opp-Dibenzoporphyrin Pyridinium Derivatives as Potential G-Quadruplex DNA Ligands
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
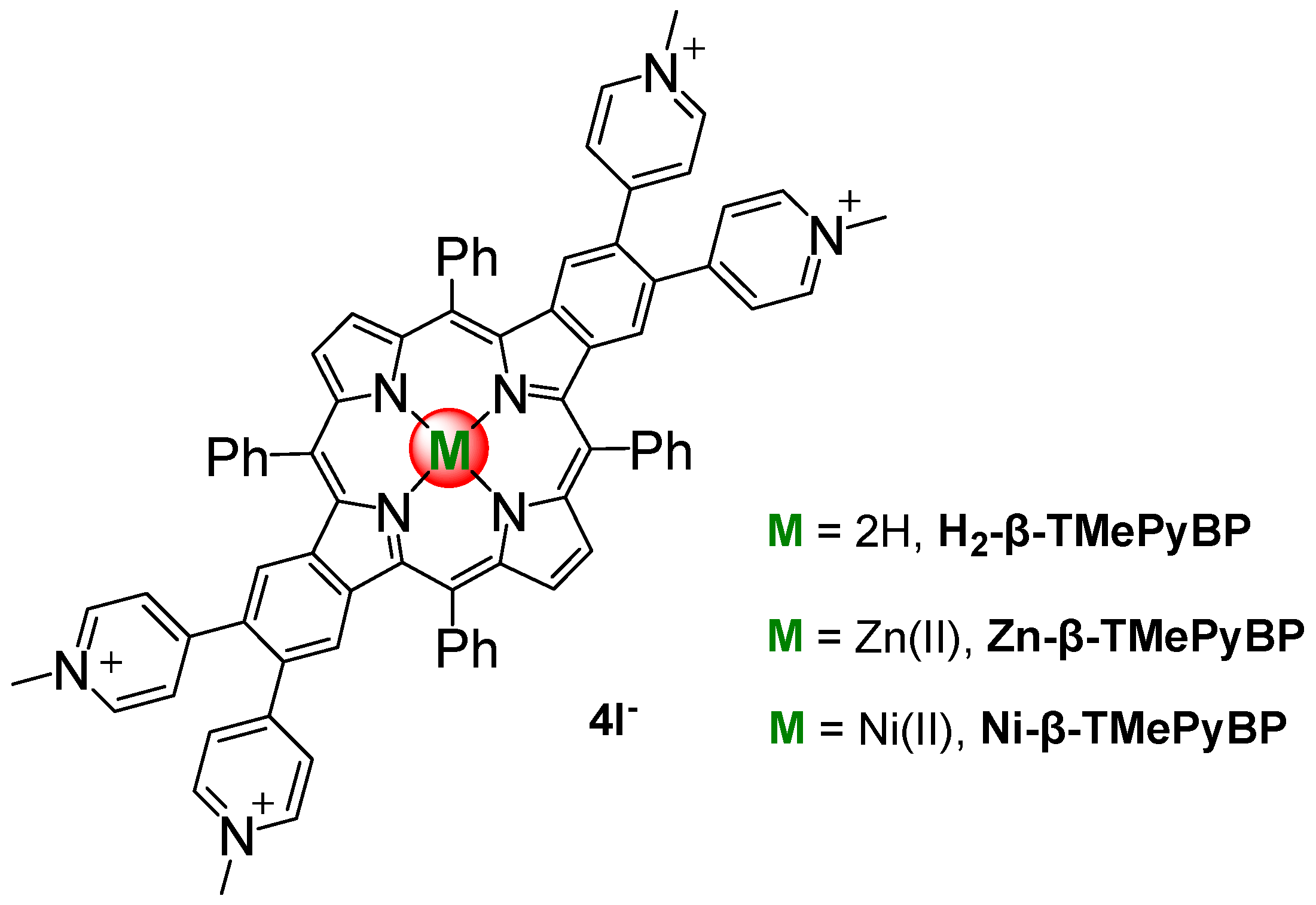
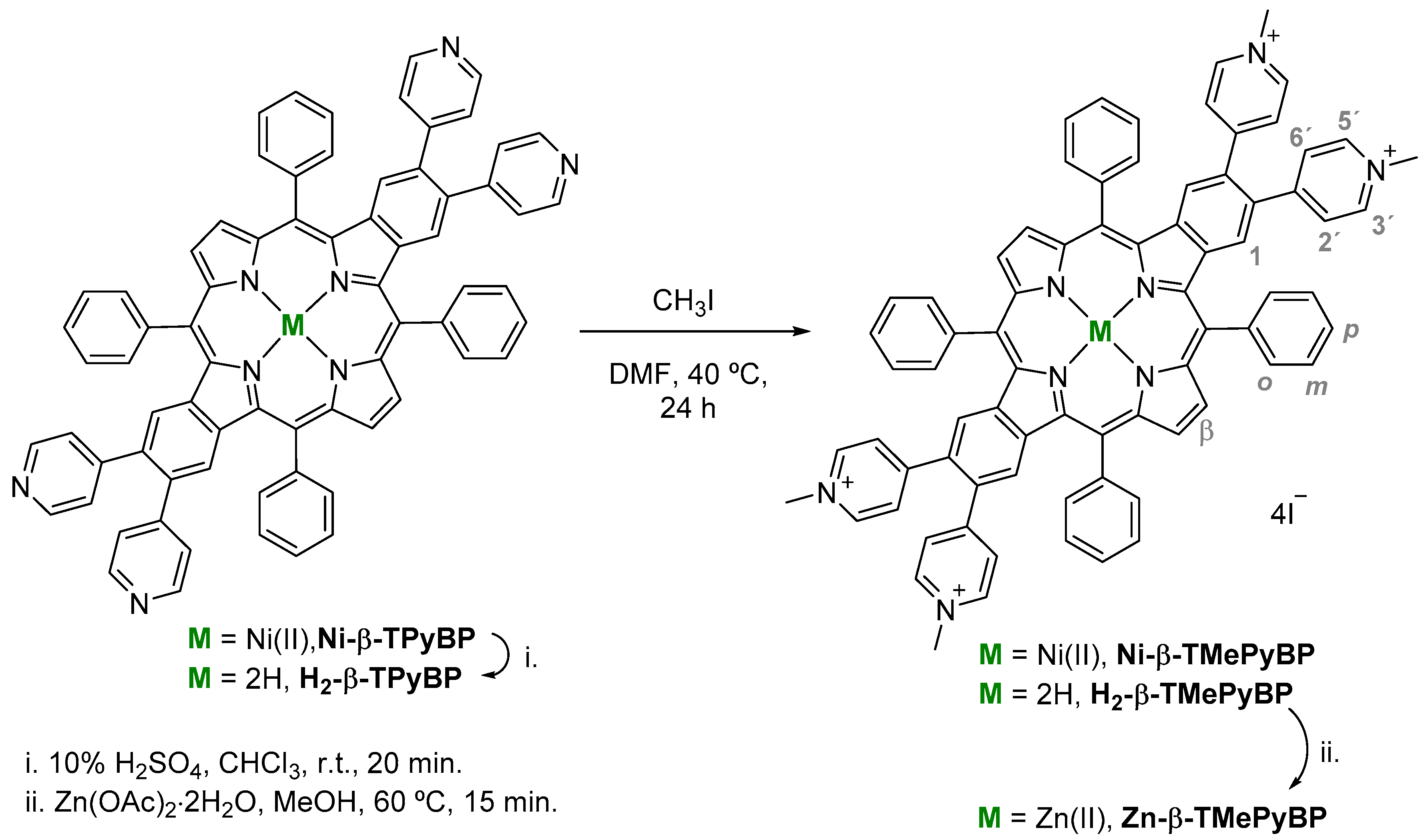
2.1. Synthesis
2.2. DNA Stabilisation Studies
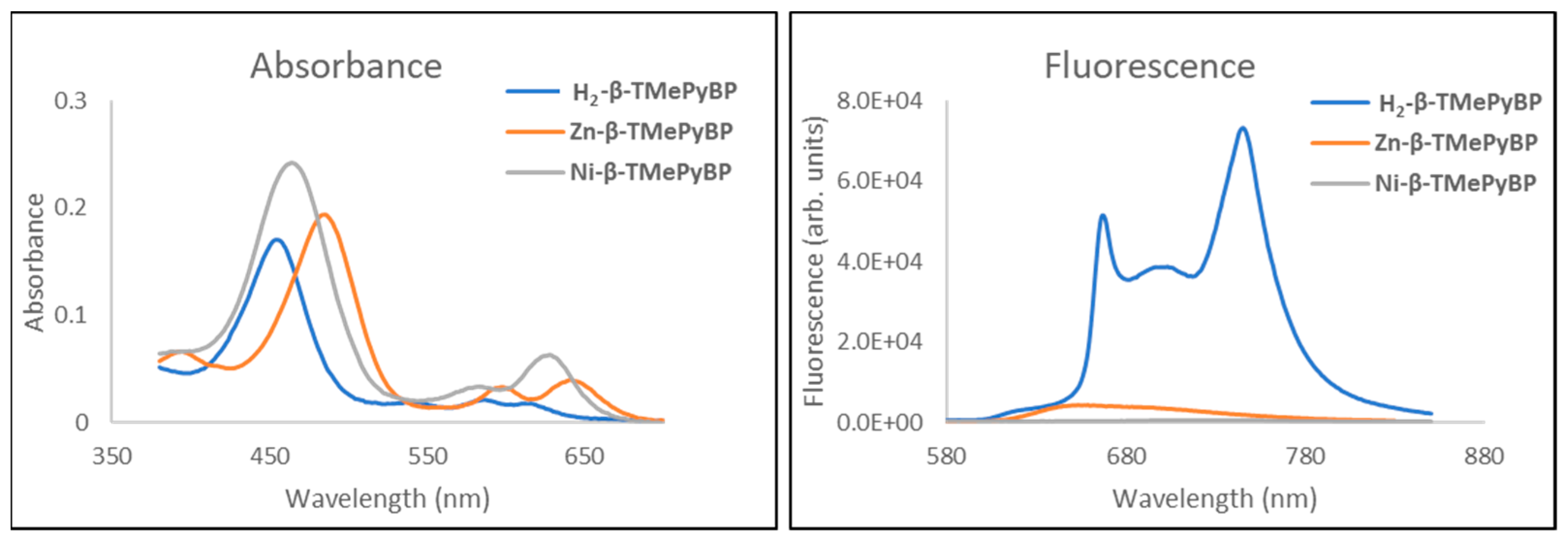
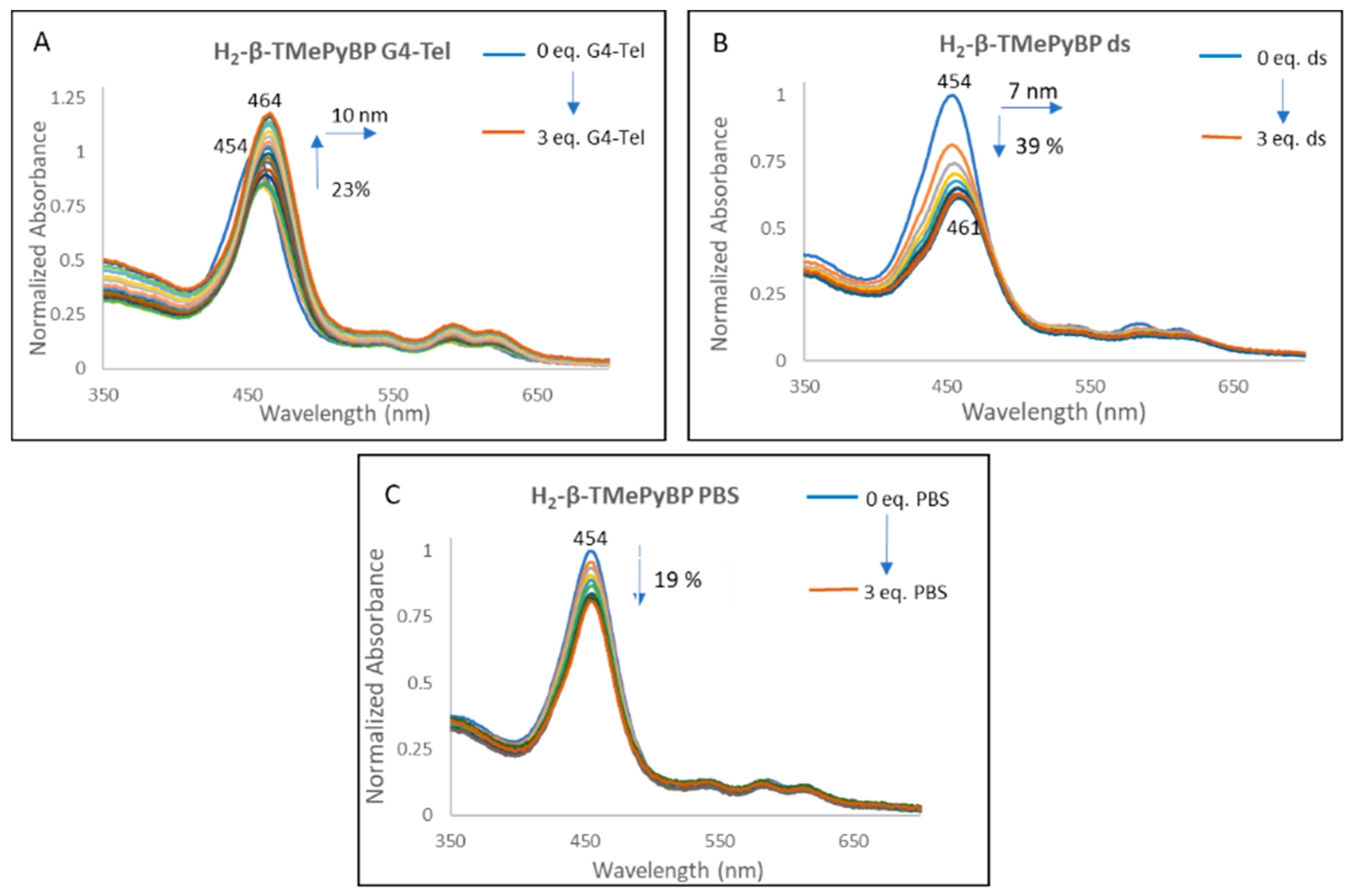
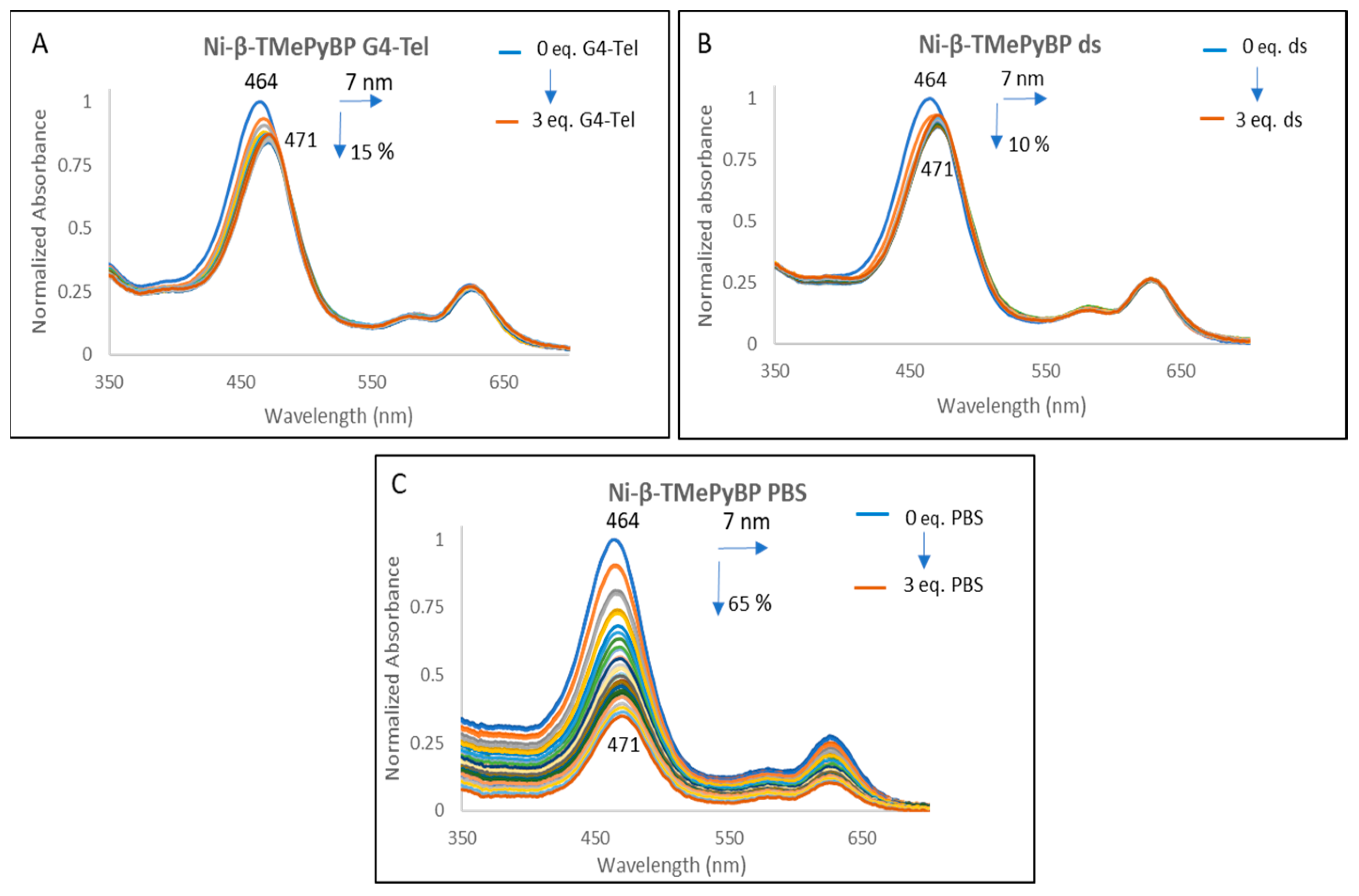
2.2.1. UV-Vis Spectroscopy
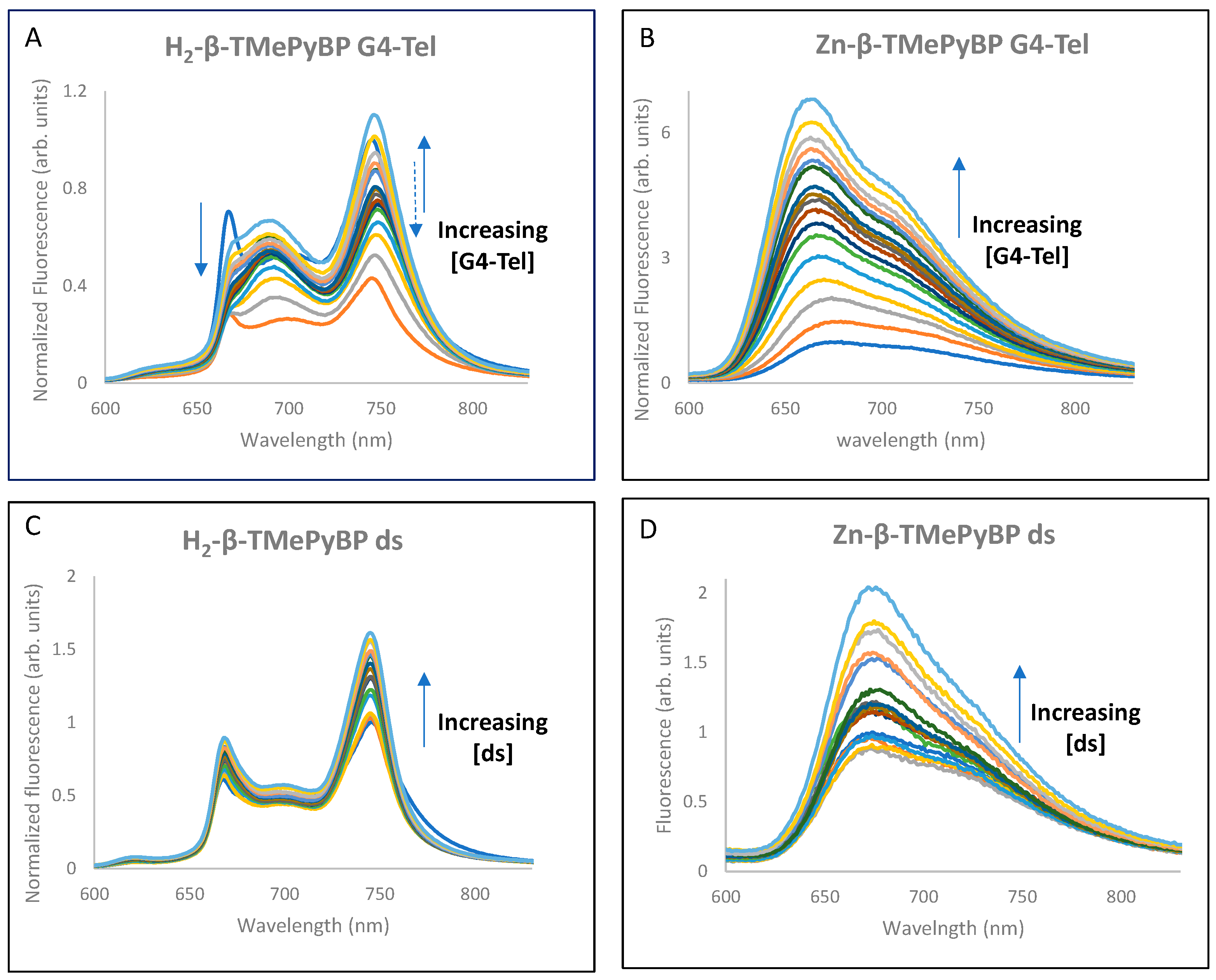
2.2.2. Fluorescence Experiments
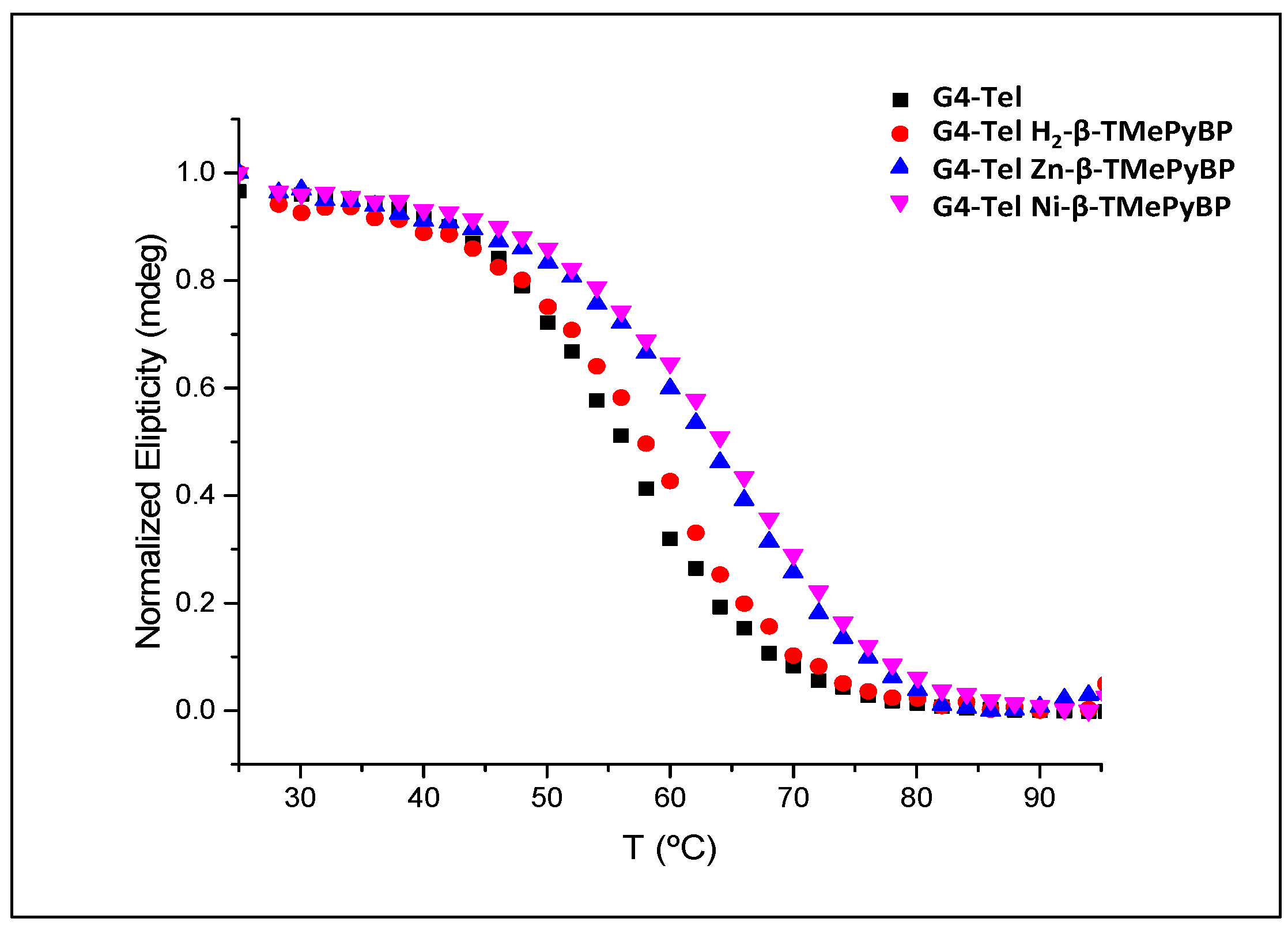
2.2.3. Circular Dichroism (CD)
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Remarks
3.2. Synthesis of Macrocyclic Ligands
3.2.1. Synthesis of Ni(II) Complex Ni-β-TPyBP and Its Corresponding Free-Base H2-β-TPyBP
3.2.2. Synthesis of Free-Base Derivative H2-β-TPyBP
3.2.3. N-Methylation of Ni-β-TMePyBP and H2-β-TMePyBP
3.2.4. Synthesis of Zn(II) Complex Zn-β-TMePyBP
3.3. Preparation of DNA Structures (Double Chain and G-Quadruplexes)
3.4. Spectroscopic Methods
3.4.1. UV-Vis Spectroscopy
3.4.2. Fluorescence Studies
3.4.3. Circular Dichroism
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Shay, J.W.; Zou, Y.; Hiyama, E.; Wright, W.E. Telomerase and cancer. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2001, 10, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cech, T.R. Beginning to Understand the End of the Chromosome. Cell 2004, 116, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrank, Z.; Khan, N.; Osude, C.; Singh, S.; Miller, R.; Merrick, C.; Mabel, A.; Kuckovic, A.; Puri, N. Oligonucleotides Targeting Telomeres and Telomerase in Cancer. Molecules 2018, 23, 2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y. Functional and mechanistic analysis of telomerase: An antitumor drug target. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 163, 24–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandakumar, J.; Cech, T.R. Finding the end: Recruitment of telomerase to telomeres. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2013, 14, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, N.W.; Piatyszek, M.A.; Prowse, K.R.; Harley, C.B.; West, M.D.; Ho, P.L.C.; Coviello, G.M.; Wright, W.E.; Weinrich, S.L.; Shay, J.W. Specific Association of Human Telomerase Activity with Immortal Cells and Cancer. Science 1994, 266, 2011–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mergny, J.L.; Mailliet, P.; Lavelle, F.; Riou, J.F.; Laoui, A.; Hélène, C. The development of telomerase inhibitors: The G-quartet approach. Anticancer Drug Des. 1999, 14, 327–339. [Google Scholar]
- Oganesian, L.; Bryan, T.M. Physiological relevance of telomeric G-quadruplex formation: A potential drug target. BioEssay 2007, 29, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besnard, E.; Babled, A.; Lapasset, L.; Milhavet, O.; Parrinello, H.; Dantec, C.; Marin, J.-M.; Lemaitre, J.-M. Unraveling cell type–specific and reprogrammable human replication origin signatures associated with G-quadruplex consensus motifs. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2012, 19, 837–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lexa, M.; Steflova, P.; Martinek, T.; Vorlickova, M.; Vyskot, B.; Kejnovsky, E. Guanine quadruplexes are formed by specific regions of human transposable elements. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, P.; Yadav, V.K.; Das, S.K.; Chowdhury, S. Genome-Wide Analyses of Recombination Prone Regions Predict Role of DNA Structural Motif in Recombination. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e4399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varshney, D.; Spiegel, J.; Zyner, K.; Tannahill, D.; Balasubramanian, S. The regulation and functions of DNA and RNA G-quadruplexes. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 459–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jara-Espejo, M.; Line, S.R. DNA G-quadruplex stability, position and chromatin accessibility are associated with CpG island methylation. FEBS J. 2020, 287, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahler, A.M.; Williamson, J.R.; Cech, T.R.; Prescott, D.M. Inhibition of telomerase by G-quartet DNA structures. Nature 1991, 350, 718–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, L.H.; Wheelhouse, R.T.; Sun, D.; Kerwin, S.M.; Salazar, M.; Fedoroff, O.Y.; Han, F.X.; Han, H.; Izbicka, E.; Von Hoff, D.D. G-quadruplexes as targets for drug design. Pharmacol. Ther. 2000, 85, 141–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Cian, A.; Lacroix, L.; Douarre, C.; Temime-Smaali, N.; Trentesaux, C.; Riou, J.-F.; Mergny, J.-L. Targeting telomeres and telomerase. Biochimie 2008, 90, 131–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moye, A.L.; Porter, K.C.; Cohen, S.B.; Phan, T.; Zyner, K.G.; Sasaki, N.; Lovrecz, G.O.; Beck, J.L.; Bryan, T.M. Telomeric G-quadruplexes are a substrate and site of localization for human telomerase. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, C.I.V.; Monteiro, A.R.; Moura, N.M.M.; Faustino, M.A.F.; Trindade, T.; Neves, M.G.P.M.S. The interactions of h2tmpyp, analogues and its metal complexes with dna g-quadruplexes—An overview. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1404–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, J.Q.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, K.W.; Chen, C.Y.; Hao, Y.H.; Tan, Z. G-quadruplex formation at the 3′ end of telomere DNA inhibits its extension by telomerase, polymerase and unwinding by helicase. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 6229–6237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidzinska, J.; Cimino-Reale, G.; Zaffaroni, N.; Folini, M. G-quadruplex structures in the human genome as novel therapeutic targets. Molecules 2013, 18, 12368–12395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artese, A.; Costa, G.; Ortuso, F.; Parrotta, L.; Alcaro, S. Identification of new natural DNA G-quadruplex binders selected by a structure-based virtual screening approach. Molecules 2013, 18, 12051–12070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.; Fujii, S.; Sato, S.; Okauchi, T.; Takenaka, S. A Selective G-Quadruplex DNA-Stabilizing Ligand Based on a Cyclic Naphthalene Diimide Derivative. Molecules 2015, 20, 10963–10979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, C.I.V.; Almodôvar, V.A.S.; Candeias, N.R.; Santos, T.; Cruz, C.; Neves, M.G.P.M.S.; Tomé, A.C. Diketopyrrolo[3,4-c]pyrrole derivative as a promising ligand for the stabilization of G-quadruplex DNA structures. Bioorganic Chem. 2022, 122, 105703–105719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, S.; Bugaut, A.; Huppert, J.L.; Balasubramanian, S. An RNA G-quadruplex in the 5′ UTR of the NRAS proto-oncogene modulates translation. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2007, 3, 218–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqui-Jain, A.; Grand, C.L.; Bearss, D.J.; Hurley, L.H. Direct evidence for a G-quadruplex in a promoter region and its targeting with a small molecule to repress c-MYC transcription. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 11593–11598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, W.; Saito, T.; Yokoyama, T.; Ferri, S.; Ikebukuro, K. Aptamer Selection Based on G4-Forming Promoter Region. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e65497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Kota, S.; Chaudhary, R.; Misra, H.S. Guanine quadruplexes and their roles in molecular processes. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2021, 56, 482–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murat, P.; Singh, Y.; Defrancq, E. Methods for investigating G-quadruplex DNA/ligand interactions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 5293–5307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, C.I.V.; M. Graça Santana-Marques, M. Electrospray mass spectrometry for the study of the non-covalent interactions of porphyrins and duplex desoxyribonucleotides. J. Porphyr. Phthalocyanines 2009, 13, 518–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaumot, J.; Gargallo, R. Experimental Methods for Studying the Interactions between G-Quadruplex Structures and Ligands. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2012, 18, 1900–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagano, B.; Cosconati, S.; Gabelica, V.; Petraccone, L.; De Tito, S.; Marinelli, L.; La Pietra, V.; Saverio di Leva, F.; Lauri, I.; Trotta, R.; et al. State-of-the-Art Methodologies for the Discovery and Characterization of DNA G-Quadruplex Binders. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2012, 18, 1880–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchand, A.; Strzelecka, D.; Gabelica, V. Selective and Cooperative Ligand Binding to Antiparallel Human Telomeric DNA G-Quadruplexes. Chem. A Eur. J. 2016, 22, 9551–9555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecours, M.J.; Marchand, A.; Anwar, A.; Guetta, C.; Hopkins, W.S.; Gabelica, V. What stoichiometries determined by mass spectrometry reveal about the ligand binding mode to G-quadruplex nucleic acids. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2017, 1861, 1353–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, C.I.V.; Tomé, J.P.C.; Santana-Marques, M.G. Charge and substituent effects on the stability of porphyrin/G-quadruplex adducts. J. Mass Spectrom. 2012, 47, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casagrande, V.; Salvati, E.; Alvino, A.; Bianco, A.; Ciammaichella, A.; Angelo, C.D.; Ginnari-satriani, L.; Serrilli, A.M.; Iachettini, S.; Leonetti, C.; et al. N-Cyclic Bay-Substituted Perylene G-Quadruplex Ligands Have Selective Antiproliferative Effects on Cancer Cells and Induce Telomere Damage. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 1140–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, J.; Pereira, E.; Marquevielle, J.; Campello, M.P.C.; Mergny, J.L.; Paulo, A.; Salgado, G.F.; Queiroz, J.A.; Cruz, C. Fluorescent light-up acridine orange derivatives bind and stabilize KRAS-22RT G-quadruplex. Biochimie 2018, 144, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, T.M.; Lu, Y.J.; Tan, J.H.; Huang, Z.S.; Wong, K.Y.; Gu, L.Q. G-quadruplexes: Targets in anticancer drug design. ChemMedChem 2008, 3, 690–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavaluzzi, M.J.; Borer, P.N. Revised UV extinction coefficients for nucleoside-5′-monophosphates and unpaired DNA and RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawauchi, K.; Sugimoto, W.; Yasui, T.; Murata, K.; Itoh, K.; Takagi, K.; Tsuruoka, T.; Akamatsu, K.; Tateishi-Karimata, H.; Sugimoto, N.; et al. An anionic phthalocyanine decreases NRAS expression by breaking down its RNA G-quadruplex. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2271–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.; Trajkovski, M.; Teulade-Fichou, M.; Gabelica, V.; Plavec, J. Phen-DC 3 Induces Refolding of Human Telomeric DNA into a Chair-Type Antiparallel G-Quadruplex through Ligand Intercalation. Angew. Chemie Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202207384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.-Y.; Wang, X.-N.; Cheng, S.-Q.; Su, X.-X.; Ou, T.-M. Developing Novel G-Quadruplex Ligands: From Interaction with Nucleic Acids to Interfering with Nucleic Acid–Protein Interaction. Molecules 2019, 24, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupont, J.I.; Henderson, K.L.; Metz, A.; Le, V.H.; Emerson, J.P.; Lewis, E.A. Calorimetric and spectroscopic investigations of the binding of metallated porphyrins to G-quadruplex DNA. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2016, 1860, 902–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izbicka, E.; Wheelhouse, R.T.; Raymond, E.; Davidson, K.K.; Lawrence, R.A.; Sun, D.; Windle, B.E.; Hurley, L.H.; Von Hoff, D.D. Effects of cationic porphyrins as G-quadruplex interactive agents in human tumor cells. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shi, D.F.; Wheelhouse, R.T.; Sun, D.; Hurley, L.H. Quadruplex-interactive agents as telomerase inhibitors: Synthesis of porphyrins and structure-activity relationship for the inhibition of telomerase. J. Med. Chem. 2001, 44, 4509–4523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boschi, E.; Davis, S.; Taylor, S.; Butterworth, A.; Chirayath, L.A.; Purohit, V.; Siegel, L.K.; Buenaventura, J.; Sheriff, A.H.; Jin, R.; et al. Interaction of a cationic porphyrin and its metal derivatives with G-quadruplex DNA. J. Phys. Chem. B 2016, 120, 12807–12819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romera, C.; Bombarde, O.; Bonnet, R.; Gomez, D.; Dumy, P.; Calsou, P.; Gwan, J.F.; Lin, J.H.; Defrancq, E.; Pratviel, G. Improvement of porphyrins for G-quadruplex DNA targeting. Biochimie 2011, 93, 1310–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y.-C.; Kong, D.-M.; Guo, D.