mPGES-1 Inhibitor Discovery Based on Computer-Aided Screening: Pharmacophore Models, Molecular Docking, ADMET, and MD Simulations
Abstract
1. Introduction
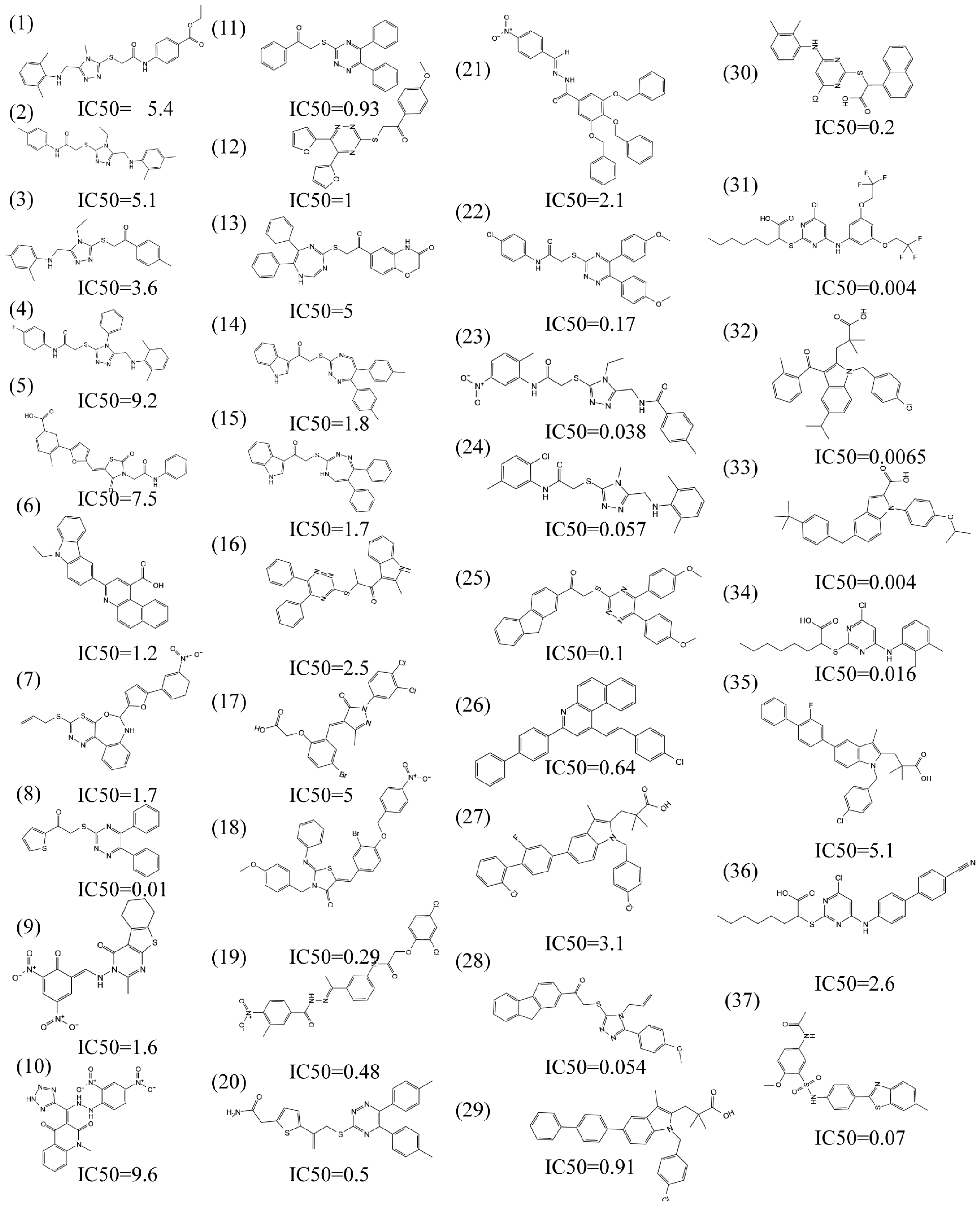
2. Results
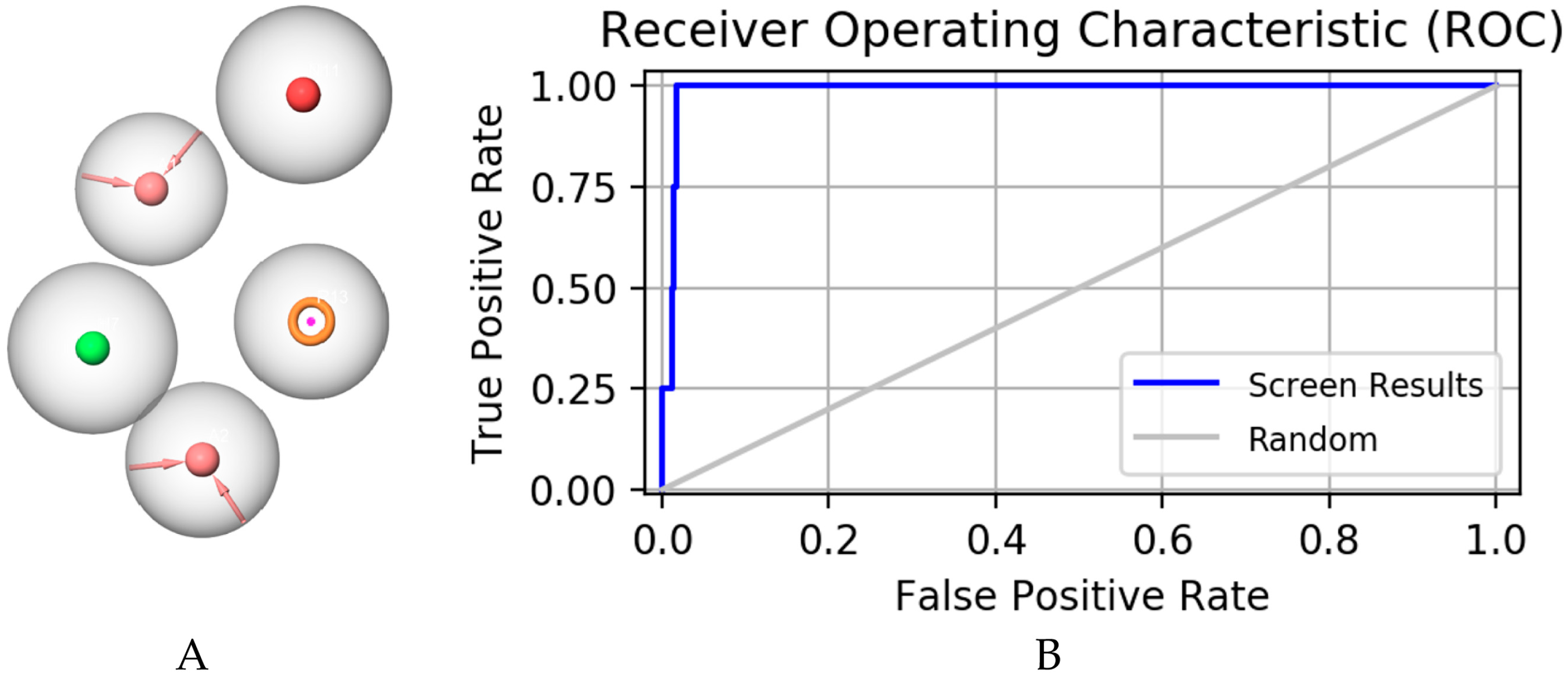
2.1. Pharmacophore Model Establishment
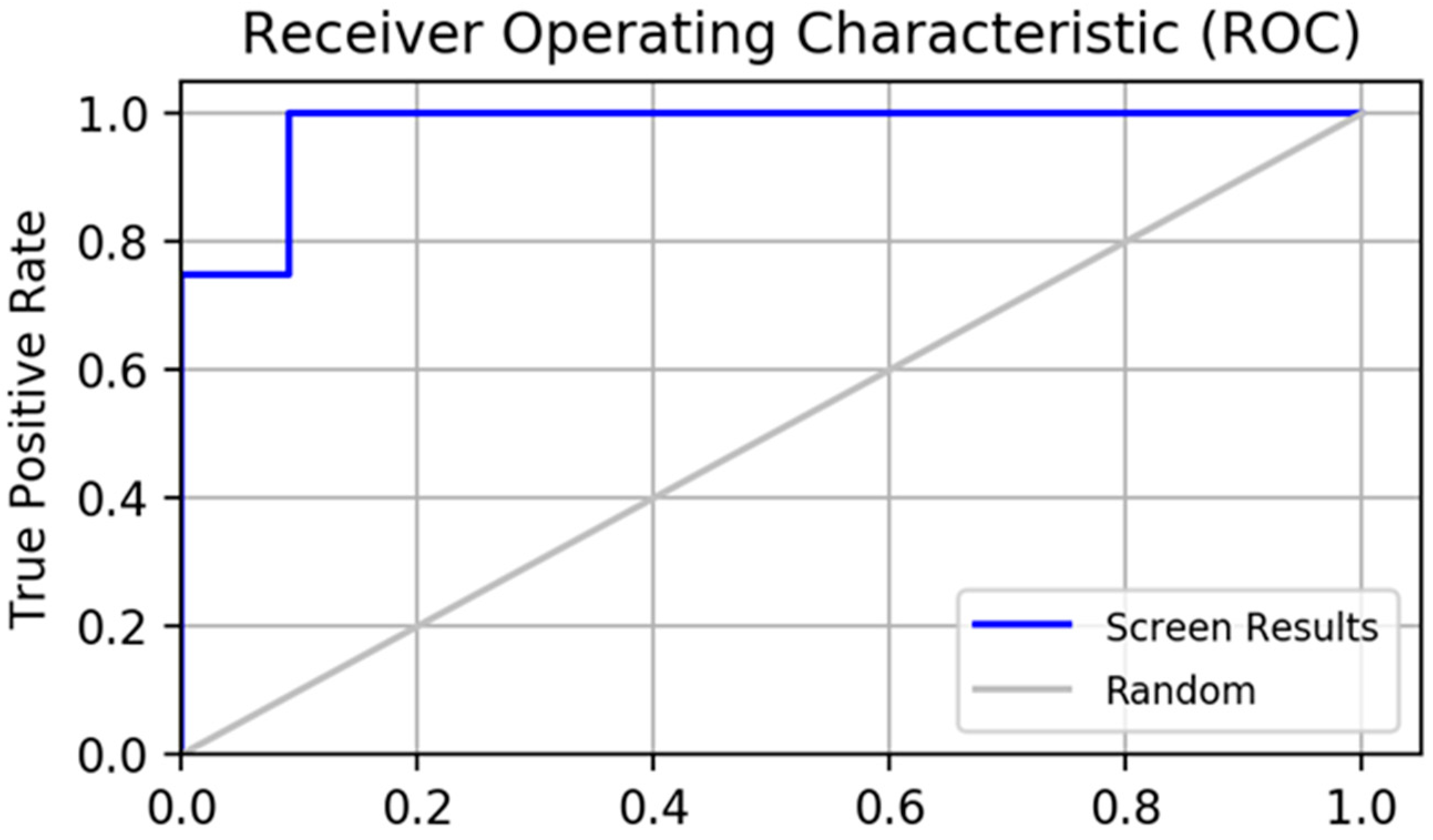
2.2. Pharmacophore Model Verification
2.3. Molecular Docking
2.4. ADMET Analysis
2.5. MD Simulation
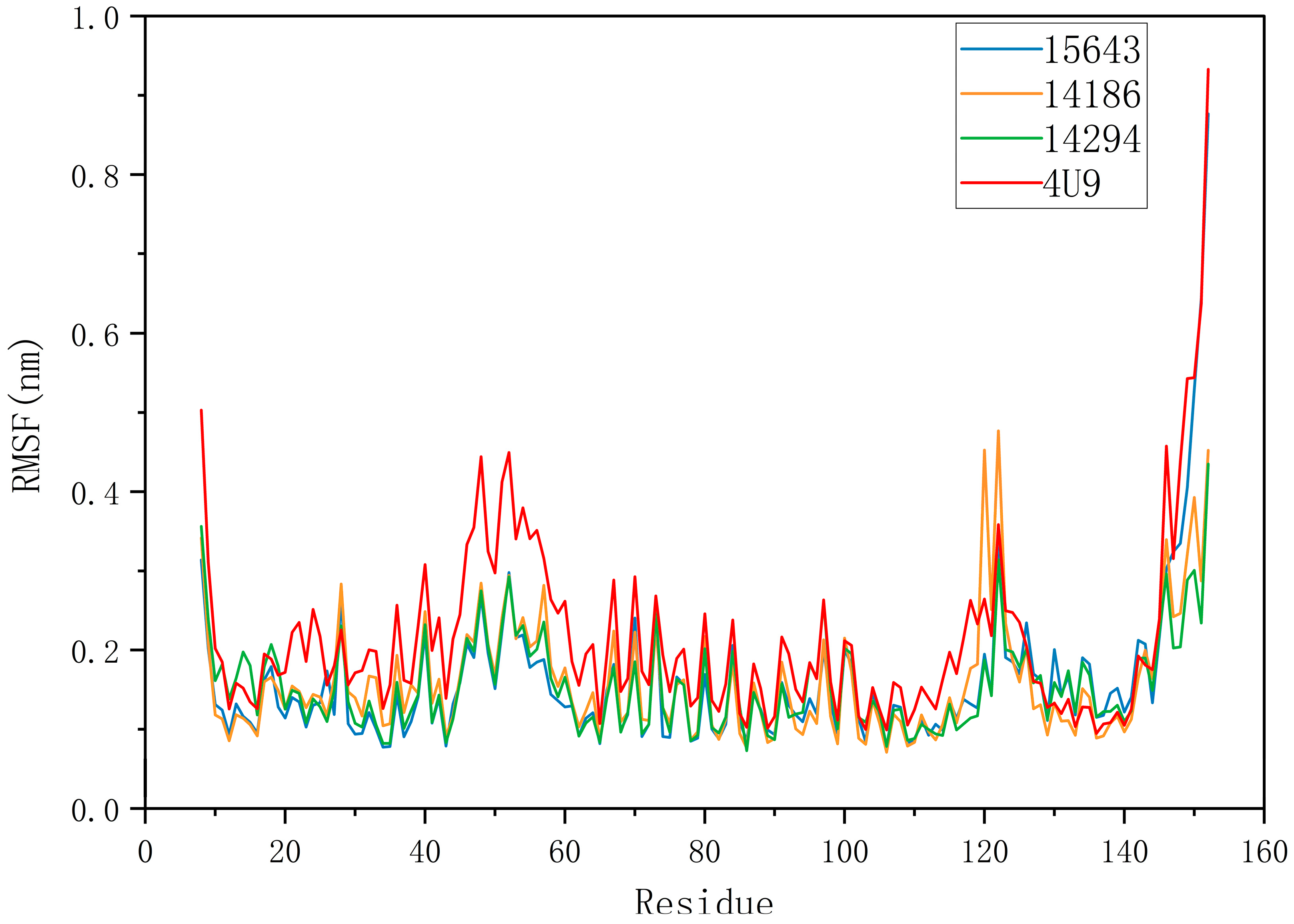
2.5.1. RMSD and RMSF Analysis
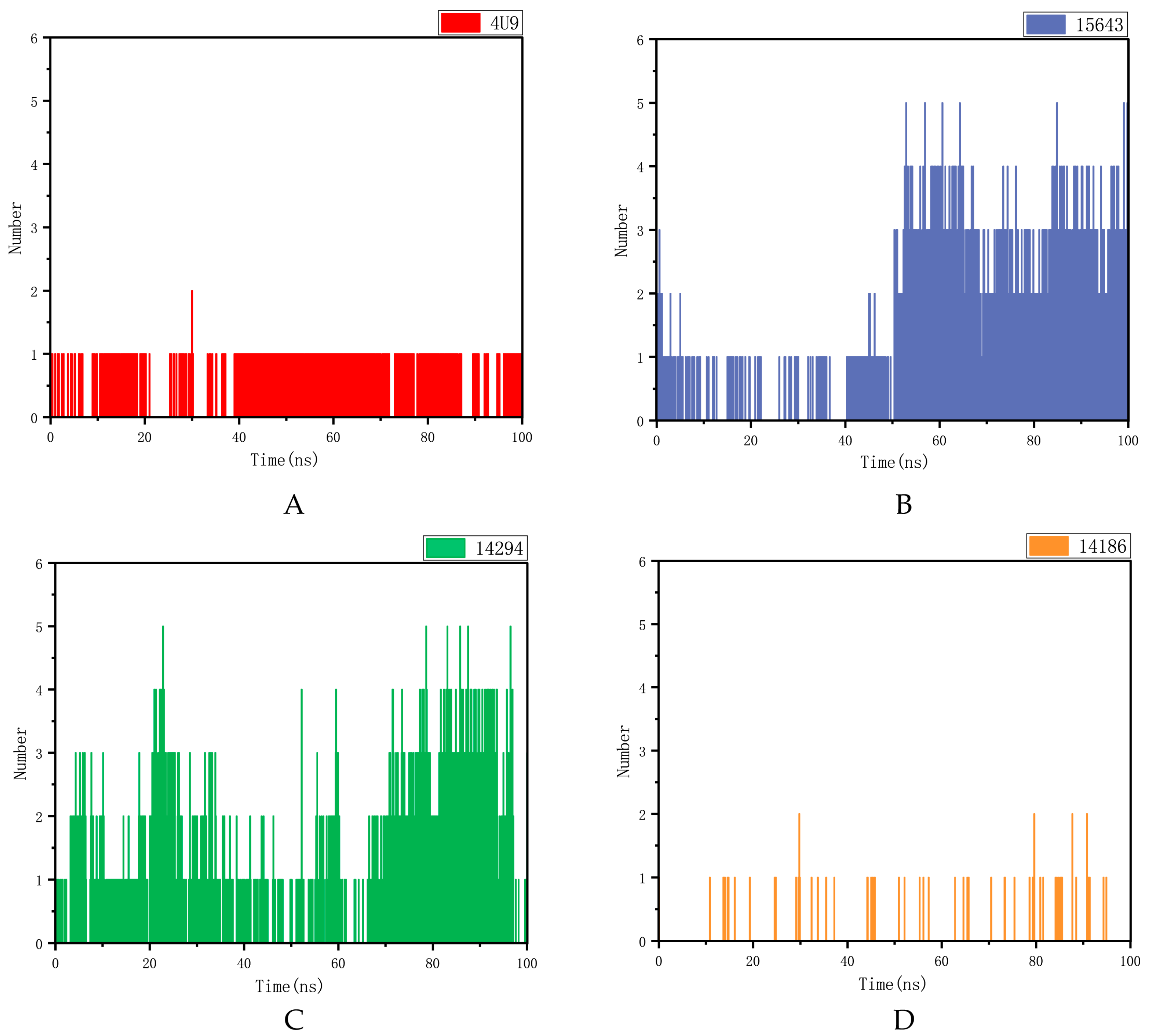
2.5.2. Hydrogen Bond Analysis
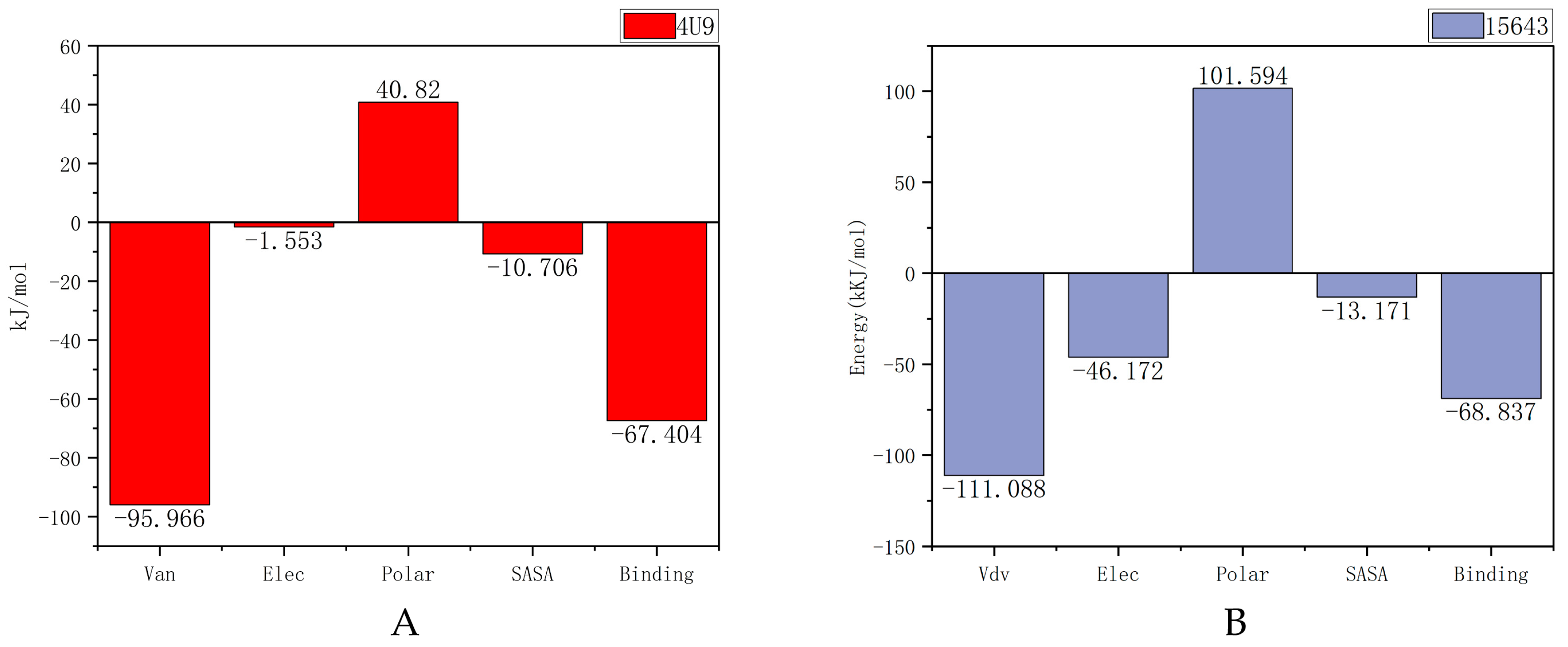
2.5.3. MM-PBSA Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Protein Structure
4.2. Data Set
4.3. Pharmacophore Analysis
4.4. Molecular Docking
4.5. ADMET
4.6. Dynamic Simulation
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Ricciotti, E.; FitzGerald, G.A. Prostaglandins and inflammation. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2011, 31, 986–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, K. [Development and repair of NSAIDs-induced small intestinal lesions: Relation to COX isozymes and EP receptor subtypes]. Nihon. Rinsho. 2011, 69, 1123–1128. [Google Scholar]
- Bogdan, D.; Falcone, J.; Kanjiya, M.P.; Park, S.H.; Carbonetti, G.; Studholme, K.; Gomez, M.; Lu, Y.; Elmes, M.W.; Smietalo, N.; et al. Fatty acid-binding protein 5 controls microsomal prostaglandin E synthase 1 (mPGES-1) induction during inflammation. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 5295–5306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, R.; Amano, H.; Ito, Y.; Eshima, K.; Satoh, T.; Iwamura, M.; Nakamura, M.; Kitasato, H.; Uematsu, S.; Raouf, J.; et al. Microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1 promotes lung metastasis via SDF-1/CXCR4-mediated recruitment of CD11b(+)Gr1(+)MDSCs from bone marrow. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 121, 109581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Rees, B.P.; Sivula, A.; Thorén, S.; Yokozaki, H.; Jakobsson, P.J.; Offerhaus, G.J.; Ristimäki, A. Expression of microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1 in intestinal type gastric adenocarcinoma and in gastric cancer cell lines. Int. J. Cancer 2003, 107, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimatsu, K.; Golijanin, D.; Paty, P.B.; Soslow, R.A.; Jakobsson, P.J.; DeLellis, R.A.; Subbaramaiah, K.; Dannenberg, A.J. Inducible microsomal prostaglandin E synthase is overexpressed in colorectal adenomas and cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2001, 7, 3971–3976. