Preparation of COPs Mixed Matrix Membrane for Sensitive Determination of Six Sulfonamides in Human Urine
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization of Tp-DMB-COPs and Tp-DMB-COPs-MMM
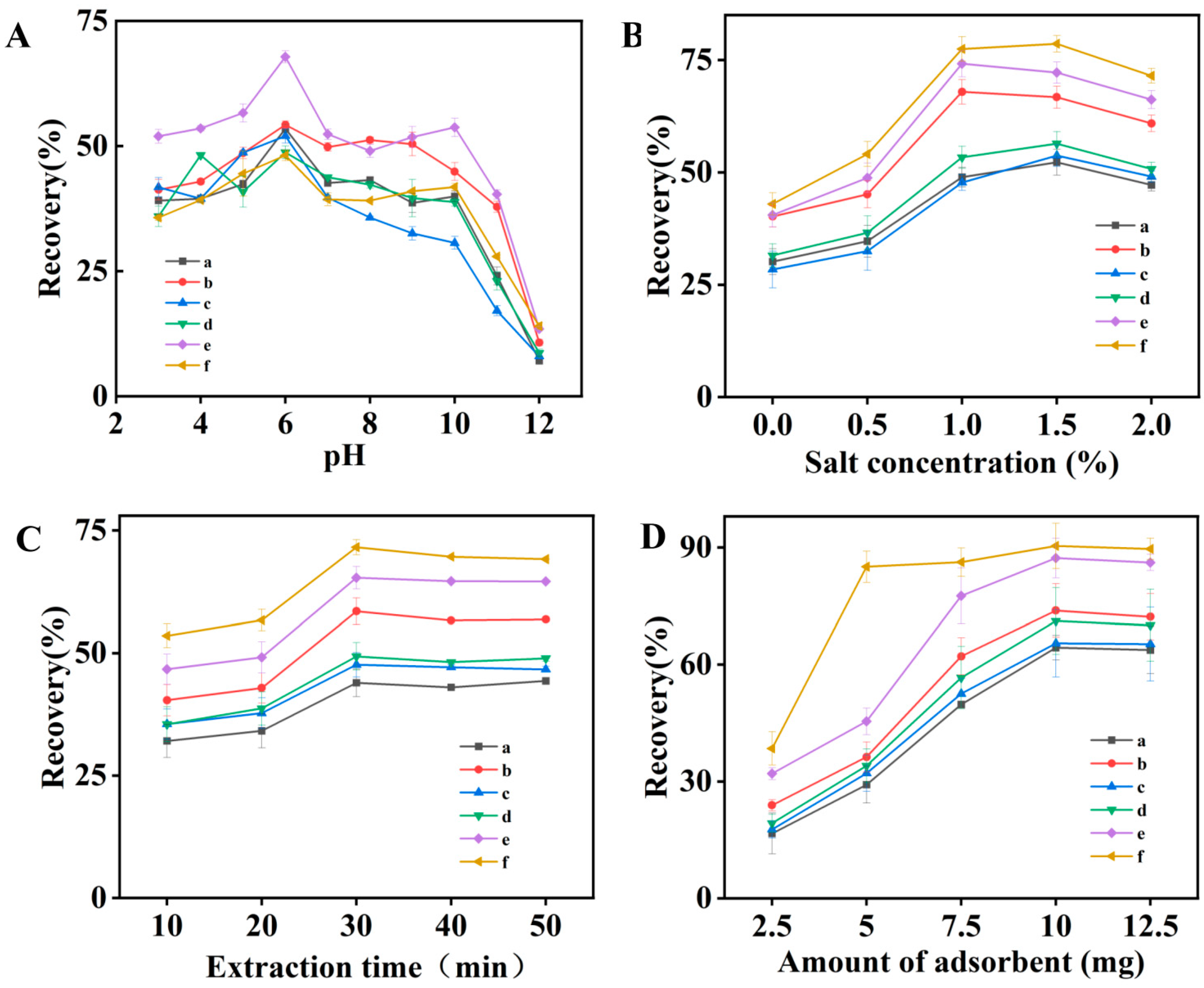
2.2. Optimization of ME Procedures
2.2.1. Effect of the Sample pH
2.2.2. Effect of the Salt Concentration
2.2.3. Effect of the Extraction Time
2.2.4. Effect of Adsorbent Amount
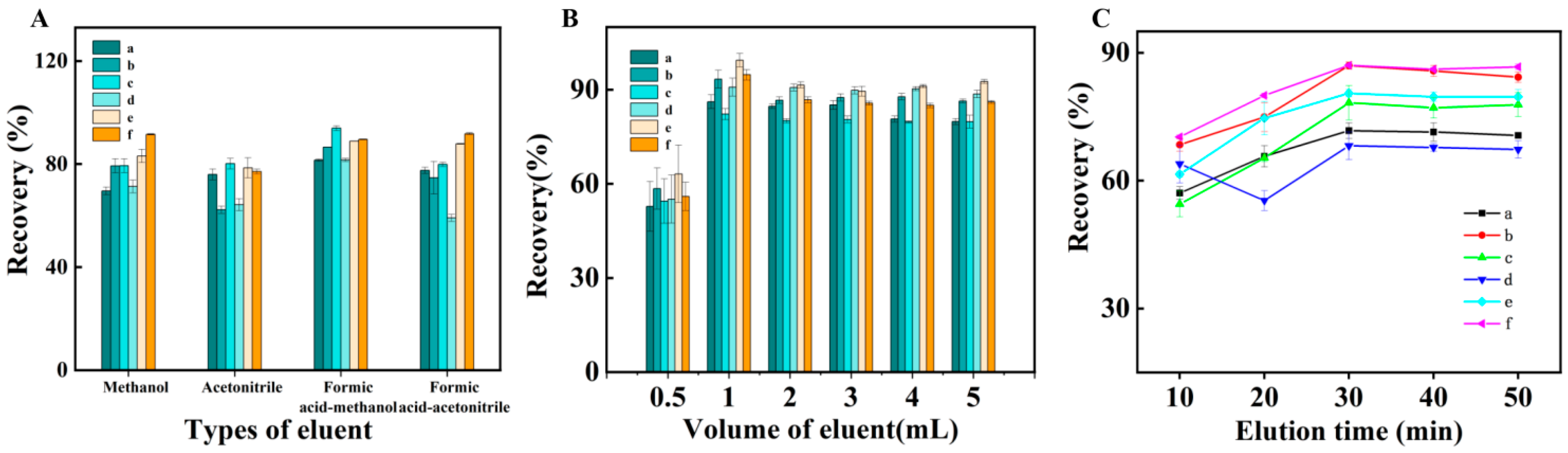
2.2.5. Effect of Eluent Type and Volume
2.2.6. Effect of Elution Time
2.2.7. Reusability of TpDMB-COPs-MMM
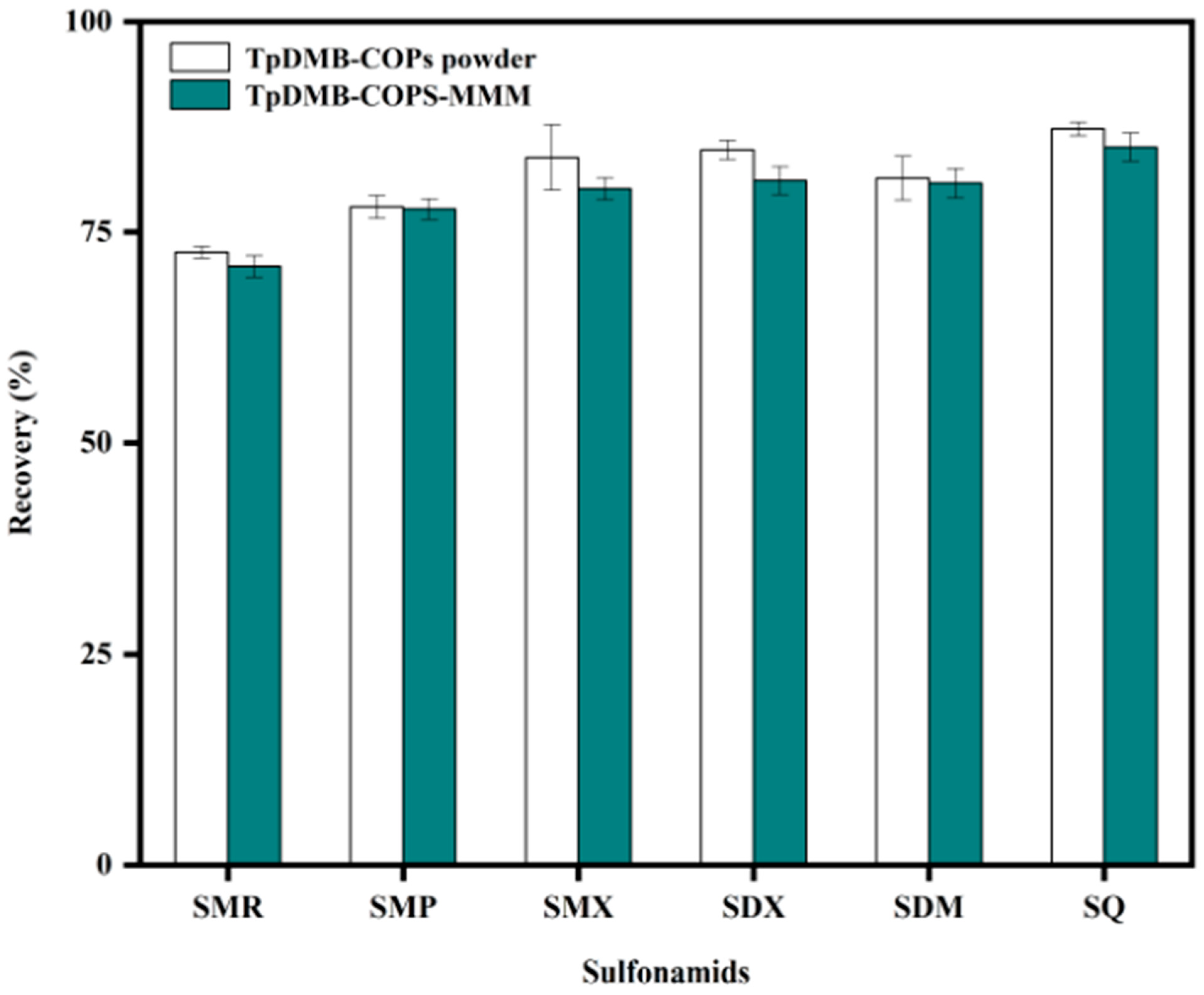
2.2.8. Comparison of Adsorption Capacity of TpDMB-COPs-MMM and TpDMB-COPs Powder
2.3. Method Validation and Application to Real Samples
2.4. Comparison of the Developed Method with Previously Reported Methods
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Reagents
3.2. Instrumentation
3.3. Synthesis of TpDMB-COPs
3.4. Preparation of TpDMB-COPs-MMM
3.5. Sample Collection
3.6. ME Procedure
3.7. HPLC Conditions
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Farooq, M.U.; Su, P.; Yang, Y. Applications of a Novel Sample Preparation Method for the Determination of Sulfonamides in Edible Meat by CZE. Chromatographia 2009, 69, 1107–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoev, G.; Michailova, A. Quantitative determination of sulfonamide residues in foods of animal origin by high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. J. Chromatogr. A 2000, 871, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Huang, S.; Zheng, J.; Ouyang, G. Trends in sensitive detection and rapid removal of sulfonamides: A review. J. Sep. Sci. 2020, 43, 1634–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Cheng, X.; Li, J.; Wang, G.; Mao, J.; Zhao, J.; Lou, X. Ultrasensitive evanescent wave optical fiber aptasensor for online, continuous, type-specific detection of sulfonamides in environmental water. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1233, 340505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li Juan, Y.; Ci Dan, Z.X.; Liao, Q.G.; Da Wen, Z.; Lin Guang, L. Pipette-tip solid-phase extraction using cetyltrimethylammonium bromide enhanced molybdenum disulfide nanosheets as an efficient adsorbent for the extraction of sulfonamides in environmental water samples. J. Sep. Sci. 2020, 43, 905–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Hu, X.; Zhao, F.; Zeng, B. Fe3O4/reduced graphene oxide-carbon nanotubes composite for the magnetic solid-phase extraction and HPLC determination of sulfonamides in milk. J. Sep. Sci. 2019, 42, 