Functional Properties of Corn Byproduct-Based Emulsifier Prepared by Hydrothermal–Alkaline
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussions
2.1. Tris-Tricine SDS-PAGE of Zein and Hydrolysates
2.2. Surface Hydrophobicity Index (SHI) and Emulsifying Properties of ZHs
2.2.1. Surface Hydrophobicity Index
2.2.2. Emulsification Activity Index and Emulsification Stability Index
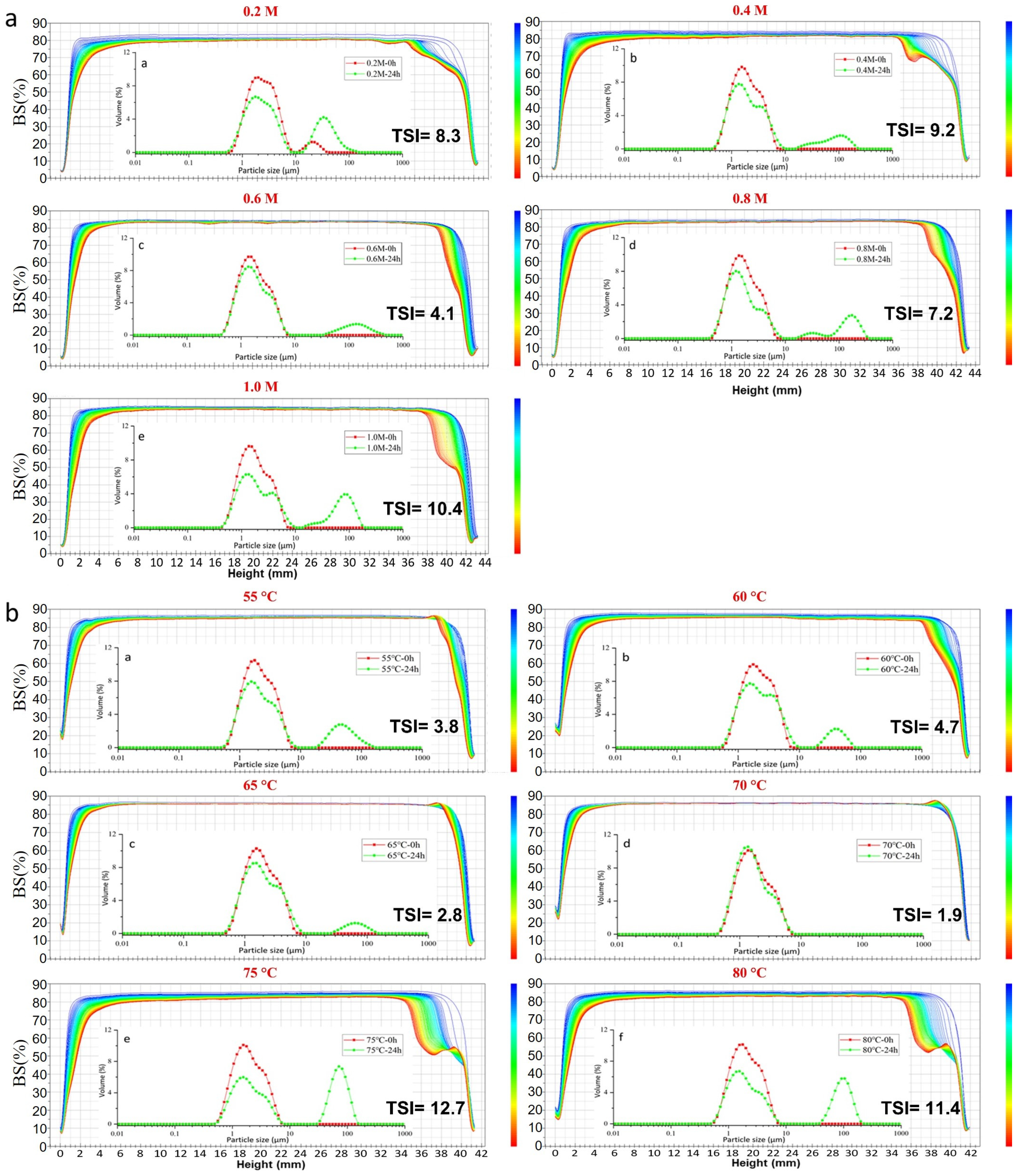
2.2.3. Particle Size Distribution and Turbiscan Stability Index
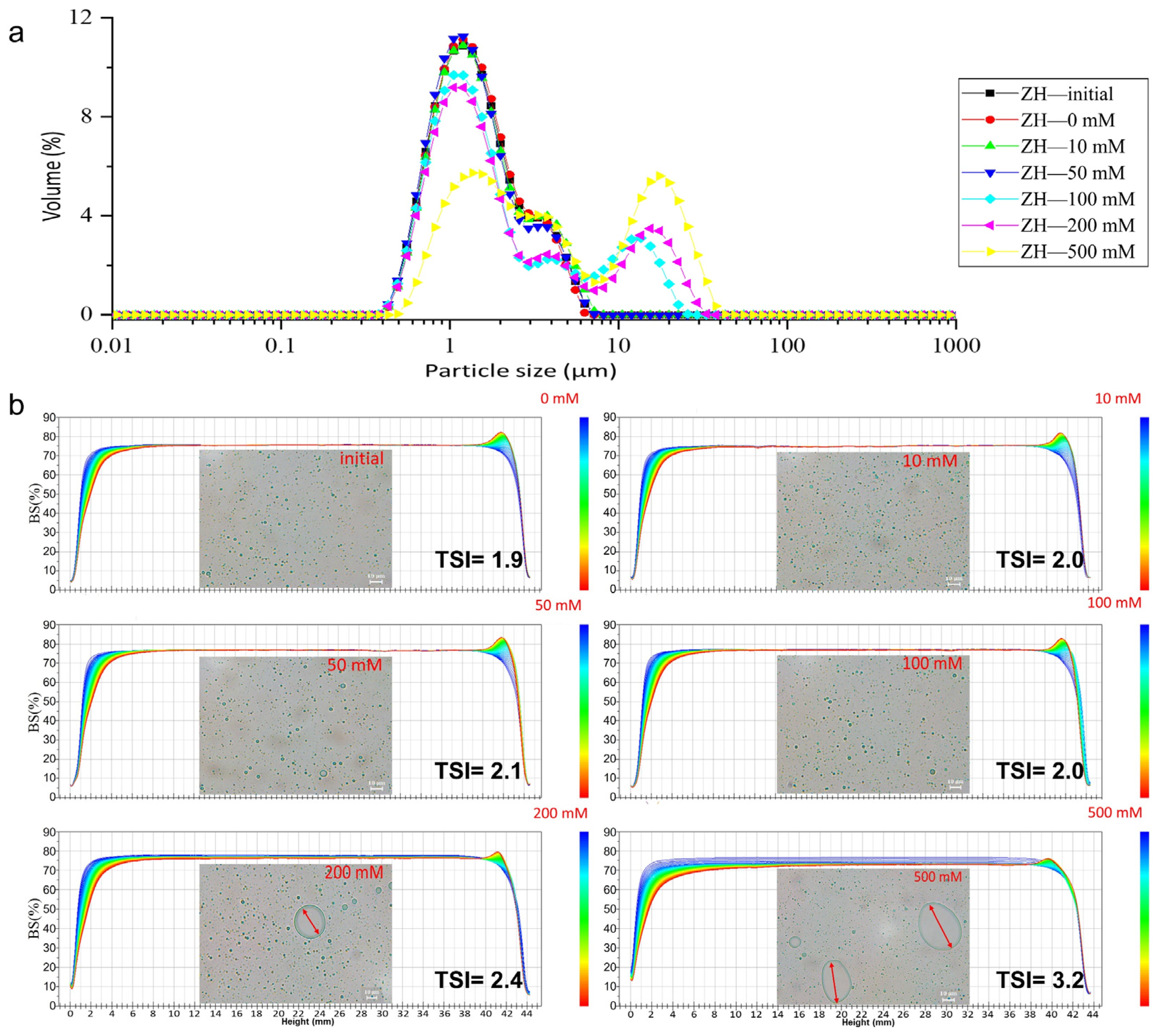
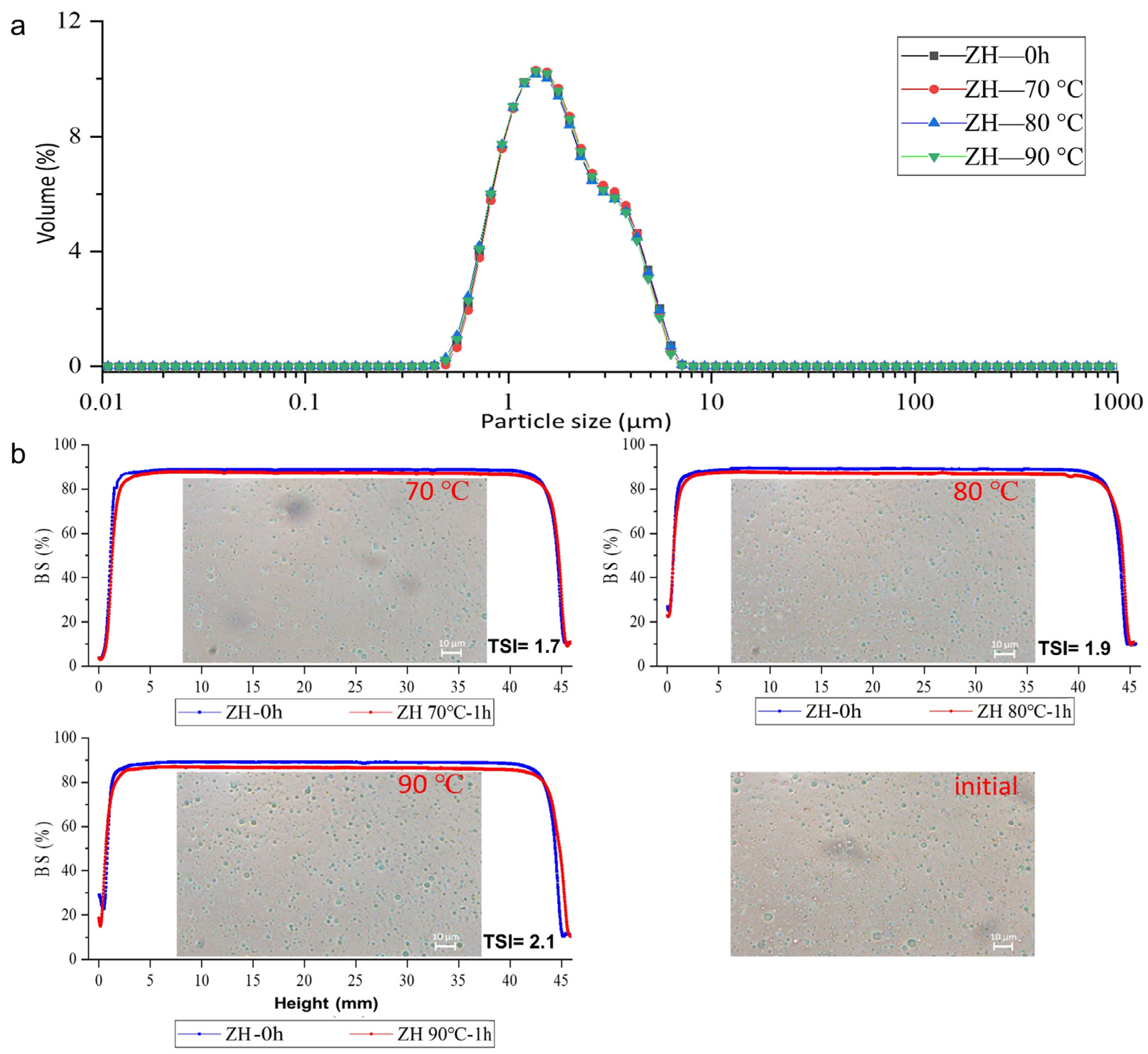
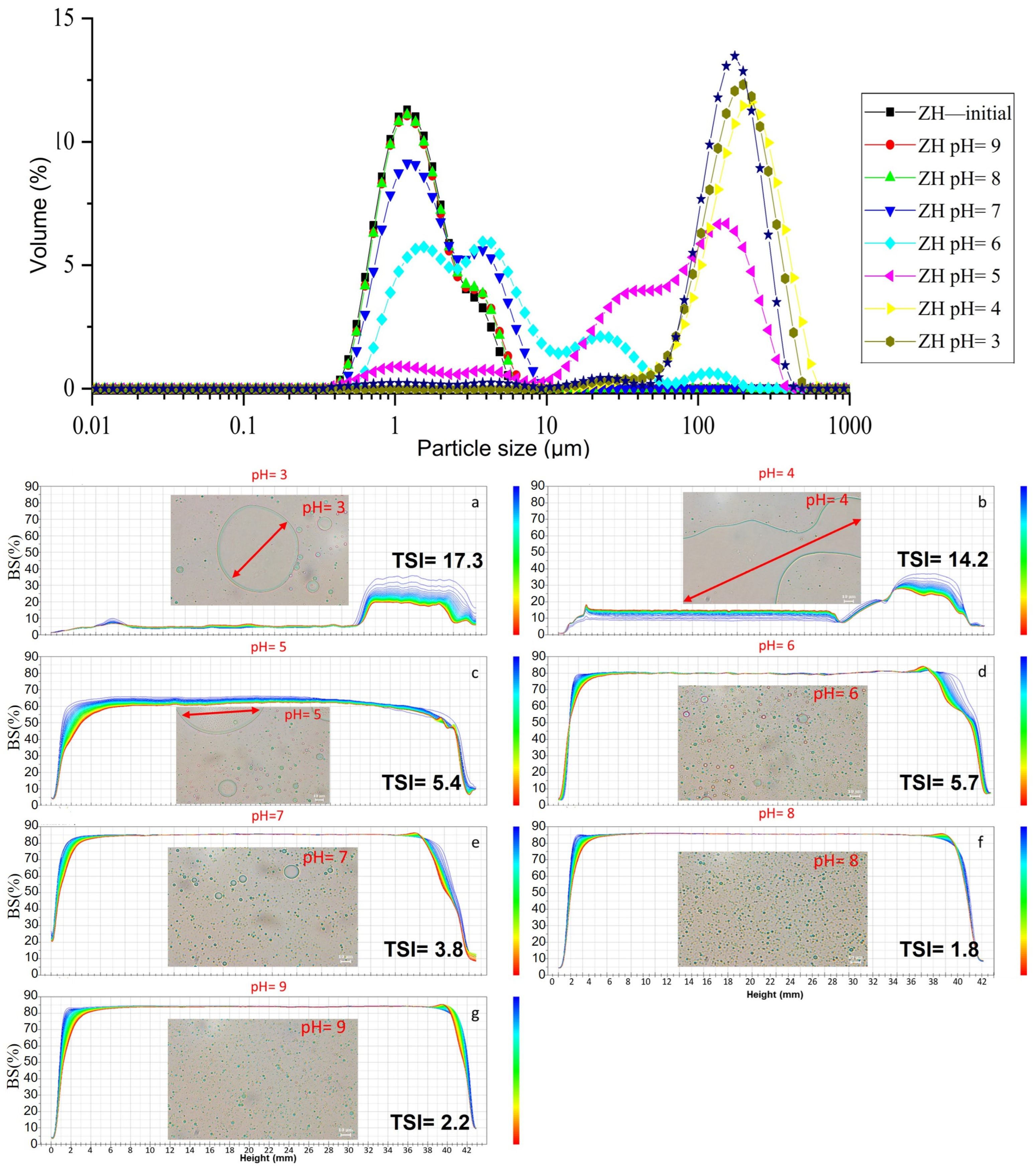
2.3. Environmental-Stress Stability of Emulsions
2.3.1. The Stability of the ZH0.6–70 Stabilized Emulsion against Ionic Strength
2.3.2. The Stability of the ZH0.6-70-Stabilized Emulsion against Thermal Process
2.3.3. The Stability of the ZH0.6–70-Stabilized Emulsion in Different pH Environments
2.4. Evaluation of Storage Stability of the ZH0.6–70-Stabilized Emulsion
2.5. Amino Acids Analysis
2.6. Circular Dichroism
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of Alkaline Hydrolyzed Zein Peptides
3.3. Tris-Tricine SDS-PAGE
3.4. Emulsification Activity Index (EAI) and Emulsification Stability Index (ESI)
3.5. Surface Hydrophobicity Index (SHI)
3.6. Preparation of Emulsions
3.7. Stability of Emulsion
3.8. Particle Size
3.9. Microscopic Observation
3.10. Emulsion Stability against Environmental Stress
3.11. Emulsion Stability during Storage at Room Temperature
3.12. Quantification of Total Amino Acids (AAs)
3.13. Circular Dichroism
3.14. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Q.; He, Q.; Xu, M.; Li, J.; Liu, X.; Wan, Z.; Yang, X. Food-Grade Emulsions and Emulsion Gels Prepared by Soy Protein–Pectin Complex Nanoparticles and Glycyrrhizic Acid Nanofibrils. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 1051–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Su, J.; Brennan, C.S.; Van der Meeren, P.; Zhang, N.; Tong, Y.; Wang, P. Recent Developments of Electrospun Zein Nanofibres: Strategies, Fabrication and Therapeutic Applications. Mater. Today Adv. 2022, 16, 100307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, A.; Wu, L.; Yan, W.; Tong, Y.; Wang, P. Circular Extraction: Innovative Use of a Switchable Composite Extractant for Prolamin Extraction from Grain Byproducts. ACS Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 2, 630–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Liu, Z.; Guo, A.; Mackie, A.; Zhang, L.; Liao, W.; Mao, L.; Yuan, F.; Gao, Y. Zein Colloidal Particles and Cellulose Nanocrystals Synergistic Stabilization of Pickering Emulsions for Delivery of β-Carotene. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 12278–12294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, S.; Jia, R.; Liu, W.; Xie, J.; Liu, M.; Cai, D.; Zheng, M.; Liu, H.; Liu, J. Lipid Oxidation and in Vitro Digestion of Pickering Emulsion Based on Zein-Adzuki Bean Seed Coat Polyphenol Covalent Crosslinking Nanoparticles. Food Chem. 2022, 386, 132513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; He, Z.; Xu, F.; Cheng, Y.; Waterhouse, G.I.N.; Sun-Waterhouse, D.; Wu, P. Enhancing the Performance of Konjac Glucomannan Films through Incorporating Zein–Pectin Nanoparticle-Stabilized Oregano Essential Oil Pickering Emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 124, 107222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Gu, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, Z. Fabrication of Pickering Emulsion Based on Particles Combining Pectin and Zein: Effects of Pectin Methylation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 256, 117515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Li, Z.; Dai, M.; He, H.; Liang, B.; Sun, C.; Li, X.; Ji, C. Fabrication and Characterization of Chitosan–Pea Protein Isolate Nanoparticles. Molecules 2022, 27, 6913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, E.M.C.; Ferreira, M.R.A.; Soares, L.A.L. Pickering Emulsions Stabilized by Zein Particles and Their Complexes and Possibilities of Use in the Food Industry: A Review. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 131, 107781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinache, A.; Pascu, M.-L.; Smarandache, A. Spectral Properties of Foams and Emulsions. Molecules 2021, 26, 7704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Qian, Y.; Xi, Y.; Lü, X. Hydrothermal and Alkaline Thermal Pretreatment at Mild Temperature in Solid State for Physicochemical Properties and Biogas Production from Anaerobic Digestion of Rice Straw. Renew. Energy 2019, 139, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.-J.; Lee, S.-D.; Han, S.