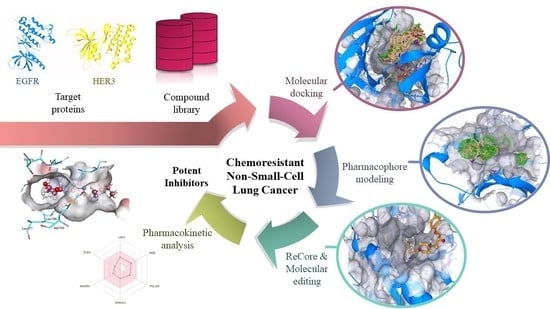
Identification of Potent Inhibitors Targeting EGFR and HER3 for Effective Treatment of Chemoresistance in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Virtual Screening
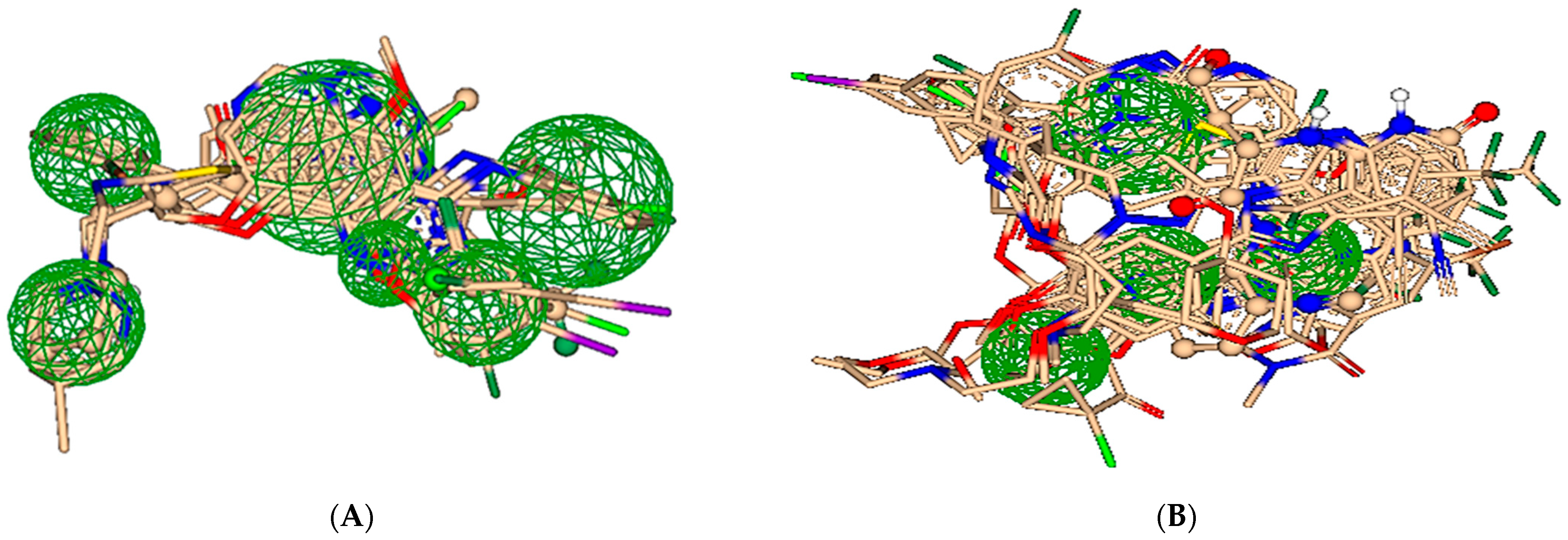
2.2. Pharmacophore Modeling
2.3. ReCore and Molecular Editing
2.4. Pre-Clinical Testing
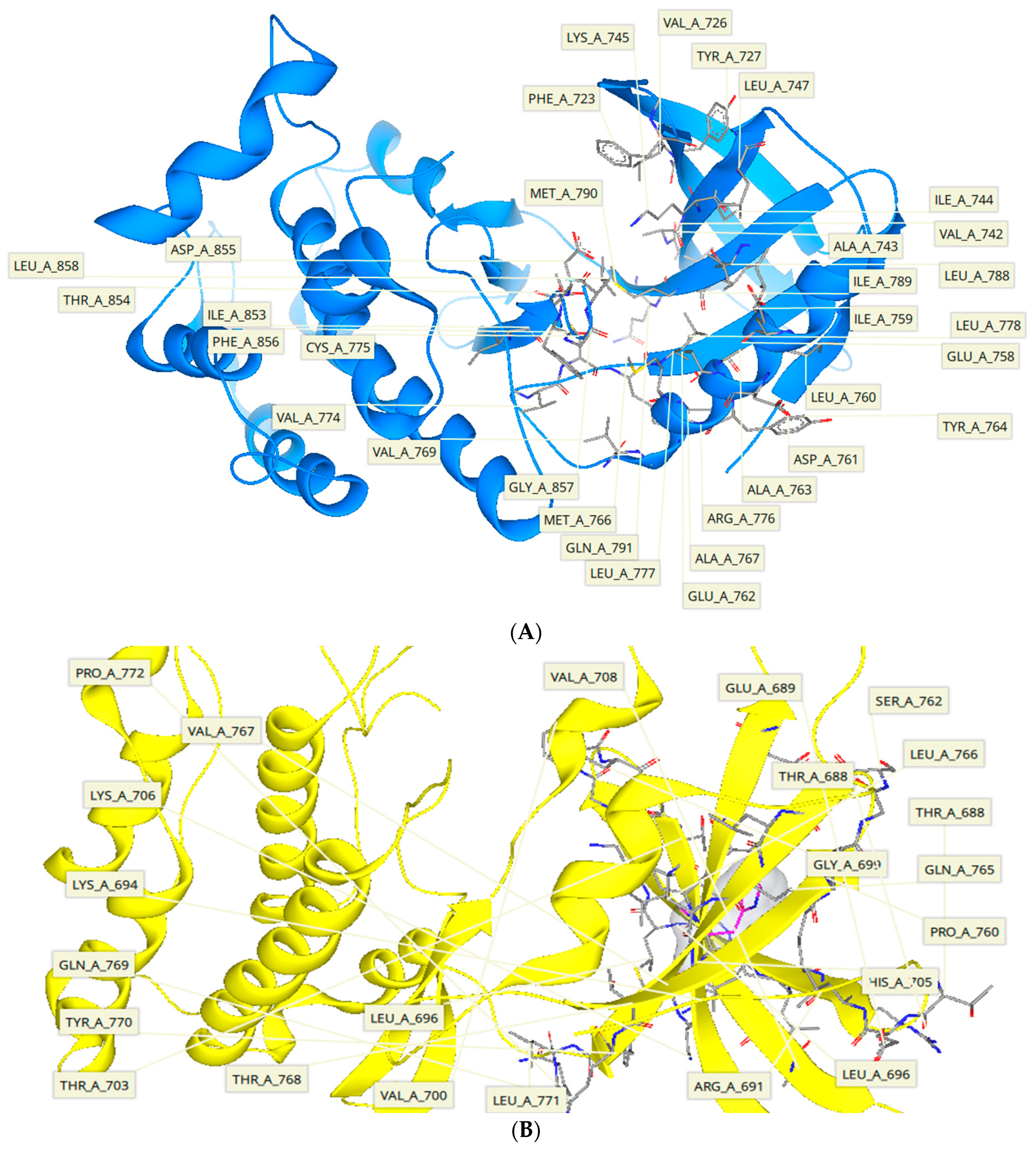
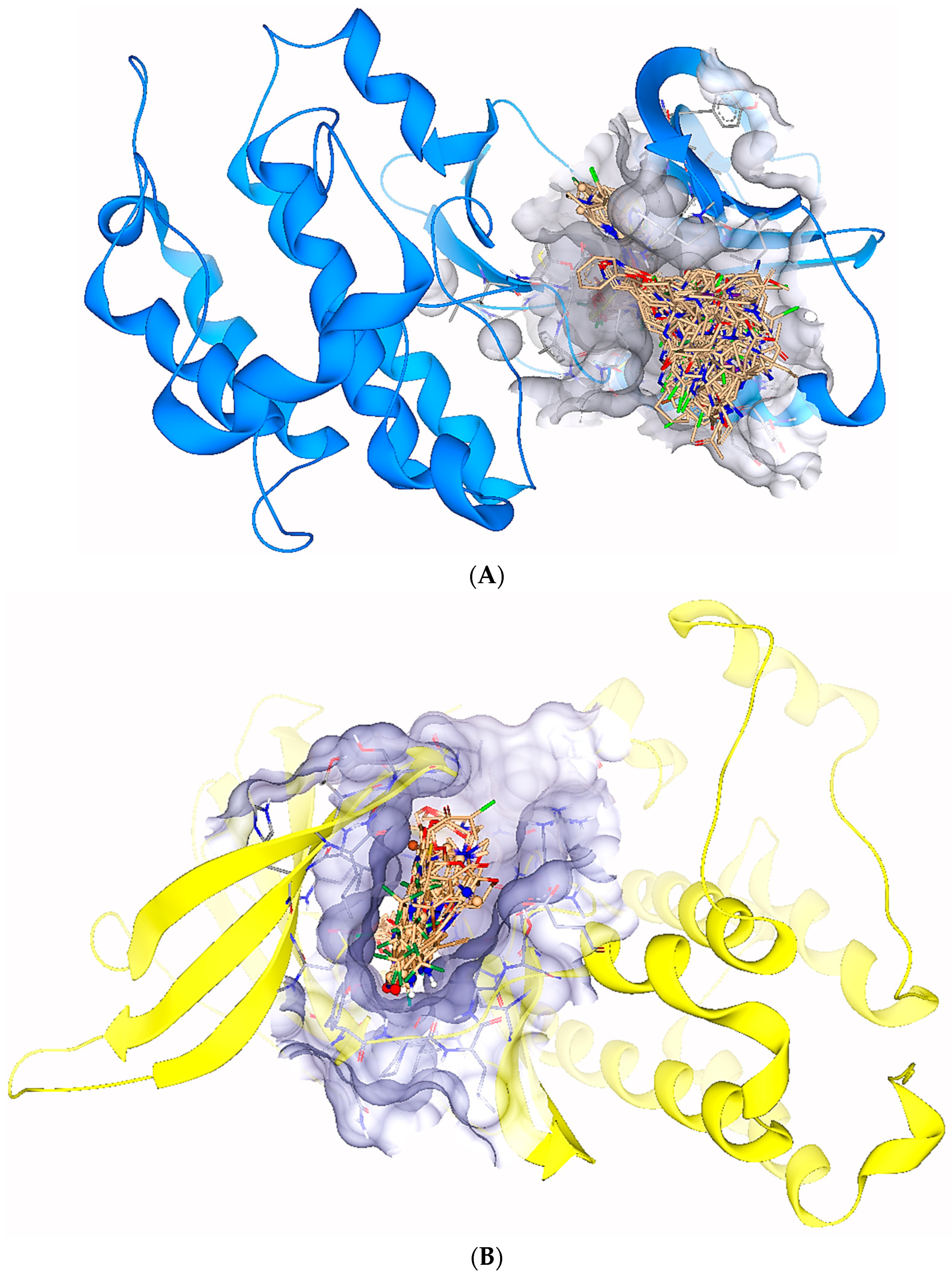
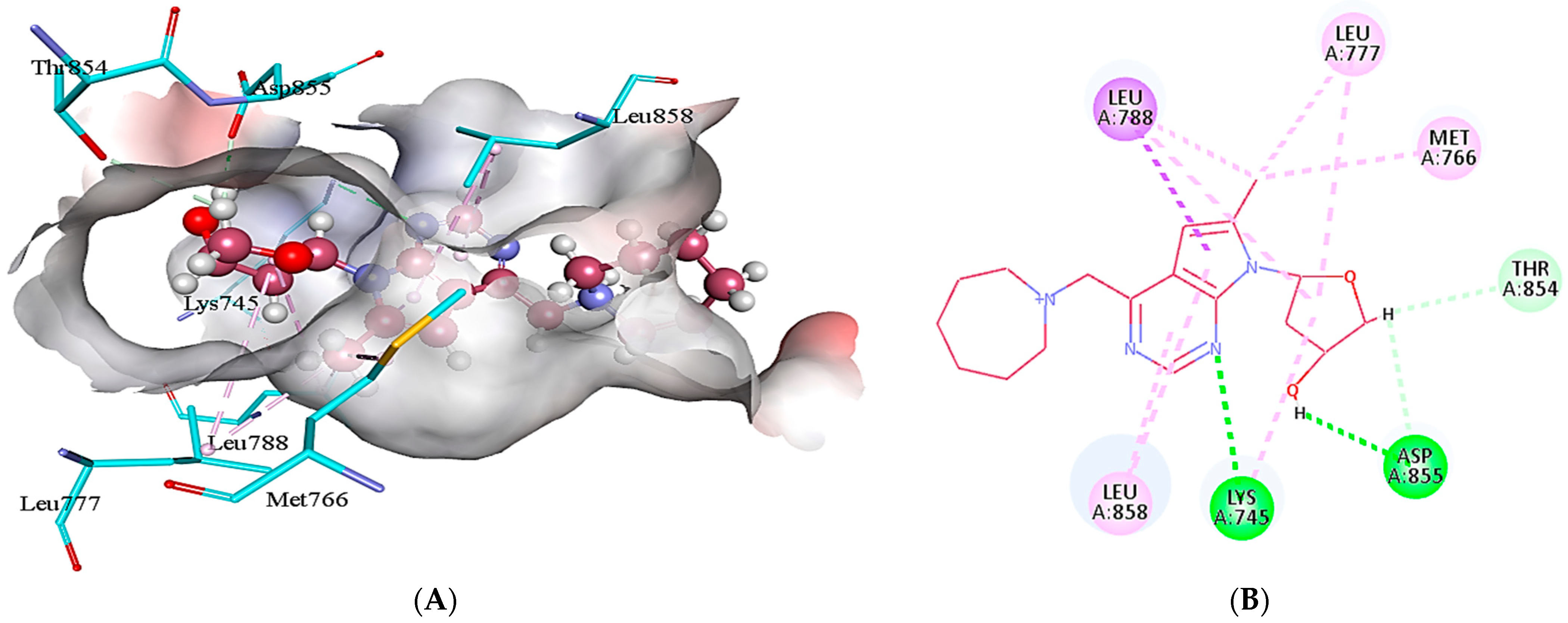
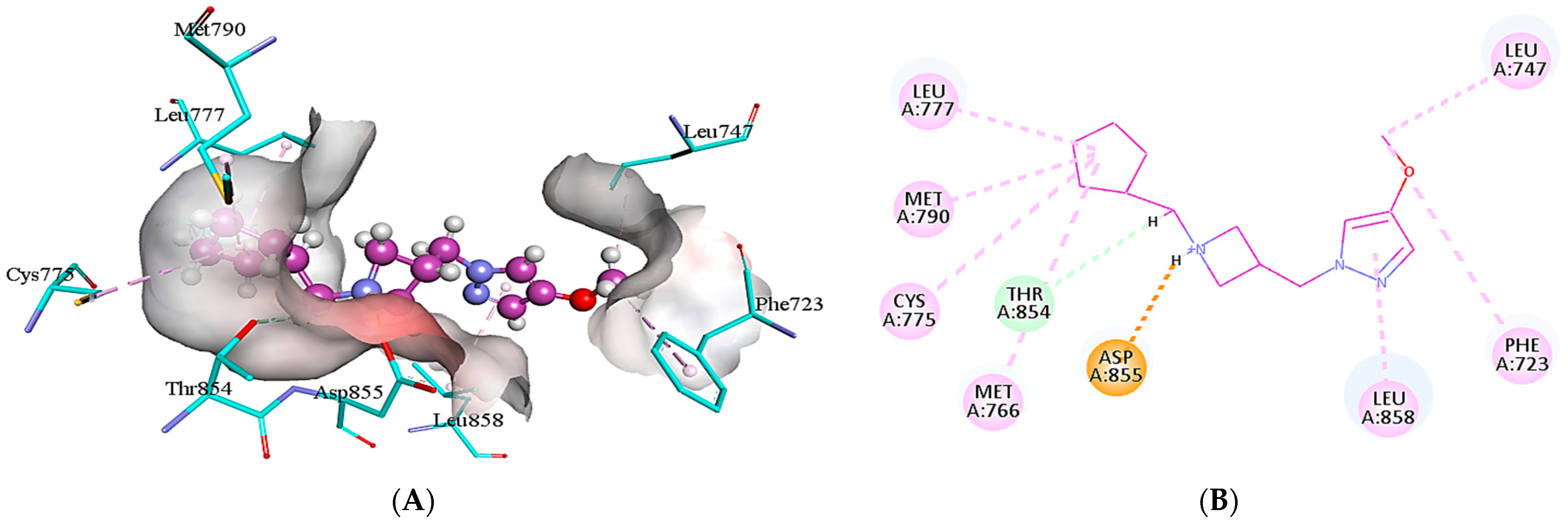
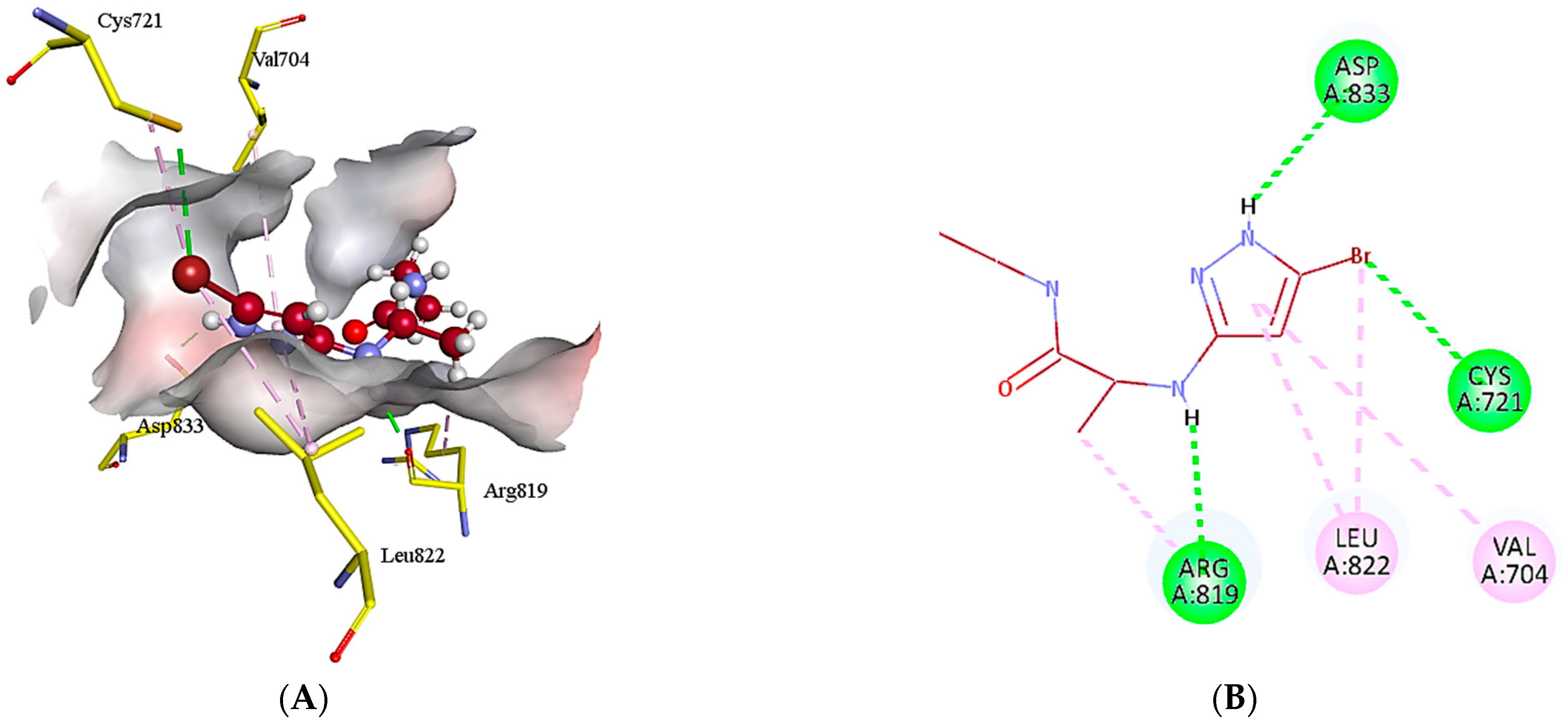
2.5. Protein-Ligand Interactions
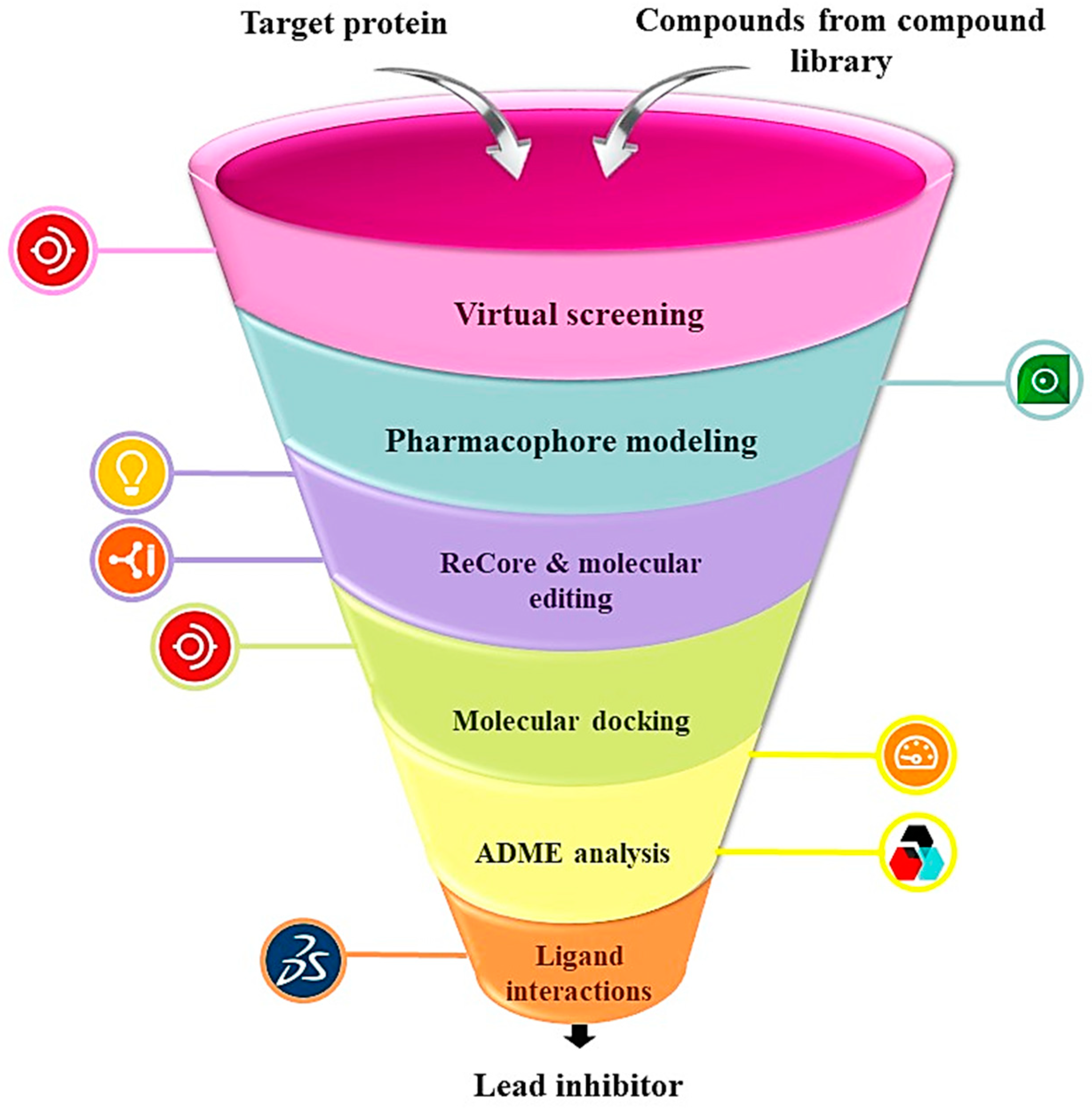
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Selection of Target Protein
3.2. Construction of Compound Library
3.3. Virtual Screening
3.4. Pharmacophore Modeling
3.5. ReCore and Molecular Editing
3.6. Molecular Docking
3.7. ADME Analysis
3.8. Ligand Interactions
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reza, R.; Dutta, T.; Baildya, N.; Ghosh, N.N.; Khan, A.A.; Das, R.K. Repurposing of anti-lung cancer drugs as multi-target inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 proteins: An insight from molecular docking and MD-simulation study. Microb. Pathog. 2022, 169, 105615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zappa, C.; Mousa, S.A. Non-small cell lung cancer: Current treatment and future advances. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2016, 5, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sher, T.; Dy, G.K.; Adjei, A.A. Small cell lung cancer. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2008, 83, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gridelli, C.; Rossi, A.; Carbone, D.P.; Guarize, J.; Karachaliou, N.; Mok, T.; Petrella, F.; Spaggiari, L.; Rosell, R. Non-small-cell lung cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2015, 1, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, F.M.; Rubin, G.; Bankhead, C.; Morris, H.C.; Hall, N.; Mills, K.; Dobson, C.; Rintoul, R.C.; Hamilton, W.; Emery, J. Symptoms and other factors associated with time to diagnosis and stage of lung cancer: A prospective cohort study. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 112, S6–S13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, M.M.; Hamilton, W.; Walter, F.M.; Rubin, G.P.; Lyratzopoulos, G. Symptom signatures and diagnostic timeliness in cancer patients: A review of current evidence. Neoplasia 2018, 20, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassim, S.; Chepulis, L.; Keenan, R.; Kidd, J.; Firth, M.; Lawrenson, R. Patient and carer perceived barriers to early presentation and diagnosis of lung cancer: A systematic review. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, L.L.E.; Collier, G.; Gemine, R.E. A patient perspective: Identifying and understanding the barriers associated with the diagnostic delay of lung cancer. EMJ Respir. 2017, 5, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghu, V.K.; Zhao, W.; Pu, J.; Leader, J.K.; Wang, R.; Herman, J.; Yuan, J.M.; Benos, P.V.; Wilson, D.O. Feasibility of lung cancer prediction from low-dose CT scan and smoking factors using causal models. Thorax 2019, 74, 643–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Lu, T.; Chen, Z.; Zhan, C.; Wang, Q. Mechanisms of resistance to pemetrexed in non-small cell lung cancer. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2019, 8, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagasaka, M.; Gadgeel, S.M. Role of chemotherapy and targeted therapy in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2018, 18, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, T.; Lievre, A.; Coriat, R.; Malka, D.; Elhajbi, F.; Di Fiore, F.; Hentic, O.; Smith, D.; Hautefeuille, V.; Roquin, G.; et al. Bevacizumab plus FOLFIRI after failure of platinum–etoposide first-line chemotherapy in patients with advanced neuroendocrine carcinoma (PRODIGE 41-BEVANEC): A randomised, multicentre, non-comparative, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2023, 24, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, H.T.; Chien, P.J.; Chen, S.H.; Sheu, G.T.; Jan, M.S.; Wang, B.Y.; Chang, W.W. BMI1-mediated pemetrexed resistance in non-small cell lung cancer cells is associated with increased SP1 activation and cancer stemness. Cancers 2020, 12, 2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igawa, S.; Sato, Y.; Ishihara, M.; Kasajima, M.; Kusuhara, S.; Nakahara, Y.; Otani, S.; Fukui, T.; Katagiri, M.; Sasaki, J.; et al. EGFR Mutation Genotype Impact on the Efficacy of Pemetrexed in Patients with Nonsquamous Nonsmall Cell Lung Cancer. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2016, 17, 3249–3253. [Google Scholar]
- He, Q.; Qu, M.; Bao, H.; Xu, Y.; Shen, T.; Tan, D.; Barkat, M.Q.; Xu, C.; Zeng, L.H.; Wu, X. Multiple post-translational modifications ensure EGFR functionality: Potential therapeutic targets to overcome its drug-resistance mutations. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2023, 70, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovacs, E.; Zorn, J.A.; Huang, Y.; Barros, T.; Kuriyan, J. A Structural Perspective on the Regulation of the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 2015, 84, 739–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uribe, M.L.; Marrocco, I.; Yarden, Y. EGFR in cancer: Signaling mechanisms, drugs, and acquired resistance. Cancers 2021, 13, 2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shtiegman, K.; Kochupurakkal, B.S.; Zwang, Y.; Pines, G.; Starr, A.; Vexler, A.; Citri, A.; Katz, M.; Lavi, S.; Ben-Basat, Y.; et al. Defective ubiquitinylation of EGFR mutants of lung cancer confers prolonged signaling. Oncogene 2007, 26, 6968–6978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosesson, Y.; Mills, G.B.; Yarden, Y. Derailed endocytosis: An emerging feature of cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2008, 8, 835–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, R.; Patel, H.; Alanazi, S.; Yuan, L.; Garrett, J.T. HER3 signaling and targeted therapy in cancer. Oncol. Rev. 2018, 12, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.B.S.; Peyton, M.; He, B.; Liu, C.; Girard, L.; Caudler, E.; Lo, Y.; Baribaud, F.; Mikami, I.; Reguart, N.; et al. Targeting ADAM-mediated ligand cleavage to inhibit HER3 and EGFR pathways in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Cell 2006, 10, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paez, J.G.; Janne, P.A.; Lee, J.C.; Tracy, S.; Greulich, H.; Gabriel, S.; Herman, P.; Kaye, F.J.; Lindeman, N.; Boggon, T.J.; et al. EGFR mutations in lung cancer: Correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science 2004, 304, 1497–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pao, W.; Miller, V.; Zakowski, M.; Doherty, J.; Politi, K.; Sarkaria, I.; Singh, B.; Heelan, R.; Rusch, V.; Fulton, L.; et al. EGF receptor gene mutations are common in lung cancers from “never smokers” and are associated with sensitivity of tumors to gefitinib and erlotinib. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 13306–13311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riely, G.J.; Ladanyi, M. KRAS mutations: An old oncogene becomes a new predictive biomarker. J. Mol. Diagn. 2008, 10, 493–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, H.Y.; Lee, H.Y. Mechanisms of resistance to chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2021, 44, 146–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Shen, M.; Yang, L.; Yang, X.; Tsai, Y.; Keng, P.C.; Chen, Y.; Lee, S.O.; Chen, Y. Simultaneous targeting of ATM and Mcl-1 increases cisplatin sensitivity of cisplatin-resistant non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2021, 22, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Cao, S.; Su, P.C.; Patel, R.; Shah, D.; Chokshi, H.B.; Szukala, R.; Johnson, M.E.; Hevener, K.E. Hit identification and optimization in virtual screening: Practical recommendations based on a critical literature analysis: Miniperspective. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 6560–6572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morley, A.D.; Pugliese, A.; Birchall, K.; Bower, J.; Brennan, P.; Brown, N.; Chapman, T.; Drysdale, M.; Gilbert, I.H.; Hoelder, S.; et al. Fragment-based hit identification: Thinking in 3D. Drug Discov. Today 2013, 18, 1221–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlin, J.L.; Inglese, J.; Walters, M.A. Mitigating risk in academic preclinical drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015, 14, 279–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissADME: A free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42717. Available online: http://www.swissadme.ch/index.php (accessed on 24 September 2022). [CrossRef]
