Deep Eutectic Solvents Formed by Glycerol and Xylitol, Fructose and Sorbitol: Effect of the Different Sugars in Their Physicochemical Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
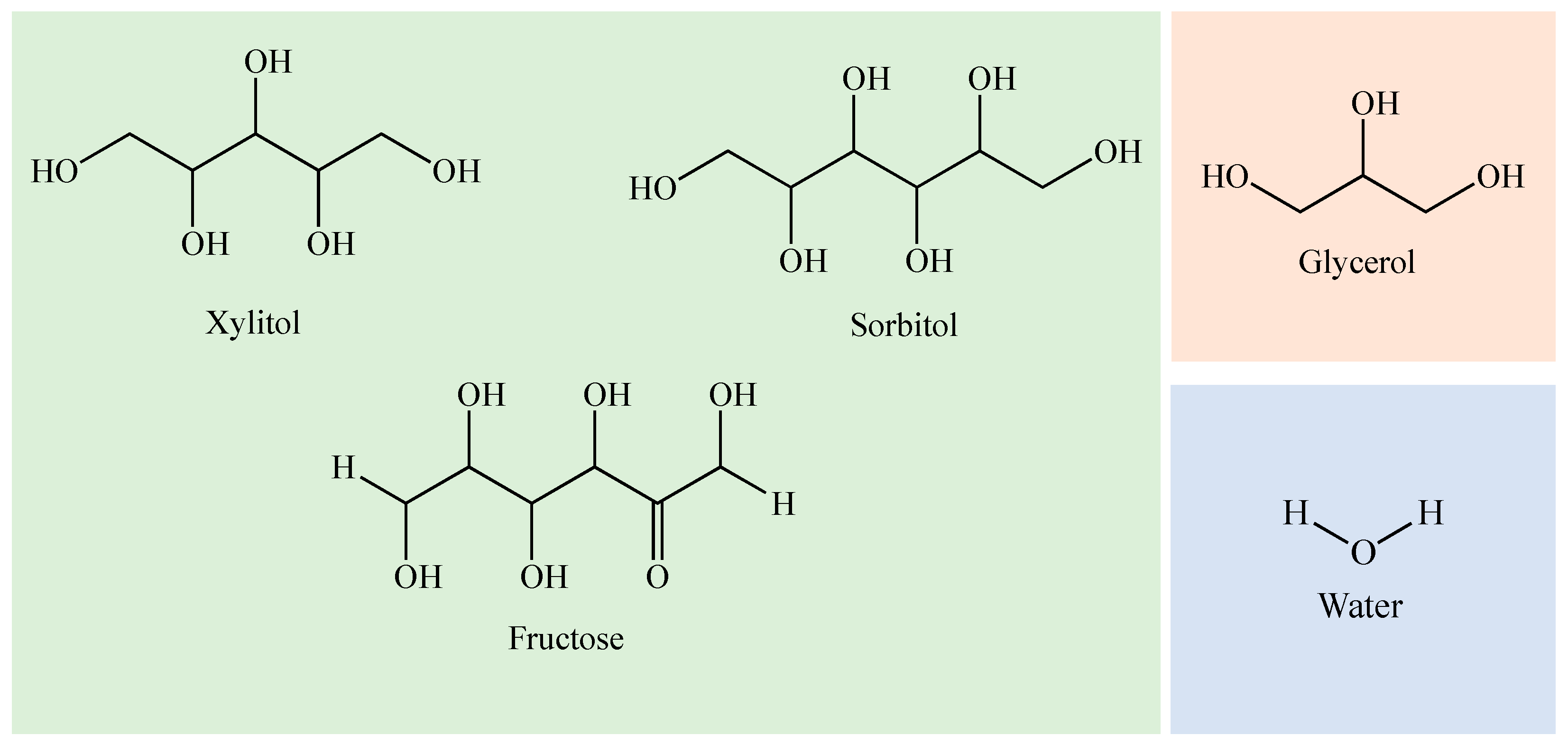
2.1. Preparation of DES
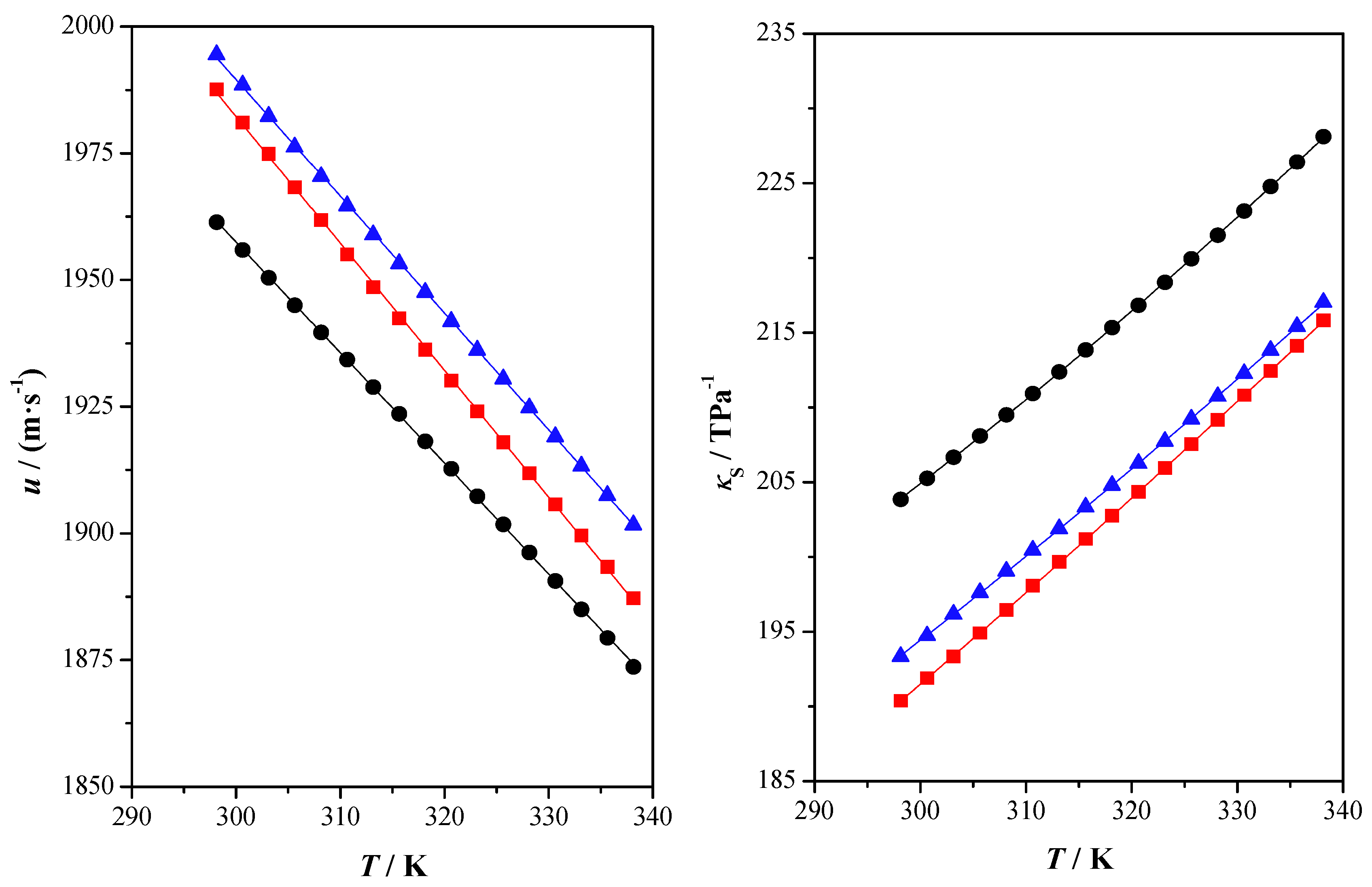
2.2. Thermophysical Properties
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. Preparation of Deep Eutectic Solvents
3.3. Thermophysical Properties
3.4. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Biernacki, K.; Souza, H.K.S.; Almeida, C.M.R.; Magalhaes, A.L.; Goncalves, M.P. Physicochemical Properties of Choline Chloride-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents with Polyols: An Experimental and Theoretical Investigation. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 18712–18728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, C.J.; Tu, W.C.; Levers, O.; Brohl, A.; Hallett, J.P. Green and Sustainable Solvents in Chemical Processes. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 747–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, A.P.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Rasheed, R.K.; Tambyrajah, V. Novel solvent properties of choline chloride/urea mixtures. Chem. Commun. 2003, 39, 70–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atilhan, M.; Costa, L.T.; Aparicio, S. On the behaviour of aqueous solutions of deep eutectic solvents at lipid biomembranes. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 247, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florindo, C.; Branco, L.C.; Marrucho, I.M. Quest for Green-Solvent Design: From Hydrophilic to Hydrophobic (Deep) Eutectic Solvents. Chemsuschem 2019, 12, 1549–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z. Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents and Their Applications in Biotechnology. Appl. Ion. Liq. Biotechnol. 2019, 168, 31–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huerta Ochoa, S.; Castillo Araiza, C.O.; Quijano, G. Advances and Applications of Partitioning Bioreactors. Adv. Appl. Partit. Bioreact. 2019, 54, 1–371. [Google Scholar]
- Sekharan, T.R.; Chandira, R.M.; Tamilvanan, S.; Rajesh, S.C.; Venkateswarlu, B.S. Deep Eutectic Solvents as an Alternate to Other Harmful Solvents. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2022, 12, 847–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzetti, A.S.; Fiego, M.J.L.; Silva, M.F.; Domini, C.; Gomez, F.J.V. Water behavior study for tailoring fructose-citric acid based natural deep eutectic solvent properties towards antibiotics solubilization. