The Content and Principle of the Rare Ginsenosides Produced from Gynostemma pentaphyllum after Heat Treatment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
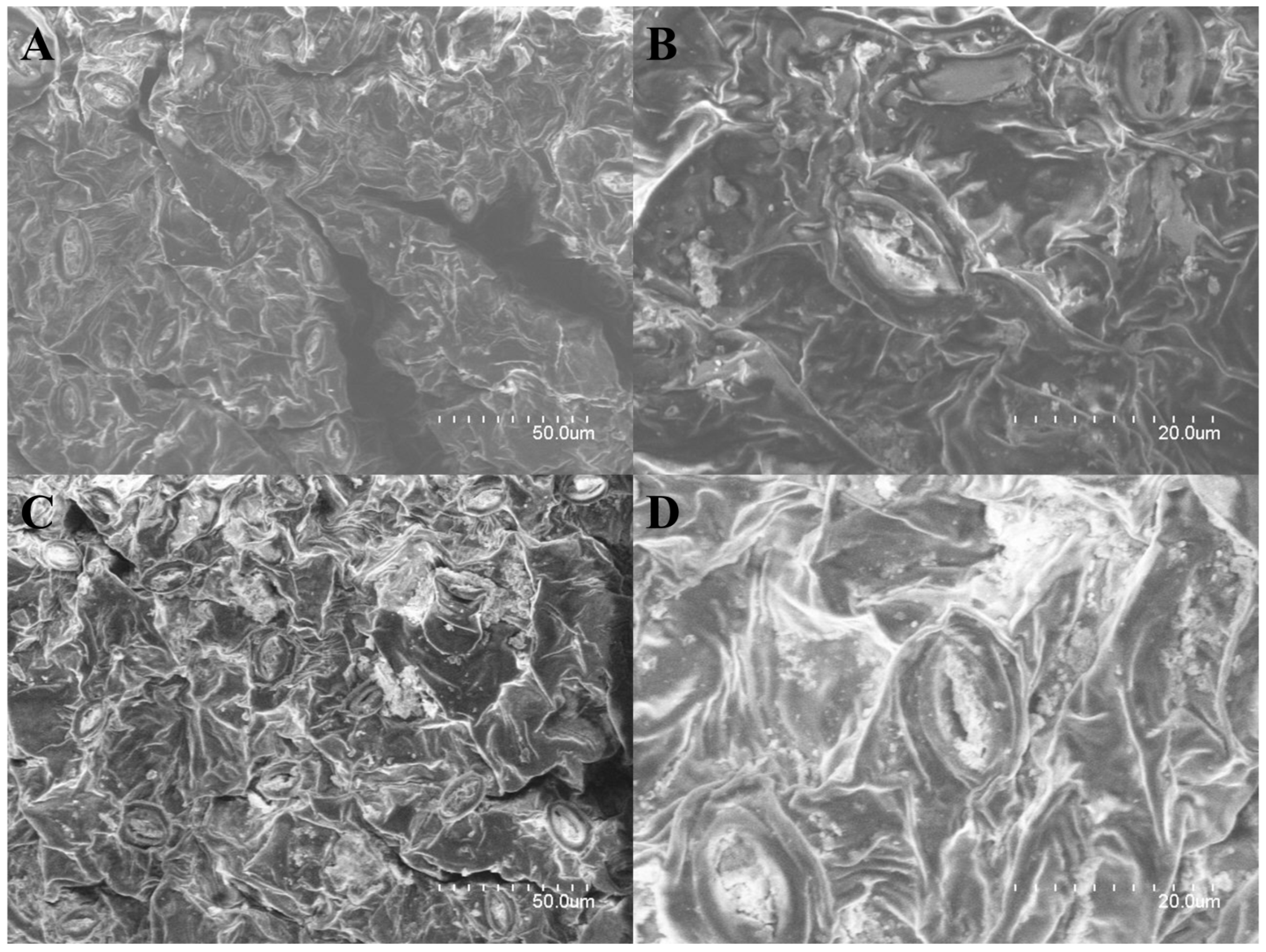
2.1. Surface Changes in G. pentaphyllum Leaves before and after Heat Processing
2.2. Changes in the Internal Structure of G. pentaphyllum before and after Heat Processing
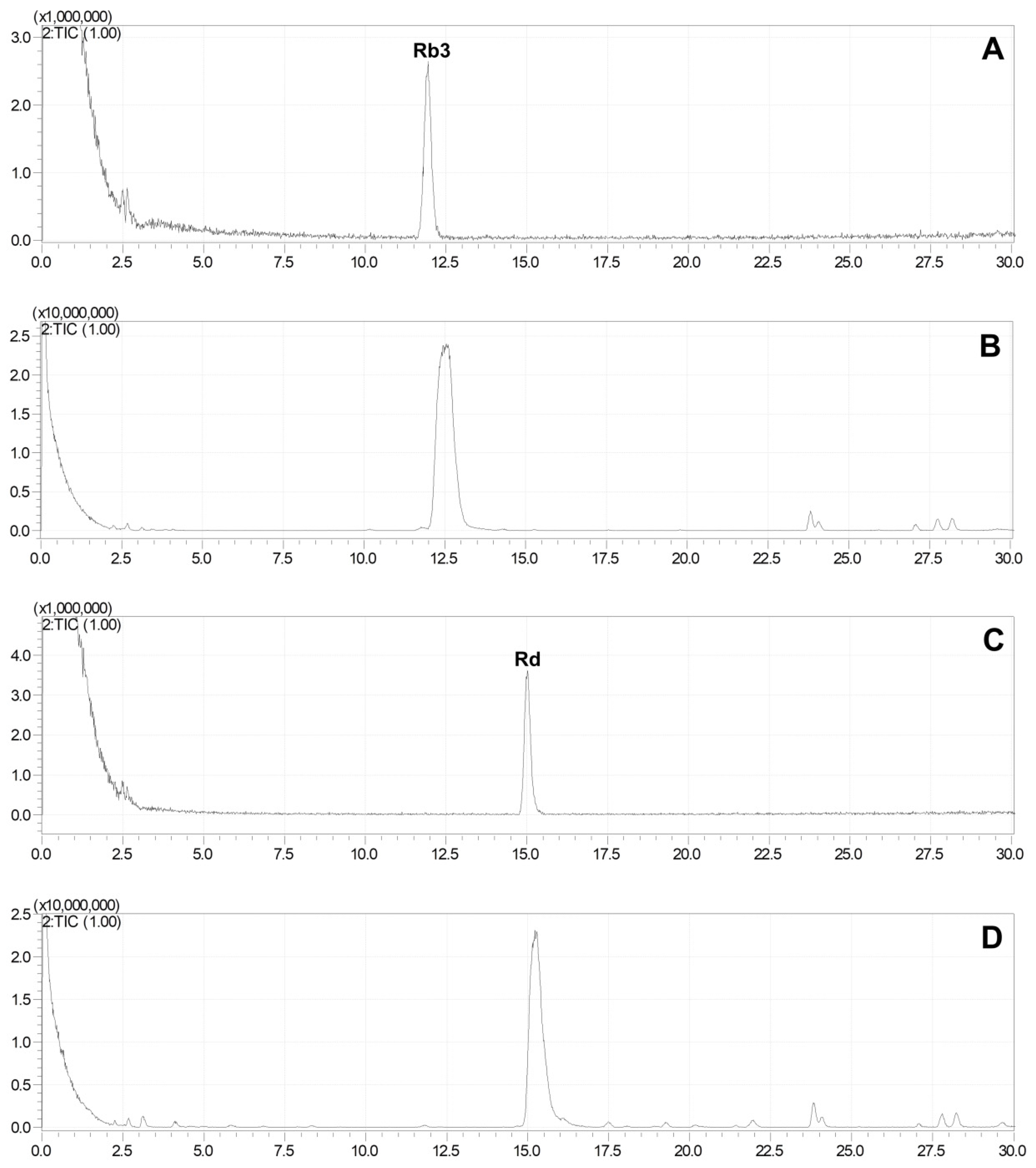
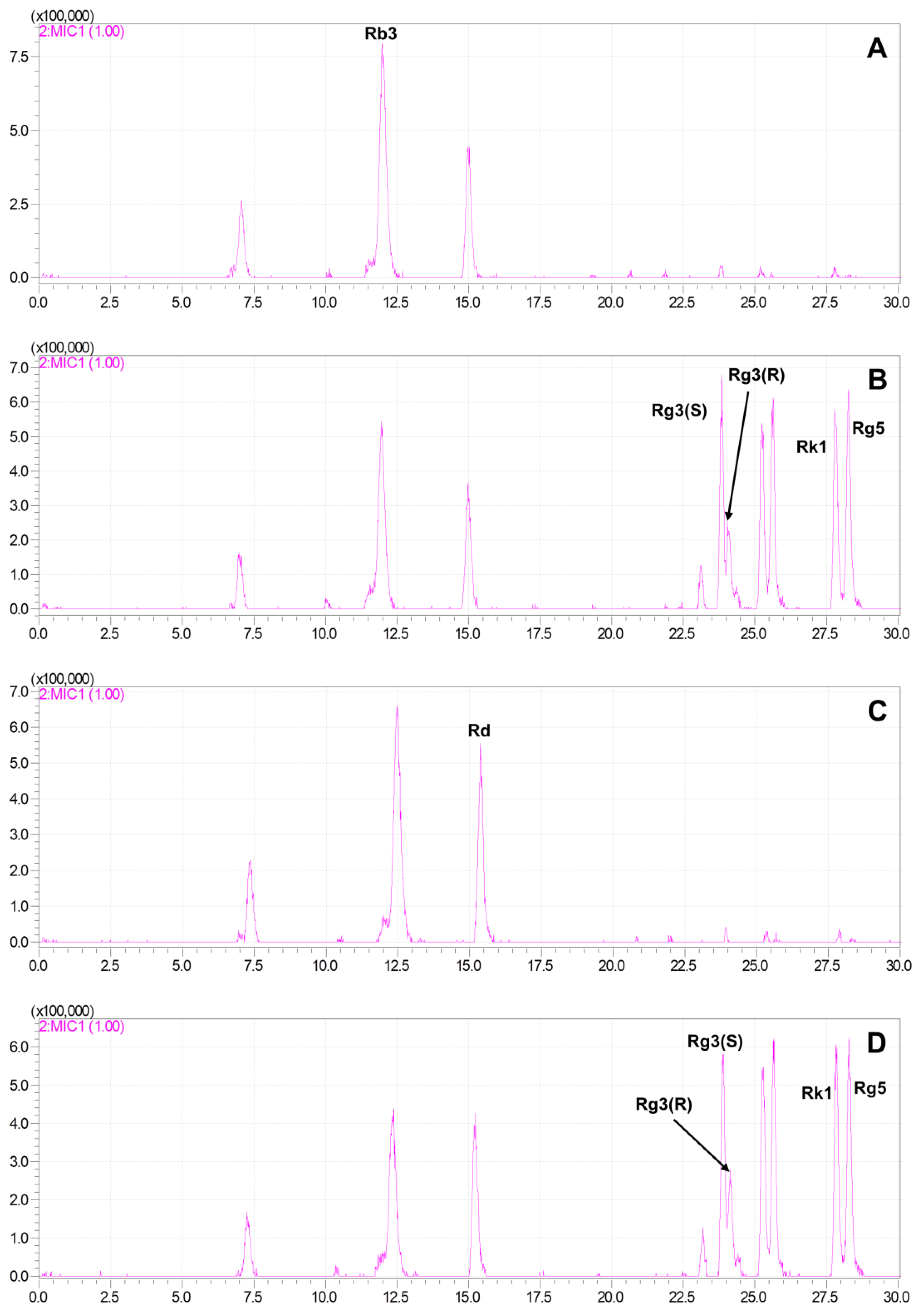
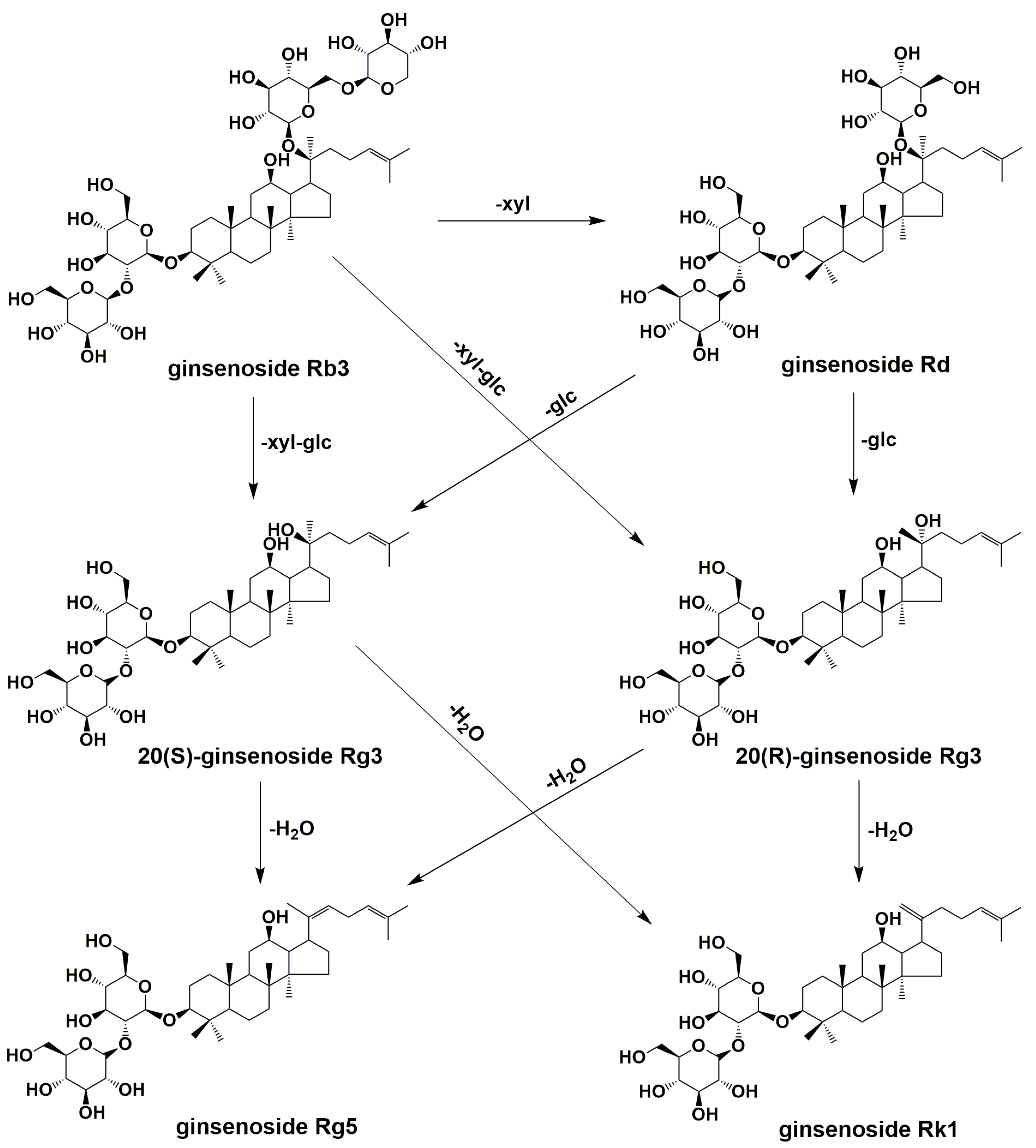
2.3. Production of Rare Ginsenosides from G. pentaphyllum
2.4. Quantitative Analysis of Ginsenosides of G. pentaphyllum before and after Heat Processing
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Materials
4.2. Heat Processing of G. pentaphyllum
4.3. SEM Analysis
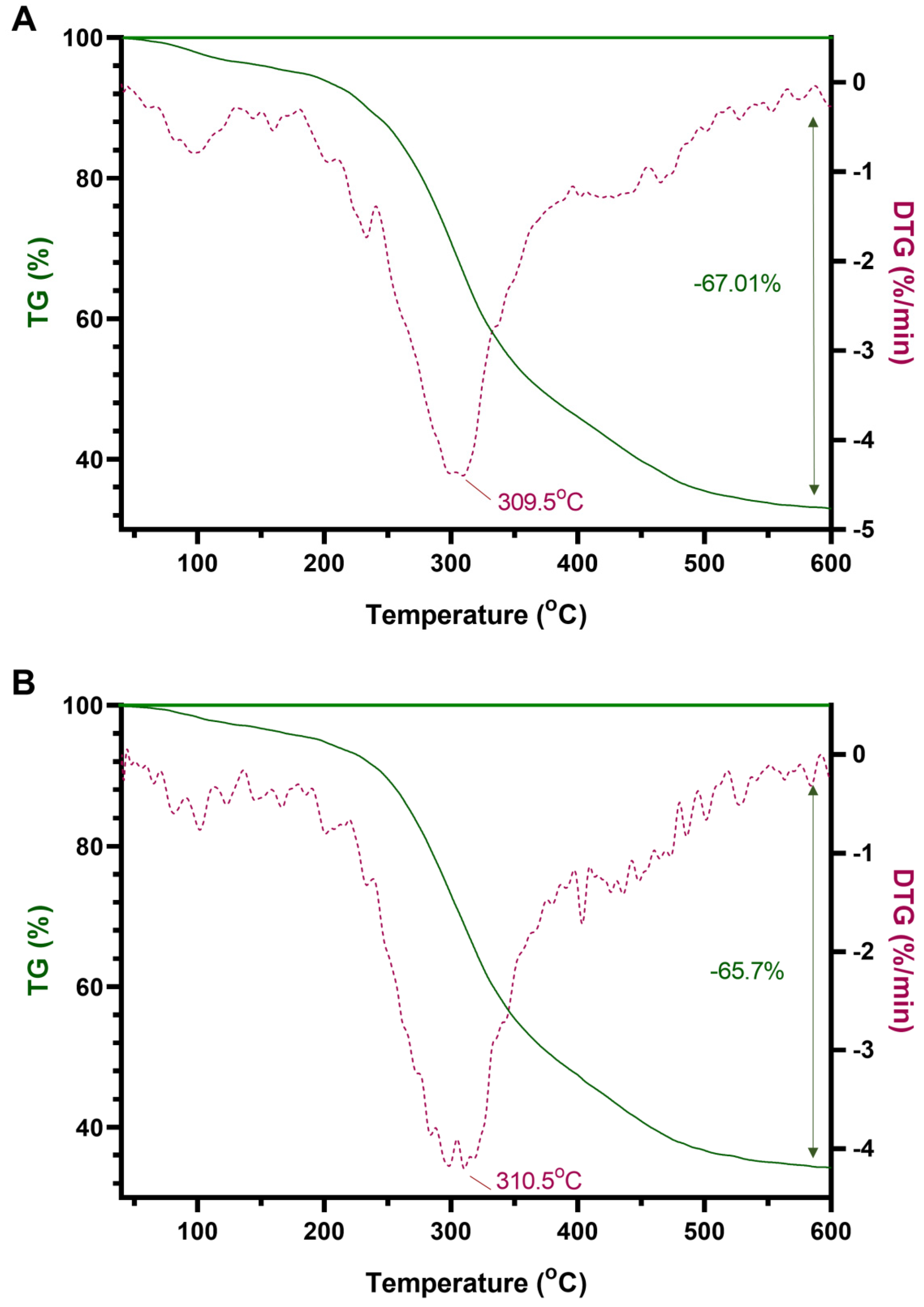
4.4. TG and DTG Analysis
4.5. Sample Preparation for HPLC and LC-MS
4.6. Preparation of Standard Stock Solutions
4.7. Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry Analysis
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Man, S.; Luo, C.; Yan, M.; Zhao, G.; Ma, L.; Gao, W. Treatment for liver cancer: From sorafenib to natural products. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 224, 113690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Yin, H.; Qu, L.; Ma, X.; Fu, R.; Fan, D. Ginsenoside Rk1 regulates glutamine metabolism in hepatocellular carcinoma through inhibition of the ERK/c-Myc pathway. