Determination of Pentachlorophenol in Seafood Samples from Zhejiang Province Using Pass-Through SPE-UPLC-MS/MS: Occurrence and Human Dietary Exposure Risk
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Optimization of the UPLC-MS/MS Analytical Method
2.1.1. Determination of the Mobile Phase
2.1.2. Selection of Chromatographic Columns
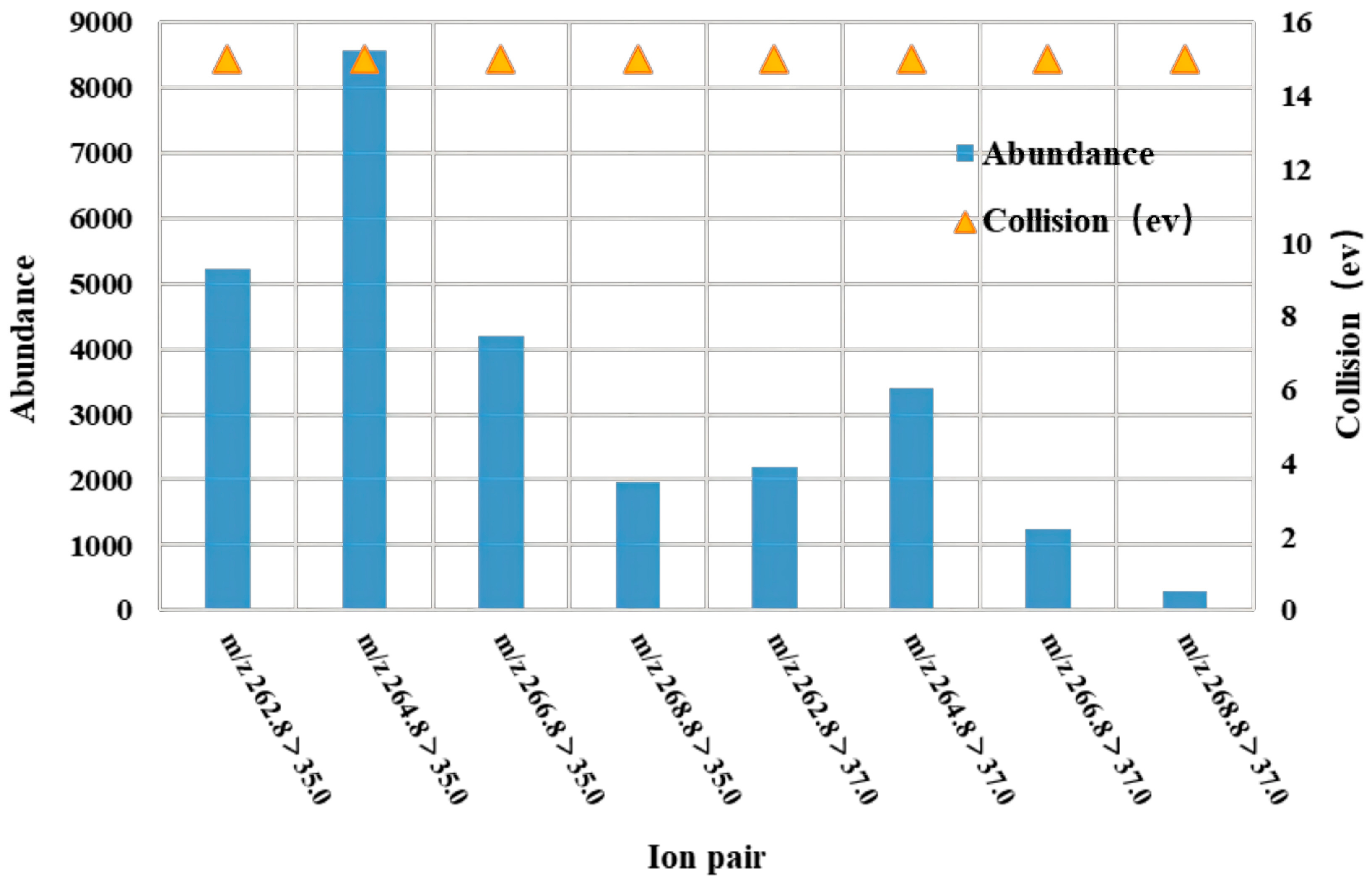
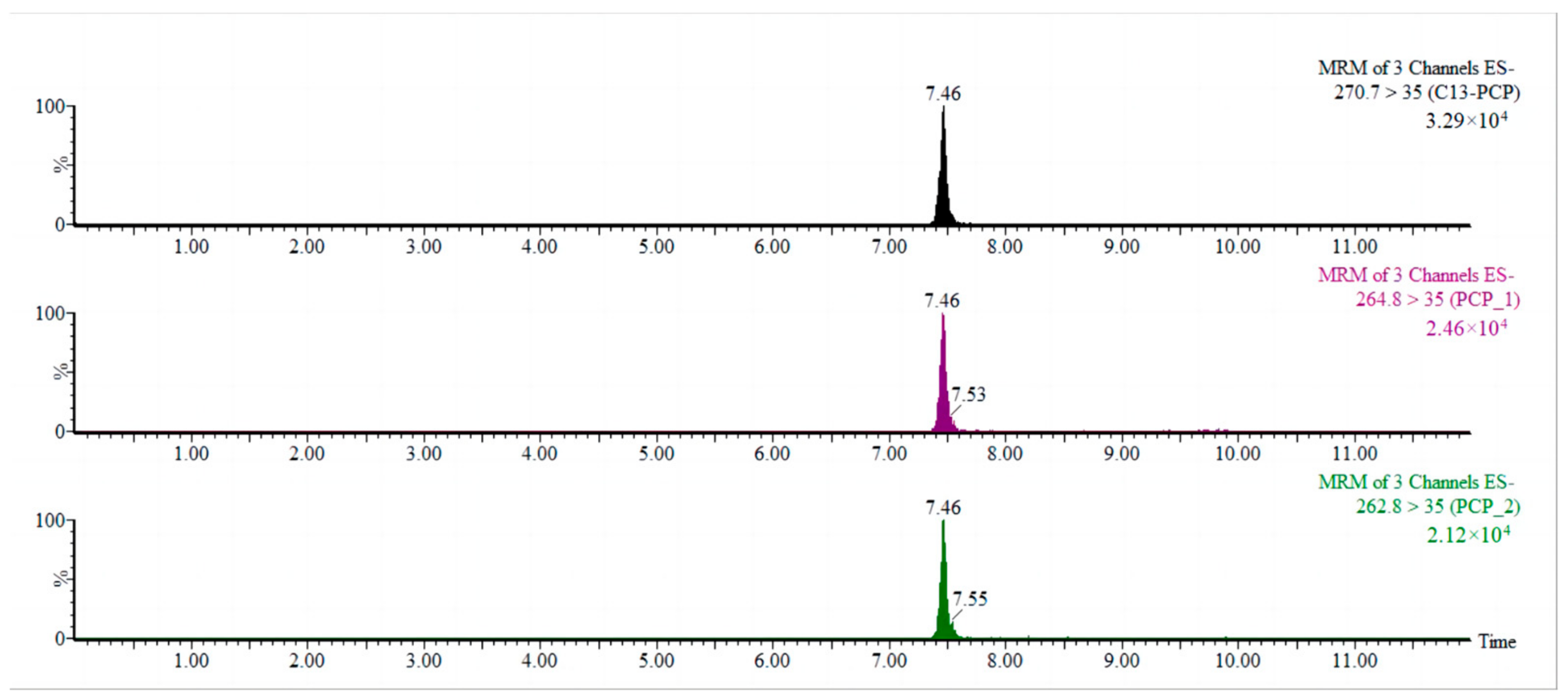
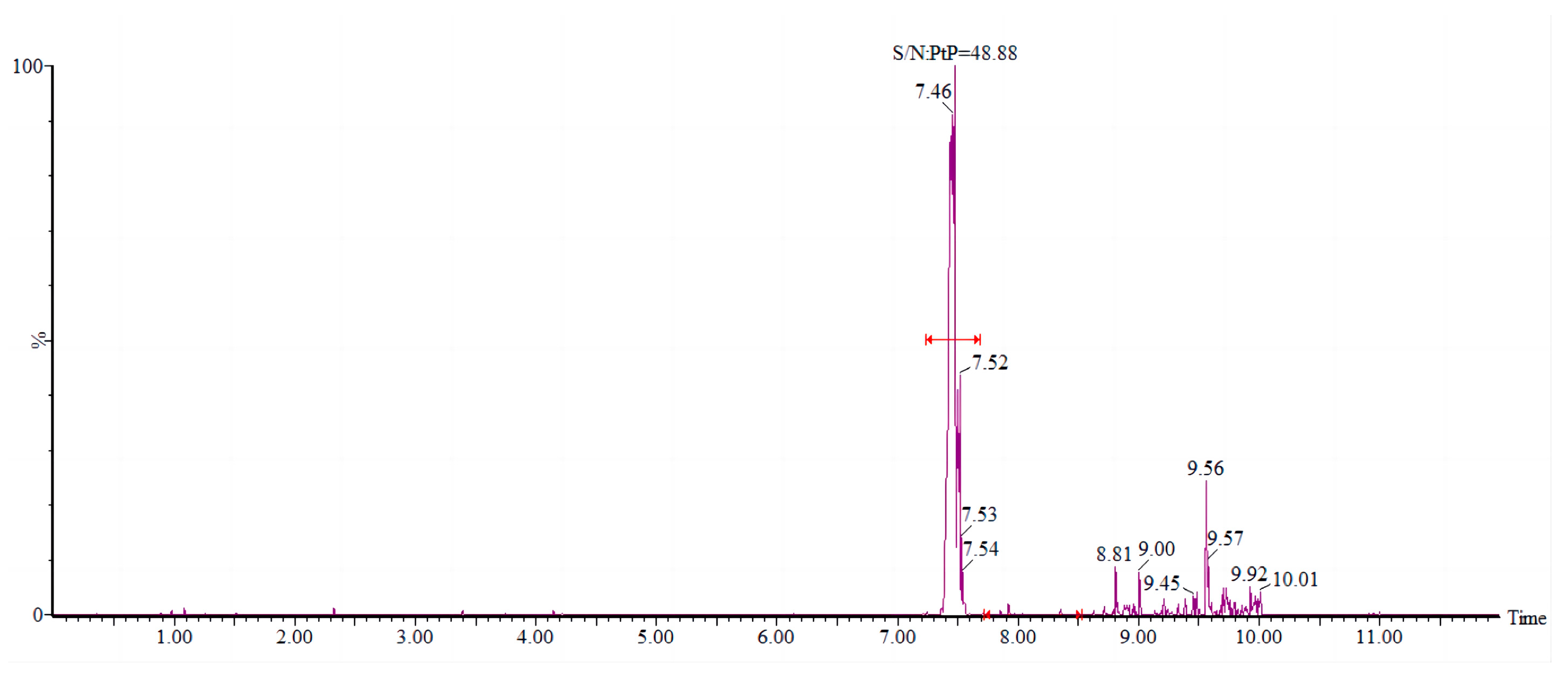
2.1.3. Determination of Mass Spectrometry Conditions
2.2. Optimization of Pretreatment Conditions
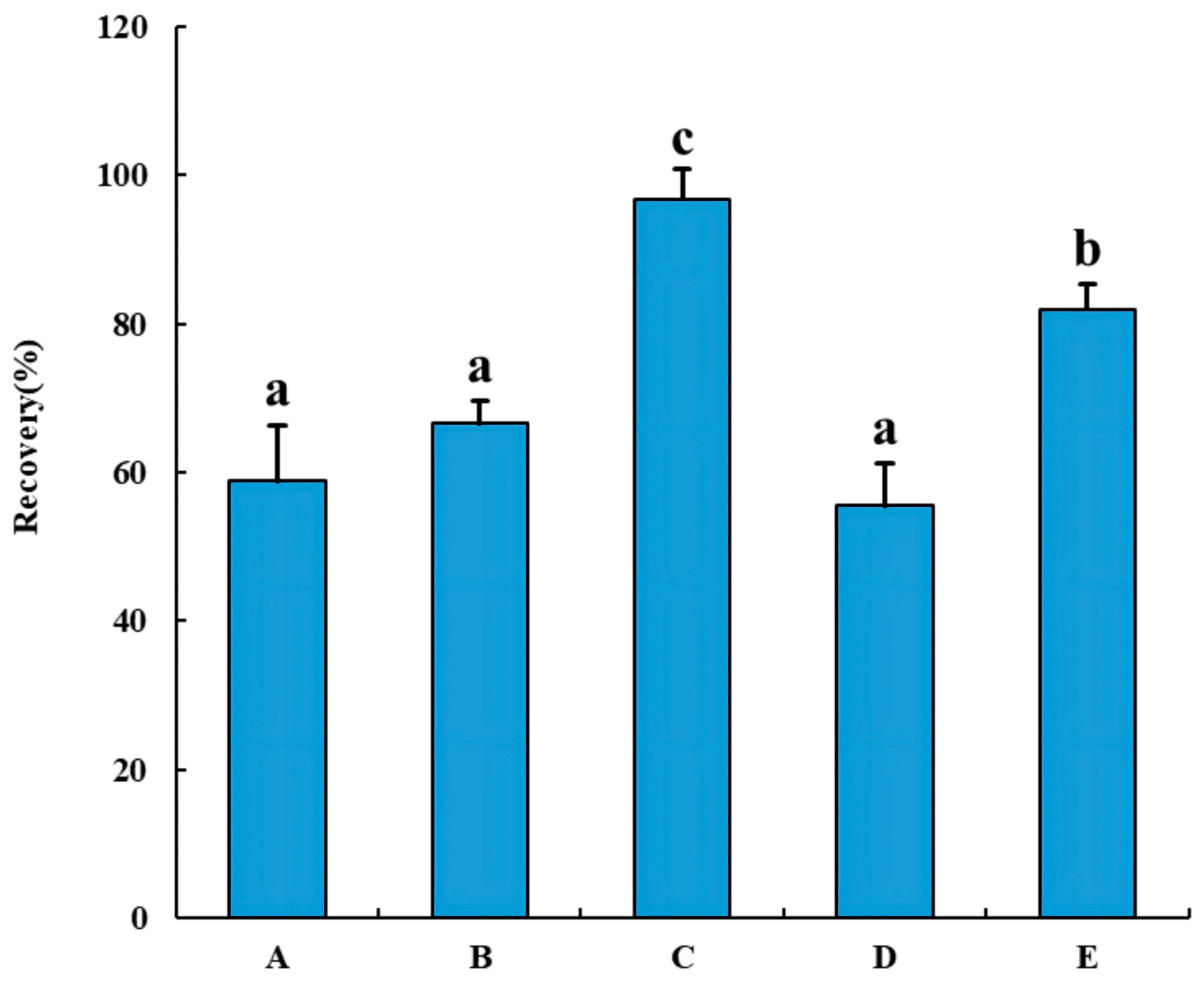
2.2.1. The Comparison and Optimization of Solid-Phase Extraction Columns
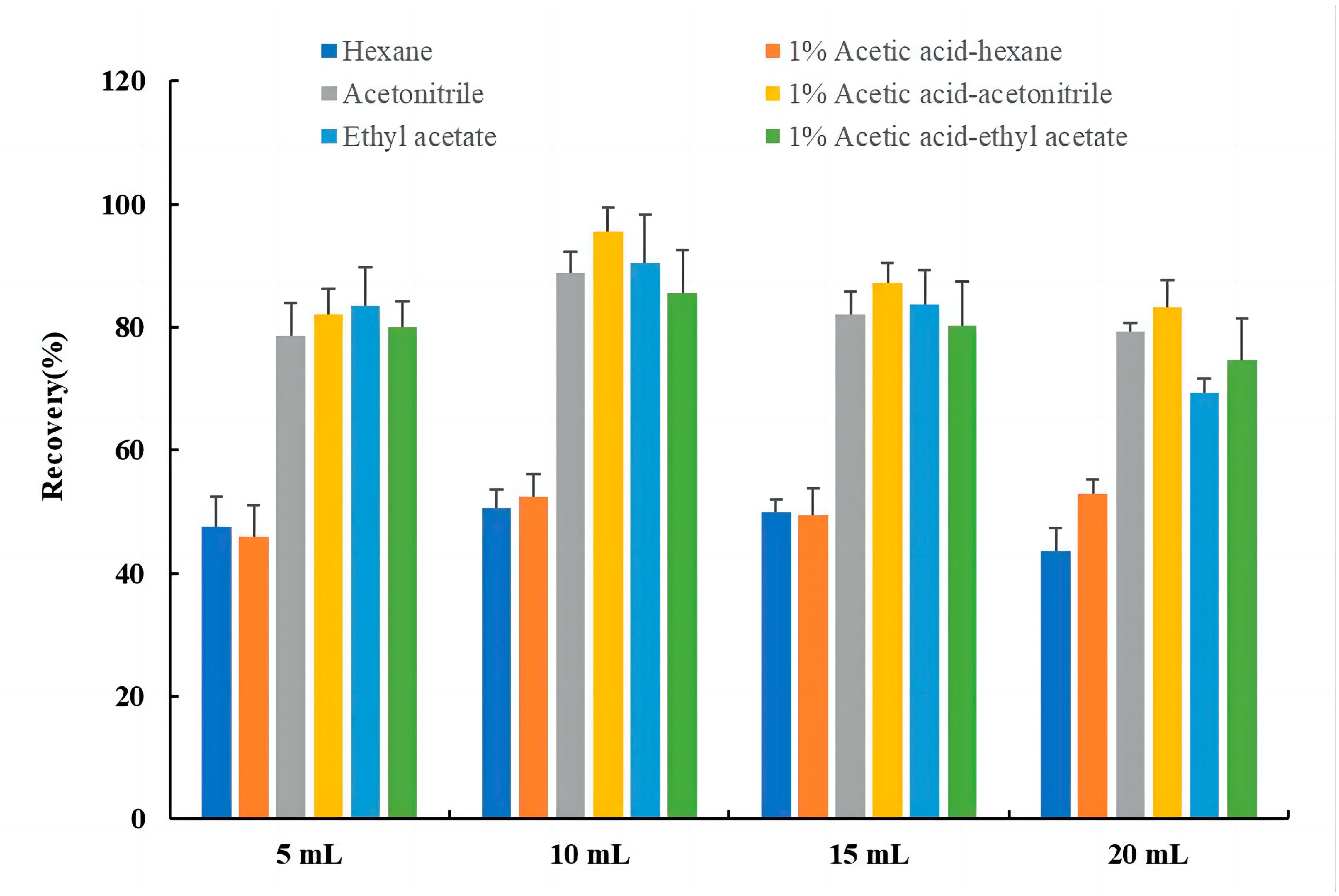
