Evaluation of Silk Fibroin/Gellan Gum Hydrogels with Controlled Molecular Weight through Silk Fibroin Hydrolysis for Tissue Engineering Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Properties of Hydrolyzed Silk Fibroin
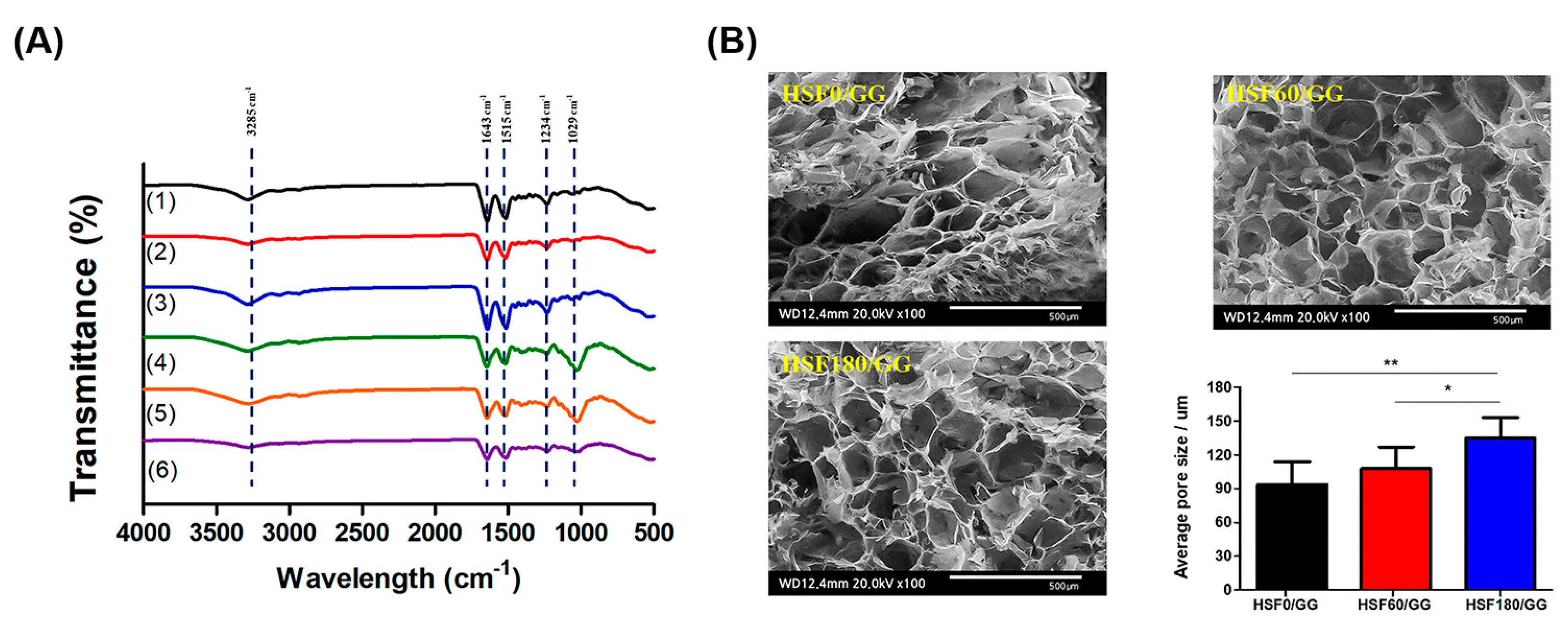
2.2. Physicochemical Properties of HSF/GG Hydrogel
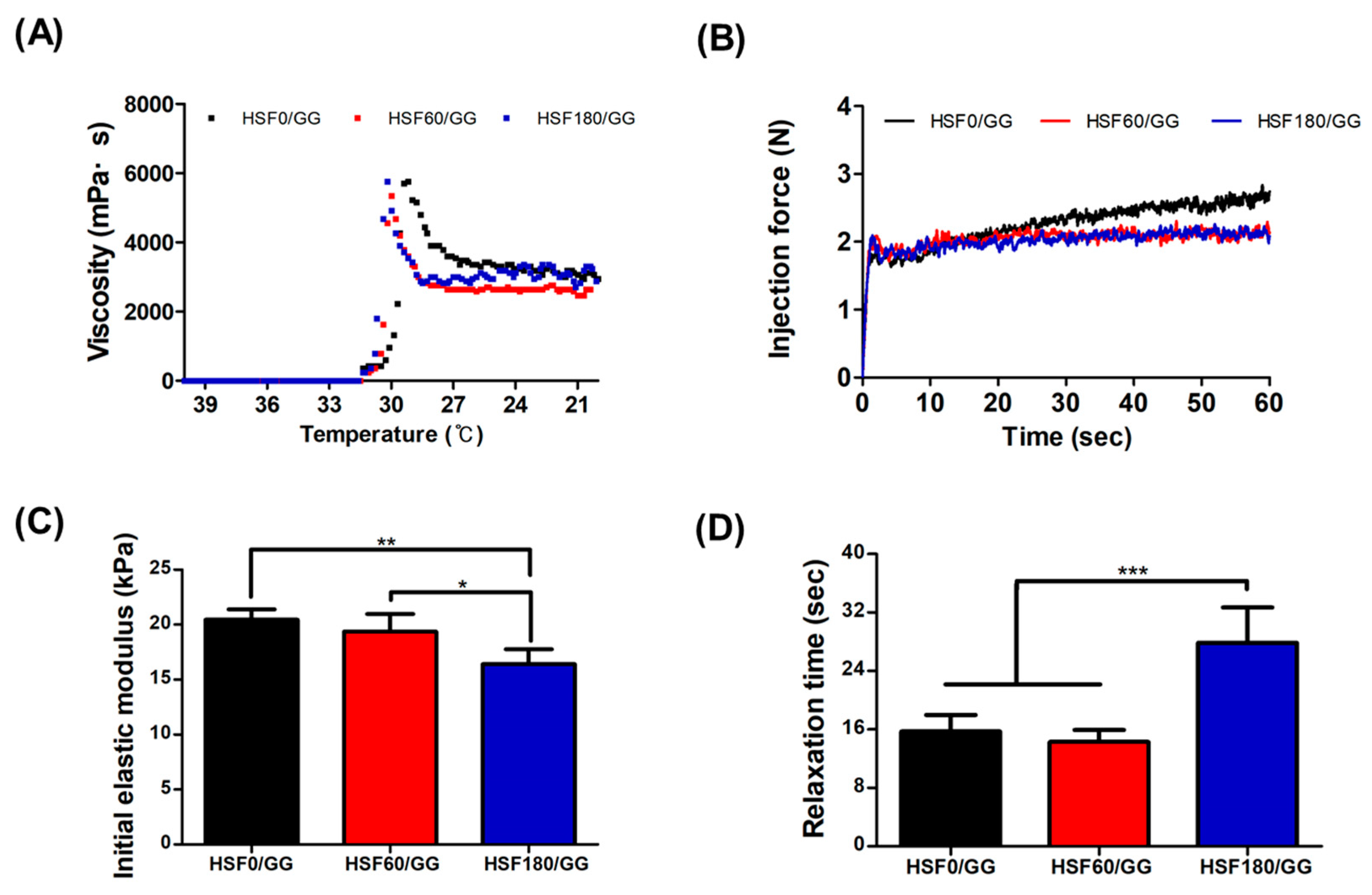
2.3. Mechanical Properties of HSF/GG Hydrogel
2.4. In Vitro Analysis
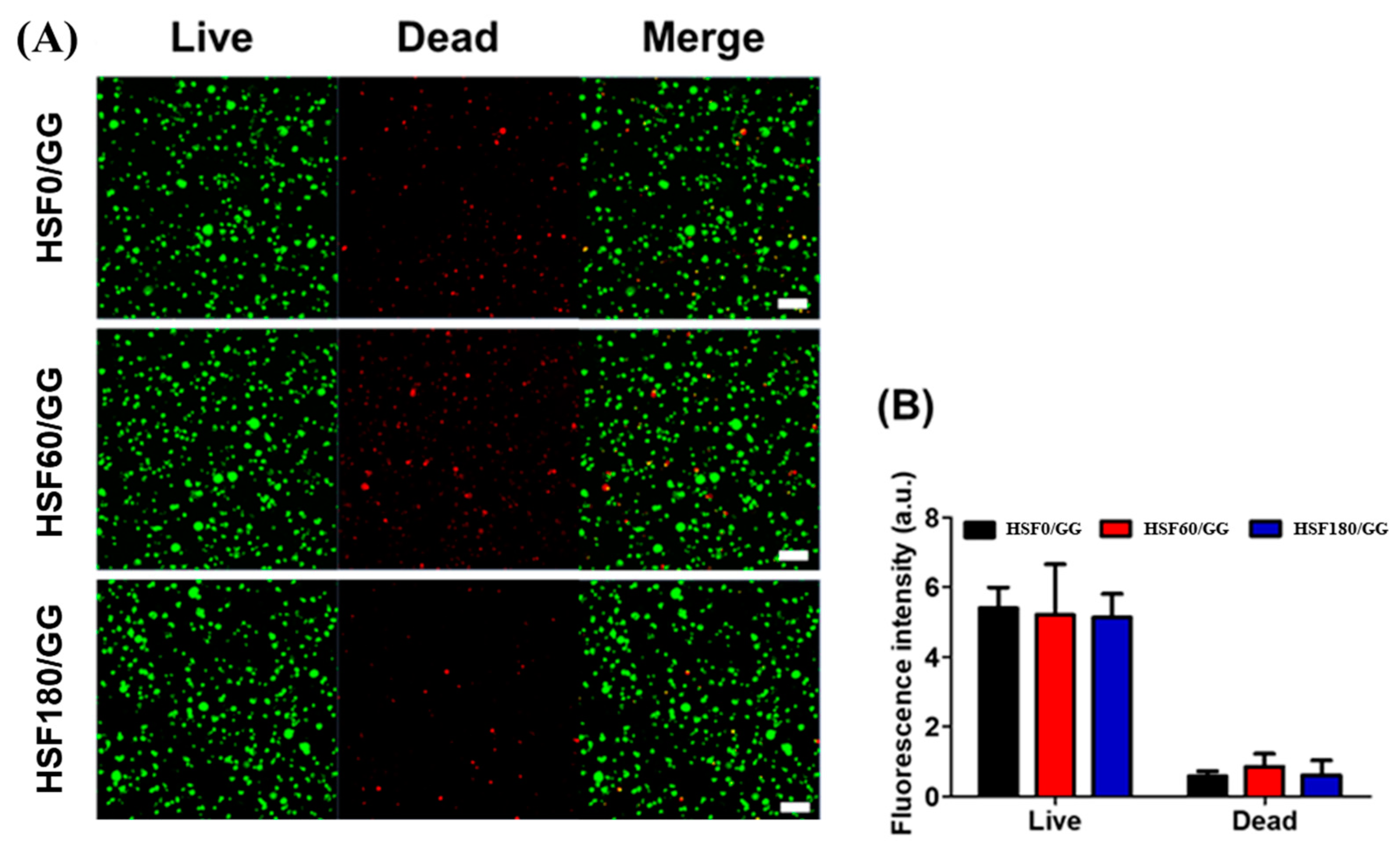
2.4.1. Live/Dead Staining
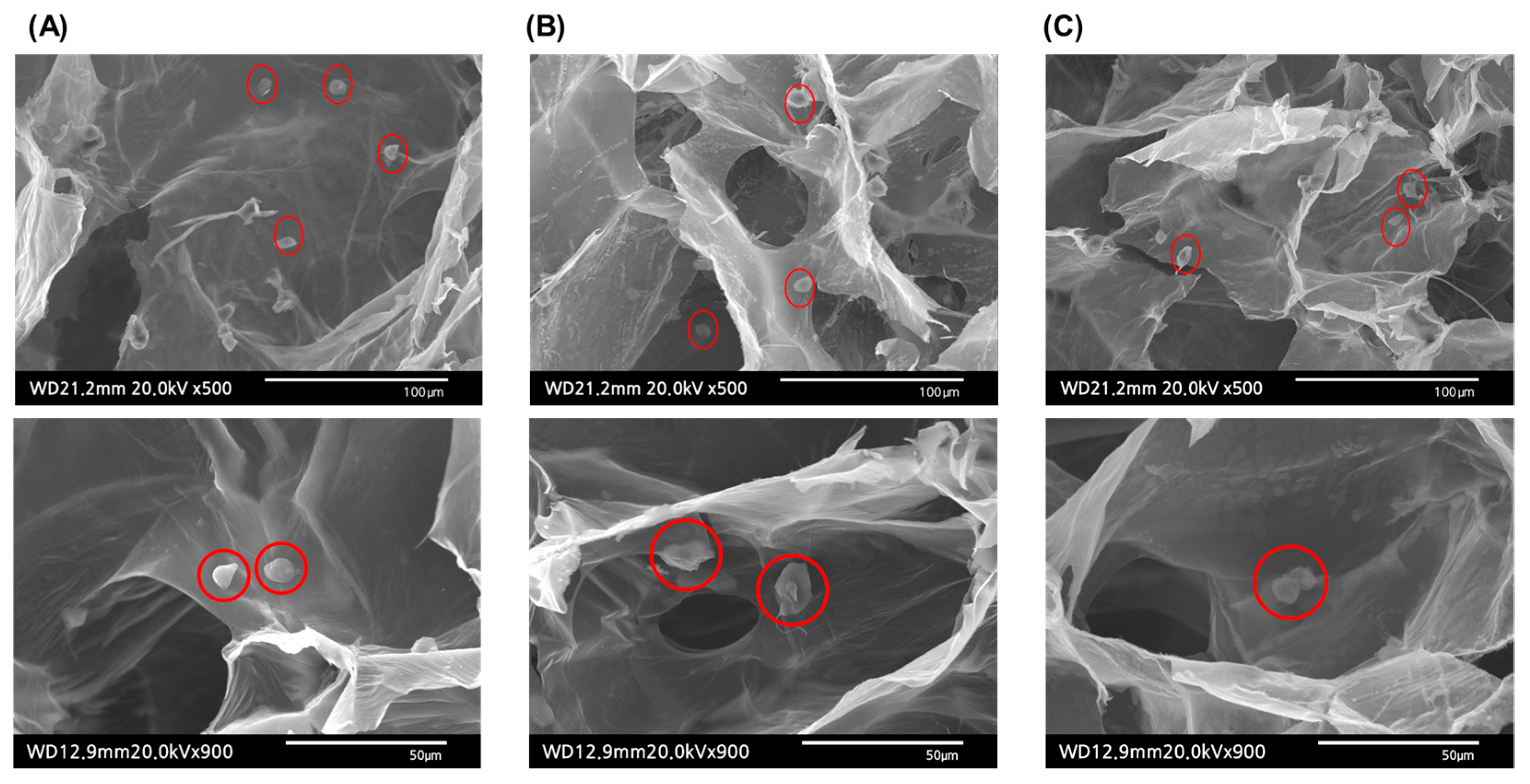
2.4.2. Cell-Laden Hydrogel Morphology
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Preparation of Hydrolyzed Silk Fibroin
3.2. Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate-Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE)
3.3. Fabrication of Hydrogels
3.4. Physicochemical Property
3.4.1. Morphological Structure Study
3.4.2. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR)
3.4.3. Sol Fraction (%)
3.4.4. Swelling Ratio
3.4.5. Weight Loss (%)
3.5. Mechanical Property Analysis
3.5.1. Viscosity Test
3.5.2. Injectability Test
3.5.3. Compression and Relaxation Tests
3.6. In Vitro Study
3.6.1. Cell Culture and Preparation of Cell-Laden Hydrogels
3.6.2. Live/Dead Staining
3.7. Statistics
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Sharma, S.; Tiwari, S. A review on biomacromolecular hydrogel classification and its applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 162, 737–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.; Liu, S.; Cheng, X.; Qin, Z.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, K.; Zhao, J. Intensified stiffness and photodynamic provocation in a collagen-based composite hydrogel drive chondrogenesis. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1900099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.H.; Kim, S.I.; Seo, J.S.; Tumursukh, N.-E.; Kim, S.E.; Choe, S.H.; Kim, S.J.; Park, S.; Song, J.E.; Khang, G. Fast stress relaxing gellan gum that enhances the microenvironment and secreting function of bone mesenchymal stem cells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 222, 2144–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johari, N.; Moroni, L.; Samadikuchaksaraei, A. Tuning the conformation and mechanical properties of silk fibroin hydrogels. Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 134, 109842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keten, S.; Xu, Z.; Ihle, B.; Buehler, M.J. Nanoconfinement controls stiffness, strength and mechanical toughness of β-sheet crystals in silk. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.H.; Park, W.H. Chemically cross-linked silk fibroin hydrogel with enhanced elastic properties, biodegradability, and biocompatibility. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 2967. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, O.J.; Lee, J.M.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.; Kweon, H.; Jo, Y.Y.; Park, C.H. Biodegradation behavior of silk fibroin membranes in repairing tympanic membrane perforations. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2012, 100, 2018–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, I.M.; Gonçalves, C.; Shin, M.E.; Lee, S.; Reis, R.L.; Khang, G.; Oliveira, J.M. Anti-inflammatory properties of injectable betamethasone-loaded tyramine-modified gellan gum/silk fibroin hydrogels. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Li, Q.; Yu, H.; Cheng, J.; Wu, N.; Shi, W.; Zhao, F.; Shao, Z.; Meng, Q.; Chen, H. Cryo-self-assembled silk fibroin sponge as a biodegradable platform for enzyme-responsive delivery of exosomes. Bioact. Mater. 2022, 8, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yodmuang, S.; McNamara, S.L.; Nover, A.B.; Mandal, B.B.; Agarwal, M.; Kelly, T.-A.N.; Chao, P.-H.G.; Hung, C.; Kaplan, D.L.; Vunjak-Novakovic, G. Silk microfiber-reinforced silk hydrogel composites for functional cartilage tissue repair. Acta Biomater. 2015, 11, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.; Olsen, B.D.; Khademhosseini, A. The mechanical properties and cytotoxicity of cell-laden double-network hydrogels based on photocrosslinkable gelatin and gellan gum biomacromolecules. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 3143–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, A.; Choi, J.H.; Lee, S.; Been, S.; Song, J.E.; Khang, G. Application of double network of gellan gum and pullulan for bone marrow stem cells differentiation towards chondrogenesis by controlling viscous substrates. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2020, 14, 1592–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva-Correia, J.; Zavan, B.; Vindigni, V.; Silva, T.H.; Oliveira, J.M.; Abatangelo, G.; Reis, R.L. Biocompatibility evaluation of ionic-and photo-crosslinked methacrylated gellan gum hydrogels: In vitro and in vivo study. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2013, 2, 568–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muthukumar, T.; Song, J.E.; Khang, G. Biological role of gellan gum in improving scaffold drug delivery, cell adhesion properties for tissue engineering applications. Molecules 2019, 24, 4514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.K.; Choi, J.H.; Shin, M.E.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, P.Y.; Kim, N.; Song, J.E.; Khang, G. Evaluation of cartilage regeneration of chondrocyte encapsulated gellan gum-based hyaluronic acid blended hydrogel. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 141, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rim, M.A.; Choi, J.H.; Park, A.; Youn, J.; Lee, S.; Kim, N.E.; Song, J.E.; Khang, G. Characterization of gelatin/gellan gum/glycol chitosan ternary hydrogel for retinal pigment epithelial tissue reconstruction materials. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 6079–6087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Numata, K.; Katashima, T.; Sakai, T. State of water, molecular structure, and cytotoxicity of silk hydrogels. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 2137–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, U.-J.; Park, J.; Li, C.; Jin, H.-J.; Valluzzi, R.; Kaplan, D.L. Structure and properties of silk hydrogels. Biomacromolecules 2004, 5, 786–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Song, D.; Kim, M.; Ryu, S.; Um, I.; Ki, C.; Park, Y. Effect of silk fibroin molecular weight on physical property of silk hydrogel. Polymer 2016, 90, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.Z.; Confalonieri, F.; Jacquet, M.; Perasso, R.; Li, Z.G.; Janin, J. Silk fibroin: Structural implications of a remarkable amino acid sequence. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2001, 44, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, A.; Moztarzadeh, F.; Mohandesi, J.A. Investigating the effect of chitosan on hydrophilicity and bioactivity of conductive electrospun composite scaffold for neural tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 121, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dave, K.; Gomes, V.G. Interactions at scaffold interfaces: Effect of surface chemistry, structural attributes and bioaffinity. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 105, 110078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Tian, W.; Zhang, Y.; Song, H.; Yu, Y.; Chen, X.; Yong, N.; Li, X.; Yin, Y.; Fan, Q. Enhanced silk fibroin/sericin composite film: Preparation, mechanical properties and mineralization activity. Polymers 2022, 14, 2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Luo, Z.-G.; Xiao, Z.-G. Preparation, physicochemical characterization and in vitro release behavior of resveratrol-loaded oxidized gellan gum/resistant starch hydrogel beads. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 260, 117794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, V.P.; da Silva Morais, A.; Maia, F.R.; Canadas, R.F.; Costa, J.B.; Oliveira, A.L.; Oliveira, J.M.; Reis, R.L. Combinatory approach for developing silk fibroin scaffolds for cartilage regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2018, 72, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrowska-Czubenko, J.; Gierszewska-Drużyńska, M. Effect of ionic crosslinking on the water state in hydrogel chitosan membranes. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 77, 590–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Guo, X.; Temenoff, J.S.; Tabata, Y.; Caplan, A.I.; Kasper, F.K.; Mikos, A.G. Effect of swelling ratio of injectable hydrogel composites on chondrogenic differentiation of encapsulated rabbit marrow mesenchymal stem cells in vitro. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Choi, J.H.; Park, A.; Rim, M.; Youn, J.; Lee, W.; Song, J.E.; Khang, G. Advanced gellan gum-based glycol chitosan hydrogel for cartilage tissue engineering biomaterial. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 158, 452–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maqsoudlou, A.; Sadeghi Mahoonak, A.; Mora, L.; Mohebodini, H.; Ghorbani, M.; Toldrá, F. Controlled enzymatic hydrolysis of pollen protein as promising tool for production of potential bioactive peptides. J. Food Biochem. 2019, 43, e12819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diab, T.; Pritchard, E.M.; Uhrig, B.A.; Boerckel, J.D.; Kaplan, D.L.; Guldberg, R.E. A silk hydrogel-based delivery system of bone morphogenetic protein for the treatment of large bone defects. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2012, 11, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, A.M.; De Laporte, L.; Tortelli, F.; Spedden, E.; Staii, C.; Atherton, T.J.; Hubbell, J.A.; Kaplan, D.L. Silk hydrogels as soft substrates for neural tissue engineering. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 5140–5149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, A.; Doumit, M.; Rockwell, G. The biomechanics and optimization of the needle-syringe system for injecting triamcinolone acetonide into keloids. J. Med. Eng. 2016, 2016, 162394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Sun, T.L.; Cui, K.; King, D.R.; Kurokawa, T.; Saruwatari, Y.; Gong, J.P. Facile synthesis of novel elastomers with tunable dynamics for toughness, self-healing and adhesion. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 17334–17344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Ludescher, R.D. Effects of glycerol on the molecular mobility and hydrogen bond network in starch matrix. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 115, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhuri, O.; Gu, L.; Klumpers, D.; Darnell, M.; Bencherif, S.A.; Weaver, J.C.; Huebsch, N.; Lee, H.-P.; Lippens, E.; Duda, G.N. Hydrogels with tunable stress relaxation regulate stem cell fate and activity. Nat. Mater. 2016, 15, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, R.G. The role of matrix stiffness in regulating cell behavior. Hepatology 2008, 47, 1394–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maggi, A.; Li, H.; Greer, J.R. Three-dimensional nano-architected scaffolds with tunable stiffness for efficient bone tissue growth. Acta Biomater. 