Investigation of New Psychoactive Substances (NPS), Other Illicit Drugs, and Drug-Related Compounds in a Taiwanese Wastewater Sample Using High-Resolution Mass-Spectrometry-Based Targeted and Suspect Screening
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
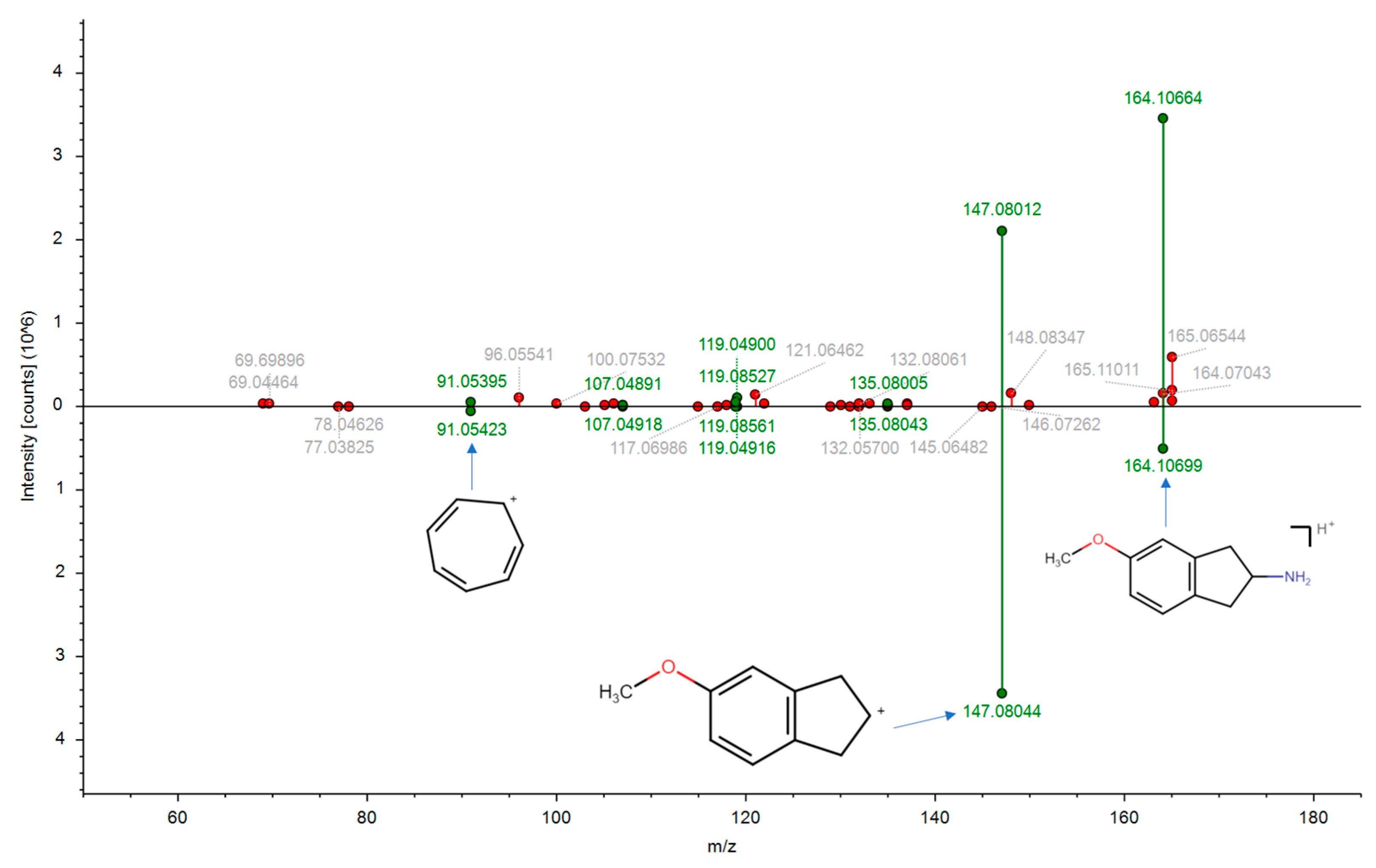
2.1. Suspect Screening Results
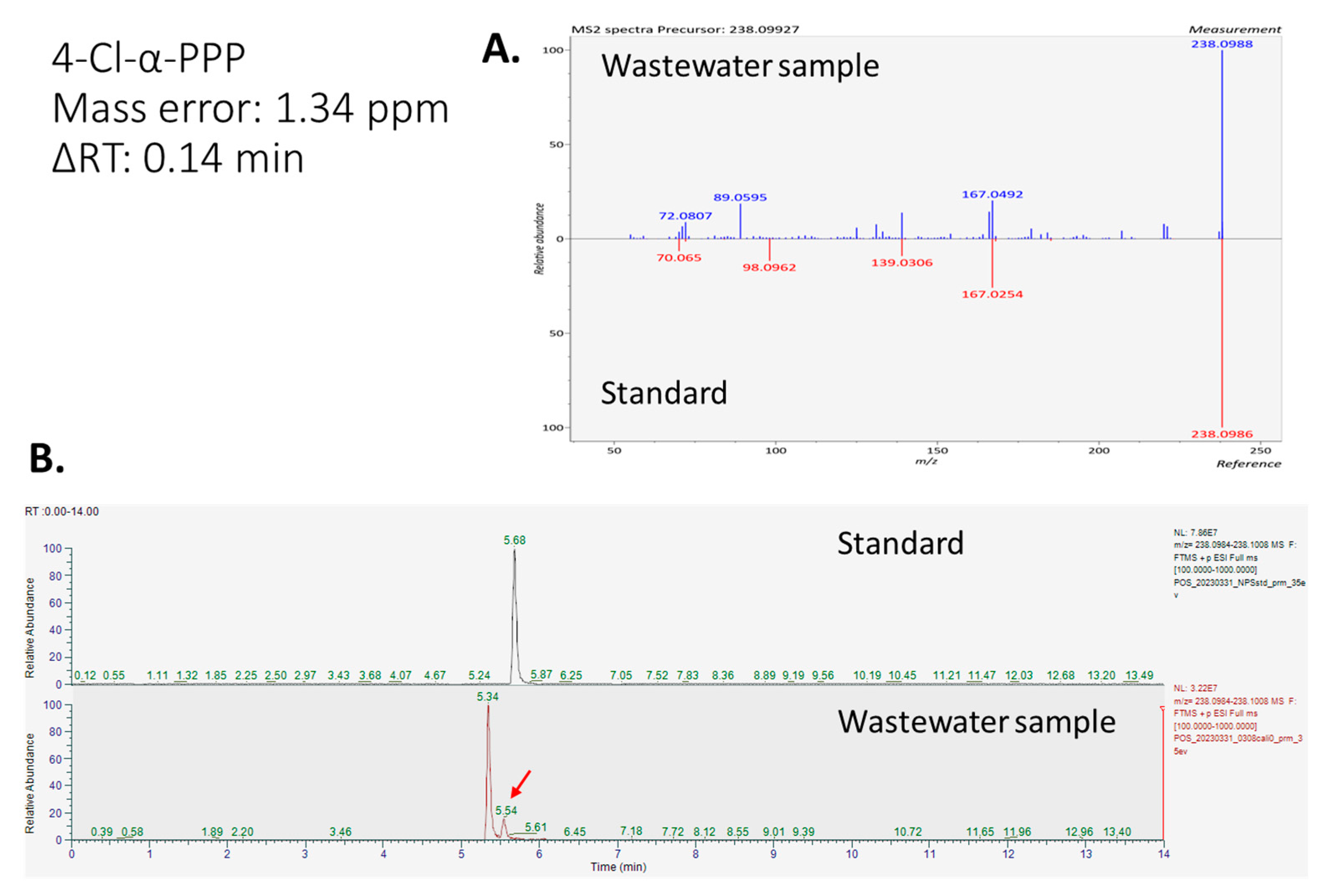
2.2. Targeted Analysis Results
3. Discussion
3.1. The Identification of NPSs and Other Illicit Drugs Based on Standards
3.2. The Identification of Illicit Drugs Based on Suspect Screening
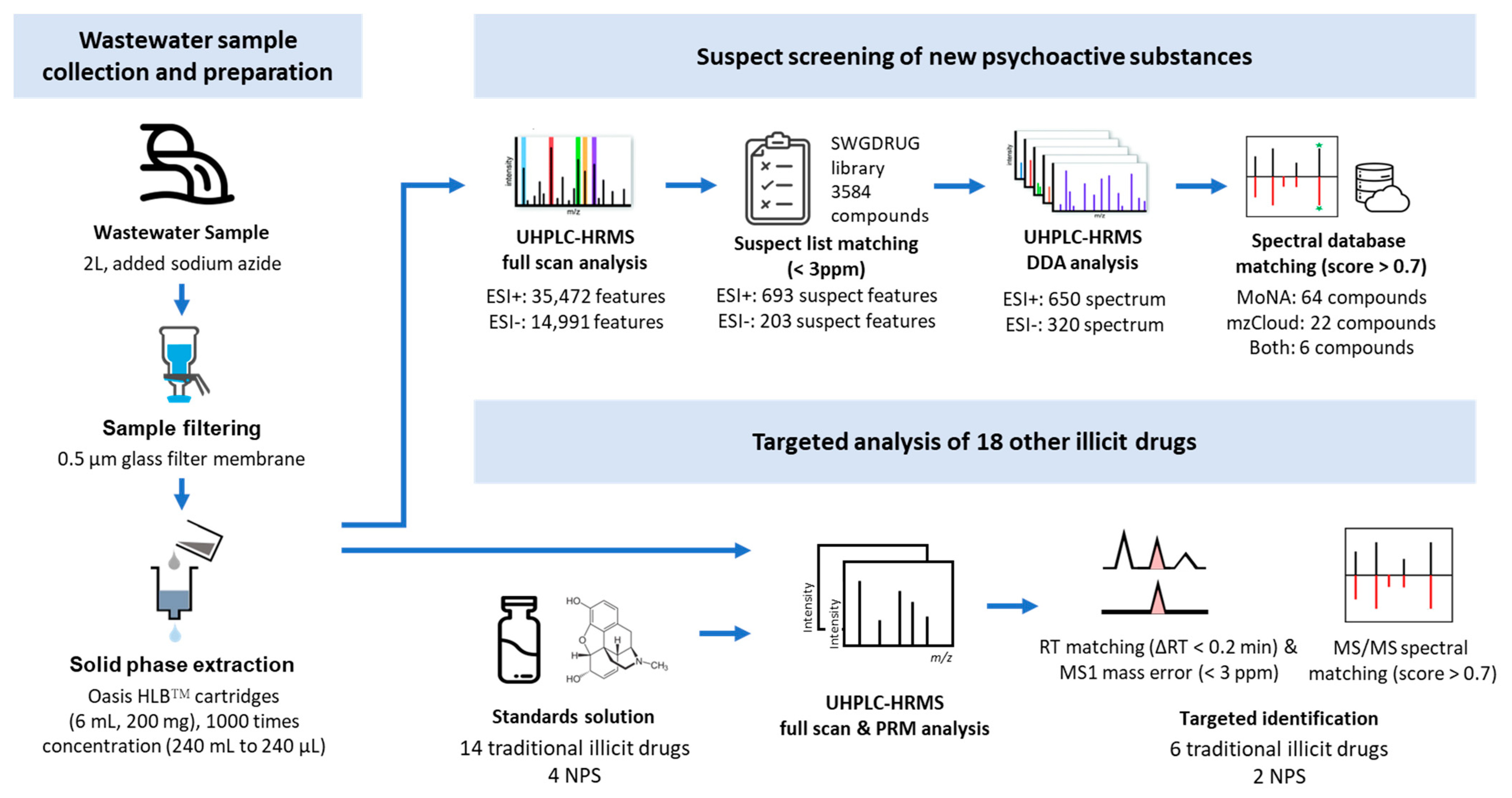
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design
4.2. Reagents and Materials
4.3. Sample Collection
4.4. Sample Preparation
4.5. UHPLC–HRMS Analysis
4.6. Data Processing and Drugs Identification
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- UNODC. World Drug Report 2022; United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime: New York, NY, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Simão, A.Y.; Antunes, M.; Cabral, E.; Oliveira, P.; Rosendo, L.M.; Brinca, A.T.; Alves, E.; Marques, H.; Rosado, T.; Passarinha, L.A. An update on the implications of new psychoactive substances in public health. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 4869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debruyne, D.; Le Boisselier, R. Emerging drugs of abuse: Current perspectives on synthetic cannabinoids. Subst. Abus. Rehabil. 2015, 6, 113–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Food and Drug Administration. List of New Psychoactive Substances (NPS) Detected in Taiwan. Available online: https://antidrug.moj.gov.tw/dl-3078-679beaf8-ba28-4ff2-bd0d-7d31d397b46d.html (accessed on 19 December 2022).
- Feng, L.-Y.; Li, J.-H. New psychoactive substances in Taiwan: Challenges and strategies. Curr. Opin. Psychiatry 2020, 33, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huizer, M.; Ter Laak, T.L.; de Voogt, P.; van Wezel, A.P. Wastewater-based epidemiology for illicit drugs: A critical review on global data. Water Res. 2021, 207, 117789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wel, J.; Gracia-Lor, E.; Van Nuijs, A.; Kinyua, J.; Salvatore, S.; Castiglioni, S.; Bramness, J.G.; Covaci, A.; Van Hal, G. Investigation of agreement between wastewater-based epidemiology and survey data on alcohol and nicotine use in a community. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2016, 162, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PricePrice, M.; WilkinsWilkins, C.; Tscharke, B.J.; Baker, T.; Mueller, J.F.; Trowsdale, S. Spatial, temporal and socioeconomic patterns of illicit drug use in New Zealand assessed using wastewater-based epidemiology timed to coincide with the census. New Zeal. Med. J. (Online) 2021, 134, 11–26. [Google Scholar]
- Gushgari, A.J.; Driver, E.M.; Steele, J.C.; Halden, R.U. Tracking narcotics consumption at a Southwestern US university campus by wastewater-based epidemiology. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 359, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polo, D.; Quintela-Baluja, M.; Corbishley, A.; Jones, D.L.; Singer, A.C.; Graham, D.W.; Romalde, J.L. Making waves: Wastewater-based epidemiology for COVID-19–approaches and challenges for surveillance and prediction. Water Res. 2020, 186, 116404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gracia-Lor, E.; Rousis, N.I.; Hernández, F.; Zuccato, E.; Castiglioni, S. Wastewater-Based Epidemiology as a Novel Biomonitoring Tool to Evaluate Human Exposure to Pollutants; ACS Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Daughton, C.G. Illicit drugs in municipal sewage. Pharm. Care Prod. Environ. 2001, 791, 348–364. [Google Scholar]
- Zuccato, E.; Chiabrando, C.; Castiglioni, S.; Calamari, D.; Bagnati, R.; Schiarea, S.; Fanelli, R. Cocaine in surface waters: A new evidence-based tool to monitor community drug abuse. Environ. Health 2005, 4, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappell, A.; Armstrong, B.; Jay, E.; Phung, K.; McCormick, S.; Grigg, S.; Waite, B. Illicit drug consumption estimated using wastewater analysis and compared by settlement size in New Zealand. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 843, 156956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Wang, Y.; Wu, D.-F.; Sun, F.-M.; Di, B.; Xu, H.; Song, M.; Lu, Y.-T.; Hang, T.-J. Identification and monitoring of fentanyls-related substances in east China sewage water samples by LC-MS for drug enforcement. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 797, 149109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, N.; Jones-Lepp, T.; Margetts, M.; Sykes, J.; Alvarez, D.; Keil, D.E. Wastewater-based epidemiology pilot study to examine drug use in the Western United States. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 745, 140697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kankaanpää, A.; Ariniemi, K.; Heinonen, M.; Kuoppasalmi, K.; Gunnar, T. Current trends in Finnish drug abuse: Wastewater based epidemiology combined with other national indicators. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 568, 864–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatidou, G.; Kinyua, J.; van Nuijs, A.L.; Gracia-Lor, E.; Castiglioni, S.; Covaci, A.; Stasinakis, A.S. Drugs of abuse and alcohol consumption among different groups of population on the Greek Island of Lesvos through sewage-based epidemiology. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 563, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, F.Y.; O’Brien, J.; Bruno, R.; Hall, W.; Prichard, J.; Kirkbride, P.; Gartner, C.; Thai, P.; Carter, S.; Lloyd, B. Spatial variations in the consumption of illicit stimulant drugs across Australia: A nationwide application of wastewater-based epidemiology. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 568, 810–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Mariño, I.; Baz-Lomba, J.A.; Alygizakis, N.A.; Andrés-Costa, M.J.; Bade, R.; Bannwarth, A.; Barron, L.P.; Been, F.; Benaglia, L.; Berset, J.D. Spatio-temporal assessment of illicit drug use at large scale: Evidence from 7 years of international wastewater monitoring. Addiction 2020, 115, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bade, R.; Rousis, N.I.; Bijlsma, L.; Gracia-Lor, E.; Castiglioni, S.; Sancho, J.V.; Hernandez, F. Screening of pharmaceuticals and illicit drugs in wastewater and surface waters of Spain and Italy by high resolution mass spectrometry using UHPLC-QTOF MS and LC-LTQ-Orbitrap MS. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 8979–8988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamanti, K.; Aalizadeh, R.; Alygizakis, N.; Galani, A.; Mardal, M.; Thomaidis, N.S. Wide-scope target and suspect screening methodologies to investigate the occurrence of new psychoactive substances in influent wastewater from Athens. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 685, 1058–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baz-Lomba, J.A.; Reid, M.J.; Thomas, K.V. Target and suspect screening of psychoactive substances in sewage-based samples by UHPLC-QTOF. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 914, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, F.; Ibáñez, M.; Bade, R.; Bijlsma, L.; Sancho, J.V. Investigation of pharmaceuticals and illicit drugs in waters by liquid chromatography-high-resolution mass spectrometry. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2014, 63, 140–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.C.; Hsu, J.F.; Chang, C.W.; Li, S.W.; Yang, Y.C.; Chao, M.R.; Chen, H.J.C.; Liao, P.C. Connecting chemical exposome to human health using high-resolution mass spectrometry-based biomonitoring: Recent advances and future perspectives. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2022, e21805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salgueiro-González, N.; Castiglioni, S.; Gracia-Lor, E.; Bijlsma, L.; Celma, A.; Bagnati, R.; Hernandez, F.; Zuccato, E. Flexible high resolution-mass spectrometry approach for screening new psychoactive substances in urban wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 689, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bade, R.; Tscharke, B.J.; White, J.M.; Grant, S.; Mueller, J.F.; O’Brien, J.; Thomas, K.V.; Gerber, C. LC-HRMS suspect screening to show spatial patterns of New Psychoactive Substances use in Australia. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 2181–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-J.; Oh, J.