-W. Functional Properties of Rice Bran Proteins Extracted from Low-Heat-Treated Defatted Rice Bran. Molecules 2022, 27, 7212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Jin, Y.; Xiong, Y.L. Heating-Aided PH Shifting Modifies Hemp Seed Protein Structure, Cross-Linking, and Emulsifying Properties. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 10827–10834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Guan, Y.; Wen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, T. Mild Heating Assisted Alkaline PH Shifting Modify the Egg White Protein: The Mechanism and the Enhancement of Emulsifying Properties. LWT 2021, 151, 112094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matoba, T.; Hata, T. Relationship between Bitterness of Peptides and Their Chemical Structures. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1972, 36, 1423–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinsholm, S.; Oterhals, Å.; Underhaug, J.; Måge, I.; Malmendal, A.; Aspevik, T. Sensory Assessment of Fish and Chicken Protein Hydrolysates. Evaluation of NMR Metabolomics Profiling as a New Prediction Tool. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 3881–3890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aspevik, T.; Totland, C.; Lea, P.; Oterhals, Å. Sensory and Surface-Active Properties of Protein Hydrolysates Based on Atlantic Salmon (Salmo Salar) by-Products. Process Biochem. 2016, 51, 1006–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.-Y.; Zhu, K.-X.; Peng, W.; Guo, X.-N.; Zhou, H.-M. Effect of Sequential Hydrolysis with Endo- and Exo-Peptidase on Bitterness Properties of Wheat Gluten Hydrolysates. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 27659–27668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.; Zhou, F.; Niu, Z.; Shen, P.; Zhao, M. Formation of Mucus-Permeable Nanoparticles from Soy Protein Isolate by Partial Enzymatic Hydrolysis Coupled with Thermal and PH-Shifting Treatment. Food Chem. 2023, 398, 133851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, W.; Zhou, J.; Jin, R. Proteins Recovery from Waste Activated Sludge by Thermal Alkaline Treatment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäkinen, O.E.; Zannini, E.; Koehler, P.; Arendt, E.K. Heat-Denaturation and Aggregation of Quinoa (Chenopodium Quinoa) Globulins as Affected by the PH Value. Food Chem. 2016, 196, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Jiang, S.; Feng, X.; Wang, R.; Zeng, M.; Zhao, Y. Physicochemical State and in Vitro Digestibility of Heat Treated Water-Soluble Protein from Pacific Oyster (Crassostrea Gigas). Food Biosci. 