2.2.2. Selection of Extraction Solvent and Extraction Volume
2.3. Validation of the Method
3. Sample Analysis and Health Risk Assessment
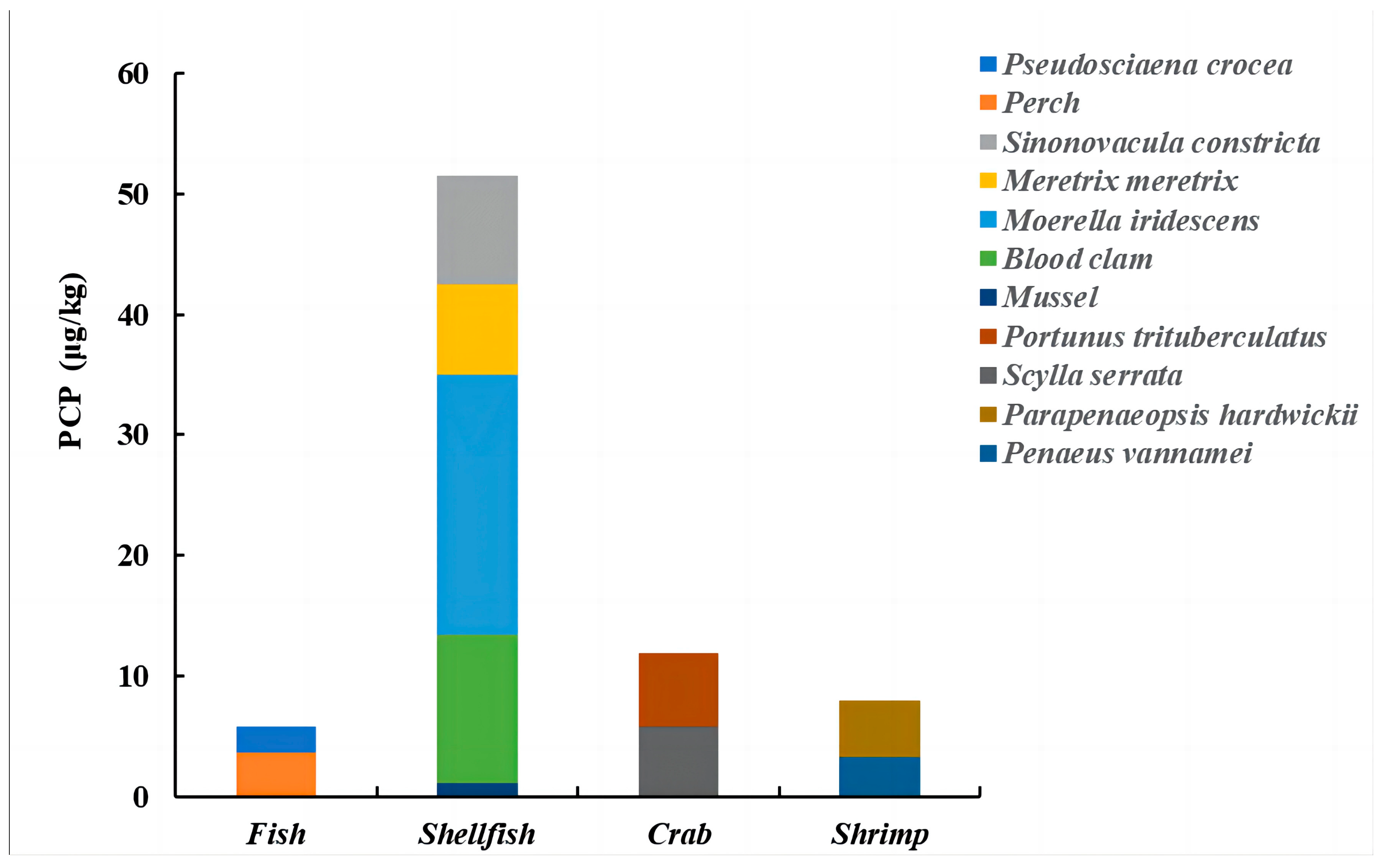
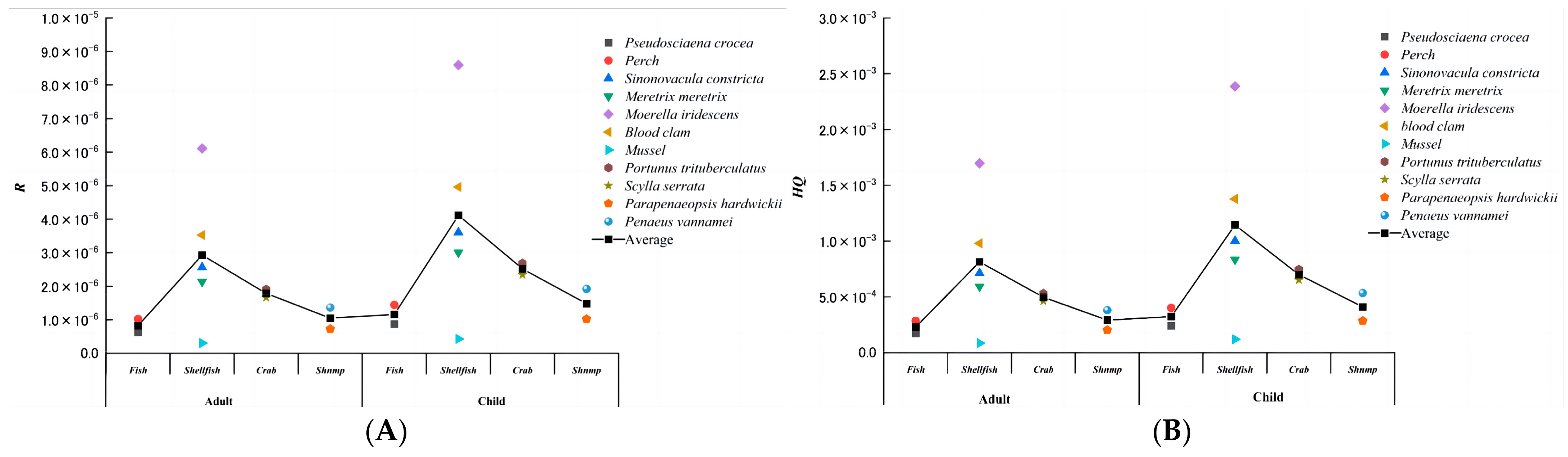
3.1. Sample Analysis
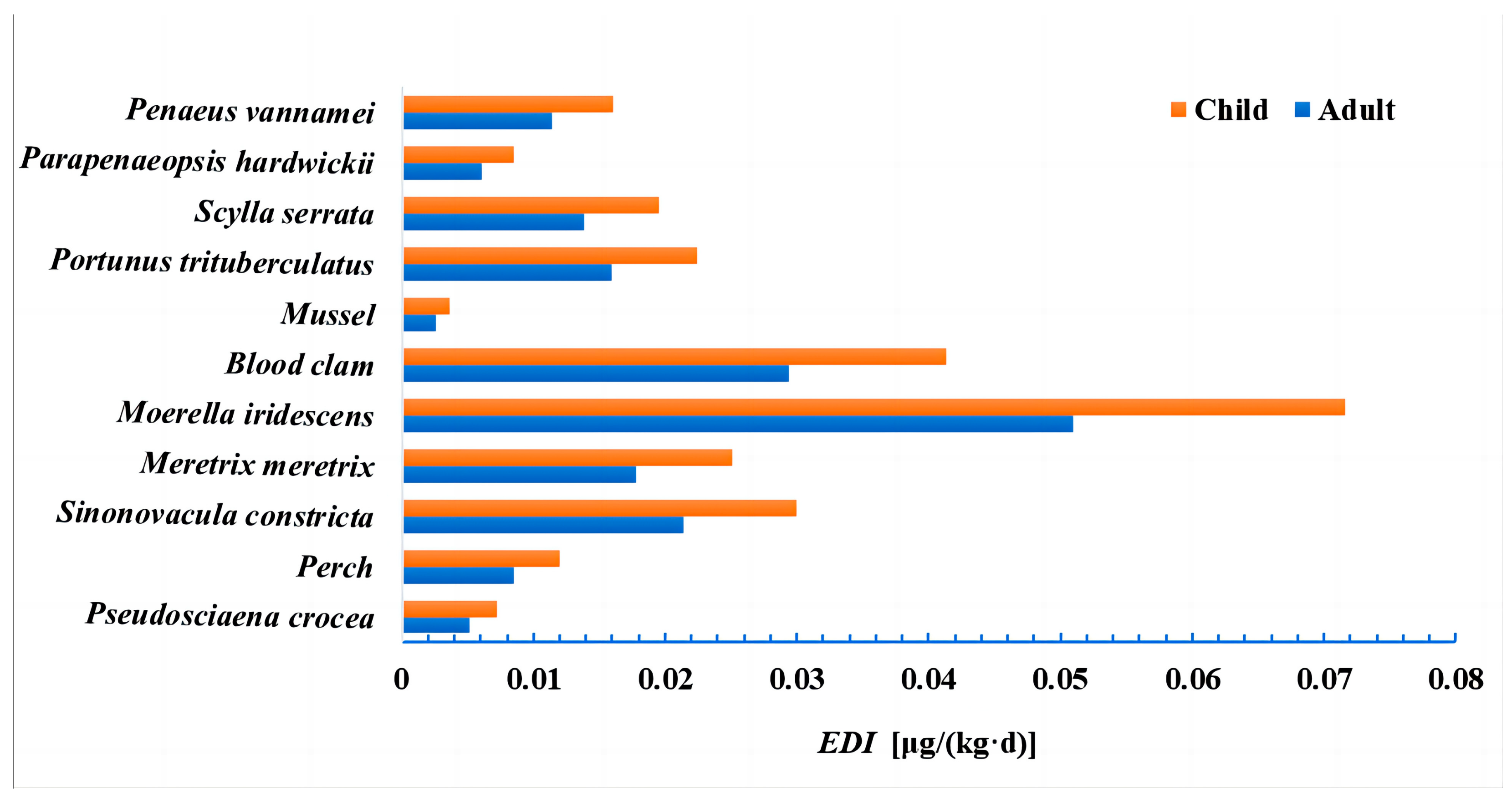
3.2. Health Risk Assessment
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials and Reagents
4.2. Instruments and Equipment
4.3. Preparation of Standard Solutions
4.4. Sample Collection and Preparation
4.5. Operating Conditions of the Instrument
4.6. Method Validation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Yakamercan, E.; Aygün, A. Fate and removal of pentachlorophenol and diethylhexyl phthalate from textile industry wastewater by sequencing batch biofilm reactor: Effects of hydraulic and solid retention times. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Tang, Y.; Han, Y.; Huang, L.; Zhou, W.; Zhou, C.; Hu, Y.; Lu, R.; Wang, F.; Shi, W.; et al. Immunotoxicity of pentachlorophenol to a marine bivalve species and potential toxification mechanisms underpinning. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 439, 129681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Peng, Q.; Xuan, D.; Qu, W. Development of a solid phase microextraction-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry method for the determination of pentachlorophenol in human plasma using experimental design. Chemosphere 2007, 70, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Xia, X.; Li, P.; Yu, H.; Xie, Y.; Guo, Y.; Yao, W.; Qian, H.; Cheng, Y. A facile “off-on” fluorescence sensor for pentachlorophenol detection based on natural N and S co-doped carbon dots from crawfish shells. Food Chem. 2023, 405, 134802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, L.; Guo, L.; Lv, X.; Li, Y. Modification of polychlorinated phenols and evaluation of their toxicity, biodegradation and bioconcentration using three-dimensional quantitative structure-activity relationship models. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2017, 71, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thota, S.; Begum, R.; Kaur, G.; Bagam, P.; Dorsey, W.; Batra, S. Pentachlorophenol mediated regulation of DAMPs and inflammation: In vitro study. Toxicol. Vitro 2022, 83, 105378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Kang, H.; Peng, L.; Song, D.; Jiang, X.; Li, Y.; Chen, H.; Zeng, X. Pentachlorophenol inhibits CatSper function to compromise progesterone’s action on human sperm. Chemosphere 2020, 259, 127493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization International Agency for Research on Cancer Carcinogen List. 2017. Available online: https://www.nmpa.gov.cn/xxgk/mtbd/20171030163101383.html (accessed on 21 May 2023).
- Commission Delegated Regulation (EU) 2021/277 of 16 December 2020 Amending Annex I to Regulation (EU) 2019/1021 of the European Parliament and of the Council on Persistent Organic Pollutants as regards Pentachlorophenol and Its Salts and Esters (Text with EEA Relevance). 2020. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IARC_group_1_Carcinogens (accessed on 22 August 2023).
- TSCA Chemical Substance Inventory. 2023. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/tsca-inventory/how-access-tsca-inventory#download (accessed on 22 August 2023).
- Chemical Substances Control List Ver.2.3-b. 2018. Available online: https://web-material3.yokogawa.com/31/10019/tabs/PTPD-T-N01-S01-0015-en.pdf (accessed on 22 May 2023).
- Ministry of Agriculture. No 235Bulletin of the Ministry of Agriculture of People’s Republic of China. 2019. Available online: https://www.lssyjc.com/5/2018-06-25/830.html (accessed on 23 May 2023).
