Implications of Pharmacokinetic Potentials of Pioglitazone Enantiomers in Rat Plasma Mediated through Glucose Uptake Assay
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
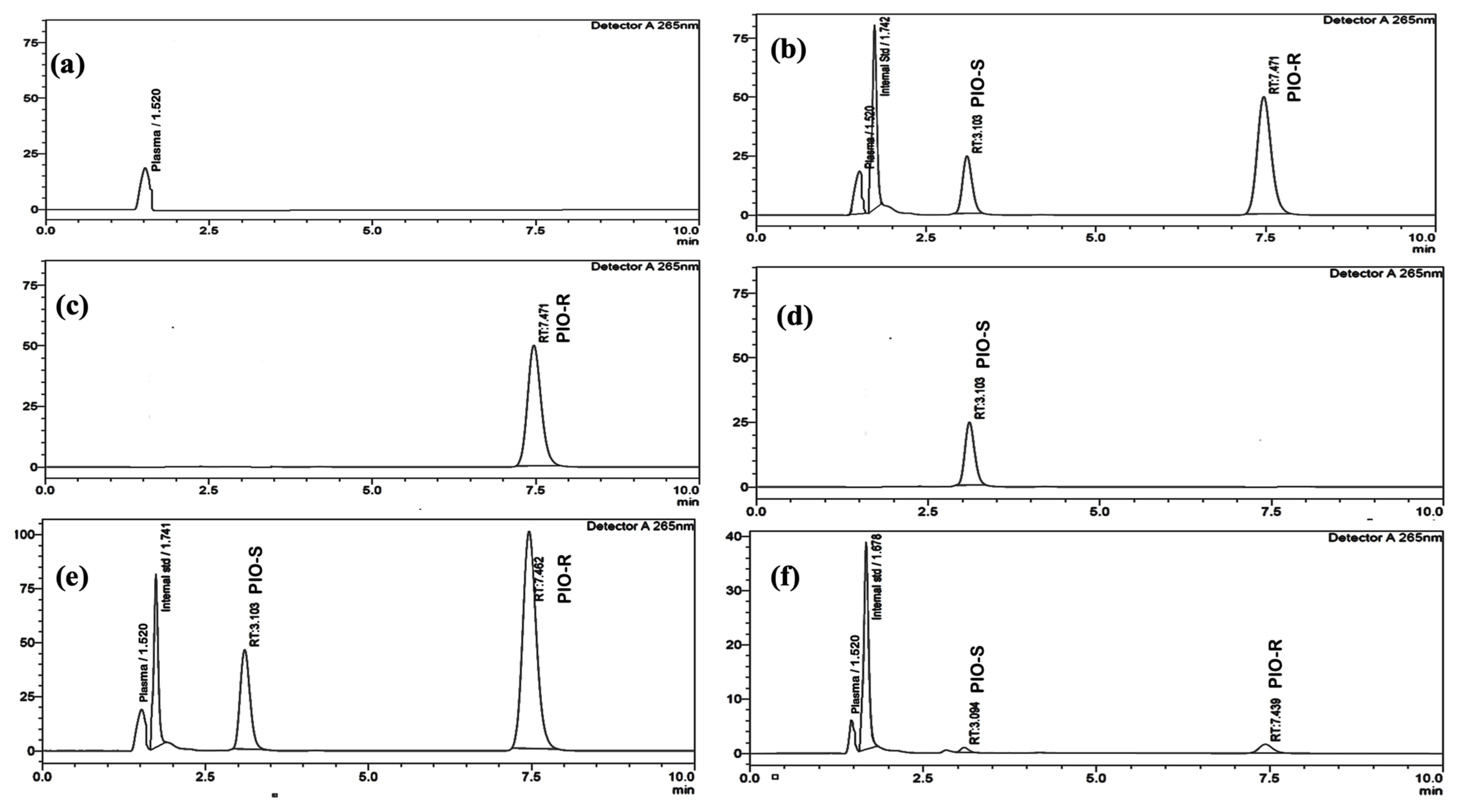
2.1. Implications of Assay Conditions on Segregation
2.2. Specificity and Chromatography
2.3. Validation of Assay
2.3.1. Linearity and Calibration Curve
2.3.2. Accuracy and Precision
2.3.3. Stability
2.3.4. Recovery
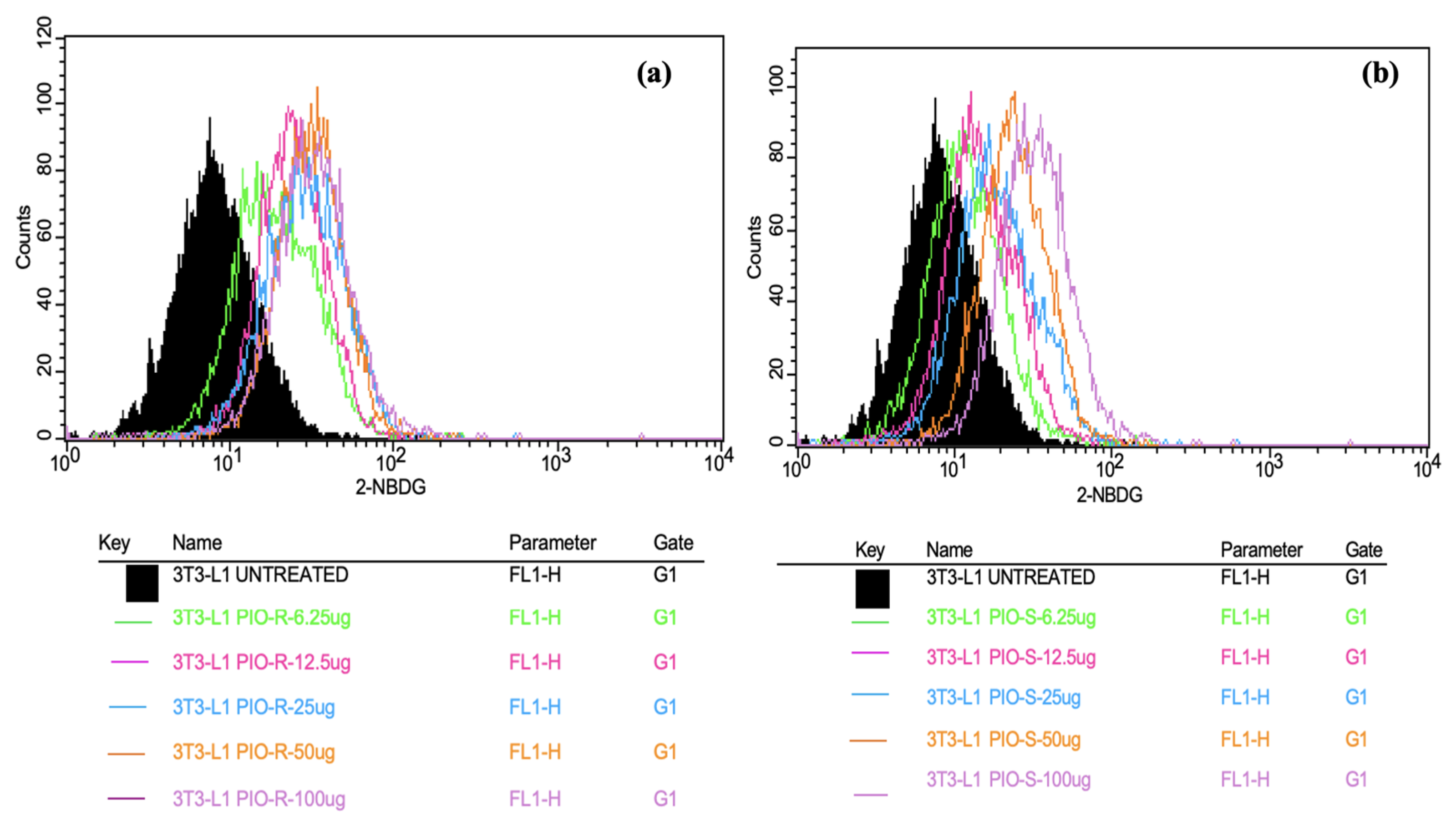
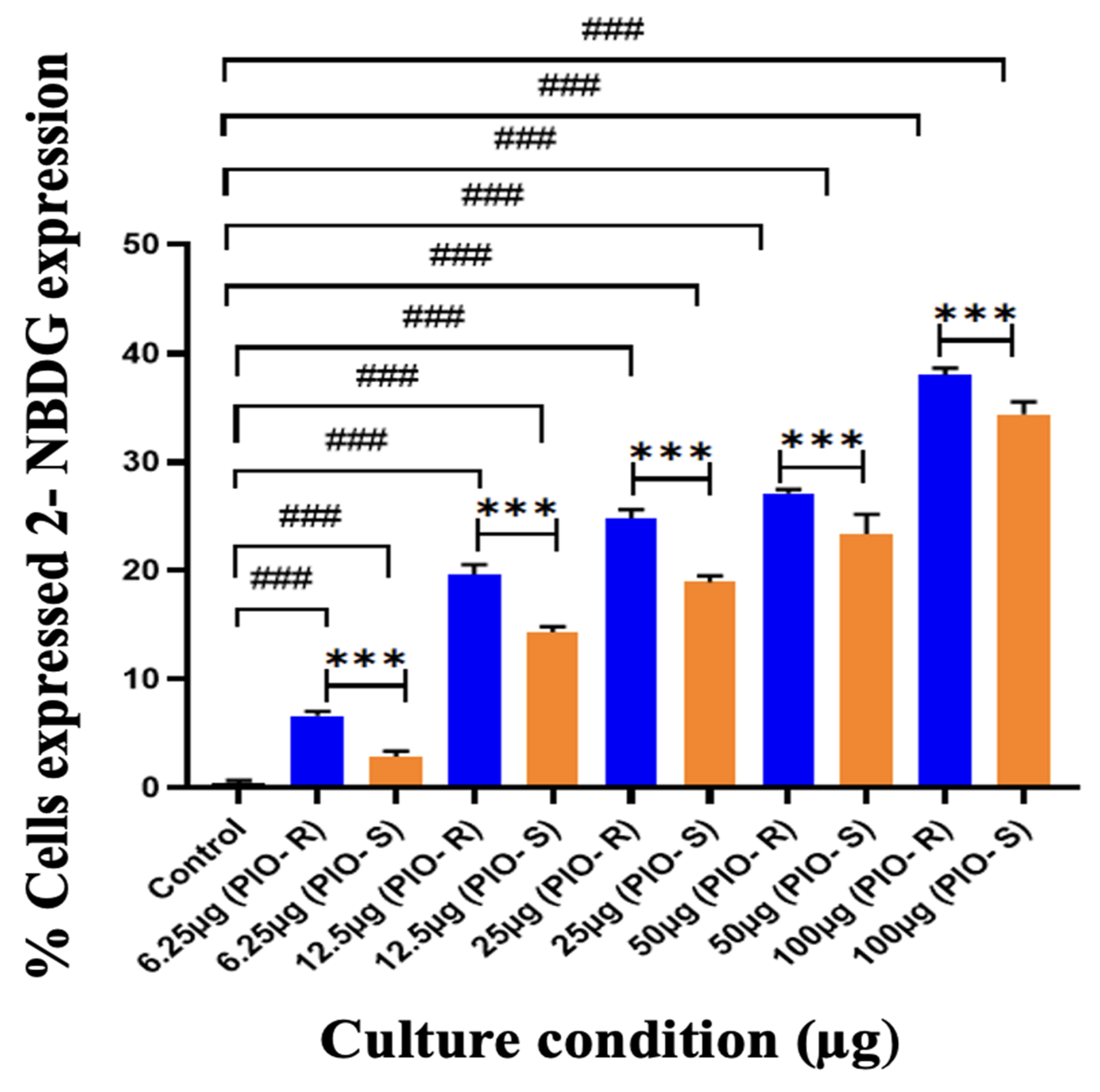
2.4. Invitro Assay on Glucose Uptake Study on 3T3-L1 Cell Lines by Flow Cytometry
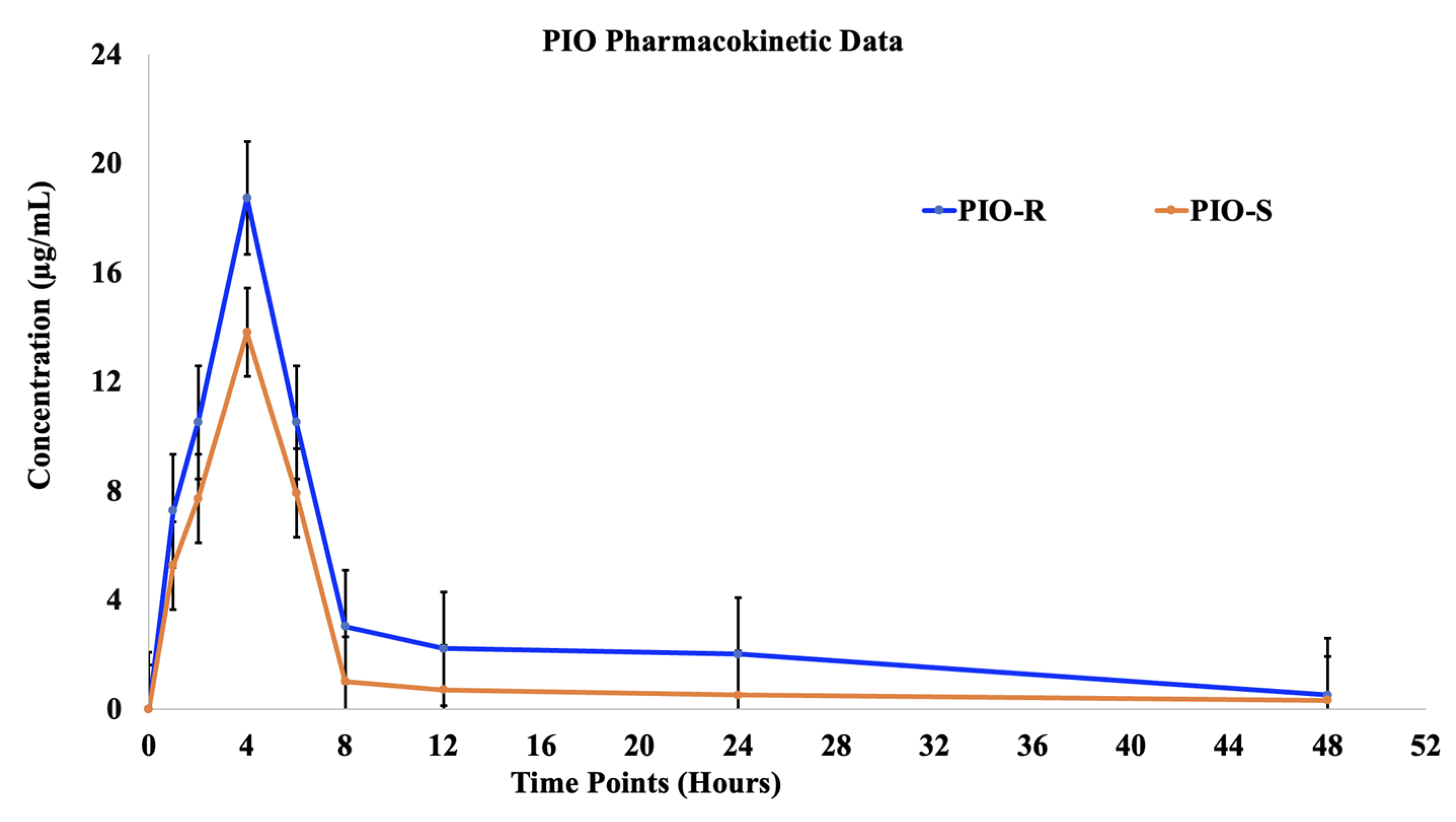
2.5. Applications of Pharmacokinetics of Pioglitazone (PIO)
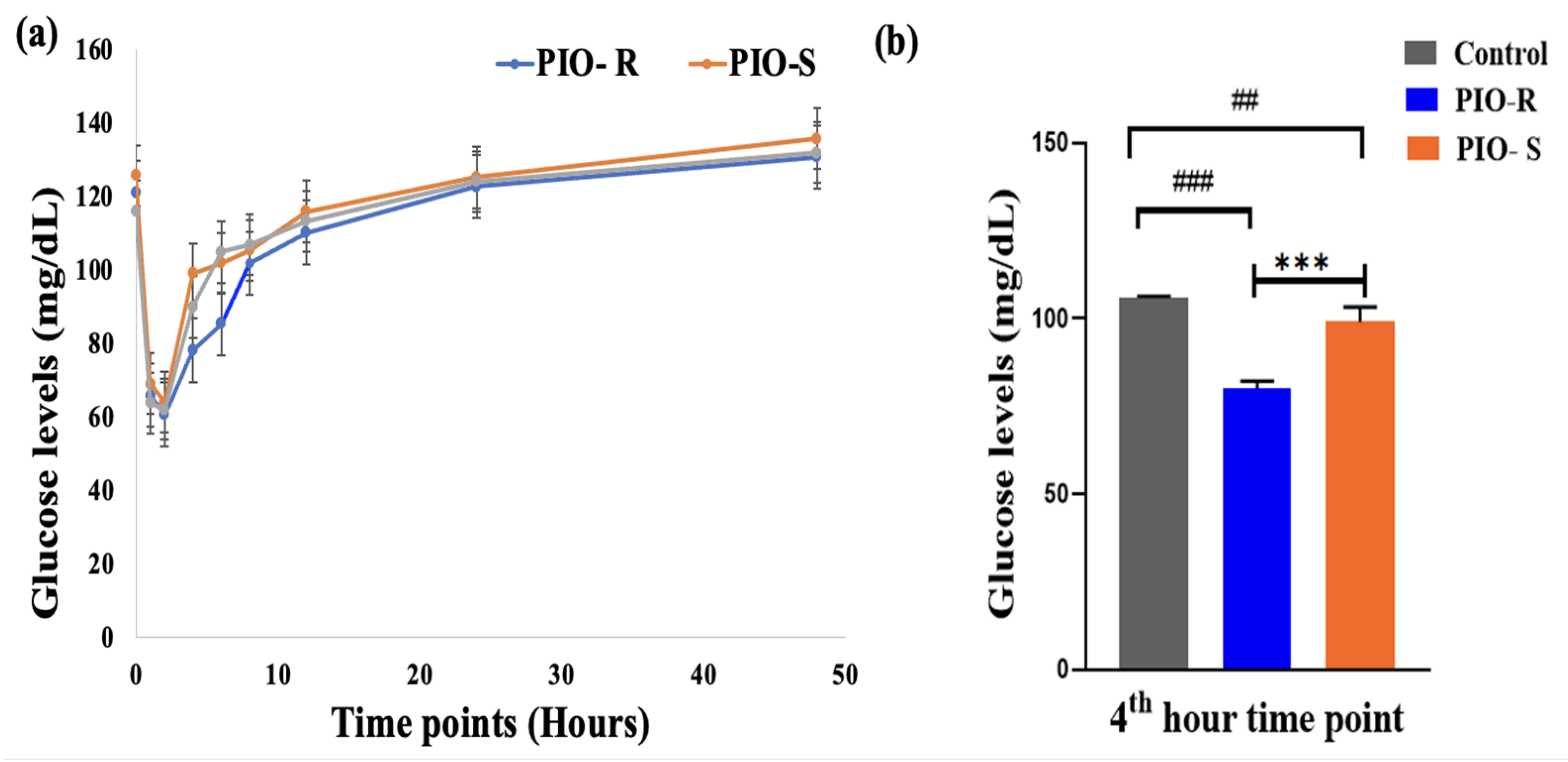
2.6. Estimation of Glucose in Rat Plasma by Semi Automated Biochemistry Analyzer
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Reagents
3.2. Animals
3.3. Chromatographic Parameters
3.4. Standard and Stock Solution Preparations
3.5. Sample Preparation
3.6. Non-Radioactive Glucose Uptake Assay of 3T3L1 Cell Lines Utilizing Flow Cytometry
3.7. Estimation of Glucose in Rat Plasma by Semi Automated Biochemistry Analyzer
3.8. Validation of Bioanalytical Methods
3.8.1. Calibration Curve
3.8.2. Recovery
