Analysis of Dielectric Parameters of Fe2O3-Doped Polyvinylidene Fluoride/Poly(methyl methacrylate) Blend Composites
Abstract
1. Introduction
- The capacitive behavior of the composite described by complex electrical permittivity (εr), which quantifies the ability of the material to store electrical energy in an electric field;
- The conductive behavior of the composite material characterized by the electrical conductivity (σ), which represents the ability of the material to conduct electrical current.
- Charge storage in the polymer blend resulting in the enhancement of the dielectric constant;
- Fe2O3 nanoparticles acting as conductive fillers, providing additional pathways for electron transport resulting in an increase in overall conductivity;
- An expected enhancement of dielectric losses, as conductivity would be increasing;
- An alteration in the relaxation timescales and the distribution of relaxation processes, resulting in changes in impedance and frequency-dependent electrical behavior.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. XRD Analysis of Prepared Polymer Blend Nanocomposite PNC Films
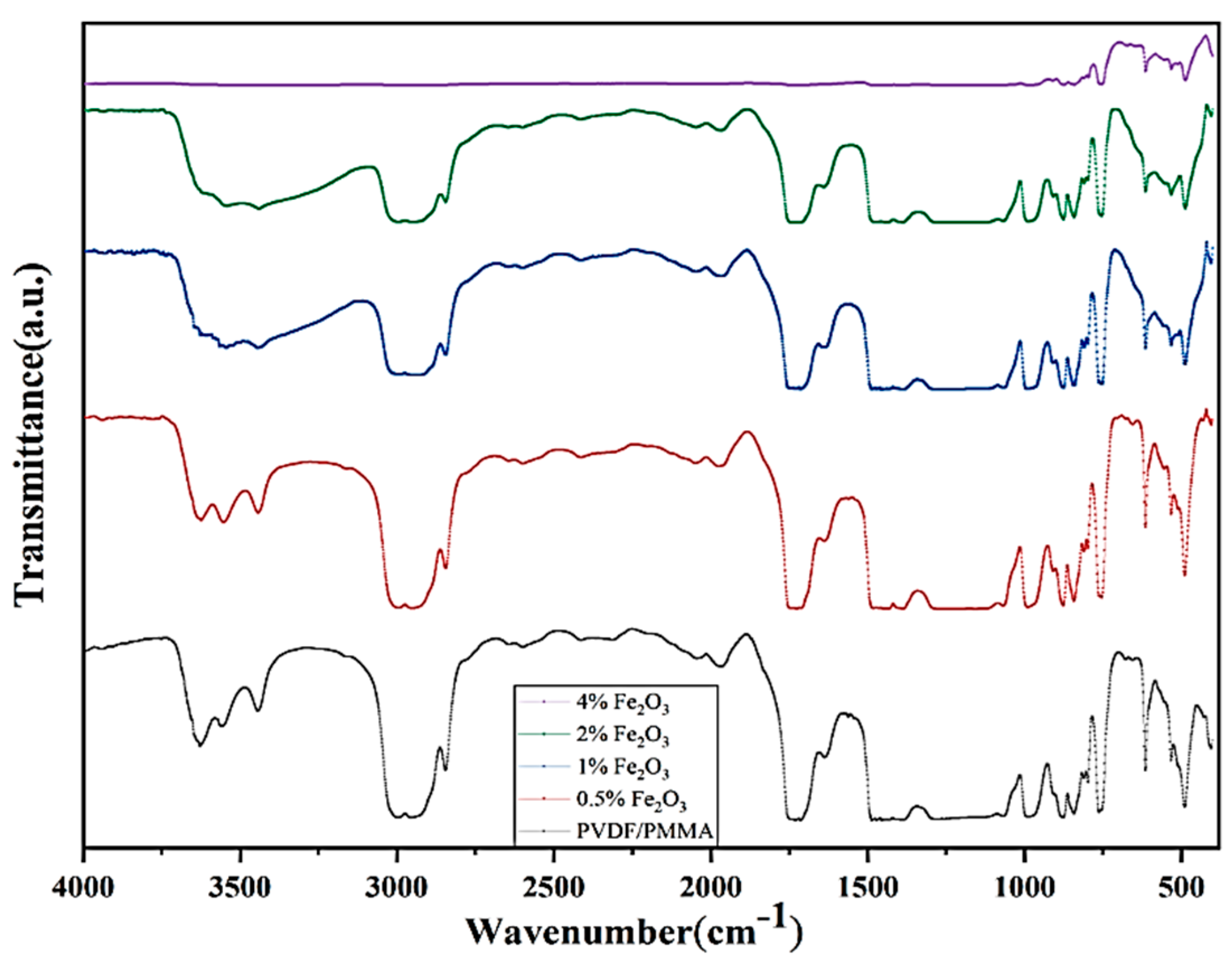
2.2. FTIR Spectra and Polymer Blend—Nanofiller Interaction
2.3. Variation of Dielectric Parameters with Frequency and Composition
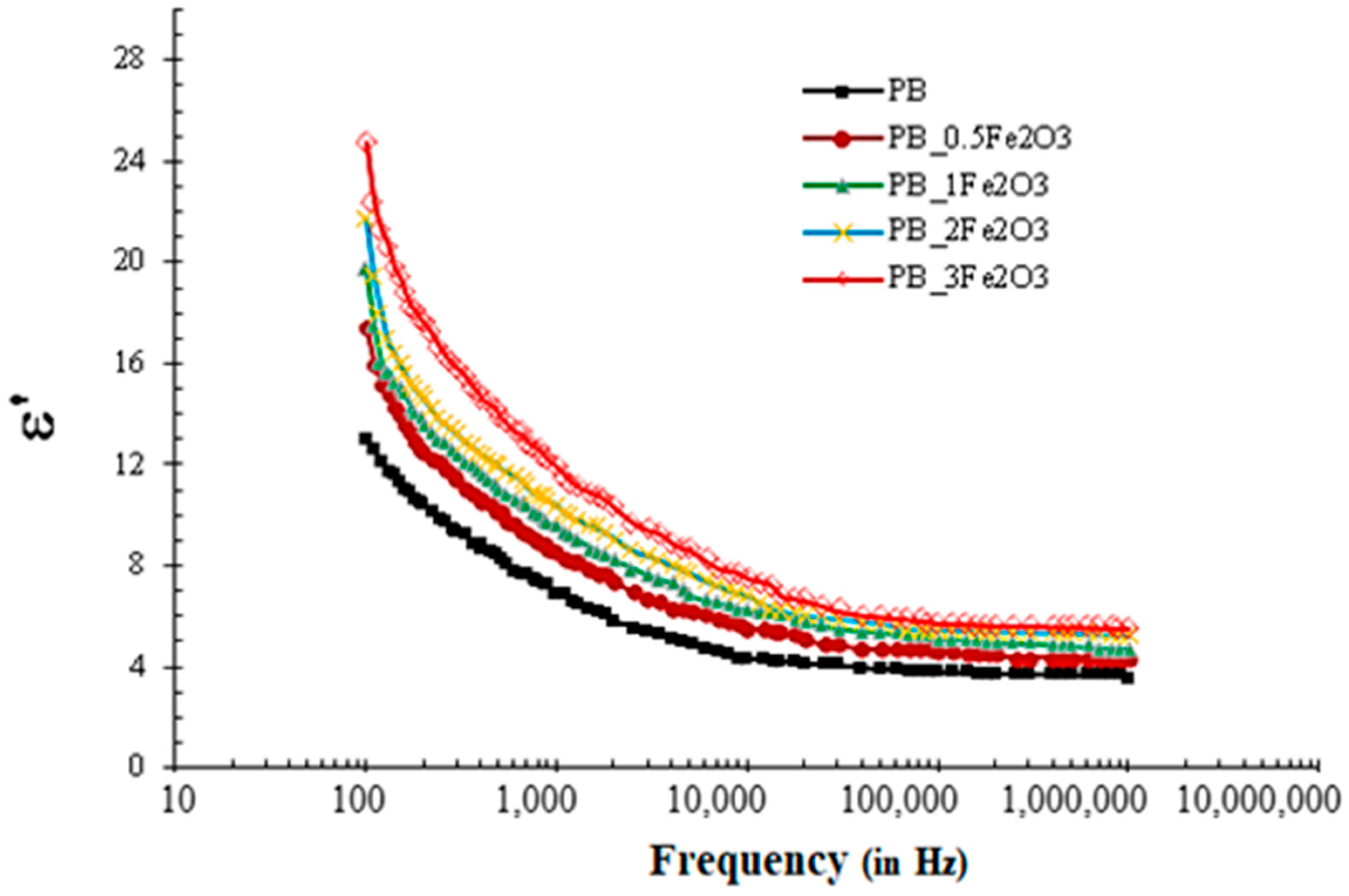
2.3.1. Variation in Dielectric Constant
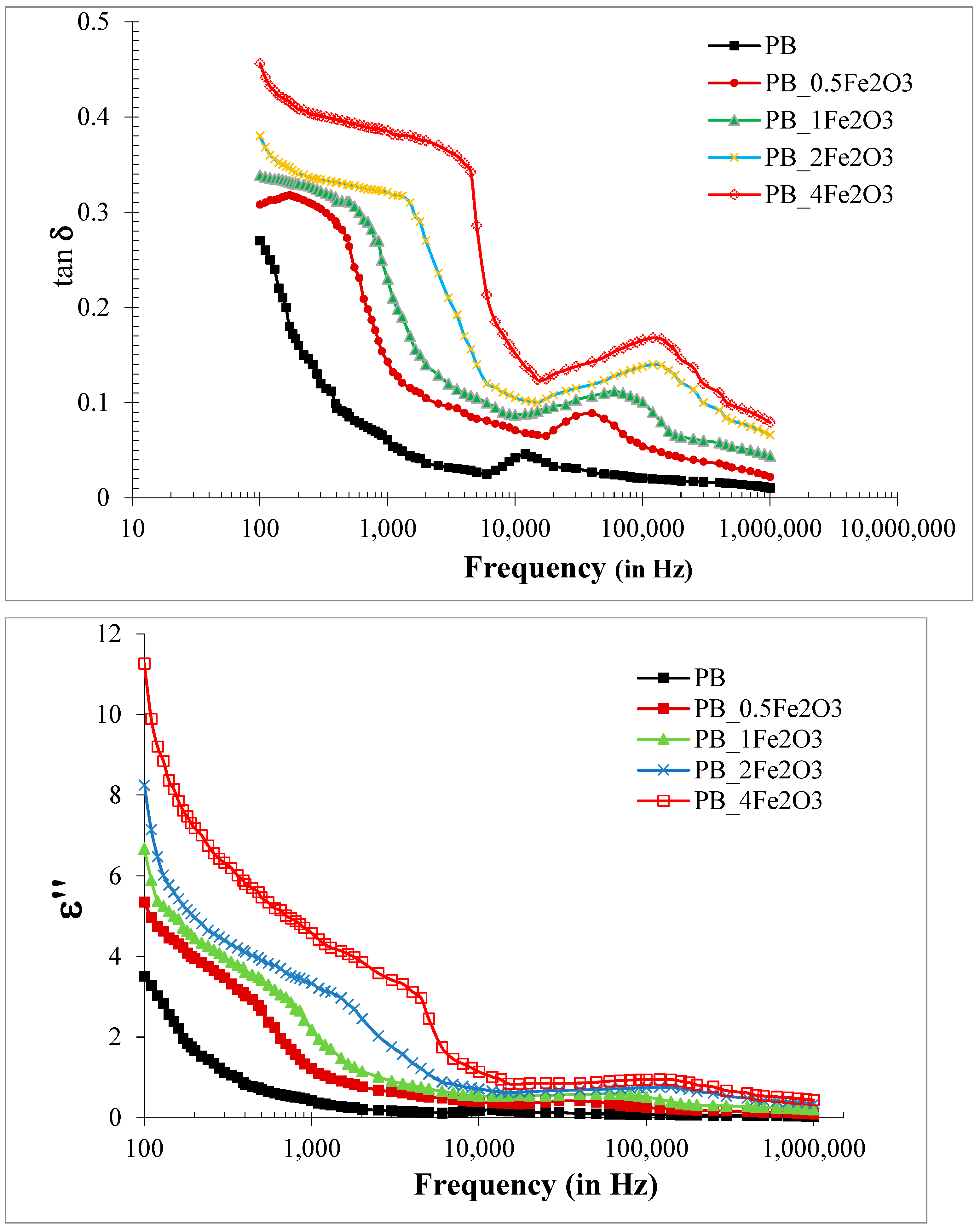
2.3.2. Variation of Loss Tangent and Dielectric Loss (ε)
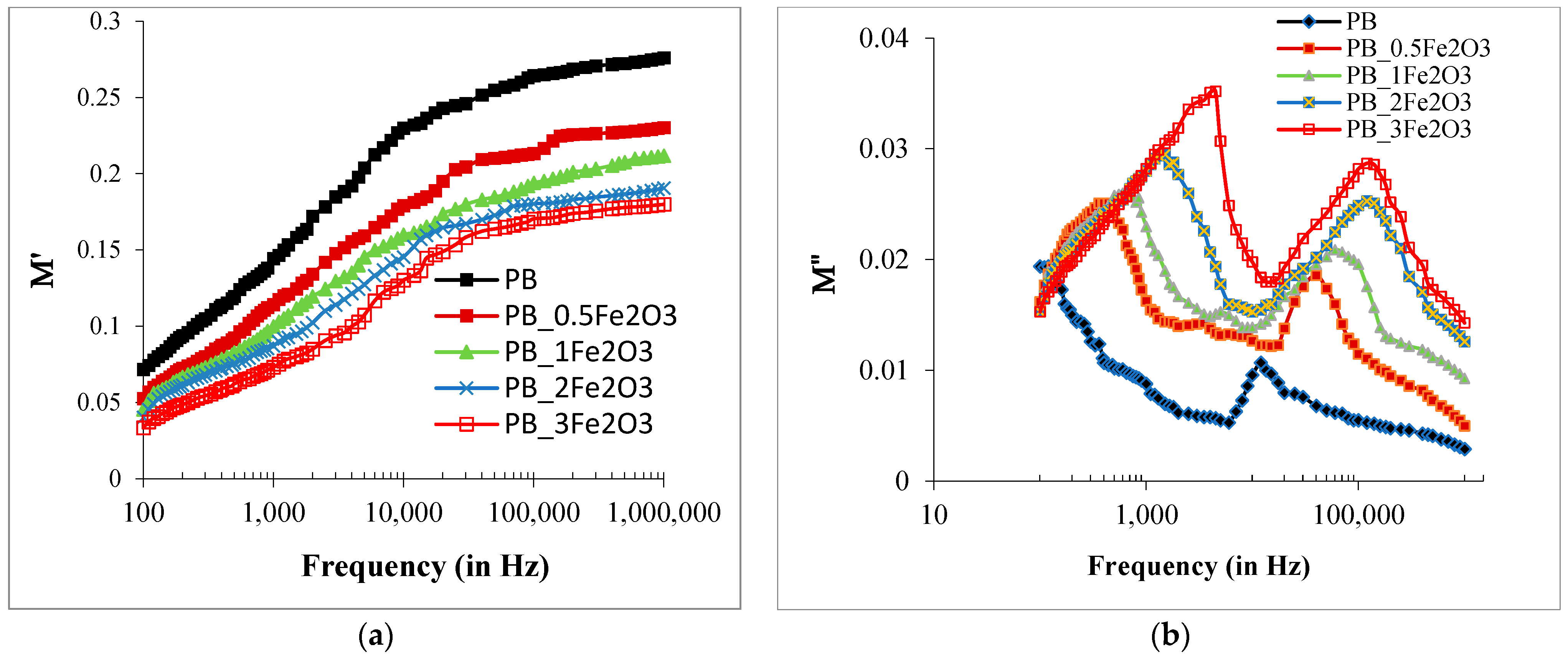
2.3.3. Variations in Electric Modulus Spectra (M*) Dielectric Parameters with Frequency and Composition
2.3.4. Electric Conductivity (σ)
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Composite Fabrication and Characterization
- (1)
- Michelson interferometry was performed, where straight-line fringes were obtained only for films of uniform thickness. The fringes were curved and disturbed for films with non-uniform thickness;
- (2)
- The prepared films were measured at different points using a screw gauge with a least count of 0.01 mm;
- (3)
- The measured thickness was verified by performing a volumetric analysis, where, from the measured values of density and mass and the radius of the petri dish, the thickness of the film was calculated;
- (4)