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 363, 119917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obluchinskaya, E.D.; Pozharitskaya, O.N.; Shevyrin, V.A.; Kovaleva, E.G.; Flisyuk, E.V.; Shikov, A.N. Optimization of Extraction of Phlorotannins from the Arctic Fucus vesiculosus Using Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents and Their HPLC Profiling with Tandem High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, P.S.; Singh, P.P.; Kapoor, S.; Padwad, Y.S.; Sharma, U.; Anmol, U. Lactic acid-based deep eutectic solvent: An efficient green media for the selective extraction of steroidal saponins from Trillium govanianum. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 294, 121105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrochenko, A.A.; Orlova, A.; Frolova, N.; Serebryakov, E.B.; Soboleva, A.; Flisyuk, E.V.; Frolov, A.; Shikov, A.N. Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents for the Extraction of Triterpene Saponins from Aralia elata var. mandshurica (Rupr. & Maxim.) J. Wen. Molecules 2023, 28, 3614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Li, Q. Study on extraction and antioxidant activity of polysaccharides from Radix Bupleuri by natural deep eutectic solvents combined with ultrasound-assisted enzymolysis. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2022, 30, 100877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Wang, D.; Belwal, T.; Xie, J.; Xu, Y.; Li, L.; Zou, L.; Zhang, L.; Luo, Z. Natural deep eutectic solvent enhanced pulse-ultrasonication assisted extraction as a multi-stability protective and efficient green strategy to extract anthocyanin from blueberry pomace. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 144, 111220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shikov, A.N.; Kosman, V.M.; Flissyuk, E.V.; Smekhova, I.E.; Elameen, A.; Pozharitskaya, O.N. Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents for the Extraction of Phenyletanes and Phenylpropanoids of Rhodiola rosea L. Molecules 2020, 25, 1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Doert, T.; Wang, H.; Zhang, S.J.; Ruck, M. Inorganic Synthesis Based on Reactions of Ionic Liquids and Deep Eutectic Solvents. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 22148–22165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devi, T.J.; Singh, T.P.; Singh, O.M. The one-pot four-component eco-friendly synthesis of spirooxindoles in deep eutectic solvent. J. Chem. Sci. 2020, 132, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrone, S.; Messa, F.; Troisi, L.; Salomone, A. N-, O- and S-Heterocycles Synthesis in Deep Eutectic Solvents. Molecules 2023, 28, 3459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.T.; Pei, D.; Yu, P.L.; Wei, J.T.; Wang, N.L.; Di, D.L.; Liu, Y.W. Aqueous two-phase systems based on deep eutectic solvents and their application in green separation processes. J. Sep. Sci. 2020, 43, 348–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghobadi, R.; Divsalar, A. Enzymatic behavior of bovine liver catalase in aqueous medium of sugar based deep eutectic solvents. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 310, 113207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taklimi, S.M.; Divsalar, A.; Ghalandari, B.; Ding, X.T.; Di Gioia, M.L.; Omar, K.A.; Saboury, A.A. Effects of deep eutectic solvents on the activity and stability of enzymes. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 377, 121562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svigelj, R.; Dossi, N.; Grazioli, C.; Toniolo, R. Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) and Their Application in Biosensor Development. Sensors 2021, 21, 4263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.M.; Li, M.R.; Garg, S.; Wu, Y.M.; Idros, M.N.; Hocking, R.; Duan, H.R.; Gao, S.; Yago, A.J.; Zhuang, L.Z.; et al. Cobalt Electrochemical Recovery from Lithium Cobalt Oxides in Deep Eutectic Choline Chloride plus Urea Solvents. Chemsuschem 2021, 14, 2972–2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayyan, A.; Mjalli, F.S.; AlNashef, I.M.; Al-Wahaibi, T.; Al-Wahaibi, Y.M.; Hashim, M.A. Fruit sugar-based deep eutectic solvents and their physical properties. Thermochim. Acta 2012, 541, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomba, L.; Polo, A.; Alejandre, J.; Martinez, N.; Giner, B. Solubility enhancement of caffeine and furosemide using deep eutectic solvents formed by choline chloride and xylitol, citric acid, sorbitol or glucose. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 79, 104010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomba, L.; Garralaga, M.P.; Werner, A.; Giner, B.; Baptista, P.M.; Sánchez-Romero, N. Ibuprofen solubility and cytotoxic study of deep eutectic solvents formed by xylitol, choline chloride and water. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 82, 104327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, M.; Hassan, P.A.; Shelar, S.B. Modulation of surfactant self-assembly in deep eutectic solvents and its relevance to drug delivery—A review. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 375, 121301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araki, Y.; Hamada, Y.; Imamura, N.; Yamasaka, K.; Sakuragi, M. Evaluation of terpene-based hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents as skin permeation enhancers. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2023, 62, 15003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, F.; Leitao, M.I.P.S.; Duarte, A.R.C. Properties of Therapeutic Deep Eutectic Solvents of L-Arginine and Ethambutol for Tuberculosis Treatment. Molecules 2019, 24, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, J.; Mandal, A.; Dhawan, S.; Shevachman, M.; Mitragotri, S.; Joshi, N. Clinical translation of choline and geranic acid deep eutectic solvent. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2021, 6, e10191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, X.Y.L.; Liu, Y.Y.; Wu, K.J.; Zhu, Y.M.; Lu, H.F.; Liang, B. Insights into the relationships between physicochemical properties, solvent performance, and applications of deep eutectic solvents. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 35537–35563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogel, D.H. Das Temperaturabhaengigkeitsgesetz der Viskositaet von Fluessigkeiten. Phys. Z. 1921, 22, 645–646. [Google Scholar]
