Unlocking the Potential: Novel NSAIDs Hybrids Unleash Chemopreventive Power toward Liver Cancer Cells through Nrf2, NF-κB, and MAPK Signaling Pathways
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Spectral Characteristics of the OAO Conjugates with Ibuprofen and Ketoprofen
2.2.1. Conjugates of OAO and Ibuprofen (5a–d)
2.2.2. Conjugates of OAO and Ketoprofen (6a–d)
2.3. Conjugation with OAO Derivatives Decreases the Cytotoxicity of Ibuprofen and Ketoprofen
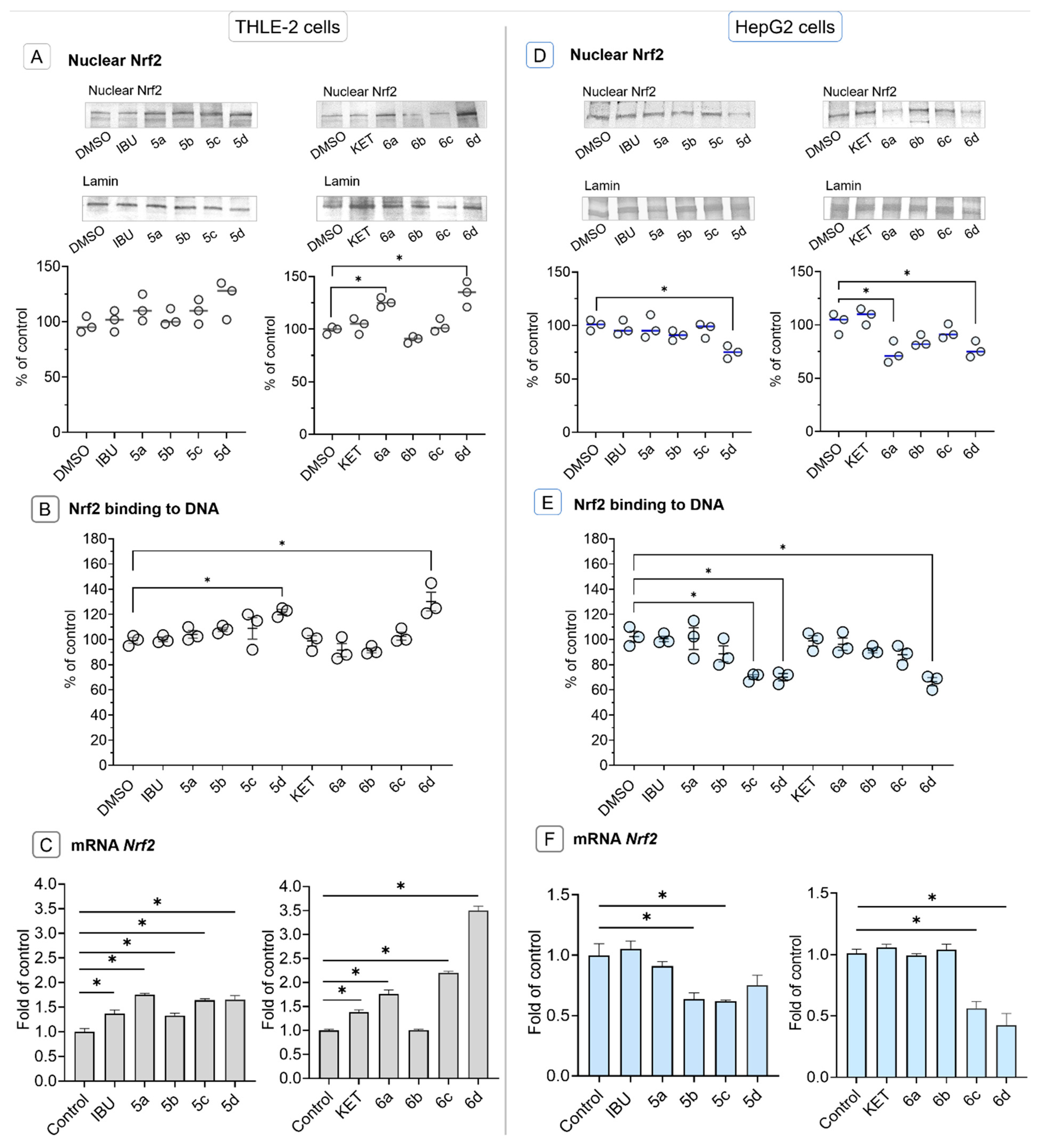
2.4. Conjugation of Ibuprofen and Ketoprofen with OAO Derivatives Increases Activation and Expression of Nrf2 in THLE-2 Cells but Reduces in HepG2 Cells
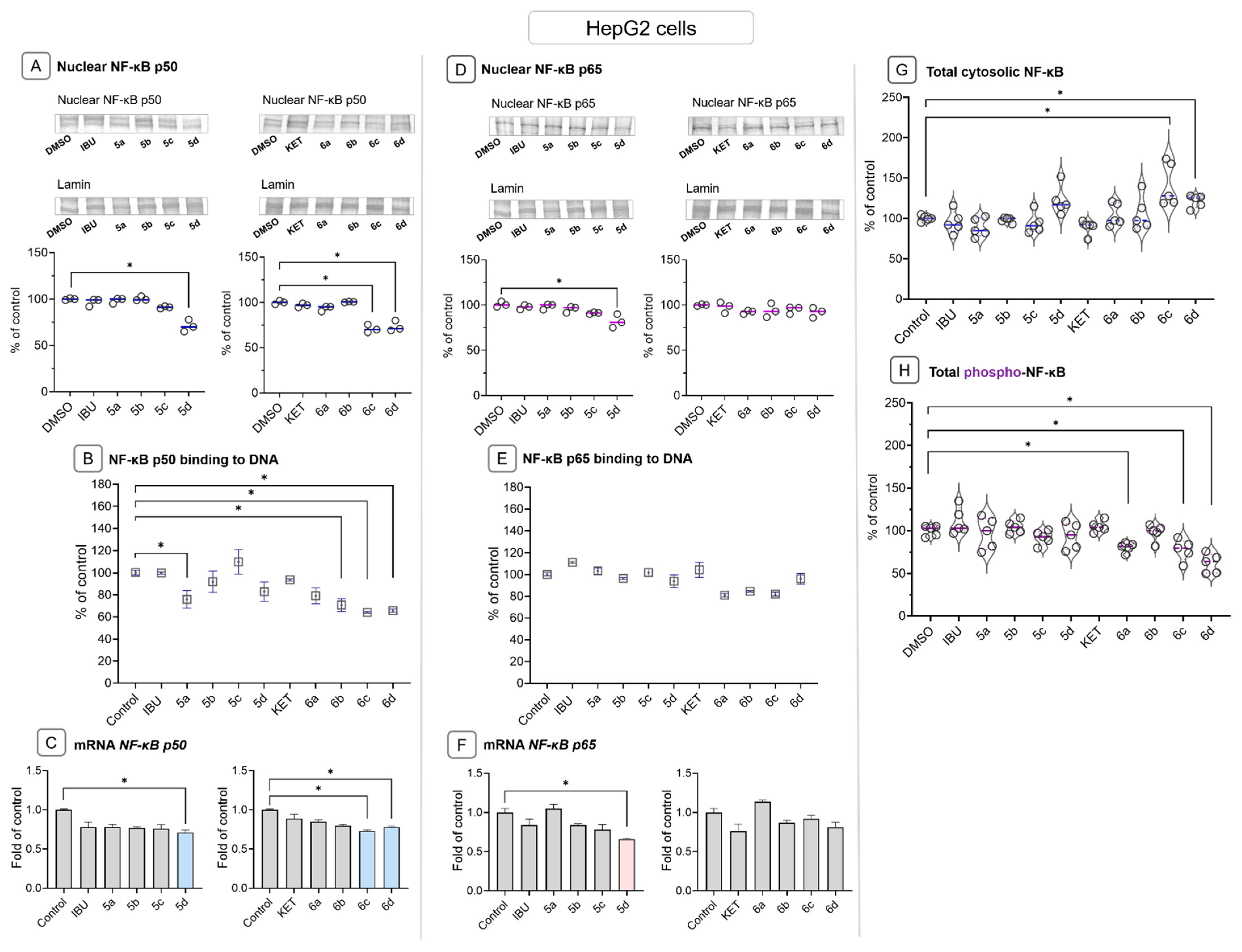
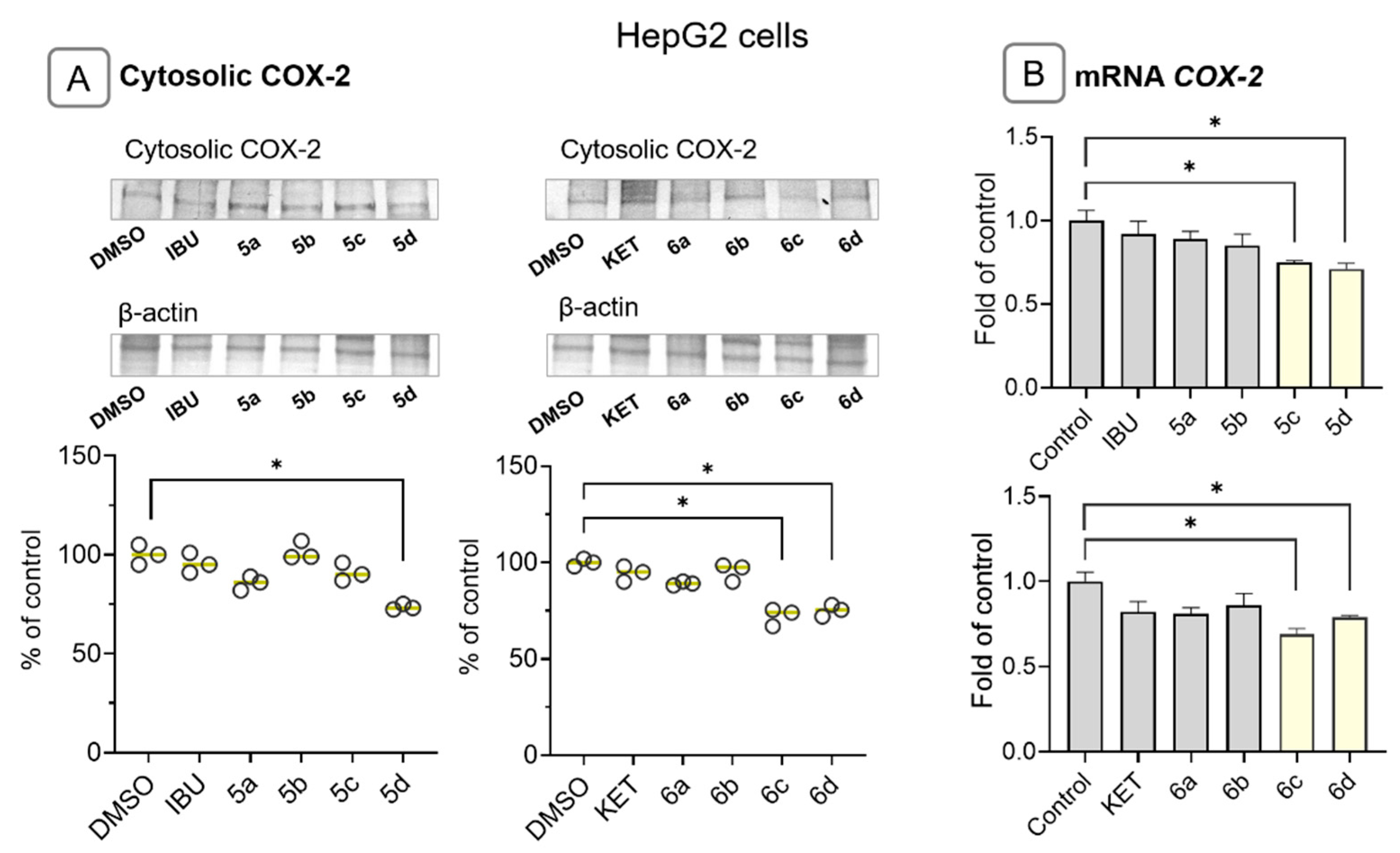
2.5. Ibuprofen and Ketoprofen—OAO Conjugates Reduce the Activation and Expression of NF-κB and COX-2 in HepG2 Cells
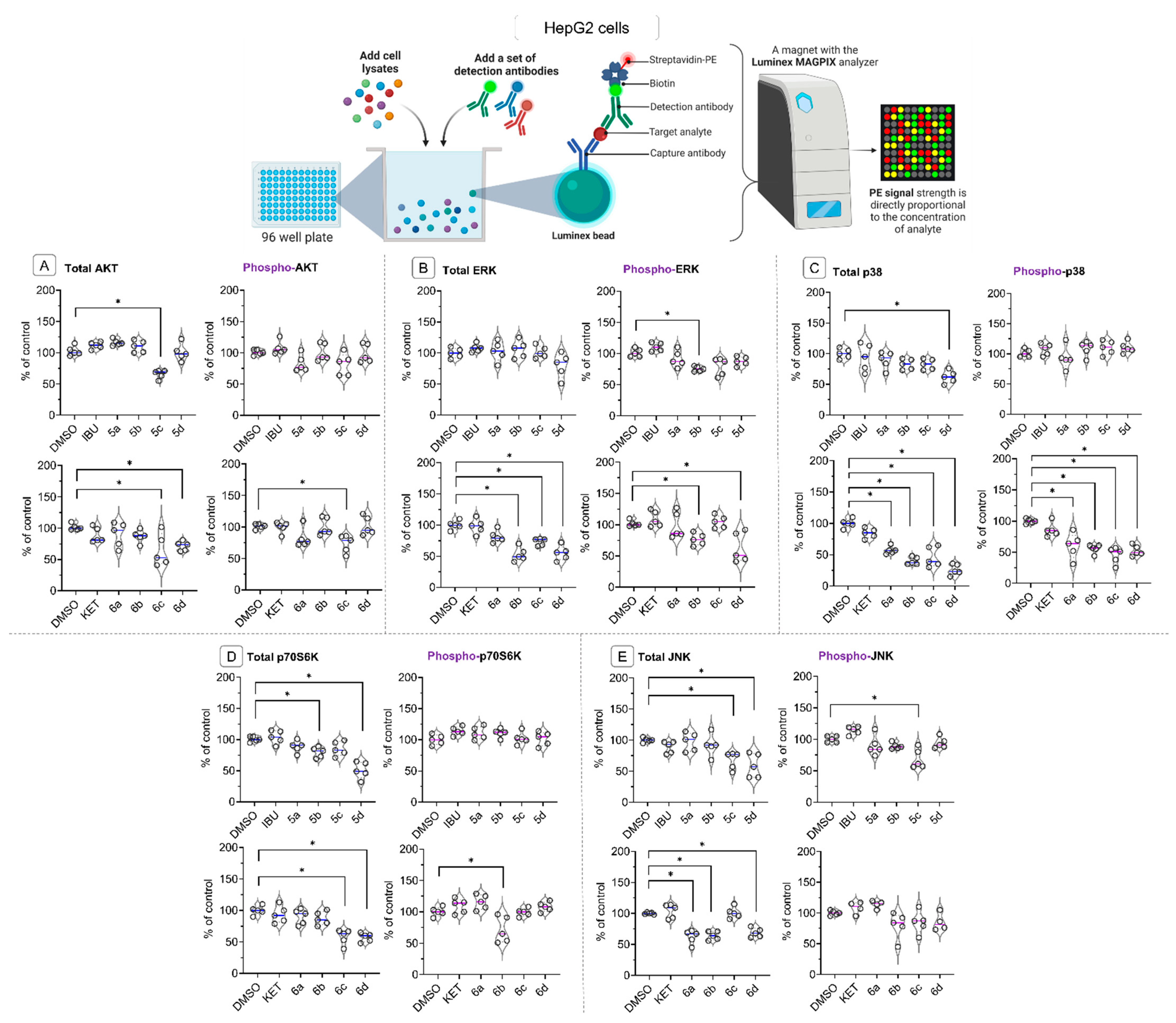
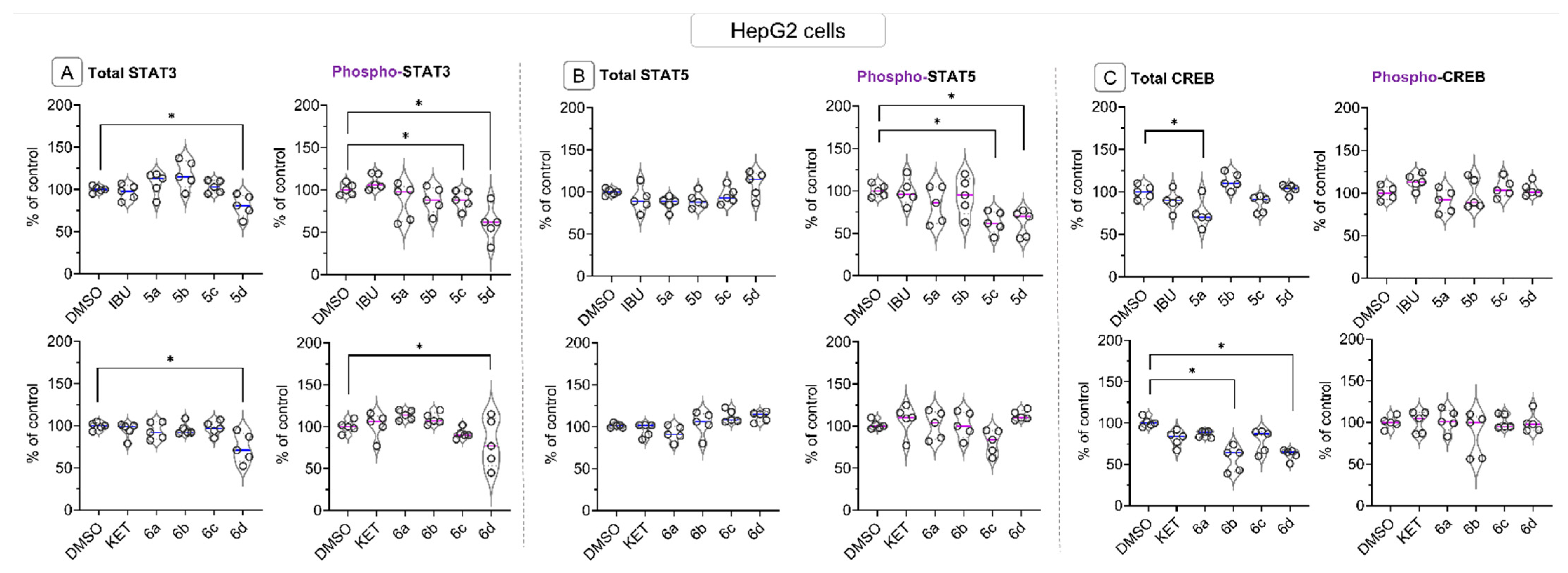
2.6. Bead-Based Multiplex Immunoassay Revealed Possible Modulation of Protein Regulating Several Signaling Pathways by Ibuprofen and Ketoprofen—OAO Derivatives Conjugates
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemistry
- The conjugate of oleanolic acid oxime and Ibuprofen, 3-ibuprofenoxyiminoolean-12-en-28-oic acid (5a):
- The conjugate of methyl oleanolate oxime and Ibuprofen, 3-ibuprofenoxyiminoolean-12-en-28-oic acid methyl ester (5b):
- The conjugate of benzyl oleanolate oxime and Ibuprofen, 3-ibuprofenoxyiminoolean-12-en-28-oic acid benzyl ester (5c):
- The conjugate of morpholide of oleanolic acid oxime and Ibuprofen, 3-ibuprofenoxyiminoolean-12-en-28-oic acid morpholide (5d):
- The conjugate of oleanolic acid oxime and Ketoprofen, 3-ketoprofenoxyiminoolean-12-en-28-oic acid (6a):
- Conjugate of methyl oleanolate oxime and Ketoprofen, 3-ketoprofenoxyiminoolean-12-en-28-oic acid methyl ester (6b):
- The conjugate of benzyl oleanolate oxime and Ketoprofen, 3-ketoprofenoxyiminoolean-12-en-28-oic acid benzyl ester (6c):
- The conjugate of morpholide of oleanolic acid oxime and Ketoprofen, 3-ketoprofenoxyiminoolean-12-en-28-oic acid morpholide (6d):
4.2. Biological Assays
4.2.1. Cell Culture and Viability Assay
4.2.2. Nuclear, Cytosolic, and Total Protein Lysates Preparation
4.2.3. Total RNA Isolation, cDNA Synthesis, and Quantitative Real-Time PCR (R-T PCR)
4.2.4. Western Blot Analysis
4.2.5. Nrf2 and NF-ĸB Binding Assay