-E. Target and suspect screening of (new) psychoactive substances by LC-HRMS in South Korea. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 875, 162613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castiglioni, S.; Salgueiro-González, N.; Bijlsma, L.; Celma, A.; Gracia-Lor, E.; Beldean-Galea, M.S.; Mackuľak, T.; Emke, E.; Heath, E.; Kasprzyk-Hordern, B. New psychoactive substances in several European populations assessed by wastewater-based epidemiology. Water Res. 2021, 195, 116983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feeney, W.; Moorthy, A.S.; Sisco, E. Spectral trends in GC-EI-MS data obtained from the SWGDRUG mass spectral library and literature: A resource for the identification of unknown compounds. Forensic Chem. 2022, 31, 100459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schymanski, E.L.; Jeon, J.; Gulde, R.; Fenner, K.; Ruff, M.; Singer, H.P.; Hollender, J. Identifying Small Molecules via High Resolution Mass Spectrometry: Communicating Confidence; ACS Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Food and Drug Administration. Report on Drug Seizures in Taiwan. Available online: https://www.fda.gov.tw/tc/includes/GetFile.ashx?id=f638155229375192027&type=3&iid=12492 (accessed on 3 April 2023).
- Feng, L.-Y.; Yu, W.-J.; Chang, W.-T.; Han, E.; Chung, H.; Li, J.-H. Comparison of illegal drug use pattern in Taiwan and Korea from 2006 to 2014. Subst. Abus. Treat. Prev. Policy 2016, 11, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandopulos, A.J.; Bade, R.; O’Brien, J.W.; Tscharke, B.J.; Mueller, J.F.; Thomas, K.; White, J.M.; Gerber, C. Towards an efficient method for the extraction and analysis of cannabinoids in wastewater. Talanta 2020, 217, 121034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijlsma, L.; Bade, R.; Been, F.; Celma, A.; Castiglioni, S. Perspectives and challenges associated with the determination of new psychoactive substances in urine and wastewater–A tutorial. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1145, 132–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsugawa, H.; Cajka, T.; Kind, T.; Ma, Y.; Higgins, B.; Ikeda, K.; Kanazawa, M.; VanderGheynst, J.; Fiehn, O.; Arita, M. MS-DIAL: Data-independent MS/MS deconvolution for comprehensive metabolome analysis. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Class | Compound Names | Molecular Formula | Measured m/z | Mass Error | MS/MS Similarity Scores | Classification in U.S. | Classification in Taiwan |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Opiate analgesics | Tapentadol | C14H23NO | 222.1847 | −2.4 | 0.76 | 2 | 2 |
| Meperidine | C15H21NO2 | 248.1642 | −0.2 | 0.82 | 2 | 2 | |
| Levorphanol | C17H23NO | 258.1848 | −1.7 | 0.86 | 2 | 2 | |
| Tramadol | C16H25NO2 | 264.1956 | −0.8 | 0.86 | 4 | 4 | |
| Hydromorphone | C17H19NO3 | 286.1433 | −1.6 | 0.83 | 2 | 2 | |
| Dihydromorphine | C17H21NO3 | 288.1590 | −1.5 | 0.78 | 1 | 2 | |
| Synthetic cathinones | 4-Methyl-N,N-dimethylcathinone | C12H17NO | 192.1381 | −1.0 | 0.75 | - | 3 |
| Methylenedioxypyrovalerone, (MDPV) | C16H21NO3 | 276.1591 | −1.2 | 0.74 | 1 | 2 | |
| Phenethylamine derivatives | 5-(2-Aminoethyl)-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran (5-AEDB) | C10H13NO | 164.1068 | −1.2 | 0.70 | - | 3 |
| Tryptamine derivatives | Bufotenin | C12H16N2O | 205.1335 | −0.2 | 0.70 | 1 | 3 |
| Phenylalkylamines derivatives | N-methyl-2-aminoindane | C10H13N | 148.1121 | −0.5 | 0.78 | - | 3 |
| Steroids | 1,4-Androstadiene-3,17-dione | C19H24O2 | 285.1845 | −1.4 | 0.87 | 3 | - |
| Methenolone | C20H30O2 | 303.2314 | −1.5 | 0.74 | 3 | - | |
| Others | Ephedrine | C10H15NO | 166.1225 | −0.8 | 0.93 | - | 4 |
| N-Methylephedrine | C11H17NO | 180.1382 | 0.5 | 0.90 | - | 4 |
| Class | Compound Name | Molecular Formula | Theoretical m/z ([M + H]+) | Measured m/z ([M − H]+) | Mass Error (ppm) | ∆RT (min) | MS/MS Similarity Scores |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional drugs | Amphetamine | C9H13N | 136.1121 | 136.1123 | 1.52 | 0.03 | 0.78 |
| Methamphetamine | C10H15N | 150.1277 | 150.1278 | 0.50 | 0.01 | 0.95 | |
| Norketamine | C12H14ClNO | 224.0837 | 224.0838 | 0.59 | 0.07 | 0.76 | |
