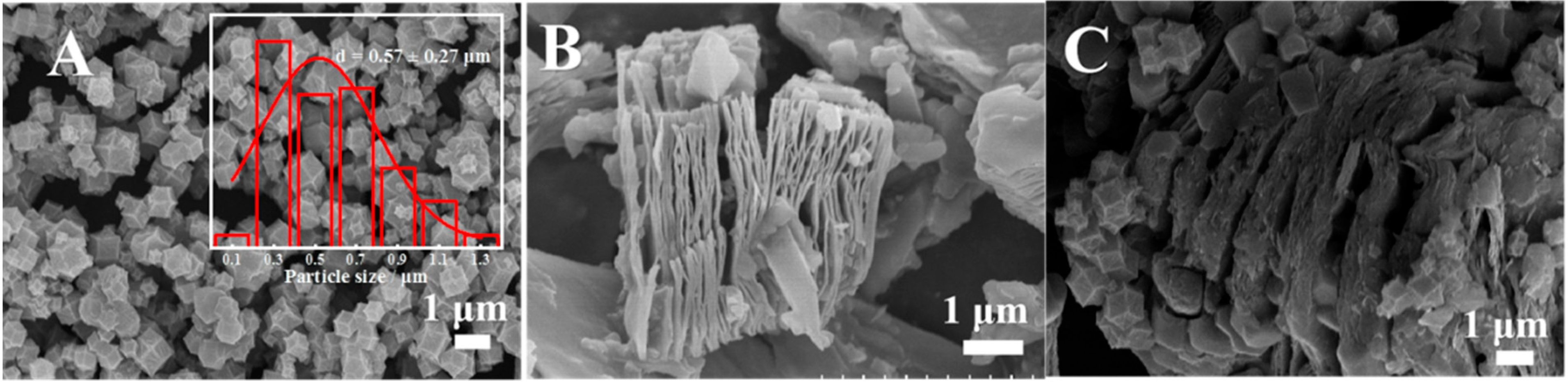
SEM was applied to verify the micromorphologies of Co/NC, MXene, and MXene@Co/NC. As shown, Co/NC (Figure 1A) displays a polyhedral morphology with a wrinkled surface. The particle size of Co/NC was statistically analyzed via Nano Measurer, in which the minimum particle size is 0.14 μm and the average particle size is 0.57 μm (inset of Figure 1A). MXene presents the representative delaminated structure (Figure 1B). According to the SEM of the MXene@Co/NC composite (Figure 1C), it is clearly seen that a part of the small-size Co/NC particles are well embedded between the fluffy MXene interlayer and some large-size particles are attached to the edge of the MXene. The unique structure could provide a large utilization space, expose more active sites, and ultimately increase catalytic activity. Moreover, the energy-dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) mapping images show that the Co (Figure S1A), N (Figure S1B), and Ti (Figure S1C) elements are uniformly distributed on the MXene@Co/NC surface, indicating the successful combination of Co/NC with Mxene.

Figure 1.
SEM images of Co/NC, insert is the particle size statistical analysis of Co/NC (A), MXene (B), MXene@Co/NC (C).
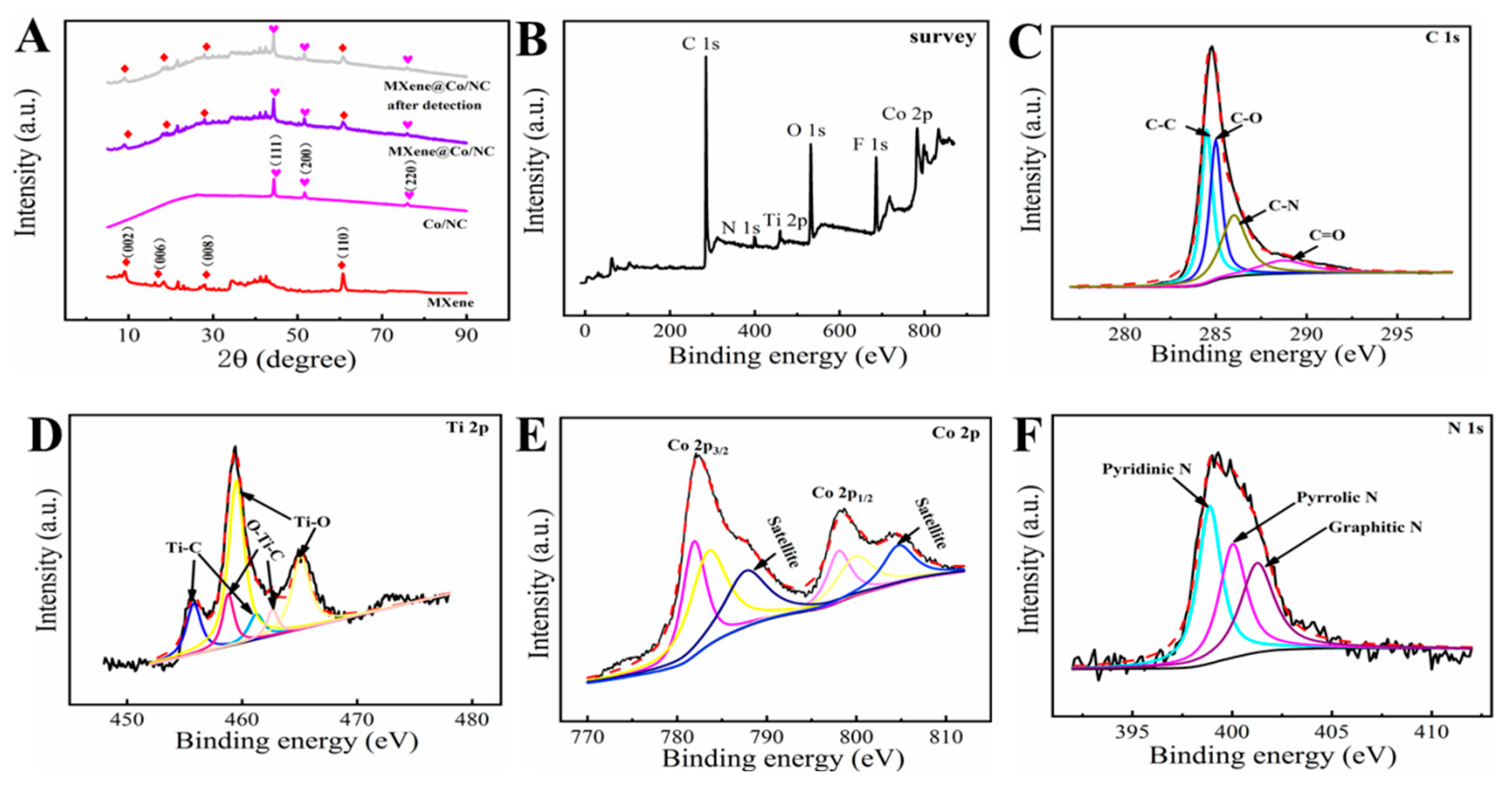
The crystallographic structure of Co/NC, MXene, and MXene@Co/NC were proved by XRD analysis (Figure 2A). In the diffract gram of MXene, the diffraction peaks positioned at 9.1°, 18.4°, 28.0°, and 60.8° match the (002), (006), (008), and (110) planes of MXene. For the Co/NC, the diffraction peaks at 44.3°, 51.6°, and 76.0° match the (111), (200), and (220) crystal planes of the Co particle, which are consistent with previous reports [30]. The XRD pattern of MXene@Co/NC simultaneously presents the typical peaks of Co/NC and primary characteristic peaks of MXene, confirming that the MXene@Co/NC nanohybrid was successfully constructed. Furthermore, compared with the MXene@Co/NC, the diffraction peak of the MXene@Co/NC after detection has no obvious change, which means that the crystal structure of the MXene@Co/NC after the sensing process remains stable.
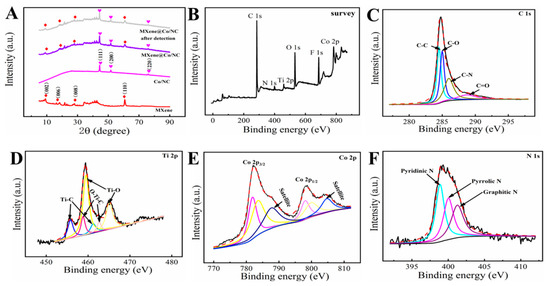
Figure 2.