-S. Tetraphenylethene Derivatives with Different Numbers of Positively Charged Side Arms Have Different Multimeric G-Quadruplex Recognition Specificity. Chem. A Eur. J. 2015, 21, 13253–13260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haq, I.; Trent, J.O.; Chowdhry, B.Z.; Jenkins, T.C. Intercalative G-tetraplex stabilization of telomeric DNA by a cationic porphyrin. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 1768–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.N.; Wu, B.; Kong, D.M. Specific recognition and stabilization of monomeric and multimeric G-quadruplexes by cationic porphyrin TMPipEOPP under molecular crowding conditions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 4324–4335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menilli, L.; Monteiro, A.R.; Lazzarotto, S.; Morais, F.M.P.; Gomes, A.T.P.C.; Moura, N.M.M.; Fateixa, S.; Faustino, M.A.F.; Neves, M.G.P.M.S.; Trindade, T.; et al. Graphene oxide and graphene quantum dots as delivery systems of cationic porphyrins: Photo-antiproliferative activity evaluation towards t24 human bladder cancer cells. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, J.Q.; Chen, S.B.; Zan, L.P.; Ou, T.M.; Tan, J.H.; Luyt, L.G.; Huang, Z.S. Identification of a selective G-quadruplex DNA binder using a multistep virtual screening approach. Chem. Comm. 2015, 51, 198–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowland, G.B.; Barnett, K.; Dupont, J.I.; Akurathi, G.; Le, V.H.; Lewis, E.A. The effect of pyridyl substituents on the thermodynamics of porphyrin binding to G-quadruplex DNA. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 7515–7522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschin, M.; Lombardo, C.M.; Pascucci, E.; D’Ambrosio, D.; Micheli, E.; Bianco, A.; Ortaggi, G.; Savino, M. The number and distances of positive charges of polyamine side chains in a series of perylene diimides significantly influence their ability to induce G-quadruplex structures and inhibit human telomerase. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2008, 16, 2292–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.B.; Shi, Q.X.; Peng, D.; Huang, S.Y.; Ou, T.M.; Li, D.; Tan, J.H.; Gu, L.Q.; Huang, Z.S. The role of positive charges on G-quadruplex binding small molecules: Learning from bisaryldiketene derivatives. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2013, 1830, 5006–5013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, E.M.P.; Ramos, C.I.V.; Pereira, P.M.R.; Giuntini, F.; Faustino, M.A.F.; Tomé, J.P.C.; Tomé, A.C.; Silva, A.M.S.; Santana-Marques, M.G.; Neves, M.G.P.M.S.; et al. Cationic β-vinyl substituted meso-tetraphenylporphyrins: Synthesis and non-covalent interactions with a short poly(dGdC) duplex. J. Porphyr. Phthalocyanines 2012, 16, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, C.I.V.; Pereira, P.M.R.; Santana-Marques, M.G.; De Paula, R.; Simões, M.M.Q.; Neves, M.G.P.M.S.; Cavaleiro, J.A.S. Imidazole and imidazolium porphyrins: Gas-phase chemistry of multicharged ions. J. Mass Spectrom. 2014, 49, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, C.I.V.; Moura, N.M.M.; Santos, S.M.F.; Faustino, M.A.F.; Tomé, J.P.C.; Amado, F.M.L.; Neves, M.G.P.M.S. An insight into the gas-phase fragmentations of potential molecular sensors with porphyrin-chalcone structures. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2015, 392, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, C.I.V.; Santana-Marques, M.G.; Ferrer-Correia, A.J.; Barata, J.F.B.; Tomé, A.C.; Neves, M.G.P.M.S.; Cavaleiro, J.A.S.; Abreu, P.E.; Pereira, M.M.; Pais, A.A.C.C. Differentiation of aminomethyl corrole isomers by mass spectrometry. J. Mass Spectrom. 2012, 47, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iglesias, B.A.; Barata, J.F.B.; Ramos, C.I.V.; Santana-Marques, M.G.; Neves, M.G.P.M.S.; Cavaleiro, J.A.S. Adventures in corrole features by electrospray ionization mass spectrometry studies. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 16824–16838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, C.I.V.; Santana Marques, M.G.; Correia, A.J.F.; Serra, V.V.; Tomé, J.P.C.; Tomé, A.C.; Neves, M.G.P.M.S.; Cavaleiro, J.A.S. Reduction of Cationic Free-Base meso-Tris-N-Methylpyridinium-4-yl Porphyrins in Positive Mode Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2007, 18, 762–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ramos, C.I.; Figueira, F.; Polêto, M.D.; Amado, F.M.; Verli, H.; Tomé, J.P.; Neves, M.G.P.M.S. ESI-MS/MS of expanded porphyrins: A look into their structure and aromaticity. J. Mass Spectrom. 2016, 51, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshpande, R.; Jiang, L.; Schmidt, G.; Rakovan, J.; Wang, X.; Wheeler, K.; Wang, H. A Concise Approach to the Synthesis of opp-Dibenzoporphyrins through the Heck Reaction. Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 4251–4253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.K.; Bhyrappa, P.; Varghese, B. An improved protocol for the synthesis of antipodal β-tetrabromo-tetraphenylporphyrin and the crystal structure of its Zn(II) complex. Tetrahedron Lett. 2003, 44, 4849–4851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchler, J.W. Porphyrins and Metalloporphyrins. In Porphyrins and Metalloporphyrins; Smith, K.M., Ed.; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1975; pp. 157–231. [Google Scholar]
- Gouterman, M. Spectra of porphyrins. J. Mol. Spectrosc. 1961, 6, 138–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, T.; Choe, Y.K.; Nakano, H.; Hirao, K. Theoretical study of the Q and B bands of free-base, magnesium, and zinc porphyrins, and their derivatives. J. Phys. Chem. A 1999, 103, 1894–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maximiano, R.V.; Piovesan, E.; Zílio, S.C.; Machado, A.E.H.; De Paula, R.; Cavaleiro, J.A.S.; Borissevitch, I.E.; Ito, A.S.; Gonalves, P.J.; Barbosa Neto, N.M. Excited-state absorption investigation of a cationic porphyrin derivative. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2010, 214, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Patel, D.J. Solution structure of the human telomeric repeat d[AG3(T2AG3)3] G-tetraplex. Structure 1993, 1, 263–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Jia, G.; Yuan, J.; Feng, Z.; Li, C. A Spectroscopic Study on the Interactions of Porphyrin with G-Quadruplex DNAs. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 6681–6691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Ji, F.; Liu, R.; Lin, J.; Xu, Q.; Gao, C. Interaction mechanism of 2-aminobenzothiazole with herring sperm DNA. J. Lumin. 