A Novel Chromatographic Method to Assess the Binding Ability towards Dicarbonyls
Abstract
1. Introduction
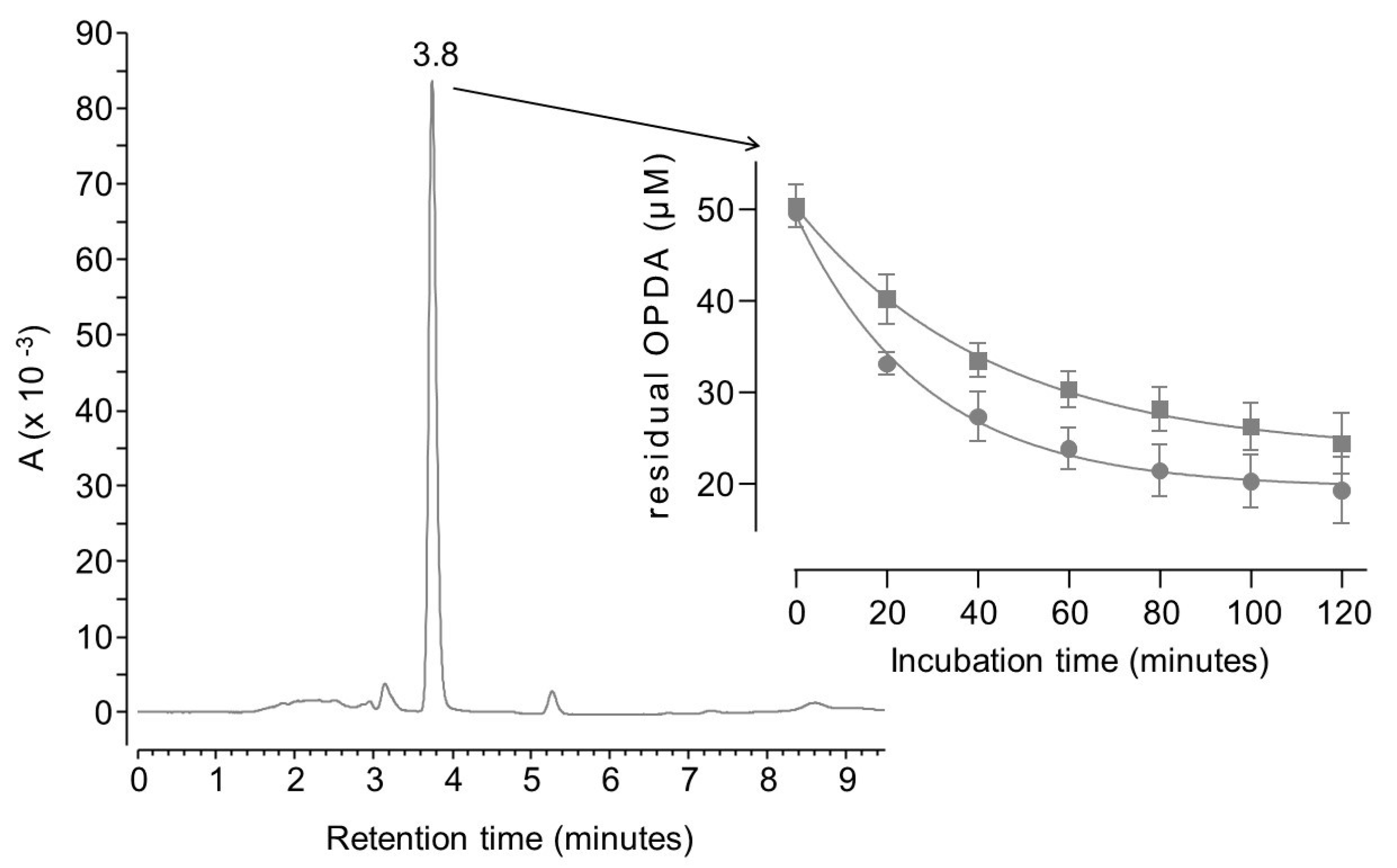
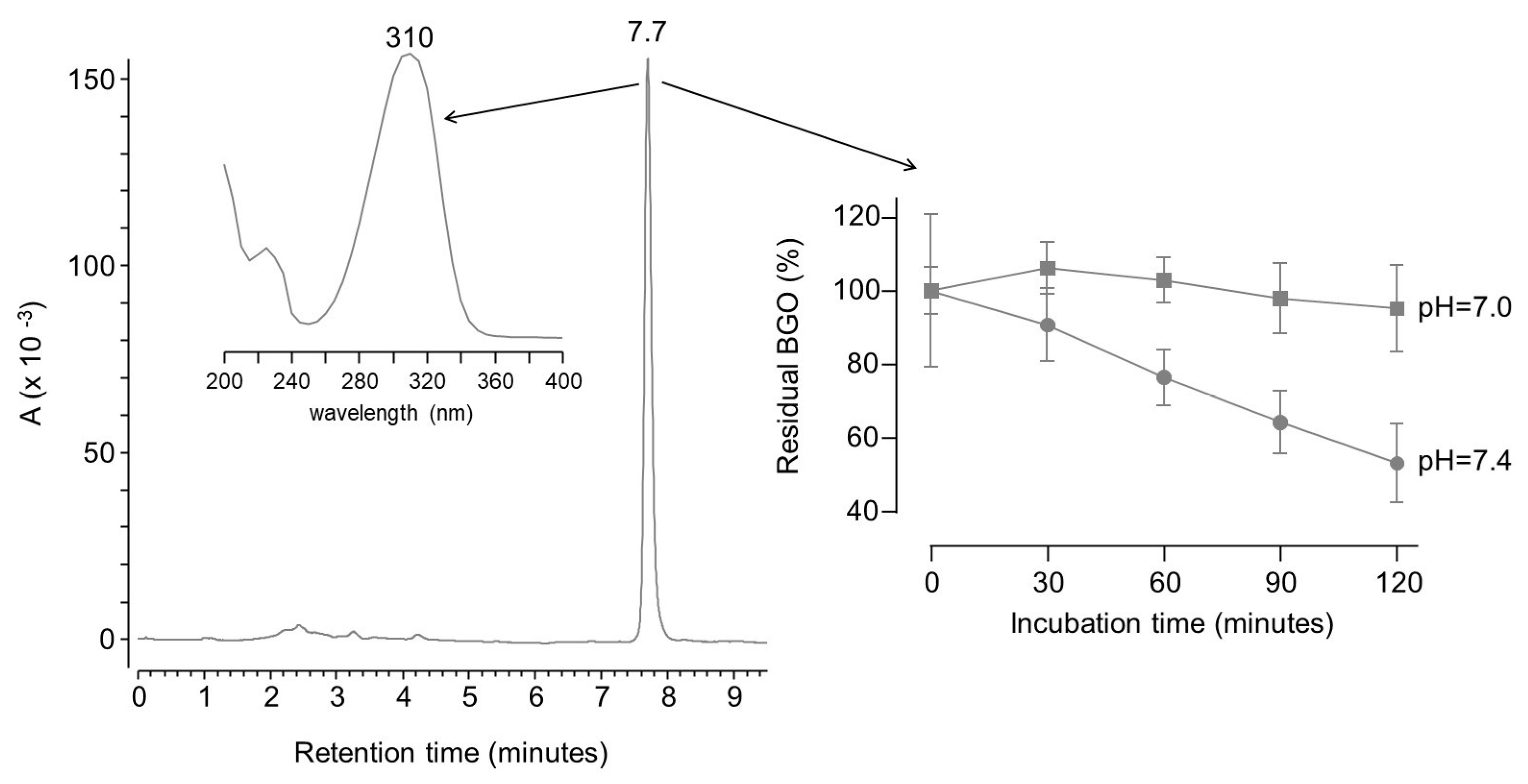
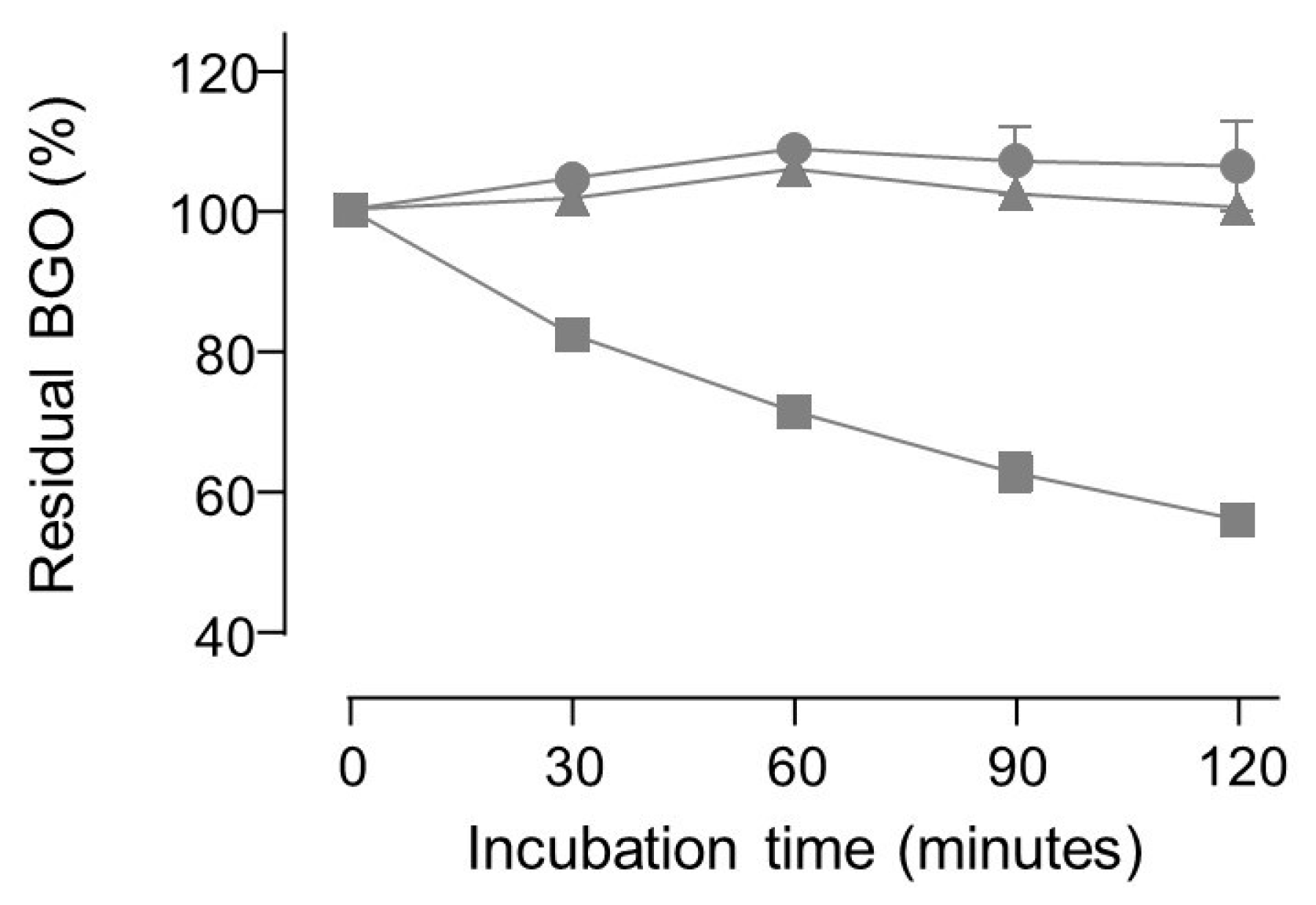
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. Synthesis of Benzylglyoxal Diethylacetal
3.2.1. Synthesis of 2,2-Diethoxyacetic Acid (Compound 2, Figure 6)
3.2.2. Synthesis of 2,2-Diethoxy-N-methoxy-N-methyl-acetamide (Compound 3, Figure 6)
3.2.3. Synthesis of Benzylglyoxal Diethylacetal (Compound 4, Figure 6)
3.3. Stock Solutions for Chromatographic and Mass Spectrometric Analyses
3.4. Methods
3.4.1. OPDA Binding Kinetics
3.4.2. Direct Determination of Dicarbonyl Binding Activity
3.4.3. Mass Spectrometry
3.4.4. NMR Spectroscopy
3.4.5. Data Analysis and Statistics
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Arribas-Lorenzo, G.; Morales, F.J. Analysis, distribution, and dietary exposure of glyoxal and methylglyoxal in cookies and their relationship with other heat-induced contaminants. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 2966–2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwak, S.; Choi, Y.S.; Na, H.G.; Bae, C.H.; Song, S.Y.; Kim, Y.D. Glyoxal and Methylglyoxal as E-cigarette Vapor Ingredients-Induced Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine and Mucins Expression in Human Nasal Epithelial Cells. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2021, 35, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Ho, C.T. Flavour chemistry of methylglyoxal and glyoxal. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 4140–4149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, M.; Ishida, J.; Xuan, Z.X.; Nakamura, A.; Yoshitake, T. Determination of Glyoxal, Methylglyoxal, Diacethyl, and 2, 3-Pentanedione in Fermented Foods by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography with Fluorescence Detection. J. Liq. Chromatogr. 1994, 17, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, J.N.; Wood, K.D.; Knight, J.; Assimos, D.G.; Holmes, R.P. Glyoxal formation and its role in endogenous oxalate synthesis. Adv. Urol. 2012, 2012, 819202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornalley, P.J.; Langborg, A.; Minhas, H.S. Formation of glyoxal, methylglyoxal and 3-deoxyglucosone in the glycation of