- Fulcher, G.S. Analysis of recent measurements of the viscosity of glasses. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1925, 8, 339–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tammann, G.W.H. Die Abhängigkeit der Viscosität von der Temperatur bie unterkühlten Flüssigkeiten. Z. Für Anorg. Und Allg. Chem. 1926, 156, 254–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, M.M.; Cardeira, M.; Matias, A.A.; Bronze, M.R.; Fernandez, N. Lactic Acid-Based Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents to Extract Bioactives from Marine By-Products. Molecules 2022, 27, 4356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovacs, S.; Hawes, S.E.; Maley, S.N.; Mosites, E.; Wong, L.; Stergachis, A. Technologies for Detecting Falsified and Substandard Drugs in Low and Middle-Income Countries. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, G.; Aparicio, S.; Ullah, R.; Atilhan, M. Deep Eutectic Solvents: Physicochemical Properties and Gas Separation Applications. Energy Fuels 2015, 29, 2616–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Walvekar, R.; Khalid, M.; Wong, W.Y.; Gupta, T. Thermophysical properties of glycerol and polyethylene glycol (PEG 600) based DES. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 252, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapena, D.; Lomba, L.; Artal, M.; Lafuente, C.; Giner, B. The NADES glyceline as a potential Green Solvent: A comprehensive study of its thermophysical properties and effect of water inclusion. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2019, 128, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Achkar, T.; Greige-Gerges, H.; Fourmentin, S. Basics and properties of deep eutectic solvents: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 3397–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starodubtsev, Y.N.; Tsepelev, V.S. Isobaric Thermal Expansivity and Isothermal Compressibility of Liquid Metals. Materials 2023, 16, 3801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafari, K.; Fatemi, M.H.; Lugo, L. An experimental study of novel nanofluids based on deep eutectic solvents (DESs) by Choline chloride and ethylene glycol. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 360, 119521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leron, R.B.; Wong, D.S.H.; Li, M.H. Densities of a deep eutectic solvent based on choline chloride and glycerol and its aqueous mixtures at elevated pressures. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2012, 335, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, S.; Kato, E.; Drennen, J.K.; Anderson, C.A. Refractive Index Measurement of Pharmaceutical Solids: A Review of Measurement Methods and Pharmaceutical Applications. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 108, 3478–3495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Sanea, M.M.; Gamal, M. Critical analytical review: Rare and recent applications of refractive index detector in HPLC chromatographic drug analysis. Microchem. J. 2022, 178, 107339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S. Studies on the Interactions of Paracetamol in Water and Binary Solvent Mixtures at T = (298.15-313.15) K: Viscometric and Surface Tension Approach. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2022, 12, 2776–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayyan, A.; Mjalli, F.S.; AlNashef, I.M.; Al-Wahaibi, Y.M.; Al-Wahaibi, T.; Hashim, M.A. Glucose-based deep eutectic solvents: Physical properties. J. Mol. Liq. 2013, 178, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyrovedin, H.; Haghbakhsh, R.; Duarte, A.R.C.; Raeissi, S. A Global Model for the Estimation of Speeds of Sound in Deep Eutectic Solvents. Molecules 2020, 25, 1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraro, C.F. Organic solvents: Physical properties and methods of purification. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1956, 61, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadhom, M.A.; Abdullah, G.H.; Al-Bayati, N. Studying Two Series of Ternary Deep Eutectic Solvents (Choline Chloride-Urea-Glycerol) and (Choline Chloride-Malic Acid-Glycerol), Synthesis and Characterizations. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2017, 42, 1579–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oroian, M.; Ropciuc, S.; Amariei, S.; Gutt, G. Correlations between density, viscosity, surface tension and ultrasonic velocity of different mono- and di-saccharides. J. Mol. Liq. 2015, 207, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wazeer, I.; Hizaddin, H.F.; Hashim, M.A.; Hadj-Kali, M.K. An overview about the extraction of heavy metals and other critical pollutants from contaminated water via hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majova, V.; Jablonsky, M.; Lelovsky, M. Delignification of unbleached pulp by ternary deep eutectic solvents. Green Process. Synth. 2021, 10, 666–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabi, M.; Ghassab, N.; Hemmati, M.; Asghari, A. Emulsification microextraction of amphetamine and methamphetamine in complex matrices using an up-to-date generation of eco-friendly and relatively hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1576, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngasotter, S.; Sampath, L.; Xavier, K.A.M. Nanochitin: An update review on advances in preparation methods and food applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 291, 