- Ertl, P.; Schuffenhauer, A. Estimation of synthetic accessibility score of drug-like molecules based on molecular complexity and fragment contributions. J. Cheminform. 2009, 1, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, I.; Shaikh, M.; Surana, S.; Ghosh, A.; Patel, H. p38α MAP kinase inhibitors to overcome EGFR tertiary C797S point mutation associated with osimertinib in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): Emergence of fourth-generation EGFR inhibitor. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2022, 40, 3046–3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Yao, M.Y.; Zhu, S.J.; Chen, J.Y.; Yun, C.H. Crystal structure of EGFR T790M/C797S/V948R in complex with EAI045. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 502, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burley, S.K.; Berman, H.M.; Kleywegt, G.J.; Markley, J.L.; Nakamura, H.; Velankar, S. Protein Data Bank (PDB): The single global macromolecular structure archive. In Protein Crystallography; Humana: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 627–641. Available online: https://www.rcsb.org (accessed on 14 January 2022).
- Littlefield, P.; Liu, L.; Mysore, V.; Shan, Y.; Shaw, D.E.; Jura, N. Structural analysis of the EGFR/HER3 heterodimer reveals the molecular basis for activating HER3 mutations. Sci. Signal. 2014, 7, ra114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irwin, J.J.; Shoichet, B.K. ZINC—A free database of commercially available compounds for virtual screening. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2005, 45, 177–182. Available online: https://zinc.docking.org/ (accessed on 27 January 2022). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Chen, J.; Cheng, T.; Gindulyte, A.; He, J.; He, S.; Li, Q.; Shoemaker, B.A.; Thiessen, P.A.; Yu, B.; et al. PubChem 2019 update: Improved access to chemical data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D1102–D1109. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ (accessed on 18 February 2022). [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Southall, N.; Wang, Y.; Yasgar, A.; Shinn, P.; Jadhav, A.; Nguyen, D.T.; Austin, C.P. The NCGC pharmaceutical collection: A comprehensive resource of clinically approvedzinc drugs enabling repurposing and chemical genomics. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, 80ps16. Available online: https://tripod.nih.gov/?p=182 (accessed on 11 March 2022). [CrossRef]
- Irwin, J.J.; Tang, K.G.; Young, J.; Dandarchuluun, C.; Wong, B.R.; Khurelbaatar, M.; Moroz, Y.S.; Mayfield, J.; Sayle, R.A. ZINC20—A free ultralarge-scale chemical database for ligand discovery. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2020, 60, 6065–6073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Infinisee Version 4.3.0. BioSolveIT GmbH: Sankt Augustin, Germany, 2022. Available online: www.biosolveit.de/infiniSee (accessed on 21 February 2022).
- Lessel, U.; Wellenzohn, B.; Lilienthal, M.; Claussen, H. Searching Fragment Spaces with Feature Trees. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2009, 49, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SeeSAR Version 12.1.0. BioSolveIT GmbH: Sankt Augustin, Germany, 2022. Available online: www.biosolveit.de/SeeSAR (accessed on 9 August 2022).
