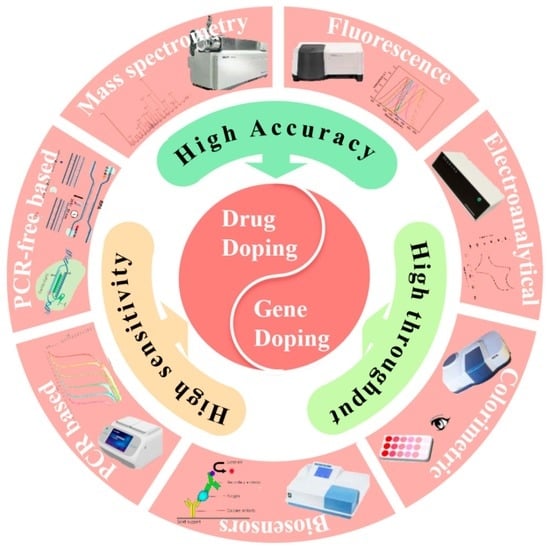
A Review of Recent Progress in Drug Doping and Gene Doping Control Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Drug Doping Detection
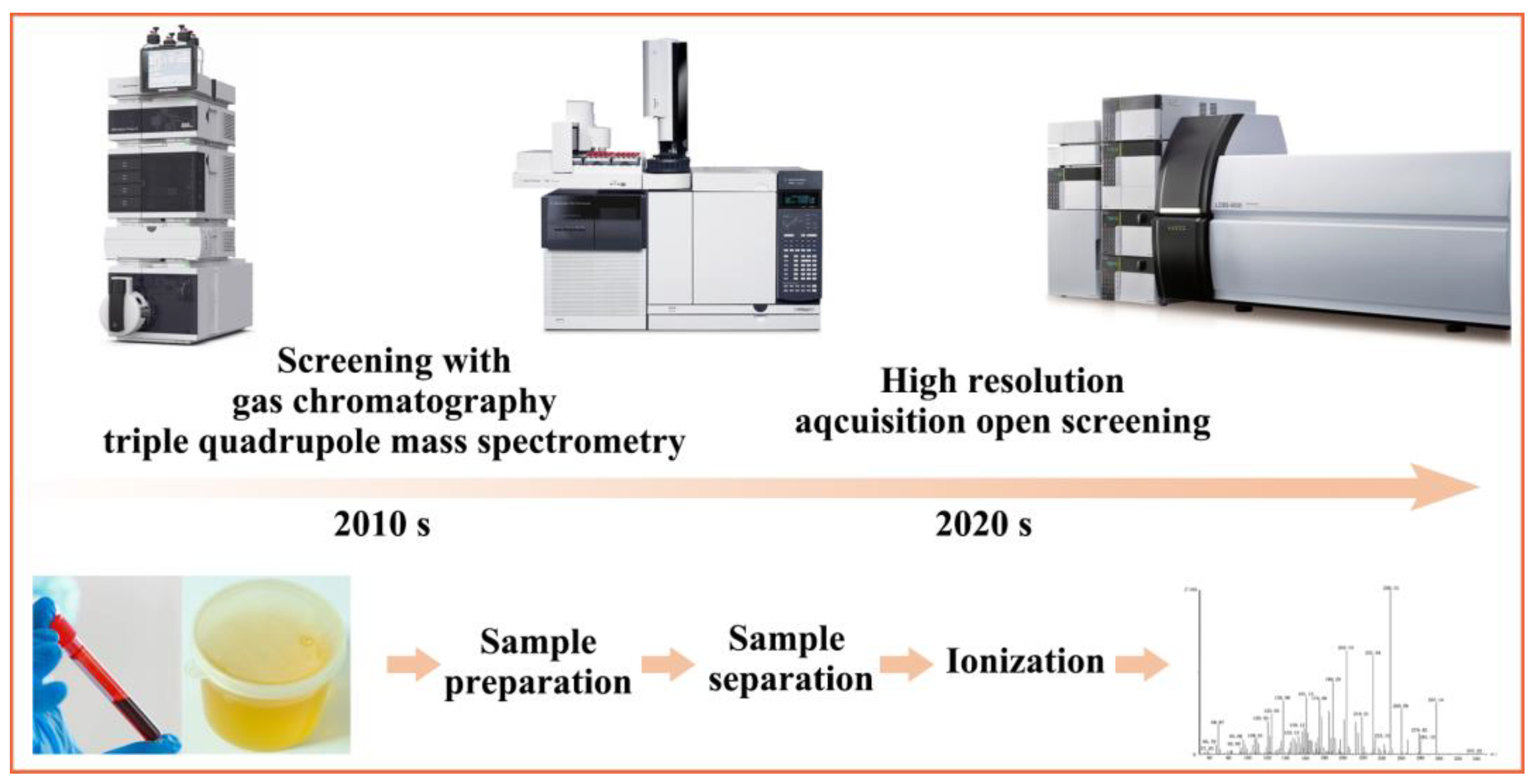
2.1. MS-Based Methods
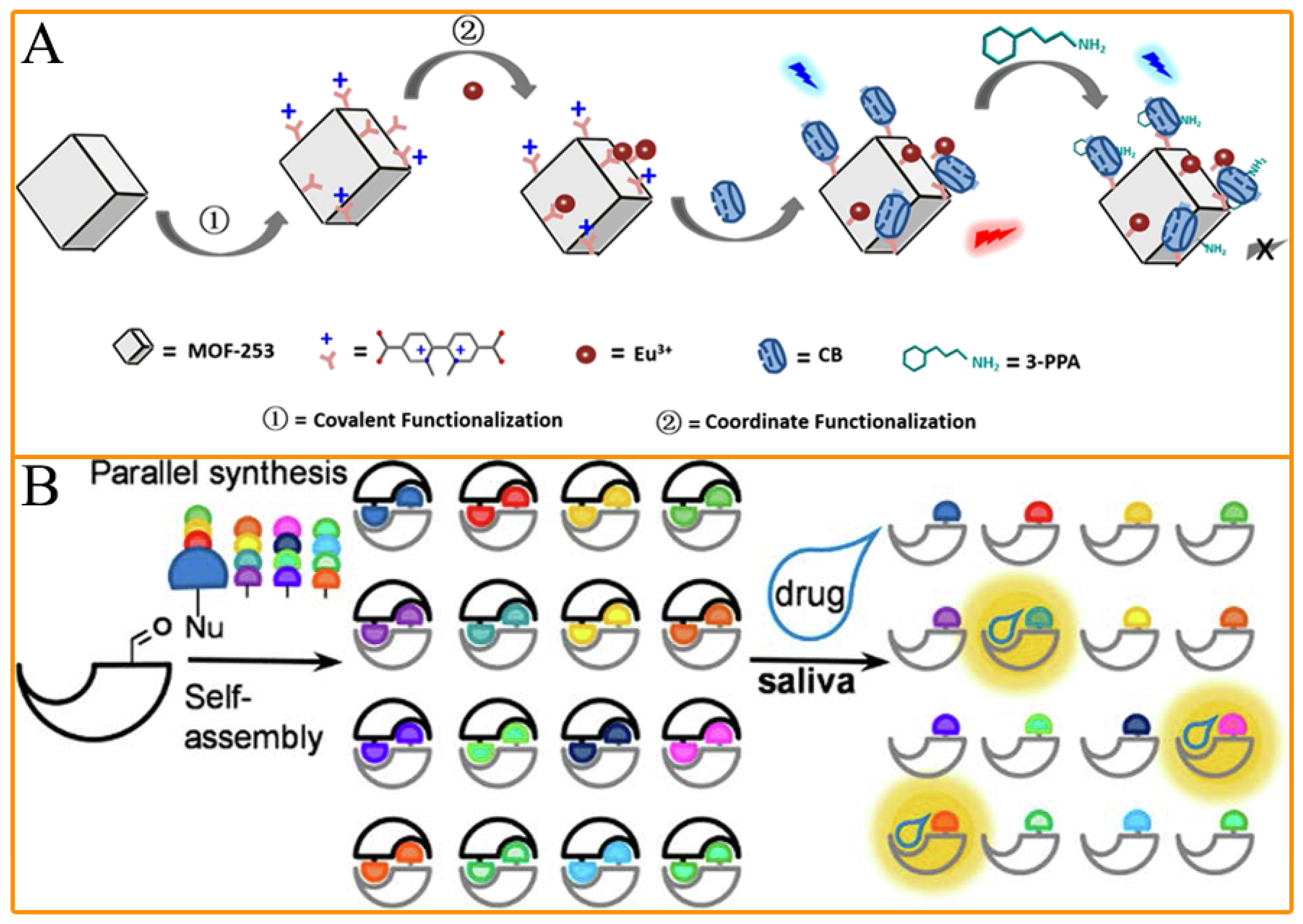
2.2. Fluorescence Methods
2.3. Electroanalytical Methods
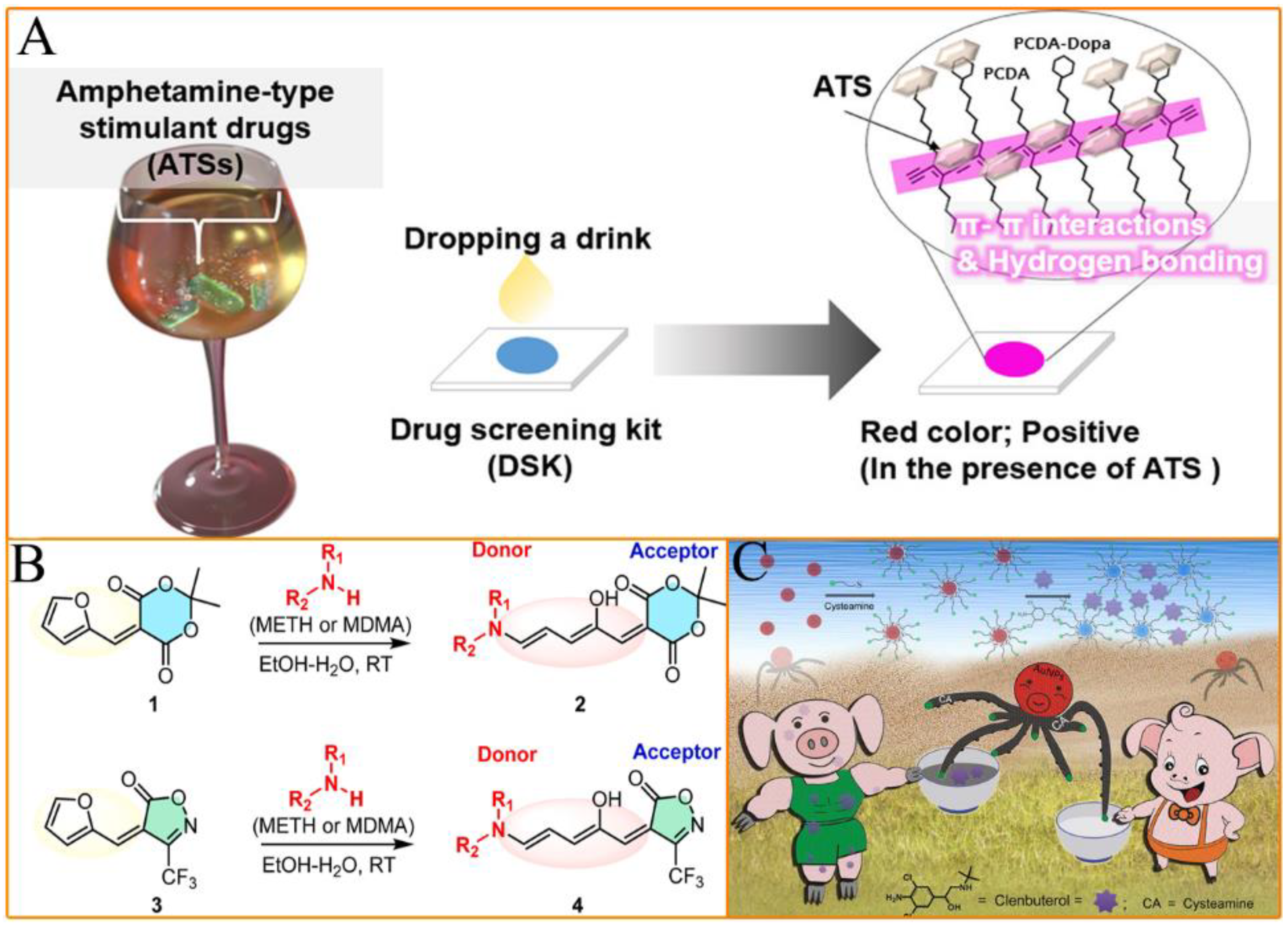
2.4. Colorimetric Methods
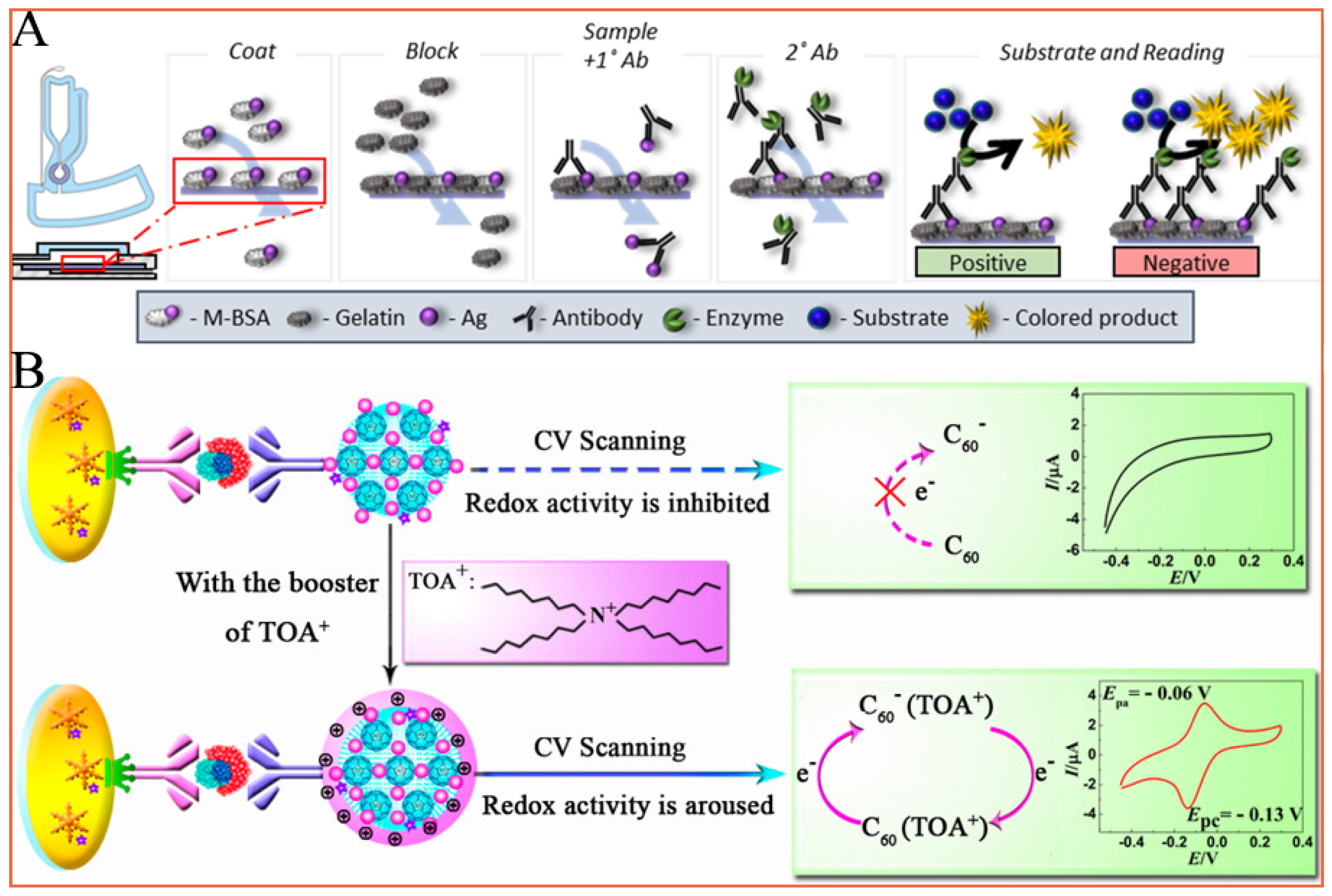
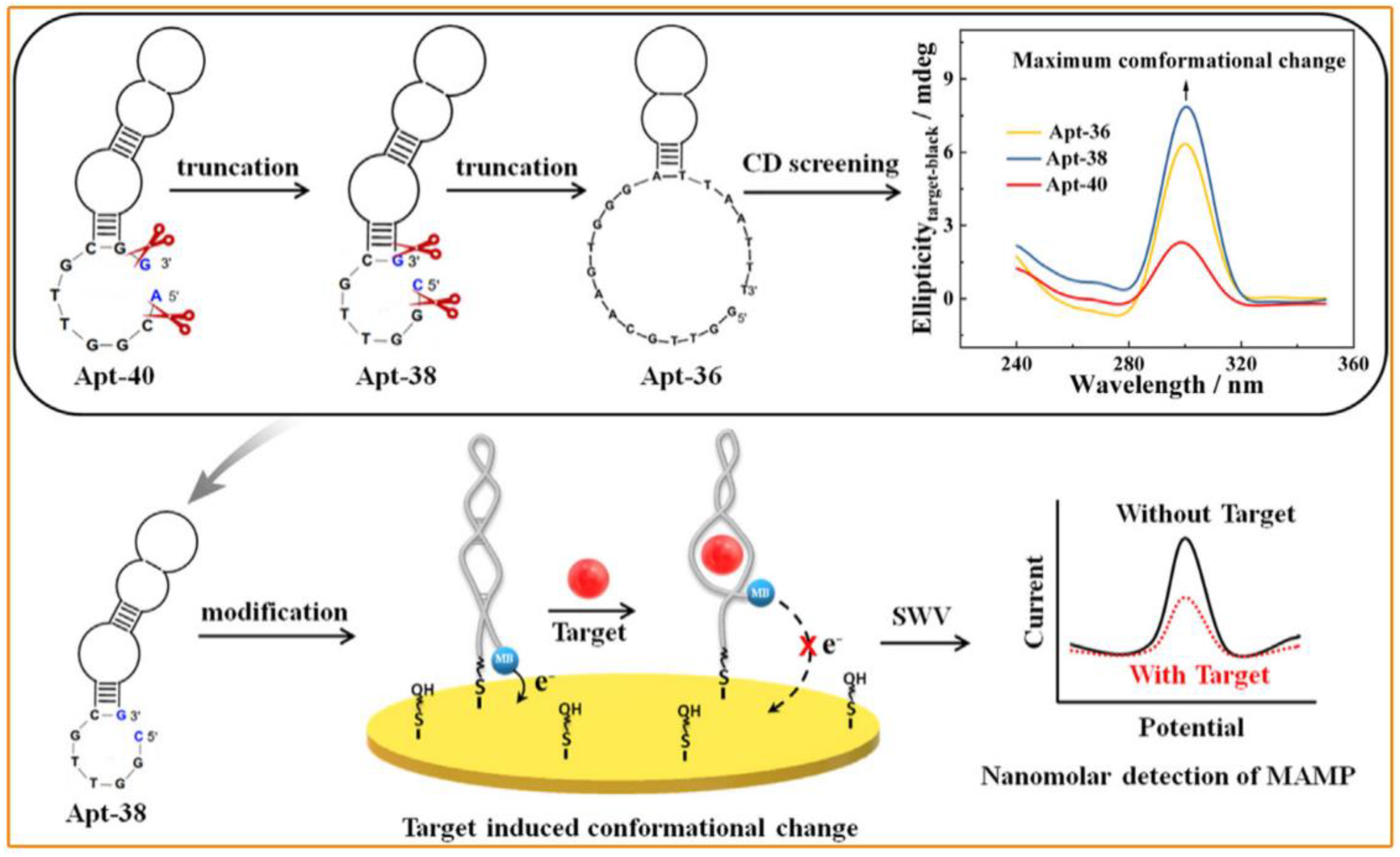
2.5. Biosensors
3. Gene Doping Detection
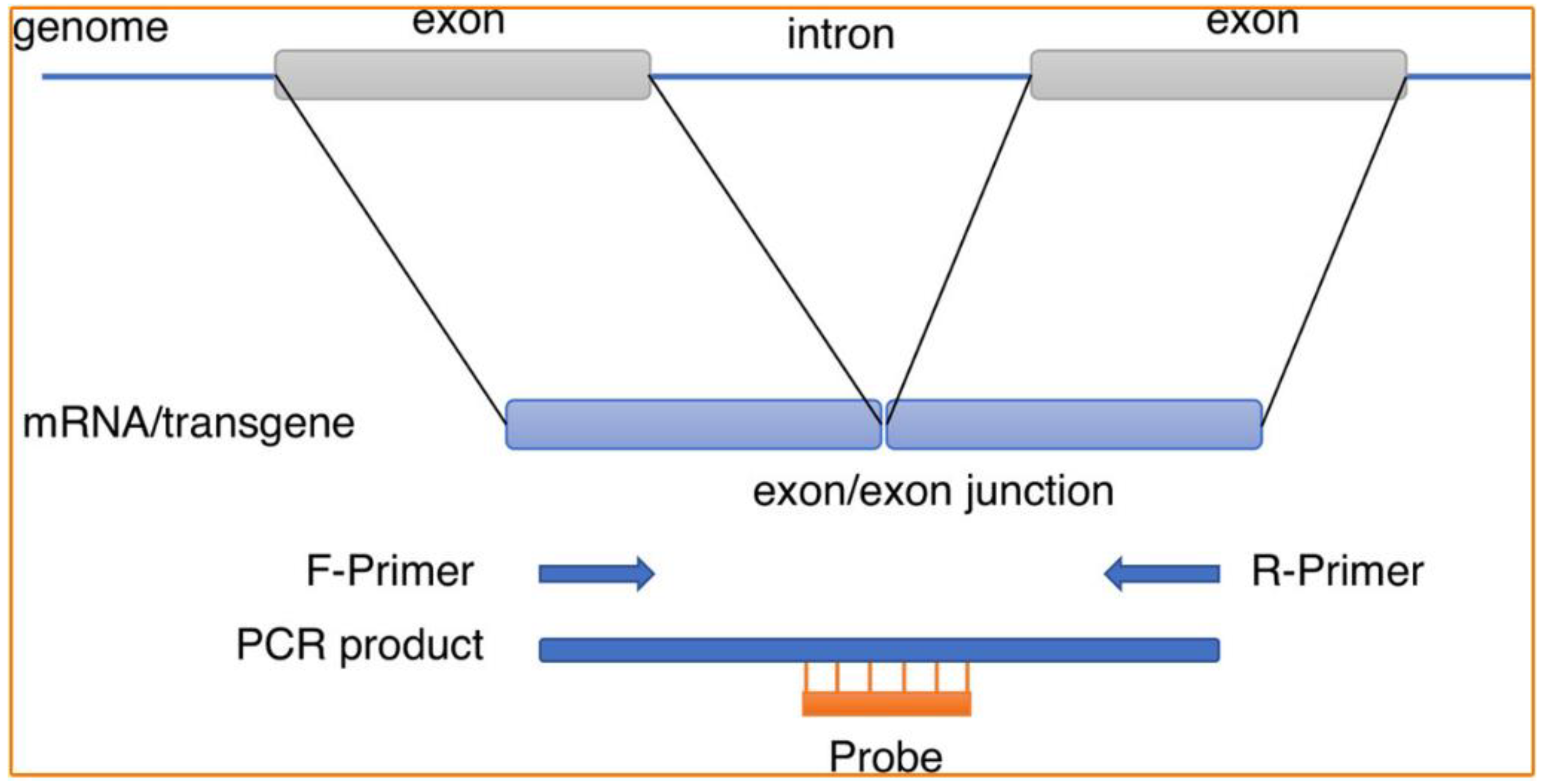
3.1. Typical PCR Methods
3.2. Sequencing-Based Methods
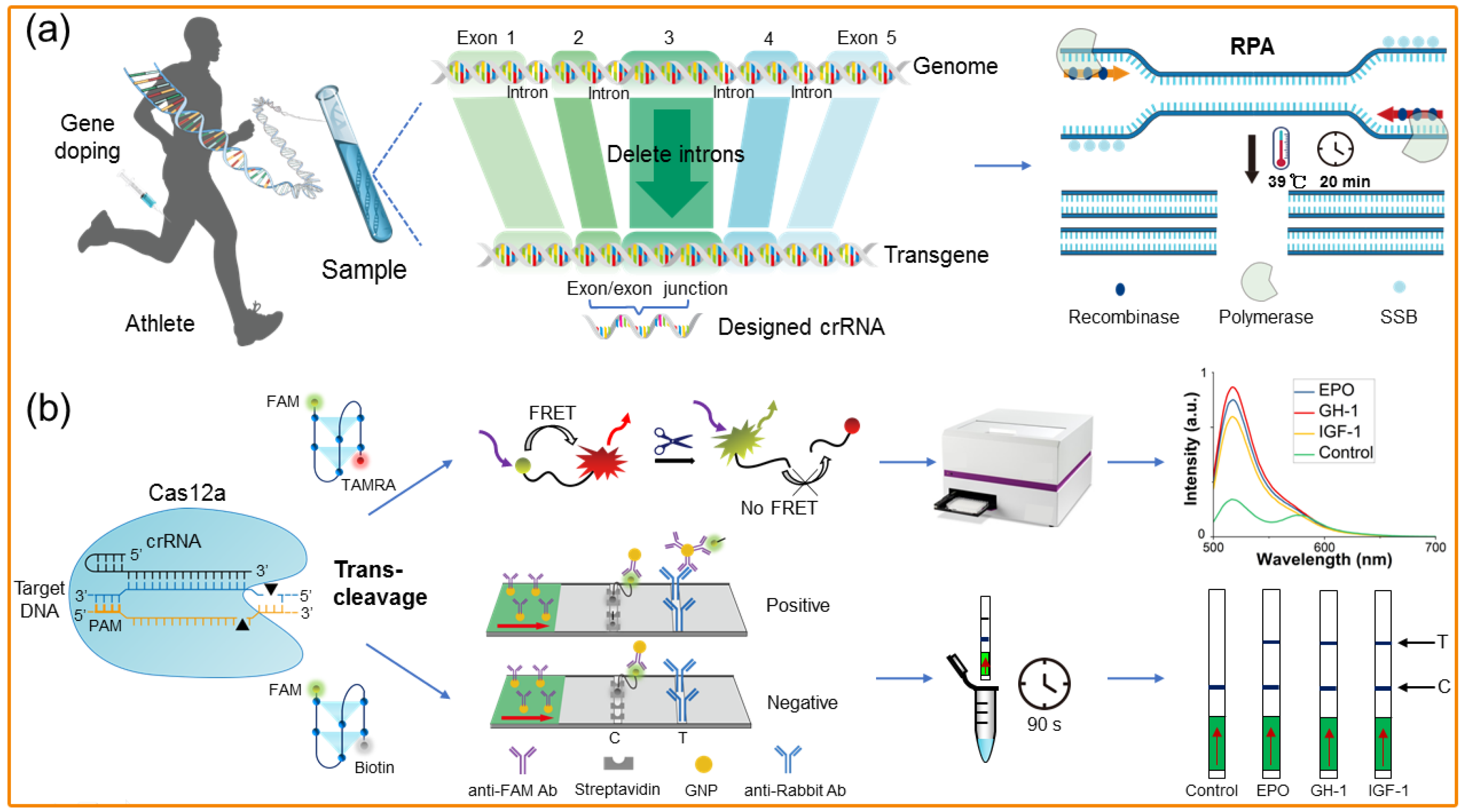
3.3. CRISPR Methods
3.4. MS-Based Methods
4. Comparison of the Reported Assays
5. Conclusions and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nicoli, R.; Guillarme, D.; Leuenberger, N.; Baume, N.; Robinson, N.; Saugy, M.; Veuthey, J.L. Analytical Strategies for Doping Control Purposes: Needs, Challenges, and Perspectives. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 508–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Judak, P.; Esposito, S.; Coppieters, G.; Van Eenoo, P.; Deventer, K. Doping control analysis of small peptides: A decade of progress. J. Chromatogr. B 2021, 1173, 122551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malekzad, H.; Zangabad, P.S.; Mohammadi, H.; Sadroddini, M.; Jafari, Z.; Mahlooji, N.; Abbaspour, S.; Gholami, S.; Ghanbarpoor, M.; Pashazadeh, R.; et al. Noble metal nanostructures in optical biosensors: Basics, and their introduction to anti-doping detection. Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 100, 116–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Zhuo, Y.; Chai, Y.Q.; Xiang, Y.; Yuan, R. New type of redox nanoprobe: C60-based nanomaterial and its application in electrochemical immunoassay for doping detection. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 1669–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Yuan, Y.; Wei, H.; Fei, Q.; Luan, Z.; Wang, X.; Xu, Y.; Lu, J. Identification and characterization of higenamine metabolites in human urine by quadrupole-orbitrap LC-MS/MS for doping control. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2022, 214, 114732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Lian, K.; Zhang, H.; An, J.; Zhang, Y.; Kang, W.; Ai, L. Doping-control analysis of 14 diuretics in animal-derived foods using ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Microchem. J. 2022, 174, 106948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polet, M.; Van Gansbeke, W.; Van Eenoo, P. Development and validation of an open screening method for doping substances in urine by gas chromatography quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1042, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minhas, R.S.; Rudd, D.A.; Al Hmoud, H.Z.; Guinan, T.M.; Kirkbride, K.P.; Voelcker, N.H. Rapid Detection of Anabolic and Narcotic Doping Agents in Saliva and Urine By Means of Nanostructured Silicon SALDI Mass Spectrometry. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 31195–31204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Wei, Q.; Zhang, P.; Li, S.; Xue, L.; Yang, R.; Wang, C.; Zhou, L. An up-converting phosphor technology-based lateral flow assay for point-of-collection detection of morphine and methamphetamine in saliva. Analyst 2018, 143, 4646–4654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adegoke, O.; Zolotovskaya, S.; Abdolvand, A.; Daeid, N.N. Biomimetic graphene oxide-cationic multi-shaped gold nanoparticle-hemin hybrid nanozyme: Tuning enhanced catalytic activity for the rapid colorimetric apta-biosensing of amphetamine-type stimulants. Talanta 2020, 216, 120990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, W.T.P.; Compton, R.G. A simple method to detect the stimulant modafinil in authentic saliva using a carbon-nanotube screen-printed electrode with adsorptive stripping voltammetry. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 285, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, I.; Kiguchi, Y.; Oyama, H.; Takeuchi, A.; Tode, C.; Tanaka, R.; Ogata, J.; Kikura-Hanajiri, R.; Kobayashi, N. Derivatization-assisted enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for identifying hallucinogenic mushrooms with enhanced sensitivity. Anal. Methods 2021, 13, 3954–3962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarano, S.; Ermini, M.L.; Spiriti, M.M.; Mascini, M.; Bogani, P.; Minunni, M. Simultaneous detection of transgenic DNA by surface plasmon resonance imaging with potential application to gene doping detection. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 6245–6253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dignan, L.M.; Woolf, M.S.; Ross, J.A.; Baehr, C.; Holstege, C.P.; Pravetoni, M.; Landers, J.P. A Membrane-Modulated Centrifugal Microdevice for Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay-Based Detection of Illicit and Misused Drugs. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 16213–16221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsenedi, K.A.; Morrison, C. Determination of amphetamine-type stimulants (ATSs) and synthetic cathinones in urine using solid phase micro-extraction fibre tips and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 1431–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Wu, S.; Chen, Z.; Jiang, J.; Sun, J. Rapid nanomolar detection of methamphetamine in biofluids via a reagentless electrochemical aptamer-based biosensor. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1207, 339742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raro, M.; Ibanez, M.; Gil, R.; Fabregat, A.; Tudela, E.; Deventer, K.; Ventura, R.; Segura, J.; Marcos, J.; Kotronoulas, A.; et al. Untargeted metabolomics in doping control: Detection of new markers of testosterone misuse by ultrahigh performance liquid chromatography coupled to high-resolution mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 8373–8380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bade, R.; Abdelaziz, A.; Nguyen, L.; Pandopulos, A.J.; White, J.M.; Gerber, C. Determination of 21 synthetic cathinones, phenethylamines, amphetamines and opioids in influent wastewater using liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry. Talanta 2020, 208, 120479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tozaki, T.; Ohnuma, A.; Iwai, S.; Kikuchi, M.; Ishige, T.; Kakoi, H.; Hirota, K.; Kusano, K.; Nagata, S. Robustness of Digital PCR and Real-Time PCR in Transgene Detection for Gene-Doping Control. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 7133–7139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passreiter, A.; Thomas, A.; Grogna, N.; Delahaut, P.; Thevis, M. First Steps toward Uncovering Gene Doping with CRISPR/Cas by Identifying SpCas9 in Plasma via HPLC-HRMS/MS. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 16322–16328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, H.W.; Wong, K.S.; Lin, V.Y.C.; Wan, T.S.M.; Ho, E.N.M. A duplex qPCR assay for human erythropoietin (EPO) transgene to control gene doping in horses. Drug Test. Anal. 2021, 13, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tozaki, T.; Ohnuma, A.; Kikuchi, M.; Ishige, T.; Kakoi, H.; Hirota, K.I.; Kusano, K.; Nagata, S.I. Robustness of digital PCR and real-time PCR against inhibitors in transgene detection for gene doping control in equestrian sports. Drug Test. Anal. 2021, 13, 1768–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuberger, E.W.; Jurkiewicz, M.; Moser, D.A.; Simon, P. Detection of EPO gene doping in blood. Drug Test. Anal. 2012, 4, 859–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorribes-Soriano, A.; Esteve-Turrillas, F.A.; Armenta, S.; Amoros, P.; Herrero-Martinez, J.M. Amphetamine-type stimulants analysis in oral fluid based on molecularly imprinting extraction. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1052, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, P.; Sun, S.; Wang, X.; Ma, L.; Guo, C.; Li, J.; Guan, M. Rapid and sensitive detection of amphetamine by SERS-based competitive immunoassay coupled with magnetic separation. Anal. Methods 2022, 14, 2608–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.; Son, S.U.; Kang, B.; Kim, J.; Lim, J.; Seo, S.; Kang, T.; Jung, J.; Lee, K.S.; Kim, H.; et al. Electrospun Nanofibrous Membrane-Based Colorimetric Device for Rapid and Simple Screening of Amphetamine-Type Stimulants in Drinks. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 3535–3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; He, Q.; Deng, C.; Shi, L.; Fu, Y.; Cao, H.; Cheng, J. Determination of Methamphetamine Hydrochloride by highly fluorescent polyfluorene with NH2-terminated side chains. Synth. Met. 2011, 161, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, F.; You, Y.; Fay, S.; Li, X.; Robinson, M.A. Novel Algorithms for Comprehensive Untargeted Detection of Doping Agents in Biological Samples. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 7746–7753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thevis, M.; Walpurgis, K.; Thomas, A. Analytical Approaches in Human Sports Drug Testing: Recent Advances, Challenges, and Solutions. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 506–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.R.; Swortwood, M.J. Analysis of methylphenidate, ethylphenidate, lisdexamfetamine, and amphetamine in oral fluid by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Forensic Sci. 2022, 67, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czerwinska, J.; Jang, M.; Costa, C.; Parkin, M.C.; George, C.; Kicman, A.T.; Bailey, M.J.; Dargan, P.I.; Abbate, V. Detection of mephedrone and its metabolites in fingerprints from a controlled human administration study by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry and paper spray-mass spectrometry. Analyst 2020, 145, 3038–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Wang, W.; Li, H.; Xing, Y.; Hou, K.; Li, H. Rapid On-Site Detection of Illegal Drugs in Complex Matrix by Thermal Desorption Acetone-Assisted Photoionization Miniature Ion Trap Mass Spectrometer. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 3845–3851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pena-Herrera, J.M.; Montemurro, N.; Barcelo, D.; Perez, S. Combining quantitative and qualitative approaches using Sequential Window Acquisition of All Theoretical Fragment-Ion methodology for the detection of pharmaceuticals and related compounds in river fish extracted using a sample miniaturized method. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1620, 461009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Garcia, E.; Mastroianni, N.; Postigo, C.; Barcelo, D.; Lopez de Alda, M. A fully automated approach for the analysis of 37 psychoactive substances in raw wastewater based on on-line solid phase extraction-liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1576, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppieters, G.; Deventer, K.; Van Eenoo, P.; Judak, P. Combining direct urinary injection with automated filtration and nanoflow LC-MS for the confirmatory analysis of doping-relevant small peptide hormones. J. Chromatogr. B 2021, 1179, 