(A) XRD spectra for Co/NC, MXene, MXene@Co/NC, and MXene@Co/NC after detection; (B) XPS survey spectra of MXene@Co/NC; the C 1s (C), Ti 2p (D), Co 2p (E), and N 1s (F) core-level spectra of MXene@Co/NC.
Figure S2A reveals the N2 adsorption/desorption isotherms of the MXene@Co/NC at 77 k. It displays that the specific surface area of MXene@Co/NC is 239.5 m2 g−1 and there is a typical type I curve, indicating the presence of numerous micropores [31].
XPS was employed to investigate the elemental composition and chemical state analysis of the MXene@Co/NC composite. As shown in Figure 2B, the XPS survey spectra of MXene@Co/NC manifest that the composite contains C, N, Ti, O, F, and Co elements. According to the C 1s high-resolution spectrum (Figure 2C), four peaks are positioned at 284.51 eV, 285.00 eV, 286.00 eV, and 288.71 eV, which are indexed in C-C, C-O, C-N, and O=C, respectively. The XPS spectra of the Ti 2p peak (Figure 2D) consist of three pairs of spin orbital peaks, including Ti-C 2p3/2/Ti-C 2p1/2 (455.79 eV/461.22 eV), O-Ti-C 2p3/2/O-Ti-C 2p1/2 (458.80 eV/462.64 eV), and Ti-O 2p3/2/Ti-O 2p1/2 (459.50 eV/465.09 eV). In the Co 2p high-resolution section (Figure 2E), two pairs of strong peaks located at 781.88 eV/798.03 eV and 783.50 eV /799.84 eV can well match Co3+ 2p3/2/Co3+ 2p1/2 and Co2+ 2p3/2/Co2+ 2p1/2 [32]. Meanwhile, there are two satellite peaks located at 787.65 and 804.73 eV. The high-resolution spectra of N 1s (Figure 2F) is a deconvolution of three parts, including pyridine N (398.87 eV), pyridine N (400.03 eV), and graphite N (401.26 eV) [33].
2.2. EIS Characterization
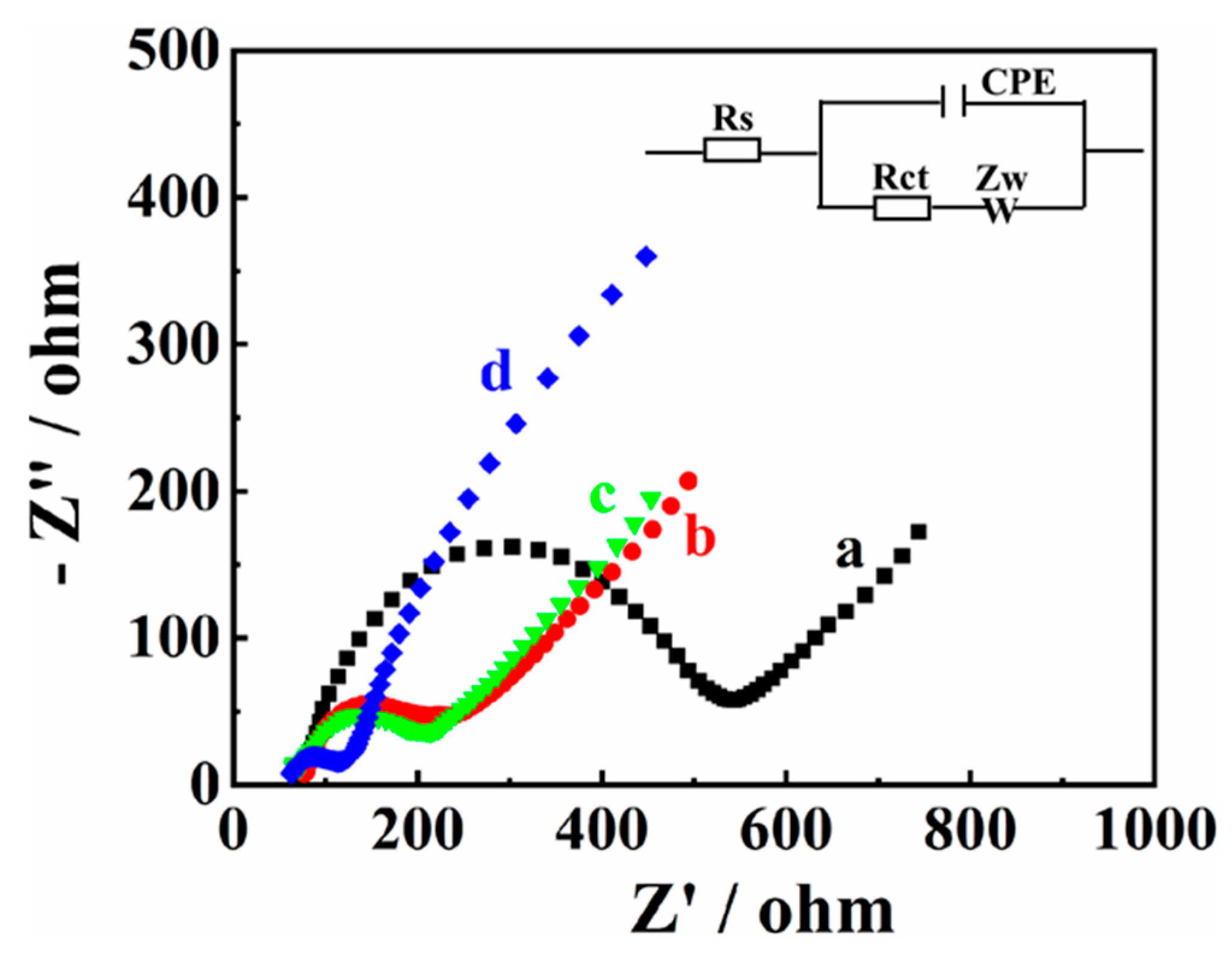
Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) was employed to research the surface impedance of the modified electrode. The Nyquist curves of bare GCE (a), MXene/GCE (b), Co/NC/GCE (c), and MXene@Co/NC/GCE (d) are exhibited in Figure 3. Impedance data are simulated using associated equivalent circuits, which involves the constant phase element (CPE), active electrolyte resistance (Rs), Warburg impedance (Zw), and charge transfer resistance (Rct).
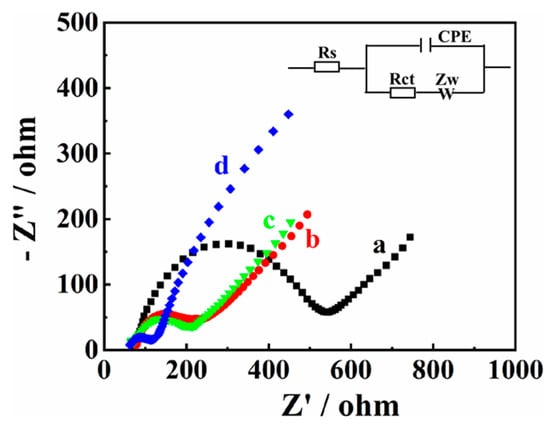
Figure 3.
Nyquist plots of bare GCE (a), MXene/GCE (b), Co/NC/GCE (c), and MXene@CO/NC/GCE (d) in 5 mM [Fe(CN)6]3−/4− solution containing 0.1 M KCl.
According to the fitted data, the Rct values of bare GCE (a), MXene/GCE (b), and Co/NC/GCE (c) are calculated as 483.3 Ω, 181.4 Ω, and 169.9 Ω, respectively. The Rct values of MXene/GCE and Co/NC/GCE are lower than bare GCE, signifying the admirable electrical conductivity of MXene and Co/NC/GCE. In addition, the lowest Rct value (80.7 Ω) is obtained at MXene@Co/NC/GCE, testifying that the combination of MXene and Co/NC can reduce the electron transfer resistance.
