A New Impregnated Adsorbent for Noble Metal Ion Sorption
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
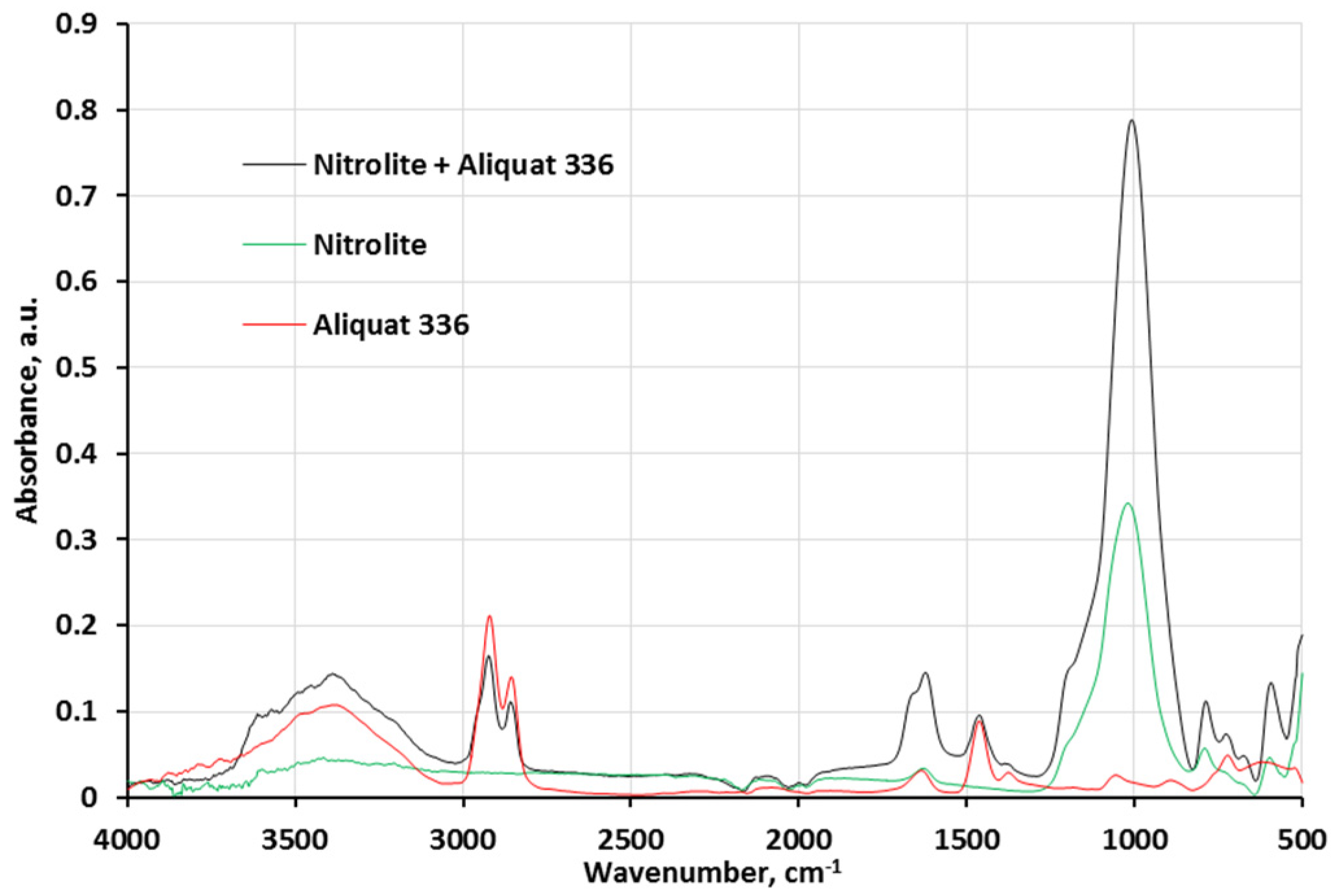
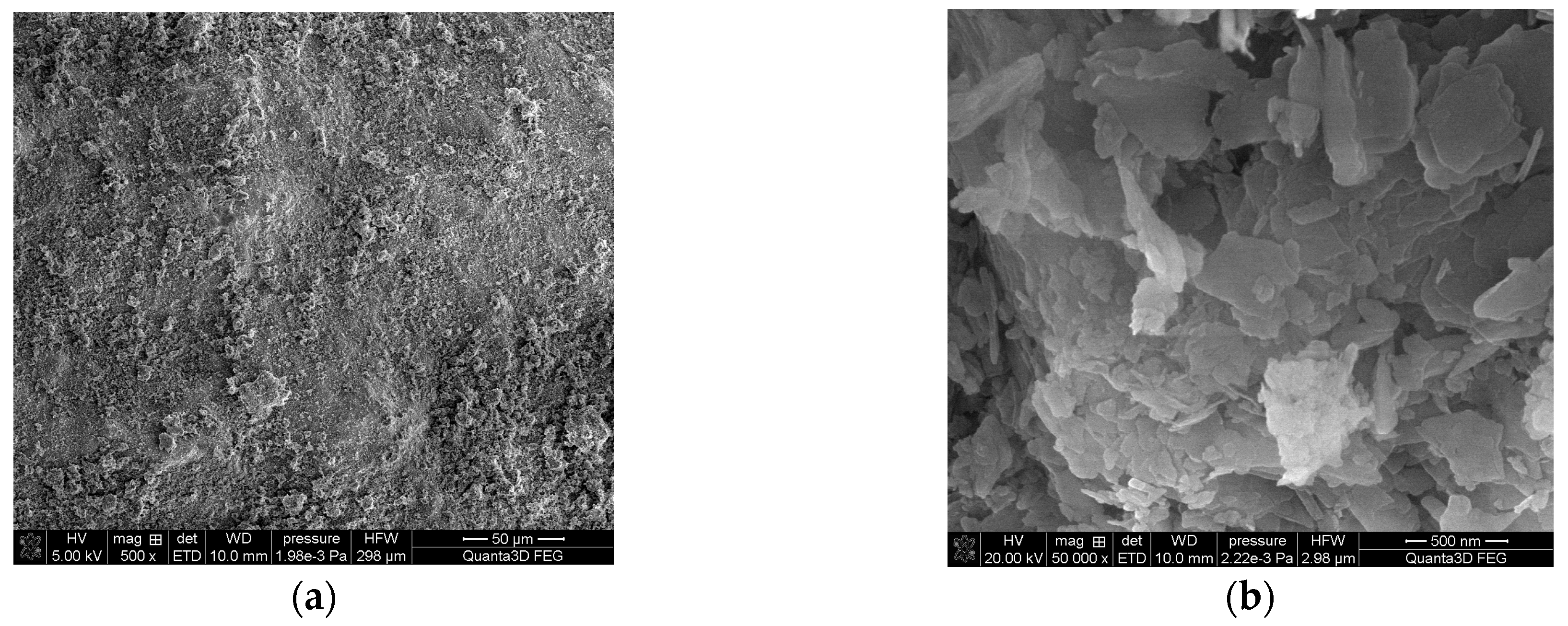
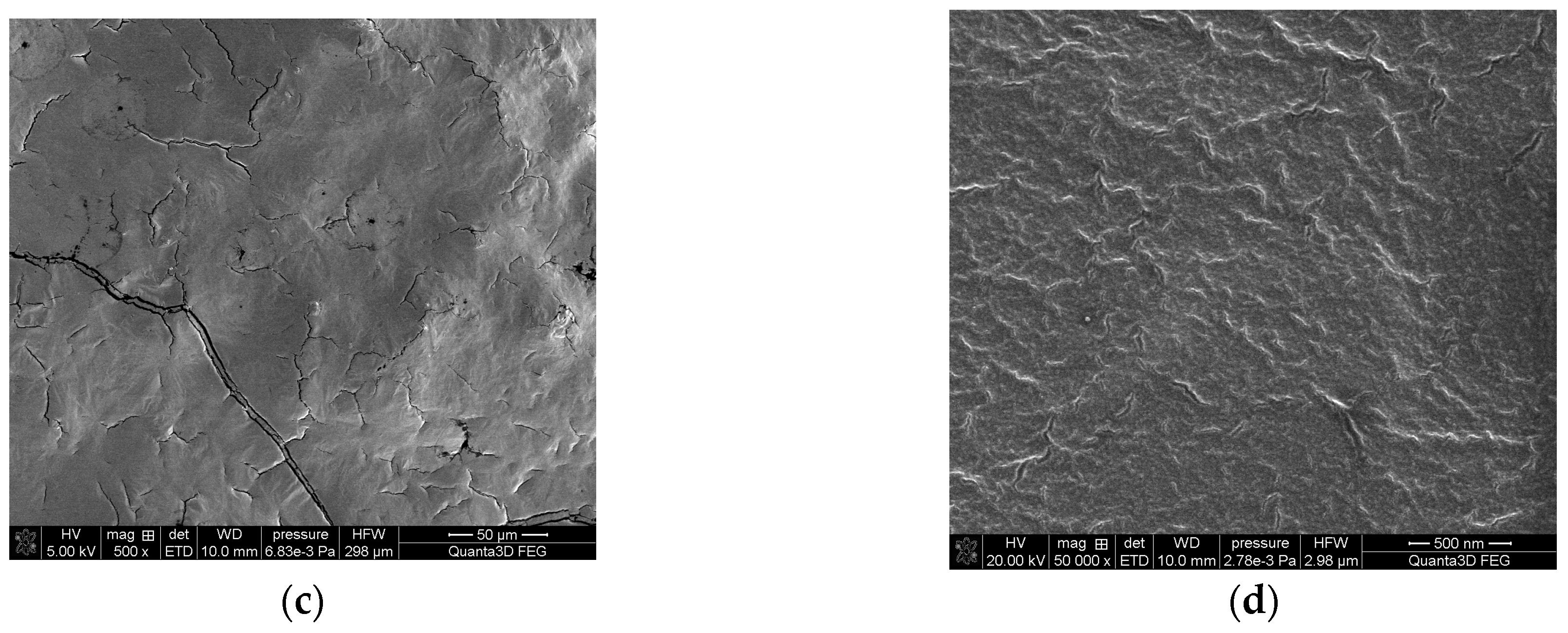
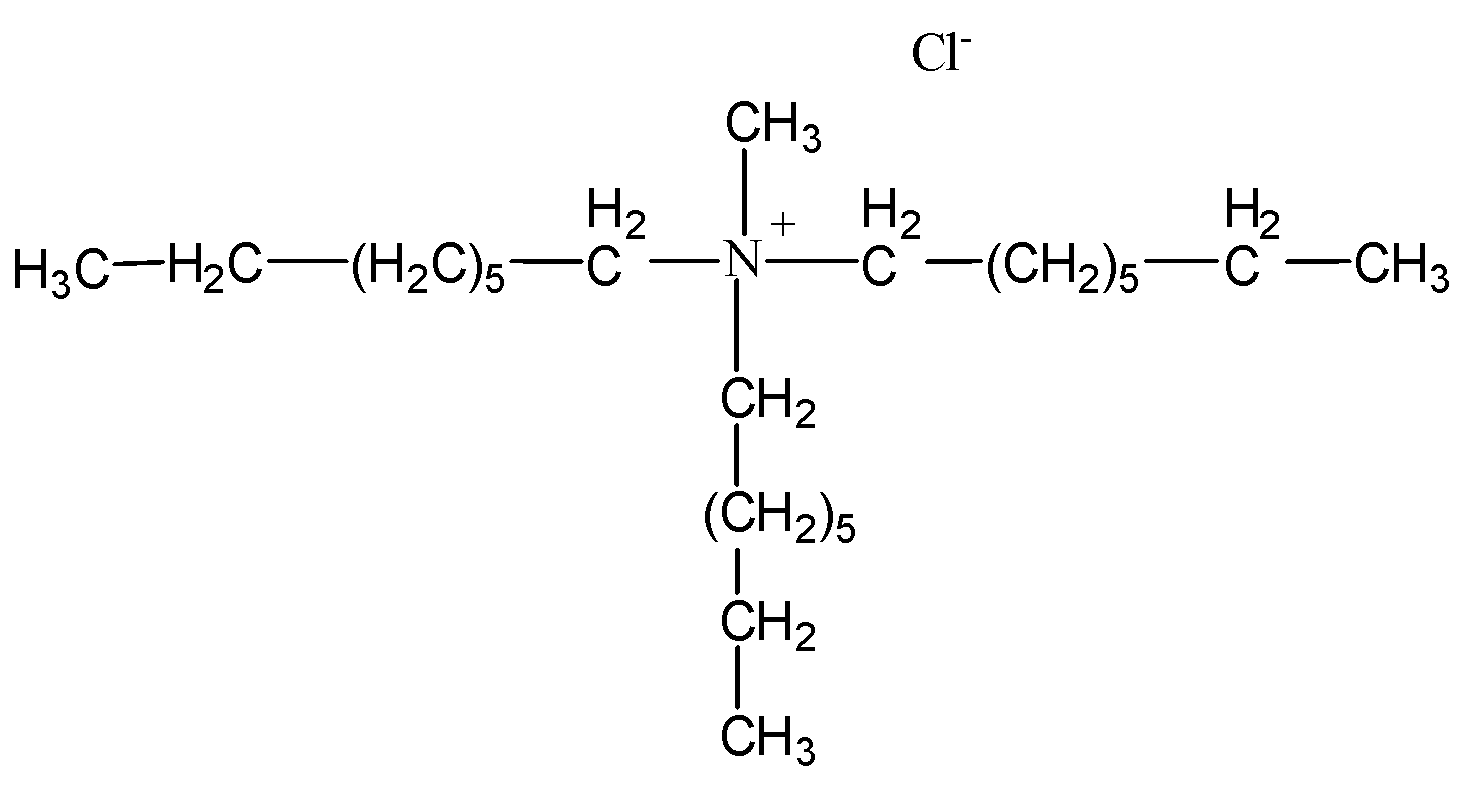
2.1. Preparation of the Impregnated Sorbent Nitrolite–Aliquat 336
Analysis of the Impregnated Sorbent Nitrolite–Aliquat 336
2.2. Kinetics of Noble Metal Ion Sorption on the Impregnated Sorbent Nitrolite–Aliquat 336
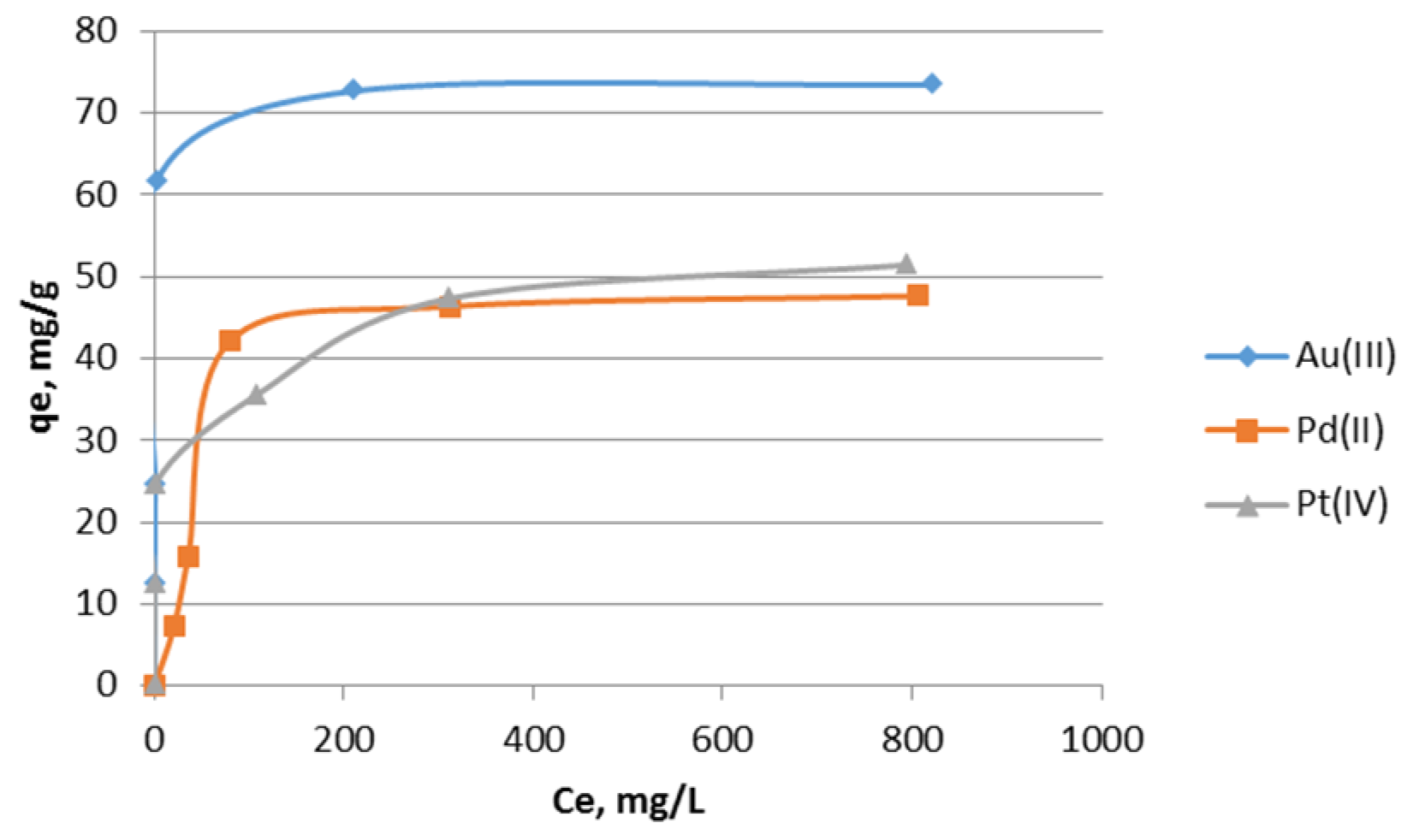
2.3. Isotherms of Noble Metal Ion Sorption on the Impregnated Sorbent Nitrolite–Aliquat 336
2.4. Mechanism of Noble Metal Ion Sorption
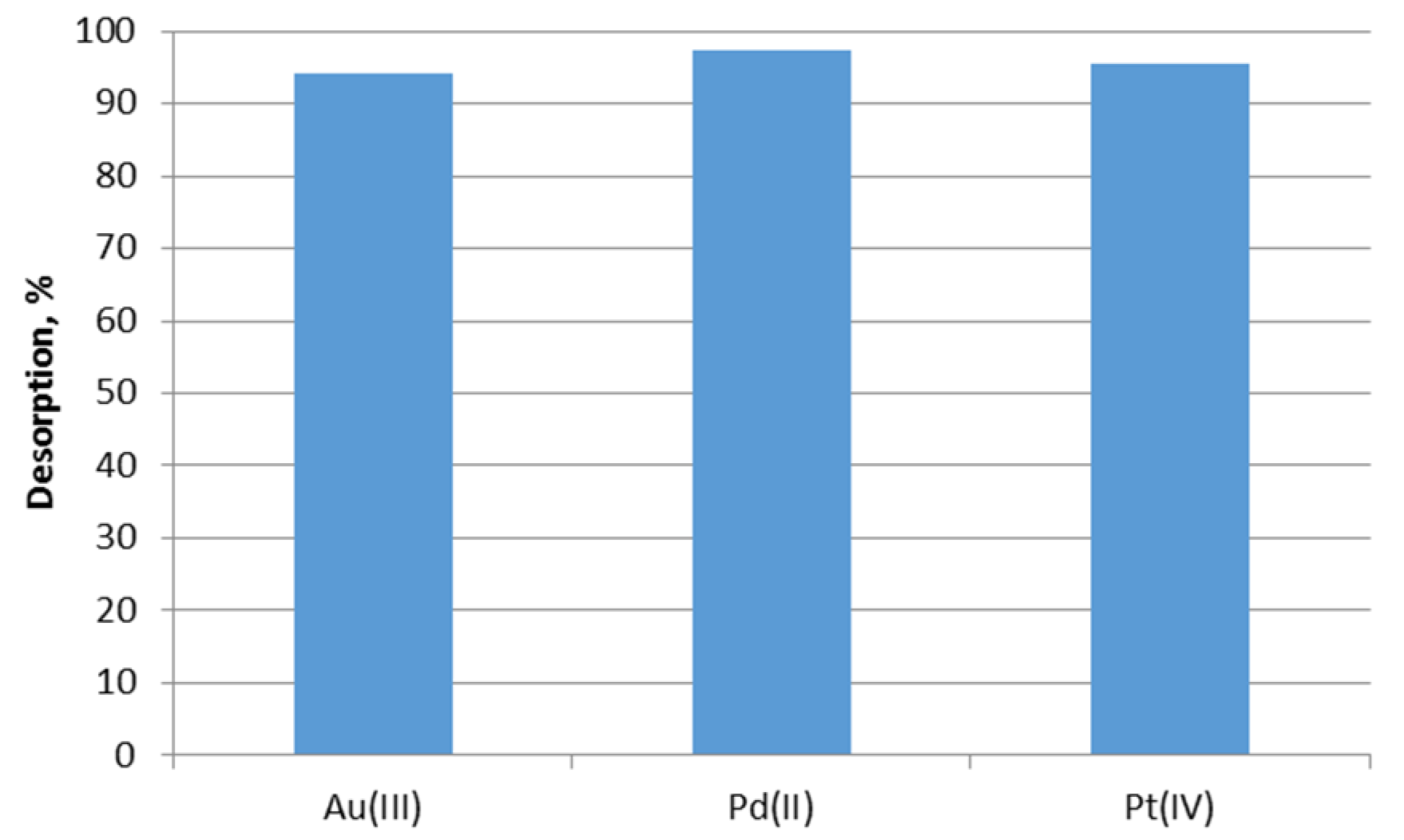
2.5. Desorption
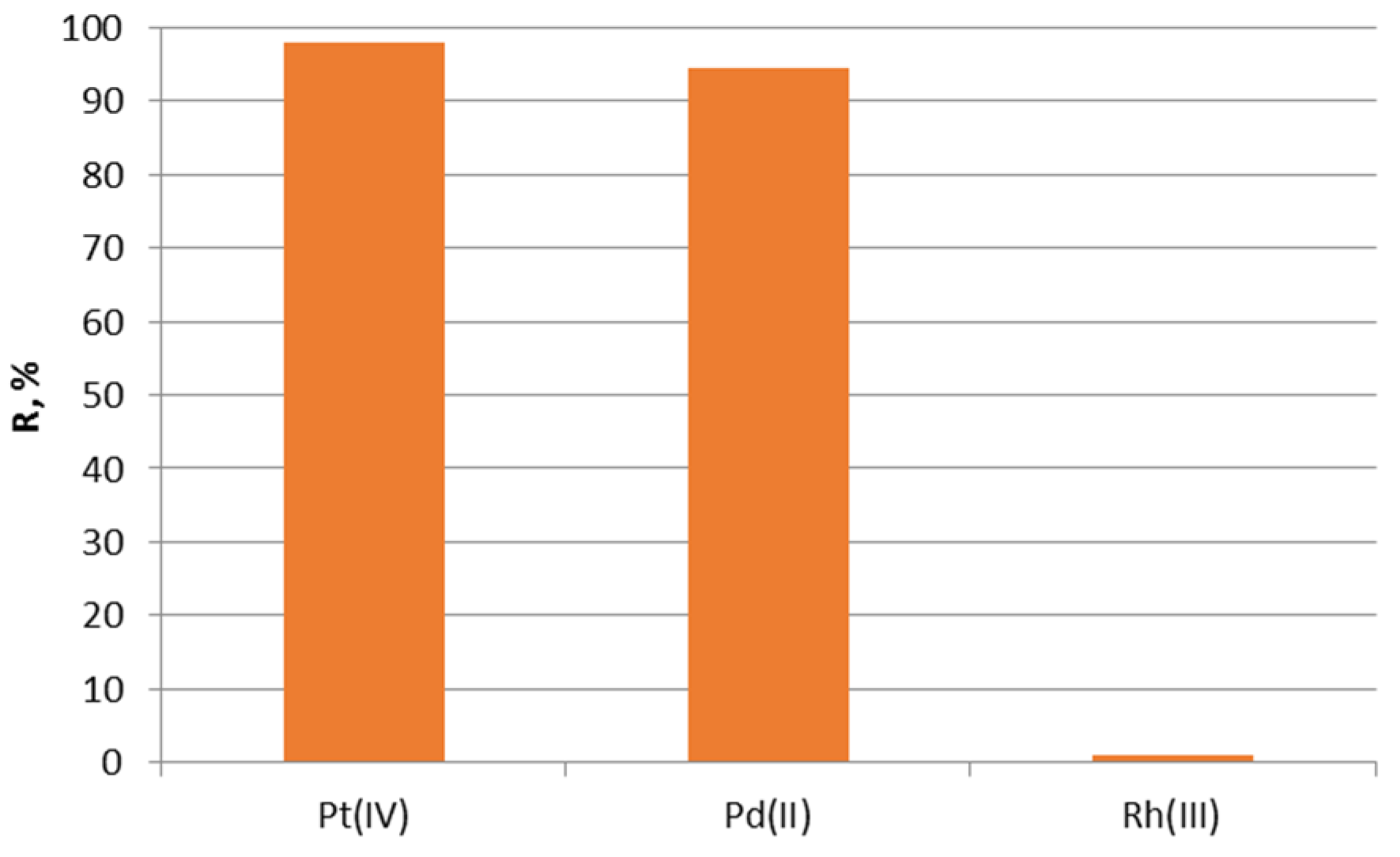
2.6. Recovery of Noble Metals from the Exhausted Catalytic Converter
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Instrumentation
3.3. Methods
3.3.1. Nitrolite Impregnation Procedure
3.3.2. Determination of Aliquat 336 Concentration in Nitrolite
3.3.3. Kinetic Studies
3.3.4. Isotherm Studies
3.3.5. Catalytic Converter Digestion and Sorption Platinum Metals
3.3.6. Desorption Studies
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Vlachou, M.C.; Marchbank, H.R.; Brooke, E.; Kolpin, A. Challenges and Opportunities for Platinum in the Modern Three-Way Catalyst: Flexibility and performance in gasoline emissions control. Johns. Matthey Technol. Rev. 2023, 67, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellissier, H. Recent Developments in Enantioselective Domino Reactions. Part A: Noble Metal Catalysts. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2023, 365, 620–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuiyan, R.A.; Husain, A.; Zhang, C. Diversification evidence of bitcoin and gold from wavelet analysis. Financ. Innov. 2023, 9, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimura, A.; Matsuno, Y. The improvement of platinum recovery ratio in the recycling process using “dry aqua regia”. Mater. Trans. 2019, 60, 2223–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousif, A.M. Recovery and then individual separation of platinum, palladium, and rhodium from spent car catalytic converters using hydrometallurgical technique followed by successive precipitation methods. J. Chem. 2019, 2019, 2318157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, D.; Chen, L. Gold cementation from thiocyanate solutions by iron powder. Miner. Eng. 2007, 20, 581–590. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, W.D.; Lee, M.S. A process for the separation of noble metals from HCL liquor containing gold(III), palladium(II), platinum(IV), rhodium(III), and iridium(IV) by solvent extraction. Processes 2019, 7, 18–20. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.H.; Lee, M.S. Effect of HCl concentration on the oxidation of LIX 63 and the subsequent separation of Pd(II), Pt(IV), Ir(IV) and Rh(III) by solvent extraction. J. Korean Inst. Met. Mater. 2016, 54, 768–774. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, P.P.; Lee, J.Y.; Lee, M.S. Separation of Pt(IV) and Rh(III) from Chloride Solution by Solvent Extraction with Amine and Neutral Extractants. Mater. Trans. 