First-Row Transition Metal Complexes Incorporating the 2-(2′-pyridyl)quinoxaline Ligand (pqx), as Potent Inflammatory Mediators: Cytotoxic Properties and Biological Activities against the Platelet-Activating Factor (PAF) and Thrombin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemistry
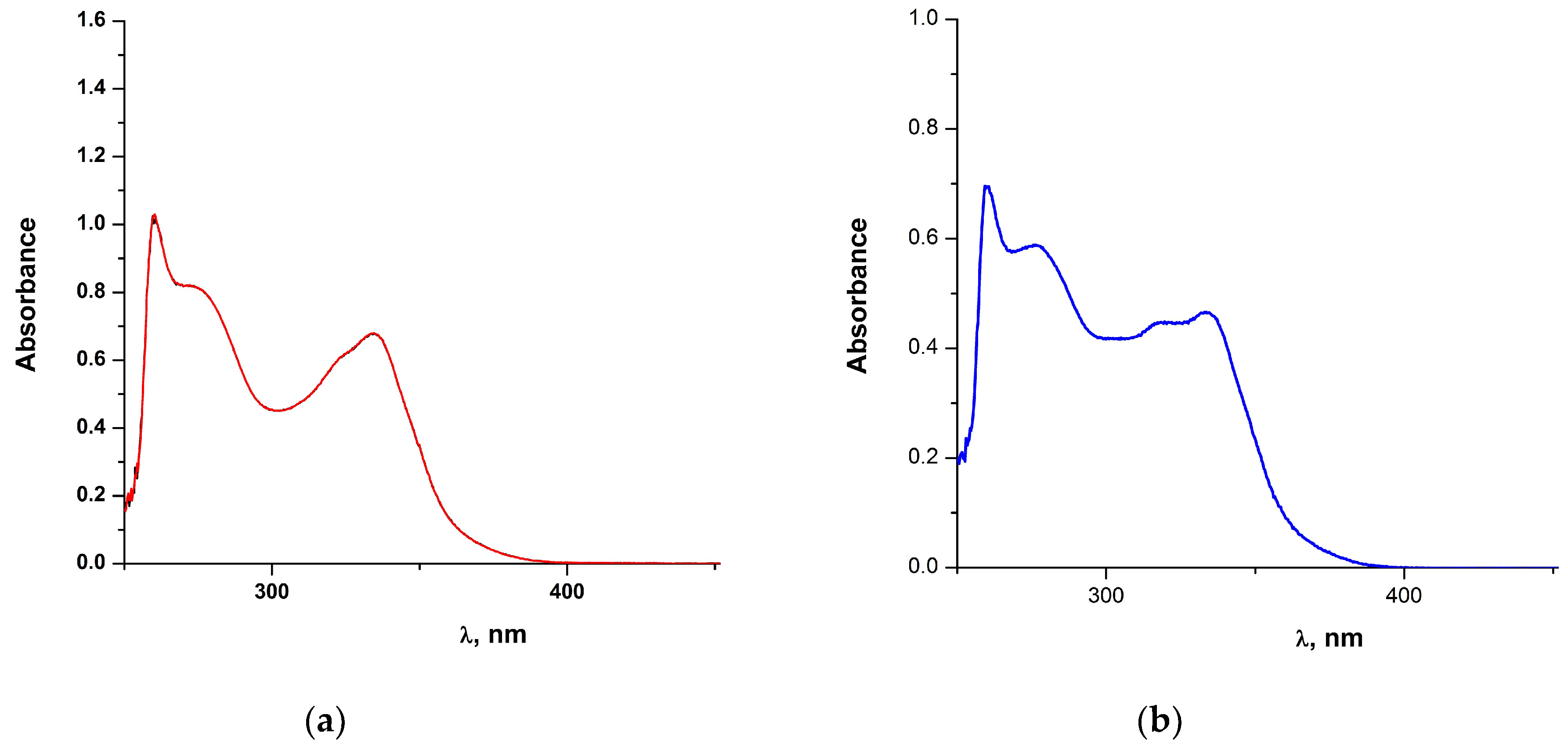
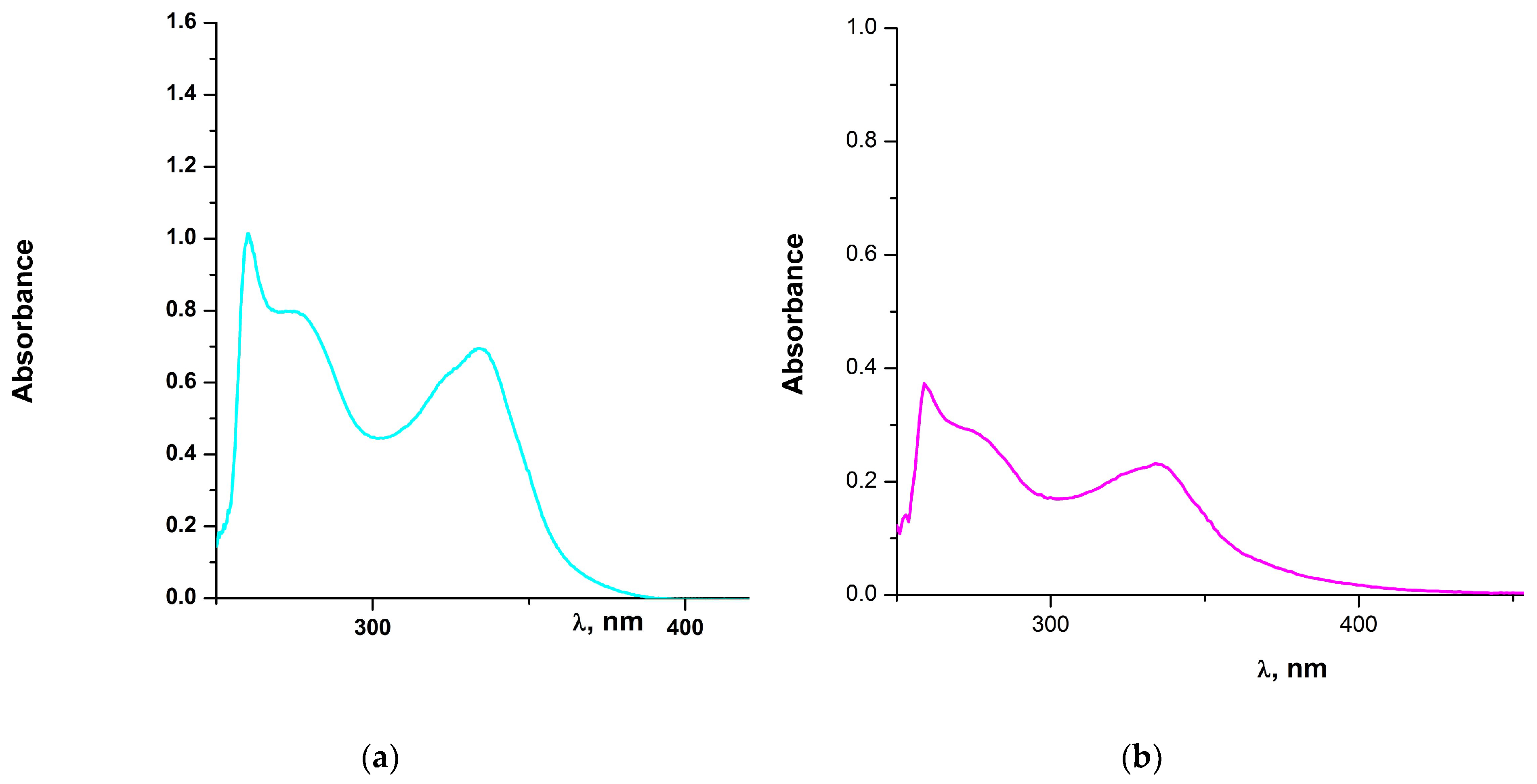
2.1.1. Solution Behavior (Conductivity Measurements, UV-Vis Spectroscopy, Solution ATR-IR Measurements and High Resolution Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry (ESI-HRMS))
2.2. Evaluation of Biological Activity
2.2.1. Inhibitory Effects against the Biological Activities of PAF in Washed Rabbit Platelets (WRPs)
2.2.2. Inhibitory Effect against Thrombin
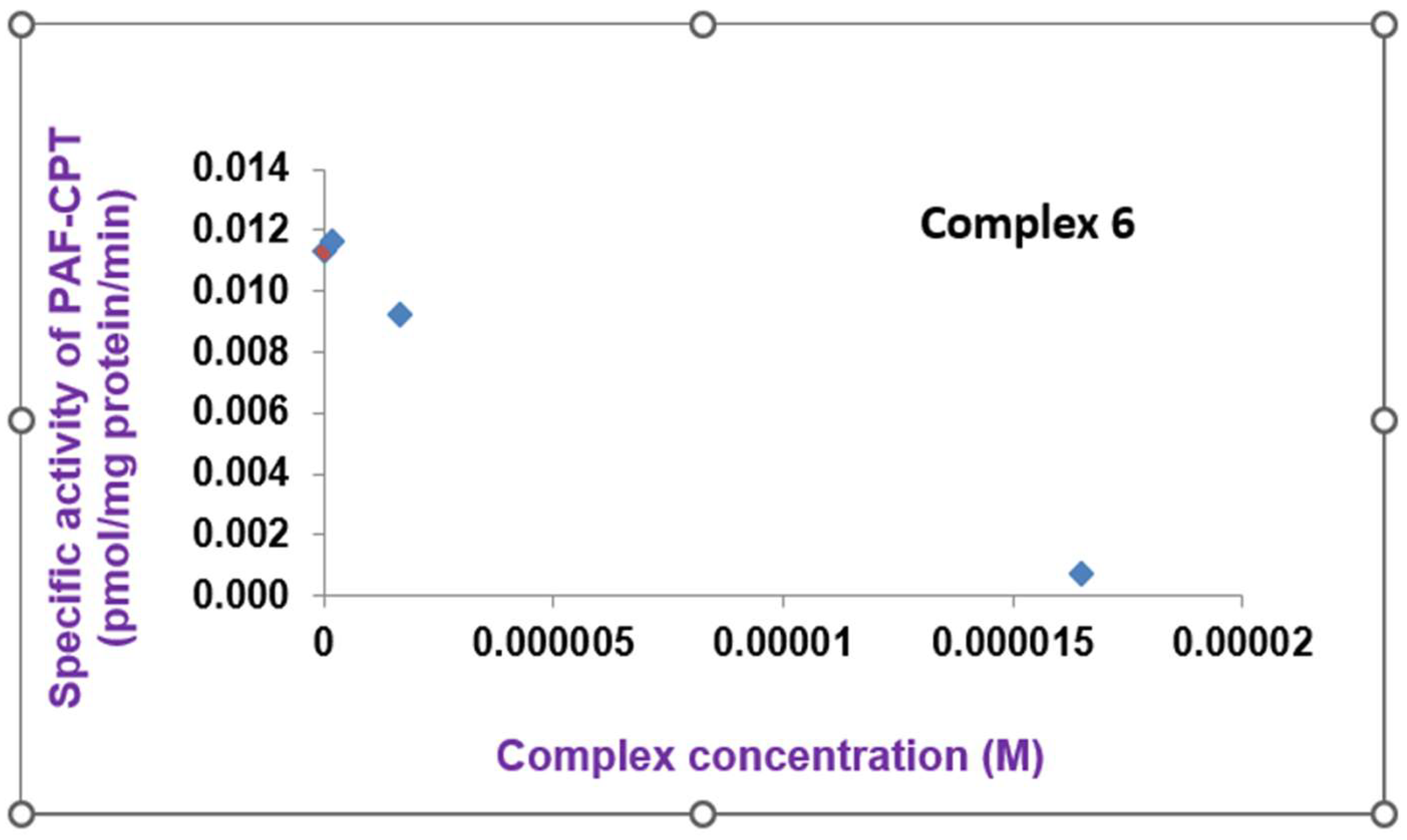
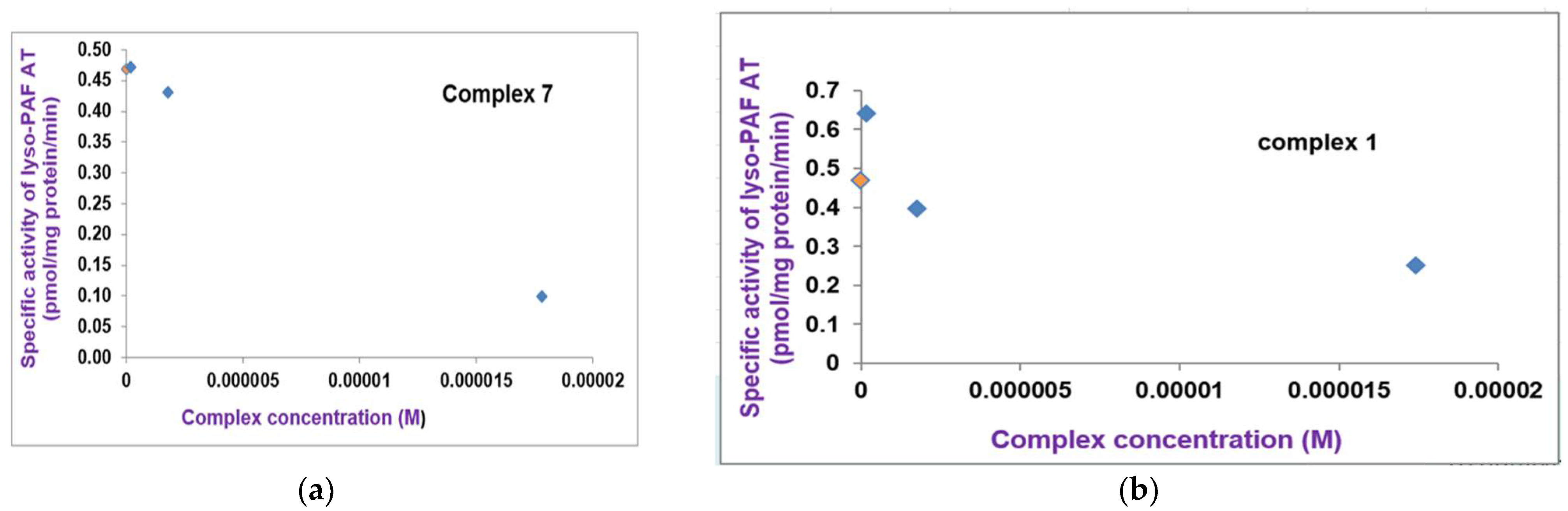
2.2.3. Biosynthesis of PAF
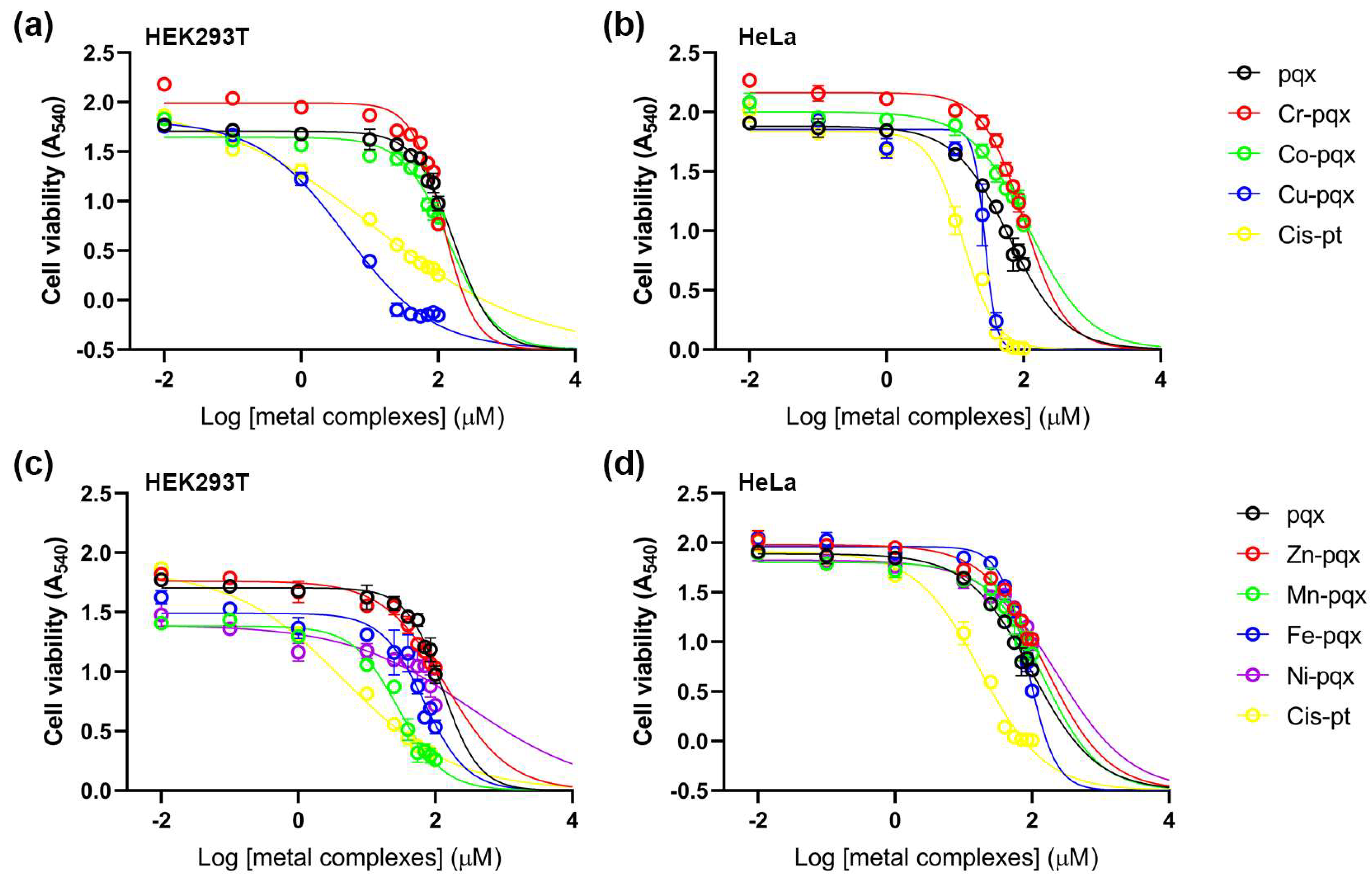
2.2.4. Cell Viability Assay
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization
3.1.1. Synthesis of Complex 3
3.1.2. Data for Complexes 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7
3.2. Single-Crystal X-ray Structural Determination
3.3. Biological Evaluation
3.3.1. Materials and Methods for Biological Experiments in Washed Rabbit Platelets (WRPs)
3.3.2. Methods for Determining the Effect on the Activity of PAF Metabolic Enzymes
PAF-CPT Activity Assay
Lyso PAF-AT Activity Assay
Determination of Produced PAF by the Biosynthetic Enzymes (PAF-CPT and Lyso PAF-AT)
Plasma PAF-AH (LpPLA2) Activity Assay
3.3.3. Cell Viability Assay
MTT Assay
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Boros, E.; Dyson, P.J.; Gasser, G. Classification of Metal-based Drugs According to Their Mechanisms of Action. Chem 2020, 9, 641–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medici, S.; Peana, M.; Nurchi, M.V.; Lachowicz, J.I.; Crisponi, G.; Zoroddu, M.A. Noble metals in medicine: Latest advances. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2015, 284, 329–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lippard, S.J. New metal complexes as potential therapeutics. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2003, 7, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovejoy, K.S.; Lippard, S.J. Non-traditional platinum compounds for improved accumulation, oral bioavailability, and tumor targeting. Dalton Trans. 2009, 10651–10659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makovec, T. Cisplatin and beyond: Molecular mechanisms of action and drug resistance development in cancer chemotherapy. Radiol. Oncol. 2019, 53, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergamo, A.; Gaiddon, C.; Schellens, J.H.M.; Beijnen, J.H.; Sava, G. Approaching tumour therapy beyond platinum drugs: Status of the art and perspectives of ruthenium drug candidates. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2012, 106, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldinucci, D.; Ronconi, L.; Fregona, D. Groundbreaking gold(III) anticancer agents. Drug Discov. Today 2009, 14, 1075–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messori, L.; Marcon, G. Metal Ions in Biological Systems; Sigel, A., Sigel, H., Eds.; Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 2004; Volume 41, p. 279. [Google Scholar]