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 3793–3811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Fan, D. The Preparation of Ginsenoside Rg5, Its Antitumor Activity against Breast Cancer Cells and Its Targeting of PI3K. Nutrients 2020, 12, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhao, J.; Fu, R.; Zhu, C.; Fan, D. The ginsenoside Rk3 exerts anti-esophageal cancer activity in vitro and in vivo by mediating apoptosis and autophagy through regulation of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, J.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, M.; Li, L.; Deng, J.; Wang, X.; Su, J.; Zhu, Y.; He, F.; Mao, J.; et al. Ginsenoside Rg3 ameliorates myocardial glucose metabolism and insulin resistance via activating the AMPK signaling pathway. J. Ginseng Res. 2022, 46, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Yang, H.; Deng, J.; Fan, D. Ginsenoside Rg5 Improves Insulin Resistance and Mitochondrial Biogenesis of Liver via Regulation of the Sirt1/PGC-1α Signaling Pathway in db/db Mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 8428–8439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.H.; Kwon, H.W.; Irfan, M.; Rhee, M.H.; Lee, D.H. Ginsenoside Rk1 suppresses platelet mediated thrombus formation by downregulation of granule release and α(IIb)β(3) activation. J. Ginseng Res. 2021, 45, 490–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Xu, X.; Wei, J.; Xu, J.; Luo, W.; Li, A.; Liang, G.; Wang, M. Ginsenoside Rg5 alleviates Ang II-induced cardiac inflammation and remodeling by inhibiting the