Simultaneous Extraction and Determination of Lignans from Schisandra chinensis (Turcz.) Baill. via Diol-Based Matrix Solid-Phase Dispersion with High-Performance Liquid Chromatography
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Validation of the Method
2.2. MSPD Extraction Procedure
2.2.1. The Selection of Parameters in MSPD Procedure
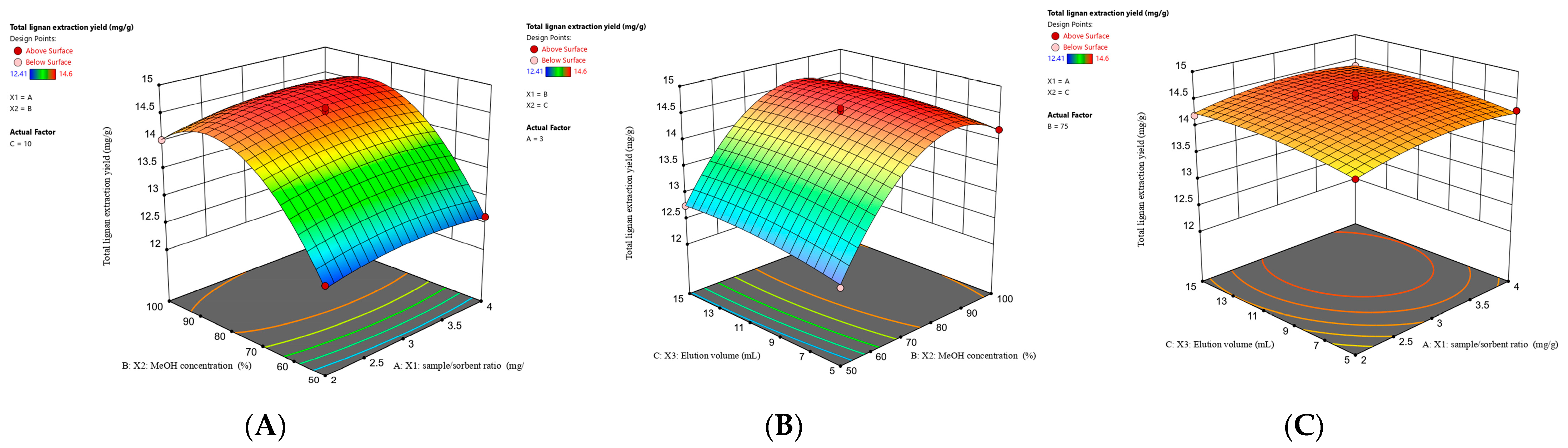
2.2.2. Optimization of MSPD Procedure with RSM
2.2.3. Analysis of Response Surface
2.2.4. Verification of Predictive Model
2.3. Comparison with Traditional Extraction Method
2.4. Application
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Reagents
3.2. Plant Materials
3.3. Extraction of Lignans with MSPD
3.4. Ultrasonic Extraction
3.5. Determination of Lignans with HPLC-DAD
3.6. Method Validation
3.7. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China; China Medical Science Press: Beijing, China, 2020; Volume 1, p. 68. [Google Scholar]
- Kopustinskiene, D.M.; Bernatoniene, J. Antioxidant effects of Schisandra chinensis fruits and their active constituents. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 620–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Qiu, J.; Huang, Z.C.; Yu, Z.W.; Wang, W.J.; Hu, H.L.; You, Y. A comprehensive review of ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry, pharmacology, and pharmacokinetics of Schisandra chinensis (Turcz.) Baill. and Schisandra sphenanthera Rehd. et Wils. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 284, 114759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chun, J.N.; Cho, M.; So, I.; Jeon, J.H. The protective effects of Schisandra chinensis fruit extract and its lignans against cardiovascular disease: A review of the molecular mechanisms. Fitoterapia 2014, 74, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.N.; Mao, X.; Zhao, X.; Liu, Z.; Liu, B.; Li, H.; Bi, K.S.; Jia, Y. Gomisin N isolated from Schisandra chinensis augments pentobarbital-induced sleep behaviors through the modification of the serotonergic and GABAergic system. Fitoterapia 2014, 96, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.Y.; Zhang, L.N.; Wang, G.L.; Xu, Y.H.; Gao, Y.G.; Zhang, L.X. Sedative and hypnotic effects of supercritical carbon dioxide fluid extraction from Schisandra chinensis in mice. J. Food Drug Anal. 2016, 24, 831–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.M.; Fan, X.M.; Wang, Y.; Tan, H.; Chen, P.; Zeng, H.; Huang, M.; Bi, H.C. Hepato-protective effects of six schisandra lignans on acetaminophen-induced liver injury are partially associated with the inhibition of CYP-mediated bioactivation. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2015, 231, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.S.; Ok, C.Y.; Cho, E.J.; Park, J.S.; Lee, S.K.; Choi, Y.W.; Bae, Y.S. Role of CXCR2 on the immune modulating activity of a-iso-cubebenol a natural compound isolated from the Schisandra chinensis fruit. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 431, 433–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Feng, Y.; Li, J.; Mao, R.W.; Zou, Y.; Feng, W.W.; Zheng, D.H.; Wang, W.; Chen, Y.; Yang, L.Q.; et al. Schisandra polysaccharide evokes immunomodulatory activity through TLR 4-mediated activation of macrophages. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 65, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mocan, A.; Schafberg, M.; Gianina Cris, A.; Rohn, S. Determination of lignans and phenolic components of Schisandra chinensis (T urcz.) Baill. using HPLC-ESI-TOF-MS and HPLC-online TEAC: Contribution of individual components to overall antioxidant activity and comparison with traditional antioxidant assays. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 24, 579–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, X.L.; Liu, J.S.; Li, B.; Wei, X.P.; Qi, Y.D.; Zhang, B.G.; Liu, H.T.; Xiao, P.G. A comparative study on chemical characteristics, antioxidant, and hepatoprotective activity from different parts of Schisandrae chinensis Fructus. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2022, 46, e16990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.K.; Ge, J.M.; Li, M.Y.; Deng, S.; Li, J.R.; Ma, Y.C.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, Y.C.; Ma, L. Network pharmacology, molecular docking technology integrated with pharmacodynamic study to reveal the potential targets of Schisandrol A in drug-induced liver injury by acetaminophen. Bioorg. Chem. 2022, 118, 105476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, H.; Jiang, Y.M.; Chen, P.; Fan, X.M.; Li, D.S.; Liu, A.M.; Ma, X.C.; Xie, W.; Liu, P.Q.; Gonzalez, F.J.; et al. Schisandrol B protects against cholestatic liver injury through pregnane X receptors. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174, 672–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gmeiner, A.; Effenberger-Neidnicht, K.; Zoldáková, M.; Schobert, R. A methyltitanocene complex of schisandrol A with high efficacy against multi-drug resistant cervix and breast carcinoma cells. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2011, 25, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Kim, Y.M.; Chin, Y.W.; Kang, K.S. Schisandrol A exhibits estrogenic activity via estrogen receptor α-dependent signaling pathway in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer cells. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.X.; Sun, Y.Y.; Gong, G.W.; Li, Y.; Fan, K.Y.; Wu, B.; Bi, K.S.; Jia, Y. The neuroprotective effect of schisandrol A on 6-OHDA-induced PD mice may be related to PI3K/AKT and IKK/IκBα/NF-κB pathway. Exp. Gerontol. 2019, 128, 110743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Li, Z.C.; Yao, L.Q.; Li, M.; Tang, M. Schisandrin B alleviates acute oxidative stress via modulating Nrf2/Keap1-mediated antioxidant pathway. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2019, 44, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.B.; Shi, X.W.; Du, Y.; Shi, F.J.; Zhang, B.; Zheng, Z.X.; Xu, J.J.; Jiang, L.Q. Schisandrin C targets Keap1 and attenuates oxidative stress by activating Nrf2 pathway in Ang II-challenged vascular endothelium. Phytother. Res. 2019, 33, 779–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, X.; Zhao, L.; Shi, Y.; Wang, J.; Lv, H.; Song, X.; Zhao, Q.; Zhao, Q.; Jing, R.; Hu, J. Gomisin J attenuates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by inducing anti-apoptotic, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant effects in rats. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 6908–6918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.J.; Zhan, Y.K.; Zhang, Y.M.; Wu, L.A.; Wang, X.; Guo, M. Schisandrin B ameliorates non-alcoholic liver disease through anti-inflammation activation in diabetic mice. Drug Dev. Res. 2022, 83, 735–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.Q.; Kong, Y.; Wang, Q.L.; Chen, J.; Chen, H.; Xie, H.H.; Li, L. Schisandrin B attenuates airway inflammation by regulating the NF-κB/Nrf2 signaling pathway in mouse models of asthma. J. Immunol. Res. 2021, 2021, 8029963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.M.; Wang, Z.; Gu, Z.N.; Wu, J.; Bai, X.Q.; Shao, Z.X.; Miao, J.S.; Wang, Q.Q.