Enhanced Catalytic Activity of TEMPO-Mediated Aerobic Oxidation of Alcohols via Redox-Active Metal–Organic Framework Nodes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
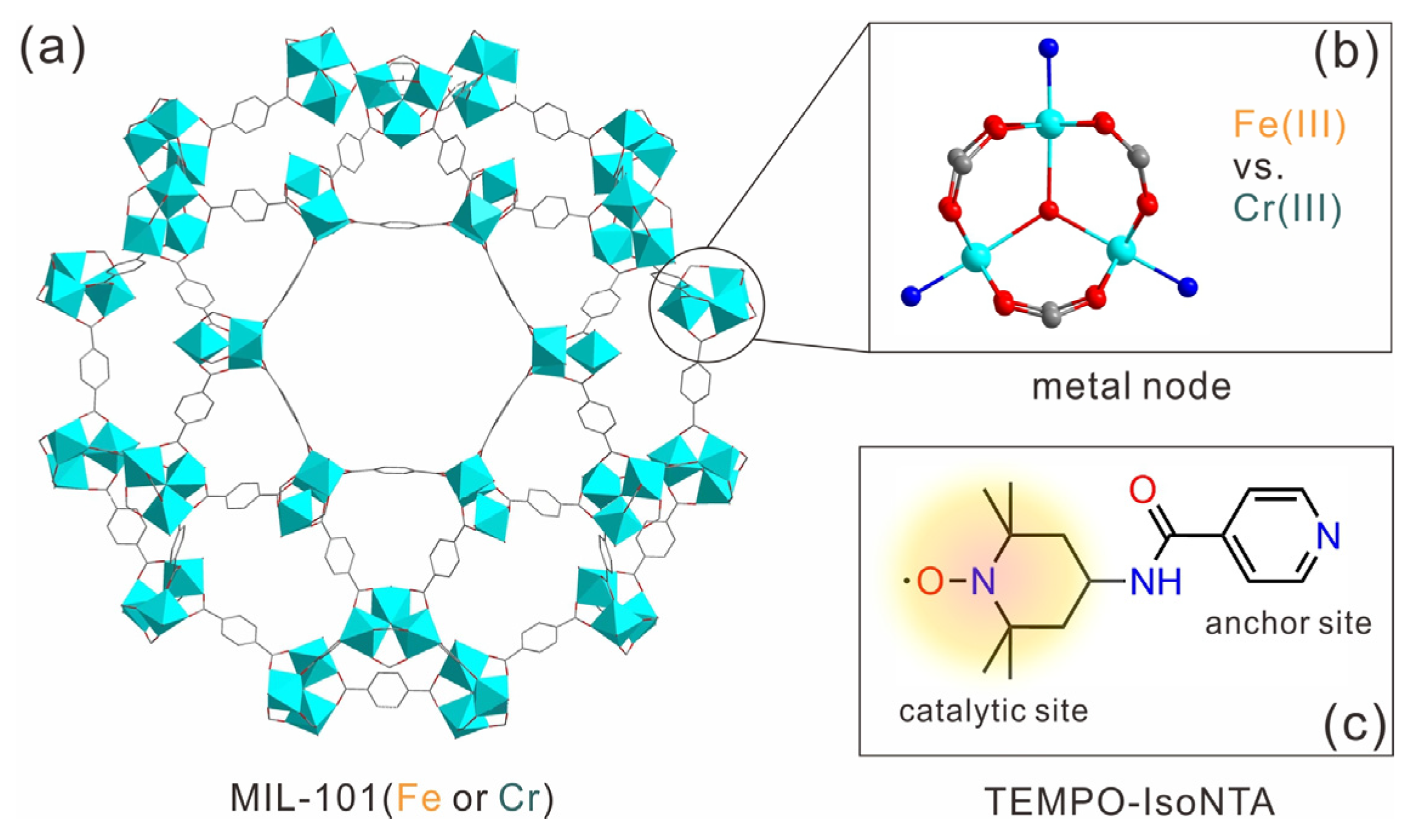
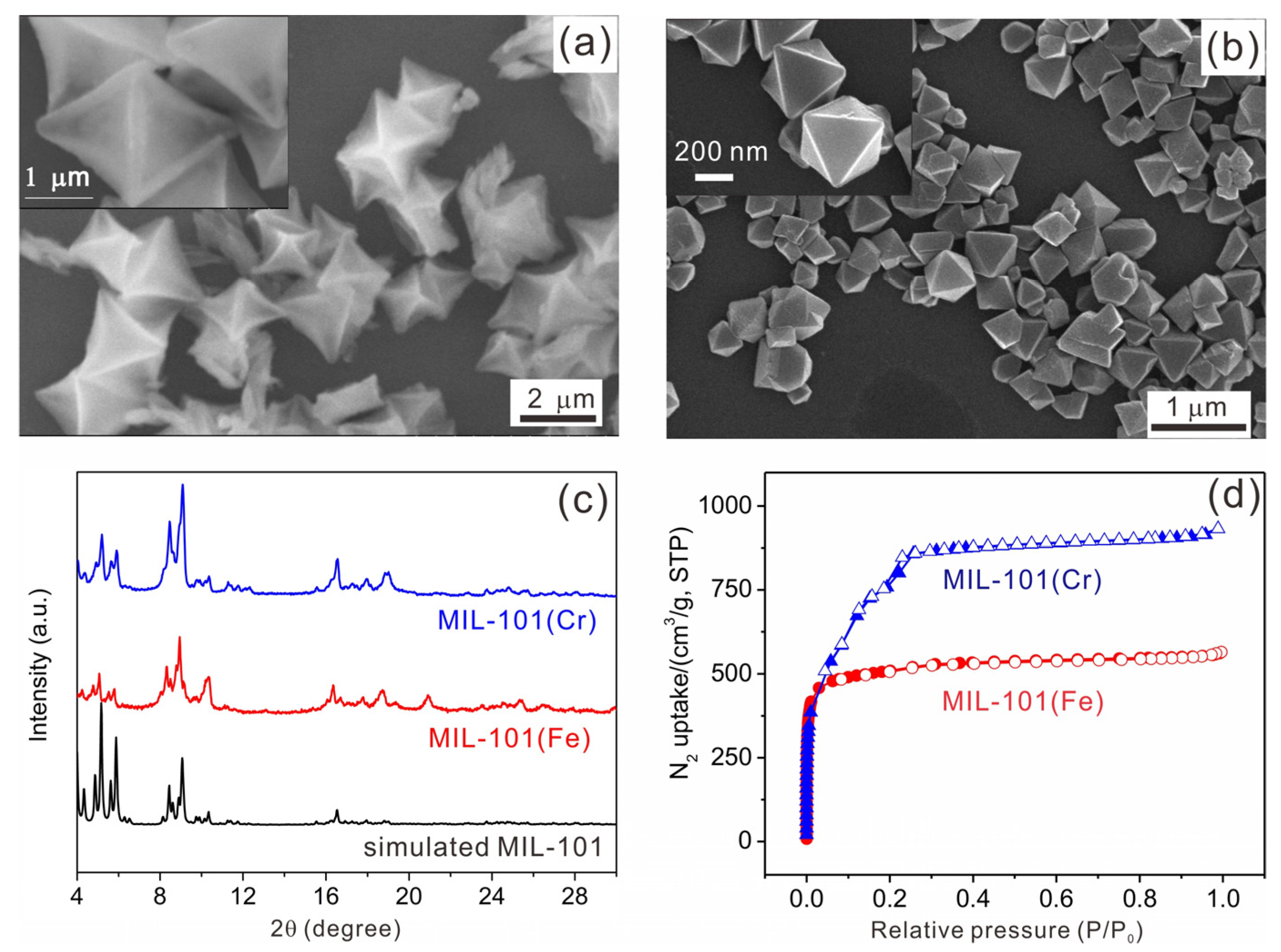
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization of TEMPO-IsoNTA, MIL-101(Fe) and MIL-101(Cr)
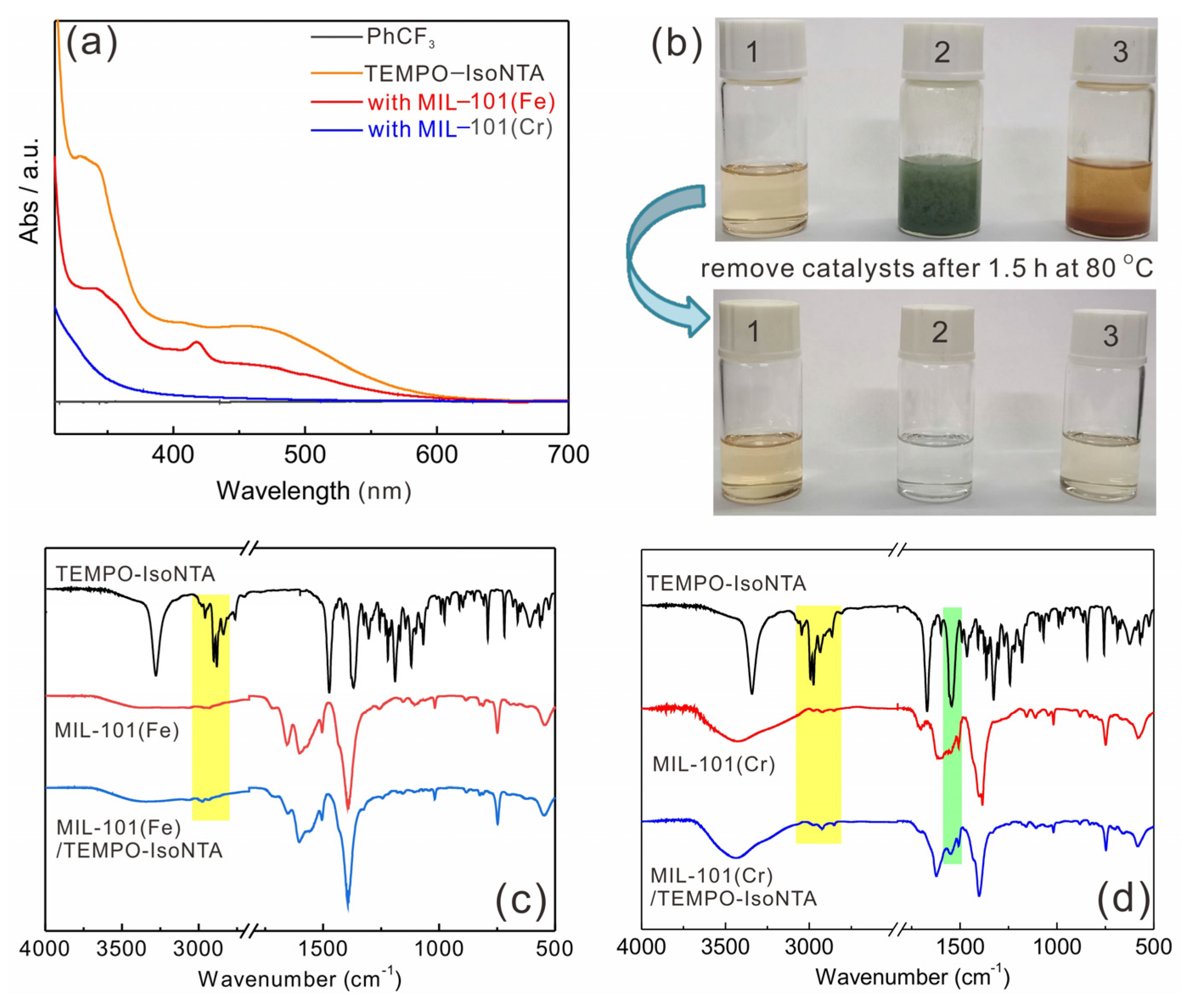
2.2. Adsorption Properties of TEMPO-IsoNTA with MIL-101(Fe) or MIL-101(Cr)
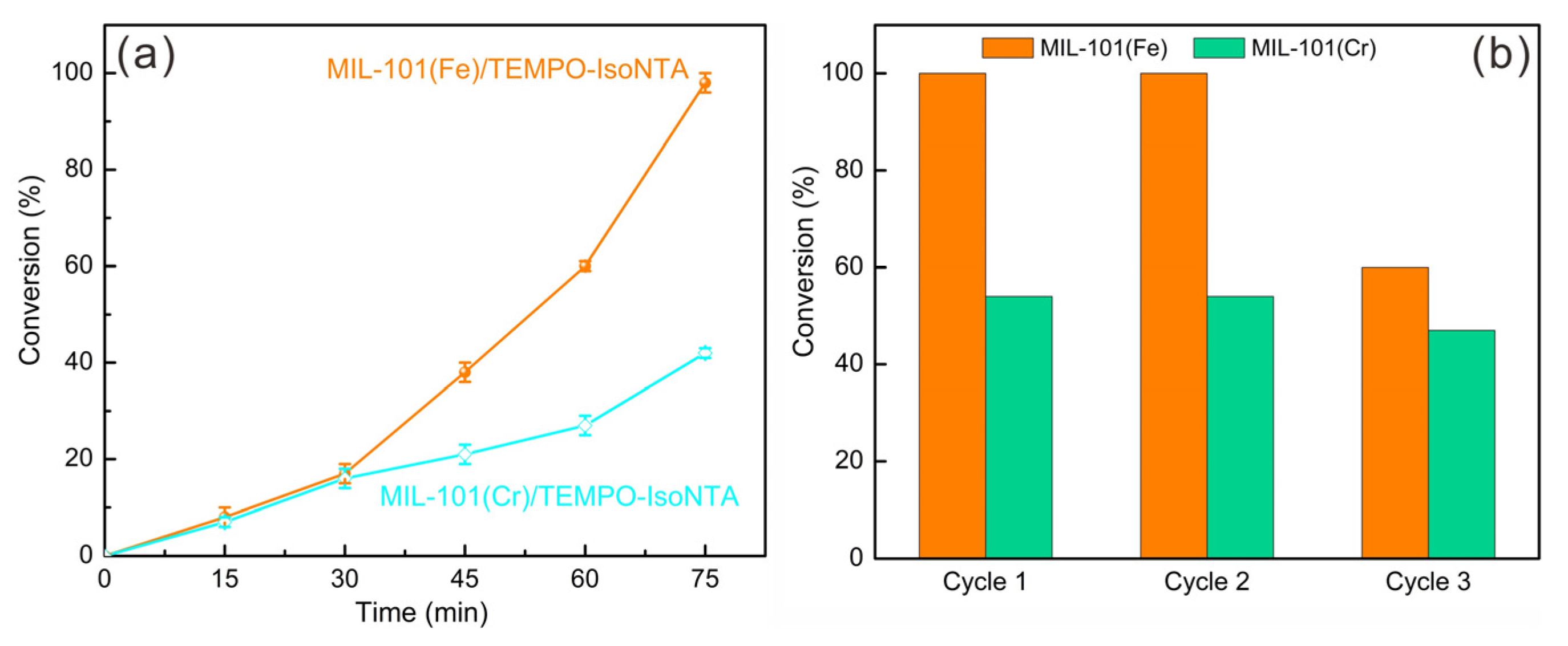
2.3. Synergistic Catalytic Studies of MIL-101(Fe) and MIL-101(Cr)
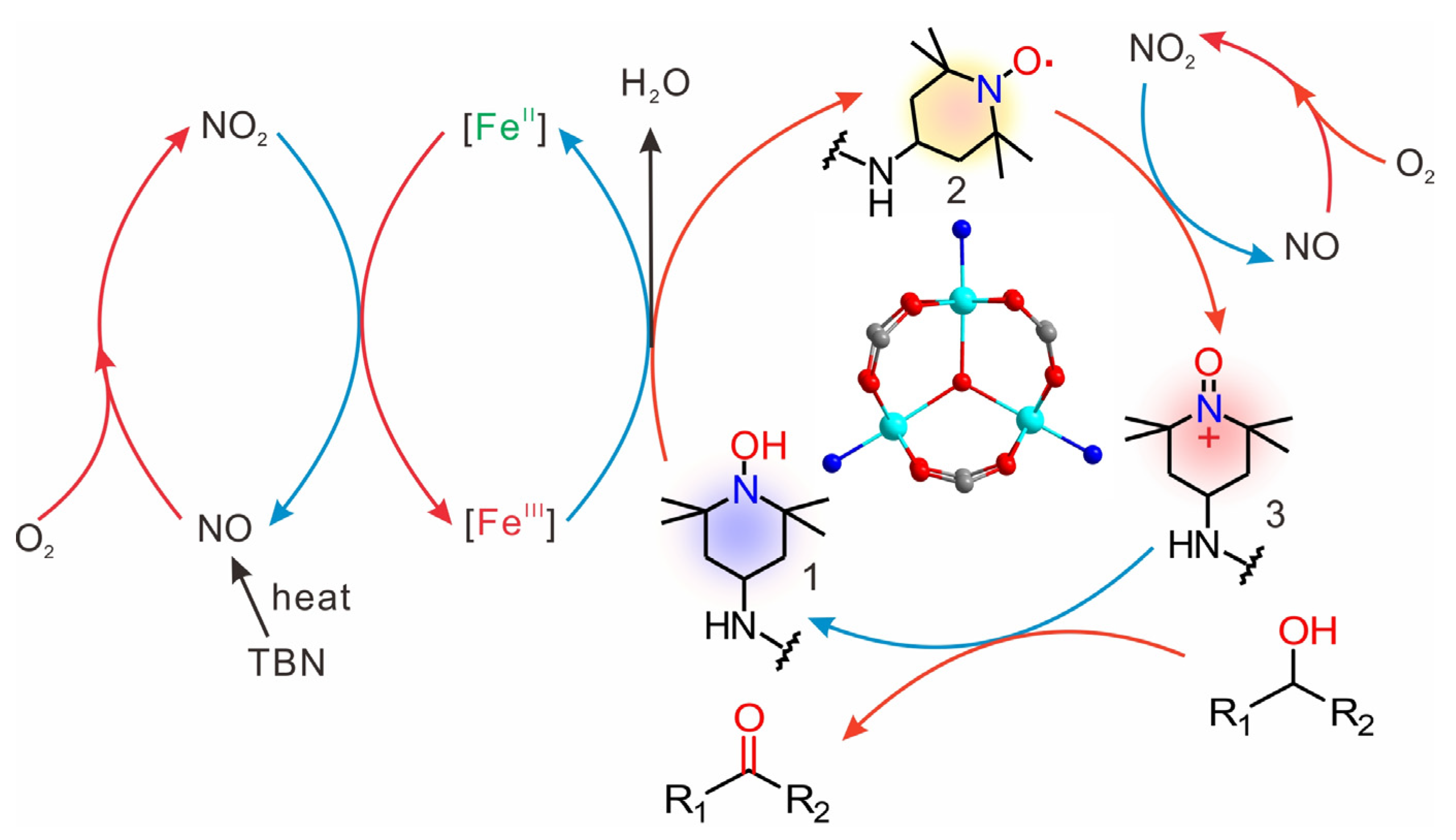
2.4. Catalytic Mechanism: Redox-Active Metal–Organic Framework Nodes Boost the Catalytic Activity
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Synthesis of TEMPO-IsoNTA
3.2. Synthesis of MOFs
3.2.1. Synthesis of MIL-101(Fe)
3.2.2. Synthesis of the MIL-101(Cr)
3.3. Studies of the Adsorption Properties of MIL-101(Fe) and MIL-101(Cr) for TEMPO-IsoNTA
3.4. Studies of the Synergistic Catalytic Properties of MIL-101(Fe)/TEMPO-IsoNTA and MIL-101(Cr)/TEMPO-IsoNTA
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Lee, J.; Farha, O.K.; Roberts, J.; Scheidt, K.A.; Nguyen, S.T.; Hupp, J.T. Metal-organic framework materials as catalysts. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 1450–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Chen, L.; Cui, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Su, C.Y. Applications of Metal-organic frameworks in heterogeneous supramolecular catalysis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 6011–6061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Xiang, S.; Qian, G. Metal-organic frameworks with