2.3. Electrochemical Behavior of CBZ at the Modified Electrodes
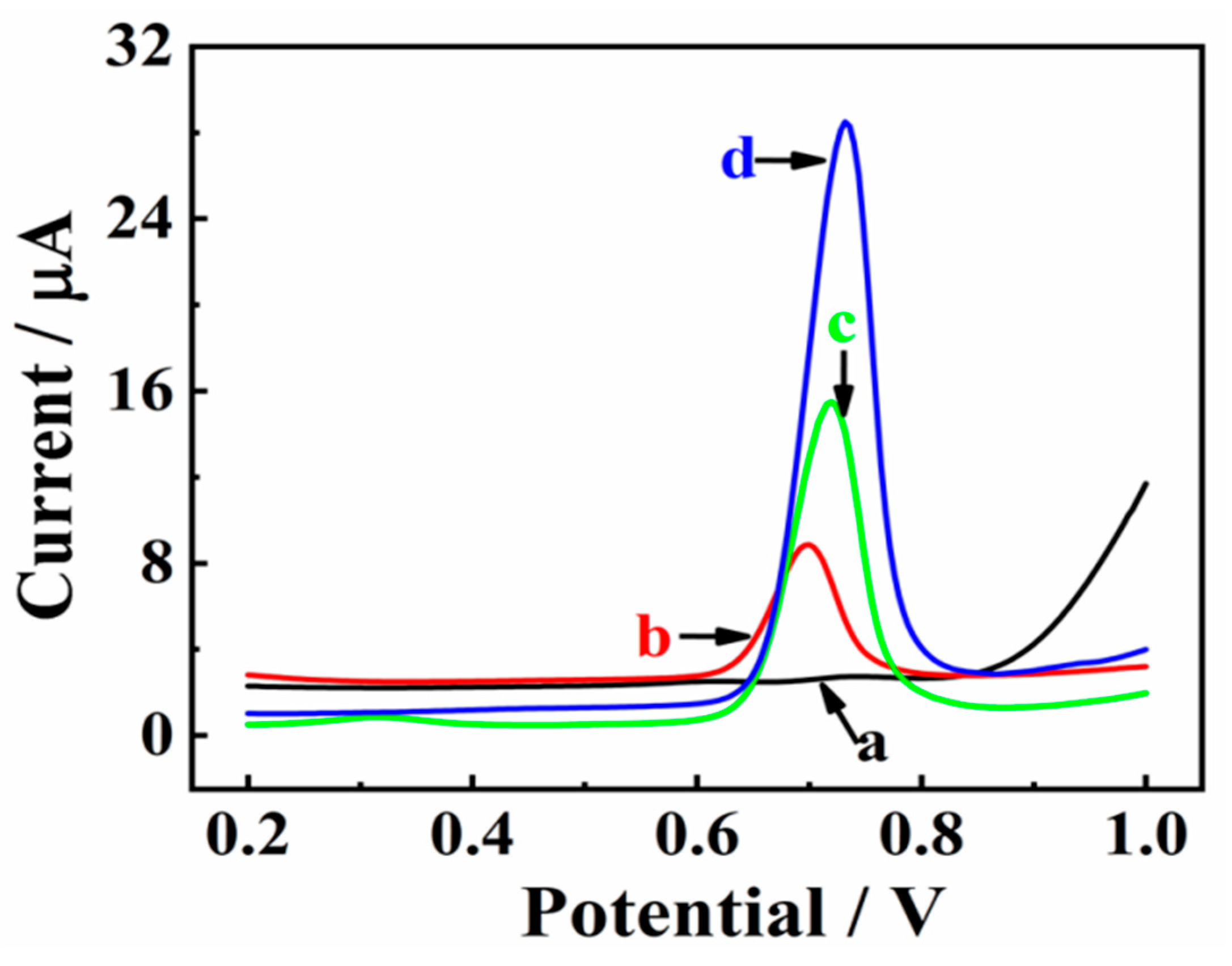
The electrochemical behaviors of CBZ (25.0 μM) at bare GCE (a), Mxene/GCE (b), Co/NC/GCE (c), and MXene@Co/NC/GCE (d) were recorded by DPV in 0.1 M PBS (pH 7.0). As displayed in Figure 4, the faintest oxidation peak appears at bare GCE (curve a). However, MXene/GCE (b) shows significant enhancement in the oxidation peak current, which could be due to the satisfactory conductivity of MXene/GCE. Furthermore, the oxidation peak at Co/NC/GCE (c) becomes much stronger, which is ascribed to abundant Co active sites and the three-dimensional carbon electron conduction structure of Co/NC/GCE. The highest oxidation peak is found at MXene@Co/NC/GCE (d). This splendid performance is mainly attributed to the synergistic effect of Co/NC and MXene. Co/NC particles embedded in MXene nanosheets prevent MXene layer accumulation and reasonably increase the available active space. MXene@Co/NC with a hierarchical architecture and good electrical conductivity provides an open mass transfer channel and facilitates electron transfer to improve electrocatalytic performance.
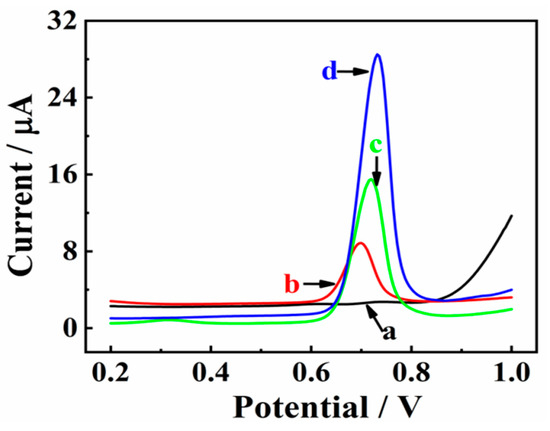
Figure 4.
DPV behaviors of CBZ (25.0 μM) in 0.1 M PBS (pH 7.0) on bare GCE (a), MXene/GCE (b), Co/NC/GCE (c), and MXene@Co/NC/GCE (d).
2.4. Optimization of Analytical Conditions
2.4.1. Effect of the Ratio of MXene and Co/NC
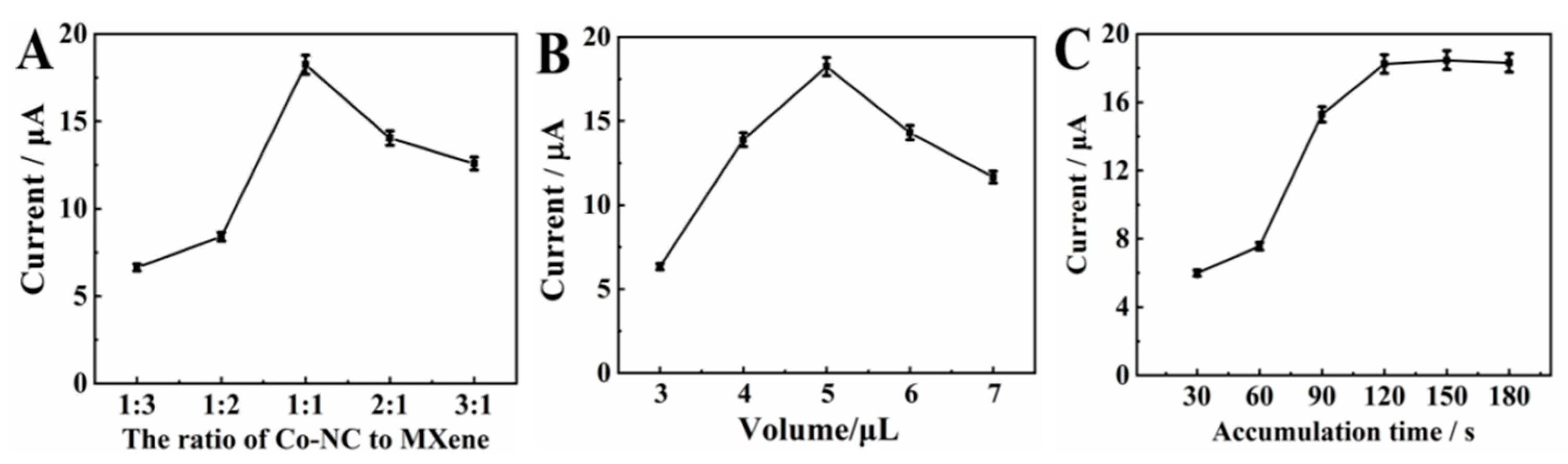
The effect of the ratio of MXene and Co/NC on the current response of CBZ was studied. The error bar and measurement data are provided in Table S1. Figure 5A shows the relationship between the current response of CBZ and the ratio of MXene and Co/NC. When the ratio of Co/NC:MXene increases from 1:3 to 1:1, the current response is significantly increased, which confirms that the increase in the proportion of Co/NC particles helps to promote the electrocatalytic ability of the composite. However, the peak current decreases with the ratio of Co/NC:MXene from 1:1 to 3:1, meaning that excessive Co/NC particles dispersed among MXene can affect the mass transfer channel. Therefore, the optimal ratio of Co/NC:MXene is 1:1.