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.W.; Qian, M.; Jia, R.P.; Xu, Z.; Wu, J.P.; Li, W.C.; Huang, W.B.; Chen, X.G. Expression and significance of microsomal prostaglandin synthase-1 (mPGES-1) and Beclin-1 in the development of prostate cancer. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2012, 13, 1639–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrotra, S.; Morimiya, A.; Agarwal, B.; Konger, R.; Badve, S. Microsomal prostaglandin E2 synthase-1 in breast cancer: A potential target for therapy. J. Pathol. 2006, 208, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herfs, M.; Herman, L.; Hubert, P.; Minner, F.; Arafa, M.; Roncarati, P.; Henrotin, Y.; Boniver, J.; Delvenne, P. High expression of PGE2 enzymatic pathways in cervical (pre)neoplastic lesions and functional consequences for antigen-presenting cells. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2009, 58, 603–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, S.; Satake, M.; Dawson, D.W.; Funahashi, H.; Angst, E.; Go, V.L.; Reber, H.A.; Hines, O.J.; Eibl, G. Expression analysis of the prostaglandin E2 production pathway in human pancreatic cancers. Pancreas 2008, 37, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Roszik, J.; Cho, S.N.; Ogata, D.; Milton, D.R.; Peng, W.; Menter, D.G.; Ekmekcioglu, S.; Grimm, E.A. The COX2 Effector Microsomal PGE2 Synthase 1 is a Regulator of Immunosuppression in Cutaneous Melanoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 1650–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leoncini, E.; Ricciardi, W.; Cadoni, G.; Arzani, D.; Petrelli, L.; Paludetti, G.; Brennan, P.; Luce, D.; Stucker, I.; Matsuo, K.; et al. Adult height and head and neck cancer: A pooled analysis within the INHANCE Consortium. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2014, 29, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omi, Y.; Shibata, N.; Okamoto, T.; Obara, T.; Kobayashi, M. Immunohistochemical demonstration of membrane-bound prostaglandin E2 synthase-1 in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Acta Histochem. Cytochem. 