functional pores for recognition of small molecules. Acc. Chem. Res. 2010, 43, 1115–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, J.L.; Liu, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Mao, H.L.; Guo, J.; Du, X.; Zhu, S.B.; Ren, B.; Terfort, A. Zr-metal-organic frameworks featuring TEMPO radicals: Synergistic effect between TEMPO and hydrophilic Zr-node defects boosting aerobic oxidation of alcohols. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 3034–3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moumen, E.; Bazzi, L.; El Hankari, S. Metal-organic frameworks and their composites for the adsorption and sensing of phosphate. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2022, 455, 214376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, N.; Biswas, S. Synthesis of Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs): Routes to various mof topologies, morphologies, and composites. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 933–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.L.; Xu, Q. Metal-organic framework composites. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 5468–5512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.B.; Liang, J.; Wang, X.S.; Cao, R. Multifunctional metal-organic framework catalysts: Synergistic catalysis and tandem reactions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 126–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Feng, L.; Wang, K.; Pang, J.; Bosch, M.; Lollar, C.; Sun, Y.; Qin, J.; Yang, X.; Zhang, P.; et al. Stable Metal-Organic Frameworks: Design, Synthesis, and Applications. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1704303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Z.; Bao, Z.; Xing, H.; Yang, Q.; Ren, Q. MIL-101(Cr) as a synergistic catalyst for the reduction of imines with trichlorosilane. Mol. Catal. 2018, 445, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serre, C.; Millange, F.; Surblé, S.; Férey, G. A Route to the Synthesis of Trivalent Transition-Metal Porous Carboxylates with Trimeric Secondary Building Units. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 6285–6289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zorainy, M.Y.; Gar Alalm, M.; Kaliaguine, S.; Boffito, D.C. Revisiting the MIL-101 metal–organic framework: Design, synthesis, modifications, advances, and recent applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 22159–22217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kholdeeva, O.A.; Skobelev, I.Y.; Ivanchikova, I.D.; Kovalenko, K.A.; Fedin, V.P.; Sorokin, A.B. Hydrocarbon oxidation over Fe- and Cr-containing metal-organic frameworks MIL-100 and MIL-101-a comparative study. Catal. Today 2014, 238, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.W.; Kim, H.G.; Cho, D.H. Catalytic performance of MIL-100 (Fe, Cr) and MIL-101 (Fe, Cr) in the isomerization of endo- to exo-dicyclopentadiene. Catal. Commun. 2016, 73, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skobelev, I.Y.; Sorokin, A.B.; Kovalenko, K.A.; Fedin, V.P.; Kholdeeva, O.A. Solvent-free allylic oxidation of alkenes with O2 mediated by Fe- and Cr-MIL-101. J. Catal. 2013, 298, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Yu, G.; Huo, Q.; Kan, Q.; Guan, J. Epoxidation of styrene over Fe(Cr)-MIL-101 metal-organic frameworks. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 38048–38054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, S.; Chen, C.; Ahn, W.S. Chromium terephthalate metal-organic framework MIL-101: Synthesis, functionalization, and applications for adsorption and catalysis. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 52500–52525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.X.; Chen, Y.Z.; Hu, Y.; Huang, G.; Yu, S.H.; Jiang, H.L. MIL-101-SO3H: A Highly Efficient Brønsted Acid Catalyst for Heterogeneous Alcoholysis of Epoxides under Ambient Conditions. Chem. Eur. J. 2014, 20, 14976–14980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldon, R.A. Recent advances in green catalytic oxidations of alcohols in aqueous media. Catal. Today 2015, 247, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Dornan, L.M.; Rogan, L.; Hughes, N.L.; Muldoon, M.J. Aerobic oxidation catalysis with stable radicals. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 4524–4543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmeggiani, C.; Cardona, F. Transition metal based catalysts in the aerobic oxidation of alcohols. Green Chem. 2012, 14, 547–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciriminna, R.; Pandarus, V.; Béland, F.; Xu, Y.J.; Pagliaro, M. Heterogeneously Catalyzed Alcohol Oxidation for the Fine Chemical Industry. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2015, 19, 1554–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Shen, Z.; Mo, W.; Sun, N.; Hu, B.; Hu, X. TEMPO-tert-Butyl Nitrite: An Efficient Catalytic System for Aerobic Oxidation of Alcohols. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2009, 351, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zhou, H.; Gu, X.; Shen, X.; Li, P. TEMPO-Mediated Oxidation of Primary Alcohols to Aldehydes under Visible Light and Air. Chin. J. Chem. 2014, 32, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.M.; Xue, Y.; Yan, M.; Mao, H.L.; Cheng, H.; Chen, Z.; Sui, Z.W.; Zhu, S.B.; Yu, X.J.; Zhuang, J.L. Synthesis of TEMPO radical decorated hollow porous aromatic frameworks for selective oxidation of alcohols. Chem. Commun. 2021, 57, 907–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, B.; Farhangi, E. A Highly Recyclable Magnetic Core-Shell Nanoparticle-Supported TEMPO catalyst for Efficient Metal- and Halogen-Free Aerobic Oxidation of Alcohols in Water. Chem. Eur. J. 2011, 17, 6056–6060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagerblom, K.; Wrigstedt, P.; Keskivali, J.; Parviainen, A.; Repo, T. Iron-Catalysed Selective Aerobic Oxidation of Alcohols to Carbonyl and Carboxylic Compounds. Chempluschem 2016, 81, 1160–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, W.; Chu, C.; Lu, Q.; Tao, J.; Liang, X.; Liu, R. Iron Chloride/4-Acetamido-TEMPO/Sodium Nitrite-Catalyzed Aerobic Oxidation of Primary Alcohols to the Aldehydes. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2010, 352, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoover, J.M.; Ryland, B.L.; Stahl, S.S. Copper/TEMPO-Catalyzed Aerobic Alcohol Oxidation: Mechanistic Assessment of Different Catalyst Systems. ACS Catal. 2013, 3, 2599–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakshinamoorthy, A.; Alvaro, M.; Garcia, H. Aerobic Oxidation of Benzylic Alcohols Catalyzed by Metal-Organic Frameworks Assisted by TEMPO. ACS Catal. 