- The thickness of samples was further measured using optical profilometry. The films were then cut into small pieces with a length–breadth ratio of 1:1 for use in XRD, FTIR, and dielectric spectroscopy to investigate their structural and dielectric properties.
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Tan, D.; Irwin, P. Polymer Based Nanodielectric Composites. In Advances in Ceramics; Sikalidis, C., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, V. Characterization Techniques for Polymer Nanocomposites; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KgaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bafna, M.; Gupta, A.K.; Khanna, R.K.; Vijay, Y.K. Development of potassium permanganate (KMnO4) doped poly methyl methacrylate (PMMA) composite using layered structure for electromagnetic shielding purpose. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 30, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keith, N.J. Dielectric Polymer Nanocomposites; Springer Science Business Media, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bafna, M.; Gupta, A.K.; Khanna, R.K. Effect of potassium chromate nanoparticles on the optical properties of poly (methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) films. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 10, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, J.W.; Zheng, M.S.; Fan, B.; Dang, Z.M. Polymer-based dielectrics with high permittivity for electric energy storage: A review. Nano Energy 2021, 89, 106438. [Google Scholar]
- Bafna, M.; Sain, N.; Khandelwal, A.; Deeba, F.; Gupta, A.K. Study of refractive index and dispersion behavior of KMnO4 doped poly-methyl-methacrylate (PMMA)composites. Mater. Today Proc. Sci. Direct. 2022, 66, 3481–3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, B.S.R. Advances in Nanocomposites-Synthesis, Characterization and Industrial Applications; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, S.; Jin, L.; Hou, H.; Zhang, L. Polymer-Based Nanocomposites with High Dielectric Permittivity. In Polymer-Based Multifunctional Nanocomposites and Their Applications; Song, K., Liu, C., Guo, J.Z., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; Chapter 8; pp. 201–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al, D.M.; Madani, M.; Ghobashy, M.M. Preparation and Dielectric Property of TiO2 Doping with Silver Dispersed in Polyvinyl Alcohol and Polyurethane (TiO2@Ag/PVA-PU) Nanocomposite Materials. Asian J. Sci. Res. 2020, 13, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.K.; Bafna, M.; Srivastava, S.; Khanna, R.K.; Vijay, Y.K. Study of electromagnetic shielding effectiveness of metal oxide polymer composite in their bulk and layered forms. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 3880–3887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengwa, R.; Dhatarwal, P. Polymer nanocomposites comprising PMMA matrix and ZnO, SnO2, and TiO2 nanofillers: A comparative study of structural, optical, and dielectric properties for multifunctional technological applications. Opt. Mater. 2021, 113, 110837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tailor, R.; Vijay, Y.K.; Bafna, M. Carbon soot polymer nanocomposites (CSPNCs): Production, surface morphological, glass transition temperature phenomenon and optical properties. In Environmental Emissions; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Sengwa, R.J.; Choudhary, S. Nonlinear enhancement of the dielectric properties of PVA-Al2O3 nanocomposite. Adv. Mater. Proc. 2017, 2, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.K.; Bafna, M.; Vijay, Y.K. Study of optical properties of KMnO4 doped poly (methylmethacrylate)(PMMA) composite films. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2018, 41, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, N.; Bafna, M. Investigation of structural, optical, electrical and mechanical properties of di-methyl-tin-di-chloride PMMA composite films. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 30, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, S.; Chatterjee, S.K.; Ghosh, J.; Meikap, A.K. Analysis of the dielectric relaxation and ac conductivity behavior of polyvinyl alcohol-cadmium selenide nanocomposite films. Polym. Compos. 2017, 38, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeba, F.; Bafna, M.; Jain, A. Tuning of electrical properties of polymer blends or composites by the doping of salts and inorganic fillers: A review. SGVU Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 8, 46–69. [Google Scholar]