3.8.3. Precision and Accuracy
3.8.4. Stability
3.9. Pharmacokinetic Investigations in Rats: A Preliminary Study
3.10. Data Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Lakshmi, K.S.; Rajesh, T.; Sharma, S. Simultaneous Determination of Metformin and Pioglitazone by Reversed Phase HPLC in Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 1, 162–166. [Google Scholar]
- Waugh, J.; Keating, G.M.; Plosker, G.L.; Easthope, S.; Robinson, D.M. Pioglitazone: A Review of Its Use in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Drugs 2006, 66, 85–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chilcott, J.; Tappenden, P.; Jones, M.L.; Wight, J.P. A Systematic ReOFTWAREview of the Clinical Effectiveness of Pioglitazone in the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Clin. Ther. 2001, 23, 1792–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamali, B.; Bjørnsdottir, I.; Nordfang, O.; Hansen, S.H. Investigation of Racemisation of the Enantiomers of Glitazone Drug Compounds at Different PH Using Chiral HPLC and Chiral CE. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2008, 46, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregoire, F.M.; Smas, C.M.; Sul, H.S. Understanding Adipocyte Differentiation. Physiol. Rev. 1998, 78, 783–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastard, J.-P.; Maachi, M.; Lagathu, C.; Kim, M.J.; Caron, M.; Vidal, H.; Capeau, J.; Feve, B. Recent Advances in the Relationship between Obesity, Inflammation, and Insulin Resistance. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 2006, 17, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vargas, E.; Podder, V.; Sepulveda, C. Physiology, Glucose Transporter Type 4; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zou, C.; Wang, Y.; Shen, Z. 2-NBDG as a Fluorescent Indicator for Direct Glucose Uptake Measurement. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 2005, 64, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gowramma, B.; Meyyanathan, S.; Krishnavenin, S.K.K. Stability Indicating Chiral HPLC Method for the Estimation of Pioglitazone Enantiomers in Pharmaceutical Formulation. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2015, 8, 63–66. [Google Scholar]
- Du, B.; Pang, L.; Yang, Y.; Shen, G.; Zhang, Z. Chiral Liquid Chromatography Resolution and Stereoselective Pharmacokinetic Study of Pioglitazone Enantiomers in Rats. J. Chromatogr. B 2014, 951, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz, A.; López-Grueso, R.; Gambini, J.; Monleón, D.; Mas-Bargues, C.; Abdelaziz, K.M.; Viña, J.; Borrás, C. Sex Differences in Age-Associated Type 2 Diabetes in Rats—Role of Estrogens and Oxidative Stress. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 6734836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiou, W.L.; Ma, C.; Wu, T.-C.; Jeong, H.Y. Unexpected Lack of Effect of the Rifampin-Induced P-Glycoprotein on the Oral Bioavailability of Its Substrate, Talinolol, in Humans: Implication in Phenotyping. J. Pharm. Sci. 2003, 92, 4–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Z.Y.; Fan, G.R.; Chai, Y.F.; Yin, X.P.; Wen, J.; Wu, Y.T. Chiral Liquid Chromatography Resolution and Stereoselective Pharmacokinetic Study of Tetrahydropalmatine Enantiomers in Dogs. J. Chromatogr. B 2005, 826, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.-Q.; Hou, B.-H.; Lalonde, S.; Takanaga, H.; Hartung, M.L.; Qu, X.-Q.; Guo, W.-J.; Kim, J.-G.; Underwood, W.; Chaudhuri, B. Sugar Transporters for Intercellular Exchange and Nutrition of Pathogens. Nature 2010, 468, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhong, D. Simultaneous Quantification of 22R and 22S Epimers of Budesonide in Human Plasma by Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry: Application in a Stereoselective Pharmacokinetic Study. J. Chromatogr. B 2013, 921, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radwan, M.A.; Abdine, H.H.; Al-Quadeb, B.T.; Aboul-Enein, H.Y.; Nakashima, K. Stereoselective HPLC Assay of Donepezil Enantiomers with UV Detection and Its Application to Pharmacokinetics in Rats. J. Chromatogr. B 2006, 830, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Pang, L.; Li, H.; Ma, S.; Li, Y.; Jia, X.; Zhang, Z. Chiral Liquid Chromatography Resolution and Stereoselective Pharmacokinetic Study of Indapamide Enantiomers in Rats. J. Chromatogr. B 2013, 932, 88–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Quality Control Samples | Concentration (µg/mL) | PIO-S | PIO-R |
|---|---|---|---|
| % RE (within runs) | |||
| LLOQ | 3.125 | 0.0843 | 0.11692 |
| LQC | 6.25 | 0.0630 | 0.10144 |
| MQC | 25 | 0.16 | 0.24584 |
| HQC | 100 | 0.0529 | 0.06424 |
| % RE (between runs) | |||
| LLOQ | 3.125 | 0.2701 | 0.04246 |
| LQC | 6.25 | 0.0624 | 0.13696 |
| MQC | 25 | 0.08 | −0.36416 |
| HQC | 100 | 0.146 | 0.02426 |
| % CV (within runs) | |||
| LLOQ | 3.125 | 0.5551 | 0.16066 |
| LQC | 6.25 | 0.7012 | 0.71591 |
| MQC | 25 | 0.3842 | 0.98899 |