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X.Y. Schisandrin B attenuates epidural fibrosis in postlaminectomy rats by inhibiting proliferation and extracellular matrix production of fibroblasts. Phytother. Res. 2018, 33, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.Q.; Xu, C.; Fu, X.L.; Jiang, Y.Y. Schisandrin B suppresses liver fibrosis in rats by targeting miR-101-5p through the TGF-β signaling pathway. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2020, 48, 473–478. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.B.; Kim, C.Y.; Lee, H.J.; Yun, J.H.; Nho, C.W. Induction of the Phase II Detoxification Enzyme NQO1 in Hepatocarcinoma Cells by Lignans from the Fruit of Schisandra chinensis through Nuclear Accumulation of Nrf2. Planta Med. 2009, 75, 1314–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.T.; Wu, C.M.; Wang, S.; Gao, S.M.; Liu, J.; Dong, Z.Q.; Zhang, B.G.; Liu, M.Y.; Sun, X.B.; Guo, P. Extracts and lignans of Schisandra chinensis fruit alter lipid and glucose metabolism in vivo and in vitro. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 19, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, H.Y.; Wu, J.H.; Su, T.; Chao, X.J.; Yu, H.; Liu, B.; Fu, X.Q.; Tse, A.K.W.; Chan, C.L.; Fong, W.F.; et al. Schisandrin B regulates lipid metabolism in subcutaneous adipocytes. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Li, Q.; Li, H.; Li, Y.; Piao, Z. Quantitative analysis of six lignans in fruits with different colours of Schisandra chinensis by HPLC. Nat. Prod. Res. 2014, 28, 581–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Watanabe, C.; Wang, L. Authentication of Schisandra chinensis and Schisandra sphenantherae in Chinese patent medicines by pyrolysis-gas chromatography/mass spectrometry and fingerprint analysis. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2019, 137, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Xu, Y.; Wang, M.; Xie, Z.; Gao, X. Application of characteristic fragment filtering with ultra high performance liquid chromatography coupled with high-resolution mass spectrometry for comprehensive identification of components in Schisandrae chinensis Fructus. J. Sep. Sci. 2019, 42, 1323–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onay, S.; Hofer, S.; Ganzera, M. Rapid analysis of nine lignans in Schisandra chinensis by supercritical fluid chromatography using diode array and mass spectrometric detection. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 185, 113254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambropoulou, D.A.; Albanis, T.A. Methods of sample preparation for determination of pesticide residues in food matrices by chromatography-mass spectrometry-based techniques: A review. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 389, 1663–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.C.; Lai, Y.C.; Chang, C.L. High throughput screening and antioxidant assay of dibenzo[a,c]cyclooctadiene lignans in modified-ultrasonic and supercritical fluid extracts of Schisandra chinensis Baill by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry and a free radical-scavenging method. J. Sep. Sci. 2008, 31, 1322–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, Y.H.; Wang, R.; Wang, Y.K.; Li, M.M.; Liu, F.X.; Huang, X.; Chen, C.B. Evaluation of multicomponent changes of Schisandra chinensis fruits with different drying process by UPLC-QQQ-MS-based targeted metabolomics analysis. J. Chem. 2022, 2022, 2616122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Cao, Y.; Fan, G.R. Microwave-assisted extraction and fingerprint studies of Schisandra chinensis (Turcz.) by high performance liquid chromatography and gas chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2007, 30, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Z.Y.; Song, H.Y.; Yang, Y.J.; Zhou, H.L.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.G. Smashing tissue extraction of five lignans from the fruit of Schisandra chinensis. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2016, 54, 246–256. [Google Scholar]
- Mayya Razgonova, A.Z.K.P.; Kim, E.; Chernyshev, V.A.; Ercisli, S.; Cravotto, G.; Golokhvast, K. Rapid mass spectrometric study of a supercritical CO2-extract from Woody Liana Schisandra chinensis by HPLC-SPD-ESI-MS/MS. Molecules 2020, 25, 2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, S.A.; Long, A.R.; Short, C.R. Isolation of drug residues from tissues by solid dispersion. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 1989, 475, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, S.A. Matrix solid-phase dispersion. J. Chromatogr. A 2000, 885, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enríquez-Gabeiras, L.; Gallego, A.; Garcinuño, R.M.; Fernández-Hernando, P.; Durand, J.S. Interference-free determination of illegal dyes in sauces and condiments by matrix solid phase dispersion (MSPD) and liquid chromatography (HPLC-DAD). Food Chem. 2012, 135, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, M.Y.; Bai, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, X.J.; Wang, H.; Gao, X.M.; Chang, Y.X. A Diol-based-matrix solid-phase dispersion method for the simultaneous extraction and determination of 13 compounds from Angelicae Pubescentis Radix by ultra high-performance liquid chromatography. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buszewski, B.; Noga, S. Hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography (HILIC)-a powerful separation technique. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 402, 231–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.H.; Zeng, W.C. Preparation and application of Diol-bonded monolithic ailica capillary column. Chin. J. Spectrosc. Lab. 2010, 27, 2537–2540. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, C.; Dane, A.; Spijksma, G.; Wang, M.; van der Greef, J.; Luo, G.; Hankemeier, T.; Vreeken, R.J. An efficient hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography separation of 7 phospholipid classes based on a diol column. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1220, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosłon, M.; Jaworska, M.; Anuszewska, E.L. Determination of glycerophospholipids in biological material using high-performance liquid chromatography with charged aerosol detector HPLC-CAD-a new approach for isolation and quantification. Molecules 2022, 27, 3356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ares, A.M.; Bernal, J.; Janvier, A.; Toribio, L. Chiral and achiral separation of ten flavanones using supercritical fluid chromatography. Application to bee pollen analysis. J. Chromatogr. A 2022, 1685, 463633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smiełowska, M.; Zabiegała, B. Matrix solid-phase dispersion (MSPD) as simple and useful sample preparation technique for determination of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in dust. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1084, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gritti, F.; Dos Santos Pereira, A.; Sandra, P.; Guiochon, G. Comparison of the adsorption mechanisms of pyridine in hydrophilic interaction chromatography and in reversed-phase aqueous liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 8496–8504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Tong, L.; Yao, L.; Zhang, P.; Xu, L. Fingerprinting of traditional Chinese medicines on the C18-Diol mixed-mode column in online or offline two-dimensional liquid chromatography on the single column modes. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 125, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.J.; Cao, J.; Peng, L.Q.; Cao, W.; Zhu, Q.Y.; Zhang, Q.Y. Characterization and determination of isomers in plants using trace matrix solid phase dispersion via ultrahigh performance liquid chromatography coupled with an ultraviolet detector and quadrupole time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1436, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.L.; Qi, L.W.; Wang, Q.; Wan, J.Y.; Liu, E.H.; Li, P. Highly efficient sample preparation and quantification of constituents from traditional Chinese herbal medicines using matrix solid-phase dispersion extraction and UPLC-MS/MS. Analyst 2013, 138, 2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.F.; Ding, N.; Zang, H.; Yeung, H.; Zhao, R.S.; Cheng, C.; Liu, J.H.; Chan, T.W.D. Fe3O4@MOF core-shell magnetic microspheres for magnetic solid-phase extraction of polychlorinated biphenyls from environmental water samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1304, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalagatur, N.K.; Kamasani, J.R.; Siddaiah, C.; Gupta, V.K.; Krishna, K.; Mudili, V. Combinational Inhibitory Action of Hedychium spicatum L. Essential Oil and γ-Radiation on Growth Rate and Mycotoxins Content of Fusarium graminearum in Maize: Response Surface Methodology. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Yang, B.; Liang, J.; Wang, J.; Kuang, H. Simultaneous quantification of five dibenzocyclooctadiene lignans in Schisandra chinensis by HPLC separation and fluorescence detection. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 5981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Kim, C.Y. Simultaneous determination of nine lignans using pressurized liquid extraction and HPLC-DAD in the fruits of Schisandra chinensis. Food Chem. 2010, 120, 1224–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Analyte | Calibration Curve | R2 | Linear Range (μg/mL) | LOD (μg/mL) | LOQ (μg/mL) | Precision (RSD%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intraday | Interday | ||||||
| Schisandrol A | Y = 25.6922X − 27.1625 | 0.9998 | 35–175 | 0.23 | 1.15 | 0.87 | 1.03 |
| Gomisin J | Y = 47.0927X − 4.0778 | 0.9999 | 0.98–5.4 | 0.34 | 0.98 | 0.48 | 0.83 |
| Schisandrol B | Y = 44.7520X − 12.7742 | 0.9999 | 3.4–20.4 | 0.30 | 0.90 | 0.80 | 0.98 |
| Angeloylgomisin H | Y = 35.3511X + 0.2585 | 0.9998 | 7–42 | 0.22 | 1.49 | 0.81 | 0.95 |
| Schisantherin A | Y = 31.6965X − 5.5645 | 0.9997 | 1.6–8 | 0.09 | 1.45 | 0.96 | 1.02 |