- Failes, T.; Cullinane, C.; Diakos, C.; Yamamoto, N.; Lyons, J.; Hambley, T. Studies of a Cobalt(III) Complex of the MMP Inhibitor Marimastat: A Potential Hypoxia-Activated Prodrug. Chem. Eur. J. 2007, 13, 2974–2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santini, C.; Pellei, M.; Gandin, V.; Porchia, M.; Tisato, F.; Marzano, C. Advances in Copper Complexes as Anticancer Agents. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 815–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsaros, N.; Anagnostopoulou, A. Rhodium and its compounds as potential agents in cancer treatment. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2002, 42, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieda, R.; Ott, I.; Dobroschke, M.; Prokop, A.; Gust, R.; Sheldrick, W.S. Structure–activity relationships and DNA binding properties of apoptosis inducing cytotoxic rhodium(III) polypyridyl complexes containing the cyclic thioether [9]aneS3. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2009, 103, 698–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Rijt, S.H.; Sadler, P.J. Current applications and future potential for bioinorganic chemistry in the development of anticancer drugs. Drug Discov. Today 2009, 14, 1089–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, C.-H.; Li, S.; Zhong, H.-J.; Ma, D.-L. Metal complexes as potential modulators of inflammatory and autoimmune responses. Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 871–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McFadyen, J.; Schaff, M.; Peter, K. Current and future antiplatelet therapies: Emphasis on preserving haemostasis. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2018, 15, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geraldo, R.B.; Bello, M.L.; Dias, L.R.S.; Vera, M.A.F.; Nagashima, T.; Abreu, P.A.; Santos, M.B.; Albuquerque, M.G.; Cabral, L.M.; Freitas, A.C.C.; et al. Antiplatelet activity and structure-activity relationship study of Pyrazolopyridine Derivatives as potential series for treating thrombotic diseases. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2010, 17, 730–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papakonstantinou, V.D.; Lagopati, N.; Tsilibary, E.C.; Demopoulos, C.A.; Philippopoulos, A.I. A Review on Platelet Activating Factor Inhibitors: Could a New Class of Potent Metal-Based Anti-Inflammatory Drugs Induce Anticancer Properties? Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2017, 2017, 6947034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilbuer, A.; Vlecken, D.H.; Schmitz, D.J.; Kräling, K.; Harms, K.; Bagowski, C.P.; Meggers, E. Iridium Complex with Antiangiogenic Properties. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 3839–3842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demopoulos, C.A.; Pinckard, R.N.; Hanahan, D.J. Platelet-activating factor. Evidence for 1-O-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glyceryl-3-phosphorylcholine as the active component (a new class of lipid chemical mediators. J. Biol. Chem. 1979, 254, 9355–9358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoupras, A.B.; Chini, M.; Tsogas, N.; Lioni, A.; Tsekes, G.; Demopoulos, C.A.; Lazanas, M.C. In vitro anti-inflammatory and anti-coagulant effects of antibiotics towards Platelet Activating Factor and thrombin. J. Inflamm. 2011, 8, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lordan, R.; Tsoupras, A.; Zabetakis, I.; Demopoulos, C.A. Forty Years Since the Structural Elucidation of Platelet-Activating Factor (PAF): Historical, Current, and Future Research Perspectives. Molecules 2019, 24, 4414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladding, P.; Webster, M.; Ormiston, J.; Olsen, S.; White, H. Antiplatelet drug non responsiveness. Am. Heart J. 2008, 155, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsoupras, A.B.; Iatrou, C.; Frangia, C.; Demopoulos, A.C. The implication of platelet activating factor in cancer growth