122842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponzetto, F.; Parasiliti-Caprino, M.; Gesmundo, I.; Marinelli, L.; Nonnato, A.; Nicoli, R.; Kuuranne, T.; Mengozzi, G.; Ghigo, E.; Settanni, F. Single-run UHPLC-MS/MS method for simultaneous quantification of endogenous steroids and their phase II metabolites in serum for anti-doping purposes. Talanta 2023, 255, 124218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Ai, L.; Zhang, H.; Kang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Lian, K. Development an automated and high-throughput analytical platform for screening 39 glucocorticoids in animal-derived food for doping control. Microchem. J. 2021, 165, 106142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.; Kim, Y. Donor–acceptor Stenhouse adduct formation for the simple and rapid colorimetric detection of amphetamine-type stimulants. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 355, 131274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Miao, L.; Wu, A. A Rapid Colorimetric Sensor of Clenbuterol Based on Cysteamine-Modified Gold Nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouhani, S.; Haghgoo, S. A novel fluorescence nanosensor based on 1,8-naphthalimide-thiophene doped silica nanoparticles, and its application to the determination of methamphetamine. Sens. Actuat. B Chem. 2015, 209, 957–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liszt, K.I.; Eder, R.; Wendelin, S.; Somoza, V. Identification of Catechin, Syringic Acid, and Procyanidin B2 in Wine as Stimulants of Gastric Acid Secretion. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 7775–7783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Shi, L.; Zhu, D.; He, C.; Wen, D.; He, Q.; Cao, H.; Cheng, J. Fluorene–thiophene-based thin-film fluorescent chemosensor for methamphetamine vapor by thiophene–amine interaction. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 180, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yan, B. A novel cucurbit[7]uril anchored bis-functionalized metal-organic framework hybrid and its potential use in fluorescent analysis of illegal stimulants in saliva. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 324, 128656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beatty, M.A.; Selinger, A.J.; Li, Y.; Hof, F. Parallel Synthesis and Screening of Supramolecular Chemosensors that Achieve Fluorescent Turn-on Detection of Drugs in Saliva. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 16763–16771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Xi, H.; Han, S.; Zhao, S. A turn-on fluorescent probe based on N-(rhodamine-B)-thiolactam-2-n-butane with ionic liquids for selective and sensitive detection of mustard gas stimulant. Anal. Methods 2021, 13, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Han, D.; Wu, Z.; Liang, Z.; Han, F.; Chen, K.; Fu, W.; Han, D.; Wang, Y.; Niu, L. Polydopamine-based molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor for the highly selective determination of ecstasy components. Analyst 2022, 147, 3291–3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasso, M.; Sarakhman, O.; Stankovic, D.M.; Svorc, L. A new voltammetric platform for reliable determination of the sport performance-enhancing stimulant synephrine in dietary supplements using a boron-doped diamond electrode. Anal. Methods 2020, 12, 4749–4758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, L.R.; de Cássica Mendonça, J.; Boareto Capelari, T.; Antigo Medeiros, R.; Teixeira Tarley, C.R. Development of a reliable and selective voltammetric method for determination of designer drug 1-(3-chlorophenyl)piperazine (mCPP) using boron-doped diamond electrode and exploiting surfactant-mediated measurements. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 310, 127812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, F.; Nitta, S.; Shimizu, R.; Shoji, T.; Tatsumi, H.; Jin, J. Sensitive screening of methamphetamine stimulant using potential-modulated electrochemiluminescence. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1191, 339229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Han, D.; Liang, Z.; Han, F.; Fu, W.; Wang, W.; Han, D.; Wang, Y.; Niu, L. Novel electrochemical-surface plasmon resonance (EC-SPR) sensor for amphetamine-type stimulants detection based on molecularly imprinted strategy. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 369, 132258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhoundian, M.; Alizadeh, T.; Ganjali, M.R.; Norouzi, P. Ultra-trace detection of methamphetamine in biological samples using FFT-square wave voltammetry and nano-sized imprinted polymer/MWCNTs -modified electrode. Talanta 2019, 200, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frasconi, M.; Mazzarino, M.; Botre, F.; Mazzei, F. Surface plasmon resonance immunosensor for cortisol and cortisone determination. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 394, 2151–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saar-Reismaa, P.; Erme, E.; Vaher, M.; Kulp, M.; Kaljurand, M.; Mazina-Sinkar, J. In Situ Determination of Illegal Drugs in Oral Fluid by Portable Capillary Electrophoresis with Deep UV Excited Fluorescence Detection. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 6253–6258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Zhou, Y.; Zhan, D.; Lai, G. Homogeneous biorecognition reaction-induced assembly of DNA nanostructures for ultrasensitive electrochemical detection of kanamycin antibiotic. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1154, 338317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alijanianzadeh, M.; Qadami, F.; Molaeirad, A. Detection of methamphetamine using aptamer-based biosensor chip and cyclic voltammetry technique. J. Indian Chem. Soc. 2021, 98, 100189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.; Ren, P.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, G.; Shen, J.; Zhao, B. Detection of Six beta-Agonists by Three Multiresidue Immunosensors Based on an Anti-bovine Serum Albumin-Ractopamine-Clenbuterol-Salbutamol Antibody. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 5548–5555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, J.Y.; Kim, M.; Ahn, J.H.; Kim, B.G.; Son, J.; Sung, C. CRISPR/deadCas9-based high-throughput gene doping analysis (HiGDA): A proof of concept for exogenous human erythropoietin gene doping detection. Talanta 2023, 258, 124455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei Hu, S.; Ding, T.; Tang, H.; Guo, H.; Cui, W.; Shu, Y. Nanobiomaterial vectors for improving gene editing and gene therapy. Mater. Today 2023, 66, 114–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzazy, H.M.; Mansour, M.M.; Christenson, R.H. Gene doping: Of mice and men. Clin. Biochem. 2009, 42, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borchers, A.; Pieler, T. Programming pluripotent precursor cells derived from Xenopus embryos to generate specific tissues and organs. Genes 2010, 1, 413–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tozaki, T.; Ohnuma, A.; Kikuchi, M.; Ishige, T.; Kakoi, H.; Hirota, K.I.; Kusano, K.; Nagata, S.I. Identification of processed pseudogenes in the genome of Thoroughbred horses: Possibility of gene-doping detection considering the presence of pseudogenes. Anim. Genet. 2022, 53, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.J.; Xu, J.F.; Shen, Y.W.; Ma, S.J.; Zhang, T.T.; Meng, Q.L.; Lan, W.J.; Zhang, C.; Liu, X.M. Detection of exogenous gene doping of IGF-I by a real-time quantitative PCR assay. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2017, 64, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugasawa, T.; Aoki, K.; Yanazawa, K.; Takekoshi, K. Detection of Multiple Transgene Fragments in a Mouse Model of Gene Doping Based on Plasmid Vector Using TaqMan-qPCR Assay. Genes 2020, 11, 750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minunni, M.; Scarano, S.; Mascini, M. Affinity-based biosensors as promising tools for gene doping detection. Trends Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salamin, O.; Kuuranne, T.; Saugy, M.; Leuenberger, N. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) as an alternative to PCR: A rapid on-site detection of gene doping. Drug Test. Anal. 2017, 9, 1731–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tozaki, T.; Ohnuma, A.; Hamilton, N.A.; Kikuchi, M.; Ishige, T.; Kakoi, H.; Hirota, K.I.; Kusano, K.; Nagata, S.I. Low-copy transgene detection using nested digital polymerase chain reaction for gene-doping control. Drug Test. Anal. 2022, 14, 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Haughan, J.; Moss, K.L.; Stefanovski, D.; Ortved, K.F.; Robinson, M.A. A quantitative PCR screening method for adeno-associated viral vector 2-mediated gene doping. Drug Test. Anal. 2022, 14, 963–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniego, J.; Pesko, B.; Hincks, P.; Taylor, P.; Stewart, G.; Proudman, C.; Scarth, J.; Ryder, E. Direct sequence confirmation of qPCR products for gene doping assay validation in horses. Drug Test. Anal. 2022, 14, 1017–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, J.Y.; Kim, M.; Min, H.; Kim, B.G.; Son, J.; Kwon, O.S.; Sung, C. New application of the CRISPR-Cas9 system for site-specific exogenous gene doping analysis. Drug Test. Anal. 2021, 13, 871–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Jung, C.; Bhadra, S.; Ellington, A.D. Phosphorothioated Primers Lead to Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification at Low Temperatures. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 8290–8294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniego, J.; Pesko, B.; Habershon-Butcher, J.; Huggett, J.; Taylor, P.; Scarth, J.; Ryder, E. Screening for gene doping transgenes in horses via the use of massively parallel sequencing. Gene Ther. 2022, 29, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Boer, E.N.; van der Wouden, P.E.; Johansson, L.F.; van Diemen, C.C.; Haisma, H.J. A next-generation sequencing method for gene doping detection that distinguishes low levels of plasmid DNA against a background of genomic DNA. Gene Ther. 2019, 26, 338–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tozaki, T.; Ohnuma, A.; Takasu, M.; Nakamura, K.; Kikuchi, M.; Ishige, T.; Kakoi, H.; Hirora, K.; Tamura, N.; Kusano, K.; et al. Detection of non-targeted transgenes by whole-genome resequencing for gene-doping control. Gene Ther. 2021, 28, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Pinto, A.; Cheng, L.Y.; Song, P.; Dai, P.; Wang, M.; Rodriguez, L.; Weller, C.; Zhang, D.Y. Hairpin Structure Facilitates Multiplex High-Fidelity DNA Amplification in Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 9586–9594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.M.; Zhuo, Y.; Tu, T.T.; Yuan, R.; Chai, Y.Q. Construction of Fast-Walking Tetrahedral DNA Walker with Four Arms for Sensitive Detection and Intracellular Imaging of Apurinic/Apyrimidinic Endonuclease. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 8732–8739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, X.; Mao, F.; Xu, G.; Liu, Q. A Versatile Platform for Sensitive and Label-Free Identification of Biomarkers through an Exo-III-Assisted Cascade Signal Amplification Strategy. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 2298–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Niu, F.; Yu, A.; Lai, G. Proximity Binding-Triggered Assembly of Two MNAzymes for Catalyzed Release of G-Quadruplex DNAzymes and an Ultrasensitive Homogeneous Bioassay of Platelet-Derived Growth Factor. Anal. Chem. 2019, 92, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Du, C.; Zhang, Q.; Xiao, K.; Zhang, X.; Chen, J. Colorimetric and Photocurrent-Polarity-Switching Photoelectrochemical Dual-Mode Sensing Platform for Highly Selective Detection of Mercury Ions Based on the Split G-Quadruplex-Hemin Complex. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 15040–15047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhao, S.; Tian, X.; Qiu, J.G.; Zhang, C.Y. Development of a CRISPR-Cas-Based Biosensor for Rapid and Sensitive Detection of 8-Oxoguanine DNA Glycosylase. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 2119–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Li, R.; Yuan, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Xu, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Yang, L. One Versatile Cas9-Integrated Single-Tube Duplex Quantitative Real-Time PCR System for Rapid Analysis of CRISPR/Cas-Induced Mutants. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 10832–10840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passreiter, A.; Naumann, N.; Thomas, A.; Grogna, N.; Delahaut, P.; Thevis, M. How to detect CRISPR with CRISPR—Employing SHERLOCK for doping control purposes. Analyst 2022, 147, 5528–5536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.; Xu, Z.; Zhou, H.; Li, T.; Du, X.; Hu, R.; Jiang, Z.; Gaozhi, O.; Ying, L.; Yang, Y. Integration of CRISPR/Cas12a and multiplexed RPA for fast detection of gene doping. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 16481–16490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thevis, M.; Geyer, H.; Thomas, A.; Schanzer, W. Trafficking of drug candidates relevant for sports drug testing: Detection of non-approved therapeutics categorized as anabolic and gene doping agents in products distributed via the Internet. Drug Test. Anal. 2011, 3, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, A.; Walpurgis, K.; Delahaut, P.; Kohler, M.; Schanzer, W.; Thevis, M. Detection of small interfering RNA (siRNA) by mass spectrometry procedures in doping controls. Drug Test. Anal. 2013, 5, 853–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, J.; Yang, S.; Zhou, X.; He, C.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Y.; Xie, M.; Yan, Y.; Su, H.; Wu, M. Detection of doping with rhGH: Excretion study with WADA-approved kits. Drug Test. Anal. 2011, 3, 784–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Category | Representative Substance | Available Detection Methods |
|---|---|---|
| S0 Non-approved substances | GC-MS/MS; LC-MS/MS; HILIC-HRMS | |
| S1 Anabolic agents | Anabolic androgenic steroids (AAS) | GC-MS/MS; LC-MS/MS; GC-C/IRMS; LC–IM–Q/TOF; LC–HRMS/MS; GC–HRMS/MS; LC-Ag+CIS/MS/MS |
| S2 Peptide hormones, growth factors, related substances, and mimetics | Erythropoietin (EPO); Growth hormone (GH) | LC-MS/MS; ELISA; Transcriptomics; Proteomics; SAGE; SELDI-TOF MS; LC-MS/MS; LC-HRMS/MS; Immunoassay |
| S3 Beta-2 agonists | Salmeterol; Tretoquinol | LC-MS/MS; UHPLC-HRMS; LC-HRMS/MS |
| S4 Hormone and metabolic modulators | Aromatase inhibitors | GC-MS/MS; GC-C/IRMS; LC-MS/MS; Hyperpolarized NMR based metabolomics |
| S5 Diuretics and masking agents | Desmopressin; Probenecid; Acetazolamide | GC-MS/MS; LC-MS/MS |
| S6 Stimulants | Cocaine; Strychnine | GC-MS/MS; LC-MS/MS; ESI-MS/MS; LC-HRMS/MS; |
| S7 Narcotics | Morphine; Pentazocine | LC-MS/MS |
