Comparison of Bioactive Compounds and Antioxidant Activities in Differentially Pigmented Cerasus humilis Fruits
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
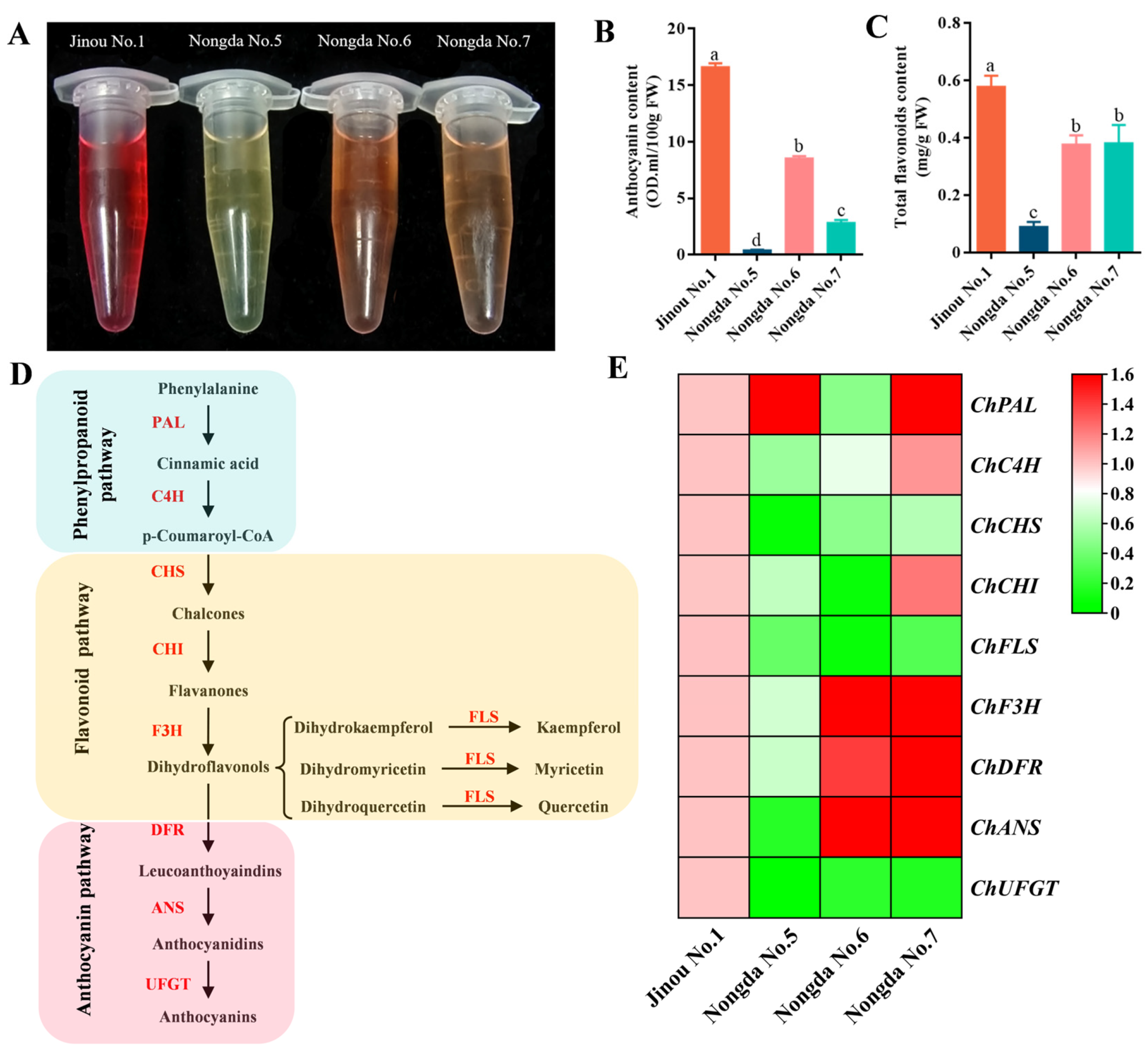
2.1. Fruit Appearance Quality Comparision Results of the Four C. humilis Varieties
2.2. Determination Results of Bioactive Substance Contents in Fruits of Four C. humilis Varieties
2.3. Comparison of Antioxidant Capacities in Fruits of Four Different C. humilis Varieties
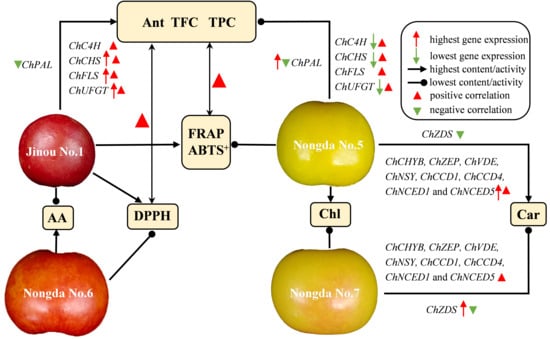
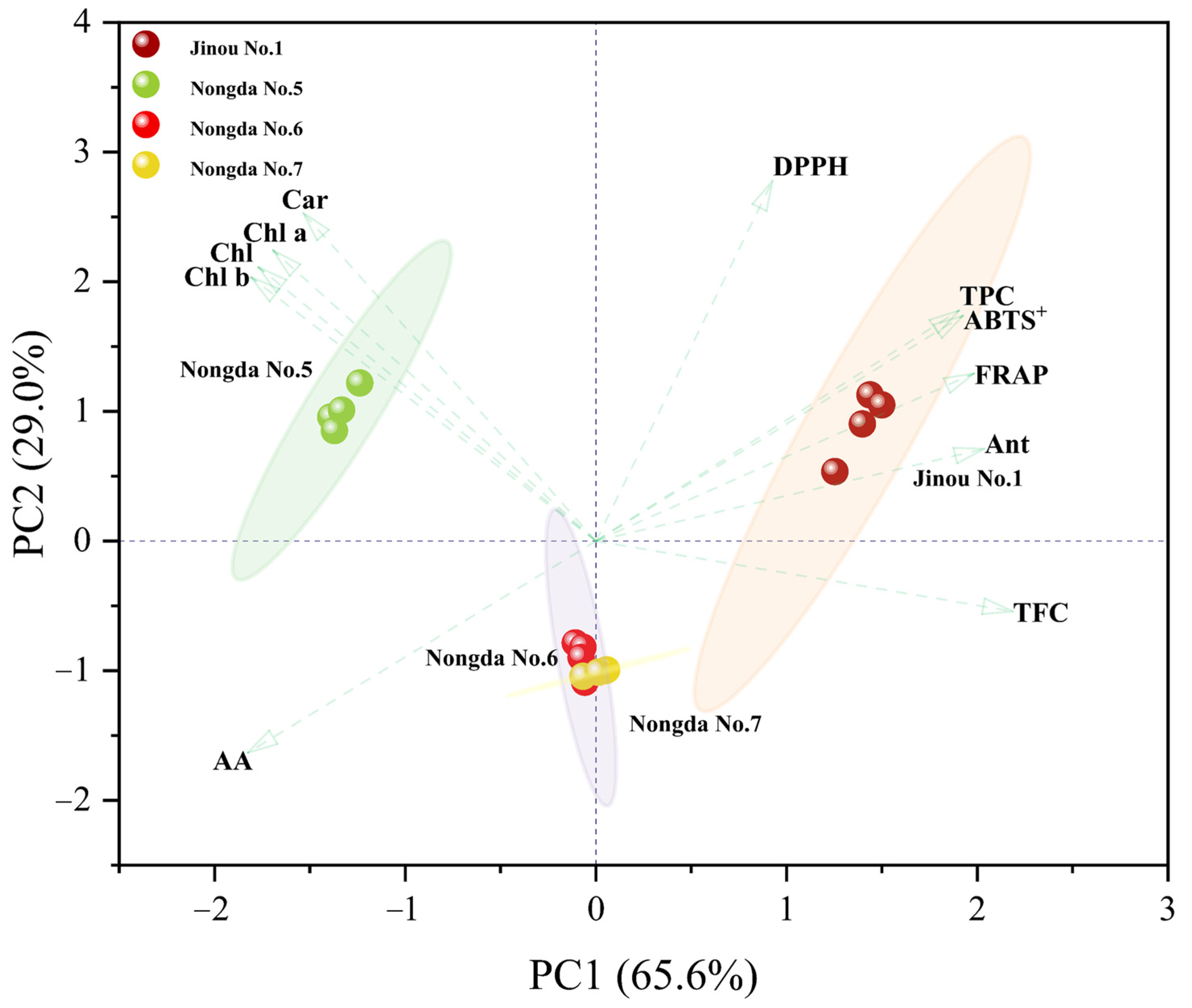
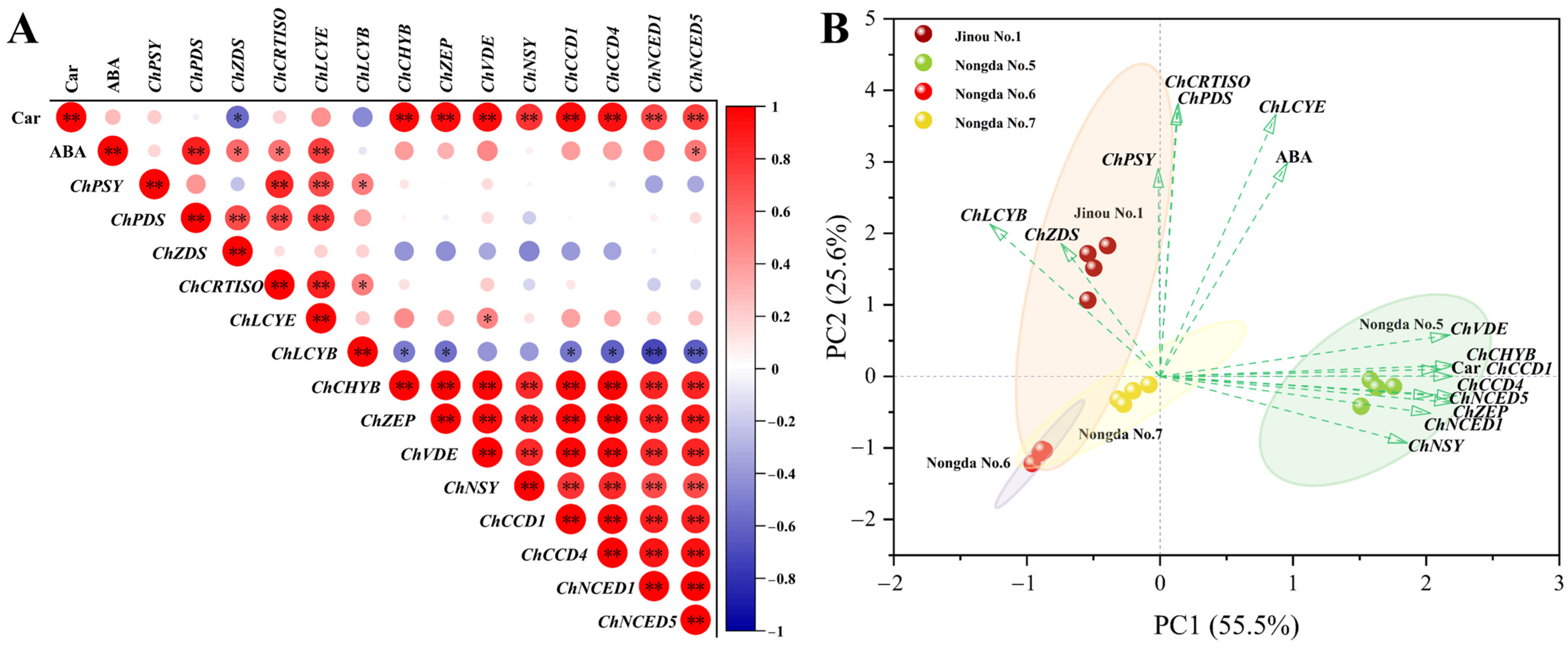
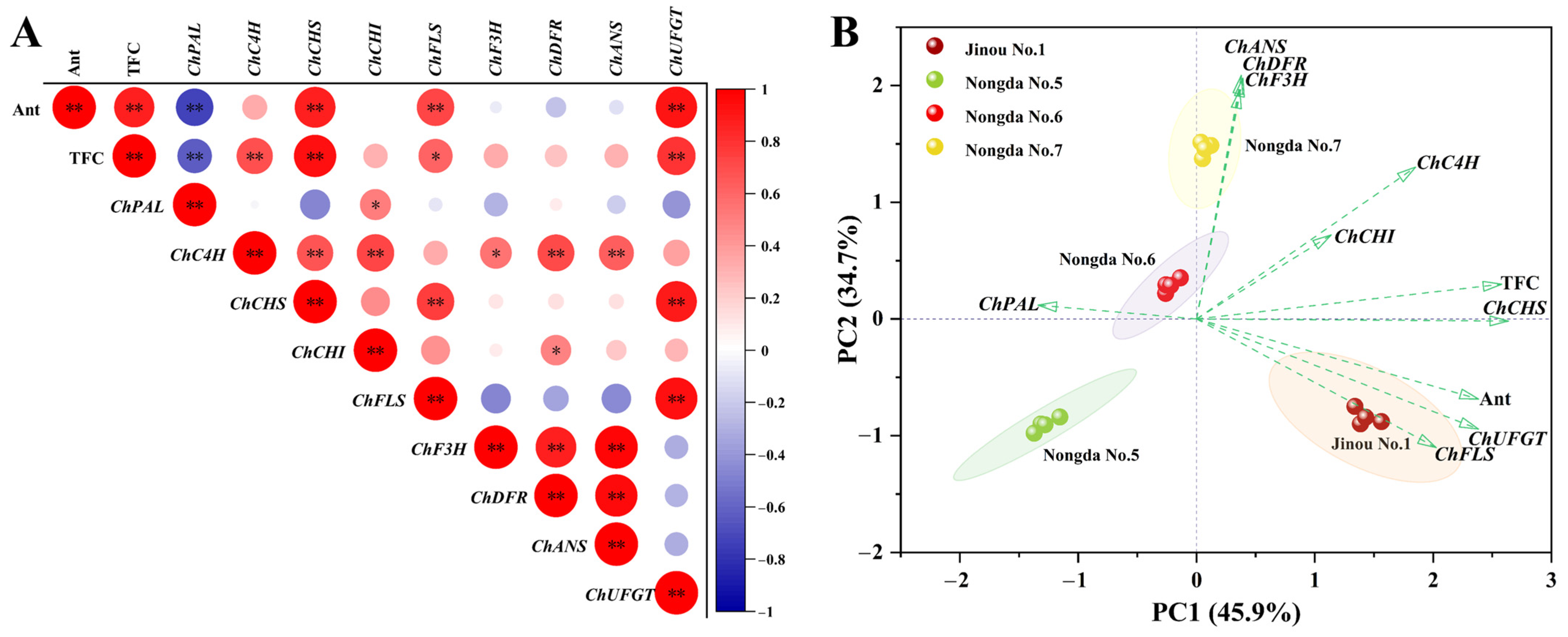
2.4. Correlation and Principal Component Analysis (PCA) of Bioactive Substance Contents and Antioxidant Capacities
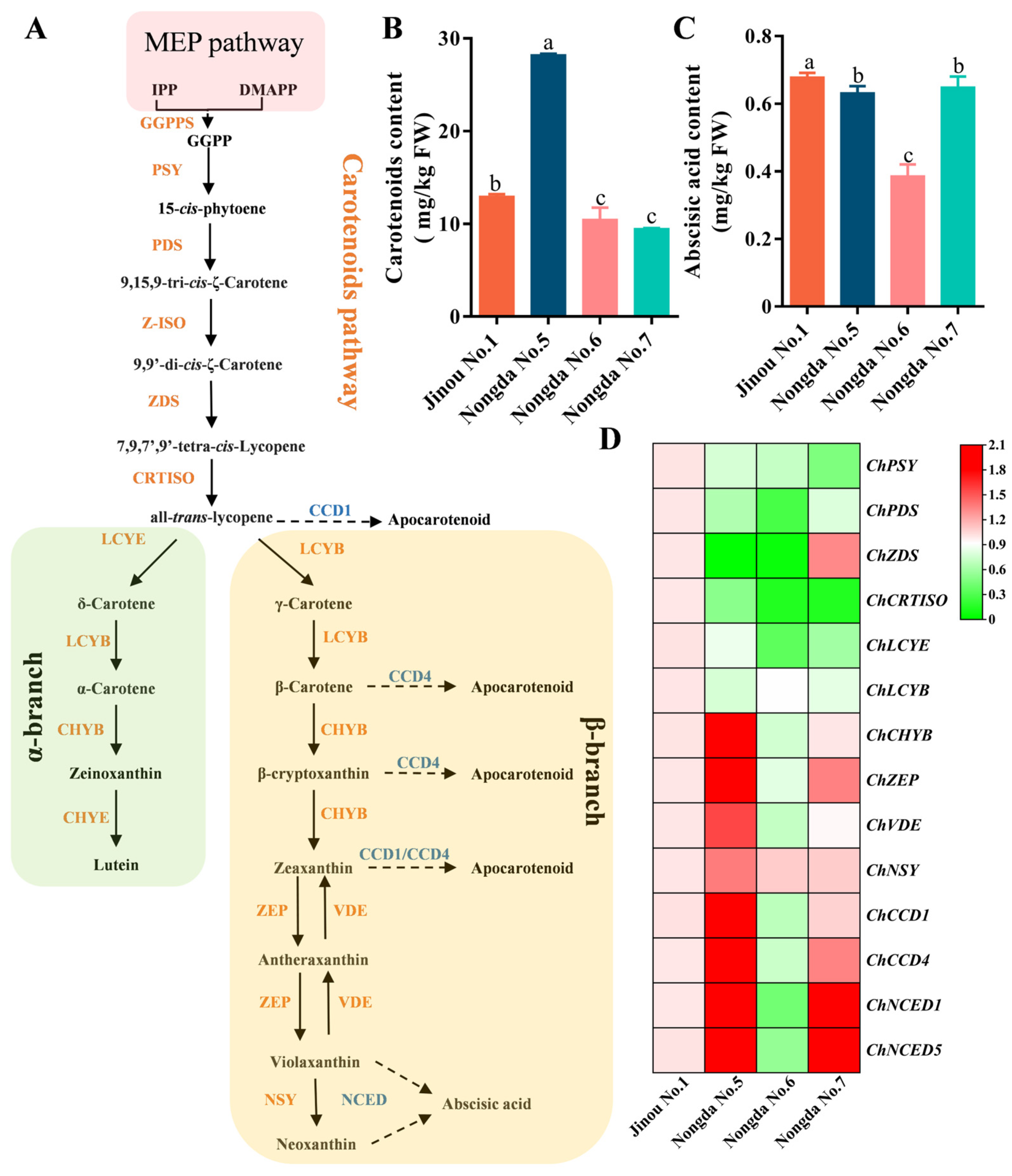
2.5. Expression Analysis of Carotenoid Biosynthesis-Related Genes in Fruits of Four C. humilis Varieties
2.6. Expression Analysis of Flavonoid Metabolism Related Genes in Fruits of Four C. humilis Varieties
3. Discussion
3.1. The Bioactive Substance Contents and Antioxidant Capacities of Differently Pigmented C. humilis Fruits Vary Greatly
3.2. Anthocyanin, Total Flavonoids, and Total Phenols Are the Three Main Components Affecting the Antioxidant Activity of C. humilis Fruits
3.3. The Accumulation of Carotenoids in Fruits of Different C. humilis Varieties Are Closely Related to the Expression of Carotenoid Metabolism-Related Genes
3.4. The Expression of Flavonoid Biosynthesis-Related Genes Such as ChCHS, ChUFGT, and ChFLS Is Very Significantly or Significantly Positively Correlated with Flavonoid Content in C. humilis Fruits
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials
4.2. Determination of Carotenoid, Chlorophyll, Anthocyanin, and Ascorbic Acid Contents
4.3. Determination of Total Flavonoids, Total Phenols, and Antioxidant Capacity
4.4. Determination of Abscisic Acid (ABA) Content
4.5. Gene Expression Analysis
4.6. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Neupane, P.; Lamichhane, J. Estimation of total phenolic content, total flavonoid content and antioxidant capacities of five medicinal plants from Nepal. Vegetos 2020, 33, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popova, M.P.; Bankova, V.S.; Bogdanov, S.; Tsvetkova, I.; Naydenski, C.; Marcazzan, G.L.; Sabatini, A.-G. Chemical characteristics of poplar type propolis of different geographic origin. Apidologie 2007, 38, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinova, D.; Ribarova, F. HPLC determination of carotenoids in Bulgarian berries. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2007, 20, 370–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, W.; Iqra; Afzal, F.; Rahim, M.A.; Abdul Rehman, A.; Faiz ul Rasul, H.; Arshad, M.S.; Ambreen, S.; Zubair, M.; Safdar, S.; et al. Industrial applications of kale (Brassica oleracea var. sabellica) as a functional ingredient: A review. Int. J. Food Prop. 2023, 26, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajalan, I.; Mohammadi, M.; Alaei, M.; Pirbalouti, A.G. Total phenolic and flavonoid contents and antioxidant activity of extracts from different populations of lavandin. Ind. Crops Prod. 2016, 87, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, Z.; Zhao, H.; Wang, X.; Pang, J.; Li, Q.; Yang, Y.; Ling, W. Anthocyanin supplementation improves anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory capacity in a dose-response manner in subjects with dyslipidemia. Redox Biol. 2020, 32, 101474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggersdorfer, M.; Wyss, A. Carotenoids in human nutrition and health. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2018, 652, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiptiyah, S.Y.; Harmayani, E.; Santoso, U.; Supriyadi. The effect of blanching and extraction method on total phenolic content, total flavonoid content and antioxidant activity of Kencur (Kaempferia galanga. L) extract. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 709, 012025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattioli, R.; Francioso, A.; Mosca, L.; Silva, P. Anthocyanins: A comprehensive review of their chemical properties and health effects on cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases. Molecules 2020, 25, 3809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Sun, L.N.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Song, X.S. Drought tolerance is correlated with the activity of antioxidant enzymes in Cerasus humilis seedlings. Biomed. Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 9851095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Chang, X.; Yu, J.; Xu, W. Cerasus humilis cherry polyphenol reduces high-fat diet-induced obesity in C57BL/6 mice by mitigating fat deposition, inflammation, and oxidation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 4424–4436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Yuan, R.; Feng, C.; Li, S.; Wang, L. Analysis of polyphenols composition and antioxidant activity assessment of Chinese dwarf cherry (Cerasus humilis (Bge.) sok.). Nat. Prod. Commun. 