- Sim, W.J.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, I.S.; Choi, S.D.; Oh, J.E. Distribution and formation of chlorophenols and bromophenols in marine and riverine environments. Chemosphere 2009, 77, 552–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fingler, S.; Drevenkar, V.; Frobe, Z. Sorption of chlorophenolates in soils and aquifer and marine sediments. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2005, 48, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beiras, R.; Tato, T. Marine environmental risk assessment and acute water quality criterion for pentachlorophenol in coastal waters. Ecotoxicology 2018, 27, 803–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Hassine, S.; Hammami, B.; Touil, S.; Driss, M.R. Determination of Chlorophenols in Water Samples Using Solid-Phase Extraction Enrichment Procedure and Gas Chromatography Analysis. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2015, 95, 654–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Xue, A.; Chen, H.; Li, S. Low-density solvent-based dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction combined with single-drop microextraction for the fast determination of chlorophenols in environmental water samples by high performance liquid chromatography-ultraviolet detection. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1280, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villar-Navarro, M.; Ramos-Payan, M.; Perez-Bernal, J.L.; Fernandez-Torres, R.; Callejon-Mochon, M.; Angel Bello-Lopez, M. Application of three phase hollow fiber based liquid phase microextraction (HF-LPME) for the simultaneous HPLC determination of phenol substituting compounds (alkyl-, chloro- and nitrophenols). Talanta 2012, 99, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovacs, A.; Kende, A.; Mortl, M.; Volk, G.; Rikker, T.; Torkos, K. Determination of phenols and chlorophenols as trimethylsilyl derivatives using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1194, 139–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, L.; Goen, T. Simultaneous determination of the full chlorophenol spectrum in human urine using gas chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 965, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amendola, L.; Cortese, M.; Vinatoru, D.; Sposato, S.; Insogna, S. Innovative analytical method for the determination of underivatized tributyltin and pentachlorophenol in seawater by gas chromatography-triple quadrupole mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 975, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Lv, J.; Zou, J. Simultaneous determination of pentachlorophenol, niclosamide and fenpropathrin in fishpond water using an LC-MS/MS method for forensic investigation. Anal. Methods 2013, 5, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zhu, P.; Xu, B.; Zhao, R.; Qiao, S.; Chen, X.; Tang, R.; Wu, D.; Song, L.; Wang, S.; et al. Determination of nine environmental phenols in urine by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2012, 36, 608–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, L.; Jiang, D.; Liang, F.; Zhang, H.; Wei, K.; Wang, J. A New Method for Detecting Environmental Pollutant Sodium Pentachlorophenate (PCP-Na) Based on PAX Solid-Phase Extraction and UPLC-MS/MS. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2022, 233, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Pan, J.; Fei, Z.; Wu, G.; Giesy, J.P. Concentrations of pentachlorophenol (PCP) in fish and shrimp in Jiangsu Province, China. Chemosphere 2007, 69, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsayei, M.; Yamini, Y.; Asiabi, H. Evaluation of highly efficient on-line yarn-in-tube solid phase extraction method for ultra-trace determination of chlorophenols in honey samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1569, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, P.; Liu, X.; Kong, F.; Tang, L.; Wang, Q.; Li, W.; Xu, W.; Wen, S.; Chen, L.; Li, Y. Multi-residue determination of 325 pesticides in chicken eggs with EMR-Lipid clean-up by UHPLC–MS/MS and GC–MS/MS. Chromatographia 2020, 83, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Chen, M.; Zhang, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhu, D.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, B.; Zhang, Z. Simultaneous quantification of five phenols in settled house dust using ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Methods 2013, 5, 5339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Communities, Commission Decision 2002/657/EC Implementing Council Directive 96/23/EC Concerning the Performance of Analytical Methods and the Interpretation of Results. 2002. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX:32002D0657 (accessed on 15 October 2022).
- Dai, J.; Lin, H.; Pan, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Y.; Qiao, J.Q.; Lian, H.Z.; Xu, C.X. Determination of chlorpromazine and its metabolites in animal-derived foods using QuEChERS-based extraction, EMR-Lipid cleanup, and UHPLC-Q-Orbitrap MS analysis. Food Chem. 2023, 403, 134298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Luo, Y.; Mu, L.; Yang, Y.; Yang, Y. Risk screening of mycotoxins and their derivatives in dairy products using a stable isotope dilution assay and LC-MS/MS. J. Sep. Sci. 2021, 44, 782–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu-Duc, N.; Nguyen-Quang, T.; Le-Minh, T.; Nguyen-Thi, X.; Tran, T.M.; Vu, H.A.; Nguyen, L.A.; Doan-Duy, T.; Van Hoi, B.; Vu, C.T.; et al. Multiresidue Pesticides Analysis of Vegetables in Vietnam by Ultrahigh-Performance Liquid Chromatography in Combination with High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry (UPLC-Orbitrap MS). J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2019, 2019, 3489634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xian, Y.; Wu, Y.; Dong, H.; Chen, L.; Zhang, C.; Hou, X.; Zeng, X.; Bai, W.; Guo, X. Modified QuEChERS purification and Fe3O4 nanoparticle decoloration for robust analysis of 14 heterocyclic aromatic amines and acrylamide in coffee products using UHPLC-MS/MS. Food Chem. 2019, 285, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Li, H.; Liang, J.; Ma, J.; Yang, J.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, W.; Bai, W.; Zeng, X.; Dong, H. High-throughput quantification of eighteen heterocyclic aromatic amines in roasted and pan-fried meat on the basis of high performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole-orbitrap high resolution mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2021, 361, 130147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kranzioch-Seipel, I.; Beckert, U.; Shen, C.; Yin, D.; Tiehm, A. Microbial dechlorination of HCB, PCP, PCB180, HCH and PCE in a Yangtze Three Gorges Reservoir enrichment culture, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kravos, A.; Zgajnar Gotvajn, A.; Lavrencic Stangar, U.; Malinovic, B.N.; Prosen, H. Combined Analytical Study on Chemical Transformations and Detoxification of Model Phenolic Pollutants during Various Advanced Oxidation Treatment Processes. Molecules 2022, 27, 1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M. Study on Distribution, Eco-Toxicolological Effects and Health Risk Assessment of Chlorophenol Contaminants in Dongting Lake; China University of Geosciences: Beijing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Cheung, K.C.; Leung, H.M.; Kong, K.Y.; Wong, M.H. Residual levels of DDTs and PAHs in freshwater and marine fish from Hong Kong markets and their health risk assessment. Chemosphere 2007, 66, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- US EPA. EPA/600/P-95/002 Fa, b, c. Exposure Factors Handbook[S]; Environmental Protection Agency Office of Research and Development: Washington, DC, USA, 1997. Available online: https://cfpub.epa.gov/si/si_public_record_report.cfm?dirEntryId=12464 (accessed on 20 October 2022).
