A Green Bridge: Enhancing a Multi-Pesticide Test for Food by Phase-Transfer Sample Treatment Coupled with LC/MS
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Selection of Food Substrates and Target Substances
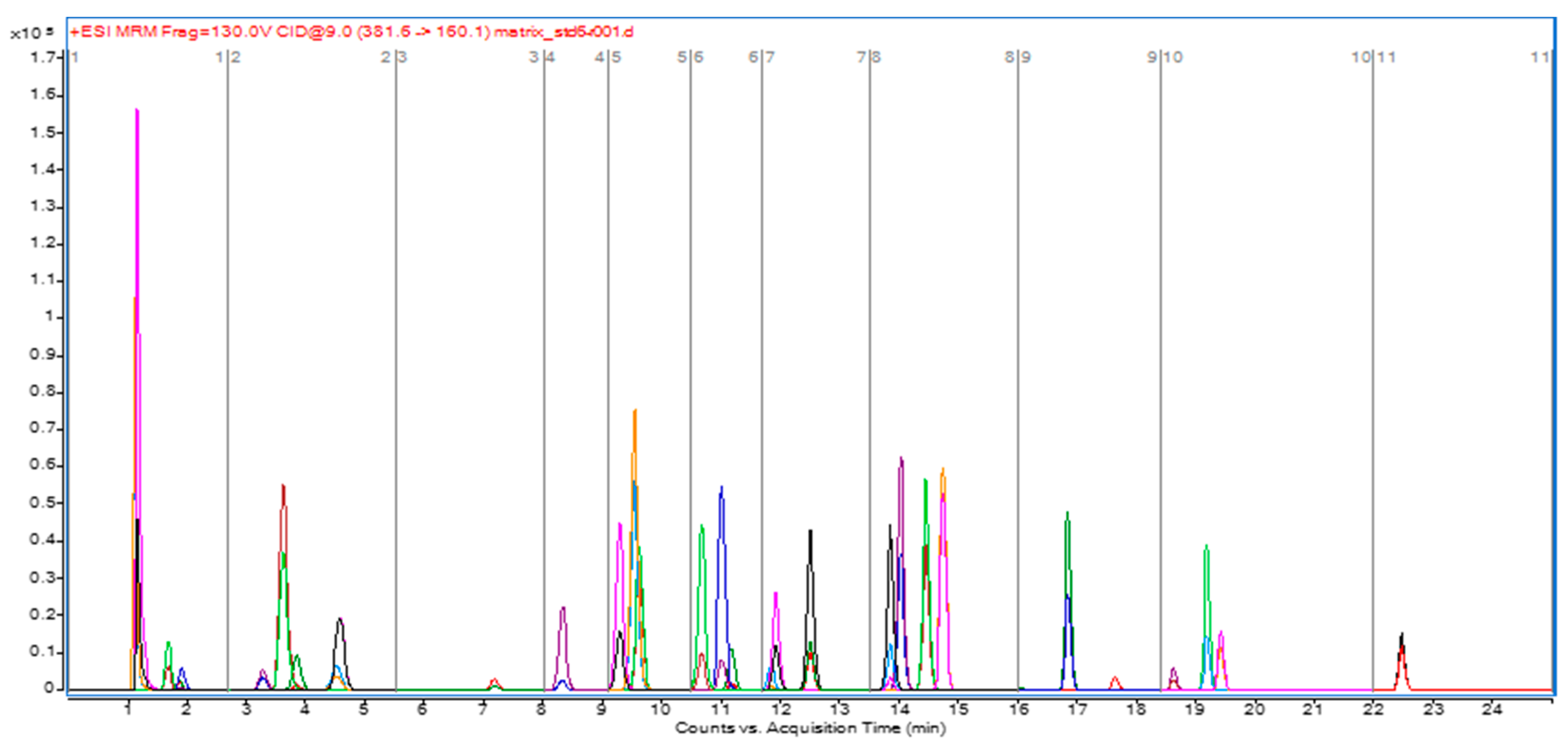
2.2. Optimization of LC–MS/MS Conditions
2.3. Optimization of Pre-Treatment Methods
2.3.1. Optimization of Pre-Treatment Method 1
Selection of Purification Materials
Choice of Carrageenan Quantity
2.3.2. Optimization of Pre-Treatment Method 2
2.4. Matrix Effect
2.5. Methodological Evaluation
2.5.1. Standard Curve and Detection Limit
2.5.2. Precision and Recovery Rate
2.6. Determination of Actual Samples
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Instruments and Reagents
3.2. Sample Pretreatment Method
3.3. LC–MS/MS Conditions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Yang, X.; Xiong, X.; Cao, J.; Luan, B.; Liu, Y.; Liu, G.; Zhang, L. Matrix precipitation: A general strategy to eliminate matrix interference for pharmaceutical toxic impurities analysis. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1379, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; He, Z.; Zeng, M.; Chen, J. Impact of matrix species and mass spectrometry on matrix effects in multi-residue pesticide analysis based on quechers-lc-ms. Foods 2023, 12, 1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, X.; Wang, L.; Jin, S.; Fu, X.; Sun, X.; Cao, J. A strategy for sample preparation: Using egg white gel to promote the determination of aflatoxin m1 content in milk samples. Molecules 2022, 27, 5039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, M.S.; Woodward, E.E.; Hladik, M.L. Evaluation of elisa for the analysis of imidacloprid in biological matrices: Cross-reactivities, matrix interferences, and comparison to lc-ms/ms. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Lin, X.; Zhao, L.; Huang, K.; Yang, Q.; Yu, H.; Xiong, X. Headspace single drop microextraction based visual colorimetry for highly sensitive, selective and matrix interference-resistant determination of sulfur dioxide in food samples. Food Chem. 2023, 426, 136659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makni, Y.; Diallo, T.; Areskoug, F.; Guérin, T.; Parinet, J. Optimisation and implementation of quechers-based sample preparation for identification and semi-quantification of 694 targeted contaminants in honey, jam, jelly, and syrup by uhplc-q/tof high-resolution mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2023, 425, 136448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, U.; Shah, F.; Khan, R.A. Quechers sample preparation integrated to dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction based on solidified floating organic droplet for spectrometric determination of sudan dyes: A synergistic approach. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2022, 159, 112742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, Y.; Matsumoto, H.; Okumura, M.; Inoue, H.; Kaji, Y.; Ando, C.; Kamei, J. Determination of neurotransmitters in mouse brain using miniaturized and tableted quechers for the sample preparation. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2022, 217, 114809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kardani, F.; Jelyani, A.Z.; Dahanzadeh, M.; Rashedinia, M. Modified quechers sample preparation method and applied for the analysis of 30 pesticide residues in iran tea in 2020–2021 using gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Appl. Food Res. 2022, 2, 100197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Chen, S.; Xu, Y. Determination of non-glucosidic cyanogen in chinese liquor-fermentation ingredients using quechers sample preparation and spectrophotometric method. Food Control 2022, 140, 109101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallagi, H.; Jha, P.K.; Faille, C.; Le-Bail, A.; Rawson, A.; Benezech, T. Removal of biocontamination in the food industry using physical methods; An overview. Food Control 2023, 148, 109645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, A.; Vaishampayan, V.; Senthil Kumar, P.; Ponnuchamy, M.; Kapoor, A. Extraction techniques in food industry: Insights into process parameters and their optimization. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2022, 166, 113207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, X.; Lu, Q.; Wang, L.; Hu, X.; Zhang, H. Preparation, flocculation and application in sugar refining of eco-friendly dextran-polylysine complex flocculant. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 306, 122673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balbinoti, J.R.; Dos Santos Junior, R.E.; de Sousa, L.B.F.; de Jesus Bassetti, F.; Balbinoti, T.C.V.; de Matos Jorge, L.M.; Jorge, R.M.M. Plant-based coagulants for food industry wastewater treatment. J. Water Process. Eng. 2023, 52, 103525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miazaki, J.B.; Dos Santos, A.R.; de Freitas, C.F.; Stafussa, A.P.; Mikcha, J.M.G.; Bergamasco, R.D.C.; Tonon, L.A.C.; Madrona, G.S.; Caetano, W.; Da Silva, L.H.; et al. Edible coatings and application of photodynamics in ricotta cheese preservation. LWT 2022, 165, 113697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, L.; Xu, W.; Wang, C.; Li, H.; Xiong, L.; Zhang, H.; Chen, X. Synthesis of polyacrylamide/polystyrene interpenetrating polymer networks and the effect of textural properties on adsorption performance of fermentation inhibitors from sugarcane bagasse hydrolysate. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 318, 124053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laad, M.; Ghule, B. Removal of toxic contaminants from drinking water using biosensors: A systematic review. Groundwater Sustain. Dev. 2023, 20, 100888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, H.; Khosravi-Darani, K. Effective variables on production and structure of xanthan gum and its food applications: A review. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2017, 10, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ta, L.P.; Bujna, E.; Antal, O.; Ladányi, M.; Juhász, R.; Szécsi, A.; Kun, S.; Sudheer, S.; Gupta, V.K.; Nguyen, Q.D. Effects of various polysaccharides (alginate, carrageenan, gums, chitosan) and their combination with prebiotic saccharides (resistant starch, lactosucrose, lactulose) on the encapsulation of probiotic bacteria lactobacillus casei 01 strain. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 183, 1136–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eghbaljoo, H.; Sani, I.K.; Sani, M.A.; Rahati, S.; Mansouri, E.; Molaee-Aghaee, E.; Fatourehchi, N.; Kadi, A.; Arab, A.; Sarabandi, K.; et al. Advances in plant gum polysaccharides; Sources, techno-functional properties, and applications in the food industry—A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 222, 2327–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Shen, Y.; Hu, F.; Zhang, X.; Thakur, K.; Rengasamy, K.R.R.; Khan, M.R.; Busquets, R.; Wei, Z. Fortification of polysaccharide-based packaging films and coatings with essential oils: A review of their preparation and use in meat preservation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 242, 124767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, D.; Batista-Silva, J.P.; Sousa, A.; Passarinha, L.A. Progress and opportunities in gellan gum-based materials: A review of preparation, characterization and emerging applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 311, 120782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ongono, J.S.; Béranger, R.; Baghdadli, A.; Mortamais, M. Pesticides used in europe and autism spectrum disorder risk: Can novel exposure hypotheses be formulated beyond organophosphates, organochlorines, pyrethroids and carbamates?—A systematic review. Environ. Res. 2020, 187, 109646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Wei, B.; Yang, W.; He, C.; Su, H.; Wan, J.; Li, P.; Wang, Y. Trace determination of carbamate pesticides in medicinal plants by a fluorescent technique. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 119, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Wang, S.; Ma, W.; Li, G.; Tu, M.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Li, H.; Li, X. Simultaneous determination of neonicotinoid and carbamate pesticides in freeze-dried cabbage by modified quechers and ultra-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Foods 2023, 12, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osaili, T.M.; Al-Natour, M.Q.; Al-Abboodi, A.R.; Alkarasneh, A.Y.; El Darra, N.; Khazaal, S.; Holley, R. Detection and risk associated with organochlorine, organophosphorus, pyrethroid and carbamate pesticide residues in chicken muscle and organ meats in jordan. Food Control 2023, 144, 109355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehotay, S.J. Quechers sample preparation approach for mass spectrometric analysis of pesticide residues in foods. In Mass Spectrometry in Food Safety: Methods and Protocols; Zweigenbaum, J., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 65–91. [Google Scholar]
- AOAC Official Method 2007.01; Pesticide Residues in Foods by Acetonitrile Extraction and Partitioning with Magnesium Sulfate. AOAC International: Rockville, MD, USA, 2007.
- GB 2763-2021; National Food Safety Standard—Maximum Residue Limits for Pesticides in Food. USDA: Washington, DC, USA, 2021.