JNK/AP-1 pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 120, 110408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, J.; Yue, J.; Qin, S.; Li, Y.; Wu, B.; He, B. Biocatalysis for Rare Ginsenoside Rh2 Production in High Level with Co-Immobilized UDP-Glycosyltransferase Bs-YjiC Mutant and Sucrose Synthase AtSuSy. Catalysts 2021, 11, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Liu, C.; Xu, L.; Song, J.; Yu, H.; Jiang, C. Optimization of Conditions for Catalytic Conversion of Ginsenosides to Rare Saponins. J. Xuzhou Inst. Technol. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2018, 33, 49–54. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, W.C.; Huang, T.H.; Yeh, K.W.; Chen, Y.L.; Shen, S.C.; Liou, C.J. Ginsenoside Rg3 ameliorates allergic airway inflammation and oxidative stress in mice. J. Ginseng Res. 2021, 45, 654–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.P.; Huo, Y.; Yang, D.U.; Yang, D.C. Influence of the plant growth promoting Rhizobium panacihumi on aluminum resistance in Panax ginseng. J. Ginseng Res. 2021, 45, 442–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Yang, J.L.; Zhou, P.P.; Meng, X.H.; Shi, Y.-P. Further New Gypenosides from Jiaogulan (Gynostemma pentaphyllum). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 5926–5934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, G.Z.; Yu, Y.H.; Yu, S.J.; Xiong, B.H.; Chen, Y.; Liu, R.C. Research progress on medicinal plant Gynostemma pentaphyllum. Agric. Technol. 