2009, 42, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattila, S.; Tuominen, H.; Koivukangas, J.; Stenbäck, F. The terminal prostaglandin synthases mPGES-1, mPGES-2, and cPGES are all overexpressed in human gliomas. Neuropathology 2009, 29, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chini, M.G.; Giordano, A.; Potenza, M.; Terracciano, S.; Fischer, K.; Vaccaro, M.C.; Colarusso, E.; Bruno, I.; Riccio, R.; Koeberle, A.; et al. Targeting mPGES-1 by a Combinatorial Approach: Identification of the Aminobenzothiazole Scaffold to Suppress PGE(2) Levels. ACS Med. Chem Lett. 2020, 11, 783–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korotkova, M.; Jakobsson, P.J. Characterization of microsomal prostaglandin E synthase 1 inhibitors. Basic Clin Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2014, 114, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y. The role of Chinese medicine in clinical oncology. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2014, 20, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Cai, T.; Xia, X.; Cai, Y.; Wu, X.Y. Research Advances in the Intervention of Inflammation and Cancer by Active Ingredients of Traditional Chinese Medicine. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 19, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar Bhardwaj, V.; Purohit, R.; Kumar, S. Himalayan bioactive molecules as potential entry inhibitors for the human immunodeficiency virus. Food Chem. 2021, 347, 128932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanwar, G.; Mazumder, A.G.; Bhardwaj, V.; Kumari, S.; Bharti, R.; Yamini; Singh, D.; Das, P.; Purohit, R. Target identification, screening and in vivo evaluation of pyrrolone-fused benzosuberene compounds against human epilepsy using Zebrafish model of pentylenetetrazol-induced seizures. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; MacKerell, A.D., Jr. Computer-Aided Drug Design Methods. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1520, 85–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H. Pharmacophore-based virtual screening. Curr. Med. Chem. 2008, 15, 1018–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Zhong, A.; Wang, Q.; Zheng, T. Structure-Based Pharmacophore Modeling, Virtual Screening, Molecular Docking, ADMET, and Molecular Dynamics (MD) Simulation of Potential Inhibitors of PD-L1 from the Library of Marine Natural Products. Mar. Drugs 2021, 20, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, W.; Lu, T.; Yuan, H.; Wang, F.; Liu, H.; Lu, S.; Leng, Y.