- US EPA Office of Water, Office of Science and Technology Agency. Guidance for Assessing Chemical Contaminant Data for Use in Fish Advisories-Volume 2: Risk Assessment and Fish Consumption Limits Third Edition. 2001. Available online: https://archive.epa.gov/pesticides/trac/web/pdf/aggregate_resp.pdf (accessed on 30 October 2022).
- Leung SS, F.; Chan, S.M.; Lui, S.; Lee WT, K.; Davies, D.P. Growth and nutrition of Hong Kong children aged 0–7 years. J. Paediatr. Child Health 2000, 36, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, R.; Xiao, G.; Miao, J.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Z.; He, Z.; Zhang, N.; Song, A.; Pan, L. Study on the toxic effects of sodium pentachlorophenol (PCP-Na) on razor clam (Sinonovacula constricta). Mar. Environ. Res 2023, 183, 105845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Sample | ME (%) | R | LOQs (μg /kg) | 1 μg/kg | 5 μg/kg | 10 μg/kg | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recoveries (%) | RSD(%) Intra-Day (n = 6) | RSD(%) Ntro-Day (n = 6) | Recoveries (%) | RSD(%) Intra-Day (n = 6) | RSD(%) Ntro-Day (n = 6) | Recoveries (%) | RSD(%) Intra-Day (n = 6) | RSD(%) Ntro-Day (n = 6) | ||||
| Pseudosciaena crocea | −9 | 0.9972 | 1 | 92.2 | 6.5 | 4.6 | 90.6 | 8.6 | 9.2 | 90.9 | 7.5 | 9.7 |
| Perch | 11 | 0.9985 | 1 | 89.5 | 7.3 | 8.4 | 87.4 | 10.7 | 7.1 | 86.4 | 6.3 | 4.5 |
| Sinonovacula constricta | 6 | 0.9997 | 1 | 88.7 | 8.4 | 6.7 | 91.8 | 9.6 | 8.8 | 87.6 | 8.6 | 5.7 |
| Meretrix meretrix | −14 | 0.9989 | 1 | 91.9 | 4.5 | 5.1 | 89.3 | 9.4 | 9.5 | 92.0 | 10.2 | 8.4 |
| Moerella iridescens | 7 | 0.9983 | 1 | 102.5 | 5.4 | 5.3 | 92.1 | 8.7 | 5.7 | 90.2 | 10.0 | 11.4 |
| Blood clam | −15 | 0.9964 | 1 | 89.1 | 3.7 | 4.0 | 90.7 | 11.2 | 12.1 | 91.4 | 8.5 | 6.9 |
| Mussel | 10 | 0.9984 | 1 | 88.0 | 8.7 | 7.5 | 90.2 | 7.3 | 6.1 | 91.5 | 6.4 | 3.1 |
| Portunus trituberculatus | 13 | 0.9982 | 1 | 92.8 | 9.3 | 11.3 | 89.7 | 8.4 | 7.3 | 89.3 | 5.7 | 3.3 |
| Scylla serrata | −17 | 0.9970 | 1 | 88.4 | 7.8 | 7.7 | 89.0 | 6.5 | 3.8 | 92.7 | 6.5 | 6.6 |
| Parapenaeopsis hardwickii | 6 | 0.9983 | 1 | 93.5 | 6.7 | 5.9 | 91.9 | 5.4 | 6.5 | 92.9 | 5.0 | 2.9 |
| Penaeus vannamei | 8 | 0.9975 | 1 | 95.2 | 5.8 | 5.6 | 92.7 | 7.6 | 7.1 | 93.2 | 7.3 | 5.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, X.; Zhao, Q.; Yan, Z.; Chen, X.; He, P.; Li, S.; Fang, Y. Determination of Pentachlorophenol in Seafood Samples from Zhejiang Province Using Pass-Through SPE-UPLC-MS/MS: Occurrence and Human Dietary Exposure Risk. Molecules 2023, 28, 6394. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28176394
Yan X, Zhao Q, Yan Z, Chen X, He P, Li S, Fang Y. Determination of Pentachlorophenol in Seafood Samples from Zhejiang Province Using Pass-Through SPE-UPLC-MS/MS: Occurrence and Human Dietary Exposure Risk. Molecules. 2023; 28(17):6394. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28176394
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Xiaoyang, Qiaoling Zhao, Zhongyong Yan, Xuechang Chen, Pengfei He, Shiyan Li, and Yi Fang. 2023. "Determination of Pentachlorophenol in Seafood Samples from Zhejiang Province Using Pass-Through SPE-UPLC-MS/MS: Occurrence and Human Dietary Exposure Risk" Molecules 28, no. 17: 6394. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28176394
APA StyleYan, X., Zhao, Q., Yan, Z., Chen, X., He, P., Li, S., & Fang, Y. (2023). Determination of Pentachlorophenol in Seafood Samples from Zhejiang Province Using Pass-Through SPE-UPLC-MS/MS: Occurrence and Human Dietary Exposure Risk. Molecules, 28(17), 6394. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28176394