119627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faraji, S.; Shekaari, H.; Zafarani-Moattar, M.T.; Mokhtarpour, M. Experimental studies on thermophysical properties of protic ionic liquids for thermal energy storage systems. J. Energy Storage 2022, 54, 105251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, L.; Zhang, X.J.; Luo, Z.M.; Saboori, T.; Dehghan, M.; Ghasemizadeh, M.; Karimi-Maleh, H.; Alagumalai, A.; Mahian, O. An overview of the applications of ionic fluids and deep eutectic solvents enhanced by nanoparticles. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2022, 147, 7589–7601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walvekar, R.; Singh, A.; Khalid, M.; Gupta, T.; Yin, W.W. Thermophysical properties of deep eutectic solvent-carbon nanotubes (DES-CNT) based nanolubricant. J. Therm. Eng. 2020, 6, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.G.; Ji, R.J.; Liu, Y.H.; Zhang, F.; Jin, H.; Li, X.F.; Zheng, Q.; Lu, S.C.; Cai, B.P. Effects of boric acid and water on the deposition of Ni/TiO2 composite coatings from deep eutectic solvent. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 409, 126834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Property | A | B | C | Syx |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xylitol: glycerol: water (1:2:3) | ||||
| ρ/(kg·m−3) | −0.6488 | 1468.51 | 0.182 | |
| u/(m·s−1) | −2.184 | 2612.57 | 0.291 | |
| nD | −0.000248 | 1.540010 | 10 × 10−5 | |
| σ/(mN·m−1) | −0.2159 | 120.47 | 0.115 | |
| Cp,m/(J·mol−1·K−1) | 0.303 | 64.4 | 0.097 | |
| η a/(mPa·s) | 0.00678 | 1424.4 | 164.87 | 4.884 |
| Fructose: glycerol: water (1:2:3) | ||||
| ρ/(kg·m−3) | −0.7056 | 1539.80 | 0.251 | |
| u/(m·s−1) | −2.505 | 2733.67 | 0.481 | |
| nD | −0.000273 | 1.559727 | 13 × 10−5 | |
| σ/(mN·m−1) | −0.2436 | 130.01 | 0.187 | |
| Cp,m/(J·mol−1·K−1) | 0.462 | 21.9 | 0.126 | |
| η a/(mPa·s) | 0.00033 | 2332.3 | 139.53 | 5.980 |
| Sorbitol: glycerol: water (1:2:3) | ||||
| ρ/(kg·m−3) | −0.6412 | 1491.30 | 0.187 | |
| u/(m·s−1) | −2.305 | 2681.22 | 0.334 | |
| nD | −0.000253 | 1.550538 | 5 × 10−5 | |
| σ/(mN·m−1) | −0.3916 | 174.78 | 0.181 | |
| Cp,m/(J·mol−1·K−1) | 0.323 | 72.1 | 0.130 | |
| η a/(mPa·s) | 0.00340 | 1692.9 | 160.20 | 8.076 |
| Chemical | CAS Number | Formula | Supplier | Purity (Mass Fraction) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xylitol | 87-99-0 | C5H12O5 | Fagron Iberica, Zaragoza, Spain | 0.997 |
| Fructose | 57-48-7 | C6H12O6 | Sigma-Aldrich, Darmstadt, Germany | 0.999 |
| Sorbitol | 50-70-4 | C6H14O6 | Sigma-Aldrich, Darmstadt, Germany | 0.990 |
| Glycerol | 56-81-5 | HOCH2CH(OH)CH2OH | Sigma-Aldrich, Darmstadt, Germany | 0.999 |
| DES | Ratio | Physical Appearance |
|---|---|---|
| Xylitol:glycerol | 1:2 | Transparent, very viscous liquid |
| Fructose:glycerol | 1:2 | Transparent, very viscous liquid |
| Sorbitol:glycerol | 1:2 | Transparent, very viscous liquid |
| Xylitol:glycerol | 1:3 | Transparent, very viscous liquid |