1058–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Li, R.; Guo, F.; Chen, X. An Efficient Method for the Preparation of Sulfonamides from Sodium Sulfinates and Amines. ChemistryOpen 2022, 11, e202200097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Wu, L.; Lu, C.; Li, N.; Hu, M.; Wang, Z. Microwave-assisted liquid-liquid microextraction based on solidification of ionic liquid for the determination of sulfonamides in environmental water samples. J. Sep. Sci. 2014, 37, 3533–3538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiadis, D.E.; Tsalbouris, A.; Kabir, A.; Furton, K.G.; Samanidou, V. Novel capsule phase microextraction in combination with high performance liquid chromatography with diode array detection for rapid monitoring of sulfonamide drugs in milk. J. Sep. Sci. 2019, 42, 1440–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Shi, Y.; Li, J.; Luan, T. In situ derivatization and hollow-fiber liquid-phase microextraction to determine sulfonamides in water using UHPLC with fluorescence detection. J. Sep. Sci. 2018, 41, 1651–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Shi, Z.G.; Zheng, M.M.; Feng, Y.Q. Multiresidue determination of sulfonamides in chicken meat by polymer monolith microextraction and capillary zone electrophoresis with field-amplified sample stacking. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1205, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mala, Z.; Gebauer, P.; Bocek, P. New methodology for capillary electrophoresis with ESI-MS detection: Electrophoretic focusing on inverse electromigration dispersion gradient. High-sensitivity analysis of sulfonamides in waters. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 935, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Yang, Y.; Wang, N.; Hao, L.; Li, L.; Guo, X.; Zhang, J.; Hu, Y.; Shen, W. Application of packed porous nanofibers-solid-phase extraction for the detection of sulfonamide residues from environmental water samples by ultra high performance liquid chromatography with mass spectrometry. J. Sep. Sci. 2015, 38, 749–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.C.; Carlson, K. Quantification of human and veterinary antibiotics in water and sediment using SPE/LC/MS/MS. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 387, 1301–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chico, J.; Rubies, A.; Centrich, F.; Companyo, R.; Prat, M.D.; Granados, M. High-throughput multiclass method for antibiotic residue analysis by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1213, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, M.R.; Mauro Lancas, F. Evaluation of ionic