2014, 34, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, S.; Chen, D.; Liu, H.; Piao, X. Isolation and Identification of Ginsenoside Rg3 from Heat-processed Gocaekmbaw of Zhuang-medicine. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Formulae 2014, 20, 120–124. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, W.; Ku, S.K.; Kim, J.E.; Choi, G.E.; Song, G.Y.; Bae, J.S. Pulmonary Protective Functions of Rare Ginsenoside Rg4 on Particulate Matter-induced Inflammatory Responses. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2019, 24, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Tang, S.; Zhao, L.; Yang, X.; Yao, Y.; Hou, Z.; Xue, P. Stem-leaves of Panax as a rich and sustainable source of less-polar ginsenosides: Comparison of ginsenosides from Panax ginseng, American ginseng and Panax notoginseng prepared by heating and acid treatment. J. Ginseng Res. 2021, 45, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paik, S.; Choe, J.H.; Choi, G.E.; Kim, J.E.; Kim, J.M.; Song, G.Y.; Jo, E.K. Rg6, a rare ginsenoside, inhibits systemic inflammation through the induction of interleukin-10 and microRNA-146a. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, S.R.; Suzuki, Y.; Suzuki, K.; Choi, K.J.; Cho, B.G. Marked production of ginsenosides Rd, F2, Rg3, and compound K by enzymatic method. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2007, 55, 1522–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Wang, A.; He, z.; Jiang, Y.; Li, J.; Bi, J. The Technology of Increasing the Content of Rare Ginsenosides in Ginseng Stem and Leaf Saponins. Food Ind. 2020, 41, 50–53. [Google Scholar]
