Nickel-Atom Doping as a Potential Means to Enhance the Photoluminescence Performance of Carbon Dots
Abstract
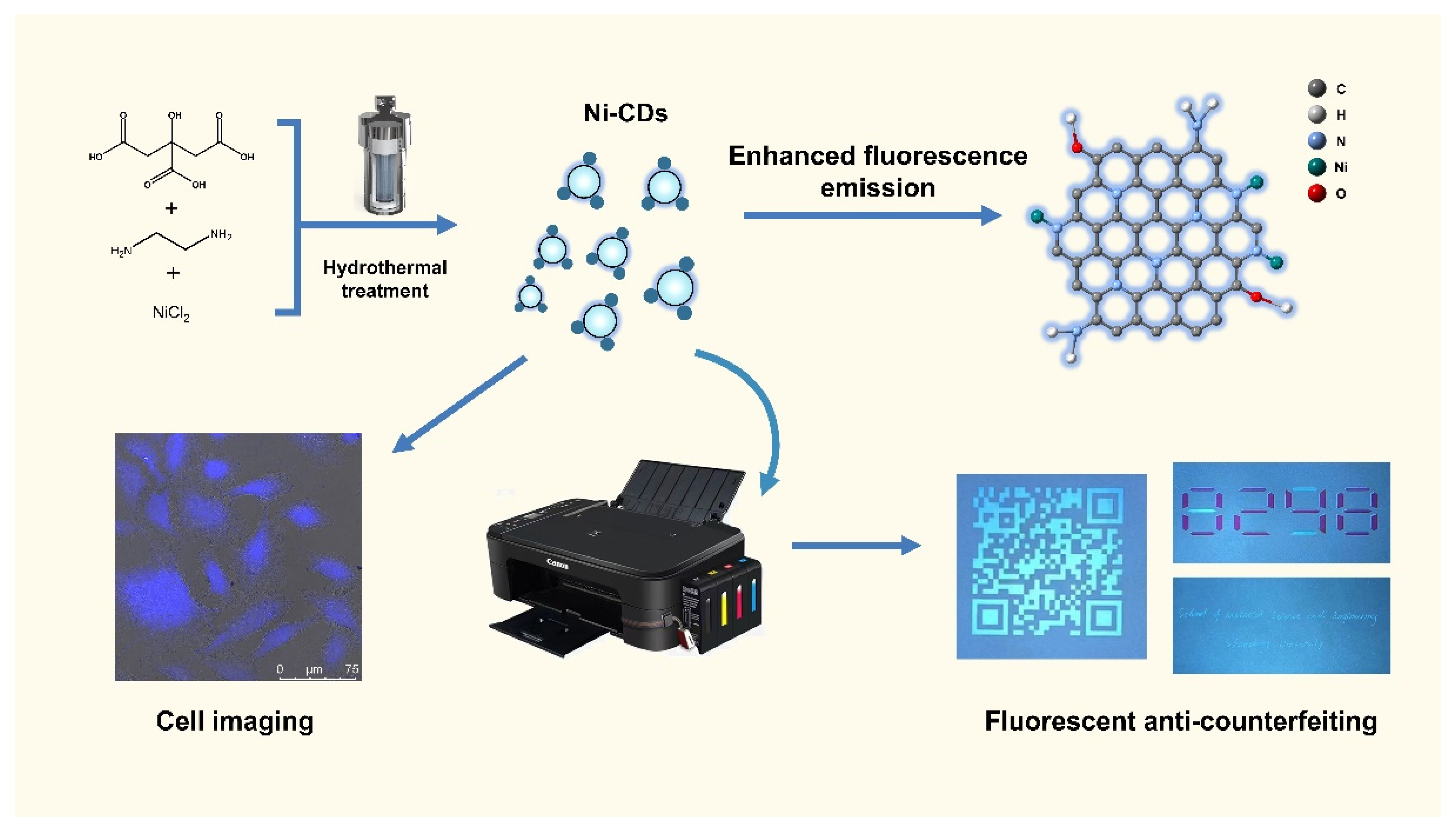
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
3. Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Synthesis of Ni-CDs and P-CDs
3.3. Ink Printing Tests
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kang, C.; Tao, S.; Yang, F.; Yang, B. Aggregation and luminescence in carbonized polymer dots. Aggregate 2022, 3, e169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Yang, F.; Zhu, G.; Yu, K.; Kou, R.; Sun, C.; Liu, Y.; Xu, J.; Liu, C.; et al. Reversible Iron Oxyfluoride (FeOF)-Graphene Composites as Sustainable Cathodes for High Energy Density Lithium Batteries. Small 2023, 19, e2206947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Cheng, G.; Dong, M.; Liu, S.; Huang, C. Carbon dots as a luminescence sensor for ultrasensitive detection of phosphate and their bioimaging properties. Luminescence 2014, 30, 411–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Li, H.; Ling, L.; Li, G.; Cheng, R.; Lu, X.; Xie, A.-Q.; Li, Q.; Wang, C.-F.; Chen, S. Green Synthesis of Carbon Dots toward Anti-Counterfeiting. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 8, 1566–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Chen, X.; Wu, W. Multiple Stimuli-Response Polychromatic Carbon Dots for Advanced Information Encryption and Safety. Small 2023, 19, e2206709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, L.; Fu, Z.; Cui, F. Synthesis of Carbon Dots and their Application as Turn Off–On Fluorescent Sensor for Mercury (II) and Glutathione. J. Fluoresc. 2020, 30, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pajewska-Szmyt, M.; Buszewski, B.; Gadzała-Kopciuch, R. Sulphur and nitrogen doped carbon dots synthesis by microwave assisted method as quantitative analytical nano-tool for mercury ion sensing. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2019, 242, 122484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.L.; Chen, B.B.; Li, C.M.; Huang, C.Z. Carbon dots: Synthesis, formation mechanism, fluorescence origin and sensing applications. Green Chem. 2019, 21, 449–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hola, K.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Giannelis, E.P.; Zboril, R.; Rogach, A.L. Carbon dots—Emerging light emitters for bioimaging, cancer therapy and optoelectronics. Nano Today 2014, 9, 590–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hu, A. Carbon quantum dots: Synthesis, properties and applications. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 6921–6939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, S.; Liang, K.; Zhu, J.; Yang, B.; Zhao, D.; Kong, B. Hetero-atom-doped carbon dots: Doping strategies, properties and applications. Nano Today 2020, 33, 100879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasija, V.; Raizada, P.; Sudhaik, A.; Singh, P.; Thakur, V.K.; Khan, A.A.P. Fabrication of Ag/AgI/WO3 heterojunction anchored P and S co-doped graphitic carbon nitride as a dual Z scheme photocatalyst for efficient dye degradation. Solid State Sci. 2020, 100, 106095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Long, Y.; Song, A.; Wang, H.; Xiang, S.; Qiu, Y.; Ge, X.; Golberg, D.; Weng, Q. Boron Dopants in Red-Emitting B and N Co-Doped Carbon Quantum Dots Enable Targeted Imaging of Lysosomes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 17045–17053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inagaki, M.; Toyoda, M.; Soneda, Y.; Morishita, T. Nitrogen-doped carbon materials. Carbon 2018, 132, 104–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, X.; Ma, C.; Ge, C.; Yan, M.