2012, 132, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, S.; Sengupta, P.K.; Bhowmik, S. Exploring the preferential interaction of quercetin with VEGF promoter G-quadruplex DNA and construction of a pH-dependent DNA-based logic gate. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 37230–37240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Wang, X.-L.; Shi, J.; Wang, S.-F.; Yin, Y.; Yang, Y.-S.; Zhang, W.-M.; Zhu, H.-L. Synthesis, molecular modeling and biological evaluation of N-benzylidene-2-((5-(pyridin-4-yl)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)thio)acetohydrazide derivatives as potential anticancer agents. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2014, 22, 468–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, C.; Almeida, S.; Lourenço, L.; Pereira, P.; Fernandes, R.; Faustino, M.A.F.; Tomé, J.; Carvalho, J.; Cruz, C.; Neves, M.G.P.M.S. Multicharged Phthalocyanines as Selective Ligands for G-Quadruplex DNA Structures. Molecules 2019, 24, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monchaud, D.; Granzhan, A.; Saettel, N.; Guédin, A.; Mergny, J.L.; Teulade-Fichou, M.P. “One ring to bind them all”—Part I: The efficiency of the macrocyclic scaffold for G-quadruplex DNA recognition. J. Nucleic Acids 2010, 2010, 525862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzeer, J.; Vummidi, B.R.; Roth, P.J.â.C.; Luedtke, N.W. Guanidinium-Modified Phthalocyanines as High-Affinity G-Quadruplex Fluorescent Probes and Transcriptional Regulators. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 9362–9365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Hurley, L.H. G-quadruplex DNA: A potential target for anti-cancer drug design. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2000, 21, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Largy, E.; Hamon, F.; Teulade-Fichou, M.P. Development of a high-throughput G4-FID assay for screening and evaluation of small molecules binding quadruplex nucleic acid structures. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 400, 3419–3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, J.; Queiroz, J.A.; Cruz, C. Circular dichroism of G-Quadruplex: A laboratory experiment for the study of topology and ligand binding. J. Chem. Educ. 2017, 94, 1547–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, A.D.; Longo, F.R.; Shergalis, W. Mechanistic Investigations of Porphyrin Syntheses. I. Preliminary Studies on ms-Tetraphenylporphin. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1964, 86, 3145–3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonsalves, A.M.d.A.R.; Varejão, J.M.T.B.; Pereira, M.M. Some new aspects related to the synthesis of meso-substituted porphyrins. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 1991, 28, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armarego, W.L.F.; Chai, C. Purification of Laboratory Chemicals, 7th ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Eddahmi, M.; Moura, N.M.M.; Ramos, C.I.V.; Bouissane, L.; Faustino, M.A.F.; Cavaleiro, J.A.S.; Mostapha Rakib, E.; Neves, M.G.P.M.S. An insight into the vicarious nucleophilic substitution reaction of 2-nitro-5,10,15,20-tetraphenylporphyrin with p-chlorophenoxyacetonitrile: Synthesis and gas-phase fragmentation studies. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 5849–5863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabharwal, N.C.; Chen, J.; Lee, J.H.; Gangemi, C.M.A.; D’Urso, A.; Yatsunyk, L.A. Interactions Between Spermine-Derivatized Tentacle Porphyrins and the Human Telomeric DNA G-Quadruplex. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, M.G.; Azzellini, G.C. Synthesis of new cationic metalloporphyrins and heterodimer formation with anionic metallophthalocyanines. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2003, 14, 914–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zsila, F.; Bikádia, Z.; Simonyia, M. Circular dichroism spectroscopic studies reveal pH dependent binding of curcumin in the minor groove of natural and synthetic nucleic acids. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2004, 2, 2902–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Oligonucleotide Sequence | Topology | Abbreviation |
|---|---|---|
| 5′-AGG GTT AGG GTTAGG GTT AGGG-3′ (human telomeric repeat) | Unimolecular G-Quadruplex | AG3(T2AG3)3 |
| long DNA strand (Calf Thymus) | Double strand DNA | ds |
| Ligand | Telomeric G4 | Calf Thymus (ds) | PBS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H2-β-TMePyBP | Red Shift (nm) | 10 | 7 | 0 |
| (%) Hypo/Hyper chromism | +23 | −39 | −19 | |
| Kb (M−1) | 6.01 ± 1.11 × 106 | 1.42 ± 0.47 × 106 | --- | |
| Zn-β-TMePyBP | Red Shift (nm) | 11 | 6 | 3 |
| (%) Hypo/Hyper chromism | −21 | −30 | −64 | |
| Kb (M−1) | 7.05 ± 1.31 × 106 | 3.17 ± 0.31 × 106 | --- | |
| Ni-β-TMePyBP | Red Shift (nm) | 7 | 7 | 7 |
| (%) Hypo/Hyper chromism | −15 | −10 | −65 | |
| Kb (M−1) | 3.71 ± 1.28 × 106 | 3.46 ± 0.89 × 106 | --- |
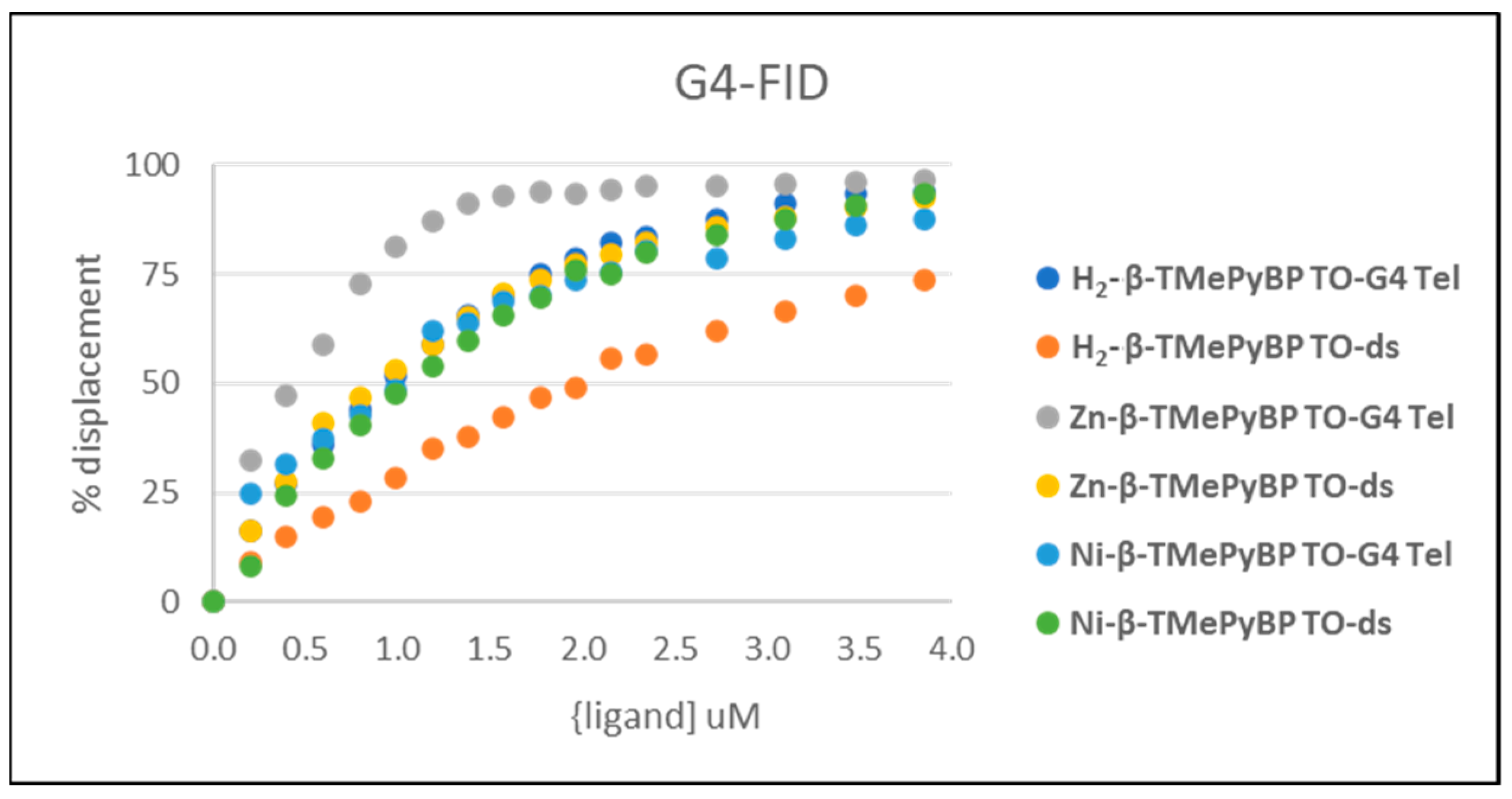
| DC50 (μM) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| TO-ds | TO-G4 | ||
| H2-β-TMePyBP | 1.99 ± 0.26 | 0.90 ± 0.04 | 2.01 |
| Zn-β-TMePyBP | 0.93 ± 0.18 | 0.42 ± 0.08 | 2.21 |
| Ni-β-TMePyBP | 1.04 ± 0.12 | 1.02 ± 0.06 | 1 |
| Tm (°C) | ΔTm (°C) | |
|---|---|---|
| G4-Tel | 56.1 ± 1.4 | --- |
| G4-Tel + H2-β-TMePyBP | 58.4 ± 1.8 | 2.3 |
| G4-Tel + Zn-β-TMePyBP | 63.5 ± 1.3 | 7.4 |
| G4-Tel + Ni-β-TMePyBP | 64.6 ± 1.6 | 8.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moura, N.M.M.; Cavaleiro, J.A.S.; Neves, M.G.P.M.S.; Ramos, C.I.V. opp-Dibenzoporphyrin Pyridinium Derivatives as Potential G-Quadruplex DNA Ligands. Molecules 2023, 28, 6318. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28176318
Moura NMM, Cavaleiro JAS, Neves MGPMS, Ramos CIV. opp-Dibenzoporphyrin Pyridinium Derivatives as Potential G-Quadruplex DNA Ligands. Molecules. 2023; 28(17):6318. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28176318
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoura, Nuno M. M., José A. S. Cavaleiro, Maria Graça P. M. S. Neves, and Catarina I. V. Ramos. 2023. "opp-Dibenzoporphyrin Pyridinium Derivatives as Potential G-Quadruplex DNA Ligands" Molecules 28, no. 17: 6318. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28176318
APA StyleMoura, N. M. M., Cavaleiro, J. A. S., Neves, M. G. P. M. S., & Ramos, C. I. V. (2023). opp-Dibenzoporphyrin Pyridinium Derivatives as Potential G-Quadruplex DNA Ligands. Molecules, 28(17), 6318. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28176318