- Gui, L.; Xu, L.; Song, J.; Yu, H. Optimization of preparation process of rare ginsenosides Rk1 and Rg5 catalyzed by metal ions. J. Dalian Polytech. Univ. 2020, 39, 401–405. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, S.; Liu, C.; Xu, L.; Song, J.; Yu, H. The Catalytic Transformation of Ginsenoside Re by Metal Ions. J. Jiangxi Norm. Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2019, 43, 96–101. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Zhu, F.; Li, J. Effect of Drying Temperature on Changes of Maillard Reaction Main Index Components in Processing of Black Ginseng. Storage Process 2020, 20, 120–125. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Balan, P.; Popovich, D.G. Changes of Ginsenoside Composition in the Creation of Black Ginseng Leaf. Molecules 2020, 25, 2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Xu, W.; Shi, D.; Balan, P.; Popovich, D. Enrichment of the less polar ginsenoside (Rg3) from ginseng grown in New Zealand by post-harvest processing and extraction. Tradit. Med. Res. 2021, 6, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popovich, D.G.; Kitts, D.D. Generation of ginsenosides Rg3 and Rh2 from North American ginseng. Phytochemistry 2004, 65, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, K.y.; Lee, N.R.; Moon, B.-D.; Song, G.Y.; Shin, H.S.; Choi, J.