- Nsengiyumva, E.M.; Heitz, M.P.; Alexandridis, P. Thermal hysteresis phenomena in aqueous xanthan gum solutions. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 144, 108973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udo, T.; Mummaleti, G.; Mohan, A.; Singh, R.K.; Kong, F. Current and emerging applications of carrageenan in the food industry. Food Res. Int. 2023, 173, 113369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Zi, Y.; Peng, J.; Shi, C.; Zheng, Y.; Zhong, J. Gelatin as a bioactive nanodelivery system for functional food applications. Food Chem. 2023, 423, 136265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portanguen, S.; Dumoulin, C.; Duconseille, A.; Meurillon, M.; Sicard, J.; Théron, L.; Chambon, C.; Sayd, T.; Mirade, P.; Astruc, T. Impact of water content and bloom index on gelatin glycation. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 145, 109096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.; Lehotay, S.J.; Geis-Asteggiante, L. Variability of matrix effects in liquid and gas chromatography—Mass spectrometry analysis of pesticide residues after quechers sample preparation of different food crops. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1270, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kmellár, B.; Fodor, P.; Pareja, L.; Ferrer, C.; Martínez-Uroz, M.A.; Valverde, A.; Fernandez-Alba, A.R. Validation and uncertainty study of a comprehensive list of 160 pesticide residues in multi-class vegetables by liquid chromatography—Tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1215, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Pesticides | Relative Retention Time ** | Transitions (m/z) | Dewell Time (mS) | Fragmentor (V) | CE (eV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| aminocarb | 0.06 | 209.3/152.1 *, 209.3/137.1 | 100 | 70 | 9, 25 |
| propamocarb | 0.06 | 189.2/102.1 *, 189.2/144.1 | 100 | 70 | 13, 9 |
| aldicarb sulfoxide | 0.11 | 229.1/166.1 *, 229.1/109.1 | 60 | 70 | 5, 13 |
| aldicarb sulfone | 0.13 | 245.1/166.1 *, 245.1/109.1 | 60 | 60 | 13, 17 |
| oxamyl | 0.13 | 242.1/72.1 *, 242.1/121.2 | 60 | 55 | 17, 9 |
| thiofanox sulfoxide | 0.26 | 257.1/200.0 *, 257.1/137.2 | 40 | 65 | 5, 13 |
| pirimicarb | 0.31 | 239.3/72.1 *, 239.3/182.1 | 40 | 65 | 20, 13 |
| thiofanox sulfone | 0.31 | 273.1/216.1 *, 273.1/137.1 | 40 | 65 | 9, 21 |
| 3-hydroxycarbofuran | 0.38 | 238.4/163.1 *, 238.4/181.1 | 40 | 100 | 9, 5 |
| dioxacarb | 0.38 | 224.2/167.1 *, 224.2/123.1 | 40 | 40 | 5, 13 |
| aldicarb | 0.63 | 213.1/89.1 *, 213.1/116.1 | 200 | 75 | 13, 9 |
| metolcarb | 0.73 | 166.2/109.1 *, 166.2/94.1 | 200 | 30 | 9, 35 |
| propoxur | 0.82 | 210.2/111.0 *, 210.2/168.3 | 60 | 30 | 9, 4 |
| carbofuran | 0.85 | 222.3/165.1 *, 222.3/123.1 | 60 | 70 | 9, 21 |
| bendiocarb | 0.85 | 224.1/167.1 *, 224.1/109.1 | 60 | 70 | 5, 17 |
| carbaryl | 0.95 | 202.1/145.0 *, 202.1/127.3 | 60 | 40 | 5, 33 |
| ethiofencarb | 1.00 | 226.1/107.1 *, 226.1/164.1 | 60 | 50 | 5, 9 |
| thiofanox | 1.02 | 241.1/184.1 *, 241.1/57.2 | 60 | 60 | 5, 17 |
| thiocarb | 1.06 | 377.0/64.1 *, 377.0/113.0 | 60 | 120 | 13, 9 |
| isoproarb | 1.13 | 194.1/137.1 *, 194.1/95.1 | 60 | 60 | 5, 9 |
| 2,3,5-trimethacarb | 1.13 | 137.1/122.0 *, 137.1/107.2 | 60 | 130 | 17, 25 |
| fenobucarb | 1.27 | 208.1/95.1 *, 208.1/152.1 | 40 | 60 | 9, 4 |
| diethofencarb | 1.29 | 268.2/226.1 *, 268.2/152.2 | 40 | 55 | 21, 5 |
| methiocarb | 1.31 | 226.1/169.1 *, 226.1/121.1 | 40 | 55 | 5, 17 |
| promecarb | 1.33 | 208.1/109.1 *, 208.1/105.1 | 40 | 50 | 5, 13 |
| fenoxycarb | 1.53 | 302.3/88.1 *, 302.3/116.1 | 100 | 100 | 17, 5 |
