Facile Synthesis of Iron and Nitrogen Co-Doped Carbon Dot Nanozyme as Highly Efficient Peroxidase Mimics for Visualized Detection of Metabolites
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
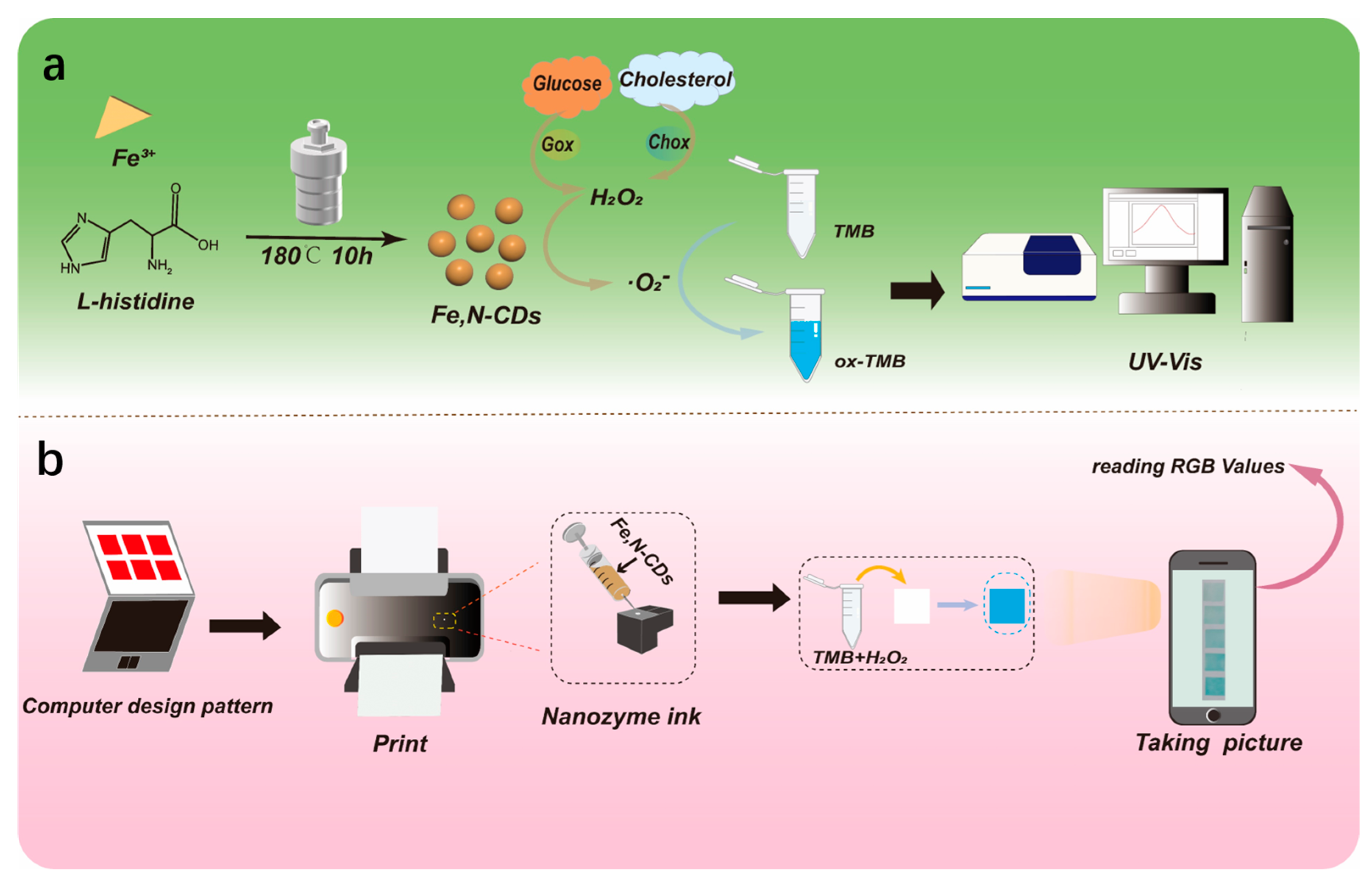
2.1. Strategy for One-Pot Synthesis of Fe,N-CDs and Colorimetric Detection of Metabolism
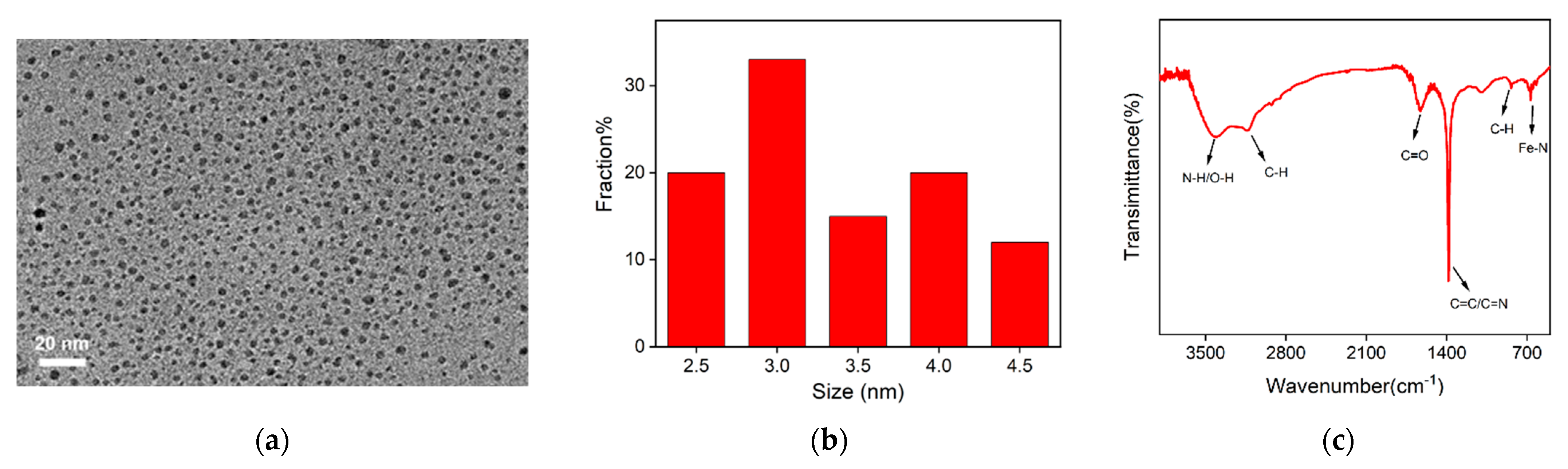
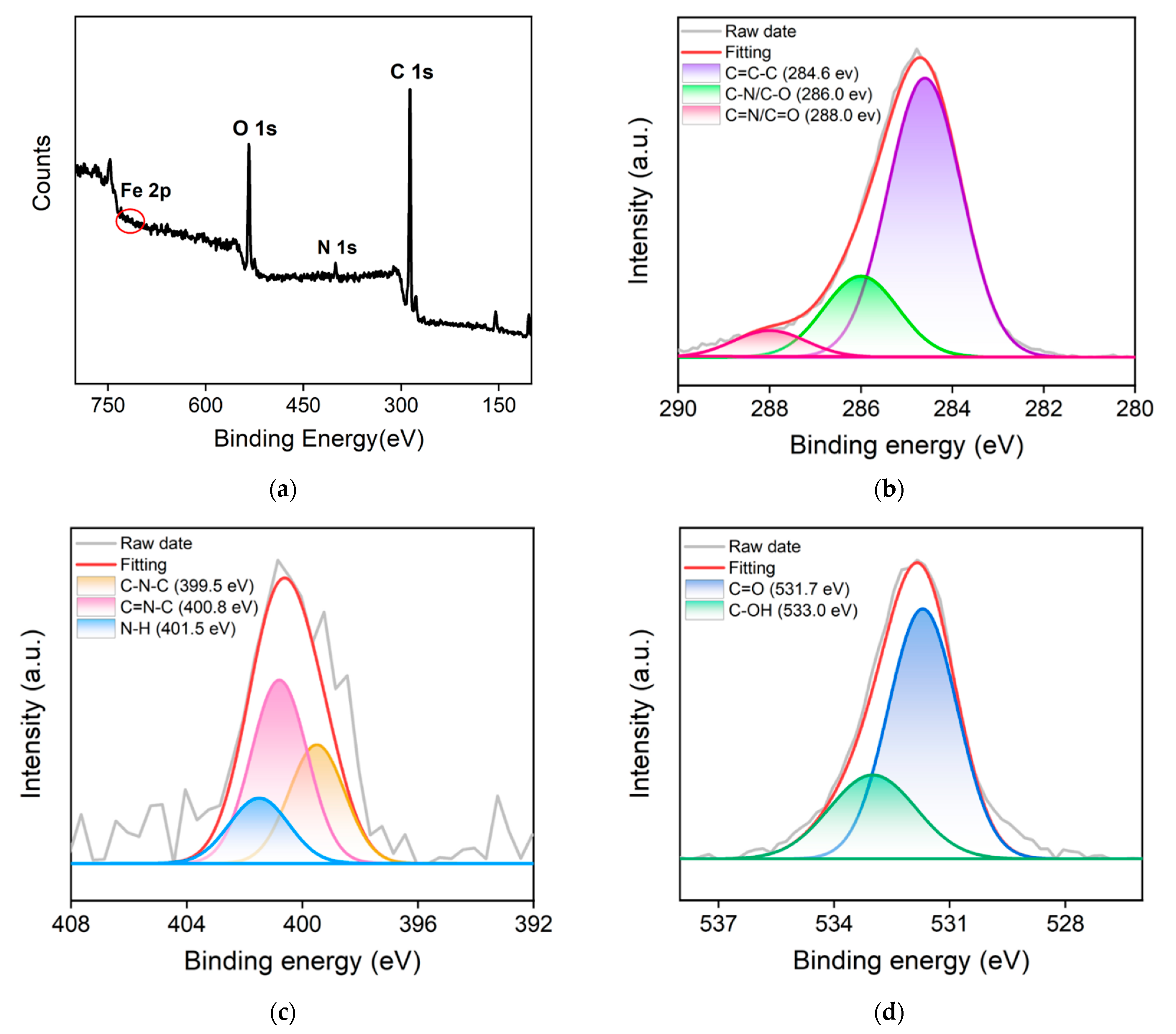
2.2. Characterization of Fe,N-CDs
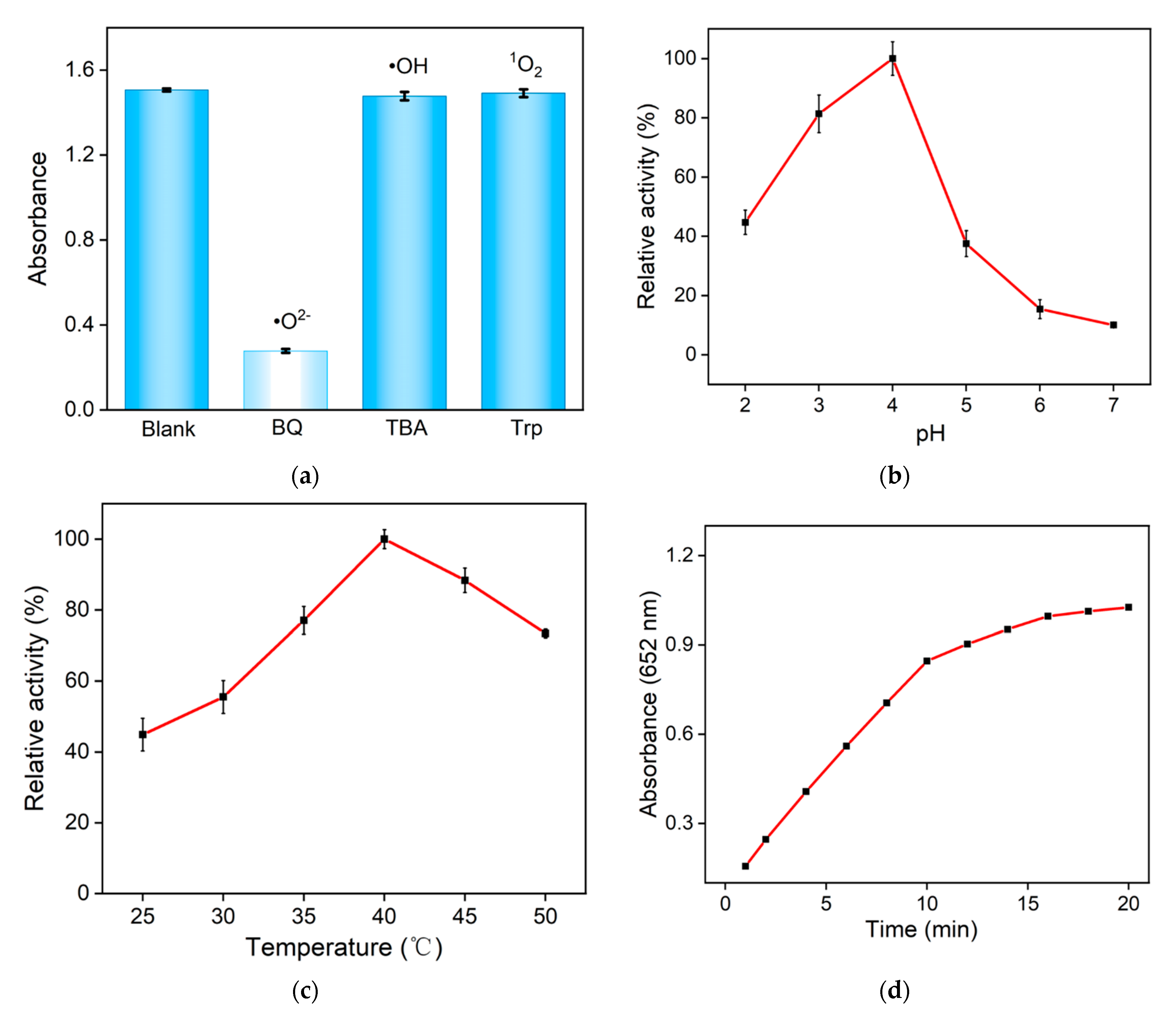
2.3. Peroxidase-like Activity of Fe,N-CDs
2.4. Catalytic Mechanism of Fe,N-CD Nanozyme
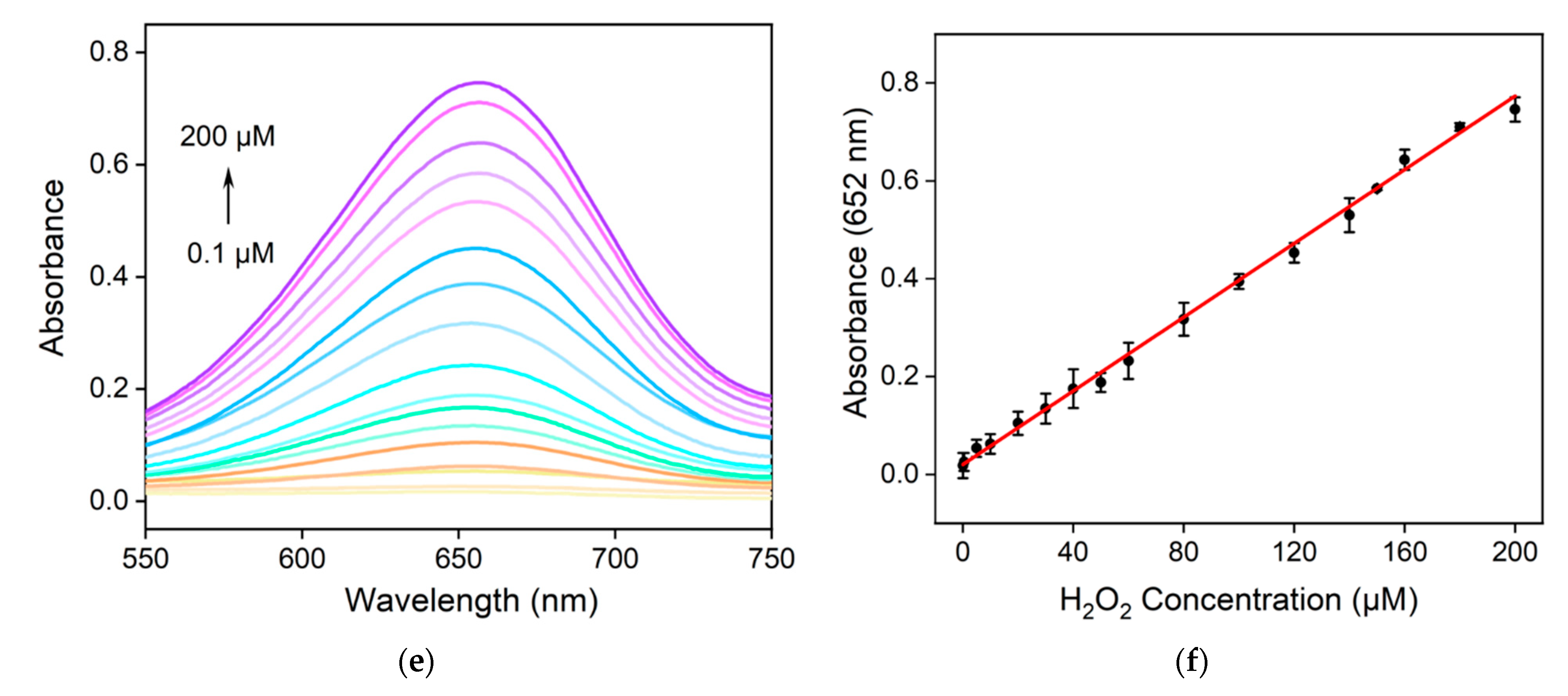
2.5. Colorimetric Detection of H2O2
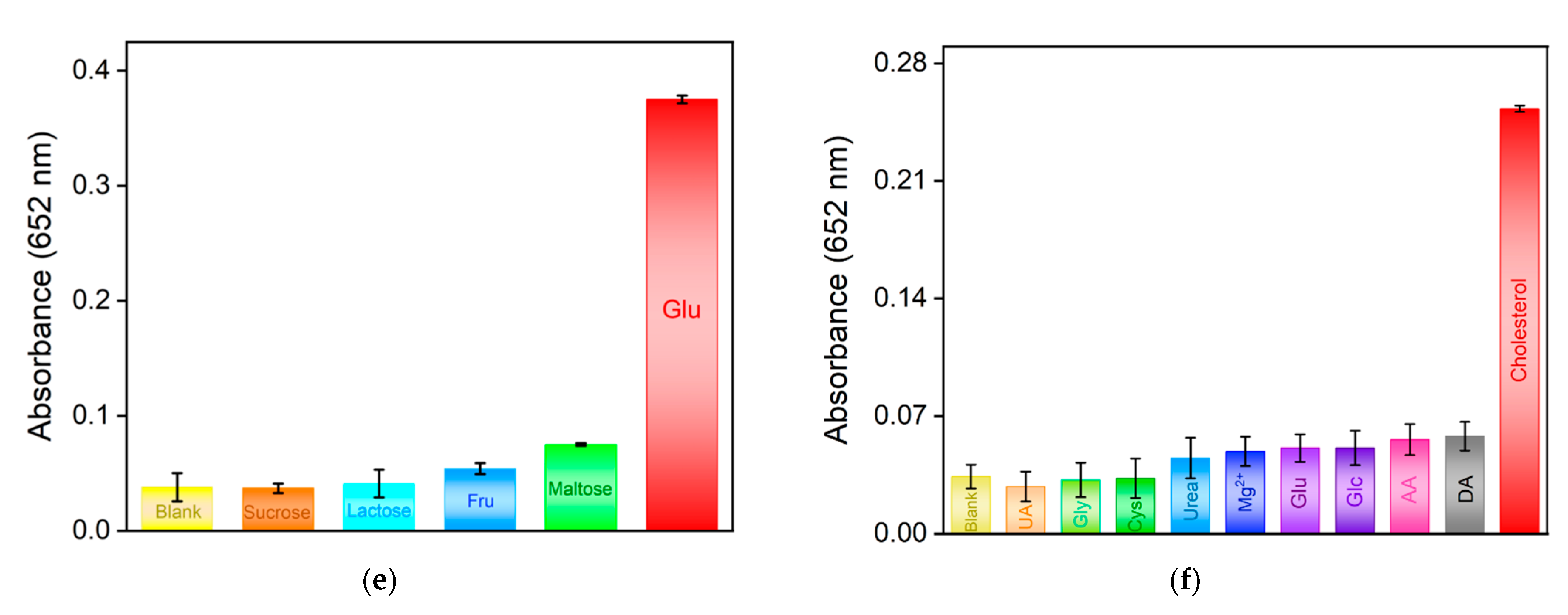
2.6. Colorimetric Detection of Glu and Chol
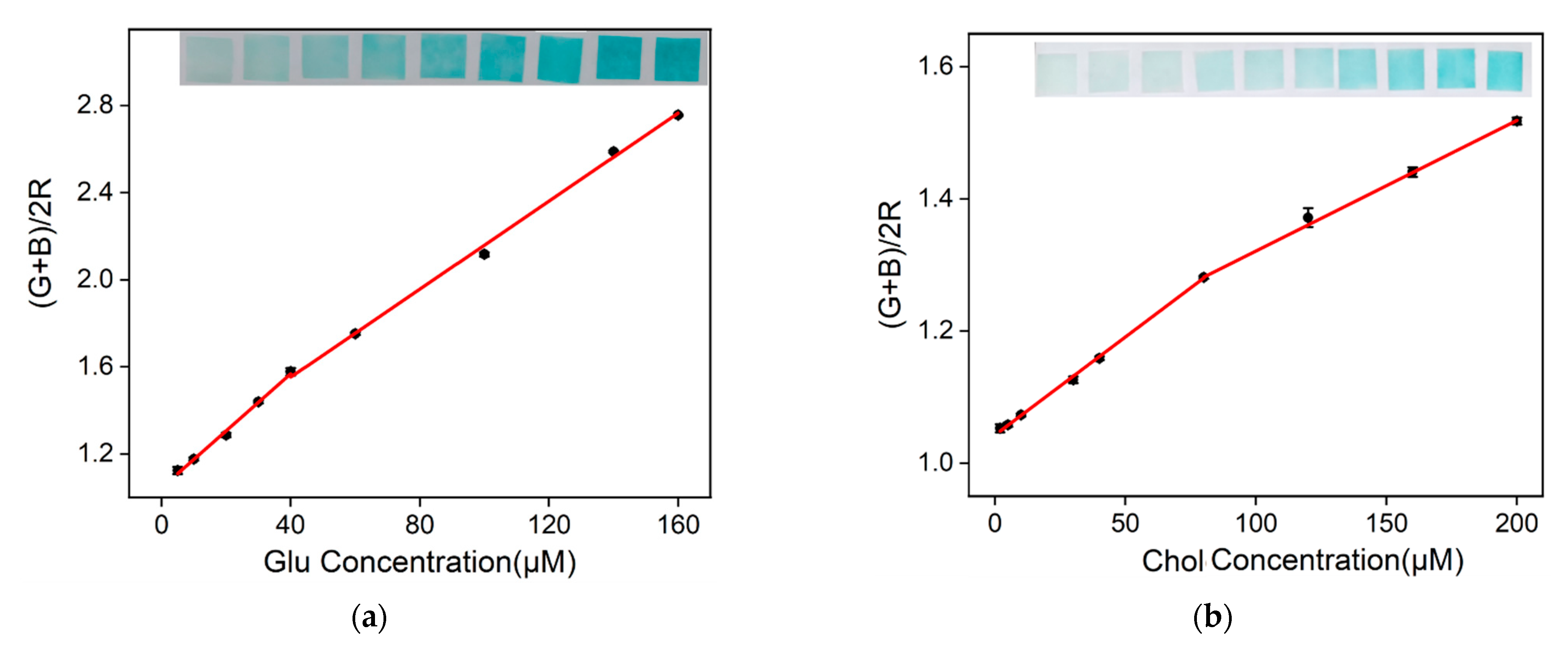
2.7. Visual Detection of Glu and Chol Using Nanozyme Paper and Smartphone
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Materials
3.2. Characterizations and Instrumentations
3.3. One-Step Synthesis of Fe,N-CD Nanozyme
3.4. Enzyme Activity Testing of Fe,N-CD Pseudo-Peroxidase
3.5. Detection of Free Radicals Generated during the Catalytic Process of Fe,N-CDs
3.6. Colorimetric Detection of H2O2
3.7. Colorimetric Detection of Glu
3.8. Colorimetric Detection of Chol
3.9. Visual Detection of H2O2, Glu, or Chol Based on Nanozyme Testing Paper
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Shi, J.; Tong, L.; Tong, W.; Chen, H.; Lan, M.; Sun, X.; Zhu, Y. Current progress in long-term and continuous cell metabolite detection using microfluidics. TrAC Trend Anal. Chem. 2019, 117, 263–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koklu, A.; Ohayon, D.; Wustoni, S.; Druet, V.; Saleh, A.; Inal, S. Organic bioelectronic devices for metabolite sensing. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 4581–4635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Xie, Y.; Wang, G.; Luo, Y. Metabolite-based biosensors for natural product discovery and overproduction. Curr. Opin. Biotech. 2022, 75, 102699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Duan, W.; Jin, Y.; Wo, F.; Xi, F.; Wu, J. Ratiometric fluorescent nanohybrid for noninvasive and visual monitoring of sweat glucose. ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 2096–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, X.; Zhao, J.; Ding, Y.; Tang, H.; Xi, F. Iron and nitrogen co-doped graphene quantum dots as highly active peroxidases for the sensitive detection of l-cysteine. New J. Chem. 2021, 45, 19056–19064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njuguna, N.M.; Masimirembwa, C.; Chibale, K. Identification and characterization of reactive metabolites in natural products-driven drug discovery. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, A.; Yan, F. Flexible electrochemical biosensors for health monitoring. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2020, 3, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez-Renedo, O.; Navarro-Cuñado, A.M.; Alonso-Lomillo, M.A. Electrochemical devices for Chol detection. J. Pharmaceut. Biomed. Anal. 2023, 224, 115195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Rana, M.; Geiwitz, M.; Khan, N.I.; Catalano, M.; Ortiz-Marquez, J.C.; Kitadai, H.; Weber, A.; Dweik, B.; Ling, X.; et al. Rapid Multianalyte detection of opioid metabolites in wastewater. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 3704–3714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, W.; Koen, Y.M.; Williams, T.D.; Hanzlik, R.P. Use of isotopic signatures for mass spectral detection of protein adduction by chemically reactive metabolites of bromobenzene: Studies with model proteins. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2005, 18, 1748–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Duan, W.; Jin, Y.; Wo, F.; Xi, F.; Wu, J. Graphene quantum dot-decorated luminescent porous silicon dressing for theranostics of diabetic wounds. Acta Biomater. 2021, 131, 544–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Chen, Z.; Wang, T.; Jiang, X.; Qu, X.; Duan, W.; Xi, F.; He, Z.; Wu, J. Tissue imprinting on 2D nanoflakes-capped silicon nanowires for lipidomic mass spectrometry imaging and cancer diagnosis. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 6916–6928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.; Jin, Y.; Cui, Y.; Xi, F.; Liu, X.; Wo, F.; Wu, J. A co-delivery platform for synergistic promotion of angiogenesis based on biodegradable, therapeutic and self-reporting luminescent porous silicon microparticles. Biomaterials 2021, 272, 120772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Shi, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Z.; Wu, H.; Zhou, Z.; Li, J.; Ping, J.; He, L.; Shen, H.; et al. Contamination-free visual detection of SARS-CoV-2 with CRISPR/Cas12a: A promising method in the point-of-care detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 169, 112642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Man, Y.; Ban, M.; Jin, X.; Li, A.; Tao, J.; Pan, L. An integrated distance-based microfluidic aptasensor for visual quantitative detection of Salmonella with sample-in-answer-out capability. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 381, 133480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahimi-Kashani, N.; Hormozi-Nezhad, M.R. A smart-phone based ratiometric nanoprobe for label-free detection of methyl parathion. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 322, 128580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajrami, B.; Hvastkovs, E.G.; Jensen, G.C.; Schenkman, J.B.; Rusling, J.F. Enzyme-DNA biocolloids for DNA adduct and reactive metabolite detection by chromatography-mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 922–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yeasmin, S.; Ullah, A.; Wu, B.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, L.J. Enzyme-mimics for sensitive and selective steroid metabolite detection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 13971–13982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wei, C.; Chen, D.; Xu, Z.; Huang, X. Construction of inorganic-organic cascade enzymes biosensor based on gradient polysulfone hollow fiber membrane for glucose detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 385, 133630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Mo, F.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, G.; Yu, W.; Liu, X. Portable and sensitive detection of non-glucose target by enzyme-encapsulated metal-organic-framework using personal glucose meter. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 198, 113819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Lin, A.; Wei, H. Nanozyme-enabled analytical chemistry. Anal. Chem. 2021, 94, 312–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Ren, J.; Qu, X. Nanozymes: Classification, catalytic mechanisms, activity regulation, and applications. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 4357–4412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, W.; Su, R.; Yu, G.; Liu, L.; Yan, F. Highly sensitive electrochemical detection of paraquat in environmental water samples using a vertically ordered mesoporous silica film and a nanocarbon composite. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Xuan, L.; Gong, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Xi, F.; Chen, J. Three-dimensional macroscopic graphene supported vertically-ordered mesoporous silica-nanochannel film for direct and ultrasensitive detection of uric acid in serum. Talanta 2022, 238, 123027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhong, H.; Chen, M.; Zhao, C.; Liu, Y.; Xi, F.; Luo, T. Functional nanostructure-loaded three-dimensional graphene foam as a non-enzymatic electrochemical sensor for reagentless glucose detection. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 33739–33746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Q.; Huang, J.; He, L.; Xi, F. Simple immunosensor for ultrasensitive electrochemical determination of biomarker of the bone metabolism in human serum. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 940795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, X.; Yan, F.; Hu, W. Silica nanochannel array on co-electrodeposited graphene-carbon nanotubes 3D composite film for antifouling detection of uric acid in human serum and urine samples. Microchem. J. 2023, 190, 108632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Ding, Y.; Su, R.; Lu, D.; Tang, H.; Xi, F. Silica nanochannel array film supported by ß-cyclodextrin-functionalized graphene modified gold film electrode for sensitive and direct electroanalysis of acetaminophen. Front. Chem. 2022, 9, 812086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Zhou, X.; Xie, L.; Tang, H.; Yan, F. Vertically-ordered mesoporous silica films grown on boron nitride-graphene composite modified electrodes for rapid and sensitive detection of carbendazim in real samples. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 939510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Zhao, J.; Deng, X.; Chen, J.; Xi, F.; Wang, X. Colorimetric and fluorescent dual-modality sensing platform based on fluorescent nanozyme. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 774486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Zheng, Y.; Pang, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Z.; Xi, F.; Chen, P. Graphene quantum dots as full-color and stimulus responsive fluorescence ink for information encryption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 579, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wareing, T.C.; Gentile, P.; Phan, A.N. Biomass-based carbon dots: Current development and future perspectives. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 15471–15501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, P.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, W.; Wang, Y.; Yan, X.; Luo, D. Carbon dots in biomedicine: A review. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2022, 5, 2031–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Guan, L.; Xu, X.; Wang, E.; Wang, C. Applications of carbon dots in electrochemical energy storage. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2022, 4, 5144–5164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.; Zhou, Y.; Leblanc, R.M.; Peng, Z. Recent developments of carbon dots in biosensing: A review. ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 2724–2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Huang, H.; Wang, T.; Zhou, D.; Chen, Q.; Li, D.; Chen, S.; Lin, P. Endoplasmic reticulum-targetable selenium-doped carbon nanodots with redox-responsive fluorescence for in situ free-radical scavenging in cells and mice. Arab. J. Chem. 2023, 16, 105036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Li, S.; Chen, B.; Wang, Y.; Shen, Z.; Qiu, M.; Pan, H.