-e.J.T.K.J.o.M.C.S. Changes of Ginsenosides and Color from Black Ginsengs Prepared by Steaming-Drying Cycles. Korean J. Med. Crop. Sci. 2012, 20, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.J.; Kim, H.D.; Lee, E.S.; Jang, G.Y.; Seong, H.A. Heat Treatment Enhances the Neuroprotective Effects of Crude Ginseng Saponin by Increasing Minor Ginsenosides. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.F.; Jin, C.A.; Zhao, H.; Liu, J.Y.; Wang, F. Determination of Saponins in Ginseng, Red Ginseng and American Ginseng by UPLC-ESI-MS/MS. Spec. Wild Econ. Anim. Plant Res. 2019, 41, 58–66. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, Y.; Yang, J.; Xie, J.B.; Xie, P.; Qi, Y.S.; Zhao, M.T.; Piao, X.L. Simultaneous quantitative analysis of nine saponins in Gynostemma pentaphyllum before and after heat processing based on UPLC-Q-Trap-MS. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2021, 46, 5314–5319. [Google Scholar]


| Compound | Content (mg/g) | |
|---|---|---|
| Raw G. pentaphyllum | Heat-Processed G. pentaphyllum | |
| Ginsenoside Rb3 | 2.248 ± 0.036 | 1.798 ± 0.036 |
| Ginsenoside Rd | 0.918 ± 0.030 | 0.917 ± 0.020 |
| 20(S)-ginsenoside Rg3 | N.D. 1 | 0.035 ± 0.049 |
| 20(R)-ginsenoside Rg3 | N.D. 1 | 0.231 ± 0.094 |
| Ginsenoside Rk1 | 0.083 ± 0.009 | 3.359 ± 0.463 |
| Ginsenoside Rg5 | 0.006 ± 0.004 | 3.347 ± 0.410 |
| Compound | Retention Time (min) | Quantitative Ion Pair (m/z) | DP (V) | CE (V) | CXP (V) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ginsenoside Rb3 | 2.08 | 1123.6/1077.6 | −40 | −34 | −21 |
