Cannabidiol-Loaded Lipid-Stabilized Nanoparticles Alleviate Psoriasis Severity in Mice: A New Approach for Improved Topical Drug Delivery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
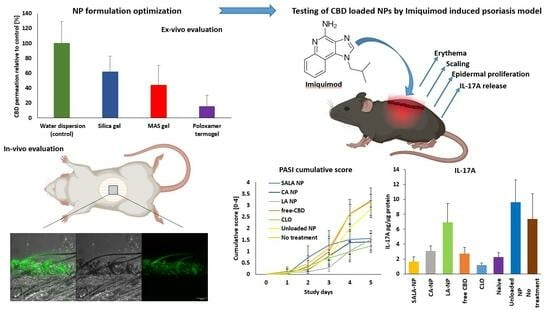
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Formulation Development
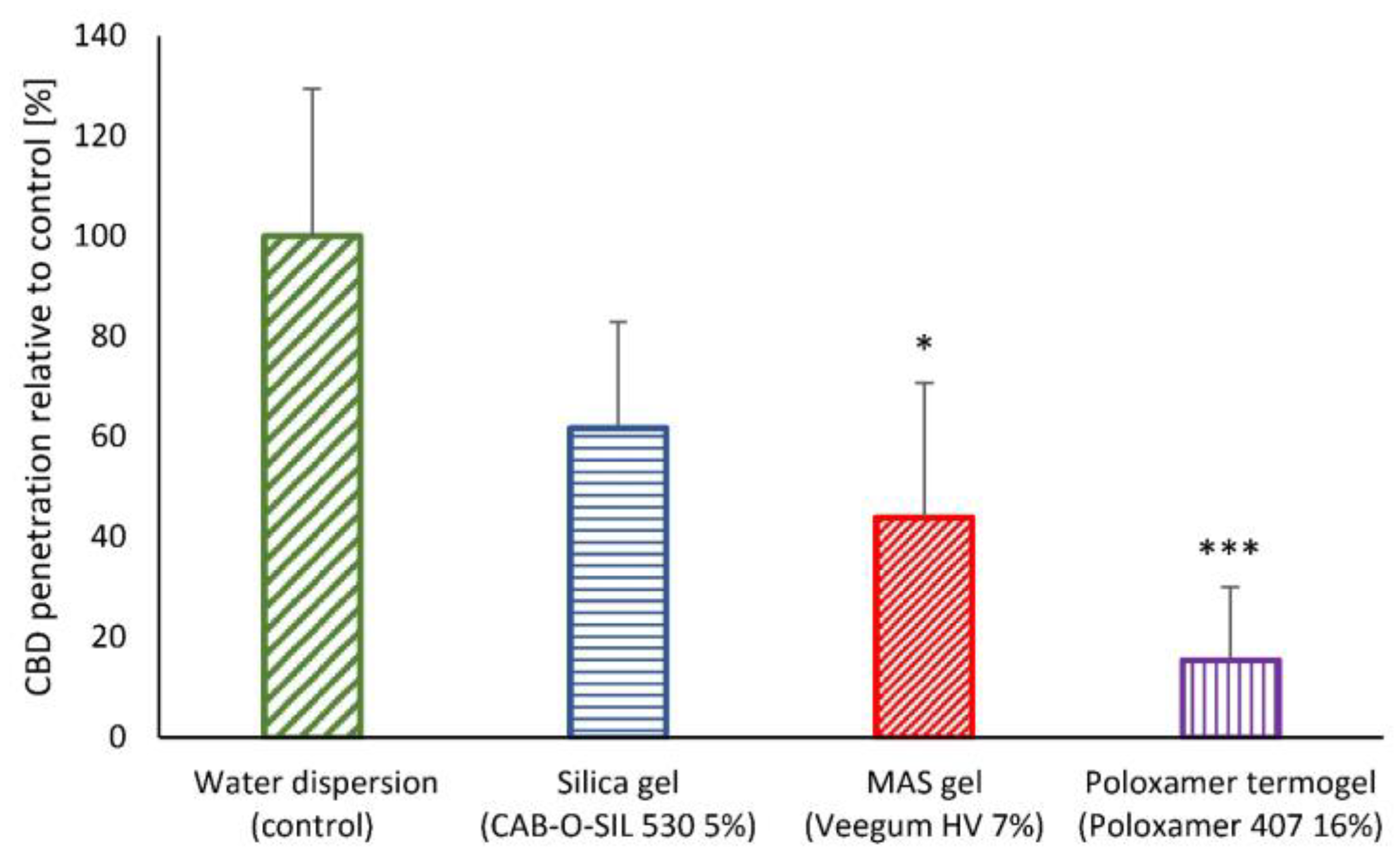
2.2. In Vitro Skin Permeability of Semi-Solid LSN Formulation Development
2.3. In-Vivo Skin Penetration and Retention
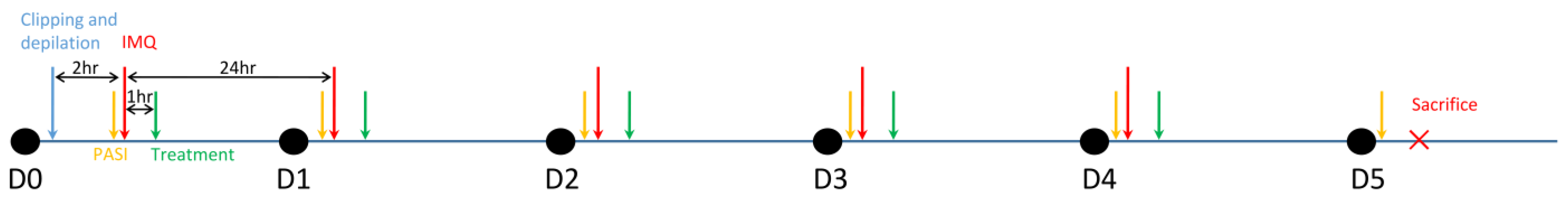
2.4. Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis Model
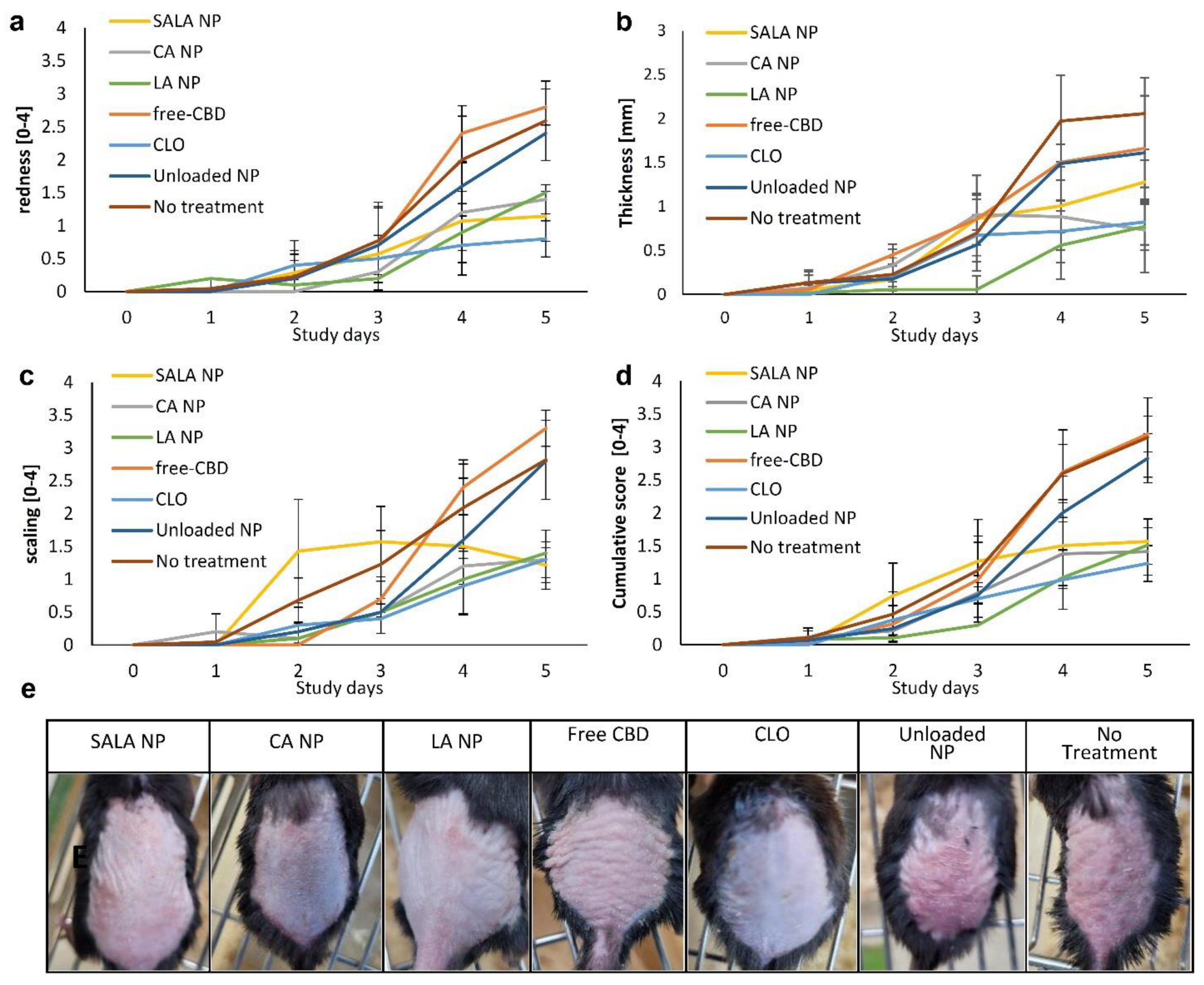
2.4.1. Erythema and Scaling
2.4.2. Skin Thickness
2.4.3. Cumulative Day-to-Day Scoring
2.4.4. Weight Loss
2.4.5. Spleen
2.4.6. Acanthosis Evaluation
2.4.7. Anti-Inflammatory Action of CBD-Loaded LSNs as Evaluated by Reduction in IL-17A Secretion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Nano-Particles Preparation
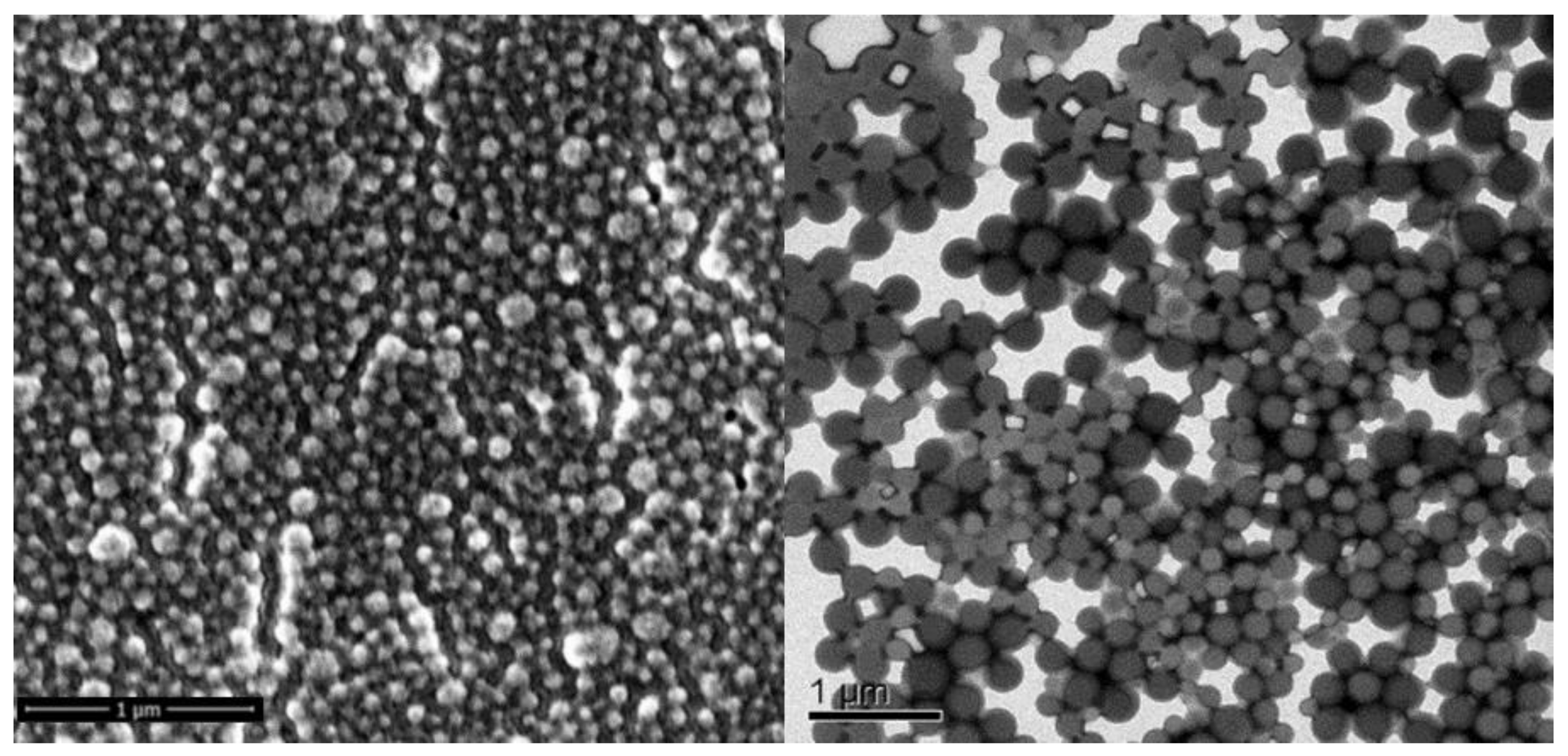
3.2. Size and Microscopic Analysis
3.2.1. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
3.2.2. Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA)
3.3. Determination of CBD in NP Dispersion
3.4. In-Vitro Skin Penetration Study
3.4.1. In-Vitro Skin Penetration
3.4.2. Preparation of NPs for Formulation Carrier Selection and Optimization
3.5. In-Vivo Skin Penetration Study and Image Analysis
3.6. Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis in Mice
3.6.1. Animals
3.6.2. Preparation of the Formulated NP Dispersions and the CBD Emulsion
3.6.3. Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis in Mice
3.6.4. Evaluation of Psoriasis Area Severity Index (PASI) Score and Spleen Index
3.6.5. Histology
3.6.6. Evaluation of IL-17A Levels in the Skin Tissue
3.7. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Peng, J.; Fan, M.; An, C.; Ni, F.; Huang, W.; Luo, J. A Narrative Review of Molecular Mechanism and Therapeutic Effect of Cannabidiol (CBD). Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2022, 130, 439–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tham, M.; Yilmaz, O.; Alaverdashvili, M.; Kelly, M.E.M.; Denovan-Wright, E.M.; Laprairie, R.B. Allosteric and Orthosteric Pharmacology of Cannabidiol and Cannabidiol-Dimethylheptyl at the Type 1 and Type 2 Cannabinoid Receptors. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 176, 1455–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Pinilla, E.; Varani, K.; Reyes-Resina, I.; Angelats, E.; Vincenzi, F.; Ferreiro-Vera, C.; Oyarzabal, J.; Canela, E.I.; Lanciego, J.L.; Nadal, X.; et al. Binding and Signaling Studies Disclose a Potential Allosteric Site for Cannabidiol in Cannabinoid CB2 Receptors. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, A.; Baillie, G.L.; Phillips, A.M.; Razdan, R.K.; Ross, R.A.; Pertwee, R.G. Cannabidiol Displays Unexpectedly High Potency as an Antagonist of CB 1 and CB 2 Receptor Agonists in Vitro. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 150, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, A.; Ferraz-De-Paula, V.; Pinheiro, M.L.; Vitoretti, L.B.; Mariano-Souza, D.P.; Quinteiro-Filho, W.M.; Akamine, A.T.; Almeida, V.I.; Quevedo, J.; Dal-Pizzol, F.; et al. Cannabidiol, a Non-Psychotropic Plant-Derived Cannabinoid, Decreases Inflammation in a Murine Model of Acute Lung Injury: Role for the Adenosine A2A Receptor. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 678, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sermet, S.; Li, J.; Bach, A.; Crawford, R.B.; Kaminski, N.E. Cannabidiol Selectively Modulates Interleukin (IL)-1β and IL-6 Production in Toll-like Receptor Activated Human Peripheral Blood Monocytes. Toxicology 2021, 464, 153016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarocka-Karpowicz, I.; Biernacki, M.; Wroński, A.; Gęgotek, A.; Skrzydlewska, E. Cannabidiol Effects on Phospholipid Metabolism in Keratinocytes from Patients with Psoriasis Vulgaris. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, J.D.; Williamson, E.M. Cannabinoids Inhibit Human Keratinocyte Proliferation through a Non-CB1/CB2 Mechanism and Have a Potential Therapeutic Value in the Treatment of Psoriasis. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2007, 45, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangiovanni, E.; Fumagalli, M.; Pacchetti, B.; Piazza, S.; Magnavacca, A.; Khalilpour, S.; Melzi, G.; Martinelli, G.; Dell’Agli, M. Cannabis sativa L. Extract and Cannabidiol Inhibit in Vitro Mediators of Skin Inflammation and Wound Injury. Phytother. Res. 2019, 33, 2083–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patzelt, A.; Lademann, J. Drug Delivery to Hair Follicles. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2013, 10, 787–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blume-Peytavi, U.; Vogt, A. Human Hair Follicle: Reservoir Function and Selective Targeting. Br. J. Dermatol. 