- Bafna, M.; Gupta, A.K.; Agarwal, A.; Sain, N.; Jain, V. Insight into the optical properties of poly-methyl-methacrylate (PMMA) loaded with ferric chloride (FeCl3) in varying concentration. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 38, 1209–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B.; Tang, S.; Jiang, Q.; Chen, C.; Chen, X.; Li, S.; Yan, X. Preparation and characterization of PEO/PMMA polymer composite electrolytes doped with nanoAl2O3. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 169, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengwa, R.J.; Dhatarwal, P.; Choudhary, S. Role of preparation methods on the structural and dielectric properties of plasticized polymer blend electrolytes:Correlation between ionic conductivity and dielectric Parameters. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 142, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.K.; Bafna, M.; Khanna, R.K. Dielectric properties of potassium permanganate (KMnO4)-PMMA composite films. J. Emerg. Technol. Innov. Res. 2018, 5, 433–436. [Google Scholar]
- Ghule, B.; Laad, M. Polymer composites with improved dielectric properties: A review. Ukr. J. Phys. 2021, 66, 166–177. [Google Scholar]
- Deeba, F.; Gupta, A.K.; Kulshrestha, V.; Bafna, M.; Jain, A. Investigations on dielectric properties of PVDF/PMMA blends. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 66, 3547–3552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.K.; Bafna, M. Study of dielectric permittivity and electrical modulus of K2CrO4 doped PMMA. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 67, 890–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shobhna, C.; Sengwa, R.J. Effect of different inorganic nanoparticles on the structural, dielectric and ion transportation properties of polymers blend based nanocomposite solid polymer electrolytes. Electrochem. Acta 2017, 247, 924–941. [Google Scholar]
- Bafna, M.; Garg, N.; Gupta, A.K. Variation of dielectric properties & AC conductivity with frequency and composition for stannous chloride _ PMMA composite films. J. Emerg. Technol. Innov. Res. 2018, 5, 494–497. [Google Scholar]
- Bafna, M.; Garg, N. Investigation of Optical properties of tin chloride (SnCl2) doped Poly methyl methacrylate (PMMA) composite films. IIS Univ. J. Sci. Technol. 2017, 6, 27–32. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, N.; Di-Benedetto, S.A.; Tewari, P.; Lanagan, M.T.; Ratner, M.A.; Marks, T.J. Nanoparticle, size, shape, and interfacial effects on leakage current density, permittivity, and breakdown strength of metal oxide-polyolefin nanocomposites: Experiment and theory. Chem. Mater. 