| Ketamine | C13H16ClNO | 238.0993 | 238.0992 | −0.42 | 0.05 | 0.99 | |
| Morphine | C17H19NO3 | 286.1438 | 286.1435 | −1.00 | 0.52 | 0.84 | |
| Codeine | C18H21NO3 | 300.1594 | 300.1598 | 1.27 | 0.06 | 0.74 | |
| NPS | Mephedrone | C11H15NO | 178.1226 | 178.1227 | 0.55 | 0.09 | 0.73 |
| 4′-chloro-alpha-pyrrolidinopropiophenone (4-Cl-α-PPP) | C13H16ClNO | 238.0993 | 238.0996 | 1.34 | 0.14 | 0.78 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.-C.; Hsu, J.-Y.; Chang, C.-W.; Chen, P.-Y.; Lin, Y.-C.; Hsu, I.-L.; Chu, C.-J.; Lin, Y.-P.; Liao, P.-C. Investigation of New Psychoactive Substances (NPS), Other Illicit Drugs, and Drug-Related Compounds in a Taiwanese Wastewater Sample Using High-Resolution Mass-Spectrometry-Based Targeted and Suspect Screening. Molecules 2023, 28, 5040. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28135040
Chen Y-C, Hsu J-Y, Chang C-W, Chen P-Y, Lin Y-C, Hsu I-L, Chu C-J, Lin Y-P, Liao P-C. Investigation of New Psychoactive Substances (NPS), Other Illicit Drugs, and Drug-Related Compounds in a Taiwanese Wastewater Sample Using High-Resolution Mass-Spectrometry-Based Targeted and Suspect Screening. Molecules. 2023; 28(13):5040. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28135040
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yuan-Chih, Jen-Yi Hsu, Chih-Wei Chang, Pin-Yu Chen, Yung-Chieh Lin, I-Lin Hsu, Chiau-Jun Chu, Yen-Ping Lin, and Pao-Chi Liao. 2023. "Investigation of New Psychoactive Substances (NPS), Other Illicit Drugs, and Drug-Related Compounds in a Taiwanese Wastewater Sample Using High-Resolution Mass-Spectrometry-Based Targeted and Suspect Screening" Molecules 28, no. 13: 5040. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28135040
APA StyleChen, Y.-C., Hsu, J.-Y., Chang, C.-W., Chen, P.-Y., Lin, Y.-C., Hsu, I.-L., Chu, C.-J., Lin, Y.-P., & Liao, P.-C. (2023). Investigation of New Psychoactive Substances (NPS), Other Illicit Drugs, and Drug-Related Compounds in a Taiwanese Wastewater Sample Using High-Resolution Mass-Spectrometry-Based Targeted and Suspect Screening. Molecules, 28(13), 5040. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28135040