2011, 165, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toll, R.; Jacobi, U.; Richter, H.; Lademann, J.; Schaefer, H.; Blume-Peytavi, U. Penetration Profile of Microspheres in Follicular Targeting of Terminal Hair Follicles. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2004, 123, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, B.C.; DeLouise, L.A. Nanoparticle-Enabled Transdermal Drug Delivery Systems for Enhanced Dose Control and Tissue Targeting. Molecules 2016, 21, 1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, K.A.; Date, A.A.; Joshi, M.D.; Patravale, V.B. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLN) of Tretinoin: Potential in Topical Delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 345, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lodzki, M.; Godin, B.; Rakou, L.; Mechoulam, R.; Gallily, R.; Touitou, E. Cannabidiol–Transdermal Delivery and Anti-Inflammatory Effect in a Murine Model. J. Control. Release 2003, 93, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sosnik, A.; Shabo, R.B.; Halamish, H.M. Cannabidiol-Loaded Mixed Polymeric Micelles of Chitosan/Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) and Poly(Methyl Methacrylate) for Trans-Corneal Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamansky, M.; Zehavi, N.; Ben-Shabat, S.; Sintov, A.C. Characterization of Nanoparticles Made of Ethyl Cellulose and Stabilizing Lipids: Mode of Manufacturing, Size Modulation, and Study of Their Effect on Keratinocytes. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 607, 121003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamansky, M.; Zehavi, N.; Sintov, A.C.; Ben-Shabat, S. The Fundamental Role of Lipids in Polymeric Nanoparticles: Dermal Delivery and Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Cannabidiol. Molecules 2023, 28, 1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swindell, W.R.; Michaels, K.A.; Sutter, A.J.; Diaconu, D.; Fritz, Y.; Xing, X.; Sarkar, M.K.; Liang, Y.; Tsoi, A.; Gudjonsson, J.E.; et al. Imiquimod Has Strain-Dependent Effects in Mice and Does Not Uniquely Model Human Psoriasis. Genome Med. 2017, 9, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Fits, L.; Mourits, S.; Voerman, J.S.A.; Kant, M.; Boon, L.; Laman, J.D.; Cornelissen, F.; Mus, A.-M.; Florencia, E.; Prens, E.P.; et al. Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis-Like Skin Inflammation in Mice Is Mediated via the IL-23/IL-17 Axis. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 5836–5845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, C.P.; Martinho, N.; Rosado, C.; Fernandes, A.S.; Roberto, A. Design of Polymeric Nanoparticles and Its Applications as Drug Delivery Systems for Acne Treatment. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2014, 40, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, A.K.; Jain, A.; Garg, N.K.; Agarwal, A.; Jain, A.; Jain, S.A.; Tyagi, R.K.; Jain, R.K.; Agrawal, H.; Agrawal, G.P. Adapalene Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles Gel: An Effective Approach for Acne Treatment. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 121, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Z.; Pan, S.; Wang, L.; Li, S. Topical Gel Based Nanoparticles for the Controlled Release of Oleanolic Acid: Design and in Vivo Characterization of a Cubic Liquid Crystalline Anti-Inflammatory Drug. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2021, 21, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manna, S.; Lakshmi, U.S.; Racharla, M.; Sinha, P.; Kanthal, L.K.; Kumar, S.P.N. Bioadhesive HPMC Gel Containing Gelatin Nanoparticles for Intravaginal Delivery of Tenofovir. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 6, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.J.; Mesquida, P.; Jones, S.A. Investigating the Ability of Nanoparticle-Loaded Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose and Xanthan Gum Gels to Enhance Drug Penetration into the Skin. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 513, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Kassas, R.; Wen, J.; Cheng, A.E.M.; Kim, A.M.J.; Liu, S.S.M.; Yu, J. Transdermal Delivery of Propranolol Hydrochloride through Chitosan Nanoparticles Dispersed in Mucoadhesive Gel. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 153, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozman, B.; Gosenca, M.; Gasperlin, M.; Padois, K.; Falson, F. Dual Influence of Colloidal Silica on Skin Deposition of Vitamins C and e Simultaneously Incorporated in Topical Microemulsions. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2010, 36, 852–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schliemann, S.; Petri, M.; Elsner, P. How Much Skin Protection Cream Is Actually Applied in the Workplace? Determination of Dose per Skin Surface Area in Nurses. Contact Dermat. 2012, 67, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenberg, C.; Larkö, O. Sunscreen Application and Its Importance for the Sun Protection Factor. Arch. Dermatol. 