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Morais, P.C.; Bi, H. Green synthesis of nitrogen-doped carbon dots from konjac flour with “off–on” fluorescence by Fe3+ and l-lysine for bioimaging. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 4631–4639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Han, L.; Gao, X.; He, W.; Chu, R.; Ma, Y. Application of Carbon Quantum dot Fluorescent Materials in Metal Ions Detection. E3S Web Conf. 2021, 245, 03080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhao, W.; Luo, L.; Liu, X.; Bi, X.; Li, J.; Jiang, P.; You, T. Electrochemiluminescence of Carbon-based Quantum Dots: Synthesis, Mechanism and Application in Heavy Metal Ions Detection. Electroanalysis 2021, 34, 608–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, S.; Praveena, M.; Mohammed, E. Exploration of highly photoluminescent first-row transition metals (manganese, iron, cobalt, nickel, copper and zinc) co-doped nano carbon dots as energy storage materials. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2021, 269, 115145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Chen, Y.; Rao, P.; Ni, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhu, J.; Li, C.; Xiong, G.; Liang, P.; He, X.; et al. Enhancing the Electron Transport, Quantum Yield, and Catalytic Performance of Carbonized Polymer Dots via Mn-O Bridges. Small 2022, 18, 2106863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Gao, F.; Zhao, L.; Wu, Y.; Wang, F.; Dong, L.; Jiang, Y. Mn-CDs with oxidase activity produces ROS to inhibit cell activity. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 25253–25260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-H.; Kong, F.-Y.; Tai, X.-S. Synthesis, Structural Characterization of a New Ni(II) Complex and Its Catalytic Activity for Oxidation of Benzyl Alcohol. Bull. Chem. React. Eng. Catal. 2022, 17, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Zhao, M.-M.; Luo, Q.-W.; Zhang, Y.-C.; Liu, T.-T.; Yang, Z.; Liao, M.; Tu, P.; Zeng, K.-W. Carbon Quantum Dots-Based Nanozyme from Coffee Induces Cancer Cell Ferroptosis to Activate Antitumor Immunity. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 9228–9239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Liu, Y.; Guo, Z.; Lei, B.; Zhuang, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Z.; Hu, C. Hydrophobic carbon dots with blue dispersed emission and red aggregation-induced emission. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Guo, S. Chemically doped fluorescent carbon and graphene quantum dots for bioimaging, sensor, catalytic and photoelectronic applications. Nanoscale 2015, 8, 2532–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhai, X.; Ma, T.; Huang, Y.; Yan, C.; Du, Y. Multifunctional cerium doped carbon dots nanoplatform and its applications for wound healing. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 423, 130301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, B.; Liu, S.; Feng, L.; Liu, S.; Gai, S.; Dai, Y.; Xie, L.; Liu, B.; Yang, P.; Zhao, Y. Renal-Clearable Nickel-Doped Carbon Dots with Boosted Photothermal Conversion Efficiency for Multimodal Imaging-Guided Cancer Therapy in the Second Near-Infrared Biowindow. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2100549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Huang, J.; Ruan, Y.; Li, H.; Gong, P.; Wang, F.; Tang, Q.; Jiang, Y. Unraveling the Structure Transition and Peroxidase Mimic Activity of Copper Sites over Atomically Dispersed Copper-Doped Carbonized Polymer Dots. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202214042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Bao, W.; Yang, F.; Yan, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, G.; Yang, W.; Li, Y. Electrochemical synthesis of FeNx doped carbon quantum dots for sensitive detection of Cu2+ ion. Green Energy Environ. 2023, 8, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danilova, J.S.; Avdoshenko, S.M.; Karushev, M.P.; Timonov, A.M.; Dmitrieva, E. Infrared spectroscopic study of nickel complexes with salen-type ligands and their polymers. J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1241, 130668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, D.; Hsu, H.; Li, R.; Feng, X.; Guo, D.; Han, X.; Lu, L.; He, X.; Gao, S.; Hou, J.; et al. A comparative investigation of aging effects on thermal runaway behavior of lithium-ion batteries. Etransportation 2019, 2, 100034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Z.; Zuo, W.; Chen, S.; Li, Z.; He, Y.; Liang, J.; Ma, F.; Wang, H.; et al. Improving the Stability of Non-Noble-Metal M–N–C Catalysts for Proton-Exchange-Membrane Fuel Cells through M–N Bond Length and Coordination Regulation. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, e2006613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Xu, H.; Ha, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, M.; Wu, R. Two-dimensional dual carbon-coupled defective nickel quantum dots towards highly efficient overall water splitting. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2019, 250, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-R.; Liu, J.-Y.; Liu, Z.-W.; Wang, W.-C.; Luo, J.; Han, X.P.; Du, X.-W.; Qiao, S.-Z.; Yang, J. Identifying the Key Role of Pyridinic-N-Co Bonding in Synergistic Electrocatalysis for Reversible ORR/OER. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, e1800005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, S.; Zhao, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Wu, Z.; Ma, T.; Zhu, B.; Yang, C.; Xiang, X.; Ma, L.; Han, X.; et al. A Library of ROS-Catalytic Metalloenzyme Mimics with Atomic Metal Centers. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, e202200255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Zhu, J.; Zhai, Y.; Wang, H.; Bai, X.; Dong, B.; Wang, H.; Song, H. A novel mechanism for red emission carbon dots: Hydrogen bond dominated molecular states emission. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 13042–13051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismail, I.; Chen, Z.; Ji, X.; Sun, L.; Yi, L.; Xi, Z. A Fast-Response Red Shifted Fluorescent Probe for Detection of H2S in Living Cells. Molecules 2020, 25, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amro, K.; Daniel, J.; Clermont, G.; Bsaibess, T.; Pucheault, M.; Genin, E.; Vaultier, M.; Blanchard-Desce, M. A new route towards fluorescent organic nanoparticles with red-shifted emission and increased colloidal stability. Tetrahedron 2014, 70, 1903–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Yu, S.-B.; Wei, J.-S.; Xiong, H.