2020, 34, 100528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Averina, E.; Konnerth, J.; D’Amico, S.; van Herwijnen, H.W.G. Protein Adhesives: Alkaline Hydrolysis of Different Crop Proteins as Modification for Improved Wood Bonding Performance. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 161, 113187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rombouts, I.; Lagrain, B.; Brijs, K.; Delcour, J.A. β-Elimination Reactions and Formation of Covalent Cross-Links in Gliadin during Heating at Alkaline PH. J. Cereal Sci. 2010, 52, 362–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thewissen, B.G.; Celus, I.; Brijs, K.; Delcour, J.A. Foaming Properties of Wheat Gliadin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 1370–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.-J.; Li, X.-L.; Li, S.-G.; Xu, B.-C.; Zhang, B. Emulsifying and Emulsion Stabilizing Properties of Hydrolysates of High-Density Lipoprotein from Egg Yolk. Food Chem. 2022, 369, 130891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Guo, J.; Wang, S. Modification of Glutenin and Associated Changes in Digestibility Due to Methylglyoxal during Heat Processing. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 10734–10743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, R.S.H.; Nickerson, M.T. Food Proteins: A Review on Their Emulsifying Properties Using a Structure–Function Approach. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 975–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Li, J.; Chang, C.; Wang, C.; Yang, Y.; Su, Y. Effect of Enzymatic Hydrolysis on Heat Stability and Emulsifying Properties of Egg Yolk. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 97, 105224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustapha, N.A.; Ruttarattanamongkol, K.; Rizvi, S.S.H. The Effects of Supercritical Fluid Extrusion Process on Surface Hydrophobicity of Whey Protein Concentrate and Its Relation to Storage and Heat Stability of Concentrated Emulsions. Food Res. Int. 2012, 48, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, M.; Tang, T.; Zhou, L.; Ling, Z.; Guo, S.; Jiang, A. Effects of Different Proteases on the Emulsifying Capacity, Rheological and Structure Characteristics of Preserved Egg White Hydrolysates. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 87, 933–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-S.; Guo, J.-H.; Lin, M.-J. Stability Evaluation of PH-Adjusted Goat Milk for Developing Ricotta Cheese with a Mixture of Cow Cheese Whey and Goat Milk. Foods 2020, 9, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huck-Iriart, C.; Rincón-Cardona, J.A.; Herrera, M.L. Stability of Whey Protein Concentrate/Sunflower Oil Emulsions as Affected by Sucrose and Xanthan Gum. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2014, 7, 2646–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, T.; Yu, G.; Li, X.; Liu, H.; Liu, T.; Zhu, J. Effect of Enzymatic Hydrolysis on the Physicochemical and Emulsification Properties of Rice Bran Albumin and Globulin Fractions. LWT 2022, 156, 113005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, A.; Ahmed, E.; Hu, T.; Xu, X.; Pan, S.; Hu, H. Effects of Different Ionic Strengths on the Physicochemical Properties of Plant and Animal Proteins-Stabilized Emulsions Fabricated Using Ultrasound Emulsification. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 58, 104627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wang, D.; Sun, C.; McClements, D.J.; Gao, Y. Utilization of Interfacial Engineering to Improve Physicochemical Stability of β-Carotene Emulsions: Multilayer Coatings Formed Using Protein and Protein–Polyphenol Conjugates. Food Chem. 2016, 205, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, T.; Kumar, G.S.; Chon, B.H.; Sangwai, J.S. Thermal Stability of Oil-in-Water Pickering Emulsion in the Presence of Nanoparticle, Surfactant, and Polymer. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 22, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taarji, N.; Bouhoute, M.; Kobayashi, I.; Tominaga, K.; Isoda, H.; Nakajima, M. Physicochemical Stability and In-Vitro Bioaccessibility of Concentrated γ-Oryzanol Nanodispersions Fabricated by Solvent Displacement Method. Food Chem. 2022, 382, 132300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Hu, X.; Wu, J.; Chen, R.; Dai, T.; Liu, Y.; Luo, S.; Liu, C. Soluble Starch/Whey Protein Isolate Complex-Stabilized High Internal Phase Emulsion: Interaction and Stability. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 111, 106377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, M.; Liu, L.; Zhang, T.; Tao, N.; Wang, X.; Zhong, J. Effect of Interfacial Layer Number on the Storage Stability and in Vitro Digestion of Fish Oil-Loaded Multilayer Emulsions Consisting of Gelatin Particle and Polysaccharides. Food Chem. 2021, 336, 127686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Hu, M.; Liu, G.; Qi, B.; Zhou, S.; Lu, K.; Xie, F.; Zhu, X.; Li, Y. Development and Evaluation of Delivery Systems for Quercetin: A Comparative Study between Coarse Emulsion, Nano-Emulsion, High Internal Phase Emulsion, and Emulsion Gel. J. Food Eng. 2022, 314, 110784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, B.; Li, X.-M.; Meng, R.; Chen, H.-Q.; Jin, Z.-Y. Preparation and Characterization of Emulsion Stabilized by Octenyl Succinic Anhydride-Modified Dextrin for Improving Storage Stability and Curcumin Encapsulation. Food Chem. 2019, 294, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Chen, J.; Ren, J.; Zhao, M. Effects of Ultrasound Pretreatment on the Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Soy Protein Isolates and on the Emulsifying Properties of Hydrolysates. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 2600–2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Cheng, N.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Z.; Zhou, W.; Wang, Y.; Cao, W. The Effects of Different Thermal Treatments on Amino Acid Contents and Chemometric-Based Identification of Overheated Honey. LWT 2018, 96, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, J.; Qin, L.; Liu, F.; Zeng, W.; Wan, J. Intracellular and Extracellular Sources, Transformation Process and Resource Recovery Value of Proteins Extracted from Wastewater Treatment Sludge via Alkaline Thermal Hydrolysis and Enzymatic Hydrolysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 852, 158512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usoltsev, D.; Sitnikova, V.; Kajava, A.; Uspenskaya, M. Systematic FTIR Spectroscopy Study of the Secondary Structure Changes in Human Serum Albumin under Various Denaturation Conditions. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Yang, R.; Feng, X.; Fan, X.; Liu, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhou, G.; Zhu, B.; Ullah, N.; Chen, L. Effects of Low-Frequency and High-Intensity Ultrasonic Treatment Combined with Curdlan Gels on the Thermal Gelling Properties and Structural Properties of Soy Protein Isolate. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 127, 107506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Xu, Z.; Mo, J.; Lyu, Y.; Tang, X.; Shen, X. Effects of Guar Gum on Adhesion Properties of Soybean Protein Isolate onto Porcine Bones. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2017, 75, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, G.; Jiang, X.; Xie, F.; Fan, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhang, M.; Qi, J.; Wang, S.; Zhou, X. Effect of High-Pressure Homogenization on Structural Changes and Emulsifying Properties of Chicken Liver Proteins Isolated by Isoelectric Solubilization/Precipitation. LWT 2021, 151, 112092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schägger, H. Tricine–SDS-PAGE. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Fu, J.; Ma, Y.; He, Y.; Fu, R.; Qayum, A.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, L. Low Temperature Extrusion Promotes Transglutaminase Cross-Linking of Whey Protein Isolate and Enhances Its Emulsifying Properties and Water Holding Capacity. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 125, 107410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, B.; Zhu, P.; Pang, X.; Xie, N.; Zhang, S.; Lv, J. Effect of Different Temperature-Controlled Ultrasound on the Physical and Functional Properties of Micellar Casein Concentrate. Foods 2021, 10, 2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Ge, H.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Su, X.; Panpipat, W.; Lai, O.-M.; Tan, C.-P.; Cheong, L.-Z. Phospholipid–Protein Structured Membrane for Microencapsulation of DHA Oil and Evaluation of Its In Vitro Digestibility: Inspired by Milk Fat Globule Membrane. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 6190–6201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Ni, F.; Liu, C.; Shi, J.; Ren, G.; Wu, Z.; Song, Z. Characterization and Stability of Peppermint Oil Emulsions Using Polyglycerol Esters of Fatty Acids and Milk Proteins as Emulsifiers. J. Food Sci. 2021, 86, 5148–5158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, A.J.; Wallace, B.A. CDtoolX, a Downloadable Software Package for Processing and Analyses of Circular Dichroism Spectroscopic Data. Protein Sci. 2018, 27, 1717–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Amino Acids | Zein | ZH0.6–70 |