| Ginsenoside Rd | 2.80 | 991.4/945.5 | −25 | −38 | −25 |
| 20(S)-ginsenoside Rg3 | 5.88 | 829.6/621.4 | −40 | −54 | −27 |
| 20®-ginsenoside Rg3 | 6.18 | 829.5/783.5 | −60 | −25 | −13 |
| Ginsenoside Rk1 | 10.78 | 811.5/765.5 | −55 | −30 | −15 |
| Ginsenoside Rg5 | 11.43 | 811.6/765.5 | −55 | −30 | −15 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.-C.; Li, F.-F.; Pei, W.-J.; Yang, J.; Gu, Y.-L.; Piao, X.-L. The Content and Principle of the Rare Ginsenosides Produced from Gynostemma pentaphyllum after Heat Treatment. Molecules 2023, 28, 6415. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28176415
Li X-C, Li F-F, Pei W-J, Yang J, Gu Y-L, Piao X-L. The Content and Principle of the Rare Ginsenosides Produced from Gynostemma pentaphyllum after Heat Treatment. Molecules. 2023; 28(17):6415. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28176415
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xin-Can, Fang-Fang Li, Wen-Jing Pei, Jing Yang, Yu-Long Gu, and Xiang-Lan Piao. 2023. "The Content and Principle of the Rare Ginsenosides Produced from Gynostemma pentaphyllum after Heat Treatment" Molecules 28, no. 17: 6415. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28176415
APA StyleLi, X.-C., Li, F.-F., Pei, W.-J., Yang, J., Gu, Y.-L., & Piao, X.-L. (2023). The Content and Principle of the Rare Ginsenosides Produced from Gynostemma pentaphyllum after Heat Treatment. Molecules, 28(17), 6415. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28176415