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y.; Li, X. Endoplasmic reticulum-targeted polymer dots encapsulated with ultrasonic synthesized near-infrared carbon nanodots and their application for in vivo monitoring of Cu2+. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 627, 705–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, S.; Ding, H.; Xu, M.; Hu, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Liu, L.; Jiang, L.; Wang, D.; Dong, C.; et al. Recent advances in synthesis, optical properties, and biomedical applications of carbon dots. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2019, 2, 2317–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Chen, J.; Qiao, S.; Zhang, W. Carbon-based nanomaterials for bone and cartilage regeneration: A review. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 7, 4718–4735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, K.; Xi, J.; Fan, L.; Wang, P.; Zhu, C.; Tang, Y.; Xu, X.; Liang, M.; Jiang, B.; Yan, X.; et al. In vivo guiding nitrogen-doped carbon nanozyme for tumor catalytic therapy. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Gao, X.J.; Zhu, Y.; Muhammad, F.; Tan, S.; Cao, W.; Lin, S.; Jin, Z.; Gao, X.; Wei, H. Nitrogen-doped carbon nanomaterials as highly active and specific peroxidase mimics. Chem. Mater. 2018, 30, 6431–6439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, Q.; Lou, Z.; Li, S.; Zhu, Y.; Qin, L.; Wei, H. Nanomaterials with enzyme-like characteristics (nanozymes): Next-generation artificial enzymes (II). Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 1004–1076. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jiao, L.; Yan, H.; Wu, Y.; Gu, W.; Zhu, C.; Du, D.; Lin, Y. When nanozymes meet single-atom catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 2565–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Analyte | Sample | Added b (μM) | Found (μM) | Recovery (%) | RSD (%, n = 3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10.0 | 9.60 | 96.0 | 1.9 | ||
| Glu | Serum a | 50.0 | 49.4 | 98.8 | 1.3 |
| 100 | 98.4 | 98.4 | 0.3 | ||
| Serum a | 10.0 | 10.3 | 103 | 2.2 | |
| Chol | 50.0 | 52.4 | 104 | 1.7 | |
| 100 | 97.5 | 97.5 | 0.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, S.; Zhang, S.; Li, Y.; Liu, J. Facile Synthesis of Iron and Nitrogen Co-Doped Carbon Dot Nanozyme as Highly Efficient Peroxidase Mimics for Visualized Detection of Metabolites. Molecules 2023, 28, 6064. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28166064
Xu S, Zhang S, Li Y, Liu J. Facile Synthesis of Iron and Nitrogen Co-Doped Carbon Dot Nanozyme as Highly Efficient Peroxidase Mimics for Visualized Detection of Metabolites. Molecules. 2023; 28(16):6064. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28166064
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Shuai, Shiyue Zhang, Yutong Li, and Jiyang Liu. 2023. "Facile Synthesis of Iron and Nitrogen Co-Doped Carbon Dot Nanozyme as Highly Efficient Peroxidase Mimics for Visualized Detection of Metabolites" Molecules 28, no. 16: 6064. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28166064
APA StyleXu, S., Zhang, S., Li, Y., & Liu, J. (2023). Facile Synthesis of Iron and Nitrogen Co-Doped Carbon Dot Nanozyme as Highly Efficient Peroxidase Mimics for Visualized Detection of Metabolites. Molecules, 28(16), 6064. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28166064