4.2.6. Bead-Based Immunoassay on the Luminex MAGPIX Instrument
4.3. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Llovet, J.M.; Kelley, R.K.; Villanueva, A.; Singal, A.G.; Pikarsky, E.; Roayaie, S.; Lencioni, R.; Koike, K.; Zucman-Rossi, J.; Finn, R.S. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2021, 7, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krajka-Kuźniak, V.; Baer-Dubowska, W. Modulation of Nrf2 and NF-κB Signaling Pathways by Naturally Occurring Compounds in Relation to Cancer Prevention and Therapy. Are Combinations Better Than Single Compounds? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorriento, D.; Campanile, A.; Santulli, G.; Leggiero, E.; Pastore, L.; Trimarco, B.; Iaccarino, G. A new synthetic protein, TAT-RH, inhibits tumor growth through the regulation of NFκB activity. Mol. Cancer 2009, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malz, M.; Pinna, F.; Schirmacher, P.; Breuhahn, K. Transcriptional regulators in hepatocarcinogenesis – Key integrators of malignant transformation. J. Hepatol. 2012, 57, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colotta, F.; Allavena, P.; Sica, A.; Garlanda, C.; Mantovani, A. Cancer-related inflammation, the seventh hallmark of cancer: Links to genetic instability. Carcinogenesis 2009, 30, 1073–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoesel, B.; Schmid, J.A. The complexity of NF-κB signaling in inflammation and cancer. Mol. Cancer 2013, 12, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.M.U.; Luo, L.; Namani, A.; Wang, X.J.; Tang, X. Nrf2 signaling pathway: Pivotal roles in inflammation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2017, 1863, 585–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghunath, A.; Sundarraj, K.; Arfuso, F.; Sethi, G.; Perumal, E. Dysregulation of Nrf2 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Role in Cancer Progression and Chemoresistance. Cancers 2018, 10, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, H.; Ro, S.W. MAPK/ERK Signaling Pathway in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimri, M.; Satyanarayana, A. Molecular Signaling Pathways and Therapeutic Targets in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers 2020, 12, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuzick, J.; Thorat, M.A.; Bosetti, C.; Brown, P.H.; Burn, J.; Cook, N.R.; Ford, L.G.; Jacobs, E.J.; Jankowski, J.A.; La Vecchia, C.; et al. Estimates of benefits and harms of prophylactic use of aspirin in the general population. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothwell, P.M.; Fowkes, F.G.R.; Belch, J.F.; Ogawa, H.; Warlow, C.P.; Meade, T.W. Effect of daily aspirin on long-term risk of death due to cancer: Analysis of individual patient data from randomised trials. Lancet 2011, 377, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuzick, J.; Otto, F.; Baron, J.A.; Brown, P.H.; Burn, J.; Greenwald, P.; Jankowski, J.; La Vecchia, C.; Meyskens, F.; Senn, H.J.; et al. Aspirin and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for cancer prevention: An international consensus statement. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zappavigna, S.; Cossu, A.M.; Grimaldi, A.; Bocchetti, M.; Ferraro, G.A.; Nicoletti, G.F.; Filosa, R.; Caraglia, M. Anti-Inflammatory Drugs as Anticancer Agents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 2, 2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindu, S.; Mazumder, S.; Bandyopadhyay, U. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and organ damage: A current perspective. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 180, 114147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayeleso, T.B.; Matumba, M.G.; Mukwevho, E. Oleanolic Acid and Its Derivatives: Biological Activities and Therapeutic Potential in Chronic Diseases. Molecules 2017, 22, 1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikh, N.R.; Mandal, A.; Bhatia, D.; Siveen, K.S.; Sethi, G.; Bishayee, A. Oleanane triterpenoids in the prevention and therapy of breast cancer: Current evidence and future perspectives. Phytochem. Rev. 2014, 13, 793–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žiberna, L.; Šamec, D.; Mocan, A.; Nabavi, S.F.; Bishayee, A.; Farooqi, A.A.; Sureda, A.; Nabavi, S.M. Oleanolic Acid Alters Multiple Cell Signaling Pathways: Implication in Cancer Prevention and Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishayee, A.; Mandal, A.; Thoppil, R.J.; Darvesh, A.S.; Bhatia, D. Chemopreventive effect of a novel oleanane triterpenoid in a chemically induced rodent model of breast cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 133, 1054–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schepetkin, I.A.; Plotnikov, M.B.; Khlebnikov, A.I.; Plotnikova, T.M.; Quinn, M.T. Oximes: Novel Therapeutics with Anticancer and Anti-Inflammatory Potential. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajka-Kuźniak, V.; Bednarczyk-Cwynar, B.; Paluszczak, J.; Szaefer, H.; Narożna, M.; Zaprutko, L.; Baer-Dubowska, W. Oleanolic acid oxime derivatives and their conjugates with aspirin modulate the NF-κB-mediated transcription in HepG2 hepatoma cells. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 93, 103326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narożna, M.; Krajka-Kuźniak, V.; Kleszcz, R.; Bednarczyk-Cwynar, B.; Szaefer, H.; Baer-Dubowska, W. Activation of the Nrf2 response by oleanolic acid oxime morpholide (3-hydroxyiminoolean-12-en-28-oic acid morpholide) is associated with its ability to induce apoptosis and inhibit proliferation in HepG2 hepatoma cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 883, 173307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narożna, M.; Krajka-Kuźniak, V.; Bednarczyk-Cwynar, B.; Kucińska, M.; Kleszcz, R.; Kujawski, J.; Piotrowska-Kempisty, H.; Plewiński, A.; Murias, M.; Baer-Dubowska, W. Conjugation of diclofenac with novel oleanolic acid derivatives modulate nrf2 and nf-κb activity in hepatic cancer cells and normal hepatocytes leading to enhancement of its therapeutic and chemopreventive potential. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narożna, M.; Krajka-Kuźniak, V.; Bednarczyk-Cwynar, B.; Kleszcz, R.; Baer-Dubowska, W. The Effect of Novel Oleanolic Acid Oximes Conjugated with Indomethacin on the Nrf2-ARE And NF-κB Signaling Pathways in Normal Hepatocytes and Human Hepatocellular Cancer Cells. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 14, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunaydin, C.; Bilge, S.S. Effects of Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs at the Molecular Level. Eurasian J. Med. 2018, 50, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, S.J.; Eling, T.; Kolawole, O.R.; Kashfi, K. NSAIDs and Cancer Resolution: New Paradigms beyond Cyclooxygenase. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukuri, M.; Takashima-Hirano, M.; Tokuda, K.; Takashima, T.; Matsumura, K.; Inoue, O.; Doi, H.; Suzuki, M.; Watanabe, Y.; Onoe, H. In Vivo Expression of Cyclooxygenase-1 in Activated Microglia and Macrophages During Neuroinflammation Visualized by PET with 11C-Ketoprofen Methyl Ester. J. Nucl. Med. 2011, 52, 1094–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazaleuskaya, L.L.; Theken, K.N.; Gong, L.; Thorn, C.F.; Fitzgerald, G.A.; Altman, R.B.; Klein, T.E. PharmGKB summary: Ibuprofen pathways. Pharmacogenet. Genom. 