and metastasis: Potent beneficial role of PAF-inhibitors and antioxidants. Infect. Disord. Drug Targets 2009, 9, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyland, I.K.; O’Toole, R.F.; Smith, J.A.; Bissember, A.C. Progress in the Development of Platelet-Activating Factor Receptor (PAFr) Antagonists and Applications in the Treatment of Inflammatory Diseases. ChemMedChem 2018, 13, 1873–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsoupras, A.B.; Papakyriakou, A.; Demopoulos, A.C.; Philippopoulos, A.I. Synthesis, biochemical evaluation and molecular modeling studies of novel rhodium complexes with nanomolar activity against Platelet Activating Factor. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2013, 120, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margariti, A.; Papakonstantinou, V.D.; Stamatakis, G.M.; Demopoulos, C.A.; Schnakenburg, G.; Andreopoulou, A.K.; Giannopoulos, P.; Kallitsis, J.K.; Philippopoulos, A.I. Substituted pyridine-quinoline ligands as building blocks for neutral rhodium(III) complexes. Synthesis, structural characterization studies and anti-platelet activity towards the Platelet-Activating Factor (PAF). Polyhedron 2020, 178, 114336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalampalidis, A.; Peppas, A.; Schnakenburg, G.; Papakyriakoy, A.; Tsoupras, A.; Zabetakis, I.; Philippopoulos, A.I. Antithrombotic and antiplatelet activity of an organometallic rhodium(I) complex incorporating a substituted thieno-[2,3-d]-pyrimidine ligand: Synthesis, structural characterization, and molecular docking calculations. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2021, 35, e6210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peppas, A.; Kalabalidis, A.; Papakonstantinou, V.D.; Demopoulos, C.A.; Schnakenburg, G.; Philippopoulos, A.I. Rhodium-based Inhibitors of the Platelet Activating Factor (PAF): A new class of potent anti-inflammatory drugs. In Chemical Elements (Fluorine, Rhodium and Rubidium): Properties, Synthesis and Applications; Huff, A., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 127–169. [Google Scholar]
- Prokopi, M. Ir(I) and Ir(III) Complexes and Study of Their Biological Activity against the Platelet Acivating Factor. Master’s Thesis, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, Athens, Greece, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Tsoupras, A.-B.; Papakonstantinou, V.; Stamatakis, G.M.; Demopoulos, C.A.; Falaras, P.; Philippopoulos, A.I. Biochemical evaluation of ruthenium-based complexes towards PAF (Platelet Activating Factor) and Thrombin. Potent anti-inflammatory agents. Sci. Lett. J. 2015, 4, 208. [Google Scholar]
- Khamrang, T.; Hung, K.-C.; Hsia, C.-H.; Hsieh, C.-Y.; Velusamy, M.; Jayakumar, T.; Sheu, J.-R. Antiplatelet Activity of a Newly Synthesized Novel Ruthenium (II): A Potential Role for Akt/JNK Signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalampalidis, A.; Damati, A.; Matthopoulos, D.; Tsoupras, A.B.; Demopoulos, C.A.; Schnakenburg, G.; Philippopoulos, A.I. Tin(II) and Tin(IV) Complexes Incorporating the Oxygen Tripodal Ligands [(η5-C5R5)Co{P(OEt)2O}3]−, (R = H, Me; Et = -C2H5) as Potent Inflammatory Mediator Inhibitors: Cytotoxic Properties and Biological Activities against the Platelet-Activating Factor (PAF) and Thrombin. Molecules 2023, 28, 1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohrabi, M.; Saeedi, M.; Larijani, B.; Mahdavi, M. Recent advances in biological activities of rhodium complexes: Their applications in drug discovery research. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 216, 113308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravishankar, D.; Salamah, M.; Attina, M.A.; Pothi, R.; Vallance, T.M.; Javed, M.; Williams, H.F.; Alzahranil, E.M.S.; Kabove, E.; Vaiyapuri, R.; et al. Ruthenium-conjugated chrysin analogues modulate platelet activity, thrombus formation and haemostasis with enhanced efficacy. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayakumar, T.; Hsu, C.-Y.; Khamrang, T.; Hsia, C.-H.; Hsia, C.-W.; Manubolu, M.; Sheu, J.-R. Possible molecular targets of novel ruthenium complexes in antiplatelet therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crans, D.C.; Kostenkova, K. Open questions on the biological roles of first-row transition metals. Commun. Chem. 2020, 3, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philippopoulos, A.I.; Tsantila, N.; Demopoulos, C.A.; Raptopoulou, C.P.; Likodimos, V.; Falaras, P. Synthesis, characterization and crystal structure of the cis-[RhL2Cl2]Cl complex with the bifunctional ligand (L) 2-(2’-pyridyl)quinoxaline. Biological activity towards PAF (Platelet Activating Factor) induced platelet aggregation. Polyhedron 2009, 28, 3310–3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippopoulos, A.; Falaras, P.; Chatzivasiloglou, E.; Igglessi-Markopoulou, O.; Likodimos, V.; Konti, G.-C. Synthesis and spectroscopic characterization of new heteroleptic ruthenium(II) complexes incorporating 2-(2′- pyridyl)quinoxaline and 4-carboxy-2-(2′-pyridyl)quinoline. J. Coord. Chem. 2012, 65, 2535–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pages, B.J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, F.; Sakoff, J.; Gilbert, J.; Aldrich-Wright, J.R. Cytotoxicity and Structural Analyses of 2,2′-Bipyridine-, 4,4′-Dimethyl-2,2′-bipyridine- and 2-(2′-Pyridyl)quinoxaline platinum(II) Complexes. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2015, 2015, 4146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balou, S.; Zarkadoulas, A.; Koukouvitaki, M.; Marchiò, L.; Efthimiadou, E.K.; Mitsopoulou, C.A. Synthesis, DNA-Binding, Anticancer Evaluation, and Molecular Docking Studies of Bishomoleptic and Trisheteroleptic Ru-Diimine Complexes Bearing 2-(2-Pyridyl)-quinoxaline. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2021, 2021, 5599773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constable, E.C. Homoleptic complexes of 2,2′-bipyridine. Adv. Inorg. Chem. 1989, 34, 1–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaim, W. The Versatile Chemistry of 1,4-Diazines: Organic, Inorganic and Biochemical Aspects. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1983, 22, 171–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasselouri, S.; Garoufis, A.; Katehanakis, A.; Kalkanis, G.; Perlepes, S.P.; Hadjiliadis, N. 1:1 Metal complexes of 2-(2′-pyridyl)quinoxaline, a ligand unexpectedly formed by the reaction between 2-acetylpyridine and 1,2-phenylenediamine. Inorg. Chim. Acta 1993, 207, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Housecroft, C.E.; Sharpe, A.G. Inorganic Chemistry, 4th ed.; Pearson Education Limited: London, UK, 2012; p. 639. ISBN 9780273742784. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamoto, K. Infrared and Raman Spectra of Inorganic and Coordination Compounds: Part B: Applications in Coordination, Organometallic and Bioinorganic Chemistry, 6th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008; ISBN 9780470405888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plakatouras, J.C.; Hadjiliadis, N.; Perlepes, S.P.; Albinati, A.; Kalkanis, G. Preparation and characterization of [Cu2Cl4L2]: The first structural determination of a complex containing the novel ligand 2-(2’-pyridyl)quinoxaline. Polyhedron 1993, 12, 2069–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reza, H.; Sasan, K.K.; Hashjin, S.S.; Zahedi, M. A new mixed-ligand complex of copper(II) containing N-(2-pyridylmethyl)-2-pyrazinecarboxamide (NPyPzCa): Synthesis, molecular and crystal structure and properties of [Cu(NPyPzCa)(NO3)(DMSO)]. C. R. Chim. 2011, 14, 563–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lider, E.; Sukhikh, T.; Smolentsev, A.; Semitut, E.; Filatov, E.; Potapov, A. Synthesis, Crystal Structure, Thermal Analysis, and DFT Calculations of Molecular Copper(II) Chloride Complexes with Bitopic Ligand 1,1,2,2-tetrakis(pyrazol-1-yl)ethane. Crystals 2019, 9, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giziroglu, E.; Aygün, M.; Sarikurkcu, C.; Didem, K.; Orhan, N.; Firinci, E.; Soyleyici, H.C.; Gokcen, C. Synthesis, characterization and antioxidant activity of new dibasic tridentate ligands: X-ray crystal structures of DMSO adducts of 1,3-dimethyl-5-acetyl-barbituric acid o-hydroxybenzoyl hydrazone copper(II) complex. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2013, 36, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chebbi, H.; Chebbi, M.; Guesmi, A.; Arfaoui, Y. Crystal structure determination, and DFT Calculations of dichlorobis-(dimethylsulfoxide-O)copper(II). J Struct. Chem. 2016, 57, 1104–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarafder, M.T.H.; Chew, K.B.; Crouse, K.A.; Ali, A.M.; Yamin, B.M.; Fun, H.K. Synthesis and characterization of Cu(II), Ni(II) and Zn(II) metal complexes of bidentate NS isomeric Schiff bases derived from S-methyldithiocarbazate (SMDTC): Bioactivity of the bidentate NS isomeric Schiff bases, some of their Cu(II), Ni(II) and Zn(II) complexes and the X-ray structure of the bis[S-methyl-β-N-(2-furyl-methyl)methylenedithiocarbazato]zinc(II) complex. Polyhedron 2002, 21, 2683–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inada, Y.; Hayashi, H.; Sugimoto, K.; Funahashi, S. Solvation Structures of Manganese(II), Iron(II), Cobalt(II), Nickel(II), Copper(II), Zinc(II), and Gallium(III) Ions in Methanol, Ethanol, Dimethyl Sulfoxide, and Trimethyl Phosphate as Studied by EXAFS and Electronic Spectroscopies. J. Phys. Chem. A 1999, 103, 1401–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markarian, S.A.; Ghazoyan, H.H.; Sargsyan, H.R.; Shahinyan, G.A. Thermodynamic and Spectroscopic (UV–Vis, FT IR) Studies of Solutions of CoCl2 (or NiCl2) in Diethylsulfoxide. J. Solut. Chem. 2019, 48, 1378–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lever, A.B.P. Inorganic Electronic Spectroscopy, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1984; ISBN 0444423893. [Google Scholar]
- Wallace, V.M.; Dhumal, N.R.; Zehentbauer, F.M.; Kim, H.J.; Kiefer, J. Revisiting the Aqueous Solutions of Dimethyl Sulfoxide by Spectroscopy in the Mid- and Near-Infrared: Experiments and Car–Parrinello Simulations. J. Phys. Chem. B 2015, 119, 14780–14789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shikata, T.; Sugimoto, N. Dimeric Molecular Association of Dimethyl Sulfoxide in Solutions of Nonpolar Liquids. J. Phys. Chem. A 2012, 116, 990–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.-K.; Liu, S.-D.; Duan, B.; Xu, Y.-F.; Li, Z.-Q.; Huang, Y.; Hu, L.-H.; Zhu, J.; Dai, S.-Y. Controllable intermediates by molecular self-assembly for optimizing the fabrication of large-grain perovskite films via one-step spin-coating. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 705, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geary, W.J. The use of conductivity measurements in organic solvents for the characterisation of coordination compounds. Coord. Chem. Rev. 1971, 7, 81–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsierkezos, N.G.; Ritter, U.; Philippopoulos, A.I.; Schröder, D. Electrochemical studies of the bis (triphenyl phosphine) ruthenium(II) complex, cis-[RuCl2(L)(PPh3)2], with L = 2-(2′-pyridyl)quinoxaline. J. Coord. Chem. 2010, 63, 3517–3530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferentinos, E.; Tsoupras, A.B.; Roulia, M.; Chatziefthimiou, S.D.; Demopoulos, C.A.; Kyritsis, P. Inhibitory activity of the novel Zn[(OPPh 2)(SePPh 2)N]2 complex towards the Platelet Activating Factor (PAF) and thrombin: Comparison with its isomorphous Co(II) and Ni(II) analogues. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2011, 378, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sioriki, E.; Lordan, R.; Nahra, F.; van Hecke, K.; Zabetakis, I.; Nolan, S.P. In vitro Anti-atherogenic Properties of N-Heterocyclic Carbene Aurate(I) Compounds. ChemMedChem 2018, 13, 2484–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, M.A.; Huang, T.N.; Matheson, T.W.; Smith, K. Inorganic Synthesis; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1982; Volume 21, pp. 74–77. [Google Scholar]
- Pujante-Galián, M.A.; Pérez, S.A.; Montalbán, M.G.; Carissimi, G.; Fuster, M.G.; Víllora, G.; García, G. p-Cymene Complexes of Ruthenium(II) as Antitumor Agents. Molecules 2020, 25, 5063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, E.J.; Gao, X.N.; Guan, F.; Zhu, M.C.; Liu, L.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.X.; Wang, Y.; Wen, Z.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Synthesis and crystal structure of two new dinuclear cobalt(II) complexes interaction with HeLa cells. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 46, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onuchic, A.C.; Machado, C.M.; Saito, R.F.; Rios, F.J.; Jancar, S.; Chammas, R. Expression of PAFR as Part of a Prosurvival Response to Chemotherapy: A Novel Target for Combination Therapy in Melanoma. Mediators Inflamm. 2012, 2012, 175408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bussolati, B.; Biancone, L.; Cassoni, P.; Russo, S.; Rola-Pleszczynski, M.; Montrucchio, G.; Camussi, G. PAF produced by human breast cancer cells promotes migration and proliferation of tumor cells and neo-angiogenesis. Am. J. Pathol. 2000, 157, 1713–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Freitas Saito, R.; Rangel, M.C.; Chandler, M.; Beasock, D.; Afonin, K.A.; Chammas, R. Cancer Therapy-Induced Inflammation and Its Consequences. In Biotechnology Applied to Inflammatory Diseases; Ribeiro de Araujo, D., Carneiro-Ramos, M., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2023; pp. 49–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garoufis, A.; Kasselouri, S.; Raptopoulou, C.P. Six- and five-coordinated complexes of Co(II) with 2-(2′-pyridyl)quinoxaline. Crystal structures of the complexes, [CoLCl2(DMF)] and [CoL2(H2O)2](ClO4)2·H2O2CH3OH. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2000, 3, 251–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perlepes, S.P.; Spyridoula, K.; Garoufis, A.; Lutz, F.; Bau, R.; Hadjiliadis, N. Reaction of the biheteroaromatic ligand 2-(2′-pyridyl)quinoxaline (L) were zinc(II) and cadmium(II) halides: Preparation and characterization of the 1:1 complexes. Polyhedron 1995, 14, 1461–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garoufis, A.; Kasselouri, S.; Boyatzis, S.; Raptopoulou, C.P. Preparation, crystal structure and solution studies of [Mn2L2Cl4(H2O)2], where L=2-(2′-pyridyl)quinoxaline. Polyhedron 1999, 18, 1615–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, C.; Sun, W.