liquids supported on silica as a sorbent for fully automated online solid-phase extraction with LC-MS determination of sulfonamides in bovine milk samples. J. Sep. Sci. 2018, 41, 2237–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osinski, Z.; Patyra, E.; Kwiatek, K. HPLC-FLD-Based Method for the Detection of Sulfonamides in Organic Fertilizers Collected from Poland. Molecules 2022, 27, 2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fikarova, K.; Horstkotte, B.; Machian, D.; Sklenarova, H.; Solich, P. Lab-In-Syringe for automated double-stage sample preparation by coupling salting out liquid-liquid extraction with online solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatographic separation for sulfonamide antibiotics from urine. Talanta 2021, 221, 121427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Zhu, L.; Wang, Y. On-line preconcentration and determination of sulfadiazine in food samples using surface molecularly imprinted polymer coating by capillary electrophoresis. J. Chromatogr. A 2023, 1696, 463965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Yang, T.; Ma, S.; Peng, F.; Yi, M.; Wan, M.; Mao, C.; Shen, J. Label-free immunosensor based on hyperbranched polyester for specific detection of alpha-fetoprotein. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 92, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, H.; Han, Y.; Bai, L.; Yan, H. On-line enrichment and determination of aristolochic acid in medicinal plants using a MOF-based composite monolith as adsorbent. J. Chromatogr. B 2020, 1159, 122343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wei, K.; Wang, L.; Gao, G. A membrane solid-phase extraction method based on MIL-53-mixed-matrix membrane for the determination of estrogens and parabens: Polyvinylidene difluoride membrane versus polystyrene-block-polybutadiene membrane. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2022, 36, e5454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, J.; Gao, Q.; Li, X.S.; Huang, W.; Shi, Z.G.; Feng, Y.Q. Magnetic solid-phase extraction based on magnetic carbon nanotube for the determination of estrogens in milk. J. Sep. Sci. 2011, 34, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Marenco, A.R.; Giraldo, L.; Moreno-Pirajan, J.C. Parabens Adsorption onto Activated Carbon: Relation with Chemical and Structural Properties. Molecules 2019, 24, 4313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Yu, C.; Xi, J.; Tang, S.; Bao, T.; Zhang, J. A hybrid material prepared by controlled growth of a covalent organic framework on amino-modified MIL-68 for pipette tip solid-phase extraction of sulfonamides prior to their determination by HPLC. Mikrochim. Acta 2019, 186, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Li, T.