2019, 14, 1934578X19856509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yue, J.; Xia, W.; Li, T.T.; Huang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, X. Exploring the beneficial effects and mechanisms of Cerasus humilis (Bge.) Sok fruit for calcium supplementation and promotion. Food Biosci. 2023, 54, 102846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Li, O.; Zhang, A.; Li, L.; Hao, J.; Jin, J.; Yin, S. Genotypic diversity of phenolic compounds and antioxidant capacity of Chinese dwarf cherry (Cerasus humilis (Bge.) Sok.) in China. Sci. Hortic. 2014, 175, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Cui, Q.; Cheng, J.; Chen, J.; Zhao, Z.; Guo, R.; Dai, X.; Wei, Z.; Li, W. Probiotic-fermented Chinese dwarf cherry [Cerasus humilis (Bge.) Sok.] juice modulates the intestinal mucosal barrier and increases the abundance of Akkermansia in the gut in association with polyphenols. J. Funct. Foods 2021, 80, 104424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, B.; Guo, C.-E.; Zhang, Y.; Han, C.; Cao, T.; Huang, H.; Geng, Z.; Li, W. Preventive effect of Chinese dwarf cherry [Cerasus humilis (Bge.) Sok.] fermentation juice on dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis rats through the regulation of IgA and the intestinal immune barrier. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 5766–5781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Han, C.; Cheng, J.; Wang, Z.; Liu, L.; Huang, H.; Liang, Q.; Liu, R.; Ran, B.; Li, W. Fermented Cerasus humilis fruits protect against high-fat diet induced hyperlipidemia which is associated with alteration of gut microbiota. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2022, 103, 2554–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petriccione, M.; Mastrobuoni, F.; Pasquariello, M.S.; Zampella, L.; Nobis, E.; Capriolo, G.; Scortichini, M. Effect of chitosan coating on the postharvest quality and antioxidant enzyme system response of strawberry fruit during cold storage. Foods 2015, 4, 501–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernukha, I.; Kupaeva, N.; Kotenkova, E.; Khvostov, D. Differences in antioxidant potential of Allium cepa husk of red, yellow, and white varieties. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.H.; Kim, M.H.; Han, Y.S. Physicochemical properties and antioxidant activity of colored peppers (Capsicum annuum L.). Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2023, 32, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, W.; Zhang, L.; Liu, S.; Zhao, G. The genes of CYP, ZEP, and CCD1/4 play an important role in controlling carotenoid and aroma volatile apocarotenoid accumulation of apricot fruit. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 607715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Y.; Han, M.; Wang, R.H.; Gao, M.G. Comparative transcriptome analysis identifies genes associated with chlorophyll levels and reveals photosynthesis in green flesh of radish taproot. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0252031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kou, X.; Han, L.; Li, X.; Xue, Z.; Zhou, F. Antioxidant and antitumor effects and immunomodulatory activities of crude and purified polyphenol extract from blueberries. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 2016, 10, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.R.; Krych, L.; Ahmad, H.F.; Nejsum, P.; Skovgaard, K.; Nielsen, D.S.; Thamsborg, S.M. A polyphenol-enriched diet and Ascaris suum infection modulate mucosal immune responses and gut microbiota composition in pigs. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Jiang, H.; Fang, J. Regulation of immune function by polyphenols. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 1264074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, X.; Chen, Q.; Li, X.; Li, M.; Kan, C.; Chen, B.; Zhang, Y.; Xue, Z. Quantitative assessment of bioactive compounds and the antioxidant activity of 15 jujube cultivars. Food Chem. 2015, 173, 1037–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mditshwa, A.; Magwaza, L.S.; Tesfay, S.Z.; Mbili, N.C. Effect of ultraviolet irradiation on postharvest quality and composition of tomatoes: A review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 54, 3025–3035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Yang, H.; Wu, W.; Lyu, L.; Li, W. Variation in bioactive compounds and antioxidant activity of Rubus fruits at different developmental stages. Foods 2022, 11, 1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero-Gonzalez, J.; Shun Ah-Hen, K.; Lemus-Mondaca, R.; Munoz-Farina, O. Total phenolics, anthocyanin profile and antioxidant activity of maqui, Aristotelia