-H.; Li, Z.; Hu, Y.; Han, L. Ethylene oligomerization promoted by group 8 metal complexes containing 2-(2-pyridyl)quinoxaline ligands. Catal. Commun. 2002, 3, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margariti, A.; Schnakenburg, G.; Mitrikas, G.; Philippopoulos, A. Synthesis, structural and spectroscopic characterization of the mer-[Cr(pqx)Cl3(H2O)] complex, where pqx stands for the 2-(2′-pyridyl)quinoxaline ligand. 2023; manuscript in preparation. [Google Scholar]
- Sheldrick, G.M. A short history of SHELX. Acta Cryst. 2008, A64, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolomanov, O.V.; Bourhis, L.J.; Gildea, R.J.; Howard, J.A.K.; Puschmann, H. OLEX2: A complete structure solution, refinement, and analysis program. J. Appl. Cryst. 2009, 42, 339–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoupras, A.B.; Chini, M.; Mangafas, N.; Tsogas, N.; Stamatakis, G.; Tsantila, N.; Fragopoulou, E.; Antonopoulou, S.; Gargalianos, P.; Demopoulos, C.A.; et al. Platelet-activating factor and its basic metabolic enzymes in blood of naive HIV-infected patients. Angiology 2012, 63, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonopoulou, S.; Demopoulos, C.A.; Iatrou, C.; Moustakas, G.; Zirogiannis, P. Platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase (PAF-AH) in human kidney. Int. J. Biochem. 1994, 26, 1157–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonopoulou, S.; Fragopoulou, E.; Karantonis, H.C.; Mitsou, E.; Sitara, M.; Rementzis, J.; Mourelatos, A.; Ginis, A.; Phenekos, C. Effect of traditional Greek Mediterranean meals on platelet aggregation in normal subjects and in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Med. Food 2006, 9, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoupras, A.B.; Chini, M.; Tsogas, N.; Fragopoulou, E.; Nomikos, T.; Lioni, A.; Mangafas, N.; Demopoulos, C.A.; Antonopoulou, S.; Lazanas, M.C. Anti-Platelet-Activating Factor Effects of Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy (HAART): A New Insight in the Drug Therapy of HIV Infection? AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2008, 24, 1079–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoupras, A.B.; Fragopoulou, E.; Nomikos, T.; Iatrou, C.; Antonopoulou, S.; Demopoulos, C.A. Characterization of the de novo biosynthetic enzyme of platelet activating factor, DDT-insensitive cholinephosphotransferase, of human mesangial cells. Mediat. Inflamm. 2007, 2007, 27683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

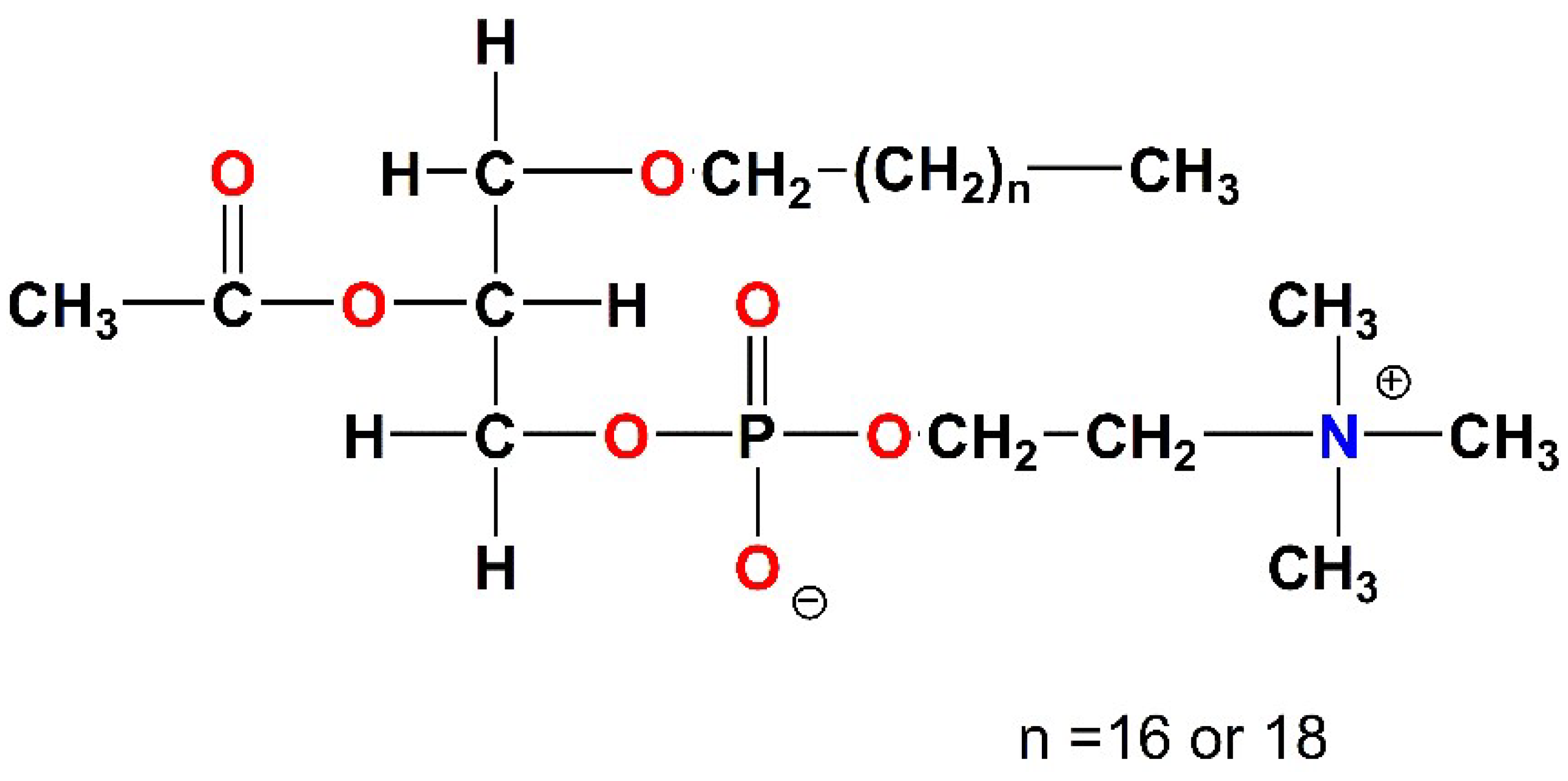
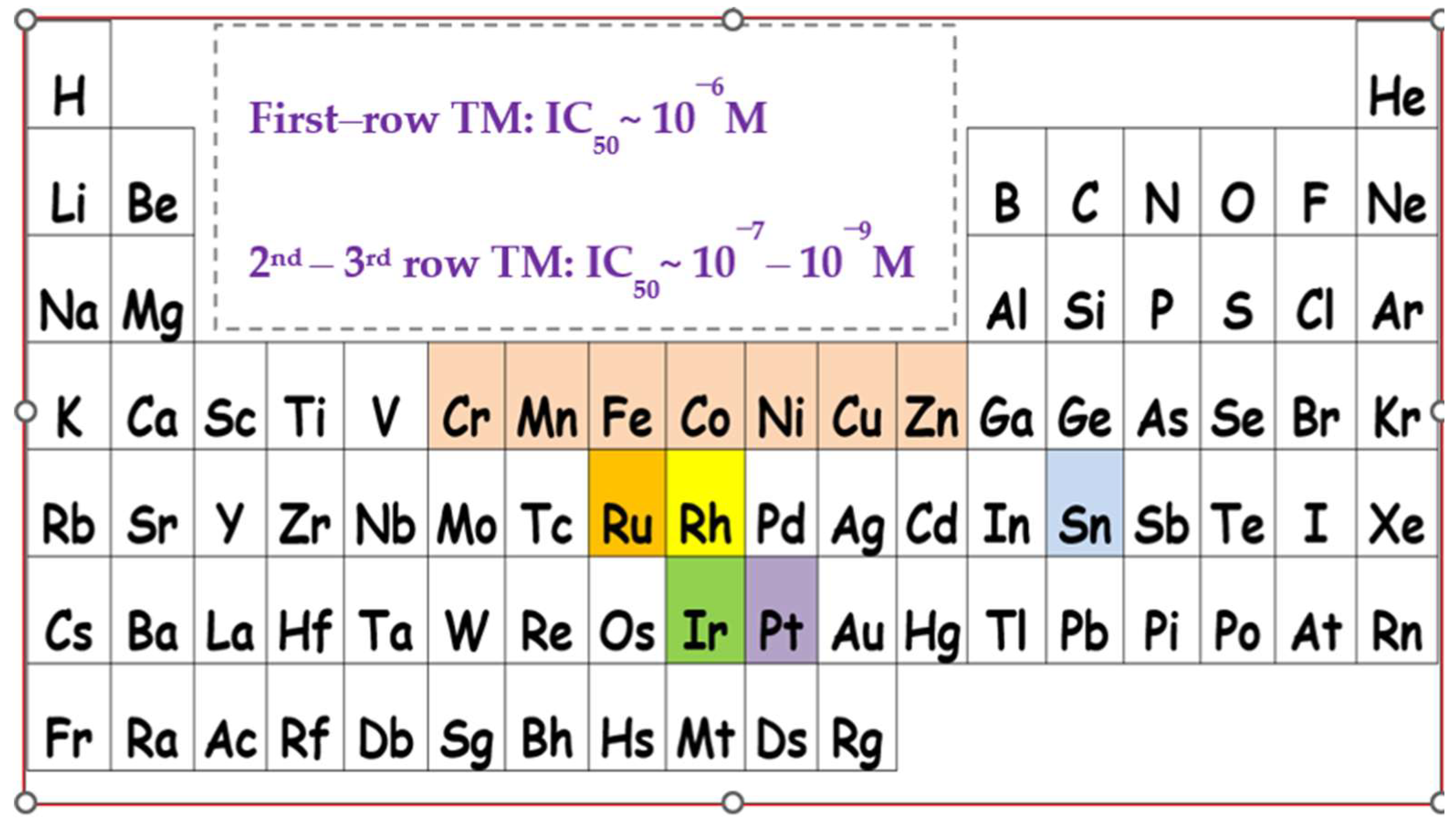
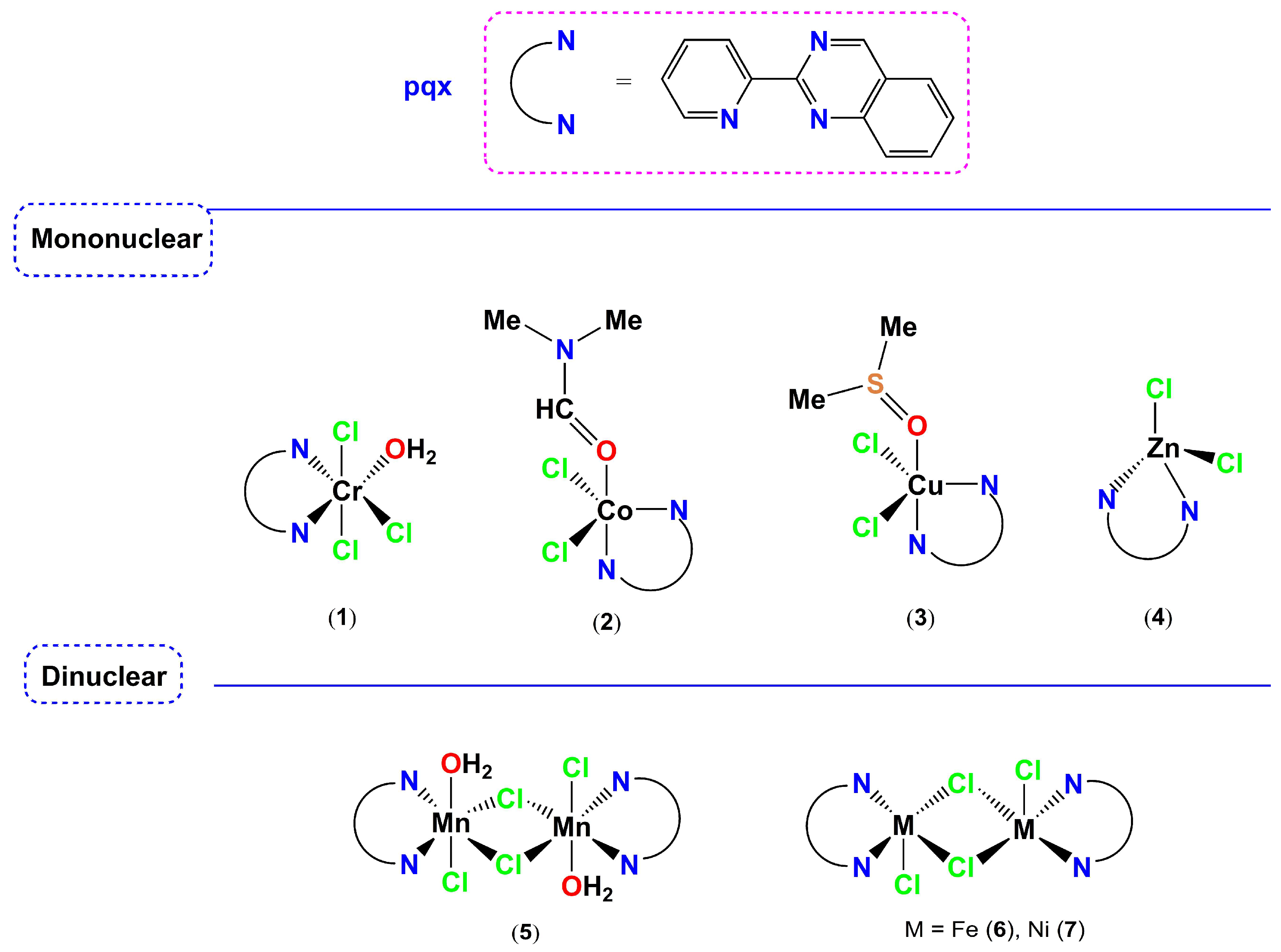
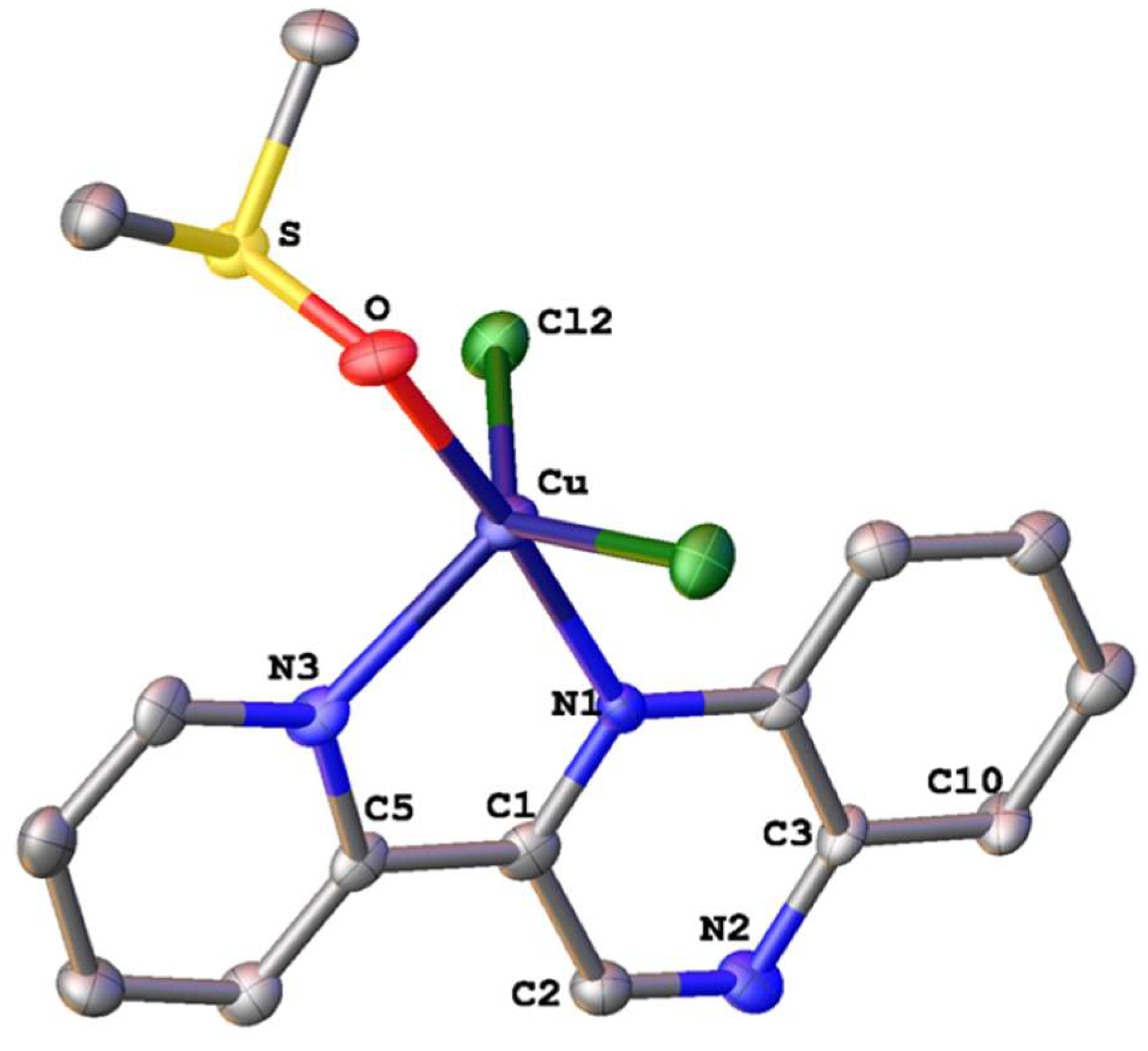

| Precursors and Metal Complexes | IC50 (μM) towards PAF in WRPs | IC50 (μM) towards Thrombin in WRPs |
|---|---|---|
| pqx | 32 ± 15 | no inhibition |
| Metal precursors | ||
| CrCl3 × 6H2O | 537 ± 59 | 611 ± 67 |
| CoCl2 × 6H2O | no inhibition 1 | no inhibition |
| CuCl2 × 2H2O | 22 ± 3 | 3.23 ± 0.39 ** |
| ZnCl2 | 30 ± 3 | 41.4 ± 3.7 |
| MnCl2 × 4H2O | 302 ± 30 | 466 ± 47 |
| FeCl2 × 4H2O | 261 ± 37 | 13.80 ± 1.93 |
| NiCl2 × 6H2O | 30 ± 2.7 | 4.90 ± 0.44 |
| Complexes | ||
| [Cr(pqx)Cl2(DMSO)2]Cl (1) | 4.5 ± 0.9 ** | 54.6 ± 10.4 |
| [Co(pqx)Cl(DMSO)]Cl (2) | 4.1 ± 0.6 ** | 8.9 ± 1.3 |
| [Cu(pqx)Cl2(DMSO)] (3) | 10.6 ± 1.4 | 3.1 ± 0.4 ** |
| [Zn(pqx)Cl2] (4) | 3.3 ± 0.3 *** | 3.5 ± 0.3 ** |
| [Mn(pqx)Cl(DMSO)]Cl (5) | 39 ± 6 | 14.0 ± 2.1 |
| [Fe(pqx)Cl(DMSO)3]Cl(6) | 1.79 ± 0.12 *** | 0.46 ± 0.03 *** |