| S8 Cannabinoids | Cannabinoids | GC-MS/MS; LC-MS/MS |
| S9 Glucocorticoids | Cortisone; Dexamethasone | LC-MS/MS |
| M1 Manipulation of blood and blood components | Blood doping | LC-MS/MS; Proteomics; Transcriptomics |
| M2 Chemical and physical manipulation | Sample substitution and/or adulteration | Vigilance |
| M3 Gene and cell doping | Gene editing; Gene silencing; Gene transfer technologies | Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) (WADA-approved); NGS; WGR; HPLC-MS; CRISPR-Cas based systems |
| P1 Beta-blockers | Bunolol; Propranolol | LC-MS/MS |
| Categories | Drug Doping Detection | Gene Doping Detection |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The use of prohibited drugs to enhance performance in sports | The use of gene therapy or genetic manipulation to enhance athletic performance |
| Detection Methods | Testing urine or blood samples for the presence of banned substances. | Analyzing DNA samples to detect specific genetic modifications or enhancements. |
| Types of Enhancements Detected | Use of stimulants, anabolic steroids, peptide hormones, etc. | Introduction of specific genes to improve muscle growth, oxygen utilization, endurance, etc. |
| Detection Window | Limited timeframe after drug administration, as drugs are metabolized and excreted from the body. | Potential for indefinite detection as genetic modifications can persist for a longer period. |
| Challenges | Constant development of new undetectable substances. | Complex and evolving methods of gene delivery and manipulation. |
| Ethical Concerns | Public health risks and long-term detrimental effects on athletes’ health. | Alteration of natural genetic traits, fairness in competition, and potential health risks. |
| Method | Detection Time | Detection Cost | Target | Sample Information | LOD | LOQ | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MS based | Less than 15 min | High | pharmaceuticals active compounds | Fish sampling points | 5–50 ng/g | 2.0 ng/g | [33] (2020) |
| Fluorescence | Less than 15 min | Low | amphetamine-type stimulants | 2 mL saliva | 10−3–10−9 M | 0.72 µM | [43] (2020) |
| Electroanalytical | Less than 5 min | Low | 3,4-Methylenedioxyamphetamine and 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine | 10 μL urine | 0.05–7.5 μM and 0.1–7.5 μM | 37 nM and 54 nM | [50] (2022) |
| Colorimetric | Less than 10 min | Low | amphetamine-type stimulants | 20 μL urine | 0–50 μg/mL | 0.66 μg/mL | [38] (2022) |
| Biosensors | More than 120 min | Medium | methamphetamine | saliva, serum and urine, | 0.02–20 µM | 20 nM | [16] (2022) |
| PCR-based | More than 120 min | High | myostatin gene | 2.2 μL horse plasmid solution | No mention | No mention | [19] (2021) |
| PCR-free based | Less than 40 min | Medium | human EPO gene | 10 μL human plasmid solution | 10−11–10−8 M | 1 aM | [82] (2023) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, Y.; Yan, J.; Ou, G.; Fu, L. A Review of Recent Progress in Drug Doping and Gene Doping Control Analysis. Molecules 2023, 28, 5483. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28145483
Lu Y, Yan J, Ou G, Fu L. A Review of Recent Progress in Drug Doping and Gene Doping Control Analysis. Molecules. 2023; 28(14):5483. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28145483
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Yuze, Jiayu Yan, Gaozhi Ou, and Li Fu. 2023. "A Review of Recent Progress in Drug Doping and Gene Doping Control Analysis" Molecules 28, no. 14: 5483. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28145483
APA StyleLu, Y., Yan, J., Ou, G., & Fu, L. (2023). A Review of Recent Progress in Drug Doping and Gene Doping Control Analysis. Molecules, 28(14), 5483. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28145483