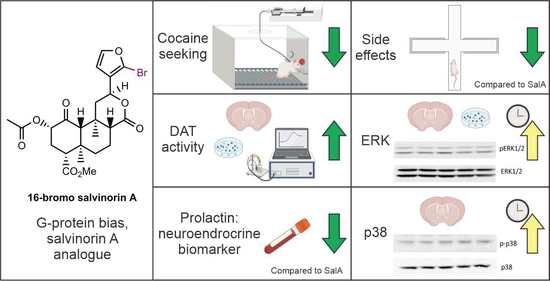
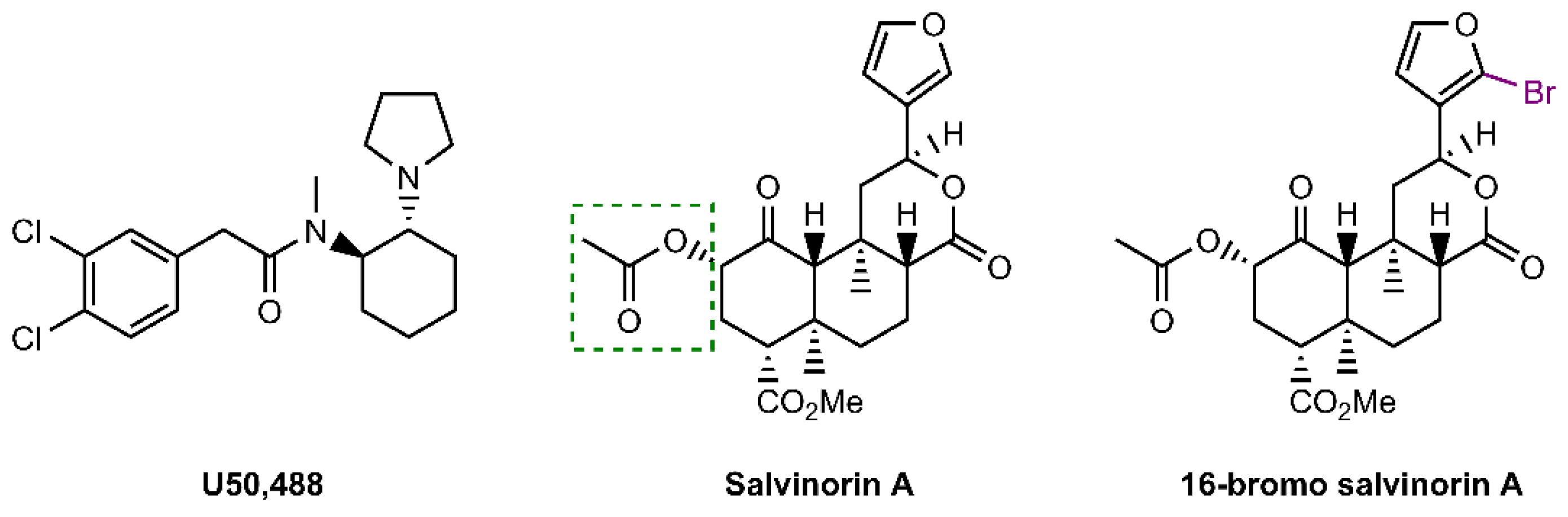
The Kappa Opioid Receptor Agonist 16-Bromo Salvinorin A Has Anti-Cocaine Effects without