2010, 1, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lammert, M.; Wharmby, M.T.; Smolders, S.; Bueken, B.; Lieb, A.; Lomachenko, K.A.; Vos, D.D.; Stock, N. Cerium-based metal organic frameworks with UiO-66 architecture: Synthesis, properties and redox catalytic activity. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 12578–12581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Z.; Zhang, J.; Peng, L.; Han, B.; Mu, T.; Li, J.; Yang, G. Poly(ethylene glycol) Stabilized Mesoporous Metal-Organic Framework Nanocrystals: Efficient and Durable Catalysts for the Oxidation of Benzyl Alcohol. ChemPhysChem 2014, 15, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Gao, H.; Tan, L.; Luan, Y.; Yang, M. Superparamagnetic Core-Shell Metal-Organic Framework Fe3O4/Cu3(btc)2 Microspheres and Their Catalytic Activity in the Aerobic Oxidation of Alcohols and Olefins. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 4906–4912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, X.; Yu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Luan, Y.; Ramella, D. Direct synthesis of Fe(III) immobilized Zr-based metal–organic framework for aerobic oxidation reaction. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2017, 31, e3862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Zhang, J.; Ma, S. Iron Catalysis for Room-Temperature Aerobic Oxidation of Alcohols to Carboxylic Acids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 8344–8347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, T.; Hayes, P. Analysis of XPS spectra of Fe2+ and Fe3+ ions in oxide materials. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2008, 254, 2441–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, M.; Das, S.; Yoon, M.; Choi, H.J.; Hyun, M.H.; Park, S.M.; Seo, G.; Kim, K. Postsynthetic Modification Switches an Achiral Framework to Catalytically Active Homochiral Metal-Organic Porous Materials. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 7524–7525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Sun, Y.; Chu, J.; Zhang, X.; Deng, H. Multivariate Metal–Organic Frameworks for Dialing-in the Binding and Programming the Release of Drug Molecules. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 14209–14216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Yuan, K.; Wang, Y.; Li, G.; Guo, J.; Gu, L.; Hu, W.; Zhao, H.; Tang, Z. Metal–organic frameworks as selectivity regulators for hydrogenation reactions. Nature 2016, 539, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
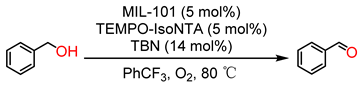 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | Catalyst | Co-Catalyst | Activator | Time (h) | Con. (%) | Sel. (%) |
| 1 | — | TEMPO-IsoNTA | TBN | 1.5 | 23/60 a | >99 |
| 2 | MIL-101(Fe) | TEMPO-IsoNTA | TBN | 1.5 | 100/100 a | >99 |
| 3 | MIL-101(Cr) | TEMPO-IsoNTA | TBN | 1.5 | 9/51 a | >99 |
| 4 | MIL-101(Fe) | — | TBN | 1.5 | 5 | >99 |
| 5 | MIL-101(Cr) | — | TBN | 1.5 | 5 | >99 |
| 6 | MIL-101(Fe) | TEMPO-IsoNTA | — | 1.5 | 4 | >99 |
| 7 | MIL-101(Cr) | TEMPO-IsoNTA | — | 1.5 | 4 | >99 |
| 8 | MIL-101(Fe) | — | — | 1.5 | <1 | — |
| 9 | MIL-101(Cr) | — | — | 1.5 | <1 | — |
| 10 | MIL-101(Fe) | TEMPO | TBN | 1.5 | 42 | >99 |
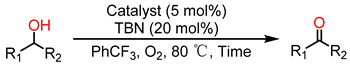 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | Product | Time (h) | Fe-MOF Cat. Con. (%) | Cr-MOF Cat. Con. (%) | Sel. (%) |
| 1 |  | 1.5 | >99 | 8 | >99 |
| 2 | 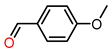 | 1.5 | >99 | 30 | >99 |