| indoxacarb | 1.70 | 528.1/150.2 *, 528.1/293.2 | 100 | 150 | 21, 9 |
| benfuracarb | 1.75 | 411.2/195.0 *, 411.2/252.1 | 100 | 90 | 21, 9 |
| furathiocarb | 1.80 | 383.2/252.1 *, 383.2/167.1 | 100 | 90 | 5, 25 |
| carbosuifan | 2.06 | 381.6/118.1 *, 381.6/160.1 | 200 | 130 | 13, 9 |
| Substrates | Pesticide | Carrageenan Addition/g in 20 mL | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 1.1 | ||
| Banana | Oxamyl | 95.2 | 97.6 | 97.1 | 96.3 | 95.9 |
| Ethiofencarb | 94.2 | 96.1 | 96.3 | 95.4 | 95.4 | |
| Lemon | Oxamyl | 95.3 | 97.4 | 97.1 | 97.1 | 96.5 |
| Ethiofencarb | 96.4 | 98.2 | 97.7 | 97.5 | 96.4 | |
| Apple | Oxamyl | 95.4 | 97.5 | 97.2 | 97.1 | 96.5 |
| Ethiofencarb | 94.3 | 98 | 97.9 | 96.4 | 96.2 | |
| Spinach | Oxamyl | 91.4 | 94 | 94.1 | 95.2 | 96.3 |
| Ethiofencarb | 92 | 93.1 | 95.7 | 96.4 | 96.8 | |
| Cabbage | Oxamyl | 96.7 | 98.2 | 98 | 97.4 | 97.1 |
| Ethiofencarb | 95.7 | 97.8 | 97.1 | 96.4 | 96.4 | |
| Rice | Oxamyl | 97.9 | 97.2 | 96.5 | 96.5 | 95.9 |
| Ethiofencarb | 98.1 | 97.2 | 97.1 | 96.8 | 96.1 | |
| Pesticide | Banana | Lemon | Apple | Spinach | Cabbage | Rice | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 * | M2 ** | M1 * | M2 ** | M1 * | M2 ** | M1 * | M2 ** | M1 * | M2 ** | M1 * | M2 ** | |
| aminocarb | 0.8 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.3 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 0.9 |
| propamocarb | 1.1 | 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.8 |
| aldicarb sulfoxide | 1.1 | 1.1 | 0.9 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 1.1 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 0.9 |
| aldicarb sulfone | 1.1 | 1.1 | 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.7 | 0.6 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.9 |
| oxamyl | 1.1 | 1.1 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.9 |
| thiofanox sulfoxide | 1.1 | 1.1 | 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.9 |
| pirimicarb | 1.1 | 1.2 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.9 |
| thiofanox sulfone | 1.1 | 1.1 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.9 |
| 3-hydroxycarbofuran | 1.1 | 1.1 | 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.6 | 0.9 | 0.9 |
| dioxacarb | 1.1 | 1.1 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.7 | 0.6 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.8 |
| aldicarb | 1.1 | 1.1 | 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.7 | 0.6 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.6 |
| metolcarb | 1.1 | 1.1 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.7 | 0.6 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.9 |
| propoxur | 1.1 | 1.1 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.5 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.9 |
| carbofuran | 1.1 | 1.2 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.7 | 0.7 |
| bendiocarb | 1.1 | 1.1 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.8 |
| carbaryl | 1.1 | 1.2 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.8 |
| ethiofencarb | 1.1 | 1.1 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.7 | 0.4 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.7 |
| thiofanox | 1.1 | 1.2 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.7 | 0.7 |
| thiocarb | 1.2 | 1.3 | 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.9 |
| isoproarb | 1.1 | 1.1 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.7 | 0.6 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.9 |
| 2,3,5-trimethacarb | 0.9 | 1.1 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.6 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.7 | 0.7 |
