Functionalized Calixarenes as Promising Antibacterial Drugs to Face Antimicrobial Resistance
Abstract
:1. Introduction/Context
2. Objectives of this Review
3. Bibliographic Search
4. Summary Description of the Structure of Calixarenes
5. Overview of Functionalization of Calix[4]arene
6. Cytotoxicity of Calix[n]arenes
7. Antibacterial Activities of Calix[n]arenes
7.1. Intrinsically Active Calixarenes
7.2. Molecular Carrier/Drug Delivery
7.3. Complexes
8. Outlook
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chinemerem Nwobodo, D.; Ugwu, M.C.; Oliseloke Anie, C.; Al-Ouqaili, M.T.S.; Chinedu Ikem, J.; Victor Chigozie, U.; Saki, M. Antibiotic Resistance: The Challenges and Some Emerging Strategies for Tackling a Global Menace. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2022, 36, e24655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coque, T.M.; Cantón, R.; Pérez-Cobas, A.E.; Fernández-de-Bobadilla, M.D.; Baquero, F. Antimicrobial Resistance in the Global Health Network: Known Unknowns and Challenges for Efficient Responses in the 21st Century. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayukekbong, J.A.; Ntemgwa, M.; Atabe, A.N. The Threat of Antimicrobial Resistance in Developing Countries: Causes and Control Strategies. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2017, 6, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutescu, I.A.; Hillier, S.A. Encouraging the Development of New Antibiotics: Are Financial Incentives the Right Way Forward? A Systematic Review and Case Study. Infect Drug Resist. 2021, 14, 415–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miethke, M.; Pieroni, M.; Weber, T.; Brönstrup, M.; Hammann, P.; Halby, L.; Arimondo, P.B.; Glaser, P.; Aigle, B.; Bode, H.B.; et al. Towards the Sustainable Discovery and Development of New Antibiotics. Nat Rev Chem 2021, 5, 726–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO | Worldwide Country Situation Analysis: Response to Antimicrobial Resistance. WHO. Available online: http://www.who.int/drugresistance/documents/situationanalysis/en/ (accessed on 23 September 2020).
- Salam, M.A.; Al-Amin, M.Y.; Salam, M.T.; Pawar, J.S.; Akhter, N.; Rabaan, A.A.; Alqumber, M.A.A. Antimicrobial Resistance: A Growing Serious Threat for Global Public Health. Healthcare 2023, 11, 1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reygaert, W.C. An Overview of the Antimicrobial Resistance Mechanisms of Bacteria. AIMS Microbiol 2018, 4, 482–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaïbi, K.; Jaureguy, F.; Do Rego, H.; Ruiz, P.; Mory, C.; El Helali, N.; Mrabet, S.; Mizrahi, A.; Zahar, J.-R.; Pilmis, B. What to Do with the New Antibiotics? Antibiotics 2023, 12, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed Ahmed, M.A.E.-G.; Zhong, L.-L.; Shen, C.; Yang, Y.; Doi, Y.; Tian, G.-B. Colistin and Its Role in the Era of Antibiotic Resistance: An Extended Review (2000–2019). Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 868–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antibacterial Agents in Clinical Development: An Analysis of the Antibacterial Clinical Development Pipeline. WHO. 2019. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications-detail-redirect/9789240000193 (accessed on 23 September 2020).
- Duval, R.E.; Grare, M.; Demoré, B. Fight Against Antimicrobial Resistance: We Always Need New Antibacterials but for Right Bacteria. Molecules 2019, 24, 3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, E.Y.; Van Boeckel, T.P.; Martinez, E.M.; Pant, S.; Gandra, S.; Levin, S.A.; Goossens, H.; Laxminarayan, R. Global Increase and Geographic Convergence in Antibiotic Consumption between 2000 and 2015. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E3463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neill, J. Publications | AMR Review. Available online: http://amr-review.org/sites/default/files/160518_Final%20paper_with%20cover.pdf (accessed on 23 September 2020).
- Azzi, J.; Jraij, A.; Auezova, L.; Fourmentin, S.; Greige-Gerges, H. Novel Findings for Quercetin Encapsulation and Preservation with Cyclodextrins, Liposomes, and Drug-in-Cyclodextrin-in-Liposomes. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 81, 328–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, P.S.S.; Lucchese, A.M.; Araújo-Filho, H.G.; Menezes, P.P.; Araújo, A.A.S.; Quintans-Júnior, L.J.; Quintans, J.S.S. Inclusion of Terpenes in Cyclodextrins: Preparation, Characterization and Pharmacological Approaches. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 151, 965–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.-D.; Guo, Y.-F.; Zhang, J.-Q.; Yang, Z.-K.; Li, X.; Yang, B.; Yang, R. Inclusion of Lycorine with Natural Cyclodextrins (α-, β- and γ-CD): Experimental and in Vitro Evaluation. J. Mol. Struct. 2017, 1130, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avilés-Moreno, J.R.; Berden, G.; Oomens, J.; Martínez-Haya, B. Complexes of Crown Ether Macrocycles with Methyl Guanidinium: Insights into the Capture of Charge in Peptides. ChemPhysChem 2018, 19, 2169–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, A.; Barman, B.K.; Mahato, B.; Rahaman, H.; Roy, M.N. Study to Explore Complexation of Crown Ether with Antidepressant Drug Prevalent in Aqueous System by Physicochemical Contrivance. Indian J. Adv. Chem. Sci. 2018, 6, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barman, S.; Yasmin, A.; Roy, M.N. Interactions of an Antifungal Sulfa Drug with Diverse Macrocyclic Polyethers Explaining Mechanism, Performance and Physiognomies Leading to Formation of Stable Complexes. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 243, 420–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, S.K.; Modi, N.R.; Mistry, B.; Joshi, K. Improvement of Some Pharmaceutical Properties of Mycophenolate Mofetil (MMF) by Para Sulphonatocalix[4]Resorcinarene Inclusion Complex. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2011, 70, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syakaev, V.V.; Morozova, J.E.; Bogdanov, A.V.; Shalaeva, Y.V.; Ermakova, A.M.; Voloshina, A.D.; Zobov, V.V.; Nizameev, I.R.; Kadirov, M.K.; Mironov, V.F.; et al. Solubilization of Azo-Dye-Modified Isatin Derivative by Amphiphilic Carboxyresorcinarenes: The Effect of Macrocycle Structure on the Supramolecular Association. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 553, 368–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botta, B.; Fraschetti, C.; Novara, F.R.; Tafi, A.; Sacco, F.; Mannina, L.; Sobolev, A.P.; Mattay, J.; Letzel, M.C.; Speranza, M. Interactions of Vinca Alkaloid Subunits with Chiral Amido[4]Resorcinarenes: A Dynamic, Kinetic, and Spectroscopic Study. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2009, 7, 1798–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, J.; Song, K.; Wang, H.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, T. Study on the Inclusion Interaction of P-Sulfonatocalix[n]Arenes with Norfloxacin. Phys. Chem. Liq. 2017, 55, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seridi, L.; Boufelfel, A.; Soltani, S. Structural, Electronic and QTAIM Analysis of Host-Guest Interaction of Warfarin with β-Cyclodextrin and Calix[4]Arene. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 221, 885–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meenakshi, C.; Jayabal, P.; Ramakrishnan, V. Molecular Recognition Study of Carbamazepine, Antiseizure Drug, by p-t-Butyl Calix(8)Arene. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2014, 122, 447–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, K.; Badshah, S.L.; Ahmad, N.; Rashid, H.U.; Mabkhot, Y. Inclusion Complexes of a New Family of Non-Ionic Amphiphilic Dendrocalix[4]Arene and Poorly Water-Soluble Drugs Naproxen and Ibuprofen. Molecules 2017, 22, 783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehra, C.; Gala, R.; Kakatkar, A.; Kumar, V.; Khurana, R.; Chatterjee, S.; Kumar, N.N.; Barooah, N.; Bhasikuttan, A.C.; Mohanty, J. Cooperative Enhancement of Antibacterial Activity of Sanguinarine Drug through p-Sulfonatocalix[6]Arene Functionalized Silver Nanoparticles. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 14275–14278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.J.; Shee, N.K.; Son, J.-I.; Karthikeyan, S.; Jhee, K.-H.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, H.-J. Supramolecular Complexation of Homocysteine and Cysteine with Cucurbit[7]Uril. Supramol. Chem. 2019, 31, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.; Soni, V.K.; Choudhary, G.; Sharma, P.R.; Sharma, R.K. Understanding Behaviour of Vitamin-C Guest Binding with the Cucurbit[6]Uril Host. Supramol. Chem. 2017, 29, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yin, H.; Martinz, G.; Wyman, I.W.; Bardelang, D.; Macartney, D.H.; Wang, R. Supramolecular Encapsulation of Benzocaine and Its Metabolite Para-Aminobenzoic Acid by Cucurbit[7]Uril. New J. Chem. 2016, 40, 3484–3490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Shuai, X.; Bin, L.; Ren, K.; Jiang, X.; Chen, H.; Hu, S.; Cai, Z. P-Nitro-Tetradecyloxy-Calix[4]Arene as a Highly Selective Stationary Phase for Gas Chromatographic Separations. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 16960–16967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Qi, L.; Li, W.; Li, Y.; Shuai, X.; Cai, Z.; Chen, H.; Qiao, X.; Ma, L. Amphiphilic Calix[4]Arenes as a Highly Selective Gas Chromatographic Stationary Phase for Aromatic Amine Isomers. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1601, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Zhang, W.; Yang, H.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, W.; Yu, A.; Zhang, S. Calixarene Ionic Liquid Modified Silica Gel: A Novel Stationary Phase for Mixed-Mode Chromatography. Talanta 2016, 152, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahojb Noruzi, E.; Molaparast, M.; Zarei, M.; Shaabani, B.; Kariminezhad, Z.; Ebadi, B.; Shafiei-Irannejad, V.; Rahimi, M.; Pietrasik, J. Para-Sulfonatocalix[n]Arene-Based Biomaterials: Recent Progress in Pharmaceutical and Biological Applications. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 190, 112121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahimi, M.; Karimian, R.; Noruzi, E.B.; Ganbarov, K.; Zarei, M.; Kamounah, F.S.; Yousefi, B.; Bastami, M.; Yousefi, M.; Kafil, H.S. Needle-Shaped Amphoteric Calix[4]Arene as a Magnetic Nanocarrier for Simultaneous Delivery of Anticancer Drugs to the Breast Cancer Cells. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 2619–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahmy, S.A.; Ponte, F.; Abd El-Rahman, M.K.; Russo, N.; Sicilia, E.; Shoeib, T. Investigation of the Host-Guest Complexation between 4-Sulfocalix[4]Arene and Nedaplatin for Potential Use in Drug Delivery. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2018, 193, 528–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauerhof, D.; Niemeyer, J. Functionalized Macrocycles in Supramolecular Organocatalysis. ChemPlusChem 2020, 85, 889–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peramo, A.; Abdellah, I.; Pecnard, S.; Mougin, J.; Martini, C.; Couvreur, P.; Huc, V.; Desmaële, D. A Self-Assembling NHC-Pd-Loaded Calixarene as a Potent Catalyst for the Suzuki-Miyaura Cross-Coupling Reaction in Water. Molecules 2020, 25, 1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-X.; Yang, J.; Xu, X.; Ma, J.-F. Highly Stable Copper(I)–Thiacalix[4]Arene-Based Frameworks for Highly Efficient Catalysis of Click Reactions in Water. Chem. A Eur. J. 2019, 25, 16660–16667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, L.-J.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Xu, G.-H.; Ma, J.-F. Calix[4]Arene-Based Polyoxometalate Organic–Inorganic Hybrid and Coordination Polymer as Heterogeneous Catalysts for Azide–Alkyne Cycloaddition and Knoevenagel Condensation Reaction. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 15871–15878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhuang, S. Cesium Separation from Radioactive Waste by Extraction and Adsorption Based on Crown Ethers and Calixarenes. Nucl. Eng. Technol. 2020, 52, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtari, B.; Pourabdollah, K.; Dallali, N. A Review of Calixarene Applications in Nuclear Industries. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2011, 287, 921–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrin, R.; Lamartine, R.; Perrin, M. The Potential Industrial Applications of Calixarenes. Pure Appl. Chem. 1993, 65, 1549–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, T.; Ashraf, P.M.; Srinives, S.; Mulchandani, A. Calixarene-Functionalized Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes for Sensitive Detection of Volatile Amines. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 268, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdemir, S.; Tabakci, B.; Tabakci, M. A Highly Selective Fluorescent Sensor Based on Calix[4]Arene Appended Benzothiazole Units for Cu2+, S2− and HSO4− Ions in Aqueous Solution. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 228, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.-K.; Ikejiri, Y.; Jin, C.-C.; Wu, C.; Zhao, J.-L.; Ni, X.-L.; Zeng, X.; Redshaw, C.; Yamato, T. Synthesis and Evaluation of a Novel Fluorescent Sensor Based on Hexahomotrioxacalix[3]Arene for Zn2+ and Cd2+. Tetrahedron 2016, 72, 4854–4858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohto, K.; Fuchiwaki, N.; Yoshihara, T.; Chetry, A.B.; Morisada, S.; Kawakita, H. Extraction of Scandium and Other Rare Earth Elements with a Tricarboxylic Acid Derivative of Tripodal Pseudcalix[3]Arene Prepared from a New Phenolic Tripodal Framework. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 226, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morohashi, N.; Iijima, S.; Akasaka, K.; Hattori, T. Selective Extraction of Pd(II) by p-Tert-Butylcalix[4]Arenedicarboxylic Acid. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 2231–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konczyk, J.; Nowik-Zajac, A.; Kozlowski, C.A. Calixarene-Based Extractants for Heavy Metal Ions Removal from Aqueous Solutions. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 2394–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeyer, A. Ueber Die Verbindungen Der Aldehyde Mit Den Phenolen. Berichte Der Dtsch. Chem. Ges. 1872, 5, 280–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeyer, A. Ueber Die Verbindungen Der Aldehyde Mit Den Phenolen Und Aromatischen Kohlenwasserstoffen. Berichte Der Dtsch. Chem. Ges. 1872, 5, 1094–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niederl, J.B.; Vogel, H.J. Aldehyde—Resorcinol Condensations1. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1940, 62, 2512–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinke, A.; Ziegler, E. Zur Kenntnis Des Härtungsprozesses von Phenol-Formaldehyd-Harzen. V. Mitteilung. Berichte Der Dtsch. Chem. Ges. (A B Ser.) 1941, 74, 541–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutsche, C.D.; Muthukrishnan, R. Calixarenes. 1. Analysis of the Product Mixtures Produced by the Base-Catalyzed Condensation of Formaldehyde with Para-Substituted Phenols. J. Org. Chem. 1978, 43, 4905–4906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutsche, C.D. Calixarenes Revisited; Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arduini, A.; Pochini, A.; Raverberi, S.; Ungaro, R. P-t-Butyl-Calix[4]Arene Tetracarboxylic Acid. A Water Soluble Calixarene in a Cone Structure. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1984, 15, 981–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutsche, C.D.; Alam, I. Calixarenes. 23. the Complexation and Catalytic Properties of Water Soluble Calixarenes. Tetrahedron 1988, 44, 4689–4694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinkai, S.; Mori, S.; Tsubaki, T.; Sone, T.; Manabe, O. New Water-Soluble Host Molecules Derived from Calix[6]Arene. Tetrahedron Lett. 1984, 25, 5315–5318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinkai, S.; Araki, K.; Tsubaki, T.; Arimura, T.; Manabe, O. New Syntheses of Calixarene-p-Sulphonates and p-Nitrocalixarenes. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1987, 1, 2297–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiji, S.; Seiichi, M.; Hiroshi, K.; Takayuki, T.; Osamu, M. Hexasulfonated Calix[6]Arene Derivatives: A New Class of Catalysts, Surfactants, and Host Molecules. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1986, 108, 2409–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinkai, S.; Mori, S.; Koreishi, H.; Tsubaki, T.; Manabe, O. Chloromethylation of Calixarenes and Synthesis of New Water Soluble Macrocyclic Hosts. Tetrahedron 1989, 45, 2177–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutsche, C.D.; Iqbal, M.; Nam, K.S.; See, K.; Alam, I. Conformational and Complexational Characteristics of Calixarenes. Pure Appl. Chem. 1988, 60, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutsche, C.D.; Nam, K. Chun. Calixarenes. 22. Synthesis, Properties, and Metal Complexation of Aminocalixarenes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1988, 110, 6153–6162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohseto, F.; Murakami, H.; Araki, K.; Shinkai, S. Substitution of OH with NH2 Calix[4]Arenes: An Approach to the Synthesis of Aminocalixarenes. Tetrahedron Lett. 1992, 33, 1217–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleksiuk, O.; Grynszpan, F.; Biali, S.E. Spirodienone Route for Aminodehydroxylation: Monoaminotrihydroxy-p-Tert-Butylcalix[4]Arene. J. Org. Chem. 1993, 58, 1994–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marra, A.; Dondoni, A.; Sansone, F. Calixsugars:† Preparation of Upper Rim O-Ketopyranosyl Calix[4]Arenes. J. Org. Chem. 1996, 61, 5155–5158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dondoni, A.; Kleban, M.; Marra, A. The Assembly of Carbon-Linked Calixarene-Carbohydrate Structures (C-Calixsugars) by Multiple Wittig Olefination. Tetrahedron Lett. 1997, 38, 7801–7804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newkome, G.R.; Hu, Y.; Saunders, M.J.; Fronczek, F.R. Silvanols: Water-Soluble Calixarenes. Tetrahedron Lett. 1991, 32, 1133–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Koch, H.F.; Roundhill, D.M. Synthesis and Characterization of Calix[4]Arene Functionalized Poly(Ethylene Glycol) Derivatives. J. Incl. Phenom. 2000, 38, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudic, M.; Colombo, A.; Sansone, F.; Casnati, A.; Donofrio, G.; Ungaro, R. A General Synthesis of Water Soluble Upper Rim Calix[n]Arene Guanidinium Derivatives Which Bind to Plasmid DNA. Tetrahedron 2004, 60, 11613–11618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourer, M.; Duval, R.E.; Finance, C.; Regnouf-de-Vains, J.-B. Functional Organisation and Gain of Activity: The Case of the Antibacterial Tetra-Para-Guanidinoethyl-Calix[4]Arene. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2006, 16, 2960–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutsche, C.D.; Pagoria, P.F. Calixarenes. 16. Functionalized Calixarenes: The Direct Substitution Route. J. Org. Chem. 1985, 50, 5795–5802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conner, M.; Janout, V.; Regen, S.L. Synthesis and Alkali Metal Binding Properties of “Upper Rim” Functionalized Calix[4]Arenes. J. Org. Chem. 1992, 57, 3744–3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verboom, W.; Durie, A.; Egberink, R.J.M.; Asfari, Z.; Reinhoudt, D.N. Ipso Nitration of P-Tert-Butylcalix[4]Arenes. J. Org. Chem. 1992, 57, 1313–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redon, S.; Li, Y.; Reinaud, O. Unprecedented Selective Ipso-Nitration of Calixarenes Monitored by the O-Substituents. J. Org. Chem. 2003, 68, 7004–7008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcillac, A.; Choquard, P.; Vains, J.-B.R.D.; Lamartine, R. Process for the Dealkylating Sulfonation of P-Alkyl Calixarenes. CA2258904A1, 31 December 1997. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/CA2258904A1/en (accessed on 21 September 2023).