2011, 52, 2071–2076. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, B.; Singh, I.; Mahandra, H. Extraction and separation studies on Pt(IV), Ir(III) and Rh(III) using sulphur containing extractant. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 132, 102–109. [Google Scholar]
- Swain, B.; Jeong, J.; Kim, S.; Lee, J. Separation of platinum and palladium from chloride solution by solvent extraction using Alamine 300. Hydrometallurgy 2010, 104, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, H.; Nishihama, S.; Yoshizuka, K. Separation and recovery of gold from waste LED using ion exchange method. Hydrometallurgy 2015, 157, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikoloski, A.N.; Ang, K.-L.; Li, D. Recovery of platinum, palladium and rhodium from acidic chloride leach solution using ion exchange resins. Hydrometallurgy 2015, 152, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabay, N.; Cortina, J.L.; Trochimczuk, A.; Streat, M. Solvent-impregnated resins (SIRs)—Methods of preparation and their applications. React. Funct. Polym. 2010, 70, 484–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamang, A.M.; Singh, N.; Chandraker, S.K.; Ghosh, M.K. Solvent impregnated resin a potential alternative material for separation dyes, metal and phenolic compounds: A review. Curr. Res. Green Sustain. Chem. 2022, 5, 100232. [Google Scholar]
- Wójcik, G.; Górska-Parat, M.; Hubicki, Z.; Zinkowska, K. Selective Recovery of Gold from Electronic Waste by New Efficient Type of Sorbent. Materials 2023, 16, 924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trochimczuk, A.W.; Kabay, N.; Arda, M.; Streat, M. Stabilization of solvent impregnated resins (SIRs) by coating with water soluble polymers and chemical crosslinking. React. Funct. Polym. 2004, 59, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Dessouky, S.I.; Borai, E.H. Extraction chromatography of thorium ion by solid phase impregnated resins containing bi-functional organic extractants. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2006, 268, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deferm, C.; Van De Voorde, M.; Luyten, J.; Oosterhof, H.; Fransaer, J.; Binnemans, K. Purification of indium by solvent extraction with undiluted ionic liquids. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 4116–4127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wójcik, G. Sorption behaviors of light lanthanides(III) (La(III), Ce(III), Pr(III), Nd(III)) and Cr(III) using nitrolite. Materials 2020, 13, 2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani Ravandi, M.; Fat’Hi, M.R. Green effervescence assisted dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction based on a hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent for determination of Sunset Yellow and Brilliant Blue FCF in food samples. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 14901–14908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, L.Y.; Morad, N.; Ismail, N.; Talebi, A.; Rafatullah, M. Optimization for liquid-liquid extraction of cd(Ii) over cu(ii) ions from aqueous solutions using ionic liquid aliquat 336 with tributyl phosphate. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, L.; Xu, Q.; Wu, H. Synthesis of Zeolite-like Material by Hydrothermal and Fusion Methods Using Municipal Solid Waste Fly Ash. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2016, 31, 662–667. [Google Scholar]
- Hubicki, Z.; Leszczyńska, M. Studies of sorption of Pd(II) microquantities on strongly basic polyacrylate anion exchangers. Desalination 2005, 175, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buriac, O.; Ciopec, M.; Duţeanu, N.; Negrea, A.; Negrea, P.; Grozav, I. Platinum (IV) recovery from waste solutions by adsorption onto Dibenzo-30-crown-10 ether immobilized on amberlite XAD7 resin-factorial design analysis. Molecules 2020, 25, 3692. [Google Scholar]
- Awual, M.R.; Khaleque, M.A.; Ratna, Y.; Znad, H. Simultaneous ultra-trace palladium(II) detection and recovery from wastewater using new class meso-adsorbent. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 21, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awual, M.R.; Hasan, M.M.; Znad, H. Organic–inorganic based nano-conjugate adsorbent for selective palladium(II) detection, separation and recovery. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 259, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awual, M.R. Investigation of potential conjugate adsorbent for efficient ultra-trace gold(III) detection and recovery. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 3493–3501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Ning, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Dong, H.; Chen, L.; Yin, X.; Fujita, T.; Wei, Y. Precise separation and efficient enrichment of palladium from wastewater by amino-functionalized silica adsorbent. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 396, 136479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, S.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Wei, Y. Separation and recovery of Rh, Ru and Pd from nitrate solution with a silica-based IsoBu-BTP/SiO2-P adsorbent. Hydrometallurgy 2020, 191, 105207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.; Nishihama, S.; Yoshizuka, K. Recovery of Platinum and Palladium from Spent Automobile Catalyst by Solvent-Impregnated Resins. Solvent Extr. Ion Exch. 2018, 36, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, A.E.; Haque, N.; Northey, S.A.; Giddey, S. Platinum group metals: A review of resources, production and usage with a focus on catalysts. Resources 2021, 10, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| PFO | PSO 1 | ||||||
| Metal Ions | HCl (M) | k1 (1/min) | qe (mg/g) | R2 | k2 (g/mg‧min) | qe (mg/g) | R2 |
| Au(III) | 0.1 | 0.0033 | 0.9528 | 0.8765 | 0.0207 | 2.5054 | 0.9996 |
| Pd(II) | 0.1 | 0.0039 | 0.5295 | 0.5750 | 0.0064 | 2.6203 | 0.9819 |
| Pt(IV) | 0.1 | 0.0023 | 1.0949 | 0.5442 | 0.0079 | 2.5284 | 0.9938 |
| Au(III) | 1 | 0.0024 | 1.2661 | 0.7178 | 0.0144 | 2.4434 | 0.9994 |
