Systematic Analysis of Covalent and Allosteric Protein Kinase Inhibitors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Covalent Protein Kinase Inhibitors
2.1.1. Warhead Distribution
2.1.2. Global Potency Analysis
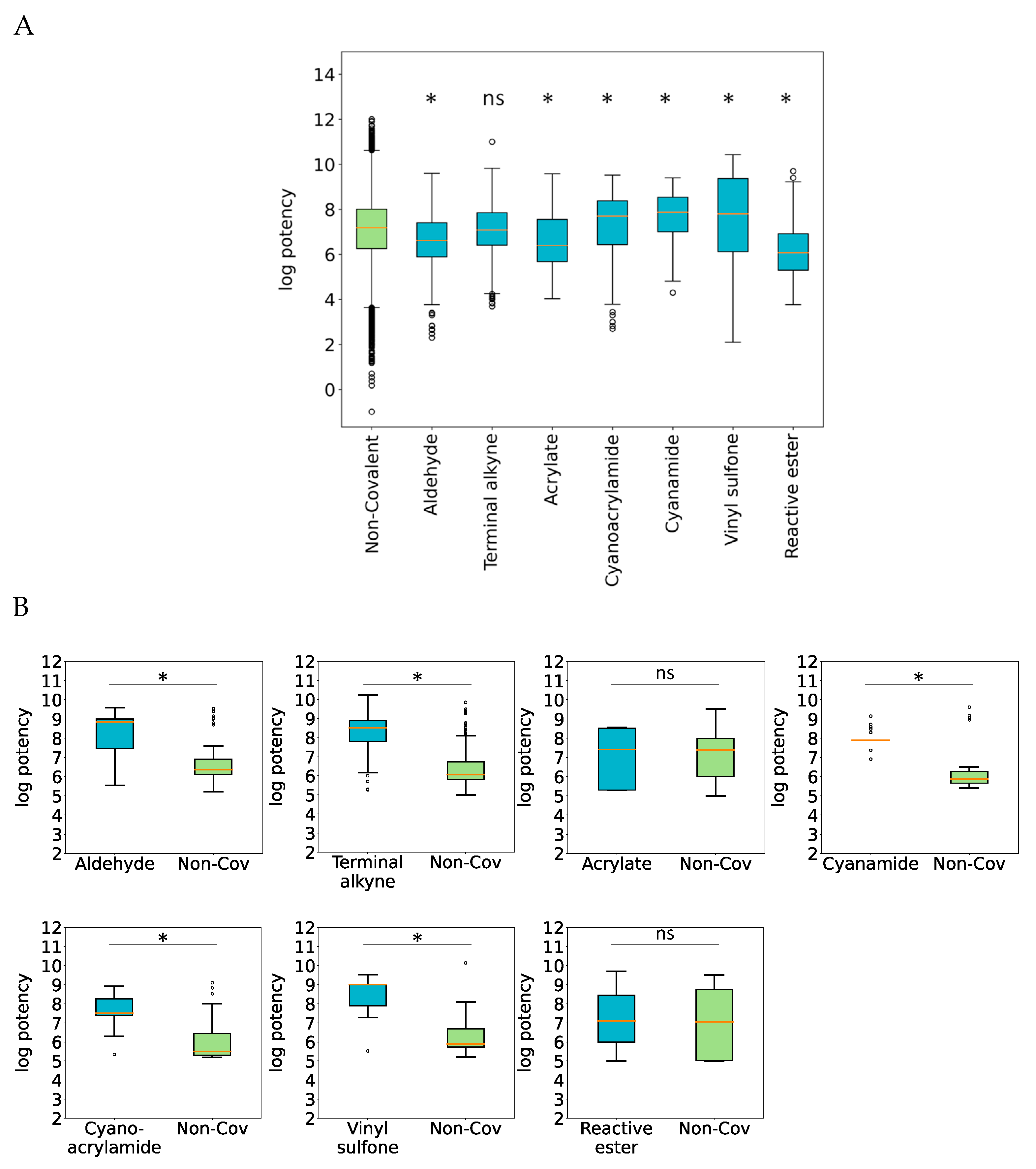
2.1.3. Potency Differences between Covalent and Non-Covalent Inhibitor Analogues
2.1.4. Promiscuity Analysis
2.2. Allosteric Protein Kinase Inhibitors
2.2.1. New Structurally Characterized Inhibitors
2.2.2. Distribution over Allosteric Binding Sites
2.2.3. Covalent Allosteric Inhibitors
2.2.4. Kinome Distribution
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Covalent Protein Kinase Inhibitors
3.1.1. Protein Kinase Inhibitor Data Retrieval and Curation
3.1.2. Identification of Covalent Inhibitors
3.1.3. Global Potency Analysis
3.1.4. Analogue Series, Analogue Pairs, and Promiscuity Degrees
3.2. Allosteric Protein Kinase Inhibitors
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Ferguson, F.M.; Gray, N.S. Kinase Inhibitors: The Road Ahead. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2018, 17, 353–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, P.; Cross, D.; Jänne, P.A. Kinase Drug Discovery 20 Years after Imatinib: Progress and Future Directions. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 551–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roskoski, R. Properties of FDA-Approved Small Molecule Protein Kinase Inhibitors: A 2023 Update. Pharmacol. Res. 2023, 187, 106552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knight, Z.A.; Lin, H.; Shokat, K.M. Targeting the Cancer Kinome through Polypharmacology. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antolin, A.A.; Clarke, P.A.; Collins, I.; Workman, P.; Al-Lazikani, B. Evolution of Kinase Polypharmacology across HSP90 Drug Discovery. Cell Chem. Biol. 2021, 28, 1433–1445.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarrin, A.A.; Bao, K.; Lupardus, P.; Vucic, D. Kinase Inhibition in Autoimmunity and Inflammation. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 39–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, F.J.; Xie, C.; Jiang, C. The Role of Hypoxia-Inducible Factors in Metabolic Diseases. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 15, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavrin, L.K.; Saiah, E. Approaches to Discover Non-ATP Site Kinase Inhibitors. Med. Chem. Commun. 2012, 4, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xerxa, E.; Miljković, F.; Bajorath, J. Data-Driven Global Assessment of Protein Kinase Inhibitors with Emphasis on Covalent Compounds. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 66, 7657–7665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miljković, F.; Bajorath, J. Computational Analysis of Kinase Inhibitors Identifies Promiscuity Cliffs across the Human Kinome. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 17295–17308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, S.; Chaikuad, A.; Gray, N.S.; Knapp, S. The Ins and Outs of Selective Kinase Inhibitor Development. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2015, 11, 818–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attwood, M.M.; Fabbro, D.; Sokolov, A.V.; Knapp, S.; Schiöth, H.B. Trends in Kinase Drug Discovery: Targets, Indications and Inhibitor Design. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 839–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Smaill, J.B.; Ding, K. New Promise and Opportunities for Allosteric Kinase Inhibitors. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2020, 59, 13764–13776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gower, C.M.; Chang, M.E.K.; Maly, D.J. Bivalent Inhibitors of Protein Kinases. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 49, 102–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kim, J.; Jo, J.; Chang, J.W.; Sim, J.; Yun, H. Recent Advances in Development of Hetero-Bivalent Kinase Inhibitors. Eur J. Med. Chem. 2021, 216, 113318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ábrányi-Balogh, P.; Keserű, G.M. Chapter 2—Warheads for Designing Covalent Inhibitors and Chemical Probes. In Advances in Chemical Proteomics; Yao, X., Ed.; Developments in Organic Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 47–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdeldayem, A.; Raouf, Y.S.; Constantinescu, S.N.; Moriggl, R.; Gunning, P.T. Advances in Covalent Kinase Inhibitors. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 2617–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaikuad, A.; Koch, P.; Laufer, S.A.; Knapp, S. The Cysteinome of Protein Kinases as a Target in Drug Development. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2018, 57, 4372–4385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehringer, M.; Laufer, S.A. Emerging and Re-Emerging Warheads for Targeted Covalent Inhibitors: Applications in Medicinal Chemistry and Chemical Biology. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 5673–5724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutanto, F.; Konstantinidou, M.; Dömling, A. Covalent Inhibitors: A Rational Approach to Drug Discovery. RSC Med. Chem. 2020, 11, 876–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boike, L.; Henning, N.J.; Nomura, D.K. Advances in Covalent Drug Discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2022, 21, 881–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Zhao, T.; Kang, D.; Zhang, J.; Song, Y.; Namasivayam, V.; Kongsted, J.; Pannecouque, C.; De Clercq, E.; Poongavanam, V.; et al. Overview of Recent Strategic Advances in Medicinal Chemistry. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 9375–9414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahnke, W.; Erlanson, D.A.; de Esch IJ, P.; Johnson, C.N.; Mortenson, P.N.; Ochi, Y.; Urushima, T. Fragment-to-Lead Medicinal Chemistry Publications in 2019. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 15494–15507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kathman, S.G.; Statsyuk, A.V. Covalent Tethering of Fragments for Covalent Probe Discovery. Med. Chem. Commun. 2016, 7, 576–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laufkötter, O.; Hu, H.; Miljković, F.; Bajorath, J. Structure- and Similarity-Based Survey of Allosteric Kinase Inhibitors, Activators, and Closely Related Compounds. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 922–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodsell, D.S.; Zardecki, C.; Di Costanzo, L.; Duarte, J.M.; Hudson, B.P.; Persikova, I.; Segura, J.; Shao, C.; Voigt, M.; Westbrook, J.D.; et al. RCSB Protein Data Bank: Enabling Biomedical Research and Drug Discovery. Protein Sci. 2020, 29, 52–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manning, G.; Whyte, D.; Martinez, R.; Hunter, T.; Sudarsanam, S. The Protein Kinase Complement of the Human Genome. Science 2002, 298, 1912–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UniProt Consortium. UniProt: The Universal Protein Knowledgebase in 2023. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D523–D531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaulton, A.; Bellis, L.J.; Bento, A.P.; Chambers, J.; Davies, M.; Hersey, A.; Light, Y.; McGlinchey, S.; Michalovich, D.; Al-Lazikani, B.; et al. ChEMBL: A Large-Scale Bioactivity Database for Drug Discovery. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D1100–D1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Lin, Y.; Wen, X.; Jorissen, R.N.; Gilson, M.K. BindingDB: A Web-Accessible Database of Experimentally Determined Protein–Ligand Binding Affinities. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, D198–D201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weininger, D. SMILES, a Chemical Language and Information System. 1. Introduction to Methodology and Encoding Rules. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 1988, 28, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daylight Theory: SMARTS—A Language for Describing Molecular Patterns. Available online: https://www.daylight.com/dayhtml/doc/theory/theory.smarts.html (accessed on 29 March 2023).
- Cox, D.R. Statistical significance. Annu. Rev. Stat. Appl. 2020, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveja, J.J.; Vogt, M.; Stumpfe, D.; Medina-Franco, J.L.; Bajorath, J. Systematic Extraction of Analogue Series from Large Compound Collections Using a New Computational Compound–Core Relationship Method. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 1027–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molecular Operating Environment, version 2021.01; Chemical Computing Group ULC: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2021.




| Ligand Type | Binding Site Description | Count |
|---|---|---|
| Type III | Adjacent to ATP site | 92 (81) |
| Type IV | Distant from ATP site | 91 (81) |
| Type V | ATP site + allosteric site | 15 (15) |
| Type VI | Allosteric site | 13 (10) |
| Activators | Allosteric site | 20 (19) |
| Multi-site ligands | ATP site and/or allosteric site(s) | 31 (26) |
| Total | 262 (232) |
| PDB ID | Binding Site | Kinase | Modified Residue | Warhead |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6HHJ | B | AKT1 | Cys310 | Acrylamide |
| 6HHF | B | AKT1 | Cys296 | Acrylamide |
| 6HHI | B | AKT1 | Cys296 | Acrylamide |
| 6HHH | B | AKT1 | Cys296 | Acrylamide |
| 6HHG | B | AKT1 | Cys310 | Acrylamide |
| 6S9X | B | AKT1 | Cys310 | Acrylamide |
| 6S9W | B | AKT1 | Cys310 | Acrylamide |
| 3ORX | C | PDPK1 | Cys148 | Sulfhydryl |
| 5O8V | D | MAPK14 | Cys251 | Acrylamide |
| 5O8U | D | MAPK14 | Cys252 | α,β-unsaturated Carbonyl |
| 5OO0 | I | CDK2 | Cys177 | Acrylamide |
| 5OSJ | I | CDK2 | Cys117 | Acrylamide |
| 5ORL | K | AURKA | Cys247 | Thiazoline |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xerxa, E.; Laufkötter, O.; Bajorath, J. Systematic Analysis of Covalent and Allosteric Protein Kinase Inhibitors. Molecules 2023, 28, 5805. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28155805
Xerxa E, Laufkötter O, Bajorath J. Systematic Analysis of Covalent and Allosteric Protein Kinase Inhibitors. Molecules. 2023; 28(15):5805. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28155805
Chicago/Turabian StyleXerxa, Elena, Oliver Laufkötter, and Jürgen Bajorath. 2023. "Systematic Analysis of Covalent and Allosteric Protein Kinase Inhibitors" Molecules 28, no. 15: 5805. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28155805
APA StyleXerxa, E., Laufkötter, O., & Bajorath, J. (2023). Systematic Analysis of Covalent and Allosteric Protein Kinase Inhibitors. Molecules, 28(15), 5805. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28155805