proteins by glucose. Biochem. J. 1999, 344 Pt 1, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Karmakar, K.; Chakravortty, D. Cells producing their own nemesis: Understanding methylglyoxal metabolism. Iubmb Life 2014, 66, 667–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, S.A.; Thornalley, P.J. The formation of methylglyoxal from triose phosphates. Investigation using a specific assay for methylglyoxal. Eur. J. Biochem. 1993, 212, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabbani, N.; Xue, M.; Thornalley, P.J. Dicarbonyls and glyoxalase in disease mechanisms and clinical therapeutics. Glycoconj J. 2016, 33, 513–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izaguirre, G.; Kikonyogo, A.; Pietruszko, R. Methylglyoxal as substrate and inhibitor of human aldehyde dehydrogenase: Comparison of kinetic properties among the three isozymes. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1998, 119, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vander Jagt, D.L.; Hunsaker, L.A. Methylglyoxal metabolism and diabetic complications: Roles of aldose reductase, glyoxalase-I, betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase and 2-oxoaldehyde dehydrogenase. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2003, 143–144, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vander Jagt, D.L.; Robinson, B.; Taylor, K.K.; Hunsaker, L.A. Reduction of trioses by NADPH-dependent aldo-keto reductases. Aldose reductase, methylglyoxal, and diabetic complications. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 4364–4369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichard, G.A., Jr.; Skutches, C.L.; Hoeldtke, R.D.; Owen, O.E. Acetone metabolism in humans during diabetic ketoacidosis. Diabetes 1986, 35, 668–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abordo, E.A.; Minhas, H.S.; Thornalley, P.J. Accumulation of alpha-oxoaldehydes during oxidative stress: A role in cytotoxicity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1999, 58, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, T.W.; Westwood, M.E.; McLellan, A.C.; Selwood, T.; Thornalley, P.J. Binding and modification of proteins by methylglyoxal under physiological conditions. A kinetic and mechanistic study with N alpha-acetylarginine, N alpha-acetylcysteine, and N alpha-acetyllysine, and bovine serum albumin. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 32299–32305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, N.; Thornalley, P.J.; Dawczynski, J.; Franke, S.; Strobel, J.; Stein, G.; Haik, G.M. Methylglyoxal-derived hydroimidazolone advanced glycation end-products of human lens proteins. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2003, 44, 5287–5292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cohenford, M.A.; Dutta, U.; Dain, J.A. The structural modification of DNA nucleosides by nonenzymatic glycation: An in vitro study based on the reactions of glyoxal and methylglyoxal with 2′-deoxyguanosine. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2008, 390, 679–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, S.W.T.; Lopez Gonzalez, E.J.; Zoukari, T.; Ki, P.; Shuck, S.C. Methylglyoxal and Its Adducts: Induction, Repair, and Association with Disease. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2022, 35, 1720–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schalkwijk, C.G.; Stehouwer, C.D.A. Methylglyoxal, a Highly Reactive Dicarbonyl Compound, in Diabetes, Its Vascular Complications, and Other Age-Related Diseases. Physiol. Rev. 2020, 100, 407–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wondrak, G.T.; Cervantes-Laurean, D.; Roberts, M.J.; Qasem, J.G.; Kim, M.; Jacobson, E.L.; Jacobson, M.K. Identification of alpha-dicarbonyl scavengers for cellular protection against carbonyl stress. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2002, 63, 361–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, D.; Wang, Y.; Lo, C.Y.; Ho, C.T. Methylglyoxal: Its presence and potential scavengers. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 17 (Suppl. S1), 261–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobner, J.; Degen, J.; Henle, T. Creatine is a scavenger for methylglyoxal under physiological conditions via formation of N-(4-methyl-5-oxo-1-imidazolin-2-yl)sarcosine (MG-HCr). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 2249–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colzani, M.; De Maddis, D.; Casali, G.; Carini, M.; Vistoli, G.; Aldini, G. Reactivity, Selectivity, and Reaction Mechanisms of Aminoguanidine, Hydralazine, Pyridoxamine, and Carnosine as Sequestering Agents of Reactive Carbonyl Species: A Comparative Study. ChemMedChem 2016, 11, 1778–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vistoli, G.; Orioli, M.; Pedretti, A.; Regazzoni, L.; Canevotti, R.; Negrisoli, G.; Carini, M.; Aldini, G. Design, synthesis, and evaluation of carnosine derivatives as selective and efficient sequestering agents of cytotoxic reactive carbonyl species. ChemMedChem 2009, 4, 967–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritzsche, S.; Billig, S.; Rynek, R.; Abburi, R.; Tarakhovskaya, E.; Leuner, O.; Frolov, A.; Birkemeyer, C. Derivatization of Methylglyoxal for LC-ESI-MS Analysis-Stability and Relative Sensitivity of Different Derivatives. Molecules 2018, 23, 2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhu, Y.; He, S.; Fan, J.; Hu, Q.; Cao, Y. Development and validation of a high-performance liquid chromatography method for the determination of diacetyl in beer using 4-nitro-o-phenylenediamine as the derivatization reagent. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 3013–3019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, A.; Rodrigues, J.A.; Almeida, P.J.; Oliva-Teles, M.T. Determination of Glyoxal, Methylglyoxal, and Diacetyl in Selected Beer and Wine, by Hplc with UV Spectrophotometric Detection, after Derivatization with o-Phenylenediamine. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 1999, 22, 2061–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brun, N.; Gonzalez-Sanchez, J.M.; Demelas, C.; Clement, J.L.; Monod, A. A fast and efficient method for the analysis of alpha-dicarbonyl compounds in aqueous solutions: Development and application. Chemosphere 2023, 319, 137977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, T.W.; Dehn, W.M. The Benzilic Acid Rearrangement. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1930, 52, 252–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, A.J.; Marques, C.S. Mechanistic and synthetic aspects rearrangements of the benzilic acid and ester. Mini-Rev. Org. Chem. 2007, 4, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K. The reactions of phenylglyoxal and related reagents with amino acids. J. Biochem. 1977, 81, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, K. Further studies on the reactions of phenylglyoxal and related reagents with proteins. J. Biochem. 