- Arduini, A.; Manfredi, G.; Pochini, A.; Sicuri, A.R.; Ungaro, R. Selective Formylation of Calix[4]Arenes at the ‘Upper Rim’ and Synthesis of New Cavitands. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1991, 14, 936–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Loon, J.D.; Arduini, A.; Coppi, L.; Verboom, W.; Pochini, A.; Ungaro, R.; Harkema, S.; Reinhoudt, D.N. Selective Functionalization of Calix[4]Arenes at the Upper Rim. J. Org. Chem. 1990, 55, 5639–5646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Loon, J.-D.; Arduini, A.; Verboom, W.; Ungaro, R.; van Hummel, G.J.; Harkema, S.; Reinhoudt, D.N. Selective Functionalization of Calix[4]Arenes at the Upper Rim. Tetrahedron Lett. 1989, 30, 2681–2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutsche, C.D.; Dhawan, B.; Levine, J.A.; Hyun No, K.; Bauer, L.J. Calixarenes 9: Conformational Isomers of the Ethers and Esters of Calix[4]Arenes. Tetrahedron 1983, 39, 409–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araki, K.; Iwamoto, K.; Shinkai, S.; Matsuda, T. “pKa” of Calixarenes and Analogs in Nonaqueous Solvents. BCSJ 1990, 63, 3480–3485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Loon, J.D.; Kraft, D.; Ankone, M.J.K.; Verboom, W.; Harkema, S.; Vogt, W.; Boehmer, V.; Reinhoudt, D.N. Calix[4]Arenes Bridged at the Lower Rim. J. Org. Chem. 1990, 55, 5176–5179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arduini, A.; Casnati, A.; Dodi, L.; Pochini, A.; Ungaro, R. Selective 1,2-Functionalization of Calix[4]Arenes at the Lower Rim. Synthesis of a New Type of Bis-Calixcrown Ether. J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun. 1990, 22, 1597–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groenen, L.C.; Ruël, B.H.M.; Casnati, A.; Timmerman, P.; Verboom, W.; Harkema, S.; Pochini, A.; Ungaro, R.; Reinhoudt, D.N. Syn-1,2-Dialkylated Calix[4]Arenes: General Intermediates in the NaH/DMF Tetraalkylation of Calix[4]Arenes. Tetrahedron Lett. 1991, 32, 2675–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- See, K.A.; Fronczek, F.R.; Watson, W.H.; Kashyap, R.P.; Gutsche, C.D. Calixarenes. 26. Selective Esterification and Selective Ester Cleavage of Calix[4]Arenes. J. Org. Chem. 1991, 56, 7256–7268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwamoto, K.; Araki, K.; Shinkai, S. Syntheses of All Possible Conformational Isomers of O-Alkyl-p-t-Butylcalix[4]Arenes. Tetrahedron 1991, 47, 4325–4342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunink, J.A.J.; Verboom, W.; Engbersen, J.F.J.; Reinhoudt, D.N.; Harkema, S. Synthesis and Cation Complexation Selectivity of Bis(Syn-Proximally) Functionalized Calix[4]Arenes. Recl. Des Trav. Chim. Des Pays Bas 1992, 111, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.; Mangiafico, T.; Gutsche, C.D. Calixarenes 21: The Conformations and Structures of the Products of Aroylation of the, Calix[4]Arenes. Tetrahedron 1987, 43, 4917–4930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottino, F.; Giunta, L.; Pappalardo, S. Calix[4]Arenes with Pyridine Pendant Groups. Regioselective Proximal Alkylation at the “Lower Rim”. J. Org. Chem. 1989, 54, 5407–5409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwamoto, K.; Fujimoto, K.; Matsuda, T.; Shinkai, S. Remarkable Metal Template Effects on Selective Syntheses of P-t-Butylcalix[4]Arene Conformers. Tetrahedron Lett. 1990, 31, 7169–7172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutsche, C.D.; Reddy, P.A. Calixarenes. 25. Conformations and Structures of the Products of Arylmethylation of Calix[4]Arenes. J. Org. Chem. 1991, 56, 4783–4791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perret, F.; Lazar, A.N.; Coleman, A.W. Biochemistry of the Para-Sulfonato-Calix[n]Arenes. Chem. Commun. 2006, 23, 2425–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perret, F.; Coleman, A.W. Biochemistry of Anionic Calix[n]Arenes. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 7303–7319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, E.; Shahgaldian, P.; Coleman, A.W. Haemolytic Properties of Some Water-Soluble Para-Sulphonato-Calix-[n]-Arenes. Int. J. Pharm. 2004, 273, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memmi, L.; Lazar, A.; Brioude, A.; Ball, V.; Coleman, A.W. Protein–Calixarene Interactions: Complexation of Bovine Serum Albumin by Sulfonatocalix[n]Arenes. Chem. Commun. 2001, 23, 2474–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paclet, M.-H.; Rousseau, C.F.; Yannick, C.; Morel, F.; Coleman, A.W. An Absence of Non-Specific Immune Response towards Para-Sulphonato-Calix[n]Arenes. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2006, 55, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, A.W.; Jebors, S.; Cecillon, S.; Perret, P.; Garin, D.; Marti-Battle, D.; Moulin, M. Toxicity and Biodistribution of Para-Sulfonato-Calix[4]Arene in Mice. New J. Chem. 2008, 32, 780–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheate, N.J.; Abbott, G.M.; Tate, R.J.; Clements, C.J.; Edrada-Ebel, R.; Johnston, B.F. Side-on Binding of p-Sulphonatocalix[4]Arene to the Dinuclear Platinum Complex Trans-[{PtCl(NH3)2}2μ-Dpzm]2+ and Its Implications for Anticancer Drug Delivery. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2009, 103, 448–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geller, C.; Fontanay, S.; Mourer, M.; Dibama, H.M.; Regnouf-de-Vains, J.-B.; Finance, C.; Duval, R.E. Antiseptic Properties of Two Calix[4]Arenes Derivatives on the Human Coronavirus 229E. Antivir. Res. 2010, 88, 343–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalor, R.; Baillie-Johnson, H.; Redshaw, C.; Matthews, S.E.; Mueller, A. Cellular Uptake of a Fluorescent Calix[4]Arene Derivative. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 2892–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourer, M.; Psychogios, N.; Laumond, G.; Aubertin, A.-M.; Regnouf-de-Vains, J.-B. Synthesis and Anti-HIV Evaluation of Water-Soluble Calixarene-Based Bithiazolyl Podands. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourer, M.; Duval, R.E.; Constant, P.; Daffé, M.; Regnouf-de-Vains, J.-B. Impact of Tetracationic Calix[4]Arene Conformation—From Conic Structure to Expanded Bolaform—On Their Antibacterial and Antimycobacterial Activities. ChemBioChem 2019, 20, 911–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mammen, M.; Choi, S.-K.; Whitesides, G.M. Polyvalent Interactions in Biological Systems: Implications for Design and Use of Multivalent Ligands and Inhibitors. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1998, 37, 2754–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasting, C.; Schalley, C.A.; Weber, M.; Seitz, O.; Hecht, S.; Koksch, B.; Dernedde, J.; Graf, C.; Knapp, E.-W.; Haag, R. Multivalency as a Chemical Organization and Action Principle. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 10472–10498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haag, R. Multivalency as a Chemical Organization and Action Principle. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2015, 11, 848–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giuliani, M.; Morbioli, I.; Sansone, F.; Casnati, A. Moulding Calixarenes for Biomacromolecule Targeting. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 14140–14159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornforth, J.W.; Hart, P.D.; Nicholls, G.A.; Rees, R.J.W.; Stock, J.A. Antituberculous Effects of Certain Surface-Active Polyoxyethylene Ethers. Br. J. Pharmacol. Chemother. 1955, 10, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornforth, J.W.; Morgan, E.D.; Potts, K.T.; Rees, R.J.W. Preparation of Antituberculous Polyoxyethylene Ethers of Homogeneous Structure. Tetrahedron 1973, 29, 1659–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
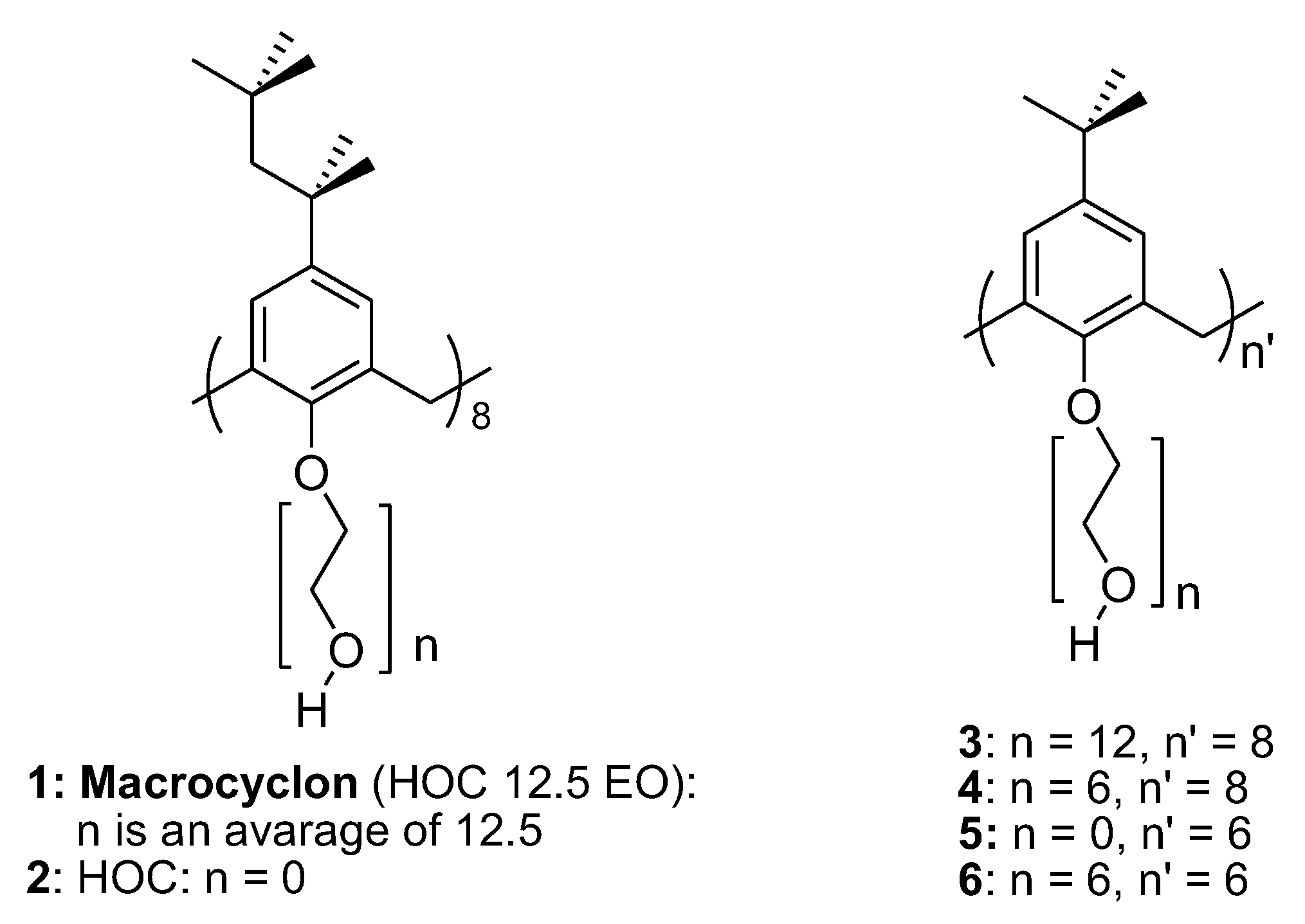
- Loiseau, F.A.; Hill, A.M.; (Mimi) Hii, K.K. Preparation of Macrocyclon Analogues: Calix[8]Arenes with Extended Polyethylene Glycol Chains. Tetrahedron 2007, 63, 9947–9959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, M.K.; Jahagirdar, D.V. Effect of Antituberculous Calixarenes on Phospholipase A2 Susceptibility and on Fusion of Phospholipid Bilayers. Biochem. J. 1985, 227, 789–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, P.D.; Armstrong, J.A.; Brodaty, E. Calixarenes with Host-Mediated Potency in Experimental Tuberculosis: Further Evidence That Macrophage Lipids Are Involved in Their Mechanism of Action. Infect. Immun. 1996, 64, 1491–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colston, M.J.; Hailes, H.C.; Stavropoulos, E.; Hervé, A.C.; Hervé, G.; Goodworth, K.J.; Hill, A.M.; Jenner, P.; Hart, P.D.; Tascon, R.E. Antimycobacterial Calixarenes Enhance Innate Defense Mechanisms in Murine Macrophages and Induce Control of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Infection in Mice. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 6318–6323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, S.J. Calixarene-Based Compounds Having Antibacterial, Antifungal, Anticancer-Hiv Activity. WO1995019974A2, 27 July 1995. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/WO1995019974A2/da (accessed on 23 September 2020).