| Pd(II) | 1 | 0.0035 | 2.4076 | 0.8363 | 0.0040 | 2.6495 | 0.9909 |
| Pt(IV) | 1 | 0.0036 | 2.8527 | 0.9548 | 0.0070 | 2.4216 | 0.9977 |
| Au(III) | 3 | 0.0033 | 2.0438 | 0.8742 | 0.0063 | 2.4534 | 0.9978 |
| Pd(II) | 3 | 0.0030 | 1.6086 | 0.8062 | 0.0021 | 2.3283 | 0.9473 |
| Pt(IV) | 3 | 0.0029 | 1.9874 | 0.7645 | 0.0042 | 2.4534 | 0.9941 |
| Au(III) | 6 | 0.0042 | 2.6528 | 0.9452 | 0.0068 | 2.4704 | 0.9981 |
| Pd(II) | 6 | 0.0030 | 0.0636 | 0.7531 | 0.0123 | 0.5878 | 0.9615 |
| Pt(IV) | 6 | 0.0028 | 1.3925 | 0.7834 | 0.0041 | 2.3656 | 0.9699 |
| Elovich | Intra-Particle Diffusion | ||||||
| Metal Ions | HCl (M) | α (g/mg‧min) | β (mg/g) | R2 | K (mg/g‧min0.5) | C (mg/g) | R2 |
| Au(III) | 0.1 | 1.0062 | 3.0774 | 0.9076 | 0.0515 | 1.0461 | 0.6029 |
| Pd(II) | 0.1 | 0.3138 | 2.3182 | 0.8721 | 0.0687 | 0.6597 | 0.5852 |
| Pt(IV) | 0.1 | 0.3749 | 2.6850 | 0.7980 | 0.0646 | 0.6428 | 0.6352 |
| Au(III) | 1 | 0.4582 | 2.8257 | 0.9348 | 0.0590 | 0.7419 | 0.6866 |
| Pd(II) | 1 | 0.1960 | 2.3831 | 0.8754 | 0.0744 | 0.3298 | 0.7270 |
| Pt(IV) | 1 | 0.2605 | 2.8944 | 0.9041 | 0.0630 | 0.4356 | 0.7960 |
| Au(III) | 3 | 0.2276 | 2.5724 | 0.9099 | 0.0668 | 0.4287 | 0.7108 |
| Pd(II) | 3 | 0.1548 | 3.0073 | 0.8785 | 0.0600 | 0.2327 | 0.7554 |
| Pt(IV) | 3 | 0.1808 | 2.6212 | 0.8713 | 0.0686 | 0.2877 | 0.7454 |
| Au(III) | 6 | 0.2441 | 2.6497 | 0.9133 | 0.0662 | 0.4441 | 0.7423 |
| Pd(II) | 6 | 0.0540 | 11.167 | 0.8911 | 0.0158 | 0.0710 | 0.7340 |
| Pt(IV) | 6 | 0.2104 | 2.6606 | 0.8987 | 0.0631 | 0.4088 | 0.6704 |