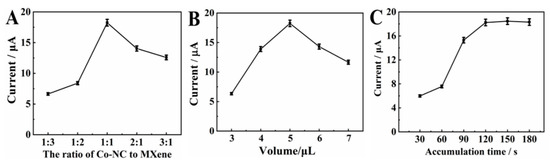
Figure 5.
Influence of (A) the ratio of Co-NC to MXene/GCE; (B) influence of the suspension volume of Co-NC/MXene/GCE; (C) effect of accumulation time with a deposition potential in 0.1 M PBS (pH 7.0) with addition of 20.0 μM CBZ.
2.4.2. Effect of the Volume of MXene@Co/NC on GCE
The effect of MXene@Co/NC modification volume on the current response of CBZ was studied. The error bar and measurement data are provided in Table S1. Figure 5B shows the relationship between the oxidation peak current of CBZ and the MXene@Co/NC modification volume on GCE. It can be clearly seen that from 3.0 μL to 5.0 μL, the oxidation peak current rises in turn. This is attributed to the fact that more active sites are generated along with an increased amount of MXene@Co/NC on the GCE. Nevertheless, the peak current drops sharply after 5.0 μL. This phenomenon is on account of the excess MXene@Co/NC on the electrode surface leading to the coverage of partial active sites. Therefore, the optimal modified volume of MXene@Co/NC is 5.0 μL.
2.4.3. Effect of Accumulation Time
The adherence amount of CBZ on MXene@Co/NC/GCE can be increased by prolonging accumulation time. The error bar and measurement data are provided in Table S1. In general, the large adhesion amount of the analyte can acquire a great current response. Figure 5C describes the correlation as regards the accumulation time and the oxidation peak current. As the accumulation time changes from 30 s to 120 s, the current response enhances gradually, whereas the current nearly stops changing with the extension of the accumulation time, signifying that the absorption of CBZ on the MXene@Co/NC/GCE surface is close to the saturation state at 120 s. In order to take into account the efficiency and sensitivity of detection, 120 s is selected as the most suitable accumulation time.
2.4.4. Effect of pH
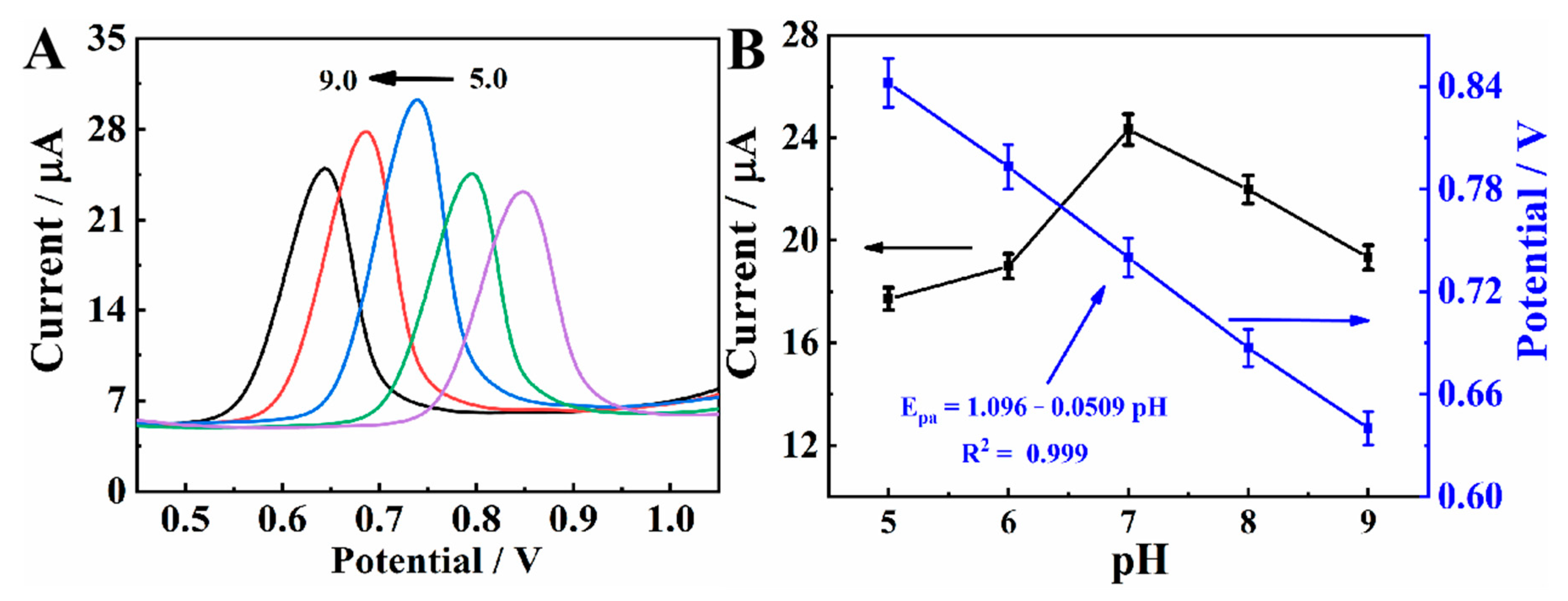
The effect of buffer pH on the electrochemical behavior of MXene@Co/NC/GCE at 25.0 μM CBZ was studied by DPV. The error bar and measurement data are provided in Table S2. As shown in Figure 6A, the oxidation peak potential shifts toward a negative direction as pH increases, verifying that protons are related to the electrode reaction. As can be seen from Figure 6B, oxidation peak potential has a good linearity with pH. The slope of −0.0509 V is approximately the theoretical value of −0.059 V, signifying that the number of protons involved in the electrode reaction is the same as the number of electrons transferred [9]. Obviously, the peak current achieves its maximum at pH 7.0. In the follow-up experiment, PBS with pH of 7.0 is used as the buffer solution.
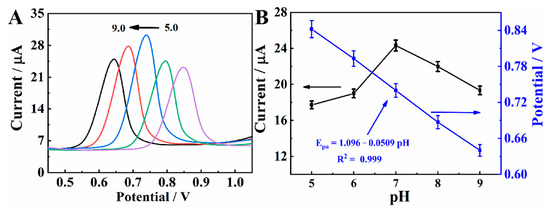
Figure 6.
(A) DPVs of MXene@Co/NC/GCE in PBS with different pH containing 25.0 μM CBZ. (B) Effect of pH value on the Epa and Ipa.
2.5. Kinetics Studies
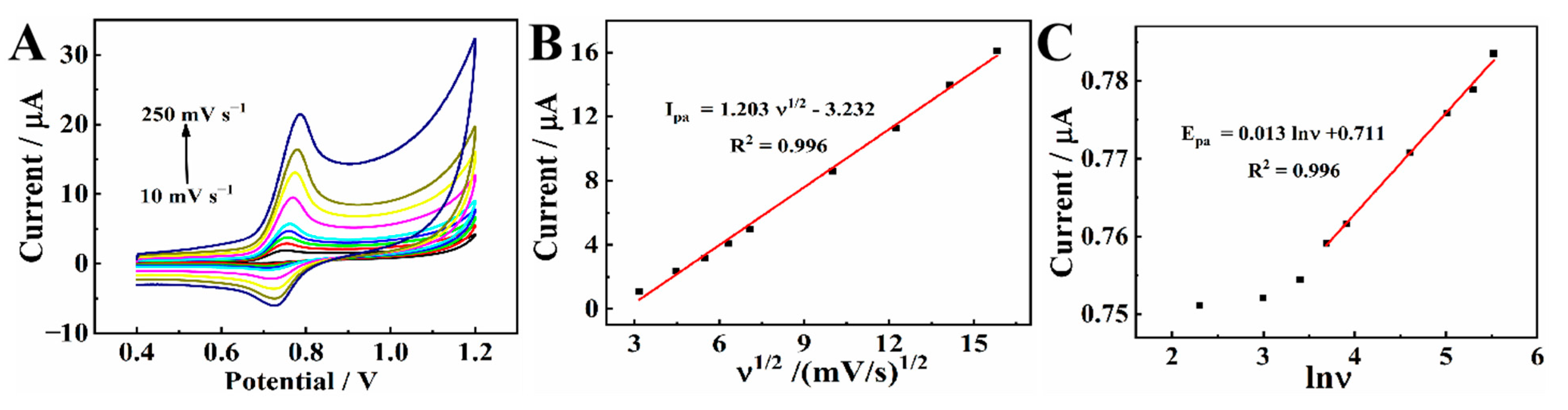
To figure out the electrochemical reaction kinetics of CBZ, CVs of CBZ were investigated with a range of scanning rates (v) on MXene@Co/NC/GCE. As shown in Figure 7A, Epa shifts toward a positive direction as the scanning rate increases. From 10 to 250 mV s−1 (Figure 7B), the current gradually increases. There is a good linear correlation between the peak current and ν1/2. The linear equation is Ipa (μA) = 1.203 ν1/2 − 3.232 (R2 = 0.996), indicating that the electrochemical reaction of CBZ on MXene@Co/NC/GCE is a diffusion-controlled process [34].