1985, 11, 1400–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Chu, B. Formation of Homogeneous Gel-like Phases by Mixed Triblock Copolymer Micelles in Aqueous Solution: FCC to BCC Phase Transition. J. Appl. Cryst. 2000, 33, 727–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brindley, G.W. Clays, Clay Minerals. In Mineralogy; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1981; pp. 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorichetti, V.; Hugouvieux, V.; Kob, W. Dynamics of Nanoparticles in Polydisperse Polymer Networks: From Free Diffusion to Hopping. Macromolecules 2021, 54, 8575–8589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dell, Z.E.; Schweizer, K.S. Theory of Localization and Activated Hopping of Nanoparticles in Cross-Linked Networks and Entangled Polymer Melts. Macromolecules 2014, 47, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binder, L.; Mazál, J.; Petz, R.; Klang, V.; Valenta, C. The Role of Viscosity on Skin Penetration from Cellulose Ether-Based Hydrogels. Skin Res. Technol. 2019, 25, 725–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finke, J.H.; Richter, C.; Gothsch, T.; Kwade, A.; Büttgenbach, S.; Müller-Goymann, C.C. Coumarin 6 as a Fluorescent Model Drug: How to Identify Properties of Lipid Colloidal Drug Delivery Systems via Fluorescence Spectroscopy? Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2014, 116, 1234–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niczyporuk, M. Rat Skin as an Experimental Model in Medicine. Prog. Health Sci. 2018, 8, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquet, F.; Grandclaude, M.-C.; Ferrari, E.; Champmartin, C. Capacity of an in vitro rat skin model to predict human dermal absorption: Influences of aging and anatomical site. Toxicol. In Vitro 2019, 61, 104623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorjsembe, B.; Ham, J.Y.; Kim, J.C. The Imiquimod Induced Psoriatic Animal “Model: Scientific Implications. Biomed. J. Sci. Tech. Res. 2019, 13, 9722–9724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liu, X.; Ge, W.; Chen, C.; Huang, Y.; Jin, Z.; Zhan, M.; Duan, X.; Liu, X.; Kong, Y.; et al. CB2R Deficiency Exacerbates Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasiform Dermatitis and Itch Through the Neuro-Immune Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 790712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, X.; Qiu, H.; Chen, W. Weight