2015, 25, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittoni, M.A.; Carbone, D.P.; Harris, R.E. Ibuprofen and fatal lung cancer: A brief report of the prospective results from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES III). Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 6, 917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, B.; Simmons, D. COX-2 Inhibition, Apoptosis, and Chemoprevention by Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 7, 1131–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahasrabuddhe, V.V.; Gunja, M.Z.; Graubard, B.I.; Trabert, B.; Schwartz, L.M.; Park, Y.; Hollenbeck, A.R.; Freedman, N.D.; Mcglynn, K.A. Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drug Use, Chronic Liver Disease, and Hepatocellular Carcinoma. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2012, 104, 1808–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Lu, Y.F.; Wu, Q.; Xu, S.F.; Shi, F.G.; Klaassen, C.D. Oleanolic acid reprograms the liver to protect against hepatotoxicants, but is hepatotoxic at high doses. Liver Int. 2019, 39, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heudobler, D.; Reichle, A.; Ghibelli, L. Editorial: Anakoinosis: An Innovative Anticancer Therapy Targeting the Aberrant Cancer Tissue Homeostasis. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 779021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tebay, L.E.; Robertson, H.; Durant, S.T.; Vitale, S.R.; Penning, T.M.; Dinkova-Kostova, A.T.; Hayes, J.D. Mechanisms of activation of the transcription factor Nrf2 by redox stressors, nutrient cues, and energy status and the pathways through which it attenuates degenerative disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 88, 108–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogoyevitch, M.A.; Ngoei, K.R.W.; Zhao, T.T.; Yeap, Y.Y.C.; Ng, D.C.H. c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) signaling: Recent advances and challenges. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Proteins Proteom. 