| Schisantherin B | Y = 33.7828X − 3.3653 | 0.9999 | 2.07–10 | 0.43 | 2.07 | 0.94 | 1.15 |
| Schisanhenol | Y = 19.7444X − 1.1312 | 0.9999 | 0.8–5.4 | 0.20 | 0.80 | 1.05 | 1.15 |
| Schisandrin A | Y = 49.157X − 1.2122 | 0.9999 | 0.75–3.75 | 0.05 | 0.75 | 0.80 | 1.04 |
| Schisandrin B | Y = 40.5254X − 19.6594 | 0.9997 | 7.5–45 | 0.35 | 0.70 | 0.61 | 0.80 |
| Schisandrin C | Y = 60.0555X + 2.1668 | 0.9991 | 0.56–5.9 | 0.04 | 0.49 | 0.21 | 0.86 |
| No. | Levels | Y: Total Lignan Extraction Yield (mg/g) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1: Sample/Dispersant Ratio | X2: Methanol (MeOH) Concentration (%) | X3: Elution Volume (mL) | ||
| 1 | 1:3 | 75 | 10 | 14.45 |
| 2 | 1:2 | 75 | 5 | 14.04 |
| 3 | 1:3 | 75 | 10 | 14.54 |
| 4 | 1:4 | 100 | 10 | 14.24 |
| 5 | 1:3 | 100 | 5 | 14.20 |
| 6 | 1:4 | 75 | 15 | 14.37 |
| 7 | 1:3 | 75 | 10 | 14.46 |
| 8 | 1:2 | 100 | 10 | 14.03 |
| 9 | 1:3 | 75 | 10 | 14.40 |
| 10 | 1:2 | 50 | 10 | 12.57 |
| 11 | 1:3 | 50 | 5 | 12.41 |
| 12 | 1:3 | 75 | 10 | 14.60 |
| 13 | 1:2 | 75 | 15 | 14.20 |
| 14 | 1:3 | 100 | 15 | 14.29 |
| 15 | 1:4 | 75 | 5 | 14.29 |
| 16 | 1:3 | 50 | 15 | 12.75 |
| 17 | 1:4 | 50 | 10 | 12.62 |
| Source | Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F-Value | p-Value Prob > F | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 9.53 | 9 | 1.06 | 182.02 | <0.0001 | Significant |
| X1 | 0.0578 | 1 | 0.0578 | 9.93 | 0.0161 | |
| X2 | 5.14 | 1 | 5.19 | 882.80 | <0.0001 | |
| X3 | 0.0561 | 1 | 0.0561 | 9.64 | 0.0172 | |
| X1·X2 | 0.0064 | 1 | 0.0064 | 1.10 | 0.3291 | |
| X1·X3 | 0.0016 | 1 | 0.0016 | 0.2750 | 0.6162 | |
| X2·X3 | 0.0156 | 1 | 0.0156 | 2.69 | 0.1453 | |
| X12 | 0.1028 | 1 | 0.1028 | 17.67 | 0.0040 | |
| X22 | 3.95 | 1 | 3.95 | 679.20 | <0.0001 | |
| X32 | 0.0498 | 1 | 0.0498 | 8.56 | 0.0222 | |
| Residual | 0.0407 | 7 | 0.0058 | |||
| Lack of fit | 0.0155 | 3 | 0.0052 | 0.8214 | 0.5462 | Not significant |
| Pure error | 0.0252 | 4 | 0.0063 | |||
| Cor total | 9.57 | 16 |
| No. | Extraction Method | Sample Amounts | Type of Solvent (Volume) | Extraction Parameter | Detection Method | Extracted Lignans | Total Lignans | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Smashing tissue extraction | 2.00 g | 75% EtOH (38 mL) | 35 min Voltage: 180 V | HPLC-UV | Schisandrol A, schisantherin A, deoxyshcisandrin, schisandrin B, schisandrin C | 13.89 mg/g | [35] |
| 2 | Ultrasound-assisted extraction | 0.5 g | MeOH (20 mL) | 40 min 60 °C, 70 kHz | HPLC-FLD | Schisandrol A, schisandrol B, schisandrin A, schisandrin B, schisandrin C | 9.35–23.51 mg/g | [53] |
| 3 | Pressurized liquid extraction | 1 g | MeOH (150 mL) | 15 min, 125 °C | HPLC-DAD | Schisandrol A, gomisin J, schisandrol B, tigloylgomisin H, angeloylgomisin H, schisandrin A, γ-schisandrin, gomisin N, schisandrin C | 17.21 mg/g | [54] |
| 4 | Diol-based MSPD | 200 mg | 85% MeOH (10 mL) | 20 min | HPLC-DAD | Schisandrol A, gomisin J, schisandrol B, schisantherin A, schisantherin B, schisanhenol, schisandrin A, schisandrin B, schisandrin C, angeloylgomisin H | 14.67 mg/g | Present work |
| No. | Cultivation Areas | Analytes (mg/g) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Schisandrol A | Gomisin J | Schisandrol B | Angeloylgomisin H | Schisantherin A | Schisantherin B | Schisanhenol | Schisandrin A | Schisandrin B | Schisandrin C | ||
| 1 | Benxi, Liaoning | 7.18 ± 0.11 | 0.24 ± 0.01 | 1.23 ± 0.03 | 1.03 ± 0.02 | 0.38 ± 0.01 | 0.62 ± 0.01 | 0.28 ± 0.01 | 0.46 ± 0.01 | 1.75 ± 0.04 | 0.16 ± 0.01 |