2010, 22, 1567. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, A.K.; Bafna, M.; Agarwal, A.; Sain, N. Dielectric studies and alternating current conductivity studies of polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) doped with ferric chloride (FeCl3) in varying concentration. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 38, 1263–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suporva, M.; Martynkova, G.S.; Barabaszova, K. Effect of Nano fillers Dispersion in Polymer Matrices: A Review. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2011, 3, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeba, F.; Gupta, A.K.; Kulshrestha, V.; Bafna, M.; Jain, A. Analysing the dielectric properties of ZnO doped PVDF/PMMA blend composite. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2022, 33, 23703–23713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhatarwa, P.; Choudhary, S.; Sengwa, R.J. Effectively Nanofiller Concentration Tunable Dielectric Properties of PVP/SnO2 Nanodielectrics. Mater. Lett. 2020, 273, 127913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhatarwal, P.; Choudhary, S.; Sengwa, R.J. Significantly Enhanced Dielectric Properties and chain segmental dynamics of PEO/SnO2 Nanocomposites. Polym. Bull. 2020, 78, 2357–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anu, M.; Pillai, S.S. Structure, thermal, optical and dielectric properties of SnO2 nanoparticles-filled HDPE polymer. Solid State Commun. 2022, 341, 114577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manivel, P.; Ramakrishnan, S.; Kothurkar, N.K.; Balamurugan, A.; Ponpandian, N.; Mangalaraj, D.; Viswanathan, C. Optical and electrochemical studies of polyaniline/SnO2 fibrous nanocomposites. Mater. Res. Bull. 2013, 48, 640–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, P.; Lopes, A.C.; Méndez, S.L. Electroactive phases of poly(vinylidene fluoride): Determination, processing and applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 683–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuvaraj, H.; Woo, M.H.; Park, E.J.; Jeong, Y.T.; Lim, K.T. Polypyrrole/γ-Fe2O3 magnetic nanocomposites synthesized in supercritical fluid. Eur. Polym. J. 2008, 44, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandgar, D.K.; Navale, S.T.; Vanalkar, S.A.; Kim, J.H.; Harale, N.S.; Patil, P.S.; Patil, V.B. Synthesis, structural, morphological, compositional and electrical transport properties of polyaniline/α-Fe2O3 hybrid nanocomposites. Synth. Met. 2014, 195, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, T.; Shakoor, A.; Ahmad, E.; Saeed, M.; Niaz, N.A.; Tirmizi, S.K. Structural, morphological, and electrical properties of polyaniline-Fe2O3 nanocomposites. Polym. Sci. Ser. B 2015, 57, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, T.; Shakoor, A.; Ahmed, E.; Niaz, N.A.; Akhtar, M.S.; Raza, M.R.; Malik, M.A.; Foot, P.J.S. Polypyrrole-Fe2O3 Nanocomposites with High Dielectric Constant: In Situ Chemical Polymerisation. Polym. Polym. Compos. 2018, 26, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Sayed, A.M.; Morsi, W.M. α-Fe2O3/(PVA + PEG) Nanocomposite films; Synthesis, optical, and dielectric characterizations. J. Mater. Sci. 2014, 15, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenichi, H. Highly improved dielectric properties of polymer/α-Fe2O3 composites at elevated temperatures. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 64871–64878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

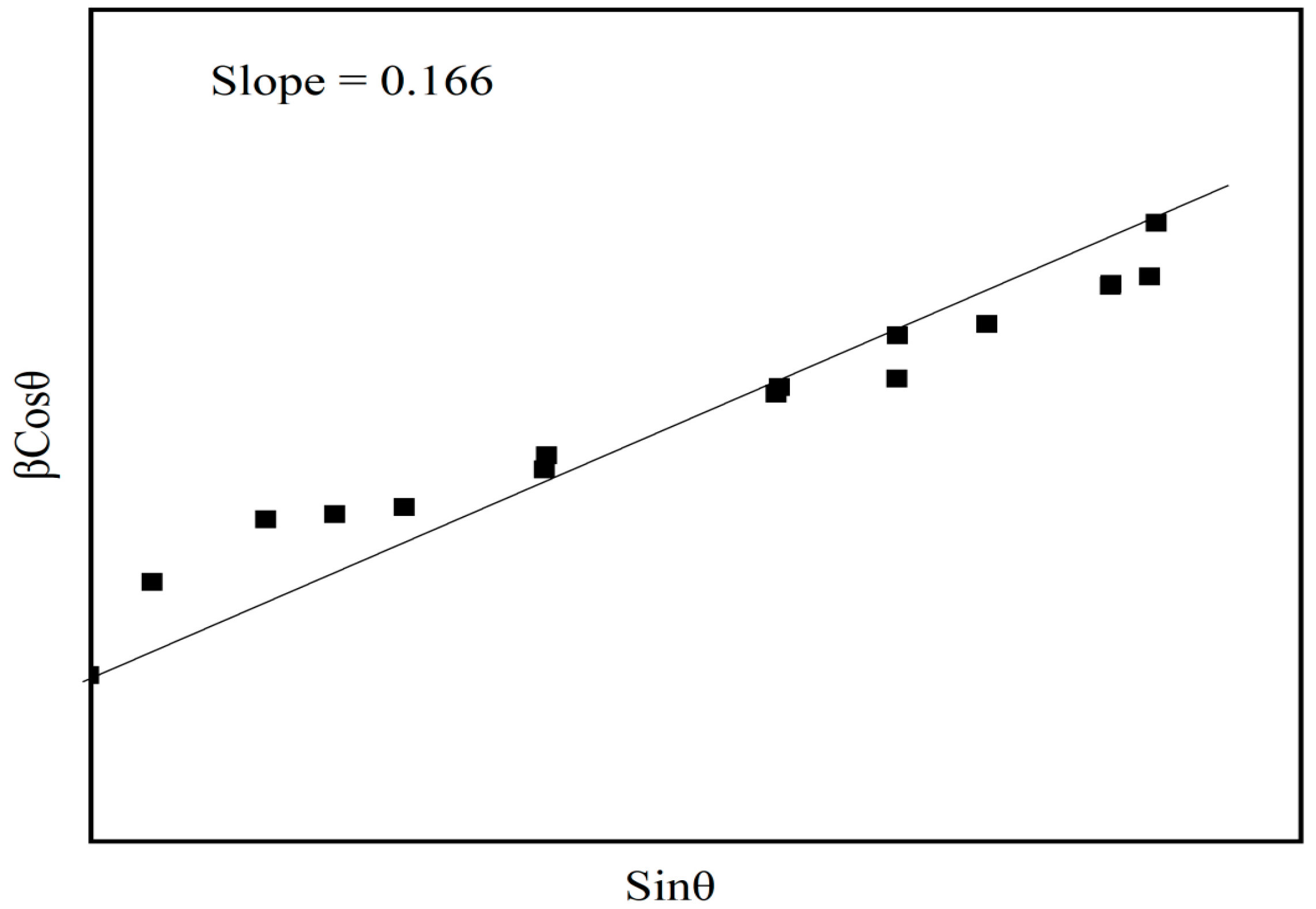


| S.No. | x wt % Fe2O3 | 2θ (in °) | d (Å) | FWHM × 10−2 (rad) | L (nm) | I (counts) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | (100) Reflection Plane Parameters | |||||
| 1. | 0 | 18.403 | 4.81 | 0.3070 | 47.755 | 8231 |
| 2. | 0.5 | 18.037 | 4.91 | 0.5117 | 28.651 | 3957 |
| 3. | 1 | 18.351 | 4.85 | 0.3070 | 47.776 | 6231 |
| 4. | 2 | 18.299 | 4.84 | 0.8187 | 17.914 | 4401 |
| 5. | 4 | 18.195 | 4.87 | 0.6140 | 23.883 | 4399 |
| II | (020) Reflection Plane Parameters | |||||
| 6. | 0 | 19.807 | 4.477 | 0.4093 | 35.912 | 7935 |
| 7. | 0.5 | 19.833 | 4.471 | 0.4861 | 30.239 | 4338 |
| 8. | 1 | 19.937 | 4.448 | 0.3582 | 41.043 | 6802 |
| 9. | 2 | 19.95 | 4.445 | 0.4350 | 33.797 | 4017 |
| 10. | 4 | 19.885 | 4.459 | 0.4349 | 33.802 | 4764 |
| III | (200) Reflection Plane Parameters | |||||
| 11. | 0 | 20.665 | 4.2930 | 0.4350 | 33.835 | 3195 |
| 12. | 0.5 | 20.327 | 4.3636 | 0.4341 | 33.887 | 2928 |
| 13. | 1 | 20.840 | 4.2573 | 0.3582 | 41.101 | 4069 |
| 14. | 2 | 20.847 | 4.2559 | 0.3879 | 37.954 | 3493 |