2017, 63, 294–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kievit, F.M.; Cooper, A.; Jana, S.; Leung, M.C.; Wang, K.; Edmondson, D.; Wood, D.; Lee, J.S.; Ellenbogen, R.G.; Zhang, M. Aligned Chitosan-Polycaprolactone Polyblend Nanofibers Promote the Migration of Glioblastoma Cells. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2013, 2, 1651–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vimal, S.K.; Ahamad, N.; Katti, D.S. A simple method for fabrication of electrospun fibers with controlled degree of alignment having potential for nerve regeneration applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 63, 616–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhuri, O. Viscoelastic hydrogels for 3D cell culture. Biomater. Sci. 2017, 5, 1480–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, S.; Kim, S.-I.; Choi, J.-H.; Kim, S.-E.; Choe, S.-H.; Son, Y.; Kang, T.-w.; Song, J.-E.; Khang, G. Evaluation of Silk Fibroin/Gellan Gum Hydrogels with Controlled Molecular Weight through Silk Fibroin Hydrolysis for Tissue Engineering Application. Molecules 2023, 28, 5222. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28135222
Park S, Kim S-I, Choi J-H, Kim S-E, Choe S-H, Son Y, Kang T-w, Song J-E, Khang G. Evaluation of Silk Fibroin/Gellan Gum Hydrogels with Controlled Molecular Weight through Silk Fibroin Hydrolysis for Tissue Engineering Application. Molecules. 2023; 28(13):5222. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28135222
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Sunjae, Soo-In Kim, Joo-Hee Choi, Se-Eun Kim, Seung-Ho Choe, Youngjun Son, Tae-woong Kang, Jeong-Eun Song, and Gilson Khang. 2023. "Evaluation of Silk Fibroin/Gellan Gum Hydrogels with Controlled Molecular Weight through Silk Fibroin Hydrolysis for Tissue Engineering Application" Molecules 28, no. 13: 5222. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28135222
APA StylePark, S., Kim, S.-I., Choi, J.-H., Kim, S.-E., Choe, S.-H., Son, Y., Kang, T.-w., Song, J.-E., & Khang, G. (2023). Evaluation of Silk Fibroin/Gellan Gum Hydrogels with Controlled Molecular Weight through Silk Fibroin Hydrolysis for Tissue Engineering Application. Molecules, 28(13), 5222. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28135222