| 2 | Tieling, Liaoning | 9.30 ± 0.08 | 0.28 ± 0.01 | 1.15 ± 0.01 | 1.27 ± 0.01 | 0.72 ± 0.01 | 0.88 ± 0.01 | 0.59 ± 0.01 | 1.36 ± 0.01 | 2.24 ± 0.02 | 0.15 ± 0.01 |
| 3 | Dandong, Liaoning | 7.23 ± 0.08 | 0.27 ± 0.01 | 0.94 ± 0.01 | 0.97 ± 0.01 | 0.55 ± 0.01 | 0.69 ± 0.01 | 0.36 ± 0.01 | 1.06 ± 0.01 | 1.96 ± 0.01 | 0.12 ± 0.01 |
| 4 | Yanbian, Jilin | 7.96 ± 0.06 | 0.23 ± 0.01 | 1.08 ± 0.01 | 1.10 ± 0.01 | 0.55 ± 0.01 | 0.71 ± 0.01 | 0.36 ± 0.01 | 0.87 ± 0.01 | 1.92 ± 0.01 | 0.13 ± 0.01 |
| 5 | Baishan, Jilin | 8.38 ± 0.01 | 0.26 ± 0.01 | 1.15 ± 0.01 | 1.07 ± 0.01 | 0.68 ± 0.01 | 0.72 ± 0.01 | 0.35 ± 0.01 | 1.02 ± 0.01 | 1.96 ± 0.01 | 0.10 ± 0.01 |
| 6 | Tonghua, Jilin | 7.36 ± 0.04 | 0.30 ± 0.01 | 1.24 ± 0.01 | 1.01 ± 0.01 | 0.48 ± 0.01 | 0.62 ± 0.01 | 0.33 ± 0.01 | 0.74 ± 0.01 | 2.02 ± 0.02 | 0.17 ± 0.01 |
| 7 | Elunchun, Inner Mongolia | 8.42 ± 0.02 | 0.26 ± 0.01 | 1.13 ± 0.01 | 1.21 ± 0.01 | 0.62 ± 0.01 | 0.76 ± 0.01 | 0.40 ± 0.01 | 1.02 ± 0.01 | 2.21 ± 0.01 | 0.16 ± 0.01 |
| 8 | Jiagedaqi, Heilongjiang | 7.21 ± 0.17 | 0.24 ± 0.01 | 1.10 ± 0.03 | 1.01 ± 0.08 | 0.40 ± 0.01 | 0.69 ± 0.02 | 0.30 ± 0.01 | 0.53 ± 0.02 | 1.79 ± 0.05 | 0.14 ± 0.01 |
| 9 | Yichun, Heilongjiang | 5.85 ± 0.06 | 0.33 ± 0.01 | 1.29 ± 0.02 | 1.09 ± 0.01 | 0.30 ± 0.01 | 0.42 ± 0.01 | 0.27 ± 0.01 | 0.71 ± 0.01 | 2.61 ± 0.03 | 0.33 ± 0.01 |
| 10 | Mudanjiang, Heilongjiang | 9.24 ± 0.06 | 0.34 ± 0.01 | 1.07 ± 0.01 | 1.37 ± 0.05 | 0.59 ± 0.01 | 0.77 ± 0.01 | 0.39 ± 0.01 | 0.85 ± 0.01 | 2.42 ± 0.01 | 0.21 ± 0.01 |
| 11 | Daxinganling, Heilongjiang | 7.16 ± 0.01 | 0.43 ± 0.01 | 1.41 ± 0.01 | 1.00 ± 0.01 | 0.71 ± 0.01 | 0.27 ± 0.01 | 0.18 ± 0.01 | 0.62 ± 0.01 | 2.46 ± 0.01 | 0.10 ± 0.01 |
| 12 | Heihe, Heilongjiang | 10.85 ± 0.01 | 0.53 ± 0.01 | 1.75 ± 0.01 | 1.34 ± 0.01 | 0.88 ± 0.01 | 1.03 ± 0.01 | 0.64 ± 0.01 | 1.27 ± 0.01 | 2.21 ± 0.01 | 0.10 ± 0.01 |
| 13 | Heihe, Heilongjiang | 9.13 ± 0.01 | 0.45 ± 0.01 | 1.49 ± 0.01 | 1.11 ± 0.01 | 0.74 ± 0.01 | 0.86 ± 0.01 | 0.53 ± 0.01 | 1.05 ± 0.01 | 1.87 ± 0.01 | 0.08 ± 0.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Du, X.; Li, Y. Simultaneous Extraction and Determination of Lignans from Schisandra chinensis (Turcz.) Baill. via Diol-Based Matrix Solid-Phase Dispersion with High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. Molecules 2023, 28, 6448. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28186448
Wang Y, Zhu J, Du X, Li Y. Simultaneous Extraction and Determination of Lignans from Schisandra chinensis (Turcz.) Baill. via Diol-Based Matrix Solid-Phase Dispersion with High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. Molecules. 2023; 28(18):6448. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28186448
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yinpeng, Jingbo Zhu, Xinxin Du, and Yumei Li. 2023. "Simultaneous Extraction and Determination of Lignans from Schisandra chinensis (Turcz.) Baill. via Diol-Based Matrix Solid-Phase Dispersion with High-Performance Liquid Chromatography" Molecules 28, no. 18: 6448. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28186448
APA StyleWang, Y., Zhu, J., Du, X., & Li, Y. (2023). Simultaneous Extraction and Determination of Lignans from Schisandra chinensis (Turcz.) Baill. via Diol-Based Matrix Solid-Phase Dispersion with High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. Molecules, 28(18), 6448. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28186448






