Monitoring the Effect of Calcium Nitrate on the Induction Period of Cement Hydration via Low-Field NMR Relaxometry
Abstract
1. Introduction
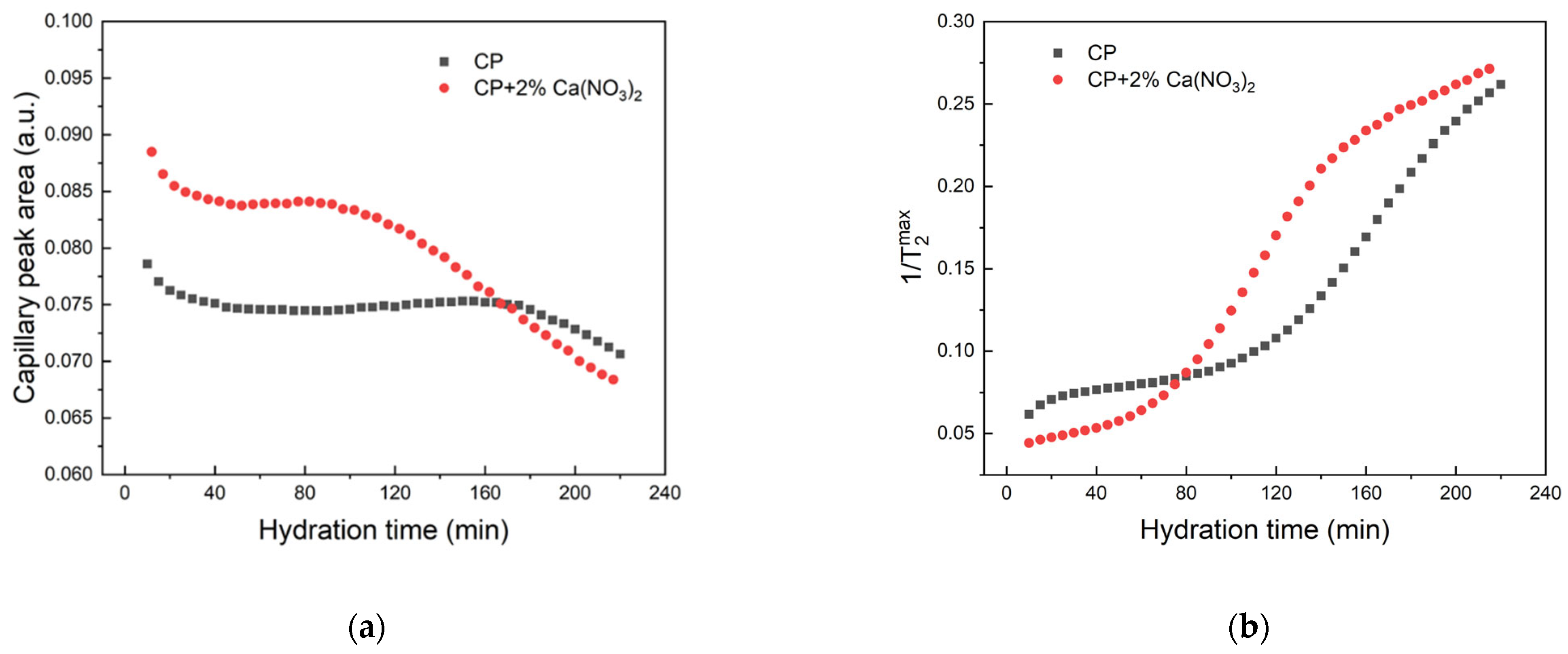
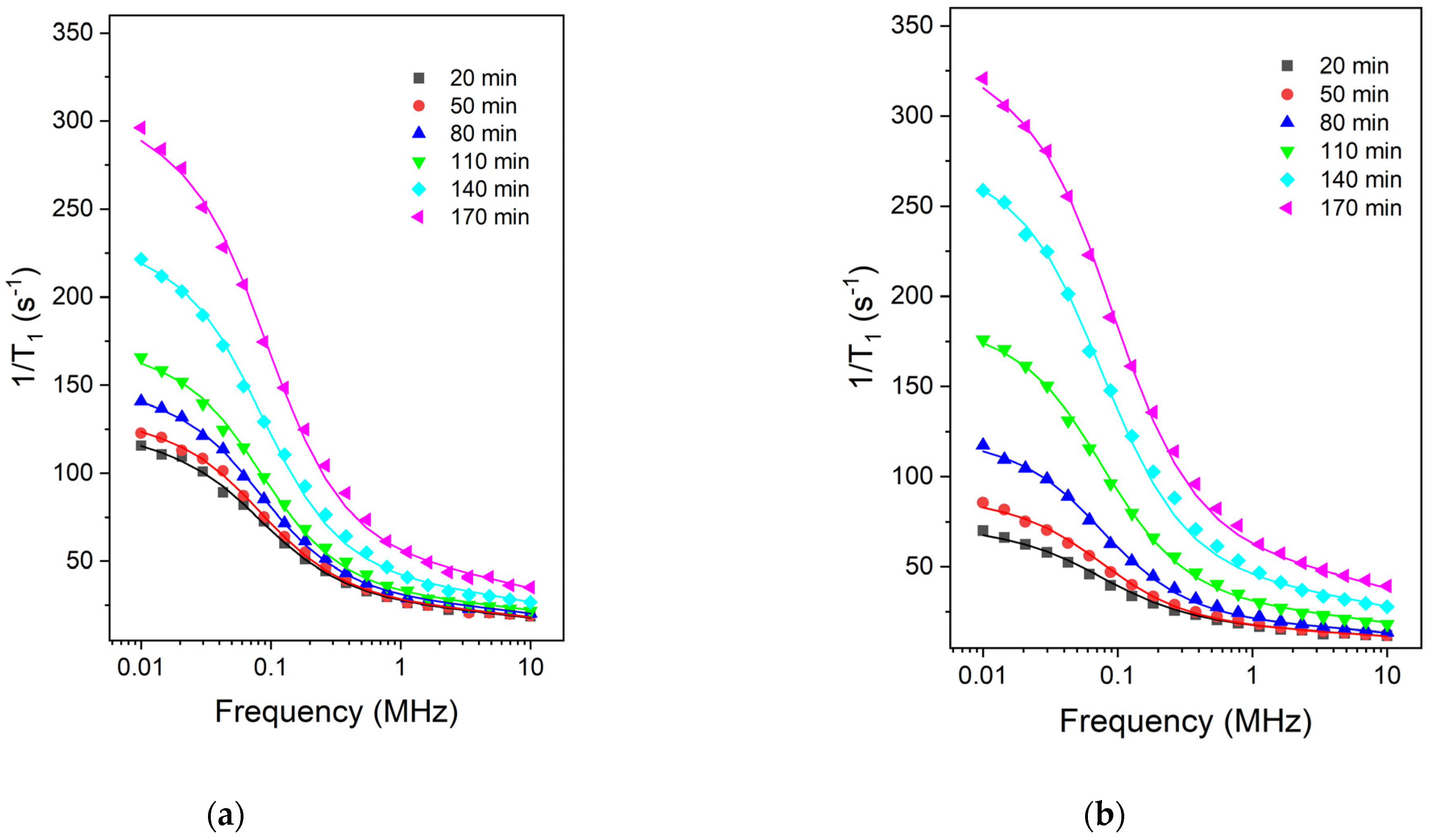
2. Results and Discussions
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Sample Preparation
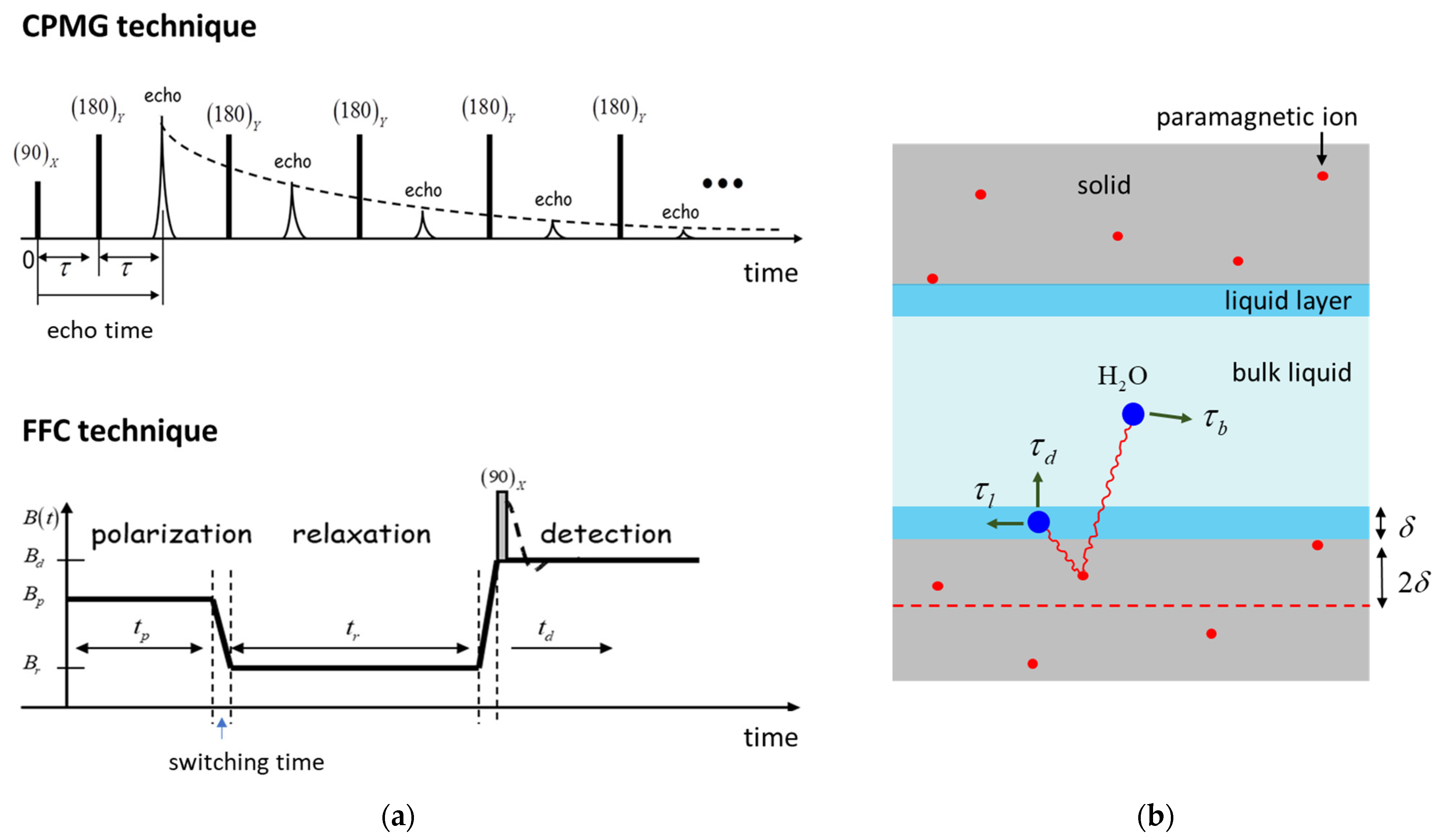
3.2. The NMR Methodology
3.3. The Relaxation Model
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Bos, F.; Wolfs, R.; Ahmed, Z.; Salet, T. Additive Manufacturing of Concrete in Construction: Potentials and Challenges of 3D Concrete Printing. Virtual Phys. Prototyp. 2016, 11, 209–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badea, C.; Pop, A.; Mattea, C.; Stapf, S.; Ardelean, I. The Effect of Curing Temperature on Early Hydration of Gray Cement via Fast Field Cycling-NMR Relaxometry. Appl. Magn. Reson. 2014, 45, 1299–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alesiani, M.; Pirazzoli, I.; Maraviglia, B. Factors Affecting Early-Age Hydration of Ordinary Portland Cement Studied by NMR: Fineness, Water-to-Cement Ratio and Curing Temperature. Appl. Magn. Reson. 2007, 32, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Yao, W.; Stephan, D. Preparation of Calcium Silicate Hydrate Seeds by Means of Mechanochemical Method and Its Effect on the Early Hydration of Cement. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2019, 11, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aïtcin, P.C. Accelerators. In Science and Technology of Concrete Admixtures; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2016; pp. 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorn, T.; Blask, O.; Stephan, D. Acceleration of Cement Hydration—A Review of the Working Mechanisms, Effects on Setting Time, and Compressive Strength Development of Accelerating Admixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 323, 126554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaidis, J.M. Chemistry of Corrosion Inhibitors. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2004, 26, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchon, D.; Flatt, R.J. Science and Technology of Concrete Admixtures; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; ISBN 9780081006931. [Google Scholar]