2010, 1804, 463–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messoussi, A.; Mence Feneyrolles, C.; Lie Bros, A.; Deroide, A.; Né Dicte Daydé -Cazals, B.; Naë, L.; Chevé, G.; Hijfte, N.V.; Né Dicte Fauvel, B.; Bougrin, K.; et al. Chemistry & Biology Review Recent Progress in the Design, Study, and Development of c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase Inhibitors as Anticancer Agents. Chem. Biol. 2014, 21, 1433–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bubici, C.; Papa, S. JNK signalling in cancer: In need of new, smarter therapeutic targets. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 171, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.X.; Sun, R.F.; Mo, X.M.; Li, W.M. The p70S6K Specific Inhibitor PF-4708671 Impedes Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Growth. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Wang, Y.C.; Li, W.S.; Du, Y. The role of mTOR and phospho-p70S6K in pathogenesis and progression of gastric carcinomas: An immunohistochemical study on tissue microarray. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 28, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telkoparan-Akillilar, P.; Panieri, E.; Cevik, D.; Suzen, S.; Saso, L. Therapeutic Targeting of the NRF2 Signaling Pathway in Cancer. Molecules 2021, 26, 1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Guo, N.; Xu, H.; Pan, T.; Lei, H.; Yan, A.; Mi, Y.; Xu, L. Ibuprofen induces ferroptosis of glioblastoma cells via downregulation of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 signaling pathway. Anticancer. Drugs 2020, 31, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Wan, Y.; Huang, C. The Biological Functions of NF-κB1 (p50) and its Potential as an Anti-Cancer Target. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2009, 9, 566–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giridharan, S.; Srinivasan, M. Mechanisms of NF-κB p65 and strategies for therapeutic manipulation. J. Inflamm. Res. 2018, 11, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younus, H. Therapeutic potentials of superoxide dismutase. Int. J. Health Sci. 2018, 12, 88. [Google Scholar]
- Christian, F.; Smith, E.L.; Carmody, R.J. The Regulation of NF-κB Subunits by Phosphorylation. Cells 2016, 5, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Cai, W.; Chu, E.S.H.; Tang, J.; Wong, C.C.; Wong, S.H.; Sun, W.; Liang, Q.; Fang, J.; Sun, Z.; et al. Hepatic cyclooxygenase-2 overexpression induced spontaneous hepatocellular carcinoma formation in mice. Oncogene 2017, 36, 4415–4426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervello, M.; Montalto, G. Cyclooxygenases in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 5113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Limón, A.; Joaquin, M.; Caballero, M.; Posas, F.; de Nadal, E. The p38 Pathway: From Biology to Cancer Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhan, X. The MAPK pathway-based drug therapeutic targets in pituitary adenomas. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 446999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papa, S.; Choy, P.M.; Bubici, C. The ERK and JNK pathways in the regulation of metabolic reprogramming. Oncogene 2018, 38, 2223–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, X.; Cao, S.; Sun, Y.; He, X.; Jiang, B.; Yu, Y.; Duan, J.; Qiu, F.; Kang, N. Berberine represses human gastric cancer cell growth in vitro and in vivo by inducing cytostatic autophagy via inhibition of MAPK/mTOR/p70S6K and Akt signaling pathways. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 128, 110245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.K.; Jang, H.D. Nrf2-Mediated HO-1 Induction Coupled with the ERK Signaling Pathway Contributes to Indirect Antioxidant Capacity of Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Ester in HepG2 Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 12149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, D.D. Phosphorylation of Nrf2 at Multiple Sites by MAP Kinases Has a Limited Contribution in Modulating the Nrf2-Dependent Antioxidant Response. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.Y.; Pyo, M.C.; Nam, M.H.; Lee, K.W. ERK/Nrf2 pathway activation by caffeic acid in HepG2 cells alleviates its hepatocellular damage caused by t-butylhydroperoxide-induced oxidative stress. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 19, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Zhang, P.; Chen, X.; He, G. PI3K and ERK/Nrf2 pathways are involved in oleanolic acid-induced heme oxygenase-1 expression in rat vascular smooth muscle cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2011, 112, 1524–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Jiang, W.; Yang, W.; Yang, C.; Yang, X.; Chen, K.; Hu, Y.; Shen, G.; Lu, L.; Cheng, F.; et al. Epigenetically modulated miR-1224 suppresses the proliferation of HCC through CREB-mediated activation of YAP signaling pathway. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2021, 23, 944–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wingelhofer, B.; Neubauer, H.A.; Valent, P.; Han, X.; Constantinescu, S.N.; Gunning, P.T.; Müller, M.; Moriggl, R. Implications of STAT3 and STAT5 signaling on gene regulation and chromatin remodeling in hematopoietic cancer. Leukemia 2018, 32, 1713–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svinka, J.; Mikulits, W.; Eferl, R. STAT3 in hepatocellular carcinoma: New perspectives. Hepatic Oncol. 2014, 1, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolomeo, M.; Cascio, A. The Multifaced Role of STAT3 in Cancer and Its Implication for Anticancer Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Gene | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer |
|---|---|---|
| Nrf2 | 5′ATTGCTACTAATCAGGCTCAG | 5′GTTTGGCTTCTGGACTTGG |
| NF-ĸB p50 | 5′ATCATCCACCTTCATTCTCAA | 5′AATCCTCCACCACATCTTCC |
| NF-ĸB p65 | 5′CGCCTGTCCTTTCTCATC | 5′ACCTCAATGTCCTCTTTCTG |
| COX-2 | 5′CCTGTGCCTGATGATTGC | 5′CAGCCCGTTGGTGAAAGC |
| PBGD | 5′TCAGATAGCATACAAGAGACC | 5′TGGAATGTTACGAGCAGTG |
| TBP | 5′GGCACCACTCCACTGTATC | 5′GGGATTATATTCGGCGTTTCG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Narożna, M.; Krajka-Kuźniak, V.; Bednarczyk-Cwynar, B.; Baer-Dubowska, W. Unlocking the Potential: Novel NSAIDs Hybrids Unleash Chemopreventive Power toward Liver Cancer Cells through Nrf2, NF-κB, and MAPK Signaling Pathways. Molecules 2023, 28, 5759. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28155759
Narożna M, Krajka-Kuźniak V, Bednarczyk-Cwynar B, Baer-Dubowska W. Unlocking the Potential: Novel NSAIDs Hybrids Unleash Chemopreventive Power toward Liver Cancer Cells through Nrf2, NF-κB, and MAPK Signaling Pathways. Molecules. 2023; 28(15):5759. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28155759
Chicago/Turabian StyleNarożna, Maria, Violetta Krajka-Kuźniak, Barbara Bednarczyk-Cwynar, and Wanda Baer-Dubowska. 2023. "Unlocking the Potential: Novel NSAIDs Hybrids Unleash Chemopreventive Power toward Liver Cancer Cells through Nrf2, NF-κB, and MAPK Signaling Pathways" Molecules 28, no. 15: 5759. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28155759
APA StyleNarożna, M., Krajka-Kuźniak, V., Bednarczyk-Cwynar, B., & Baer-Dubowska, W. (2023). Unlocking the Potential: Novel NSAIDs Hybrids Unleash Chemopreventive Power toward Liver Cancer Cells through Nrf2, NF-κB, and MAPK Signaling Pathways. Molecules, 28(15), 5759. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28155759