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, Y. Pharmacophore modeling and virtual screening studies to identify new c-Met inhibitors. J. Mol. Model. 2012, 18, 3087–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez Pérez, J.A.; Pérez Martin, P.S. [ROC curve]. Semergen 2023, 49, 101821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friesner, R.A.; Banks, J.L.; Murphy, R.B.; Halgren, T.A.; Klicic, J.J.; Mainz, D.T.; Repasky, M.P.; Knoll, E.H.; Shelley, M.; Perry, J.K.; et al. Glide: A new approach for rapid, accurate docking and scoring. 1. Method and assessment of docking accuracy. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 1739–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, L.L.G.; Andricopulo, A.D. ADMET modeling approaches in drug discovery. Drug Discov. Today 2019, 24, 1157–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissADME: A free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, M.; Kudo, I. Prostaglandin E synthase: A novel drug target for inflammation and cancer. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2006, 12, 943–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AbdulHameed, M.D.; Hamza, A.; Liu, J.; Huang, X.; Zhan, C.G. Human microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1 (mPGES-1) binding with inhibitors and the quantitative structure-activity correlation. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2008, 48, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Micco, S.; Terracciano, S.; Ruggiero, D.; Potenza, M.; Vaccaro, M.C.; Fischer, K.; Werz, O.; Bruno, I.; Bifulco, G. Identification of 2-(thiophen-2-yl)acetic Acid-Based Lead Compound for mPGES-1 Inhibition. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 676631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Rowland, S.E.; Clark, P.; Giroux, A.; Côté, B.; Guiral, S.; Salem, M.; Ducharme, Y.; Friesen, R.W.; Méthot, N.; et al. MF63 [2-(6-chloro-1H-phenanthro[9,10-d]imidazol-2-yl)-isophthalonitrile], a selective microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1 inhibitor, relieves pyresis and pain in preclinical models of inflammation. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2008, 326, 754–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthukaman, N.; Deshmukh, S.; Sarode, N.; Tondlekar, S.; Tambe, M.; Pisal, D.; Shaikh, M.; Kattige, V.G.; Honnegowda, S.; Karande, V.; et al. Discovery of 2-((2-chloro-6-fluorophenyl)amino)-N-(3-fluoro-5-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-1-methyl-7,8-dihydro-1H-[1,4]dioxino[2′,3′:3,4]benzo[1,2-d]imidazole-5-carboxamide as potent, selective and efficacious microsomal prostaglandin E(2) synthase-1 (mPGES-1) inhibitor. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 5977–5984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ergül, A.G.; Maz, T.G.; Kretzer, C.; Olğaç, A.; Jordan, P.M.; Çalışkan, B.; Werz, O.; Banoglu, E. Novel potent benzimidazole-based microsomal prostaglandin E(2) synthase-1 (mPGES-1) inhibitors derived from BRP-201 that also inhibit leukotriene C(4) synthase. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 231, 114167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arhancet, G.B.; Walker, D.P.; Metz, S.; Fobian, Y.M.; Heasley, S.E.; Carter, J.S.; Springer, J.R.; Jones, D.E.; Hayes, M.J.; Shaffer, A.F.; et al. Discovery and SAR of PF-4693627, a potent, selective and orally bioavailable mPGES-1 inhibitor for the potential treatment of inflammation. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 1114–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedes, I.A.; de Magalhães, C.S.; Dardenne, L.E. Receptor-ligand molecular docking. Biophys. Rev. 2014, 6, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Spoel, D.; Lindahl, E.; Hess, B.; Groenhof, G.; Mark, A.E.; Berendsen, H.J. GROMACS: Fast, flexible, and free. J. Comput. Chem. 2005, 26, 1701–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luz, J.G.; Antonysamy, S.; Kuklish, S.L.; Condon, B.; Lee, M.R.; Allison, D.; Yu, X.P.; Chandrasekhar, S.; Backer, R.; Zhang, A.; et al. Crystal Structures of mPGES-1 Inhibitor Complexes Form a Basis for the Rational Design of Potent Analgesic and Anti-Inflammatory Therapeutics. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 4727–4737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, I.A.; Jiffri, E.H.; Ashraf, G.M.; Kamal, M.A.; Beg, M.A. Structural studies on inhibitory mechanisms of antibiotic, corticosteroid and catecholamine molecules on lactoperoxidase. Life Sci. 2018, 207, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaoglu, Z.Y.; Kilic, D. Virtual screening, molecular simulations and bioassays: Discovering novel microsomal prostaglandin E Synthase-1 (mPGES-1) inhibitors. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 155, 106616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, D.K.; Kumar, S.; Teli, M.K.; Kim, M.H. Ligand-based pharmacophore modeling and docking studies on vitamin D receptor inhibitors. J. Cell Biochem. 2020, 121, 3570–3583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiffler, M.A.; Antonysamy, S.; Bhattachar, S.N.; Campanale, K.M.; Chandrasekhar, S.; Condon, B.; Desai, P.V.; Fisher, M.J.; Groshong, C.; Harvey, A.; et al. Discovery and Characterization of 2-Acylaminoimidazole Microsomal Prostaglandin E Synthase-1 Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekfeh, S.; Caliskan, B.; Fischer, K.; Yalcin, T.; Garscha, U.; Werz, O.; Banoglu, E. A Multi-step Virtual Screening Protocol for the Identification of Novel Non-acidic Microsomal Prostaglandin E(2) Synthase-1 (mPGES-1) Inhibitors. ChemMedChem 2019, 14, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, S.; Saini, M.; Ojha, H.; Sharma, D.; Sharma, K. Pharmacophore modelling, atom-based 3D-QSAR generation and virtual screening of molecules projected for mPGES-1 inhibitory activity. SAR QSAR Environ. Res. 2017, 28, 17–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauro, G.; Cantone, V.; Potenza, M.; Fischer, K.; Koeberle, A.; Werz, O.; Riccio, R.; Bifulco, G. Discovery of 3-hydroxy-3-pyrrolin-2-one-based mPGES-1 inhibitors using a multi-step virtual screening protocol. Medchemcomm 2018, 9, 2028–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psarra, A.; Nikolaou, A.; Kokotou, M.G.; Limnios, D.; Kokotos, G. Microsomal prostaglandin E(2) synthase-1 inhibitors: A patent review. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2017, 27, 1047–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waltenberger, B.; Wiechmann, K.; Bauer, J.; Markt, P.; Noha, S.M.; Wolber, G.; Rollinger, J.M.; Werz, O.; Schuster, D.; Stuppner, H. Pharmacophore modeling and virtual screening for novel acidic inhibitors of microsomal prostaglandin E(2) synthase-1 (mPGES-1). J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 3163–3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muschelli, J. ROC and AUC with a Binary Predictor: A Potentially Misleading Metric. J. Classif. 2020, 37, 696–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löwer, M.; Proschak, E. Structure-Based Pharmacophores for Virtual Screening. Mol. Inform. 