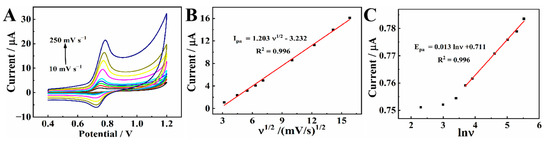
Figure 7.
(A) CVs of 20.0 μM CBZ on MXene@Co/NC/GCE in 0.1 M PBS (pH 7.0) at different scan rates: 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 100, 150, 200, and 250 mV s−1; (B) linear relationship between the peak current (Ipa) and the ν1/2; (C) the relationship between potential (Epa) and ln ν.
As shown in Figure 7C, with high scanning rates, the peak potential is linearly related to the natural logarithm of the scanning rate. The correlation formula is Epa (V) = 0.013 lnν + 0.711 (R2 = 0.996). This is on the basis of Butler–Volmer equation [35]:
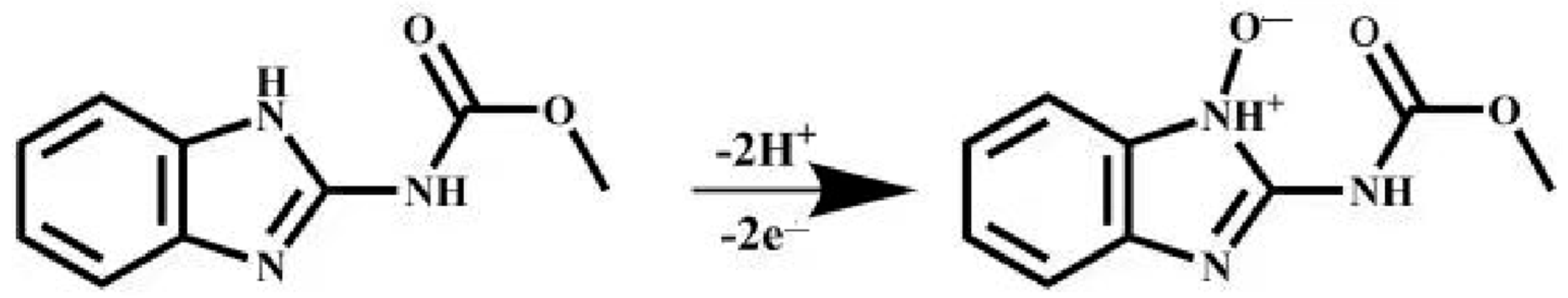
Here, R, T, and K are counted as the gas constant, absolute temperature, and standard rate coefficient, respectively. F means Faraday constant. α means the electron transfer coefficient, which is usually counted as 0.5. Hence, is estimated to be 2. From the fact that the number of electrons is consistent with the number of transferred protons, it can be considered that two electrons and two protons participate in the oxidation reaction of CBZ at MXene@Co/NC/GCE (Scheme 1).
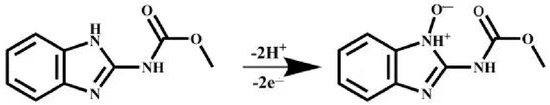
Scheme 1.
The mechanism for electrochemical process of CBZ.
2.6. Detection of CBZ at MXene@Co/NC/GCE
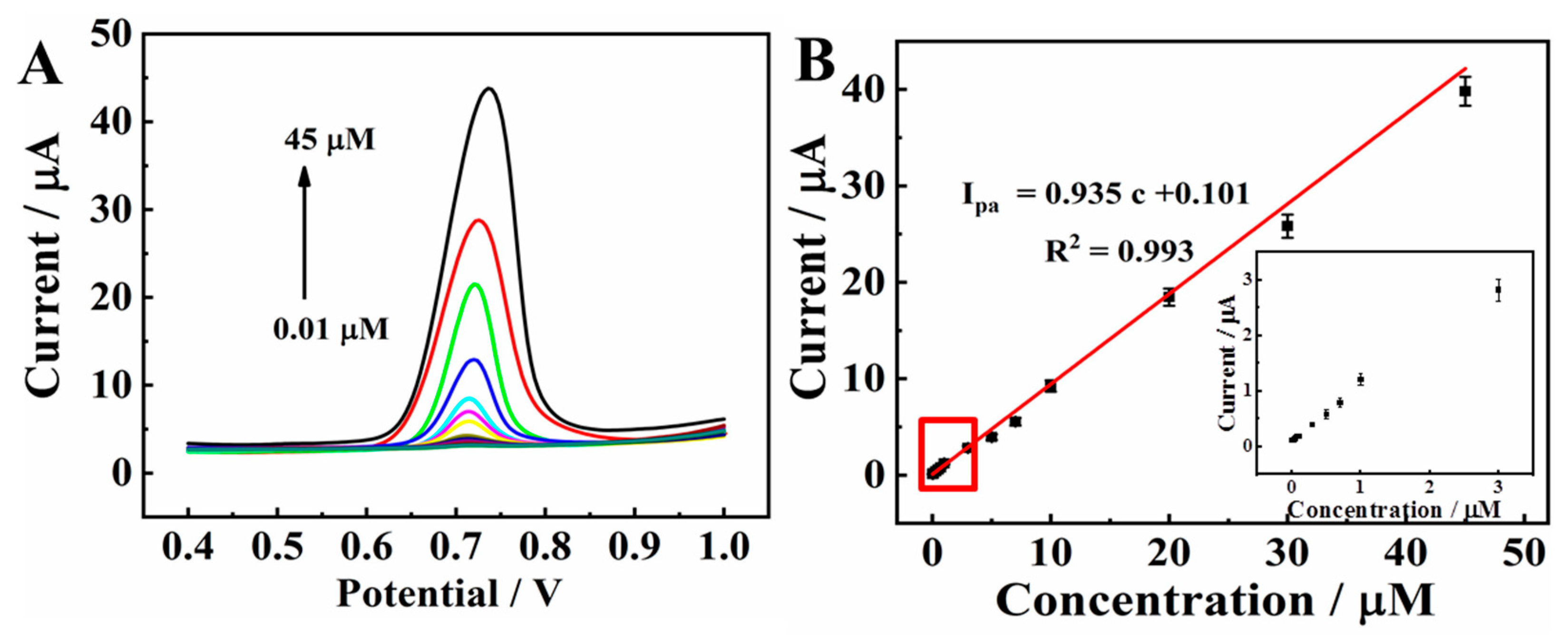
Figure 8A displays the DPV signal curves of CBZ with a series of concentrations in 0.1 M PBS (pH 7.0) on MXene@Co/NC/GCE. The current proportionally increases as the CBZ concentration changes from 0.01 μM to 45.0 μM. As displayed in Figure 8B, the peak current and c present a good linearity with the regression formula of Ipa = 0.935 c + 0.101 (R2 = 0.993). The limit of detection (LOD) is counted as 3.3 nM (S/N = 3), which is calculated using the following equation [36,37]:
where SD means the standard deviation of blank signal and S denotes the sensitivity of the method (equal to the slope of the calibration curve). The electrochemical sensing performance of MXene@Co/NC/GCE was further compared with previously reported electrochemical CBZ sensors (shown in Table 1). The results showed that the MXene@Co/NC/GCE possessed a wider linear range and lower LOD than the other sensors, including graphene-based sensing platforms [12,38], carbon nanotube-based sensing platforms [39,40], AuNPs/BC/GCE [41], and In2S3/GCE [42], which might be attributed to the synergetic effect between the large surface area, excellent catalytic performance, and rapid electronic transfer of MXene@Co/NC.