- Casnati, A.; Fabbi, M.; Pelizzi, N.; Pochini, A.; Sansone, F.; Ungaro, R.; Di Modugno, E.; Tarzia, G. Synthesis, Antimicrobial Activity and Binding Properties of Calix[4]Arene Based Vancomycin Mimics. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 1996, 6, 2699–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frish, L.; Sansone, F.; Casnati, A.; Ungaro, R.; Cohen, Y. Complexation of a Peptidocalix[4]Arene, a Vancomycin Mimic, with Alanine-Containing Guests by NMR Diffusion Measurements. J. Org. Chem. 2000, 65, 5026–5030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casnati, A.; Sansone, F.; Ungaro, R. Peptido- and Glycocalixarenes: Playing with Hydrogen Bonds around Hydrophobic Cavities. Acc. Chem. Res. 2003, 36, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamartine, R.; Tsukada, M.; Wilson, D.; Shirata, A. Antimicrobial Activity of Calixarenes. Comptes Rendus Chim. 2002, 5, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouoit-Montésinos, S.; Vocanson, F.; Bassus, J.; Lamartine, R. Synthesis of New Calix[9]Arenes. Synth. Commun. 2000, 30, 911–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grare, M.; Mourer, M.; Fontanay, S.; Regnouf-de-Vains, J.-B.; Finance, C.; Duval, R.E. In Vitro Activity of Para-Guanidinoethylcalix[4]Arene against Susceptible and Antibiotic-Resistant Gram-Negative and Gram-Positive Bacteria. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2007, 60, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grare, M.; Mourer, M.; Regnouf de Vains, J.-B.; Finance, C.; Duval, R.-E. Vers de nouvelles molécules antibactériennes. Intérêt du para-guanidinoéthylcalix[4]arène. Pathol. Biol. 2006, 54, 470–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grare, M.; Dibama, H.M.; Lafosse, S.; Ribon, A.; Mourer, M.; Regnouf-de-Vains, J.-B.; Finance, C.; Duval, R.E. Cationic Compounds with Activity against Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria: Interest of a New Compound Compared with Two Older Antiseptics, Hexamidine and Chlorhexidine. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2010, 16, 432–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grare, M.; Dague, E.; Mourer, M.; Regnouf-de-Vains, J.-B.; Finance, C.; Duval, J.-F.L.; Duval, R.-E.; Gaboriaud, F. Microélectrophorèse et microscopie à force atomique: Deux nouveaux outils d’évaluation de l’effet pariétal d’antibactériens. Pathol. Biol. 2007, 55, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formosa, C.; Grare, M.; Jauvert, E.; Coutable, A.; Regnouf-de-Vains, J.B.; Mourer, M.; Duval, R.E.; Dague, E. Nanoscale Analysis of the Effects of Antibiotics and CX1 on a Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Multidrug-Resistant Strain. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grare, M.; Duval, R.-E. Use of Calixarenes Associated with an Antibiotic in the Treatment of Bacterial Infections. US2014066365, 6 March 2014. [Google Scholar]
- L’OMS Publie une Liste de Bactéries Contre Lesquelles il est Urgent D’avoir de Nouveaux Antibiotiques. WHO. Available online: https://www.who.int/fr/news-room/detail/27-02-2017-who-publishes-list-of-bacteria-for-which-new-antibiotics-are-urgently-needed (accessed on 23 September 2020).
- Korchowiec, B.; Gorczyca, M.; Rogalska, E.; Regnouf-de-Vains, J.-B.; Mourer, M.; Korchowiec, J. The Selective Interactions of Cationic Tetra-p-Guanidinoethylcalix[4]Arene with Lipid Membranes: Theoretical and Experimental Model Studies. Soft Matter. 2015, 12, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourer, M.; Dibama, H.M.; Fontanay, S.; Grare, M.; Duval, R.E.; Finance, C.; Regnouf-de-Vains, J.-B. P-Guanidinoethyl Calixarene and Parent Phenol Derivatives Exhibiting Antibacterial Activities. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 5496–5509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourer, M.; Fontanay, S.; Duval, R.E.; Regnouf-de-Vains, J.