| Fructose:glycerol | 1:3 | Transparent, very viscous liquid |
| Sorbitol:glycerol | 1:3 | Transparent, very viscous liquid |
| Xylitol:glycerol: water | 1:3:1 | Transparent, very viscous liquid |
| Xylitol:glycerol: water | 1:3:2 | Transparent, very viscous liquid |
| Xylitol:glycerol: water | 1:3:3 | Transparent, very viscous liquid |
| Fructose:glycerol:water | 1:3:1 | Transparent, very viscous liquid |
| Fructose:glycerol:water | 1:3:2 | Transparent, very viscous liquid |
| Fructose:glycerol:water | 1:3:3 | Transparent, very viscous liquid |
| Sorbitol:glycerol:water | 1:3:1 | Transparent, very viscous liquid |
| Sorbitol:glycerol:water | 1:3:2 | Transparent, very viscous liquid |
| Sorbitol:glycerol:water | 1:3:3 | Transparent, very viscous liquid |
| Xylitol:glycerol: water | 1:2:1 | Transparent, viscous liquid |
| Xylitol:glycerol: water | 1:2:2 | Transparent, viscous liquid |
| Xylitol:glycerol: water * | 1:2:3 | Transparent, slightly viscous liquid |
| Fructose:glycerol:water | 1:2:1 | Transparent, viscous liquid |
| Fructose:glycerol:water | 1:2:2 | Transparent, viscous liquid |
| Fructose:glycerol:water * | 1:2:3 | Transparent, slightly viscous liquid |
| Sorbitol:glycerol:water | 1:2:1 | Transparent, viscous liquid |
| Sorbitol:glycerol:water | 1:2:2 | Transparent, viscous liquid |
| Sorbitol:glycerol:water * | 1:2:3 | Transparent, slightly viscous liquid |
| DES | Abbreviation | Molar Ratio | Molar Mass (g·mol−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Xylitol: glycerol: water | XylGW | 1:2:3 | 65.063 |
| Fructose: glycerol: water | FruGW | 1:2:3 | 69.732 |
| Sorbitol: glycerol: water | SorGW | 1:2:3 | 70.068 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lomba, L.; Werner, Á.; Giner, B.; Lafuente, C. Deep Eutectic Solvents Formed by Glycerol and Xylitol, Fructose and Sorbitol: Effect of the Different Sugars in Their Physicochemical Properties. Molecules 2023, 28, 6023. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28166023
Lomba L, Werner Á, Giner B, Lafuente C. Deep Eutectic Solvents Formed by Glycerol and Xylitol, Fructose and Sorbitol: Effect of the Different Sugars in Their Physicochemical Properties. Molecules. 2023; 28(16):6023. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28166023
Chicago/Turabian StyleLomba, Laura, Álvaro Werner, Beatriz Giner, and Carlos Lafuente. 2023. "Deep Eutectic Solvents Formed by Glycerol and Xylitol, Fructose and Sorbitol: Effect of the Different Sugars in Their Physicochemical Properties" Molecules 28, no. 16: 6023. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28166023
APA StyleLomba, L., Werner, Á., Giner, B., & Lafuente, C. (2023). Deep Eutectic Solvents Formed by Glycerol and Xylitol, Fructose and Sorbitol: Effect of the Different Sugars in Their Physicochemical Properties. Molecules, 28(16), 6023. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28166023