2011, 30, 398–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alogheli, H.; Olanders, G.; Schaal, W.; Brandt, P.; Karlén, A. Docking of Macrocycles: Comparing Rigid and Flexible Docking in Glide. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2017, 57, 190–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bathula, R.; Lanka, G.; Muddagoni, N.; Dasari, M.; Nakkala, S.; Bhargavi, M.; Somadi, G.; Sivan, S.K.; Rajender Potlapally, S. Identification of potential Aurora kinase-C protein inhibitors: An amalgamation of energy minimization, virtual screening, prime MMGBSA and AutoDock. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2020, 38, 2314–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wolf, R.M.; Caldwell, J.W.; Kollman, P.A.; Case, D.A. Development and testing of a general amber force field. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1157–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hornak, V.; Abel, R.; Okur, A.; Strockbine, B.; Roitberg, A.; Simmerling, C. Comparison of multiple Amber force fields and development of improved protein backbone parameters. Proteins 2006, 65, 712–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrach, M.F.; Drossel, B. Structure and dynamics of TIP3P, TIP4P, and TIP5P water near smooth and atomistic walls of different hydroaffinity. J. Chem. Phys. 2014, 140, 174501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, R.; Kumar, R.; Lynn, A. g_mmpbsa--a GROMACS tool for high-throughput MM-PBSA calculations. J. Chem. Inf. Model 2014, 54, 1951–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Ligand | SP Docking Score (kcal/mol) | XP Docking Score (kcal/mol) | MMGBSA_dG_Bind |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4U9 | −3.291 | −0.374 | −49.058 |
| Compound 13295 | −3.355 | −5.806 | −51.275 |
| Compound 14294 | −3.140 | −5.558 | −57.754 |
| Compound 14186 | −3.129 | −5.202 | −49.202 |
| Compound 9838 | −4.184 | −6.185 | −49.225 |
| Compound 15643 | −3.197 | −4.664 | −55.336 |
| Compound 12340 | −3.520 | −4.007 | −55.425 |
| Compound 13836 | −3.404 | −4.696 | −57.291 |
| Compound 13581 | −3.464 | −2.227 | −54.882 |
| Compound 12553 | −3.474 | −3.984 | −50.575 |
| Compound 13106 | −3.782 | −4.692 | −50.208 |
| 4U9 | 15643 | 14186 | 14294 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical formula | C23H11BrCIF4N3 | C21H18O12 | C21H20O10 | C19H14O12 |
| Molecular weight | 520.7 | 462.36 | 432.38 | 434.31 |