Significant Effects on Locomotion, Food Reward, Learning and Memory, or Anxiety and Depressive-like Behaviors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
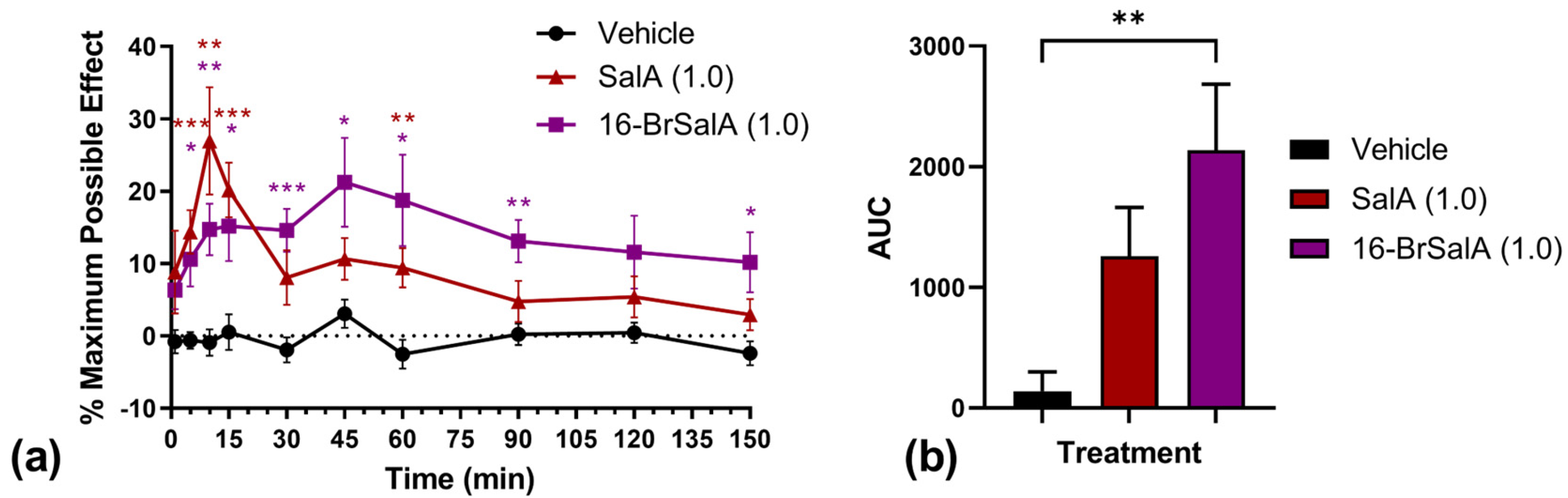
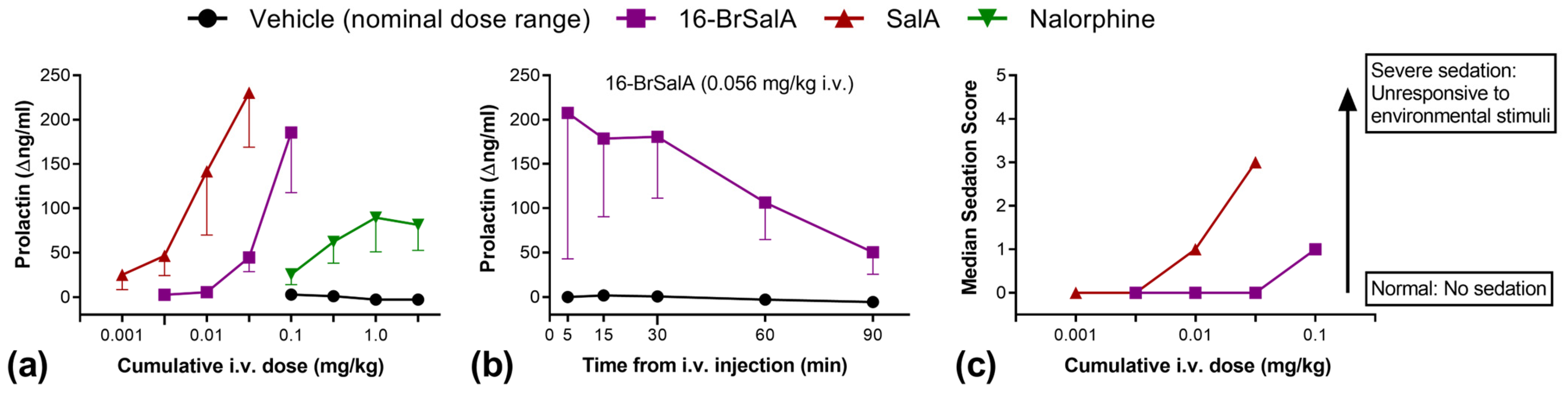
2.1. 16-BrSalA Has a Longer Duration of Action Compared to SalA In Vivo
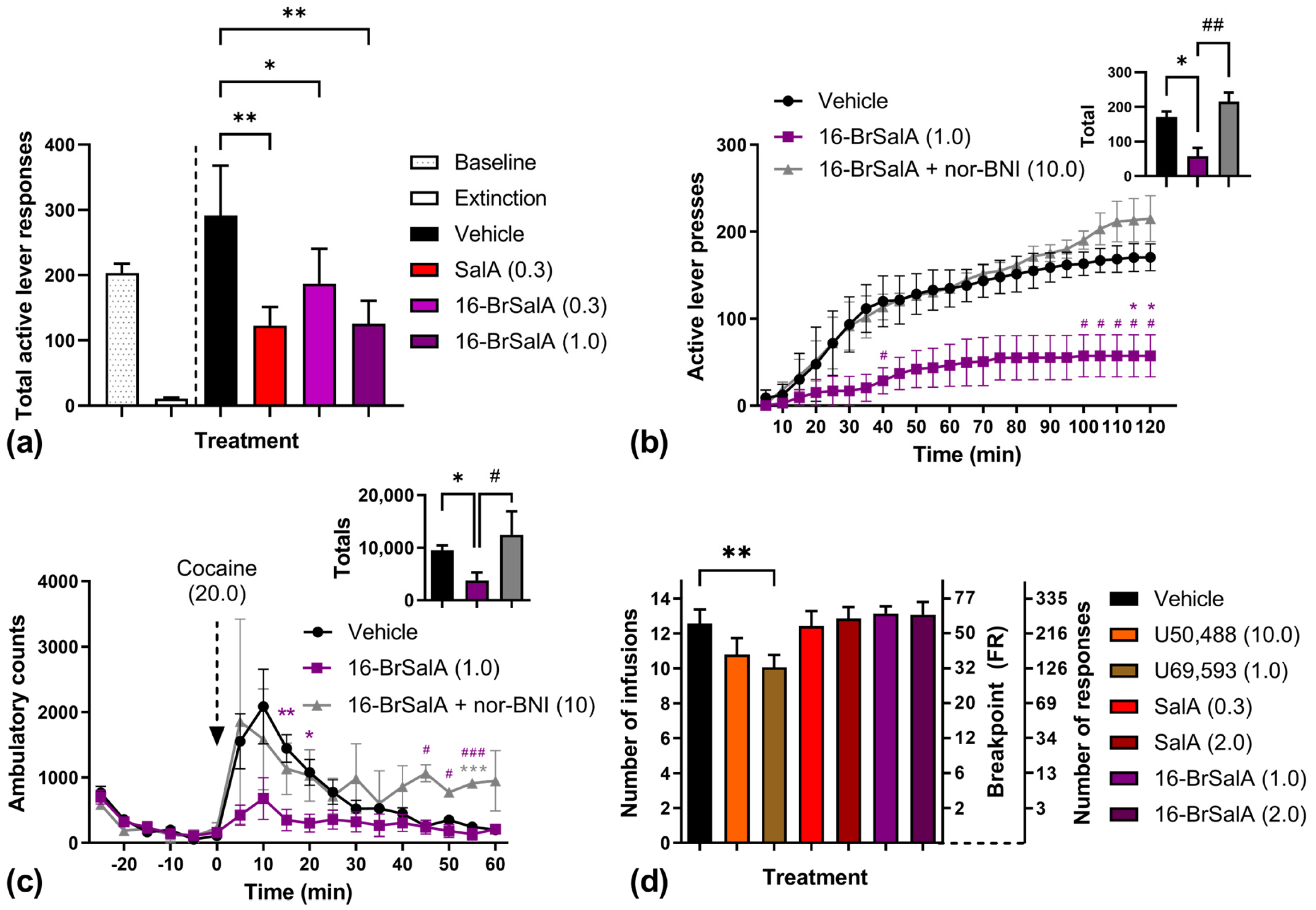