1977, 81, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thornalley, P.J. Glutathione-dependent detoxification of alpha-oxoaldehydes by the glyoxalase system: Involvement in disease mechanisms and antiproliferative activity of glyoxalase I inhibitors. Chem. Biol. Interact. 1998, 111–112, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, A.; Conti, P.; Grazioso, G.; Tamborini, L.; Madsen, U.; Nielsen, B.; De Micheli, C. Synthesis of new isoxazoline-based acidic amino acids and investigation of their affinity and selectivity profile at ionotropic glutamate receptors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 46, 787–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, F.; Wang, C.; Zhang, X.; Chiu, P.; Yin, Q. Direct asymmetric reductive amination of alpha-keto acetals: A platform for synthesizing diverse alpha-functionalized amines. Chem. Commun. 2022, 58, 513–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, B.O.; Sui, J.; Young, A.B.; Whittal, R.M. Interferences and contaminants encountered in modern mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 627, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Time (Minutes) | 10 mM NH4Cl | CH3CN |
|---|---|---|
| 0.00 | 70% | 30% |
| 1.00 | 70% | 30% |
| 6.00 | 40% | 60% |
| 6.00 | 70% | 30% |
| 9.50 | 70% | 30% |
| 22.00 | 95% | 5% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Artasensi, A.; Salina, E.; Fumagalli, L.; Regazzoni, L. A Novel Chromatographic Method to Assess the Binding Ability towards Dicarbonyls. Molecules 2023, 28, 5341. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28145341
Artasensi A, Salina E, Fumagalli L, Regazzoni L. A Novel Chromatographic Method to Assess the Binding Ability towards Dicarbonyls. Molecules. 2023; 28(14):5341. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28145341
Chicago/Turabian StyleArtasensi, Angelica, Emanuele Salina, Laura Fumagalli, and Luca Regazzoni. 2023. "A Novel Chromatographic Method to Assess the Binding Ability towards Dicarbonyls" Molecules 28, no. 14: 5341. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28145341
APA StyleArtasensi, A., Salina, E., Fumagalli, L., & Regazzoni, L. (2023). A Novel Chromatographic Method to Assess the Binding Ability towards Dicarbonyls. Molecules, 28(14), 5341. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28145341