| 15. | 4 | 20.613 | 4.3037 | 0.3520 | 41.810 | 3494 |
| IV | (110) Reflection Plane Parameters | |||||
| 16 | 0 | 22.849 | 3.8873 | 0.5117 | 28.869 | 2652 |
| 17 | 0.5 | 22.927 | 3.8743 | 0.4093 | 36.096 | 2987 |
| 18 | 1 | 22.485 | 3.9494 | 0.5117 | 28.850 | 3370 |
| 19 | 2 | 22.745 | 3.9049 | 0.3520 | 41.959 | 3537 |
| 20. | 4 | 22.641 | 3.9226 | 0.3897 | 37.893 | 4199 |
| V | (101) Reflection Plane Parameters | |||||
| 21. | 0 | 24.461 | 3.6347 | 0.3520 | 42.091 | 2151 |
| 22. | 0.5 | 24.097 | 3.6888 | 0.2047 | 72.329 | 2939 |
| 23. | 1 | 24.201 | 3.6731 | 0.2179 | 67.961 | 6547 |
| 24. | 2 | 24.071 | 3.6927 | 0.2047 | 72.326 | 5059 |
| 25. | 4 | 23.941 | 3.7124 | 0.2303 | 64.271 | 6397 |
| VI | (021) Reflection Plane Parameters | |||||
| 26. | 0 | 26.697 | 3.3351 | 0.4093 | 36.359 | 4048 |
| 27. | 0.5 | 26.593 | 3.3479 | 0.3892 | 38.228 | 2984 |
| 28. | 1 | 26.411 | 3.3706 | 0.3524 | 42.205 | 4044 |
| 29. | 2 | 26.333 | 3.3804 | 0.2343 | 63.468 | 3439 |
| 30. | 4 | 26.567 | 3.3511 | 0.2913 | 51.073 | 4683 |
| VII | (012) Reflection Plane Parameters | |||||
| 31. | 0.5 | 30.729 | 2.9061 | 0.2989 | 50.239 | 2743 |
| 32. | 1 | 30.441 | 2.9329 | 0.2814 | 53.326 | 3523 |
| 33. | 2 | 30.649 | 2.9135 | 0.2980 | 50.381 | 3279 |
| 34. | 4 | 30.623 | 2.9159 | 0.2558 | 58.688 | 4443 |
| VIII | (104) Reflection Plane Parameters | |||||
| 35. | 0.5 | 33.041 | 2.7078 | 0.2303 | 65.580 | 4646 |
| 36. | 1 | 33.197 | 2.6954 | 0.2184 | 69.182 | 12,035 |
| 37. | 2 | 33.067 | 2.7057 | 0.2558 | 59.047 | 9369 |
| 38. | 4 | 32.963 | 2.7140 | 0.2558 | 59.031 | 12,464 |
| IX | (110) Reflection Plane Parameters | |||||
| 39. | 0.5 | 35.589 | 2.5196 | 0.2303 | 66.032 | 3728 |
| 40. | 1 | 35.693 | 2.5124 | 0.2555 | 59.537 | 10,050 |
| 41. | 2 | 35.511 | 2.5249 | 0.2303 | 66.018 | 6605 |
| 42. | 4 | 35.459 | 2.5285 | 0.2558 | 59.428 | 9656 |
| X | (113) Reflection Plane Parameters | |||||
| 43. | 0.5 | 40.790 | 2.2095 | 0.2556 | 60.438 | 2916 |
| 44. | 1 | 40.867 | 2.2055 | 0.2535 | 60.954 | 4597 |
| 45. | 2 | 40.789 | 2.2095 | 0.2558 | 60.391 | 4450 |
| 46. | 4 | 40.685 | 2.2149 | 0.2558 | 60.371 | 6032 |
| XI | (024) Reflection Plane Parameters | |||||
| 47. | 0.5 | 49.395 | 1.8428 | 0.2558 | 62.305 | 2974 |
| 48. | 1 | 49.525 | 1.8383 | 0.2047 | 77.899 | 5168 |
| 49. | 2 | 49.421 | 1.8419 | 0.2558 | 62.311 | 4604 |
| 50. | 4 | 49.291 | 1.8465 | 0.2558 | 62.279 | 6554 |