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, N.; Cheng, Y.; Xiang, Z. Superior oxygen electrocatalysts derived from predesigned covalent organic polymers for zinc-air flow batteries. Nanoscale 2018, 11, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.-L.; Huang, Y.-Q.; Tang, X.-Y.; Xu, J.; Peng, C.; Tan, Y.-Z. Two-dimensional extended π-conjugated triphenylene-core covalent organic polymer. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 3066–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Zhao, D.; Wu, Q.; Fan, B.; Dan, J.; Han, A.; Ma, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, L. Amorphous CoP nanoparticle composites with nitrogen-doped hollow carbon nanospheres for synergetic anchoring and catalytic conversion of polysulfides in Li-S batteries. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 603, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Han, Q.; Han, L.; Leng, Y.; O’Carroll, T.; Yang, X.; Wu, G.; Xiang, Z. Porous Covalent Organic Polymer Coordinated Single Co Site Nanofibers for Efficient Oxygen-Reduction Cathodes in Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cells. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, e2208661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Hao, X.; Ma, S.; Wang, R.; Wang, Y. Covalent organic framework-based porous materials for harmful gas purification. Chemosphere 2022, 291, 132795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Chang, G.; Li, J.; Yang, X.; Zhang, S.; Zang, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, Z. Triazine-based covalent organic polymer: A promising coating for solid-phase microextraction. J. Sep. Sci. 2021, 44, 3608–3617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, G.; Kumar, D.; Sundarrajan, S.; Ramakrishna, S.; Kumar, P. Recent Trends in the Design, Synthesis and Biomedical Applications of Covalent Organic Frameworks. Polymers 2022, 15, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, J.; Wang, X.; Li, N.; Liu, L.; Lian, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhao, R.S. Recent applications of covalent organic frameworks and their multifunctional composites for food contaminant analysis. Food Chem. 2020, 330, 127255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.; He, Z.; Teng, Q.; Wang, R. One-pot synthesis of magnetic sulfonated covalent organic polymer for extraction of protoberberine alkaloids in herbs and human plasma. J. Sep. Sci. 2023, 