-B. Synthesis, Characterization, and Biological Evaluation as Antibacterial Agents of Water-Soluble Calix[4]Arenes and Phenol Derivatives Incorporating Carboxylate Groups. Helv. Chim. Acta 2012, 95, 1373–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.K.; Kanamathareddy, S.; Gutsche, C.D. Upper Rim Substitution of Calixarenes: Carboxylic Acids. Synthesis 1997, 1997, 1268–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourer, M.; Regnouf-de-Vains, J.-B. New Water-Soluble Calix[4]Arene-Based Bipyridyl Podands Incorporating Carboxylate Groups. Tetrahedron Lett. 2006, 47, 1895–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourer, M.; Massimba Dibama, H.; Constant, P.; Daffé, M.; Regnouf-de-Vains, J.-B. Anti-Mycobacterial Activities of Some Cationic and Anionic Calix[4]Arene Derivatives. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2012, 20, 2035–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memon, S.; Soomro, A.M.; Oad, R.K.; Qureshi, I. Bioactivity Assessment of Water Soluble Calix[4]Arene Derivative. Pak. J. Anal. Environ. Chem. 2012, 13, 39. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, M.B.; Modi, N.R.; Raval, J.P.; Menon, S.K. Calix[4]Arene Based 1,3,4-Oxadiazole and Thiadiazole Derivatives: Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2012, 10, 1785–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melezhyk, O.I.; Rodik, V.R.; Iavorska, V.N.; Klymchenko, S.A.; Mely, Y.; Shepelevych, V.V.; Skivka, M.L.; Kalchenko, I.V. Antibacterial Properties of Tetraalkylammonium and Imidazolium Tetraalkoxycalix[4]Arene Derivatives. AIA 2015, 13, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodik, R.V.; Klymchenko, A.S.; Jain, N.; Miroshnichenko, S.I.; Richert, L.; Kalchenko, V.I.; Mély, Y. Virus-Sized DNA Nanoparticles for Gene Delivery Based on Micelles of Cationic Calixarenes. Chem. A Eur. J. 2011, 17, 5526–5538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Consoli, G.M.L.; Di Bari, I.; Blanco, A.R.; Nostro, A.; D’Arrigo, M.; Pistarà, V.; Sortino, S. Design, Synthesis, and Antibacterial Activity of a Multivalent Polycationic Calix[4]Arene–NO Photodonor Conjugate. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 8, 881–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julián, E.; Baelo, A.; Gavaldà, J.; Torrents, E. Methyl-Hydroxylamine as an Efficacious Antibacterial Agent That Targets the Ribonucleotide Reductase Enzyme. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bragg, R.; Jansen, A.; Coetzee, M.; van der Westhuizen, W.; Boucher, C. Bacterial Resistance to Quaternary Ammonium Compounds (QAC) Disinfectants. In Infectious Diseases and Nanomedicine II; Adhikari, R., Thapa, S., Eds.; Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Springer: New Delhi, India, 2014; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consoli, G.M.L.; Granata, G.; Picciotto, R.; Blanco, A.R.; Geraci, C.; Marino, A.; Nostro, A. Design, Synthesis and Antibacterial Evaluation of a Polycationic Calix[4]Arene Derivative Alone and in Combination with Antibiotics. Med. Chem. Commun. 2018, 9, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, Y.; Muhamad Bunnori, N.; Susanti, D.; Muhammad Alhassan, A.; Abd Hamid, S. Synthesis, in-Vitro and in Silico Studies of Azo-Based Calix[4]Arenes as Antibacterial Agent and Neuraminidase Inhibitor: A New Look Into an Old Scaffold. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elçin, S.; İlhan, M.M.; Deligöz, H. Synthesis and Spectral Characterization of Azo Dyes Derived from Calix[4]Arene and Their Application in Dyeing of Fibers. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2013, 77, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, Y.; Agawa, T.; Nomura, E.; Taniguchi, H. Syntheses and NMR Behavior of Calix[4]Quinone and Calix[4]Hydroquinone. J. Org. Chem. 1992, 57, 3658–3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, C.M.; da Silva, D.L.; Magalhães, T.F.F.; Alves, R.B.; de Resende-Stoianoff, M.A.; Martins, F.T.; de Fátima, Â. Iminecalix[4]Arenes: Microwave-Assisted Synthesis, X-Ray Crystal Structures, and Anticandidal Activity. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 4365–4376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danila, C.; Bolte, M.; Böhmer, V. 1,3-Alternate Calix[4]Arenes, Selectively Functionalized by Amino Groups. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2005, 3, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gezelbash, Z.D.; Dilmaghani, K.A. Synthesis, Antifungal and Antibacterial Activity of Calix[4]Arene-Based 1,3,4-Oxadiazole Derivatives. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2020, 67, 1446–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padnya, P.L.; Terenteva, O.S.; Akhmedov, A.A.; Iksanova, A.G.; Shtyrlin, N.V.; Nikitina, E.V.; Krylova, E.S.; Shtyrlin, Y.G.; Stoikov, I.I. Thiacalixarene Based Quaternary Ammonium Salts as Promising Antibacterial Agents. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2021, 29, 115905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.; Dang, Y.-Y.; Li, H.; Li, H.; Liu, J.; Zhong, R.; Chen, Y.; Liu, S.; Lin, S. Membrane-Active Antibacterial Agents Based on Calix[4]Arene Derivatives: Synthesis and Biological Evaluation. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 816741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
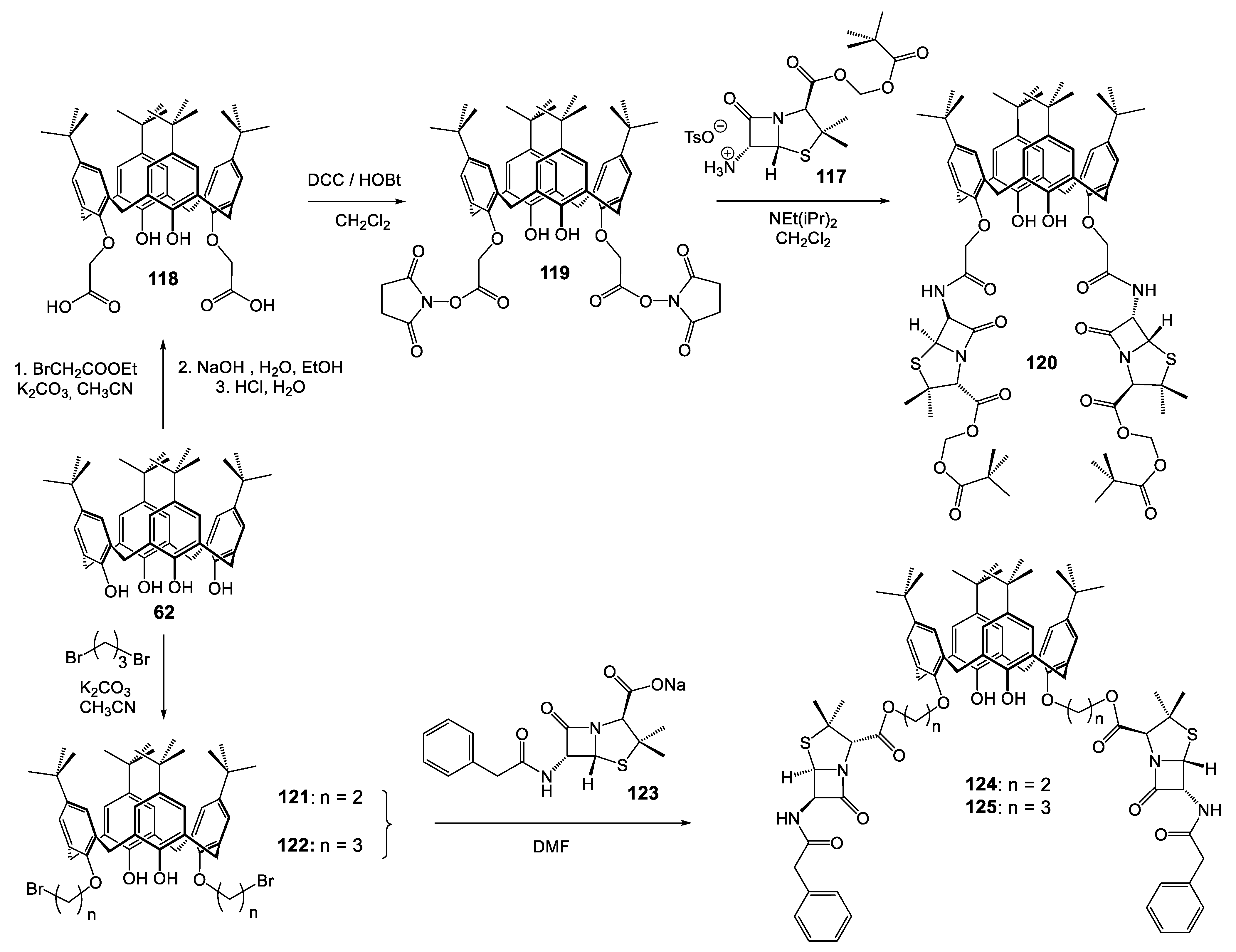
- Ben Salem, A.; Regnouf-de-Vains, J.-B. Synthesis and Characterisation of a New Podand Based on a Calixarene and a β-Lactam. Tetrahedron Lett. 2001, 42, 7033–7036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korchowiec, B.; Salem, A.B.; Corvis, Y.; Regnouf-de-Vains, J.-B.; Korchowiec, J.; Rogalska, E. Calixarenes in a Membrane Environment: A Monolayer Study on the Miscibility of Three p-Tert-Butylcalix[4]Arene β-Lactam Derivatives with 1,2-Dimyristoyl-Sn-Glycero-3-Phosphoethanolamine. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 13231–13242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben Salem, A.; Regnouf-de-Vains, J.-B. Towards a New Family of Calixarene-Based Podands Incorporating Quinolone Arms. An Example Using Nalidixic Acid. Tetrahedron Lett. 2003, 44, 6769–6771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korchowiec, B.; Orlof, M.; Sautrey, G.; Ben Salem, A.; Korchowiec, J.; Regnouf-de-Vains, J.-B.; Rogalska, E. The Mechanism of Metal Cation Binding in Two Nalidixate Calixarene Conjugates. A Langmuir Film and Molecular Modeling Study. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 10427–10435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben Salem, A.; Sautrey, G.; Fontanay, S.; Duval, R.E.; Regnouf-de-Vains, J.-B. Molecular Drug-Organiser: Synthesis, Characterization and Biological Evaluation of Penicillin V and/or Nalidixic Acid Calixarene-Based Podands. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 7534–7540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sautrey, G.; Clarot, I.; Salem, A.B.; Rogalska, E.; Regnouf-de-Vains, J.-B. Organosoluble Calixarene-Based Quinolone Carriers: Syntheses, Evaluation and Model Hydrolytic Studies at the Air–Water Interface. New J. Chem. 2011, 36, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korchowiec, B.; Korchowiec, J.; Gorczyca, M.; Regnouf de Vains, J.-B.; Rogalska, E. Molecular Organization of Nalidixate Conjugated Calixarenes in Bacterial Model Membranes Probed by Molecular Dynamics Simulation and Langmuir Monolayer Studies. J. Phys. Chem. B 2015, 119, 2990–3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dibama, H.M.; Clarot, I.; Fontanay, S.; Salem, A.B.; Mourer, M.; Finance, C.; Duval, R.E.; Regnouf-de-Vains, J.-B. Towards Calixarene-Based Prodrugs: Drug Release and Antibacterial Behaviour of a Water-Soluble Nalidixic Acid/Calix[4]Arene Ester Adduct. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 2679–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pur, F.N.; Dilmaghani, K.A. Calixpenams: Synthesis, Characterization, and Biological Evaluation of Penicillins V and X Clustered by Calixarene Scaffold. Turk. J. Chem. 2014, 38, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pur, F.N.; Dilmaghani, K.A. Calixcephems: Clustered cephalosporins analogous to calixpenams as novel potential anti-MRSA agents. Turk. J. Chem. 2014, 38, 850–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagnacani, V.; Franceschi, V.; Bassi, M.; Lomazzi, M.; Donofrio, G.; Sansone, F.; Casnati, A.; Ungaro, R. Arginine Clustering on Calix[4]Arene Macrocycles for Improved Cell Penetration and DNA Delivery. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagnacani, V.; Franceschi, V.; Fantuzzi, L.; Casnati, A.; Donofrio, G.; Sansone, F.; Ungaro, R. Lower Rim Guanidinocalix[4]Arenes: Macrocyclic Nonviral Vectors for Cell Transfection. Bioconjugate Chem. 2012, 23, 993–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagnacani, V.; Sansone, F.; Donofrio, G.; Baldini, L.; Casnati, A.; Ungaro, R. Macrocyclic Nonviral Vectors: High Cell Transfection Efficiency and Low Toxicity in a Lower Rim Guanidinium Calix[4]Arene. Org. Lett. 2008, 10, 3953–3956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bono, N.; Pennetta, C.; Sganappa, A.; Giupponi, E.; Sansone, F.; Volonterio, A.; Candiani, G. Design and Synthesis of Biologically Active Cationic Amphiphiles Built on the Calix[4]Arene Scaffold. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 549, 436–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özkan, Ş.Ç.; Yilmaz, A.; Arslan, E.; Açık, L.; Sayın, Ü.; Mutlu, E.G. Novel Copper(II) Complexes of p-Tert-Butylcalix[4]Arene Diamide Derivatives: Synthesis, Antimicrobial and DNA Cleavage Activities. Supramol. Chem. 2015, 27, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkuş, G.U.; Al, E.; Korcan, S.E. Selective Extraction of Toxic Heavy Metals and Biological Activity Studies Using Pyrimidylthioamide Functionalised Calix[4]Arene. Supramol. Chem. 2015, 27, 522–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koroglu, M.A.; Erol, I.; Korcan, E.; Konuk, M. Synthesis and Characterization of Novel Methacrylate Monomers Having Pendant Oxime Esters and Their Copolymerization with Styrene. J. Macromol. Sci. Part A 2007, 44, 817–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memon, S.; Chandio, A.A.; Memon, A.A.; Panhwar, Q.K.; Nizamani, S.M.; Bhatti, A.A.; Brohi, N.A. Synthesis, Characterization, and Exploration of Antimicrobial Activity of Copper Complex of Diamide Derivative of p-Tert-Butylcalix[4]Arene. Polycycl. Aromat. Compd. 2017, 37, 362–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahojb Noruzi, E.; Shaabani, B.; Geremia, S.; Hickey, N.; Nitti, P.; Kafil, H.S. Synthesis, Crystal Structure, and Biological Activity of a Multidentate Calix[4]Arene Ligand Doubly Functionalized by 2-Hydroxybenzeledene-Thiosemicarbazone. Molecules 2020, 25, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahojb Noruzi, E.; Kheirkhahi, M.; Shaabani, B.; Geremia, S.; Hickey, N.; Asaro, F.; Nitti, P.; Kafil, H.S. Design of a Thiosemicarbazide-Functionalized Calix[4]Arene Ligand and Related Transition Metal Complexes: Synthesis, Characterization, and Biological Studies. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


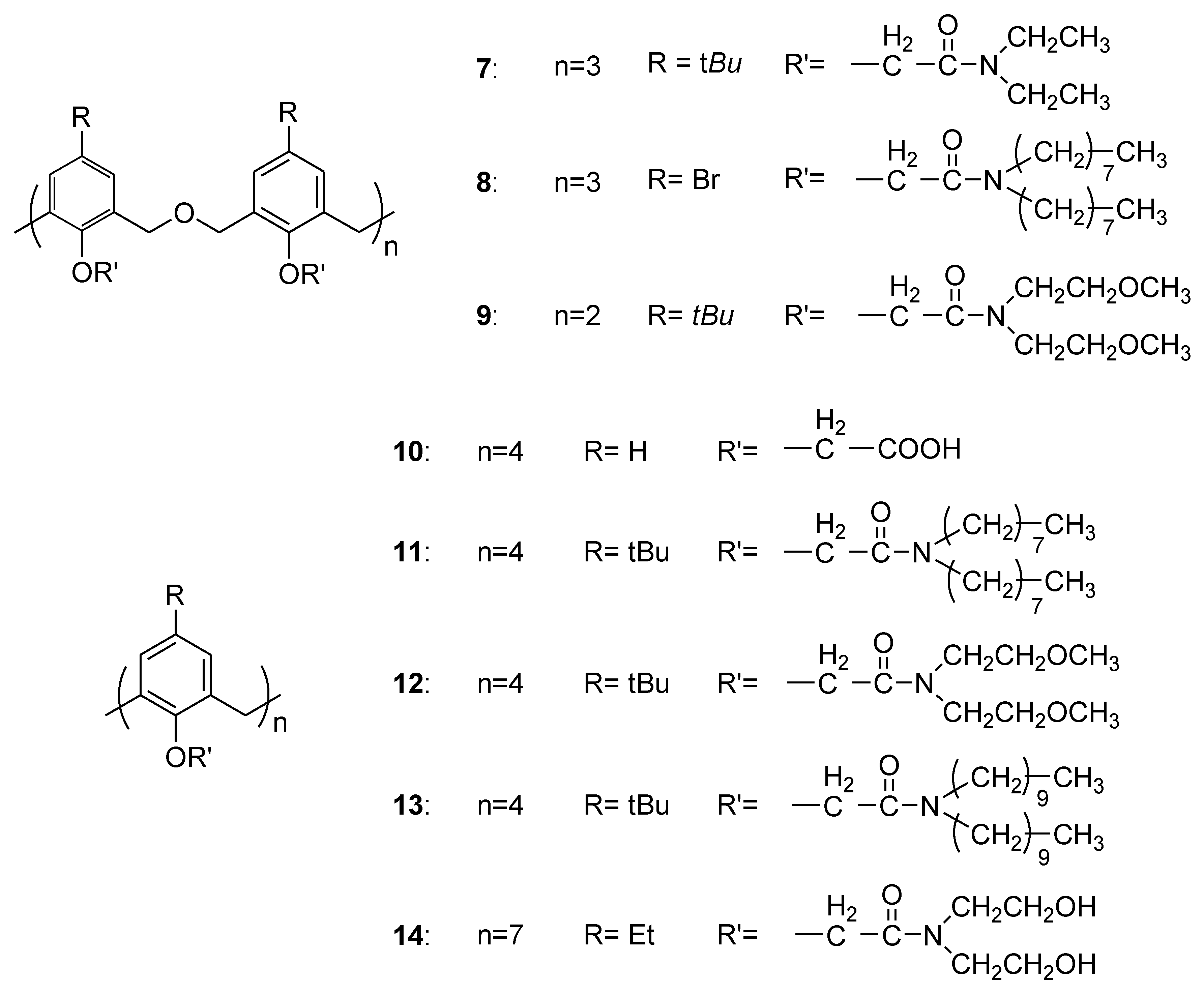
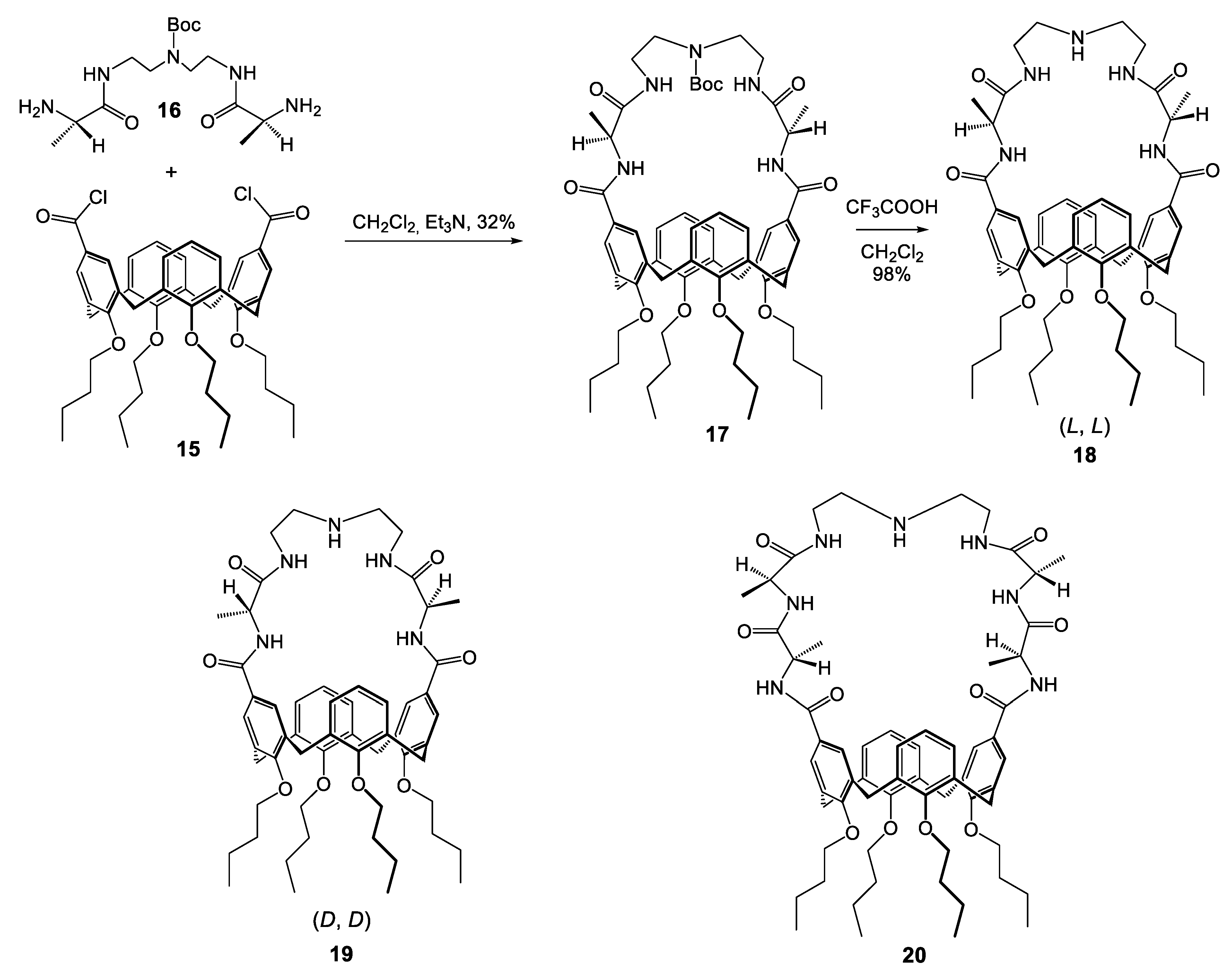
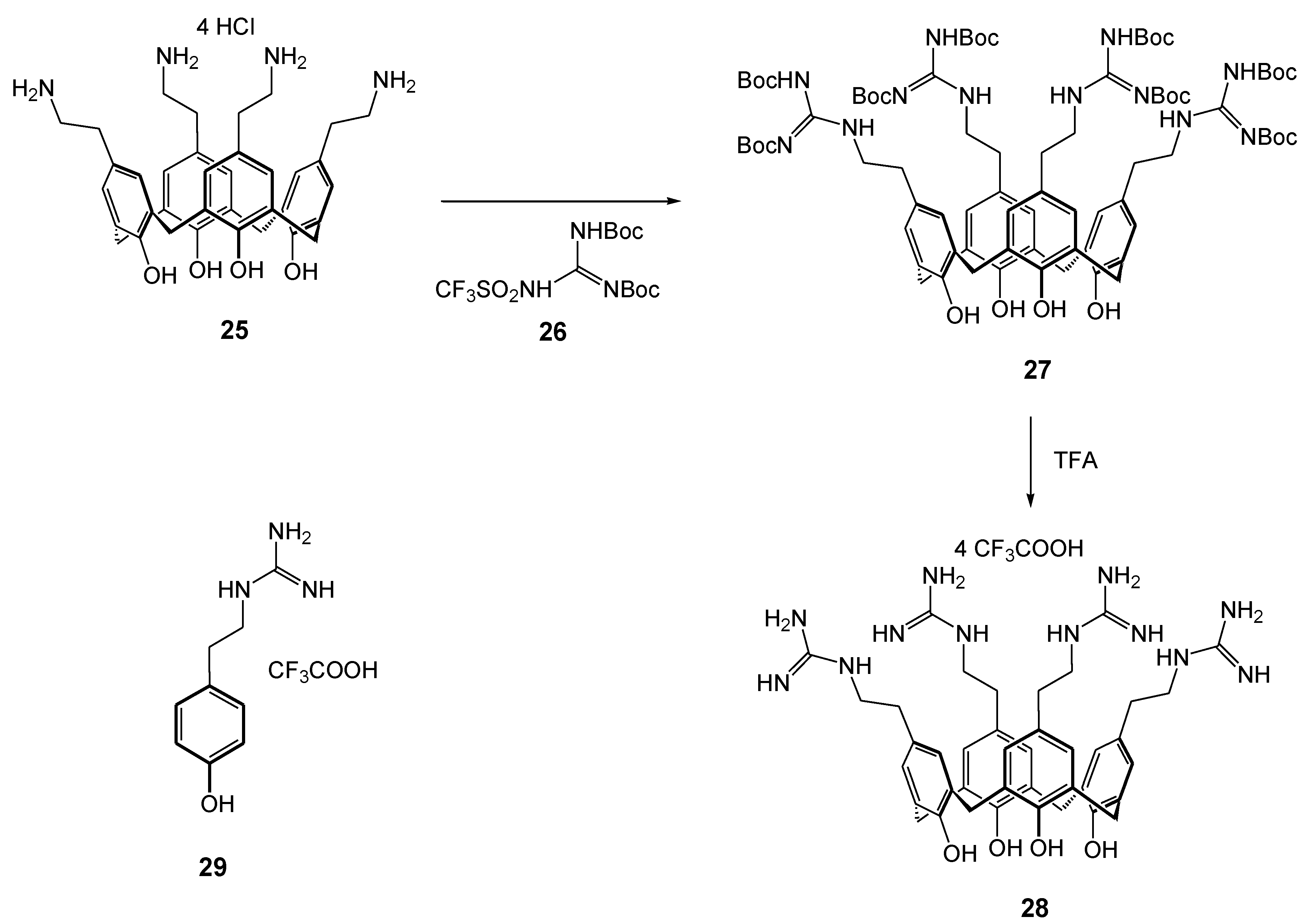
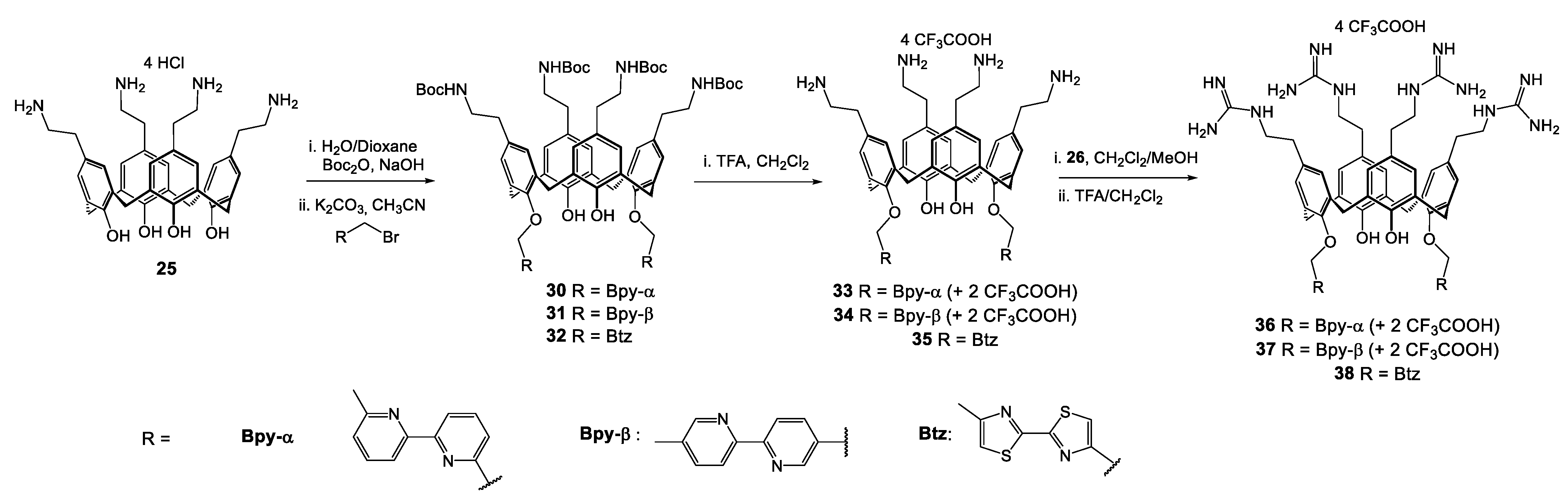

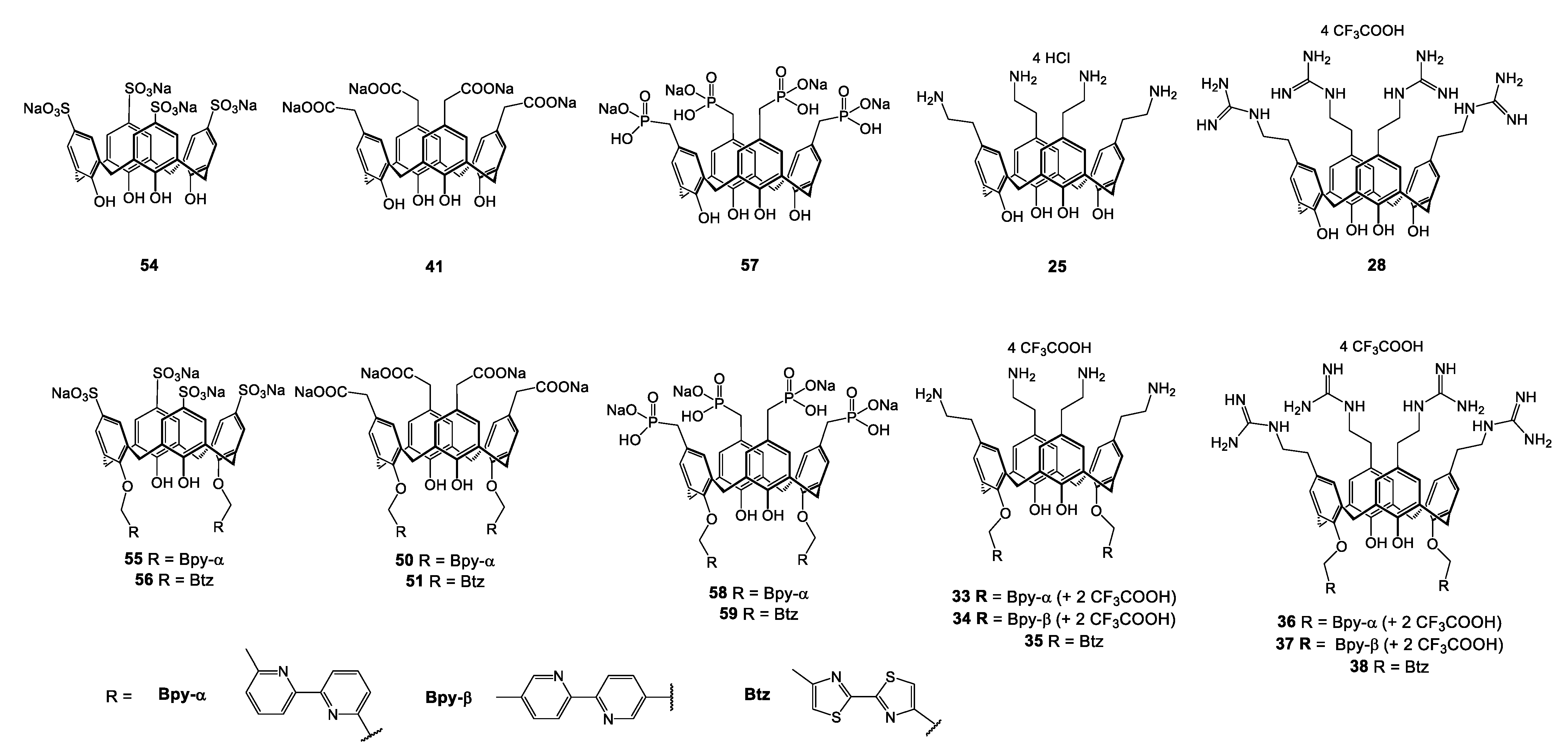
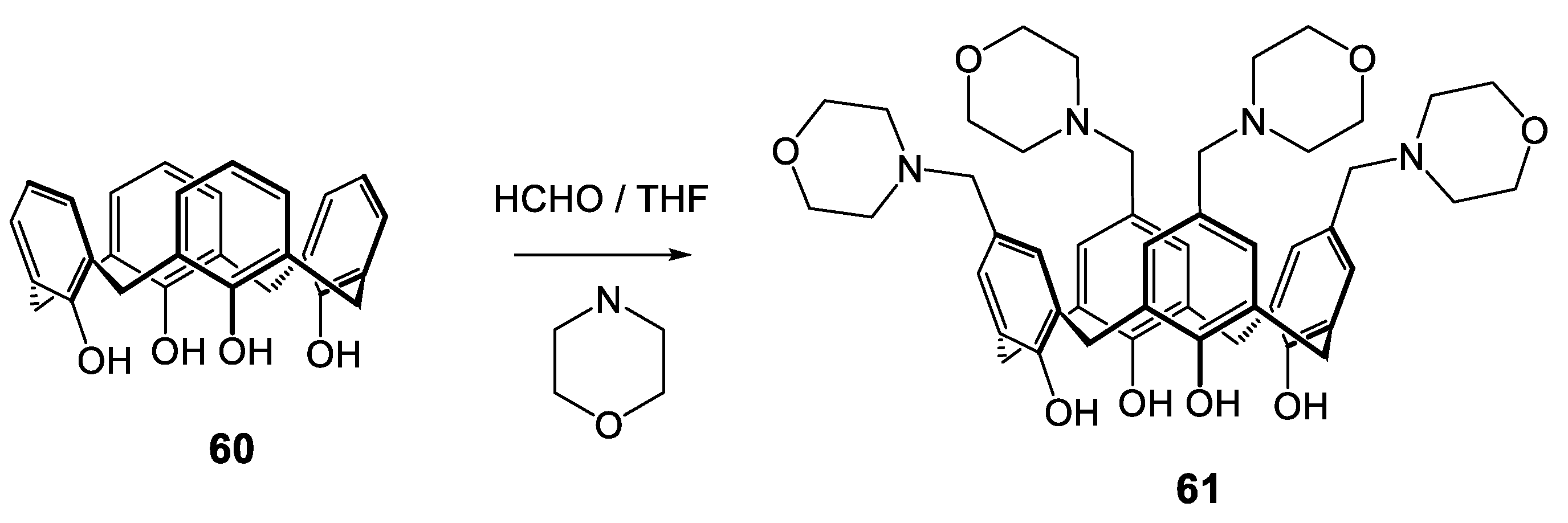
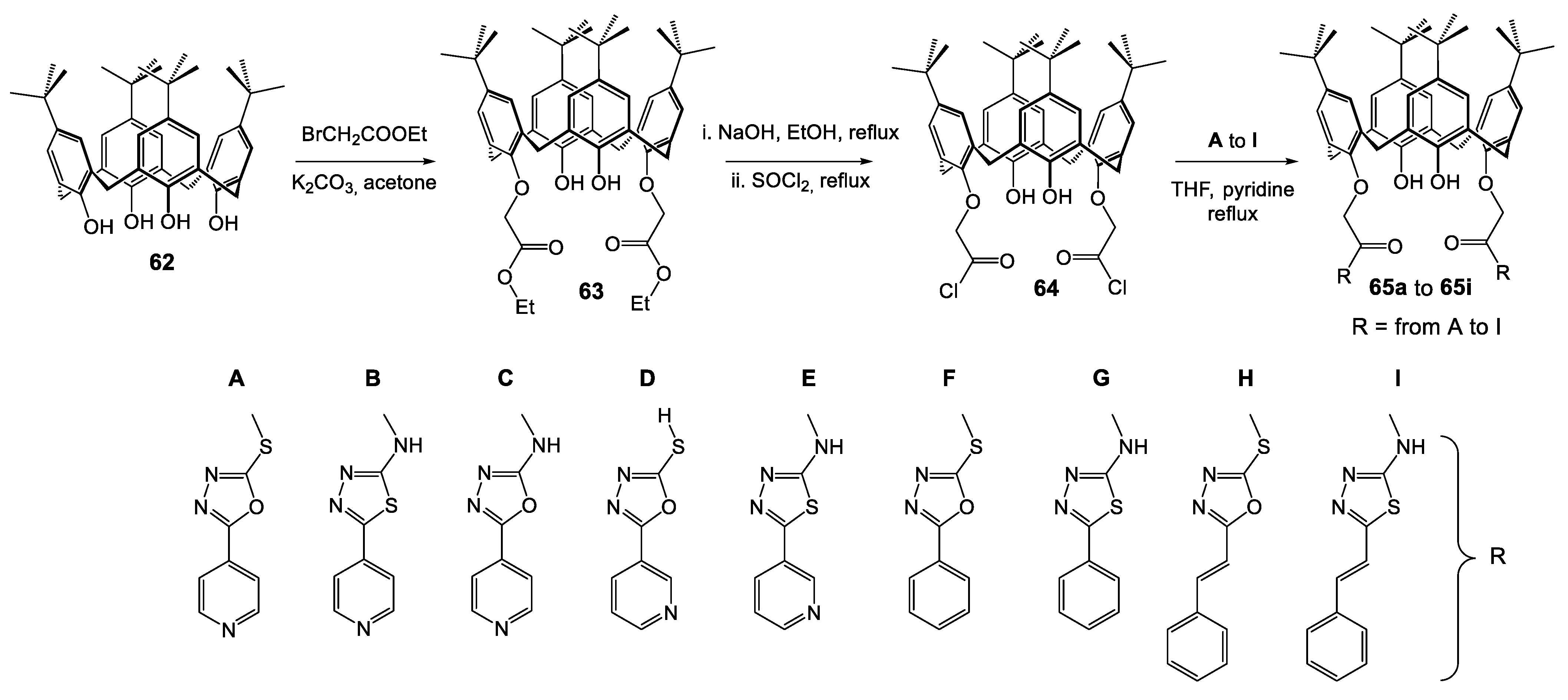



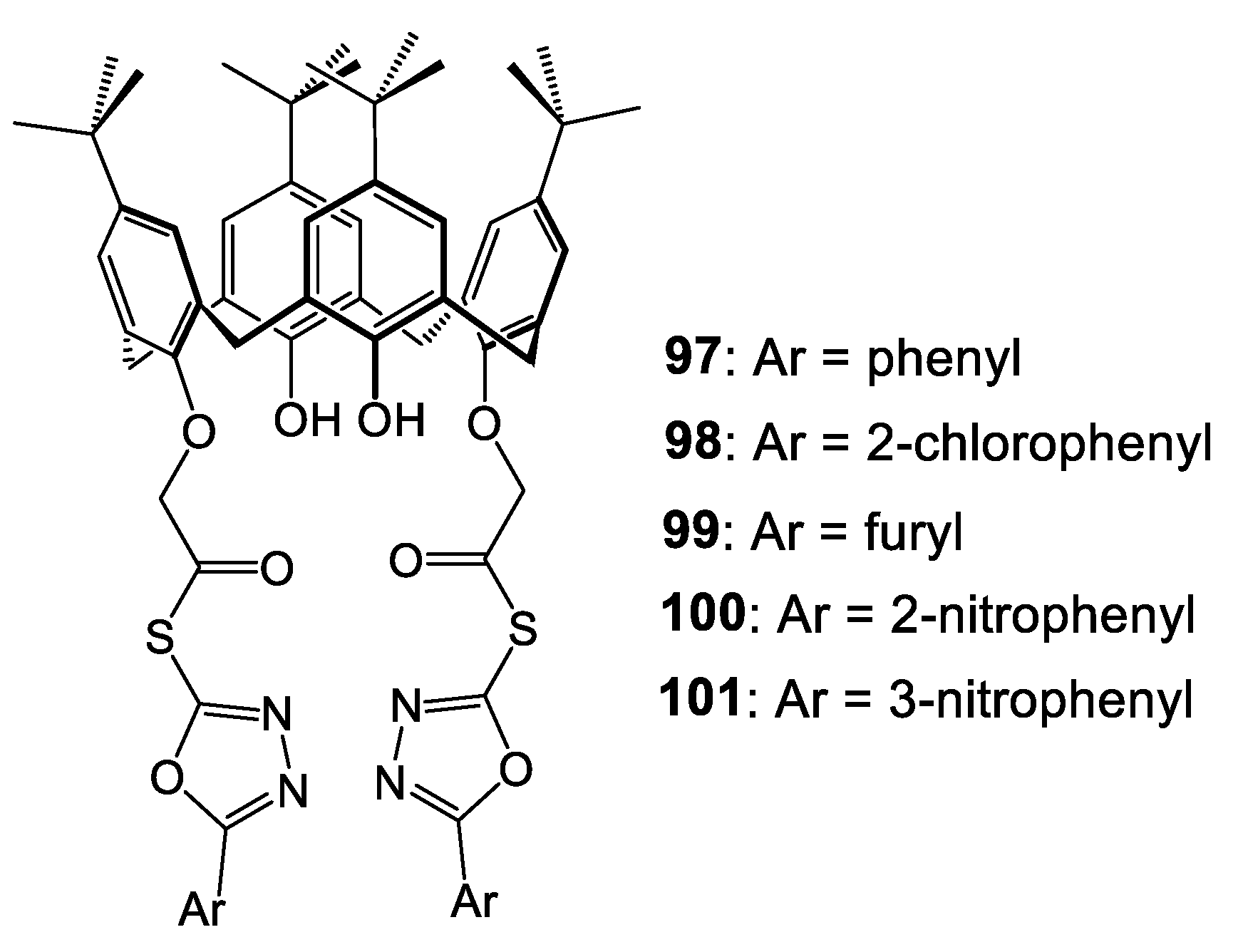
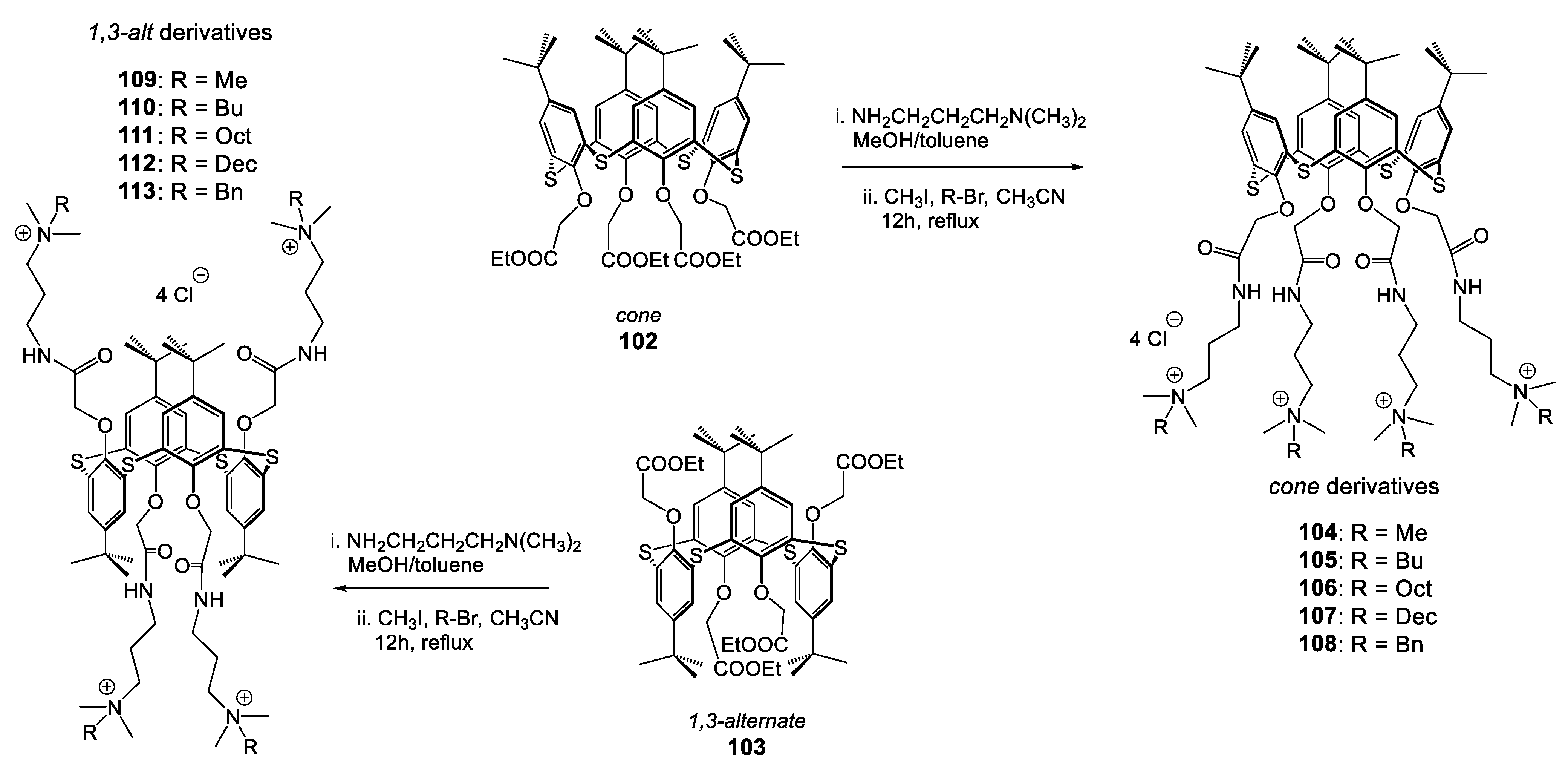
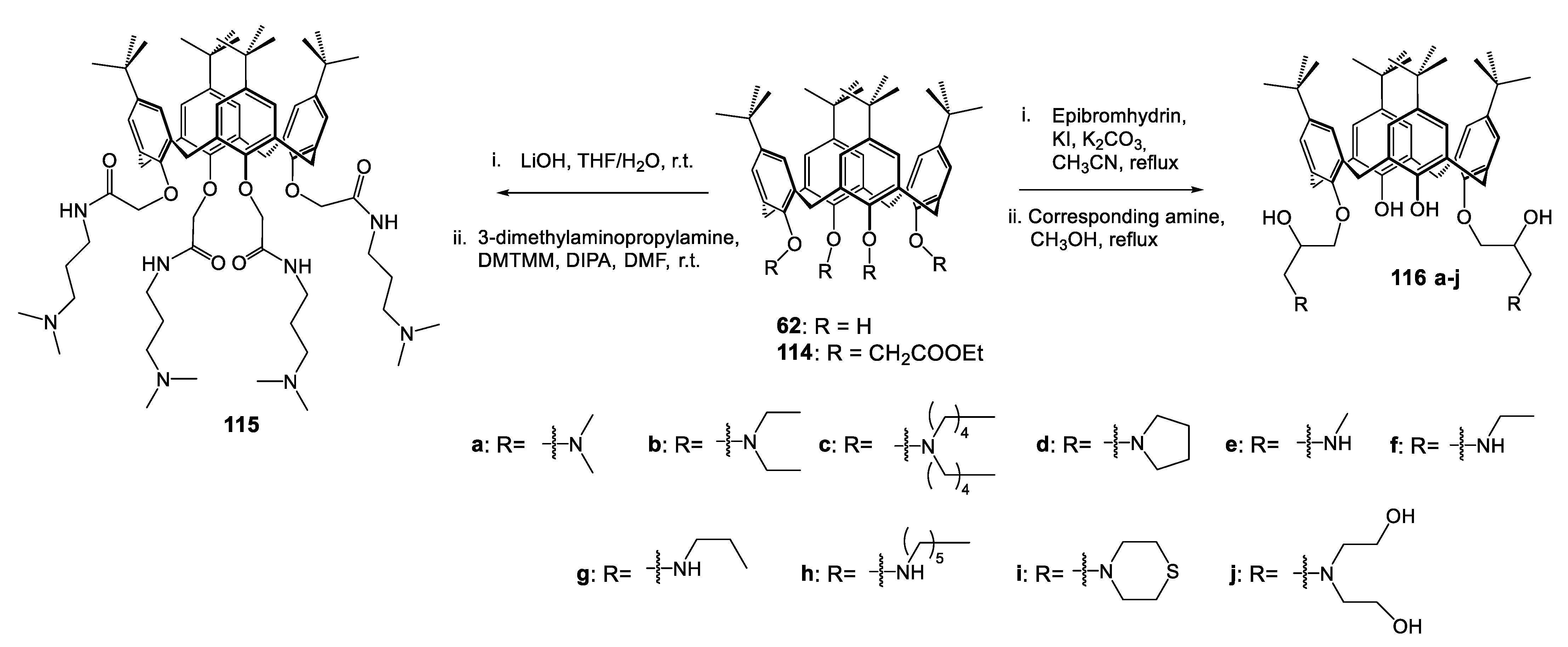
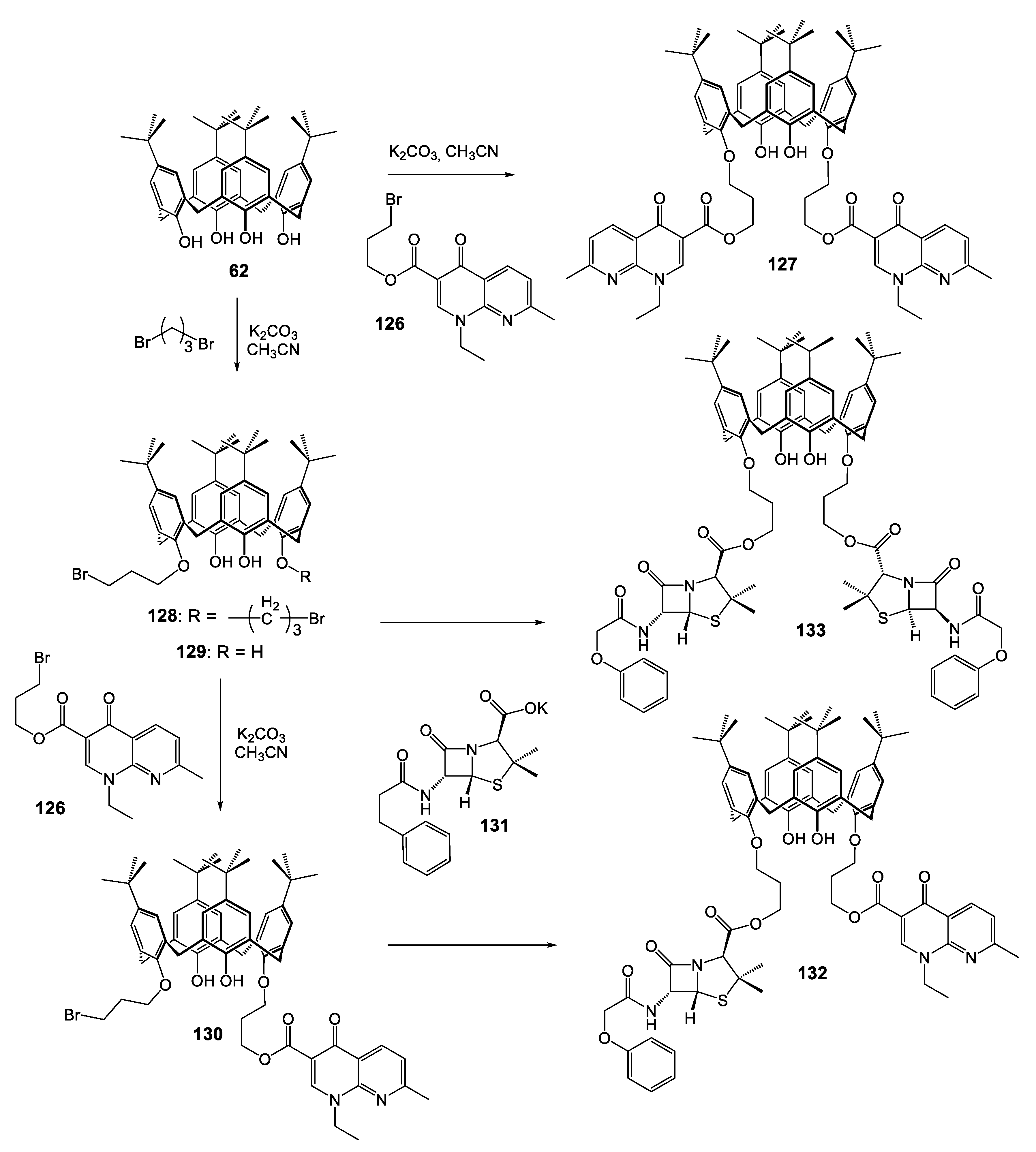
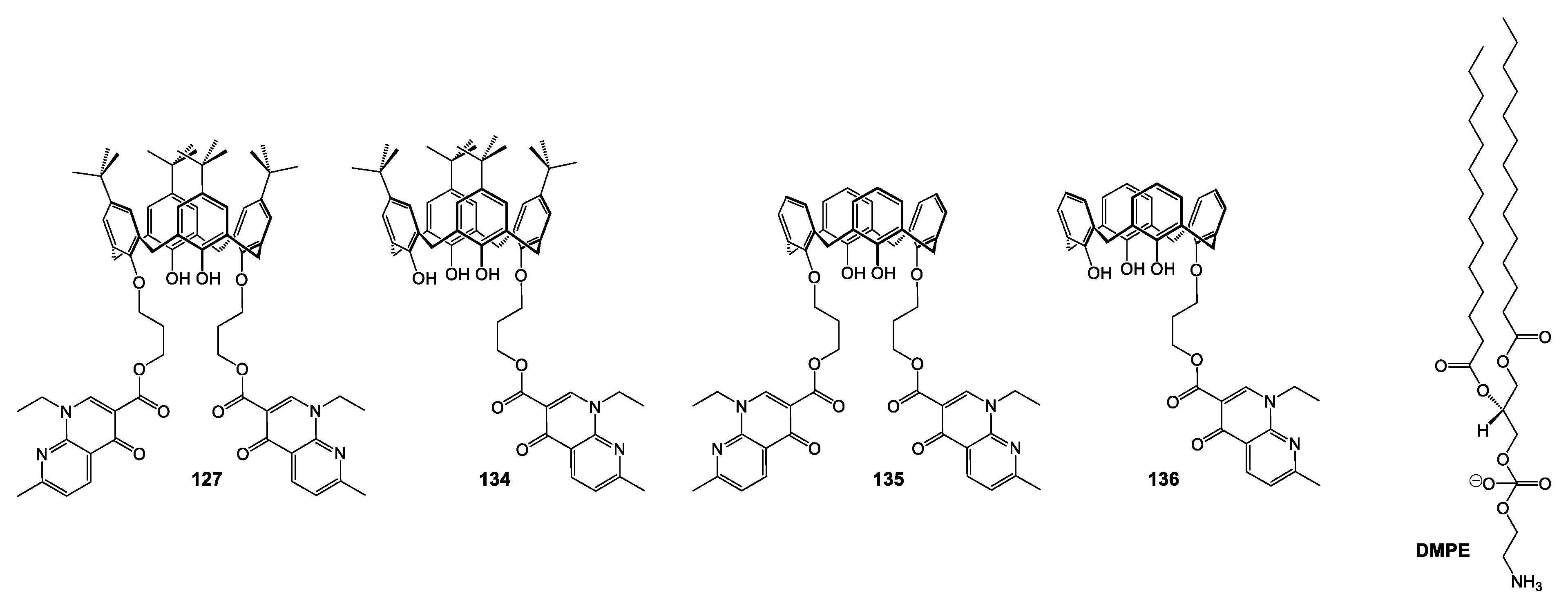
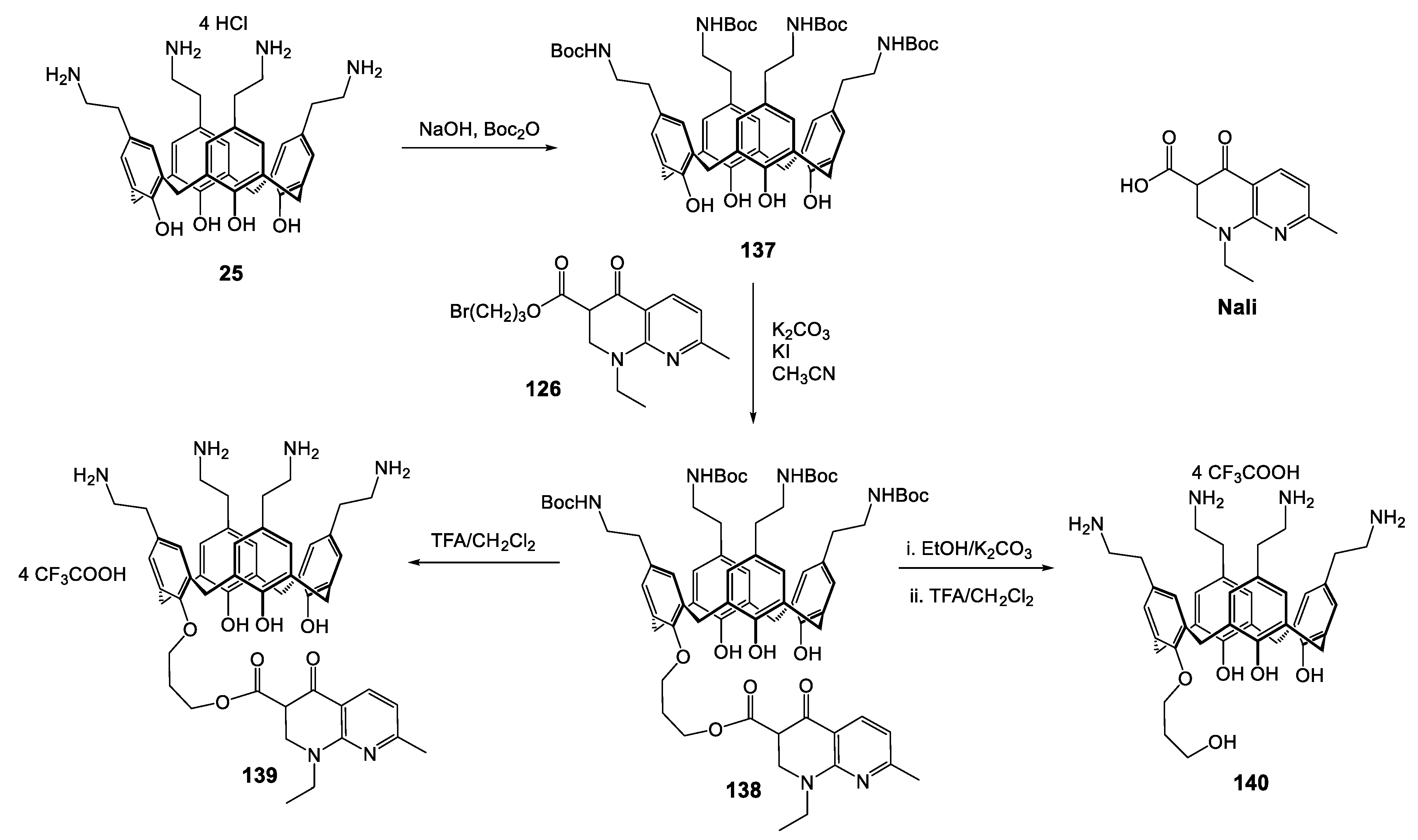


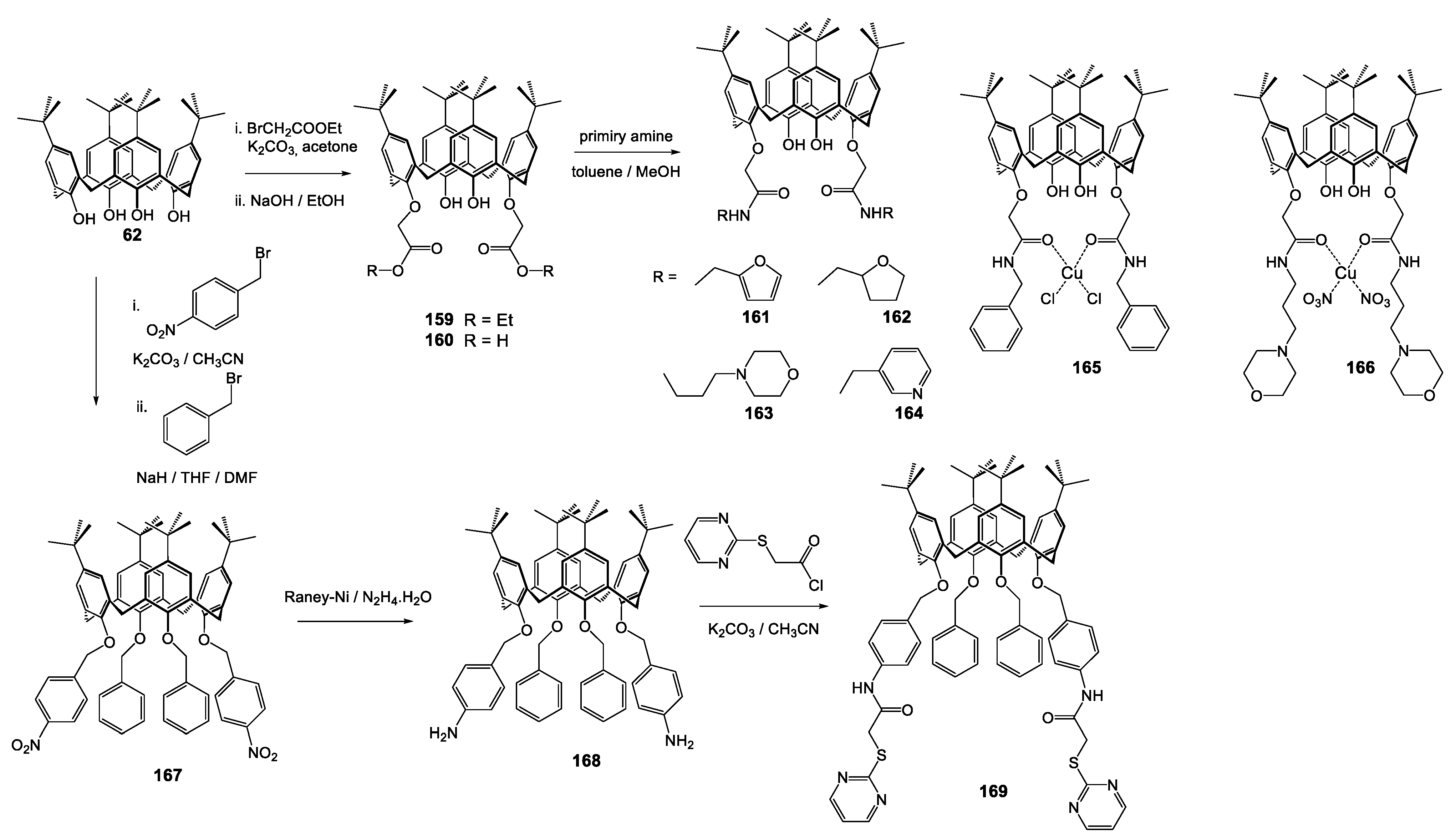
| Compounds | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacterial Strains | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | |
| E. coli | 10 mg/mL | - | ++++ | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 5 mg/mL | - | ++++ | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| S. aureus | 10 mg/mL | - | ++++ | ++++ | - | +++ | ++ | ++++ | - |
| 5 mg/mL | - | ++++ | ++++ | - | ++ | + | ++++ | - | |
| 1 mg/mL | - | ++ | +++ | - | ++ | - | + | - | |
| B. subtilis | 10 mg/mL | +++ | - | ++++ | ++++ | - | - | ++++ | - |
| 5 mg/mL | + | - | +++ | - | - | - | ++++ | - | |