- Mansley, T.E.; Hunt, P.A.; Champness, E.J.; Segall, M.D. High-Quality Hits from High-Throughput Screens: Optibrium Created a Multiparameter Approach to Identify Good SAR, Potent Compounds. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. News. 2018, 38, 12–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astolfi, A.; Kudolo, M.; Brea, J.; Manni, G.; Manfroni, G.; Palazzotti, D.; Sabatini, S.; Cecchetti, F.; Felicetti, T.; Cannalire, R.; et al. Discovery of potent p38α MAPK inhibitors through a funnel like workflow combining in silico screening and in vitro validation. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 182, 111624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Li, S.; Zhang, H.; Wang, L.L. Discovery of potentially biased agonists of mu-opioid receptor (MOR) through molecular docking, pharmacophore modeling, and MD simulation. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2021, 90, 107405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Li, X.; Peng, W.; Wang, L.; Ye, W.; Zhao, Y.; Yin, W.; Chen, W.D.; Li, W.; Wang, Y.D. Ligand-based pharmacophore modeling, virtual screening and biological evaluation to identify novel TGR5 agonists. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 9403–9409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maass, P.; Schulz-Gasch, T.; Stahl, M.; Rarey, M. Recore: A fast and versatile method for scaffold hopping based on small molecule crystal structure conformations. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2007, 47, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gastreich, M.; Lilienthal, M.; Briem, H.; Claussen, H. Ultrafast de Novo Docking Combining Pharmacophores and Combinatorics. J. Comput. Aided. Mol. Des. 2006, 20, 717–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rarey, M.; Kramer, B.; Lengauer, T.; Klebe, G. A Fast Flexible Docking Method Using an Incremental Construction Algorithm. J. Mol. Biol. 1996, 261, 470–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, R.C.; Freitas, H.F.; Campos, J.M.; Kimani, N.M.; Silva, C.H.; Borges, R.S.; Pita, S.S.; Santos, C.B. Natural products-based drug design against SARS-CoV-2 Mpro 3CLpro. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantaleão, S.Q.; Fernandes, P.O.; Gonçalves, J.E.; Maltarollo, V.G.; Honorio, K.M. Recent advances in the prediction of pharmacokinetics properties in drug design studies: A review. ChemMedChem 2022, 17, e202100542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Sharma, A.; Gupta, U. Molecular Docking studies on the Anti-fungal activity of Allium sativum (Garlic) against Mucormycosis (black fungus) by BIOVIA discovery studio visualizer 21.1. 0.0. Ann. Antivir. Antiretrovir. 2021, 5, 028–032. [Google Scholar]
- Baskaran, K.P.; Arumugam, A.; Kandasamy, R.; Alagarsamy, S. Insilico method for prediction of maximum binding affinity and ligand—Protein interaction studies on Alzheimer’s disease. Int. J. Res. Granthaalayah 2020, 8, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.F.; Zhong, W.Z. Drug Design and Discovery: Principles and Applications. Molecules 2017, 22, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Attributes | 4k | 4m | 7x |
|---|---|---|---|
| Structure | 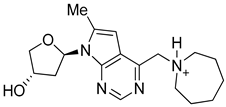 | 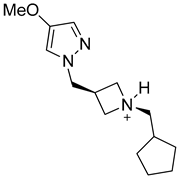 | 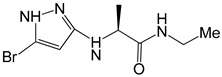 |
| Formula | C18H27N4O2+ | C14H24N3O+ | C8H13BrN4O |
| Molecular weight (g/mol) | 331.43 | 250.36 | 261.12 |
| Number of heavy atoms | 24 | 18 | 14 |
| Number of aromatic heavy atoms | 9 | 5 | 5 |
| Fraction C(sp3) | 0.67 | 0.79 | 0.50 |
| Number of rotatable bonds | 3 | 5 | 5 |
| Number of H-bond acceptors | 4 | 2 | 2 |
| Number of H-bond donors | 2 | 1 | 3 |
| Molar refractivity (m3mol−1) | 97.78 | 76.79 | 57.82 |
| TPSA (Å2) | 64.61 | 31.49 | 69.81 |
| Consensus Log Po/w | 0.88 | 1.02 | 1.18 |
| Class | Soluble | Soluble | Soluble |
| GI absorption | High | High | High |
| Blood-brain barrier | No | No | No |
| P-gp substrate | Yes | Yes | No |
| CYP1A2 inhibitor | No | No | No |
| CYP2C19 inhibitor | No | No | No |
| CYP2C9 inhibitor | No | No | No |
| CYP2D6 inhibitor | No | No | No |
| CYP3A4 inhibitor | No | No | No |
| Log Kp (cm/s) | −7.24 | −6.39 | −6.71 |
| Lipinski | Yes; 0 violation | Yes; 0 violation | Yes; 0 violation |
| Ghose | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Veber | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Egan | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Muegge | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Bioavailability score | 0.55 | 0.55 | 0.55 |
| PAINS | 0 alert | 0 alert | 0 alert |
| Brenk | 0 alert | 0 alert | 0 alert |
| Leadlikeness | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Synthetic accessibility | 3.88 | 3.39 | 2.77 |
| Best Selected Inhibitors | Binding Energies ((kcal/mol) |
|---|---|
| 4k | −7.7 |
| 4m | −6.3 |
| 7x | −5.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dera, A.A.; Zaib, S.; Areeba; Hussain, N.; Rana, N.; Javed, H.; Khan, I. Identification of Potent Inhibitors Targeting EGFR and HER3 for Effective Treatment of Chemoresistance in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Molecules 2023, 28, 4850. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28124850
Dera AA, Zaib S, Areeba, Hussain N, Rana N, Javed H, Khan I. Identification of Potent Inhibitors Targeting EGFR and HER3 for Effective Treatment of Chemoresistance in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Molecules. 2023; 28(12):4850. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28124850
Chicago/Turabian StyleDera, Ayed A., Sumera Zaib, Areeba, Nadia Hussain, Nehal Rana, Hira Javed, and Imtiaz Khan. 2023. "Identification of Potent Inhibitors Targeting EGFR and HER3 for Effective Treatment of Chemoresistance in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer" Molecules 28, no. 12: 4850. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28124850
APA StyleDera, A. A., Zaib, S., Areeba, Hussain, N., Rana, N., Javed, H., & Khan, I. (2023). Identification of Potent Inhibitors Targeting EGFR and HER3 for Effective Treatment of Chemoresistance in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Molecules, 28(12), 4850. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28124850