46, e2200613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Chen, L.; Zhang, R.; Yu, Y.; Ji, W.; Hou, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Z. An Imine-Based Porous 3D Covalent Organic Polymer as a New Sorbent for the Solid-Phase Extraction of Amphenicols from Water Sample. Molecules 2023, 28, 3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Li, G.; Zhang, Z. A hydrazone covalent organic polymer based micro-solid phase extraction for online analysis of trace Sudan dyes in food samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1419, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Z.; Cao, D. Synthesis of luminescent covalent-organic polymers for detecting nitroaromatic explosives and small organic molecules. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2012, 33, 1184–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gralinski, S.R.; Roy, M.; Baldauf, L.M.; Olmstead, M.M.; Balch, A.L. Introduction of a (Ph3P)2Pt group into the rim of an open-cage fullerene by breaking a carbon-carbon bond. Chem. Commun. 2021, 57, 10218–10221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ma, Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, Z.; Yuan, Q. New insights into the structure-performance relationships of mesoporous materials in analytical science. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 8766–8803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, N.; Zhao, M.; Liang, S.; Cao, J.; Wang, C.; Xu, Q.; Li, J. High-Throughput and High-Efficient Micro-solid Phase Extraction Based on Sulfonated-Polyaniline/Polyacrylonitrile Nanofiber Mats for Determination of Fluoroquinolones in Animal-Origin Foods. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 6892–6901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Xiao, R.; Tang, J.; Zhu, Q.; Li, X.; Xiong, Y.; Wu, X. Preparation and adsorption properties of molecularly imprinted polymer via RAFT precipitation polymerization for selective removal of aristolochic acid I. Talanta 2017, 162, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, L.; Dou, Y.; Gao, J.; Gao, Y.; Fan, W.; Li, G.; You, J. Adsorption behavior of a metal organic framework of University in Oslo 67 and its application to the extraction of sulfonamides in meat samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1619, 460949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patyra, E.; Kwiatek, K. Application of Micellar Mobile Phase for Quantification of Sulfonamides in Medicated Feeds by HPLC-DAD. Molecules 2021, 26, 3791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowlatshah, S.; Santigosa, E.; Saraji, M.; Payan, M.R. A selective and