| 1 mg/mL | - | - | ++ | - | - | - | ++ | - | |
| K. pneumoniae | 10 mg/mL | ++++ | - | - | - | +++ | ++++ | - | ++++ |
| 5 mg/mL | +++ | - | - | - | ++ | +++ | - | +++ | |
| P. aeruginosa | 10 mg/mL | ++++ | - | - | - | +++ | - | - | - |
| 5 mg/mL | +++ | - | - | - | ++ | - | - | - | |
| Compounds | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reference Strains | Vancomycin | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 |
| S. aureus 663 | 2 | 64 | 8 | 8 | 32 |
| S. aureus 853 | 2 | >64 | 16 | 8 | 32 |
| S. aureus 1131 | 2 | 64 | 4 | 4 | 32 |
| S. epidermidis | 2 | 32 | 4 | 8 | 32 |
| B. cereus | 2 | nt | 16 | nt | nt |
| Compounds | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strains | 28 | 29 | HX | CHX |
| Reference strains | ||||
| E. coli ATCC 25922 | 4 | 512 | 8 | 0.25 |
| P. aeruginosa ATCC 27853 | 32 | >512 | 32 | 8 |
| S. aureus ATCC 25923 | 8 | 512 | 4 | 0.5 |
| S. aureus ATCC 29213 | 8 | 512 | <1 | 0.5 |
| E. faecalis ATCC 29212 | 32 | >512 | 2 | 2 |
| Clinical isolates | ||||
| Penicillinase-producing E. coli | 2 | 512 | 8 | nd |
| MRSA (mecA gene) | 8 | 512 | 2 | nd |
| E. faecium (vanB gene) | 8 | >512 | 2 | nd |
| E. faecalis (vanA gene) | 64 | >512 | 4 | nd |
| P. aeruginosa (overexpression of efflux pumps) | 64 | >512 | 64 | nd |
| Compounds | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 28 | 36 | 37 | 38 | |
| CI50 | >256 | 16–32 | >128 | 64–128 |
| Reference strains | ||||
| E. coli ATCC 25922 | 4 | 16 | 32 | 16 |
| P. aeruginosa ATCC 27853 | 32 | 16 | 32 | 16 |
| S. aureus ATCC 25923 | 8 | 16 | 8 | 8 |
| S. aureus ATCC 29213 | 8 | 16 | 8 | 16 |
| E. faecalis ATCC 29212 | 32 | 16 | 8 | 8 |
| Compounds | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 | 28 | 34 | 37 | 38 | INH | |
| Strains | ||||||
| M. tuberculosis H37Rv | 2.58 | 1.0 | 1.34 | 1.51 | 2.69 | 0.08 |
| M. tuberculosis MYC5165 | 2.6 | 1.0 | 2.7 | 0.75 | 0.17 | 1.7 |
| Compounds | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reference Strains | 70 (prop) | 72 (prop) | 74 (prop) | 71 (oct) | 73 (oct) | 75 (oct) | 18/19 a | 28 a | 61 a |
| S. aureus ATCC 6538 | <10 | <10 | <10 | >1000 | >1000 | >1000 | 8 | 8 | 16 |
| P. aeruginosa ATCC 9027 | 50 | 1000 | 50 | >1000 | 500 | >1000 | nd b | 32 | nd b |
| K. pneumoniae ATCC 10031 | <10 | 100 | 500 | 500 | >1000 | >1000 | nd b | 8 | 4 |
| E. coli ATCC 25922 | <10 | 100 | 500 | 1000 | 500 | >1000 | 3.2 | 4 | 4 |
| Compounds | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacterial Strains | 81 | 82 | 83 | 84 | 85 | 86 |
| S. aureus | 7.8 | 3.9 | 7.8 | >125 | >125 | >125 |
| MRSA | 15.6 | 0.97 | 7.8 | >125 | 31.25 | >125 |
| B. subtilis | 15.6 | 0.97 | 0.97 | >125 | 125 | >125 |
| S. epidermidis | 7.8 | 1.9 | 1.9 | >125 | 62.5 | >125 |
| E. faecalis | 31.25 | 7.8 | 7.8 | >125 | 15.6 | >125 |
| E. coli | >125 | >125 | 125 | >125 | >125 | >125 |
| P. aeruginosa | 15.6 | >125 | 62.5 | >125 | 62.5 | >125 |
| Compounds | |||||
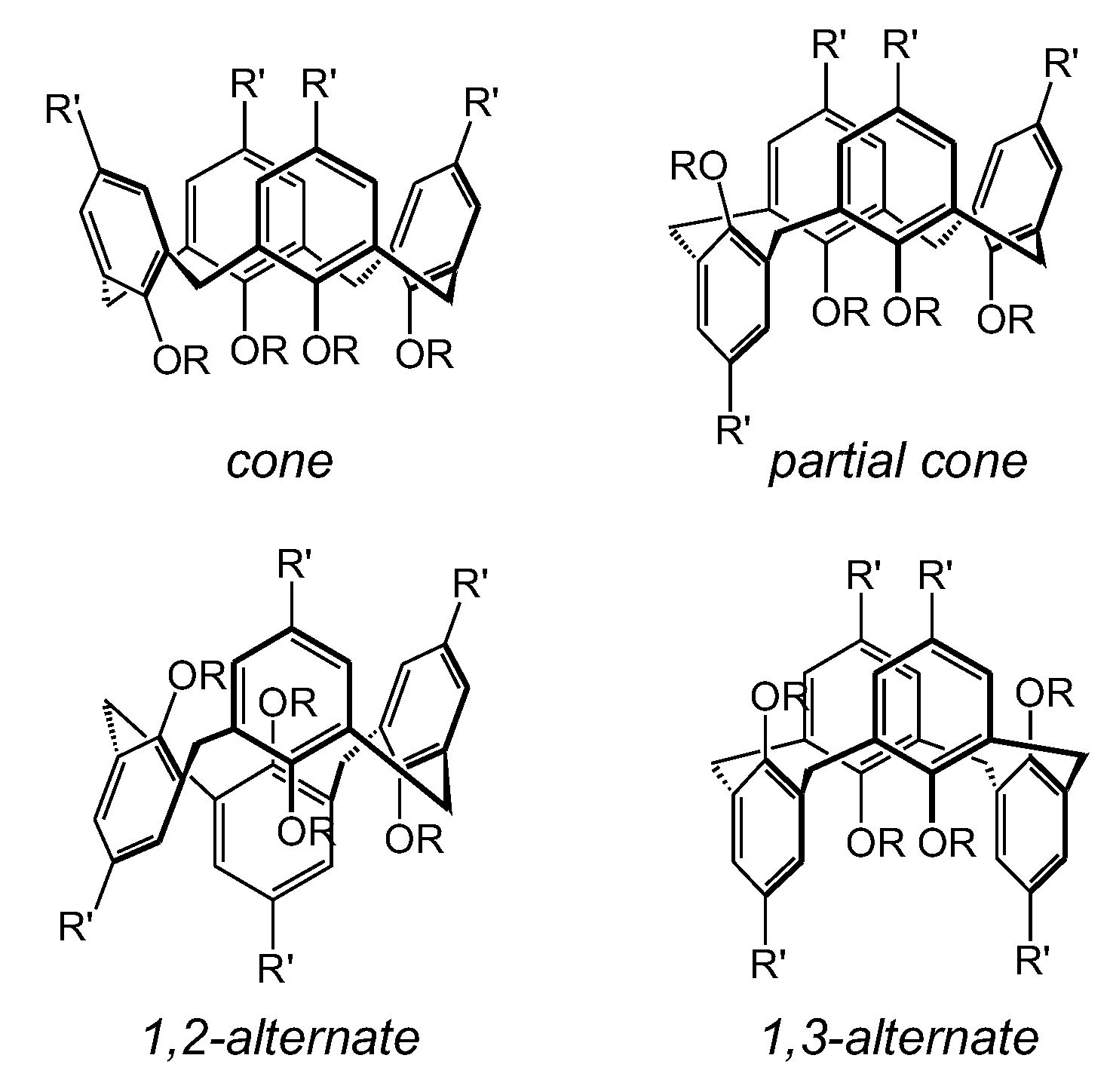
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reference Strains | 92 cone | 93 paco | 94 1,2-alt | 95 1,3-alt | 96 |
| E. coli ATCC 25922 | 64 | 8 | 8 | 4 | 64 |
| P. aeruginosa ATCC 27853 | 128 | 8 | 16 | 16 | 128 |
| S. aureus ATCC 25923 | 32 | 2 | 4 | <1 | 32 |
| S. aureus ATCC 29213 | 32 | 4 | 8 | 8 | 32 |
| E. faecalis ATCC 29212 | 8 | 4 | 8 | 8 | 128 |
| M. tuberculosis H37Rv | 78 | 38 | 39 | 5 | 10 |
| M. tuberculosis MYC5165 | 9.5 | 2.4 | 3.8 | 1.2 | 37.2 |
| Compounds | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 104 | 109 | 108 | 113 | 105 | 110 | 106 | 111 | 107 | 112 | CHX | ||
| R= | Me | Bn | Bu | Oct | Dec | |||||||
| Reference Strains | cone | 1,3-alt | cone | 1,3-alt | cone | 1,3-alt | cone | 1,3-alt | cone | 1,3-alt | ||
| S. aureus ATCC 29213 | 8 | >64 | 4 | 4 | 1 | 16 | 64 | 1 | 32 | 4 | 2 | |
| S. epidermis a | 4 | >64 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 16 | 64 | 1 | 8 | 4 | 1 | |
| B. subtilis 168 | 1 | 64 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 8 | 4 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 2 | |