| Metal Ions | Langmuir | Freundlich | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q0 | b | RL | R2 | Kf | n | R2 | |
| Au(III) | 73.49 | 0.9229 | 0.0021 | 0.9999 | 26.25 | 5.40 | 0.6886 |
| Pd(II) | 51.27 | 0.0187 | 0.0966 | 0.9784 | 2.75 | 2.11 | 0.7285 |
| Pt(IV) | 51.59 | 0.0735 | 0.0264 | 0.9957 | 19.76 | 6.92 | 0.8890 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Power (kW) | 1 |
| Plasma flow (L/min) | 15 |
| Auxiliary flow (L/min) | 1.5 |
| Nebulizer flow (L/min) | 0.75 |
| Replicate read time (s) | 1 |
| Instrument stabilization delay (s) | 15 |
| Sample uptake delay (s) | 15 |
| Pump rate (r.p.m) | 15 |
| Rinse time (s) | 15 |
| Au (nm) | 242.794 |
| Pd (nm) | 340.458 |
| Pt (nm) | 214.424 |
| Rh (nm) | 343.488 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hubicki, Z.; Zinkowska, K.; Wójcik, G. A New Impregnated Adsorbent for Noble Metal Ion Sorption. Molecules 2023, 28, 6040. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28166040
Hubicki Z, Zinkowska K, Wójcik G. A New Impregnated Adsorbent for Noble Metal Ion Sorption. Molecules. 2023; 28(16):6040. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28166040
Chicago/Turabian StyleHubicki, Zbigniew, Karolina Zinkowska, and Grzegorz Wójcik. 2023. "A New Impregnated Adsorbent for Noble Metal Ion Sorption" Molecules 28, no. 16: 6040. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28166040
APA StyleHubicki, Z., Zinkowska, K., & Wójcik, G. (2023). A New Impregnated Adsorbent for Noble Metal Ion Sorption. Molecules, 28(16), 6040. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28166040