| [Ni(pqx)Cl(DMSO)]Cl (7) | 6.83 ± 0.42 | 5.60 ± 0.34 |
| Compounds | HEK293T | HeLa |
|---|---|---|
| pqx | 97.33 ± 10.46 | 62.46 ± 5.43 |
| [Cr(pqx)Cl2(DMSO)2]Cl (1) | 99.05 ± 6.16 | 82.84 ± 3.12 |
| [Co(pqx)Cl(DMSO)]Cl (2) | 67.03 ± 12.58 | 89.12 ± 7.77 |
| [Cu(pqx)Cl2(DMSO)] (3) | 2.10 ± 0.52 | 27.20 ± 1.23 |
| [Zn(pqx)Cl2] (4) | 94.92 ± 23.16 | 77.84 ± 6.51 |
| [Mn(pqx)Cl(DMSO)]Cl (5) | 28.83 ± 6.16 | 99.96 ± 13.18 |
| [Fe(pqx)Cl(DMSO)3]Cl (6) | 65.81 ± 13.17 | 70.90 ± 2.50 |
| [Ni(pqx)Cl(DMSO)]Cl (7) | 25.53 ± 8.61 | 82.34 ± 9.49 |
| cisplatin | 4.44 ± 1.29 | 12.77 ± 1.48 |
| 6 | |
|---|---|
| Empirical formula | C15H15N3OSCl2Cu |
| Molecular weight | 419.80 |
| Crystal color | yellow plate |
| Crystal size (mm3) | 0.2 × 0.18 × 0.04 |
| Temperature (K) | 123.15 |
| Crystal system | monoclinic |
| Space group | P21 |
| Unit cell dimensions | |
| α (Å) | 7.6765(12) |
| β (Å) | 14.246(2) |
| γ (Å) | 7.6828(11) |
| α (°) | 90 |
| β (°) | 101.405(6) |
| γ (°) | 90 |
| V (Å3) | 823.6(2) |
| Z | 2 |
| ρalc (g cm−3) | 1.693 |
| μ (mm−1) | 1.783 |
| F(000) | 426.0 |
| Absorption correction | multi-scan |
| 2Θ range (°) | 5.41 to 58.492° |
| hkl range | −10, 10/−19, 18/−10, 10 |
| Total data | 14,946 |
| Data/restraints/parameters | 4423/205/212 |
| refinement method | Full matrix on F2 |
| R1, wR2 | 0.0431, 0.0863 |
| R1, wR2 (all data) | 0.0677, 0.0982 |
| Min./max. density (e Å−3) | 0.80/−1.40 |
| Goodness-of-fit | 1.078 |
| Flack parameter | 0.04(2) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Margariti, A.; Papakonstantinou, V.D.; Stamatakis, G.M.; Demopoulos, C.A.; Machalia, C.; Emmanouilidou, E.; Schnakenburg, G.; Nika, M.-C.; Thomaidis, N.S.; Philippopoulos, A.I. First-Row Transition Metal Complexes Incorporating the 2-(2′-pyridyl)quinoxaline Ligand (pqx), as Potent Inflammatory Mediators: Cytotoxic Properties and Biological Activities against the Platelet-Activating Factor (PAF) and Thrombin. Molecules 2023, 28, 6899. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28196899
Margariti A, Papakonstantinou VD, Stamatakis GM, Demopoulos CA, Machalia C, Emmanouilidou E, Schnakenburg G, Nika M-C, Thomaidis NS, Philippopoulos AI. First-Row Transition Metal Complexes Incorporating the 2-(2′-pyridyl)quinoxaline Ligand (pqx), as Potent Inflammatory Mediators: Cytotoxic Properties and Biological Activities against the Platelet-Activating Factor (PAF) and Thrombin. Molecules. 2023; 28(19):6899. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28196899
Chicago/Turabian StyleMargariti, Antigoni, Vasiliki D. Papakonstantinou, George M. Stamatakis, Constantinos A. Demopoulos, Christina Machalia, Evangelia Emmanouilidou, Gregor Schnakenburg, Maria-Christina Nika, Nikolaos S. Thomaidis, and Athanassios I. Philippopoulos. 2023. "First-Row Transition Metal Complexes Incorporating the 2-(2′-pyridyl)quinoxaline Ligand (pqx), as Potent Inflammatory Mediators: Cytotoxic Properties and Biological Activities against the Platelet-Activating Factor (PAF) and Thrombin" Molecules 28, no. 19: 6899. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28196899
APA StyleMargariti, A., Papakonstantinou, V. D., Stamatakis, G. M., Demopoulos, C. A., Machalia, C., Emmanouilidou, E., Schnakenburg, G., Nika, M.-C., Thomaidis, N. S., & Philippopoulos, A. I. (2023). First-Row Transition Metal Complexes Incorporating the 2-(2′-pyridyl)quinoxaline Ligand (pqx), as Potent Inflammatory Mediators: Cytotoxic Properties and Biological Activities against the Platelet-Activating Factor (PAF) and Thrombin. Molecules, 28(19), 6899. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28196899


.jpg)