- Bullard, J.W.; Jennings, H.M.; Livingston, R.A.; Nonat, A.; Scherer, G.W.; Schweitzer, J.S.; Scrivener, K.L.; Thomas, J.J. Mechanisms of Cement Hydration. Cem. Concr. Res. 2011, 41, 1208–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scrivener, K.; Ouzia, A.; Juilland, P.; Kunhi Mohamed, A. Advances in Understanding Cement Hydration Mechanisms. Cem. Concr. Res. 2019, 124, 105823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juilland, P.; Nicoleau, L.; Arvidson, R.S.; Gallucci, E. Advances in Dissolution Understanding and Their Implications for Cement Hydration. RILEM Tech. Lett. 2017, 2, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scrivener, K.L.; Juilland, P.; Monteiro, P.J.M. Advances in Understanding Hydration of Portland Cement. Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 78, 38–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gartner, E.M.; Jennings, H.M. Thermodynamics of Calcium Silicate Hydrates and Their Solutions. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1987, 70, 743–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennings, H.M.; Pratt, P.L. An Experimental Argument for the Existence of a Protective Membrane Surrounding Portland Cement during the Induction Period. Cem. Concr. Res. 1979, 9, 501–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juilland, P.; Gallucci, E.; Flatt, R.; Scrivener, K. Dissolution Theory Applied to the Induction Period in Alite Hydration. Cem. Concr. Res. 2010, 40, 831–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matschei, T.; Lothenbach, B.; Glasser, F.P. The AFm Phase in Portland Cement. Cem. Concr. Res. 2007, 37, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balonis, M.; Mędala, M.; Glasser, F.P. Influence of Calcium Nitrate and Nitrite on the Constitution of AFm and AFt Cement Hydrates. Adv. Cem. Res. 2011, 23, 129–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawlicki, M.; Nocuń-Wczelik, W.; Bąk, Ł. Calorimetry in the Studies of Cement Hydration: Setting and Hardening of Portland Cement-Calcium Aluminate Cement Mixtures. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2010, 100, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scrivener, K.L.; Füllmann, T.; Gallucci, E.; Walenta, G.; Bermejo, E. Quantitative Study of Portland Cement Hydration by X-Ray Diffraction/Rietveld Analysis and Independent Methods. Cem. Concr. Res. 2004, 34, 1541–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, R.A.; Hover, K.C. Mercury Porosimetry of Cement-Based Materials and Associated Correction Factors. Constr. Build. Mater. 1993, 7, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stutzman, P. Scanning Electron Microscopy Imaging of Hydraulic Cement Microstructure. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2004, 26, 957–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamantopoulos, G.; Katsiotis, M.; Fardis, M.; Karatasios, I.; Alhassan, S.; Karagianni, M.; Papavassiliou, G.; Hassan, J. The Role of Titanium Dioxide on the Hydration of Portland Cement: A Combined NMR and Ultrasonic Study. Molecules 2020, 25, 5364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusu, M.M.; Vilau, C.; Dudescu, C.; Pascuta, P.; Popa, F.; Ardelean, I. Characterization of the Influence of an Accelerator upon the Porosity and Strength of Cement Paste by Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Relaxometry. Anal. Lett. 2022, 56, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardelean, I. The Effect of an Accelerator on Cement Paste Capillary Pores: NMR Relaxometry Investigations. Molecules 2021, 26, 5328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Faure, P.; Thiéry, M.; Baroghel-Bouny, V. 1H NMR Relaxometry as an Indicator of Setting and Water Depletion during Cement Hydration. Cem. Concr. Res. 2013, 45, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pop, A.; Badea, C.; Ardelean, I. The Effects of Different Superplasticizers and Water-to-Cement Ratios on the Hydration of Gray Cement Using T2-NMR. Appl. Magn. Reson. 2013, 44, 1223–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meiboom, S.; Gill, D. Modified Spin-Echo Method for Measuring Nuclear Relaxation Times. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1958, 29, 688–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimmich, R.; Anoardo, E. Field-Cycling NMR Relaxometry. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 2004, 44, 257–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korb, J.-P.; Monteilhet, L.; McDonald, P.J.; Mitchell, J. Microstructure and Texture of Hydrated Cement-Based Materials: A Proton Field Cycling Relaxometry Approach. Cem. Concr. Res. 2007, 37, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardelean, I. Applications of Field-Cycling NMR Relaxometry to Cement Materials. In Field-Cycling NMR Relaxometry: Instrumentation, Model Theories and Applications; Kimmich, R., Ed.; Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2019; pp. 462–488. [Google Scholar]
- Faux, D.A.; Mcdonald, P.J.; Howlett, N.C. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Relaxation Due to the Translational Diffusion of Fluid Confined to Quasi-Two-Dimensional Pores. Phys. Rev. E 2017, 95, 033116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faux, D.A.; McDonald, P.J. A Model for the Interpretation of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spin-Lattice Dispersion Measurements on Mortar, Plaster Paste, Synthetic Clay and Oil-Bearing Shale. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2018, 269, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faux, D.A.; McDonald, P.J. Explicit Calculation of Nuclear-Magnetic-Resonance Relaxation Rates in Small Pores to Elucidate Molecular-Scale Fluid Dynamics. Phys. Rev. E 2017, 95, 033117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faux, D.A.; McDonald, P.J. Nuclear-Magnetic-Resonance Relaxation Rates for Fluid Confined to Closed, Channel, or Planar Pores. Phys. Rev. E 2018, 98, 063110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faux, D.; Kogon, R.; Bortolotti, V.; McDonald, P. Advances in the Interpretation of Frequency-Dependent Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Measurements from Porous Material. Molecules 2019, 24, 3688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkataramanan, L.; Song, Y.-Q.; Hurlimann, M.D. Solving Fredholm Integrals of the First Kind with Tensor Product Structure in 2 and 2.5 Dimensions. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2002, 50, 1017–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provencher, S.W. CONTIN: A General Purpose Constrained Regularization Program for Inverting Noisy Linear Algebraic and Integral Equations. Comput. Phys. Commun. 1982, 27, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bede, A.; Scurtu, A.; Ardelean, I. NMR Relaxation of Molecules Confined inside the Cement Paste Pores under Partially Saturated Conditions. Cem. Concr. Res. 2016, 89, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogon, R.; Faux, D. 3TM: Software for the 3-Tau Model. SoftwareX 2022, 17, 100979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogon, R.; Faux, D. 3TM: Fitting Software for Fast Field Cycling NMR Dispersion Date. Available online: https://zenodo.org/record/5774107#.Y7UXsBVByUk (accessed on 14 May 2022). [CrossRef]
- Stepišnik, J.; Ardelean, I. Usage of Internal Magnetic Fields to Study the Early Hydration Process of Cement Paste by MGSE Method. J. Magn. Reson. 2016, 272, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielinski, L.J. Effect of Internal Gradients in the Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Measurement of the Surface-to-Volume Ratio. J. Chem. Phys. 2004, 121, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rusu, M.M.; Faux, D.; Ardelean, I. Monitoring the Effect of Calcium Nitrate on the Induction Period of Cement Hydration via Low-Field NMR Relaxometry. Molecules 2023, 28, 476. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28020476
Rusu MM, Faux D, Ardelean I. Monitoring the Effect of Calcium Nitrate on the Induction Period of Cement Hydration via Low-Field NMR Relaxometry. Molecules. 2023; 28(2):476. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28020476
Chicago/Turabian StyleRusu, Mihai M., David Faux, and Ioan Ardelean. 2023. "Monitoring the Effect of Calcium Nitrate on the Induction Period of Cement Hydration via Low-Field NMR Relaxometry" Molecules 28, no. 2: 476. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28020476
APA StyleRusu, M. M., Faux, D., & Ardelean, I. (2023). Monitoring the Effect of Calcium Nitrate on the Induction Period of Cement Hydration via Low-Field NMR Relaxometry. Molecules, 28(2), 476. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28020476