LOD = 3 × SD/S
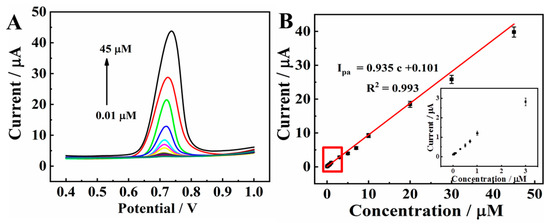
Figure 8.
(A) DPVs of 0.01, 0.03, 0.05, 0.07, 0.1, 0.3, 0.5, 0.7, 1.0, 3.0, 5.0, 7.0, 10.0, 20.0, 30.0, and 45.0 μM CBZ on MXene@Co/NC/GCE in 0.1 M PBS (pH 7.0); (B) linear curve of oxidation peak current vs. concentration, insert is the enlarged view of lower CBZ concentration.

Table 1.
Comparison of different modified electrodes used for the detection of CBZ.
2.7. Interferences, Reproducibility, Repeatability, and Long-Term Stability of MXene@Co/NC/GCE
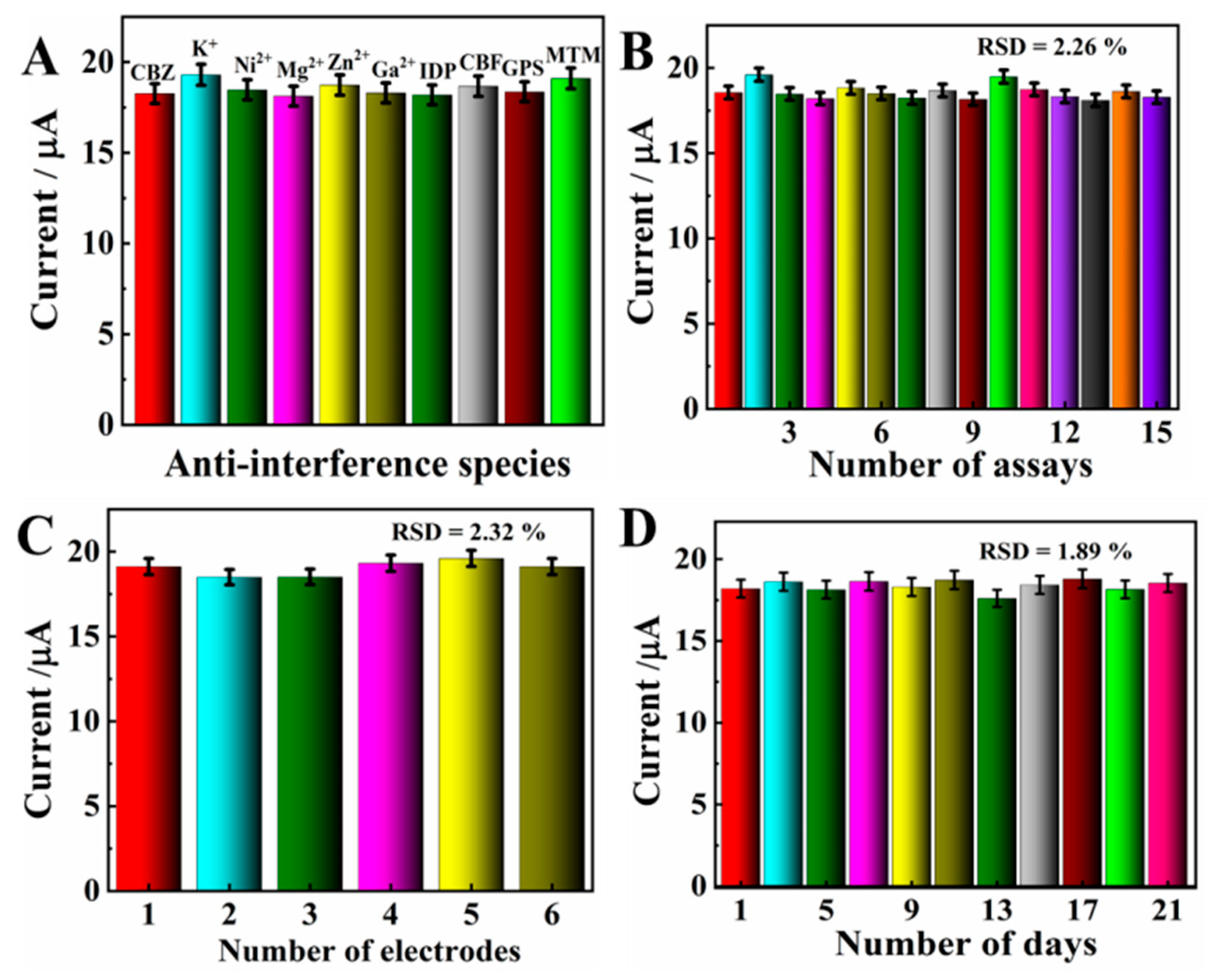
The anti-interference of MXene/NG/GCE was evaluated by measuring the DPV response of 20.0 μM CBZ with a variety of interferents. The experimental results show that all signal changes were less than 5%, which verifies 100-fold concomitant ions (K+, Ni2+, Mg2+, Zn2+, and Ca2+) and 10-fold interferents including imidacloprid (IDP), glyphosate (GPS), carbofuran (CBF), and methomyl (MTM), showing no obvious interferences with CBZ (Figure 9A). Accordingly, the MXene@Co/NC/GCE possesses gratifying selectivity.
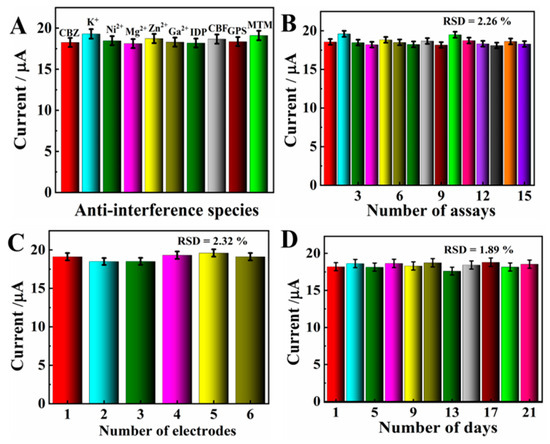
Figure 9.
(A) Anti-interference studies of MXene@Co/NC/GCE. (B) DPV was repeated 15 times for MXene@Co/NC/GCE at 100 mV s−1 in PBS solution containing 20.0 μM CBZ. (C) Repetitive DPV responses of MXene@Co/NC/GCE with the same electrode. (D) DPV responses of MXene@Co/NC/GCE toward 20.0 μM CBZ in 21 days.
To affirm the repeatability of the proposed electrode, MXene@Co/NC/GCE was employed to perform 15 consecutive tests for 20.0 μM CBZ. The result shows that the relative standard deviation (RSD) is 2.26% (Figure 9B). Meanwhile, six parallel electrodes were used to measure the response current of 20.0 μM CBZ under consistent experiment conditions (Figure 9C). The RSD of the response current is 2.32%. These values verify that MXene@Co/NC/GCE possesses pleasing repeatability and reproducibility.
Furthermore, to prove the long-term stability of MXene@Co/NC/GCE, the DPV response for 20.0 μM CBZ on MXene@Co/NC/GCE was monitored every 2 days (Figure 9D). After 21 days, the changes in peak current were below 5.0%, certifying the preeminent long-term stability of MXene@Co/NC/GCE.