| HQC | 100 | 0.5476 | 0.60702 |
| % CV (between runs) | |||
| LLOQ | 3.125 | 0.7919 | 0.77982 |
| LQC | 6.25 | 0.7014 | 0.39726 |
| MQC | 25 | 0.2080 | 0.47689 |
| HQC | 100 | 0.4585 | 0.54784 |
| Quality Control Samples | Conc (µg/mL) | Accuracy (%) | %CV | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PIO-S | PIO-R | PIO-S | PIO-R | ||
| Bench top stability | |||||
| LQC | 6.25 | 99.91 | 99.95 | 0.6471 | 0.0933 |
| HQC | 100 | 99.76 | 99.74 | 0.5394 | 0.5788 |
| Freeze–thaw stability | |||||
| LQC | 6.25 | 99.91 | 99.68 | 0.6467 | 0.9271 |
| HQC | 100 | 99.69 | 99.90 | 0.7404 | 0.4730 |
| Long-term analyte stability | |||||
| LQC | 6.25 | 99.91 | 99.95 | 0.6467 | 0.4625 |
| HQC | 100 | 99.82 | 100.20 | 0.5621 | 0.1524 |
| Concentration | Mean ± SD (n = 6) Measurable | |
|---|---|---|
| PIO-R | PIO-S | |
| Control | 0.46 ± 0.20 | 0.46 ± 0.20 |
| 6.25 µg | 6.65 ± 0.40 | 2.89 ± 0.49 |
| 12.5 µg | 19.68 ± 0.88 | 14.34 ± 0.53 |
| 25 µg | 24.84 ± 0.77 | 18.93 ± 0.60 |
| 50 µg | 27.14 ± 0.31 | 23.38 ± 1.82 |
| 100 µg | 38.05 ± 0.58 | 34.39 ± 1.15 |
| Parameters | Mean ± SD (n = 6) | |
|---|---|---|
| PIO-R | PIO-S | |
| Dose (mg/kg b.w.) | 15.00 | 15.00 |
| Cmax (μg/mL) | 18.73 ± 3.5 | 13.80 ± 5.18 |