efficient microfluidic method-based liquid phase microextraction for the determination of sulfonamides in urine samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1652, 462344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mwankuna, C.J.; Kiros, F.; Mariki, E.E.; Mabiki, F.P.; Malebo, H.M.; Mdegela, R.H.; Styrishave, B. Optimization of HPLC-MS/MS method for determination of antimalarial adulterants in herbal products. Anal. Sci. 2023, 39, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jullakan, S.; Bunkoed, O. A nanocomposite adsorbent of metallic copper, polypyrrole, halloysite nanotubes and magnetite nanoparticles for the extraction and enrichment of sulfonamides in milk. J. Chromatogr. B 2021, 1180, 122900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibarra, I.S.; Miranda, J.M.; Rodriguez, J.A.; Nebot, C.; Cepeda, A. Magnetic solid phase extraction followed by high-performance liquid chromatography for the determination of sulphonamides in milk samples. Food Chem. 2014, 157, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huertas-Perez, J.F.; Arroyo-Manzanares, N.; Havlikova, L.; Gamiz-Gracia, L.; Solich, P.; Garcia-Campana, A.M. Method optimization and validation for the determination of eight sulfonamides in chicken muscle and eggs by modified QuEChERS and liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 124, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Ji, K.; Tang, N.; Li, Y.; Gu, X.; Tang, K. Vortex-ultrasonic assisted dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction for seven sulfonamides of fish samples based on hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent and simultaneous detecting with HPLC-PDA. Microchem. J. 2023, 185, 108269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Yin, D.; Peng, J.; Hu, X. Ionic liquid-based single-drop liquid-phase microextraction combined with high-performance liquid chromatography for the determination of sulfonamides in environmental water. J. Sep. Sci. 2012, 35, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Liu, Y.; Huang, S.; Wang, X.; Yang, J.; Wang, L.; Xue, M.; Zhang, X.; Chen, J. In Situ Construction of a Multifunctional Quasi-Gel Layer for Long-Life Aqueous Zinc Metal Anodes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 29746–29754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Analytes | LOD (ng/mL) | LOQ (ng/mL) | Range (ng/mL) | r2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SMR | 1.25 | 3.50 | 3.5–20 | 0.9995 |
| SMP | 1.88 | 5.00 | 5–25 | 0.9998 |
| SMX | 2.50 | 7.00 | 7–25 | 0.9991 |
| SDX | 2.50 | 7.00 | 7–25 | 0.9997 |