2.8. Real Sample Analysis
To evaluate the practicability of the as-prepared sensing platform, MXene@Co/NC/GCE was used for the detection of CBZ in lettuce samples with the standard addition method (Table 2). The hydroponic lettuce purchased at Zhanjiang farmers market was crushed into pulp and filtered with 0.45μm nylon filter membrane. The filtered solution was diluted 100 times with 0.1 M PBS (pH 7.0). Subsequently, a specific concentration of CBZ (0 µM, 1.0 µM, 5.0 µM, 20.0 µM) was appended to the diluted sample. These samples were detected by DPV on MXene@Co/NC/GCE. The detailed DPV diagram is shown in Figure S3. As displayed in Table 2, the recoveries are 97.95~101.60% and the range of the RSD obtained by the calculation is 2.17~2.22%, certifying that MXene@Co/NC/GCE can be applied to the practical sample detection of CBZ.

Table 2.
Determination of CBZ in lettuce samples.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents
CBZ were acquired from Zhanjiang Yuetai Reagent Instrument Co., Ltd. MXene was supplied from Nanjing Mingshan new material Technology Co., Ltd. (Nanjing, China) Co(NO3)·6H2O and 2-Methylimidazole were obtained from Guangzhou Chemical reagent Factory. NaH2PO3 (99%) and Na2HPO3 (99%) were purchased from Shanghai Macklin Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). In this work, an analytical reagent was used to perform the experiment. Deionized water was used to support the experiment.
3.2. Apparatuses
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM, Hitachi Company, Tokyo, Japan) was used to observe the morphology of the materials. X-ray diffraction (XRD, smartlab9, Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS, Escalab 250Xi, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) were employed to observe the component structure of the compound. Electrochemical data were measured at an electrochemical workstation (CHI660E, Shanghai, China) using a typical three-electrode system, which is made up of the opposite electrode (Pt electrode), the reference electrode (saturated calomel electrode), and the working electrode (bare or modified GCE).
3.3. Preparation of the Co/NC
Co/NC materials were prepared according to the following steps. Firstly, 1.0 mmol Co(NO3)2·6H2O was dissolved in 25 mL methanol, followed by the addition of 4.0 mmol 2-dimethylimidazole. Subsequently, the aqueous dispersion mixture was vigorously stirred for 0.5 h and left to stand for 24 h to acquire ZIF-67. ZIF-67 was centrifuged, washed, and dried at 60 °C for 12 h under the vacuum condition. Finally, the ZIF-67 was annealed at 800 °C for 2 h under a N2 atmosphere to obtain Co/NC.
3.4. Preparation of the MXene@Co/NC Composite
The MXene@Co/NC composite was prepared with an ultrasound-assisted self-assembly method. Typically, MXene (10.0 mg) was uniformly dispersed in DMF (20 mL) and sonicated for 10 min. Co/NC (10.0 mg) was then added to the above suspension under ultrasound stirring for 30 min. Finally, the black suspensions were centrifuged and the pellets were washed three times with deionized water and absolute alcohol. The as-prepared product was named MXene@Co/NC after being dried in a vacuum at 60 °C.
3.5. Fabrication of Modified Electrodes
Firstly, the glassy carbon electrode (GCE) was perpendicularly polished on the chamois leather with a 0.5 μm alumina slurry. Subsequently, the polished GCE was ultrasonically cleaned in deionized water and ethanol successively.
To construct MXene@Co/NC/GCE, 5.0 μL of the MXene@Co/NC suspension (1 mg mL−1) was coated onto the GCE and then dried for later use. Co/NC/GCE and MXene/GCE were prepared under the analogical procedure. The manufacture process of MXene@Co/NC/GCE and its application for CBZ detection are shown in Scheme 2.
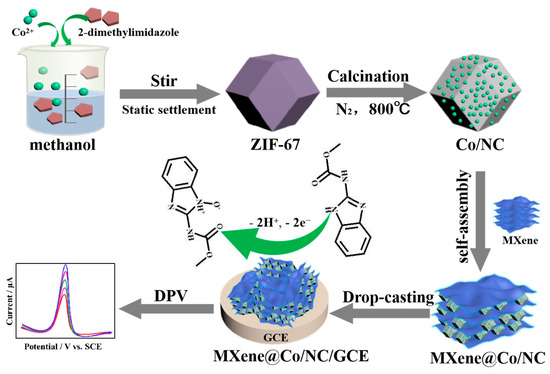
Scheme 2.
The synthesis process of MXene@Co/NC/GCE and its application for CBZ detection.
3.6. Electrochemical Method
Electrochemical measurements were performed in 5.0 mL 0.1 M phosphate buffer solution (PBS) including quantificational CBZ. Differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) was measured by scanning the potential range from 0.4 to 1.0 V with a 0.004 V Incr E, 0.5 sec pulse period, and 0.05 V amplitude. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) was performed in 5.0 mM [Fe(CN)6]3−/4− (1:1) including 0.1 M KCl; the frequency range was 1 Hz to 100 kHz and the amplitude was 0.005 V. Cyclic voltammetry (CV) was conducted with a potential scan at 0.4 V–1.2 V and a scan rate of 100 mV s−1.
4. Conclusions
In summary, a high-efficiency electrochemical sensing platform for CBZ was proposed based on MXene@Co/NC. Specifically, Co/NC was obtained with ZIF-67 as precursor and inherited its unique merits such as the three-dimensional structure, high porosity, and large specific surface area. Then, the Co/NC was inserted into the interlayer of MXene as an interlayer spacer, which not only effectively avoided the stacking of MXene nanosheets but also improved the dispersion of Co/NC, endowing the composite with rapid electron transport and an excellent catalytic property. Under the optimal conditions, MXene@Co/NC/GCE displayed a wide linear range (0.01–45.0 μM) and low LOD of 3.3 nM for CBZ. Moreover, the developed electrochemical sensor exhibited outstanding stability, repeatability and satisfactory recovery in lettuce samples, signifying that MXene@Co/NC is a prospective material for the construction of pesticide electrochemical sensors.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/molecules28217347/s1.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, writing—original draft, data curation, S.C.; methodology, investigation, validation, J.Z. and S.Y.; data curation, resources, X.P.; software, validation, S.Z.; visualization, supervision, funding acquisition, Y.L.; formal analysis, J.Y. and G.Z.; writing—review and editing, project administration, L.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research work was supported by the Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund (No.1630122023006 and No.1630122023012), Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs Financial Special Agricultural Product Quality and Safety Supervision Risk Assessment Project (No. GJFP20220206), and the Hainan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (No.321QN0927 and No.323QN289) and the Chinese Academy of Tropical Agricultural Sciences for Science and Technology Innovation Team of National Tropical Agricultural Science Center (No.CATASCXTD202314).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in the article.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund (No.1630122023006 and No. 1630122023012), Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs Financial Special Agricultural Product Quality and Safety Supervision Risk Assessment Project (No. GJFP20220206), the Hainan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 321QN0927 and No. 323QN289), and the Chinese Academy of Tropical Agricultural Sciences for Science and Technology Innovation Team of National Tropical Agricultural Science Center (No. CATASCXTD202314) for their financial support of this work.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kokulnathan, T.; Wang, T.J.; Ahmed, F.; Arshi, N. Fabrication of flower-like nickel cobalt-layered double hydroxide for electrochemical detection of carbendazim. Surf. Interfaces 2023, 36, 102570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Huo, D.; Wu, H.; Wang, X.; Yang, J.; Bian, M.; Ma, Y.; Hou, C.N. P-doped carbon quantum dots as a fluorescent sensing platform for carbendazim detection based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 274, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnapandi, A.; Babulal, S.M.; Chen, S.M.; Palanisamy, S.; Kim, S.C.; Chiesa, M. Surface etched carbon nanofiber companied ytterbium oxide for pinch level detection of fungicides carbendazim. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Song, W.; Fan, Y.; Sun, Y.; Li, Z.; Chen, S.; Xu, X. A SERS aptasensor based on a flexible substrate for interference-free detection of carbendazim in apple. Food Chem. 2023, 431, 137120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luong, H.N.; Nguyen, N.M.; Tran, C.K.; Nguyen, T.T.; Nguyen, N.P.; Huynh, T.M.H.; Dang, V.Q. Detection of carbendazim by utilizing multi-shaped Ag NPs decorated ZnO NRs on patterned stretchable substrate through surface-enhanced Raman scattering effect. Sens. Actuators A 2022, 346, 113816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Hu, X.; Fu, X.; Xia, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Peng, L.; Peng, X. Flowerlike Ni–NiO composite as magnetic solid-phase extraction sorbent for analysis of carbendazim and thiabendazole in edible vegetable oils by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2022, 374, 131761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- İlktaç, R.; Aksuner, N.; Henden, E. Selective and sensitive fluorimetric determination of carbendazim in apple and orange after preconcentration with magnetite-molecularly imprinted polymer. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2017, 174, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priya, T.S.; Nataraj, N.; Chen, T.W.; Chen, S.M.; Kokulnathan, T. Synergistic formation of samarium oxide/graphene nanocomposite: A functional electrocatalyst for carbendazim detection. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariyappan, V.; Sundaresan, R.; Chen, S.M.; Ramachandran, R. Ultrasensitive electrochemical sensor for the detection of carbamazepine based on gadolinium vanadate nanostructure decorated functionalized carbon nanofiber nanocomposite. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, R.; Xu, D.; Xie, X.; Yi, Y.; Quan, Y.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, G. Phosphorus-doped helical carbon nanofibers as enhanced sensing platform for electrochemical detection of carbendazim. Food Chem. 2017, 221, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaresan, P.; Fu, C.C.; Liu, S.H.; Juang, R.S. Facile synthesis of chitosan-carbon nanofiber composite supported copper nanoparticles for electrochemical sensing of carbendazim. Colloids Surf. A 2021, 625, 126934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, M.; Li, B.; Wang, M.; Zhao, H.; Zhao, F. Electrochemical Sensor Based on Laser-Induced Graphene for Carbendazim Detection in Water. Foods 2023, 12, 2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Yang, S.; Bai, X.; Shan, J. Bimetallic CoCu nanoparticles anchored on COF/SWCNT for electrochemical detection of carbendazim. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 902, 166530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhouati, A.; Berkani, M.; Vasseghian, Y.; Golzadeh, N. MXene-based electrochemical sensors for detection of environmental pollutants: A comprehensive review. Chemosphere 2022, 291, 132921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, A.; Zhao, H.; Huang, Y.; Lu, X.; Chen, J.; Jain, R. MXene: An emerging material for sensing and biosensing. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 105, 424–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, S.S.; Shereema, R.M.; Rakhi, R.B. Electrochemical determination of adrenaline using MXene/graphite composite paste electrodes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 43343–43351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.; Li, C.; Huang, W.; Wu, K. Simultaneous detection of 4-chlorophenol and 4-nitrophenol using a Ti3C2Tx MXene based electrochemical sensor. Analyst 2021, 146, 7593–7600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, J.; Kannan, T.S.; Dhanasekaran, L.S.; Murugan, P.; Atchudan, R.; ALOthman, Z.A.; Ouladsmane, M.; Sundramoorthy, A.K. Preparation of 2D Graphene/MXene nanocomposite for the electrochemical determination of hazardous bisphenol A in plastic products. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 132106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Han, G.; Cai, J.; Wang, X. Au@Carbon quantum Dots-MXene nanocomposite as an electrochemical sensor for sensitive detection of nitrite. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 607, 1313–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalambate, P.K.; Dhanjai, S.A.; Li, Y.; Shen, Y.; Huang, Y. An electrochemical sensor for ifosfamide, acetaminophen, domperidone, and sumatriptan based on self-assembled MXene/MWCNT/chitosan nanocomposite thin film. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Wang, S.; Jiang, C.; Zheng, M.; Bai, Z.; Srivastava, D.; Liu, J. Recent advances of sonodynamic therapy by MOFs-based platforms for biomedical applications. Dye. Pigm. 2023, 219, 111596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Peng, Z.; Peng, Y.; Li, B.; Pan, Y.; Ouyang, Q.; Liu, J. Construction of Fe-doped ZIF-8/DOX nanocomposites for ferroptosis strategy in the treatment of breast cancer. J. Mater. Chem. B 2023, 11, 6335–6345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Li, M.; Lin, M.; Lu, C.; Kumar, A.; Pan, Y.; Peng, Y. Current and promising applications of Hf (IV)-based MOFs in clinical cancer therapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2023, 11, 5693–5714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Li, C.; Chen, Y.; Li, S.; Li, F.; Wu, X.; Wang, Y. MIL-101 (Cr) molecular cage anchored on 2D Ti3C2TX MXene nanosheets as high-performance electrochemical sensing platform for detection of xanthine. Microchim. Acta 2023, 190, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wu, M.; Ma, G.; Motlak, M.; Mahdi, A. Novel electrochemical strategy for determination of anticancer drug flutamide based on MXene/MOF composite. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2023, 155, 111061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Gu, W.; Zhou, L.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Lei, J. Recent advances in MOF-derived carbon-based nanomaterials for environmental applications in adsorption and catalytic degradation. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 427, 131503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hira, S.A.; Nagappan, S.; Yusuf, M.; Chen, A.; Lee, J.M.; Park, K.H. L-Cysteine anchored Co-MOF derived cobalt-nitrogen-carbon hierarchical architecture as an efficient sensor for the electrochemical detection of catecholamine. Microchem. J. 2023, 190, 108748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Wang, X.; Zhao, P.; Zheng, J.; Yang, M.; Huo, D.; Hou, C. ZIF-67 MOF-derived Co nanoparticles supported on N-doped carbon skeletons for the amperometric determination of hydrogen peroxide. Microchim. Acta. 2021, 188, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wu, C.; Wang, F.; Jiang, G. MOF-derived CoP X nanoparticles embedded in nitrogen-doped porous carbon polyhedrons for nanomolar sensing of p-nitrophenol. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2018, 1, 5843–5853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Qin, J.; Mu, J.; Liu, B. In situ interface engineered Co/NC derived from ZIF-67 as an efficient electrocatalyst for nitrate reduction to ammonia. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 636, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Li, Z.; Zhu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, L.; Mai, X.; Li, Y. Inverse and highly selective separation of CO2/C2H2 on a thulium–organic framework. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 11933–11937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Zang, W.; Yan, H.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z.; Bu, Y.; Su, C. Engineering the coordination environment of single cobalt atoms for efficient oxygen reduction and hydrogen evolution reactions. ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 4498–4509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Xu, C.Q.; Park, I.H.; Zhao, M.; Zhu, Z.; Li, J.; Lu, J. Giant Emission Enhancement of Solid-State Gold Nanoclusters by Surface Engineering. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 8270–8276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Mak, C.H.; Zhang, J.; Jia, G.; Cheng, K.C.; Song, H.; Hsu, H.Y. Unravelling the Interfacial Dynamics of Bandgap Funneling in Bismuth-Based Halide Perovskites. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2207835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickinson, E.J.; Wain, A.J. The Butler-Volmer equation in electrochemical theory: Origins, value, and practical application. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2020, 872, 114145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Committee, A.M. Committee, Recommendations for the definition, estimation and use of the detection limit. Analyst 1987, 112, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armbruster, D.A.; Tillman, M.D.; Hubbs, L.M. Limit of detection (LQD)/limit of quantitation (LOQ): Comparison of the empirical and the statistical methods exemplified with GC-MS assays of abused drugs. Clin. Chem. 1994, 40, 1233–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhu, Y.P.; Wang, A.J.; Weng, X.; Feng, J.J. Simple pyrolysis of graphene-wrapped PtNi nanoparticles supported on hierarchically N-doped porous carbon for sensitive detection of carbendazim. Microchim. Acta 2023, 190, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Luo, X.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liang, Q.; Feng, K.; Xiong, J. An antifouling electrochemical sensor based on multiwalled carbon nanotubes functionalized black phosphorus for highly sensitive detection of carbendazim and corresponding response mechanisms analyses. Microchem. J. 2023, 190, 108671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, H.; Ming, P.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhou, Q.; Zhai, H. MWCNTs and ZnO-based Ce-MOF nanocomposites as enhanced sensing platform for electrochemical detection of carbendazim in Chinese traditional herbs samples. Microchim. Acta 2023, 190, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Zhang, X.; Gao, X.; Lin, J.; Zhao, F.; Zeng, B. Sensitive dual-mode detection of carbendazim by molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor based on biomass-derived carbon-loaded gold nanoparticles. Microchim. Acta 2023, 190, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, L.; Li, B.; Chen, X.; Gao, Y.; Kuang, X. Electrochemical Determination of Carbendazim Based on In2S3 nanotubes. ChemNanoMat 2023, 9, e202200522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).