Loss May Be Unrelated to Dietary Intake in the Imiquimod-Induced Plaque Psoriasis Mice Model. Open Life Sci. 2020, 15, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, P.; Jensen, L.E. Imiquimod Treatment Causes Systemic Disease in Mice Resembling Generalized Pustular Psoriasis in an IL-1 and IL-36 Dependent Manner. Mediat. Inflamm. 2016, 2016, 6756138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignatowska-Jankowska, B.; Jankowski, M.M.; Swiergiel, A.H. Cannabidiol Decreases Body Weight Gain in Rats: Involvement of CB2 Receptors. Neurosci. Lett. 2011, 490, 82–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, J.S.; Martel, F. Effects of Cannabidiol on Appetite and Body Weight: A Systematic Review. Clin. Drug Investig. 2022, 42, 909–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewing, L.E.; Skinner, C.M.; Quick, C.M.; Kennon-McGill, S.; McGill, M.R.; Walker, L.A.; ElSohly, M.A.; Gurley, B.J.; Koturbash, I. Hepatotoxicity of a Cannabidiol-Rich Cannabis Extract in the Mouse Model. Molecules 2019, 24, 1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Souza, L.; Badanthadka, M.; Salwa, F. Effect of Animal Strain on Model Stability to Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis. Indian J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2020, 64, 83–91. [Google Scholar]
- Salwa, F.; Badanthadka, M.; D’Souza, L. Differential Psoriatic Effect of Imiquimod on Balb/c and Swiss Mice. J. Health Allied Sci. 2021, 11, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinno-Hashimoto, H.; Eguchi, A.; Sakamoto, A.; Wan, X.; Hashimoto, Y.; Fujita, Y.; Mori, C.; Hatano, M.; Matsue, H.; Hashimoto, K. Effects of Splenectomy on Skin Inflammation and Psoriasis-like Phenotype of Imiquimod-Treated Mice. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 14738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krummen, M.B.W.; Varga, G.; Steinert, M.; Stuetz, A.; Luger, T.A.; Grabbe, S. Effect of Pimecrolimus vs. Corticosteroids on Murine Bone Marrow-Derived Dendritic Cell Differentiation, Maturation and Function. Exp. Dermatol. 2006, 15, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoepe, S.; Schäcke, H.; May, E.; Asadullah, K. Glucocorticoid Therapy-Induced Skin Atrophy. Exp. Dermatol. 2006, 15, 406–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shobeiri, S.S.; Rezaee, M.A.; Pordel, S.; Haghnnavaz, N.; Dashti, M.; Moghadam, M.; Sankian, M. Anti-IL-17A SsDNA Aptamer Ameliorated Psoriasis Skin Lesions in the Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis Mouse Model. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 110, 108963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Liu, W.; Gao, S.; Mao, Y.; Xin, Y. Application of Imiquimod-Induced Murine Psoriasis Model in Evaluating Interleukin-17A Antagonist. BMC Immunol. 2021, 22, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozela, E.; Juknat, A.; Kaushansky, N.; Rimmerman, N.; Ben-Nun, A.; Vogel, Z. Cannabinoids Decrease the Th17 Inflammatory Autoimmune Phenotype. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2013, 8, 1265–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegde, V.L.; Nagarkatti, P.S.; Nagarkatti, M. Role of Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells in Amelioration of Experimental Autoimmune Hepatitis Following Activation of TRPV1 Receptors by Cannabidiol. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wu, X.; Simonavicius, N.; Tian, H.; Ling, L. Medium-Chain Fatty Acids as Ligands for Orphan G Protein-Coupled Receptor GPR84. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 34457–34464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laine, P.S.; Schwartz, E.A.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.Y.; Karnik, S.K.; Musi, N.; Reaven, P.D. Palmitic Acid Induces IP-10 Expression in Human Macrophages via NF-ΚB Activation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 358, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, A.; Schliep, A.; Jörg, S.; Haghikia, A.; Gold, R.; Kleinewietfeld, M.; Müller, D.N.; Linker, R.A. Impact of Combined Sodium Chloride and Saturated Long-Chain Fatty Acid Challenge on the Differentiation of T Helper Cells in Neuroinflammation. J. Neuroinflamm. 2017, 14, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodin, A.; Nyqvist-Mayer, A.; Broberg, F.; Wadsten, T.; Forslund, B. Phase Diagram and Aqueous Solubility of the Lidocaine-prilocaine Binary System. J. Pharm. Sci. 1984, 73, 481–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.M.; Pereira, C.V.; Mano, F.; Silva, E.; Castro, V.I.B.; Sá-Nogueira, I.; Reis, R.L.; Paiva, A.; Matias, A.A.; Duarte, A.R.C. Therapeutic Role of Deep Eutectic Solvents Based on Menthol and Saturated Fatty Acids on Wound Healing. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2019, 2, 4346–4355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provencher, S.W. A Constrained Regularization Method for Inverting Data Represented by Linear Algebraic or Integral Equations. Comput. Phys. Commun. 