| fenobucarb | 1.1 | 1.1 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 0.7 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 0.6 |
| diethofencarb | 1.1 | 1.1 | 0.9 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 0.8 |
| methiocarb | 1.1 | 1.1 | 0.9 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.8 |
| promecarb | 1.1 | 1.1 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 0.9 |
| fenoxycarb | 1.1 | 1.1 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.6 | 0.3 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.8 |
| indoxacarb | 1.1 | 0.9 | 1.1 | 1.2 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.7 | 0.6 |
| benfuracarb | 1.1 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.5 |
| furathiocarb | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.7 | 0.6 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.8 |
| carbosuifan | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.7 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 0.9 |
| Pesticide | Rate of Linear Slope | Rate of Intercept | Comparison of Recovery | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 µg/kg | 20 µg/kg | 100 µg/kg | |||
| aminocarb | 1.2 | 0.5 | 1.05 | 1.01 | 1.03 |
| propamocarb | 1.1 | 0.4 | 1.04 | 1.04 | 1.01 |
| aldicarb sulfoxide | 1.2 | 0.5 | 1.05 | 1.03 | 1.01 |
| aldicarb sulfone | 1.2 | 0.3 | 1.03 | 1.08 | 1.02 |
| oxamyl | 1.1 | 0.6 | 1.06 | 1.01 | 1.02 |
| thiofanox sulfoxide | 1.1 | 0.7 | 1.07 | 1.03 | 1.03 |
| pirimicarb | 1.3 | 0.5 | 1.05 | 1.05 | 1.04 |
| thiofanox sulfone | 1.2 | 0.4 | 1.04 | 1.02 | 1.01 |
| 3-hydroxycarbofuran | 1.1 | 0.4 | 1.04 | 1.03 | 1.02 |
| dioxacarb | 1.2 | 0.3 | 1.03 | 1.04 | 1.01 |
| aldicarb | 1.1 | 0.4 | 1.04 | 1.01 | 1.01 |
| metolcarb | 1.1 | 0.3 | 1.03 | 1.02 | 1.07 |
| propoxur | 1.2 | 0.3 | 1.03 | 1.02 | 1.05 |
| carbofuran | 1.3 | 0.3 | 1.03 | 1.06 | 1.01 |
| bendiocarb | 1.2 | 0.4 | 1.02 | 1.04 | 1.01 |
| carbaryl | 1.2 | 0.5 | 1.04 | 1.05 | 1.04 |
| ethiofencarb | 1.2 | 0.3 | 1.03 | 1.02 | 1.01 |
| thiofanox | 1.2 | 0.3 | 1.03 | 1.01 | 1.06 |
| thiocarb | 1.1 | 0.4 | 1.02 | 1.04 | 1.01 |
| isoproarb | 1 | 0.2 | 1.02 | 1.02 | 1.04 |
| 2,3,5-trimethacarb | 1 | 0.2 | 1.02 | 1.03 | 1.05 |
| fenobucarb | 1.1 | 0.4 | 1.04 | 1.01 | 1.02 |
| diethofencarb | 1.2 | 0.3 | 1.03 | 1.01 | 1.01 |
| methiocarb | 1.1 | 0.3 | 1.03 | 1.04 | 1.03 |
| promecarb | 1.2 | 0.3 | 1.03 | 1.02 | 1.04 |
| fenoxycarb | 1.1 | 0.3 | 1.03 | 1.01 | 1.01 |
| indoxacarb | 1.1 | 0.5 | 1.05 | 1.04 | 1.05 |
| benfuracarb | 1.1 | 0.5 | 1.05 | 1.03 | 1.02 |
| furathiocarb | 1.3 | 0.5 | 1.05 | 1.01 | 1.01 |
| carbosuifan | 1.2 | 0.5 | 1.05 | 1.03 | 1.03 |
| Matrix | Supplemental Level | RSD Range | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 μg/kg | 20 μg/kg | 100 μg/kg | ||
| banana | 59.84–127.06% | 60.08–114.06% | 56.13–110.05% | 1.1–15% |
| lemon | 62.05–91.61% | 69.33–98.94% | 71.83–107.02% | 0.47–9.3% |
| apple | 74.78–106.3% | 60.51–125.2% | 75.40–117.6%, | 3.1–16% |
| cabbage | 68.62–103.0% | 69.81–99.31% | 67.62–112.3% | 1.2–13% |
| spinach | 71.11–115.3% | 77.45–125.3% | 57.36–103.2% | 3.2–14% |
| rice | 85.70–106.0% | 67.31–108.3% | 70.70–97.61% | 0.70–8.5% |
| Pesticide | IUPAC Name | Formula |
|---|---|---|
| aminocarb | [4-(dimethylamino)-3-methylphenyl] N-methylcarbamate | C11H16N2O2 |
| propamocarb | propyl N-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]carbamate | C9H20N2O2 |
| aldicarb sulfoxide | [(E)-(2-methyl-2-methylsulfinylpropylidene)amino] N-methylcarbamate | C7H14N2O3S |
| aldicarb sulfone | [(E)-(2-methyl-2-methylsulfonylpropylidene)amino] N-methylcarbamate | C7H14N2O4S |