| E. coli ATCC 25922 | >64 | >64 | >64 | 32 | >64 | 64 | >64 | 8 | >64 | 16 | 1 | |
| K. pneumoniae 1813 | >64 | 16 | >64 | 32 | >64 | 1 | 8 | 32 | 4 | 32 | 2 | |
| P. aeruginosa ATCC 27853 | >64 | >64 | >64 | >64 | >64 | >64 | >64 | 16 | >64 | 64 | 4 | |
| Compounds | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
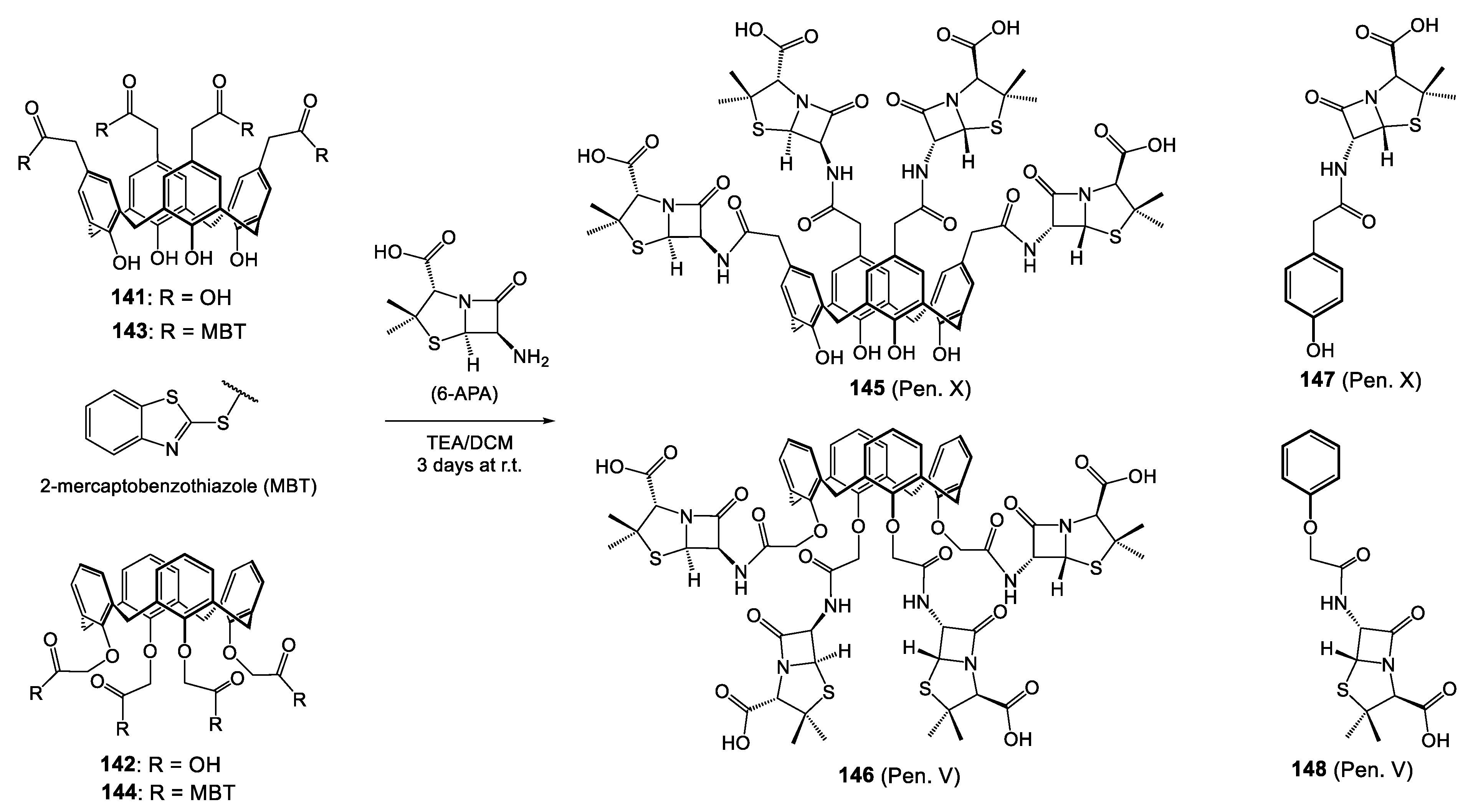
| Reference Strains | 145 (Pen. X) | 146 (Pen. V) | 147 (Pen. X) | 148 (Pen. V) | 151 (Ceph. X) | 152 (Ceph. V) | 153 (Ceph. X) | 154 (Ceph. V) |
| S. pyogenes ATCC 19615 | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.012 | 0.016 | nt | nt | nt | nt |
| S. agalactiae ATCC 12386 | 0.004 | 0.006 | 0.025 | 0.032 | nt | nt | nt | nt |
| S. pneumoniae ATCC 49619 | 0.022 | 0.024 | 0.125 | 0.125 | nt | nt | nt | nt |
| S. aureus ATCC 25923 | 0.025 | 0.032 | nt | nt | 0.225 | 0.25 | 1.775 | 1.550 |
| S. aureus ATCC 29213 | 0.24 | 0.256 | nt | nt | 0.992 | 1.012 | 5.325 | 5.150 |
| S. aureus ATCC 11632 | >64 | >64 | nt | nt | 0.912 | 0.925 | 8.775 | 8.350 |
| S. aureus ATCC 43300 | >64 | >64 | nt | nt | 1.150 | 1.225 | 11.775 | 10.950 |
| S. aureus ATCC 33591 | >64 | >64 | nt | nt | 1.550 | 1.635 | 16.650 | 16.325 |
| Compounds | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reference Strains | 159 | 160 | 161 | 162 | 163 | 164 | 165 | 166 |
| B. subtilis ATCC 6633 | 78 | 5000 | 1250 | 1250 | 10,000 | 10,000 | nd | nd |
| B. cereus NRRI-B-3711 | 39 | 10,000 | 39 | 2500 | 10,000 | 10,000 | nd | nd |
| E. faecalis (clinical isolate) | 156 | 10,000 | 39 | 1250 | 10,000 | 1250 | nd | nd |
| S. aureus NTCT 8325 | 156 | 10,000 | 39 | 1250 | 10,000 | 625 | nd | nd |
| E. coli ATCC 25922 | 39 | 10,000 | 625 | 10,000 | 10,.000 | 1250 | nd | nd |
| E. coli ATCC 35128 | 39 | 5000 | 78 | 5000 | 5000 | 2500 | nd | nd |
| P. aeruginosa ATCC 27853 | 1250 | 5000 | 5000 | 5000 | 5000 | 5000 | nd | nd |
| P. vulgaris ATCC 8427 | 156 | 10,000 | 5000 | 5000 | 5000 | 2500 | nd | nd |
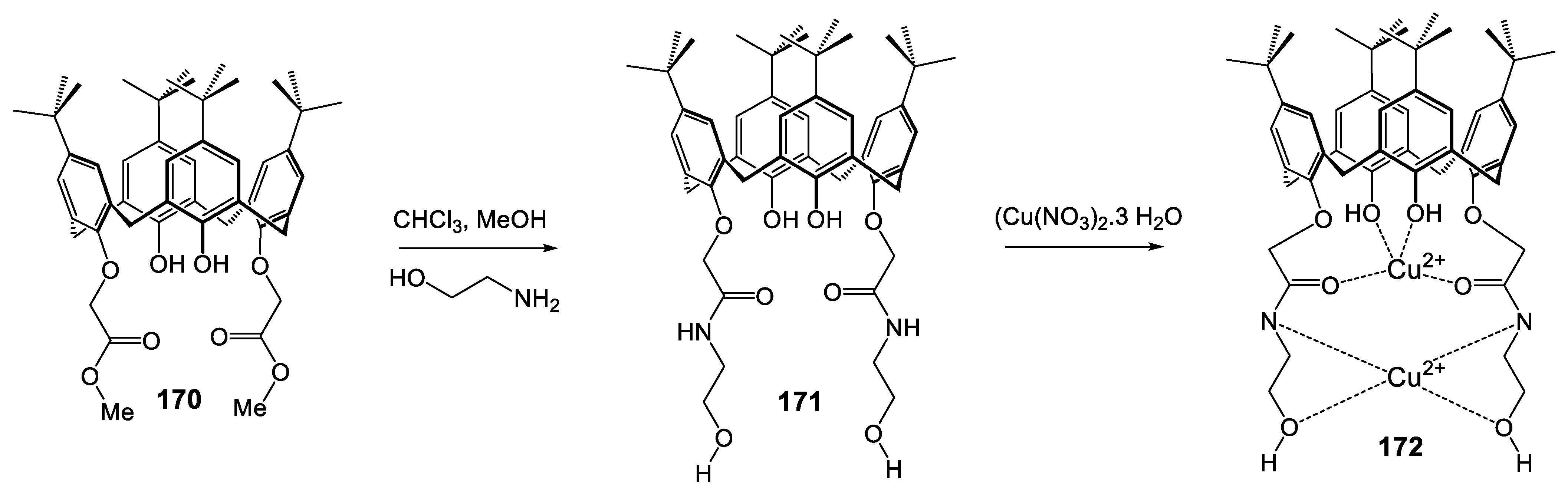
| Compounds | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 171 | 172 | |||||||||||
| Conc. in μg/mL | 6 | 3 | 1.5 | 0.75 | 0.37 | 6 | 3 | 1.5 | 0.75 | 0.37 | ||
| Reference Strains | Inhibition Zone | MIC | Inhibition Zone | MIC | ||||||||
| S. albus | 6 | 2 | - | - | - | 3 | 11 | 8 | 5 | 3 | - | 0.75 |
| E. coli | 8 | 3 | - | - | - | 3 | 12 | 10 | 7 | 5 | 2 | 0.37 |
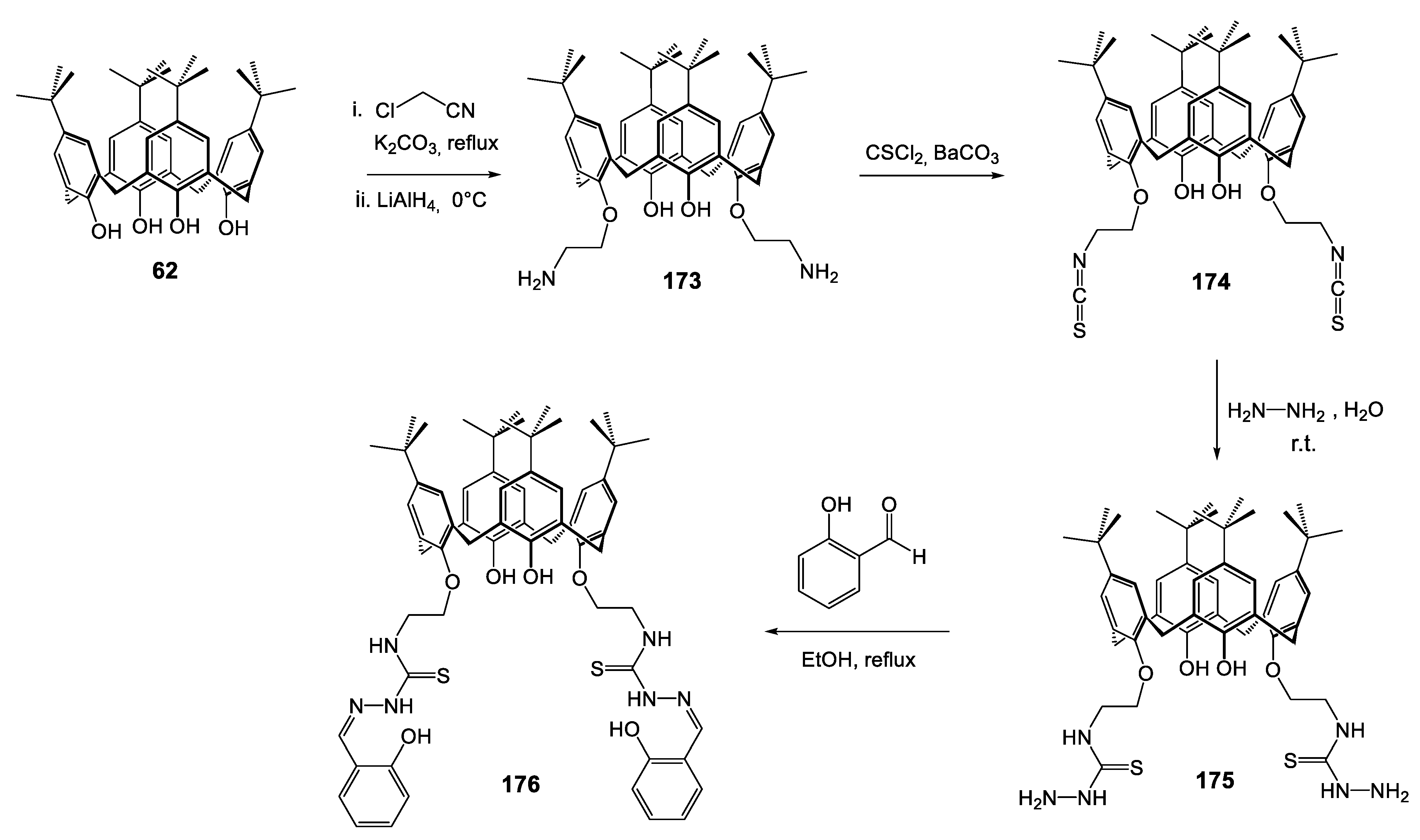
| Compounds | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reference Strains | Thiosemicarbazide | Thiosemicarbazone | ||||||||
| 175 | 175-Co | 175-Ni | 175-Cu | 175-Zn | 176 | 176-Co | 176-Ni | 176-Cu | 176-Zn | |
| S. aureus ATCC 29213 | - | 250 | - | 250 | 500 | - | - | - | 31.25 | - |
| B. subtilis ATCC 6633 | 31.25 | - | 31.25 | 31.25 | 125 | 31.25 | 31.25 | 31.25 | 31.25 | 31.25 |
| E. coli ATCC 25922 | 250 | 125 | 62.5 | 125 | 31.25 | 31.25 | 31.25 | 31.25 | 31.25 | 31.25 |
| P. aeruginosa ATCC 27853 | 62.5 | 125 | 31.25 | 62.5 | 31.25 | 31.25 | 31.25 | 31.25 | 31.25 | 31.25 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mourer, M.; Regnouf-de-Vains, J.-B.; Duval, R.E. Functionalized Calixarenes as Promising Antibacterial Drugs to Face Antimicrobial Resistance. Molecules 2023, 28, 6954. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28196954
Mourer M, Regnouf-de-Vains J-B, Duval RE. Functionalized Calixarenes as Promising Antibacterial Drugs to Face Antimicrobial Resistance. Molecules. 2023; 28(19):6954. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28196954
Chicago/Turabian StyleMourer, Maxime, Jean-Bernard Regnouf-de-Vains, and Raphaël E. Duval. 2023. "Functionalized Calixarenes as Promising Antibacterial Drugs to Face Antimicrobial Resistance" Molecules 28, no. 19: 6954. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28196954
APA StyleMourer, M., Regnouf-de-Vains, J.-B., & Duval, R. E. (2023). Functionalized Calixarenes as Promising Antibacterial Drugs to Face Antimicrobial Resistance. Molecules, 28(19), 6954. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28196954