|---|---|---|
| Alanine | 8.86 ± 0.22% b | 10.14 ± 0.27% a |
| Arginine | 1.67 ± 0.08% b | 2.18 ± 0.13% a |
| Aspartic acid | 5.11 ± 0.17% b | 6.18 ± 0.14% a |
| Cysteine | 0.54 ± 0.09% a | 0.06 ± 0.05% a |
| Glutamic acid | 24.19 ± 0.43% a | 24.69 ± 0.56% a |
| Glycine | 1.45 ± 0.21% a | 1.64 ± 0.14% a |
| Histidine | 1.59 ± 0.22% b | 2.33 ± 0.15% a |
| Isoleucine | 3.91 ± 0.16% b | 4.97 ± 0.34% a |
| Leucine | 19.20 ± 0.67% a | 18.61 ± 0.82% a |
| Lysine | 0.07 ± 0.04% a | 0.16 ± 0.07% a |
| Methionine | 1.50 ± 0.06% | n.d. |
| Phenylalanine | 6.64 ± 0.55% a | 7.32 ± 0.44% a |
| Proline | 9.25 ± 0.42% a | 8.32 ± 0.54% a |
| Serine | 5.36 ± 0.22% a | 3.30 ± 0.13% b |
| Threonine | 2.97 ± 0.14% a | 1.22 ± 0.08% b |
| Tyrosine | 4.42 ± 0.13% a | 4.16 ± 0.24% a |
| Valine | 3.28 ± 0.41% b | 4.73 ± 0.27% a |
| Total hydrophilic AA | 32.63 ± 0.68% b | 35.54 ± 0.54% a |
| Random Coil | α-Helix | β-Sheet | β-Turn | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parallel β-Sheet | Anti-Parallel β-Sheet | ||||
| Zein | 27.26% | 51.13% | 6.28% | 1.75% | 13.58% |
| ZH0.6–70 | 33.08% | 14.02% | 3.00% | 35.11% | 14.80% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, P.; Tong, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, H. Functional Properties of Corn Byproduct-Based Emulsifier Prepared by Hydrothermal–Alkaline. Molecules 2023, 28, 665. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28020665
Liu L, Zhang J, Wang P, Tong Y, Li Y, Chen H. Functional Properties of Corn Byproduct-Based Emulsifier Prepared by Hydrothermal–Alkaline. Molecules. 2023; 28(2):665. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28020665
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Lu, Jijun Zhang, Pengjie Wang, Yi Tong, Yi Li, and Han Chen. 2023. "Functional Properties of Corn Byproduct-Based Emulsifier Prepared by Hydrothermal–Alkaline" Molecules 28, no. 2: 665. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28020665
APA StyleLiu, L., Zhang, J., Wang, P., Tong, Y., Li, Y., & Chen, H. (2023). Functional Properties of Corn Byproduct-Based Emulsifier Prepared by Hydrothermal–Alkaline. Molecules, 28(2), 665. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28020665