| Hydrogen bond acceptors | 6 | 12 | 10 | 12 |
| Hydrogen bond donors | 1 | 5 | 6 | 5 |
| Water solubility (Log S) | −7.82 | −2.95 | −3.18 | −2.25 |
| Lipophilicity (Log P) | 8.76 | 0.46 | 0.38 | −0.04 |
| Gastrointestinal absorption | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| Skin permeation (Log Kp (cm/s)) | −4.5 | −9.03 | −8.33 | −9.1 |
| BBB permeation | NO | NO | NO | NO |
| P-glycoprotein substrate | YES | NO | NO | NO |
| Abbott bioavailability score | 0.17 | 0.55 | 0.55 | 0.55 |
| Toxicity of hepatotoxicity | Active | Inactive | Inactive | Inactive |
| Carcinogenicity | Inactive | Inactive | Inactive | Active |
| Immunotoxicity | Active | Active | Inactive | Active |
| Mutagenicity | Inactive | Active | Inactive | Active |
| Cytotoxicity | Inactive | Inactive | Inactive | Inactive |
| Predicted LD50 (mg/kg) | 2000 | 5000 | 2500 | 1100 |
| Predicted toxicity class | 4 | 5 | 5 | 4 |
| Criteria | Title 2 | Title 3 |
|---|---|---|
| Van der Waal energy (kJ/mol) | −95.966 | −111.088 |
| Electrostatic energy (kJ/mol) | −1.533 | −46.172 |
| Polar solvation energy (kJ/mol) | 40.820 | 101.594 |
| SASA energy (kJ/mol) | −10.706 | −13.171 |
| Binding energy (kJ/mol) | −67.404 | −68.837 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, Q.; Lai, T.; Wang, Q.; Luo, L. mPGES-1 Inhibitor Discovery Based on Computer-Aided Screening: Pharmacophore Models, Molecular Docking, ADMET, and MD Simulations. Molecules 2023, 28, 6059. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28166059
Huang Q, Lai T, Wang Q, Luo L. mPGES-1 Inhibitor Discovery Based on Computer-Aided Screening: Pharmacophore Models, Molecular Docking, ADMET, and MD Simulations. Molecules. 2023; 28(16):6059. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28166059
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Qiqi, Tianli Lai, Qu Wang, and Lianxiang Luo. 2023. "mPGES-1 Inhibitor Discovery Based on Computer-Aided Screening: Pharmacophore Models, Molecular Docking, ADMET, and MD Simulations" Molecules 28, no. 16: 6059. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28166059
APA StyleHuang, Q., Lai, T., Wang, Q., & Luo, L. (2023). mPGES-1 Inhibitor Discovery Based on Computer-Aided Screening: Pharmacophore Models, Molecular Docking, ADMET, and MD Simulations. Molecules, 28(16), 6059. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28166059