| Tmax (h) | 4.00 | 4.00 |
| AUClast (h*μg/mL) | 260.56 ± 15.36 | 127.50 ± 4.86 |
| AUCINF_obs (h*μg/mL) | 266.99 ± 19.51 | 133.38 ± 9.03 |
| AUC_%Extrap_obs (%) | 9.35 ± 2.71 | 4.41 ± 0.58 |
| T1/2 (h) | 12.47 ± 0.36 | 12.36 ± 0.55 |
| MRTlast (h) | 10.03 ± 0.54 | 10.74 ± 0.81 |
| Time Points (Hours) | Glucose Estimation in Plasma Samples Collected at Different Time Points (Mean ± SD) (n = 6) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | PIO R | PIO S | |
| 0 | 115 ± 0.38 | 120.94 ± 1.09 | 125.68 ± 1.02 |
| 1 | 63.76 ± 0.58 | 65.85 ± 1.02 | 68.99 ± 1.65 |
| 2 | 62.11 ± 0.46 | 60.71 ± 1.51 | 63.97 ± 1.77 |
| 4 | 89.91 ± 0.51 | 78.15 ± 2.02 | 99.05 ± 4.22 |
| 6 | 104.82 ± 0.41 | 85.31 ± 1.53 | 101.91 ± 1.79 |
| 8 | 106.81 ± 0.52 | 101.7 ± 1.16 | 105.42 ± 2.58 |
| 12 | 113.31 ± 0.42 | 110.16 ± 1.56 | 115.89 ± 1.97 |
| 24 | 124.11 ± 0.55 | 122.62 ± 1.68 | 125.12 ± 1.39 |
| 48 | 131.91 ± 0.49 | 130.69 ± 2.02 | 135.69 ± 1.27 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Spandana, T.; Goli, V.V.N.; Rahamathulla, M.; Talath, S.; Osmani, R.A.M.; Ahmed, M.M.; Farhana, S.A.; Hussain, S.M.; Gurupadayya, B. Implications of Pharmacokinetic Potentials of Pioglitazone Enantiomers in Rat Plasma Mediated through Glucose Uptake Assay. Molecules 2023, 28, 4911. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28134911