| oxamyl | methyl (1Z)-2-(dimethylamino)-N-(methylcarbamoyloxy)-2-oxoethanimidothioate | C7H13N3O3S |
| thiofanox sulfoxide | [(Z)-(3,3-dimethyl-1-methylsulfinylbutan-2-ylidene)amino] N-methylcarbamate | C9H18N2O3S |
| pirimicarb | [2-(dimethylamino)-5,6-dimethylpyrimidin-4-yl] N,N-dimethylcarbamate | C11H18N4O2 |
| thiofanox sulfone | [(3,3-dimethyl-1-methylsulfonylbutan-2-ylidene)amino] N-methylcarbamate | C9H18N2O4S |
| 3-hydroxycarbofuran | (3-hydroxy-2,2-dimethyl-3H-1-benzofuran-7-yl) N-methylcarbamate | C12H15NO4 |
| dioxacarb | [2-(1,3-dioxolan-2-yl)phenyl] N-methylcarbamate | C11H13NO4 |
| aldicarb | [(E)-(2-methyl-2-methylsulfonylpropylidene)amino] N-methylcarbamate | C7H14N2O4S |
| metolcarb | (3-methylphenyl) N-methylcarbamate | C9H11NO2 |
| propoxur | (2-propan-2-yloxyphenyl) N-methylcarbamate | C11H15NO3 |
| carbofuran | (2,2-dimethyl-3H-1-benzofuran-7-yl) N-methylcarbamate | C12H15NO3 |
| bendiocarb | (2,2-dimethyl-1,3-benzodioxol-4-yl) N-methylcarbamate | C11H13NO4 |
| carbaryl | naphthalen-1-yl N-methylcarbamate | C12H11NO2 |
| ethiofencarb | [2-(ethylsulfanylmethyl)phenyl] N-methylcarbamate | C11H15NO2S |
| thiofanox | [(3,3-dimethyl-1-methylsulfanylbutan-2-ylidene)amino] N-methylcarbamate | C9H18N2O2S |
| thiocarb | N,N-diethylcarbamodithioate | C5H16NNaO3S2 |
| isoproarb | (2-propan-2-ylphenyl) N-methylcarbamate | C11H15NO2 |
| 2,3,5-trimethacarb | (2,3,5-trimethylphenyl) N-methylcarbamate | C11H15NO2 |
| fenobucarb | (2-butan-2-ylphenyl) N-methylcarbamate | C12H17NO2 |
| diethofencarb | propan-2-yl N-(3,4-diethoxyphenyl)carbamate | C14H21NO4 |
| methiocarb | (3,5-dimethyl-4-methylsulfanylphenyl) N-methylcarbamate | C11H15NO2S |
| promecarb | (3-methyl-5-propan-2-ylphenyl) N-methylcarbamate | C11H15NO2S |
| fenoxycarb | ethyl N-[2-(4-phenoxyphenoxy)ethyl]carbamate | C17H19NO4 |
| indoxacarb | methyl 7-chloro-2-[methoxycarbonyl-[4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl]carbamoyl]-3,5-dihydroindeno [1,2-e][1,3,4]oxadiazine-4a-carboxylate | C22H17ClF3N3O7 |
| benfuracarb | ethyl 3-[[(2,2-dimethyl-3H-1-benzofuran-7-yl)oxycarbonyl-methylamino]sulfanyl-propan-2-ylamino]propanoate | C20H30N2O5S |
| furathiocarb | (2,2-dimethyl-3H-1-benzofuran-7-yl) N-[butoxycarbonyl(methyl)amino]sulfanyl-N-methylcarbamate | C18H26N2O5S |
| carbosuifan | (2,2-dimethyl-3H-1-benzofuran-7-yl) N-(dibutylamino)sulfanyl-N-methylcarbamate | C20H32N2O3S |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, S.; Shen, Y.; Liu, T.; Liang, R.; Ning, X.; Cao, J. A Green Bridge: Enhancing a Multi-Pesticide Test for Food by Phase-Transfer Sample Treatment Coupled with LC/MS. Molecules 2023, 28, 6756. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28196756
Jin S, Shen Y, Liu T, Liang R, Ning X, Cao J. A Green Bridge: Enhancing a Multi-Pesticide Test for Food by Phase-Transfer Sample Treatment Coupled with LC/MS. Molecules. 2023; 28(19):6756. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28196756
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Shaoming, Yi Shen, Tongtong Liu, Ruiqiang Liang, Xiao Ning, and Jin Cao. 2023. "A Green Bridge: Enhancing a Multi-Pesticide Test for Food by Phase-Transfer Sample Treatment Coupled with LC/MS" Molecules 28, no. 19: 6756. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28196756
APA StyleJin, S., Shen, Y., Liu, T., Liang, R., Ning, X., & Cao, J. (2023). A Green Bridge: Enhancing a Multi-Pesticide Test for Food by Phase-Transfer Sample Treatment Coupled with LC/MS. Molecules, 28(19), 6756. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28196756