| XII | (116) Reflection Plane Parameters | |||||
| 51. | 0.5 | 53.997 | 1.6961 | 0.2558 | 63.529 | 3094 |
| 52. | 1 | 54.023 | 1.6954 | 0.2558 | 63.536 | 4833 |
| 53. | 2 | 53.971 | 1.6969 | 0.2558 | 63.521 | 4973 |
| 54. | 4 | 53.867 | 1.6999 | 0.2558 | 63.492 | 6886 |
| XIII | (018) Reflection Plane Parameters | |||||
| 55. | 0.5 | 57.51 | 1.6006 | 0.2627 | 62.872 | 2564 |
| 56. | 1 | 57.507 | 1.6006 | 0.4097 | 40.313 | 3654 |
| 57. | 2 | 57.481 | 1.6013 | 0.3066 | 53.862 | 3479 |
| 58. | 4 | 57.429 | 1.6026 | 0.3521 | 46.890 | 4577 |
| XIV | (214) Reflection Plane Parameters | |||||
| 59. | 0.5 | 62.395 | 1.4865 | 0.3719 | 45.516 | 2813 |
| 60. | 1 | 62.421 | 1.4859 | 0.3070 | 55.146 | 4123 |
| 61. | 2 | 62.369 | 1.4870 | 0.2558 | 66.166 | 4060 |
| 62. | 4 | 62.239 | 1.4898 | 0.2558 | 66.121 | 5531 |
| XV | (300) Reflection Plane Parameters | |||||
| 63. | 0.5 | 63.980 | 1.4534 | 0.5867 | 29.098 | 2786 |
| 64. | 1 | 64.241 | 1.4481 | 0.3070 | 55.689 | 4033 |
| 65. | 2 | 63.981 | 1.4534 | 0.2558 | 66.741 | 4039 |
| 66. | 4 | 63.851 | 1.4560 | 0.2558 | 66.694 | 5655 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bafna, M.; Deeba, F.; Gupta, A.K.; Shrivastava, K.; Kulshrestha, V.; Jain, A. Analysis of Dielectric Parameters of Fe2O3-Doped Polyvinylidene Fluoride/Poly(methyl methacrylate) Blend Composites. Molecules 2023, 28, 5722. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28155722
Bafna M, Deeba F, Gupta AK, Shrivastava K, Kulshrestha V, Jain A. Analysis of Dielectric Parameters of Fe2O3-Doped Polyvinylidene Fluoride/Poly(methyl methacrylate) Blend Composites. Molecules. 2023; 28(15):5722. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28155722
Chicago/Turabian StyleBafna, Minal, Farah Deeba, Ankit K. Gupta, Kriti Shrivastava, Vaibhav Kulshrestha, and Ankur Jain. 2023. "Analysis of Dielectric Parameters of Fe2O3-Doped Polyvinylidene Fluoride/Poly(methyl methacrylate) Blend Composites" Molecules 28, no. 15: 5722. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28155722
APA StyleBafna, M., Deeba, F., Gupta, A. K., Shrivastava, K., Kulshrestha, V., & Jain, A. (2023). Analysis of Dielectric Parameters of Fe2O3-Doped Polyvinylidene Fluoride/Poly(methyl methacrylate) Blend Composites. Molecules, 28(15), 5722. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28155722