Spandana T, Goli VVN, Rahamathulla M, Talath S, Osmani RAM, Ahmed MM, Farhana SA, Hussain SM, Gurupadayya B. Implications of Pharmacokinetic Potentials of Pioglitazone Enantiomers in Rat Plasma Mediated through Glucose Uptake Assay. Molecules. 2023; 28(13):4911. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28134911
Chicago/Turabian StyleSpandana, Tatineni, Veera Venkata Nishanth Goli, Mohamed Rahamathulla, Sirajunisa Talath, Riyaz Ali M. Osmani, Mohammed Muqtader Ahmed, Syeda Ayesha Farhana, Shalam Mohamed Hussain, and Bannimath Gurupadayya. 2023. "Implications of Pharmacokinetic Potentials of Pioglitazone Enantiomers in Rat Plasma Mediated through Glucose Uptake Assay" Molecules 28, no. 13: 4911. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28134911
APA StyleSpandana, T., Goli, V. V. N., Rahamathulla, M., Talath, S., Osmani, R. A. M., Ahmed, M. M., Farhana, S. A., Hussain, S. M., & Gurupadayya, B. (2023). Implications of Pharmacokinetic Potentials of Pioglitazone Enantiomers in Rat Plasma Mediated through Glucose Uptake Assay. Molecules, 28(13), 4911. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28134911