| SDM | 2.50 | 7.00 | 7–25 | 0.9995 |
| SQ | 1.25 | 3.50 | 3.5–20 | 0.9993 |
| Number | Concentration (ng/mL) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SMR | SMP | SMX | SDX | SDM | SQ | |
| 1 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 2 | <LOQ | — | — | — | — | 5.59 |
| 3 | 17.65 | — | — | — | — | — |
| 4 | 14.39 | — | — | — | — | <LOQ |
| 5 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 6 | 9.86 | — | — | — | — | — |
| 7 | <LOQ | <LOQ | — | — | 19.82 | — |
| 8 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 9 | — | — | — | — | <LOQ | — |
| 10 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| Extraction and Analytical Method | Analytes | Sample Matrix | Amount of Adsorbent | LOD | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| d-SPE/HPLC-DAD | SMR, SMP, SMX, SDM | Chicken, Lamb, Beef | 15 mg | 2.4~4.9 ng/g | [42] |
| MLC-DAD | SMR | Medicated feeds | — | 32.7 mg/kg | [43] |
| LPME/HPLC | SMR, SMX | Urine | — | 33~57 ng/mL | [44] |
| HPLC-MS/MS | SDX | Herbal products | — | 0.002 μg/mL | [45] |
| MSPE/HPLC-DAD | SDM | Milk | 50 mg | 2.5 μg/kg | [46] |
| MSPE/HPLC–DAD | SMX, SDM, SQ | Milk | 10 mg | 12~14 μg/L | [47] |
| d-SPE/HPLC-FLD | SMX, SDM, SDX | Chicken, Muscle, Egg | 300 mg | 4.1~5.5 μg/kg | [48] |
| VUA-DLLMEDES/HPLC-PDA | SDM | Fish | 0.6 mL | 5.5 μg/kg | [49] |
| SPME/HPLC | SMP | Water | — | 2 ng/mL | [50] |
| ME/HPLC-DAD | SMR, SMP, SMX, SDX, SDM, SQ | Urine | 10 mg | 1.25~2.50 ng/mL | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, K.; Gao, S.; Cui, R.; Liu, F.; Gao, G. Preparation of COPs Mixed Matrix Membrane for Sensitive Determination of Six Sulfonamides in Human Urine. Molecules 2023, 28, 7336. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28217336
Liu Y, Zhang Y, Wang J, Wang K, Gao S, Cui R, Liu F, Gao G. Preparation of COPs Mixed Matrix Membrane for Sensitive Determination of Six Sulfonamides in Human Urine. Molecules. 2023; 28(21):7336. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28217336
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Ying, Yong Zhang, Jing Wang, Kexin Wang, Shuming Gao, Ruiqi Cui, Fubin Liu, and Guihua Gao. 2023. "Preparation of COPs Mixed Matrix Membrane for Sensitive Determination of Six Sulfonamides in Human Urine" Molecules 28, no. 21: 7336. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28217336
APA StyleLiu, Y., Zhang, Y., Wang, J., Wang, K., Gao, S., Cui, R., Liu, F., & Gao, G. (2023). Preparation of COPs Mixed Matrix Membrane for Sensitive Determination of Six Sulfonamides in Human Urine. Molecules, 28(21), 7336. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28217336