1982, 27, 213–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casiraghi, A.; Musazzi, U.M.; Centin, G.; Franzè, S.; Minghetti, P. Topical Administration of Cannabidiol: Influence of Vehicle-Related Aspects on Skin Permeation Process. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An Open-Source Platform for Biological-Image Analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundberg, J.P.; Silva, K.A. What Color Is the Skin of a Mouse? Vet. Pathol. 2012, 49, 142–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabeen, M.; Boisgard, A.S.; Danoy, A.; Kholti, N.E.; Salvi, J.P.; Boulieu, R.; Fromy, B.; Verrier, B.; Lamrayah, M. Advanced Characterization of Imiquimod-induced Psoriasis-like Mouse Model. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| LSN-Type | Size [nm] | PDI | NP Conc. [NPs/mL] | CBD Conc. [mg/g] | EE [%] |
| SALA | 238.0 | 0.028 | 2.06 × 1013 | 13.8 | 86.3 |
| CA | 220.8 | 0.102 | 1.52 × 1013 | 12.5 | 69.2 |
| LA | 245.0 | 0.182 | 1.78 × 1013 | 20.0 | 68.0 |
| Unloaded | 226.2 | 0.114 | 1.60 × 1013 | NA | NA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zamansky, M.; Yariv, D.; Feinshtein, V.; Ben-Shabat, S.; Sintov, A.C. Cannabidiol-Loaded Lipid-Stabilized Nanoparticles Alleviate Psoriasis Severity in Mice: A New Approach for Improved Topical Drug Delivery. Molecules 2023, 28, 6907. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28196907
Zamansky M, Yariv D, Feinshtein V, Ben-Shabat S, Sintov AC. Cannabidiol-Loaded Lipid-Stabilized Nanoparticles Alleviate Psoriasis Severity in Mice: A New Approach for Improved Topical Drug Delivery. Molecules. 2023; 28(19):6907. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28196907
Chicago/Turabian StyleZamansky, Mark, Doron Yariv, Valeria Feinshtein, Shimon Ben-Shabat, and Amnon C. Sintov. 2023. "Cannabidiol-Loaded Lipid-Stabilized Nanoparticles Alleviate Psoriasis Severity in Mice: A New Approach for Improved Topical Drug Delivery" Molecules 28, no. 19: 6907. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28196907
APA StyleZamansky, M., Yariv, D., Feinshtein, V., Ben-Shabat, S., & Sintov, A. C. (2023). Cannabidiol-Loaded Lipid-Stabilized Nanoparticles Alleviate Psoriasis Severity in Mice: A New Approach for Improved Topical Drug Delivery. Molecules, 28(19), 6907. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28196907