chilensis (Mol.) Stuntz, berries extract in freeze-dried polysaccharides microcapsules. Food Chem. 2020, 313, 126115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Dong, Y.; Gao, F.; Li, J.; Stevanovic, Z.D.; Li, H.; Shi, L. Comprehensive analysis of secondary metabolites of four medicinal thyme species used in folk medicine and their antioxidant activities in vitro. Molecules 2023, 28, 2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- More, P.R.; Arya, S.S. Intensification of bio-actives extraction from pomegranate peel using pulsed ultrasound: Effect of factors, correlation, optimization and antioxidant bioactivities. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 72, 105423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Tang, G.Y.; Zhao, C.N.; Feng, X.L.; Xu, X.Y.; Cao, S.Y.; Meng, X.; Li, S.; Gan, R.Y.; Li, H.B. Comparison of Antioxidant Activities of Different Grape Varieties. Molecules 2018, 23, 2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisboa, M.P.; Canal, D.; Filgueiras, J.P.C.; Turchetto-Zolet, A.C. Molecular evolution and diversification of phytoene synthase (PSY) gene family. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2022, 45, e20210411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paine, J.A.; Shipton, C.A.; Chaggar, S.; Howells, R.M.; Kennedy, M.J.; Vernon, G.; Wright, S.Y.; Hinchliffe, E.; Adams, J.L.; Silverstone, A.L.; et al. Improving the nutritional value of golden rice through increased pro-vitamin a content. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 482–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.; Yang, R.; Yin, L.; Zhang, J.; Gao, L.; Lu, R.; Yang, Y.; Wang, P.; Mu, X.; Zhang, S.; et al. Characterization of carotenoid cleavage oxygenase genes in Cerasus humilis and functional analysis of ChCCD1. Plants 2023, 12, 2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messing, S.A.J.; Gabelli, S.B.; Echeverria, I.; Vogel, J.T.; Guan, J.C.; Tan, B.C.; Klee, H.J.; McCarty, D.R.; Amzel, L.M. Structural insights into maize viviparous14, a key enzyme in the biosynthesis of the phytohormone abscisic acid. Plant Cell 2010, 22, 2970–2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moya-Leon, M.A.; Stappung, Y.; Mattus-Araya, E.; Herrera, R. Insights into the genes involved in ABA biosynthesis and perception during development and ripening of the Chilean strawberry fruit. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; He, L.; Dong, J.; Zhao, C.; Wang, Y.; Tang, R.; Wang, W.; Ji, Z.; Cao, Q.; Xie, H.; et al. Integrated metabolic and transcriptional analysis reveals the role of carotenoid cleavage dioxygenase 4 (IbCCD4) in carotenoid accumulation in sweetpotato tuberous roots. Biotechnol. Biofuels Bioprod. 2023, 16, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Ding, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Dai, L. Genome-wide identification, characterization, and expression analysis of CHS gene family members in Chrysanthemum nankingense. Genes 2022, 13, 2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Cao, Y.T.; Ye, S.R.; Irshad, M.; Pan, T.F.; Qiu, D.L. Isolation of CHS gene from Brunfelsia acuminata flowers and its regulation in anthocyanin biosysthesis. Molecules 2016, 22, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattus-Araya, E.; Guajardo, J.; Herrera, R.; Moya-Leon, M.A. ABA speeds up the progress of color in developing F. chiloensis fruit through the activation of PAL, CHS and ANS, key genes of the phenylpropanoid/flavonoid and anthocyanin pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Li, K.; Yang, D.; Liu, N.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Gao, L.; et al. Roles of the 2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase superfamily in the flavonoid pathway: A review of the functional diversity of F3H, FNS I, FLS, and LDOX/ANS. Molecules 2021, 26, 6745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Zuo, J.; Zhang, H.; Zu, M.; Liu, S. Analysis of the different growth years accumulation of flavonoids in Dendrobium moniliforme (L.) Sw. by the integration of metabolomic and transcriptomic approaches. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 928074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medda, S.; Sanchez-Ballesta, M.T.; Romero, I.; Dessena, L.; Mulas, M. Expression of structural flavonoid biosynthesis genes in dark-blue and white myrtle berries (Myrtus communis L.). Plants 2021, 10, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, M.; Singh, Z.; Khurshid, T. Pre-harvest spray application of abscisic acid (S-ABA) regulates fruit colour development and quality in early maturing M7 Navel orange. Sci. Hortic. 2018, 229, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Yang, S.; Tang, K.; Li, G.; Gao, X.; Liu, B.; Wang, S.; Feng, X. GmCCD4 controls carotenoid content in soybeans. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 801–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, L.; Huang, G.; Li, X.; Xiao, J.; Guo, L. Effect of different LED lights on aliphatic glucosinolates metabolism and biochemical characteristics in broccoli sprouts. Food Res. Int. 2022, 154, 111015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yang, Y.; Xu, C.; Rao, J. Characterization of food structures and functionalities. Int. J. Anal. Chem. 2018, 2018, 4818253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Mu, X.; Wang, P.; Zhang, J.; Fu, B.; Du, J. Fruit quality and antioxidant potential of Prunus humilis Bunge accessions. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0244445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, G.; Ting, K.N.; Wiart, C.; Fry, J. High correlation of 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radical scavenging, ferric reducing activity potential and total phenolics content indicates redundancy in use of all three assays to screen for antioxidant activity of extracts of plants from the Malaysian rainforest. Antioxidants 2013, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
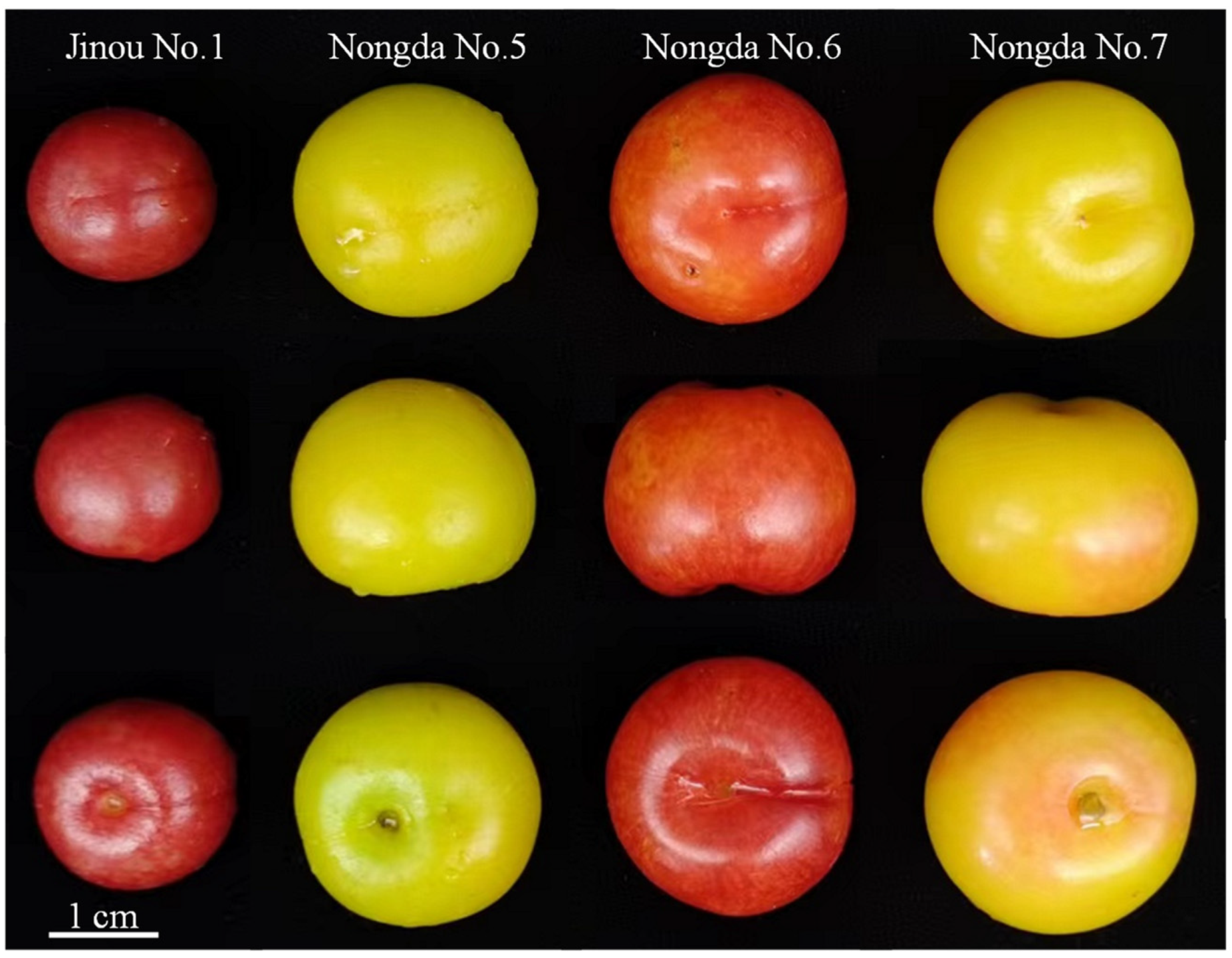

| Indexes | Jinou No.1 | Nongda No.5 | Nongda No.6 | Nongda No.7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| L* | 31.66 ± 1.78 d | 60.64 ± 1.55 a | 36.36 ± 0.54 c | 54.44 ± 0.56 b |
| a* | 27.38 ± 0.32 b | −2.22 ± 0.2 d | 28.53 ± 0.27 a | 11.4 ± 0.15 c |
| b* | 16.42 ± 0.65 d | 42.01 ± 2.22 a | 19.57 ± 1.26 c | 36.08 ± 1.72 b |
| Chlorophyll content (mg/kg FW) | 25.71 ± 0.28 b | 61.28 ± 0.40 a | 28.29 ± 0.44 ab | 23.01 ± 0.11 b |
| Chlorophyll a Content (mg/kg FW) | 10.82 ± 0.06 c | 23.03 ± 0.28 a | 11.31 ± 0.35 b | 8.90 ± 0.03 d |
| Chlorophyll b Content (mg/kg FW) | 14.89 ± 0.23 c | 38.25 ± 0.13 a | 16.98 ± 0.08 b | 14.11 ± 0.09 d |
| Carotenoids content (mg/kg FW) | 12.97 ± 0.22 b | 28.24 ± 0.10 a | 10.47 ± 1.27 c | 9.48 ± 0.05 c |
| Anthocyanin content (OD·mL/100 g FW) | 16.66 ± 0.29 a | 0.43 ± 0.10 d | 8.56 ± 0.18 b | 2.85 ± 0.23 c |
| Total flavonoids content (mg/g FW) | 0.58 ± 0.04 a | 0.09 ± 0.02 c | 0.38 ± 0.03 b | 0.38 ± 0.06 b |
| Total phenols content (mg/g FW) | 8.50 ± 0.38 a | 1.31 ± 0.21 b | 1.41 ± 0.42 b | 1.75 ± 0.77 b |
| Ascorbic acid content (mg/100 g) | 33.17 ± 2.21 c | 71.46 ± 2.10 ab | 76.10 ± 8.64 a | 63.35 ± 2.39 b |
| FRAP (mg TE/kg FW) | 2227.28 ± 277.55 a | 925.52 ± 31.64 b | 1226.52 ± 67.35 b | 1060.85 ± 96.72 b |