-M. Full-Color Light-Emitting Carbon Dots with a Surface-State-Controlled Luminescence Mechanism. ACS Nano 2015, 10, 484–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Cheng, H.; Hu, Y.; Shi, G.; Dai, L.; Qu, L. Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Quantum Dots with Oxygen-Rich Functional Groups. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 134, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, L.; Zhu, R.; Phillips, D.L.; Yu, J. Effective Prevention of Charge Trapping in Graphitic Carbon Nitride with Nanosized Red Phosphorus Modification for Superior Photo(electro)catalysis. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 201703484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Deng, Q.; Li, H.; Xia, Y.; Hou, W. A general strategy to synthesize single-atom metal-oxygen doped polymeric carbon nitride with highly enhanced photocatalytic water splitting activity. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2023, 323, 122180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balou, S.; Shandilya, P.; Priye, A. Carbon dots for photothermal applications. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 1023602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallaji, Z.; Bagheri, Z.; Oroujlo, M.; Nemati, M.; Tavassoli, Z.; Ranjbar, B. An insight into the potentials of carbon dots for in vitro live-cell imaging: Recent progress, challenges, and prospects. Microchim. Acta 2022, 189, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sargin, I.; Karakurt, S.; Alkan, S.; Arslan, G. Live Cell Imaging With Biocompatible Fluorescent Carbon Quantum Dots Derived From Edible Mushrooms Agaricus bisporus, Pleurotus ostreatus, and Suillus luteus. J. Fluoresc. 2021, 31, 1461–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caglayan, M.O.; Mindivan, F.; Şahin, S. Sensor and Bioimaging Studies Based on Carbon Quantum Dots: The Green Chemistry Approach. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2020, 52, 814–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalytchuk, S.; Wang, Y.; Poláková, K.; Zbořil, R. Carbon Dot Fluorescence-Lifetime-Encoded Anti-Counterfeiting. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 29902–29908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Liu, B.; Wang, M.; Han, G.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, Y. Highly bright carbon quantum dots for flexible anti-counterfeiting. J. Mater. Chem. C 2022, 10, 11338–11346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kong, W.; Li, C.; Sun, Z.; Gao, F.; Zheng, J.; Jiang, Y. Nickel-Atom Doping as a Potential Means to Enhance the Photoluminescence Performance of Carbon Dots. Molecules 2023, 28, 5526. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28145526
Kong W, Li C, Sun Z, Gao F, Zheng J, Jiang Y. Nickel-Atom Doping as a Potential Means to Enhance the Photoluminescence Performance of Carbon Dots. Molecules. 2023; 28(14):5526. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28145526
Chicago/Turabian StyleKong, Wenqi, Can Li, Zhongqi Sun, Fucheng Gao, Jinfan Zheng, and Yanyan Jiang. 2023. "Nickel-Atom Doping as a Potential Means to Enhance the Photoluminescence Performance of Carbon Dots" Molecules 28, no. 14: 5526. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28145526
APA StyleKong, W., Li, C., Sun, Z., Gao, F., Zheng, J., & Jiang, Y. (2023). Nickel-Atom Doping as a Potential Means to Enhance the Photoluminescence Performance of Carbon Dots. Molecules, 28(14), 5526. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28145526