| 3 | 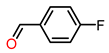 | 1.5 | >99 | 25 | >99 |
| 4 | 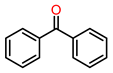 | 1.5 | >99 | 70 | >99 |
| 5 | 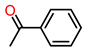 | 1.5 | >99 | 7 | >99 |
| 6 | 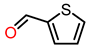 | 4 | >99 | 70 | >99 |
| 7 | 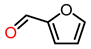 | 4 | >99 | 60 | >99 |
| 8 | 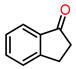 | 6 | >99 | 18 | >99 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, B.; Zhang, J.; Xue, Y.; Chong, Y.; Zhao, D.; Cheng, H.; Tian, L.; Zhuang, J. Enhanced Catalytic Activity of TEMPO-Mediated Aerobic Oxidation of Alcohols via Redox-Active Metal–Organic Framework Nodes. Molecules 2023, 28, 593. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28020593
Wang B, Zhang J, Xue Y, Chong Y, Zhao D, Cheng H, Tian L, Zhuang J. Enhanced Catalytic Activity of TEMPO-Mediated Aerobic Oxidation of Alcohols via Redox-Active Metal–Organic Framework Nodes. Molecules. 2023; 28(2):593. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28020593
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Bing, Junjie Zhang, Yun Xue, Yuliang Chong, Dongdong Zhao, Hu Cheng, Liangliang Tian, and Jinliang Zhuang. 2023. "Enhanced Catalytic Activity of TEMPO-Mediated Aerobic Oxidation of Alcohols via Redox-Active Metal–Organic Framework Nodes" Molecules 28, no. 2: 593. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28020593
APA StyleWang, B., Zhang, J., Xue, Y., Chong, Y., Zhao, D., Cheng, H., Tian, L., & Zhuang, J. (2023). Enhanced Catalytic Activity of TEMPO-Mediated Aerobic Oxidation of Alcohols via Redox-Active Metal–Organic Framework Nodes. Molecules, 28(2), 593. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28020593