| ABTS+ (mg TE/kg FW) | 2358.95 ± 174.51 a | 1160.59 ± 106.11 b | 1232.54 ± 75.17 b | 1233.99 ± 5.02 b |
| DPPH (mg TE/kg FW) | 1133.83 ± 105.51 a | 1046.90 ± 64.60 ab | 950.83 ± 41.92 b | 979.34 ± 7.72 b |
| Chl | Chl a | Chl b | Car | Ant | TFC | TPC | AA | FRAP | ABTS+ | DPPH | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chl | 1.00 ** | ||||||||||
| Chl a | 1.00 ** | 1.00 ** | |||||||||
| Chl b | 1.00 ** | 1.00 ** | 1.00 ** | ||||||||
| Car | 0.98 ** | 0.99 ** | 0.98 ** | 1.00 ** | |||||||
| Ant | −0.57 * | −0.52 * | −0.60 * | −0.48 | 1.00 ** | ||||||
| TFC | −0.87 ** | −0.84 ** | −0.88 ** | −0.79 ** | 0.86 ** | 1.00 ** | |||||
| TPC | −0.37 | −0.32 | −0.39 | −0.21 | 0.87 ** | 0.76 ** | 1.00 ** | ||||
| AA | 0.38 | 0.34 | 0.40 | 0.22 | −0.76 ** | −0.70 ** | −0.94 ** | 1.00 ** | |||
| FRAP | −0.46 | −0.41 | −0.49 | −0.33 | 0.93 ** | 0.80 ** | 0.95 ** | −0.88 ** | 1.00 ** | ||
| ABTS+ | −0.38 | −0.33 | −0.41 | −0.23 | 0.89 ** | 0.77 ** | 0.99 ** | −0.93 ** | 0.95 ** | 1.00 ** | |
| DPPH | −0.12 | 0.15 | 0.10 | −0.27 | 0.47 | 0.30 | 0.73* * | −0.70 ** | 0.56 * | 0.74 ** | 1.00 ** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, R.; Yang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Yin, L.; Qu, P.; Wang, P.; Mu, X.; Zhang, S.; Xie, P.; Cheng, C.; et al. Comparison of Bioactive Compounds and Antioxidant Activities in Differentially Pigmented Cerasus humilis Fruits. Molecules 2023, 28, 6272. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28176272
Yang R, Yang Y, Hu Y, Yin L, Qu P, Wang P, Mu X, Zhang S, Xie P, Cheng C, et al. Comparison of Bioactive Compounds and Antioxidant Activities in Differentially Pigmented Cerasus humilis Fruits. Molecules. 2023; 28(17):6272. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28176272
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Rui, Yan Yang, Yang Hu, Lu Yin, Pengyan Qu, Pengfei Wang, Xiaopeng Mu, Shuai Zhang, Peng Xie, Chunzhen Cheng, and et al. 2023. "Comparison of Bioactive Compounds and Antioxidant Activities in Differentially Pigmented Cerasus humilis Fruits" Molecules 28, no. 17: 6272. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28176272
APA StyleYang, R., Yang, Y., Hu, Y., Yin, L., Qu, P., Wang, P., Mu, X., Zhang, S., Xie, P., Cheng, C., & Zhang, J. (2023). Comparison of Bioactive Compounds and Antioxidant Activities in Differentially Pigmented Cerasus humilis Fruits. Molecules, 28(17), 6272. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28176272