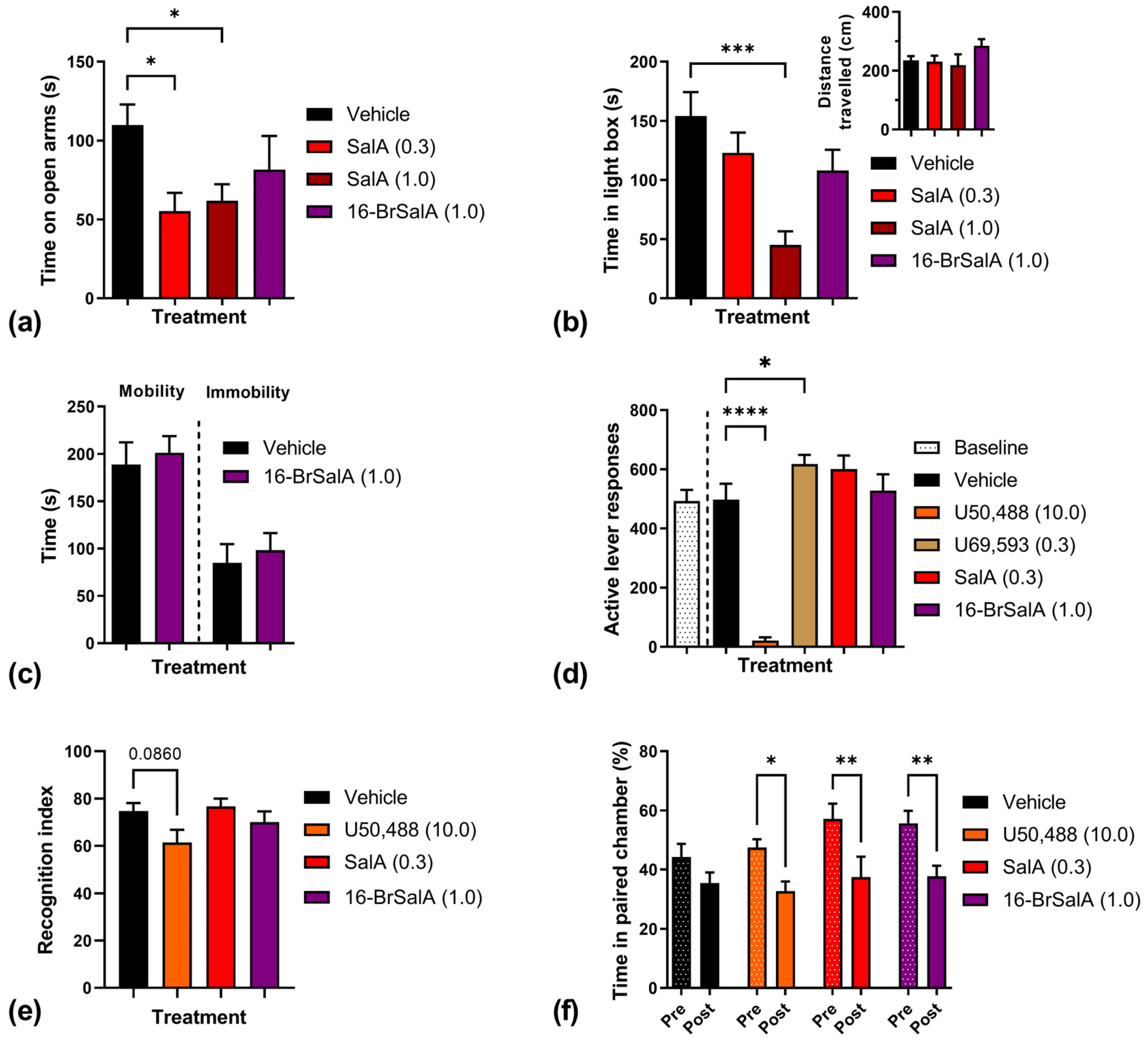
2.2. 16-BrSalA Attenuates Cocaine-Primed Reinstatement and Hyperactivity, but Not Progressive Ratio Responding
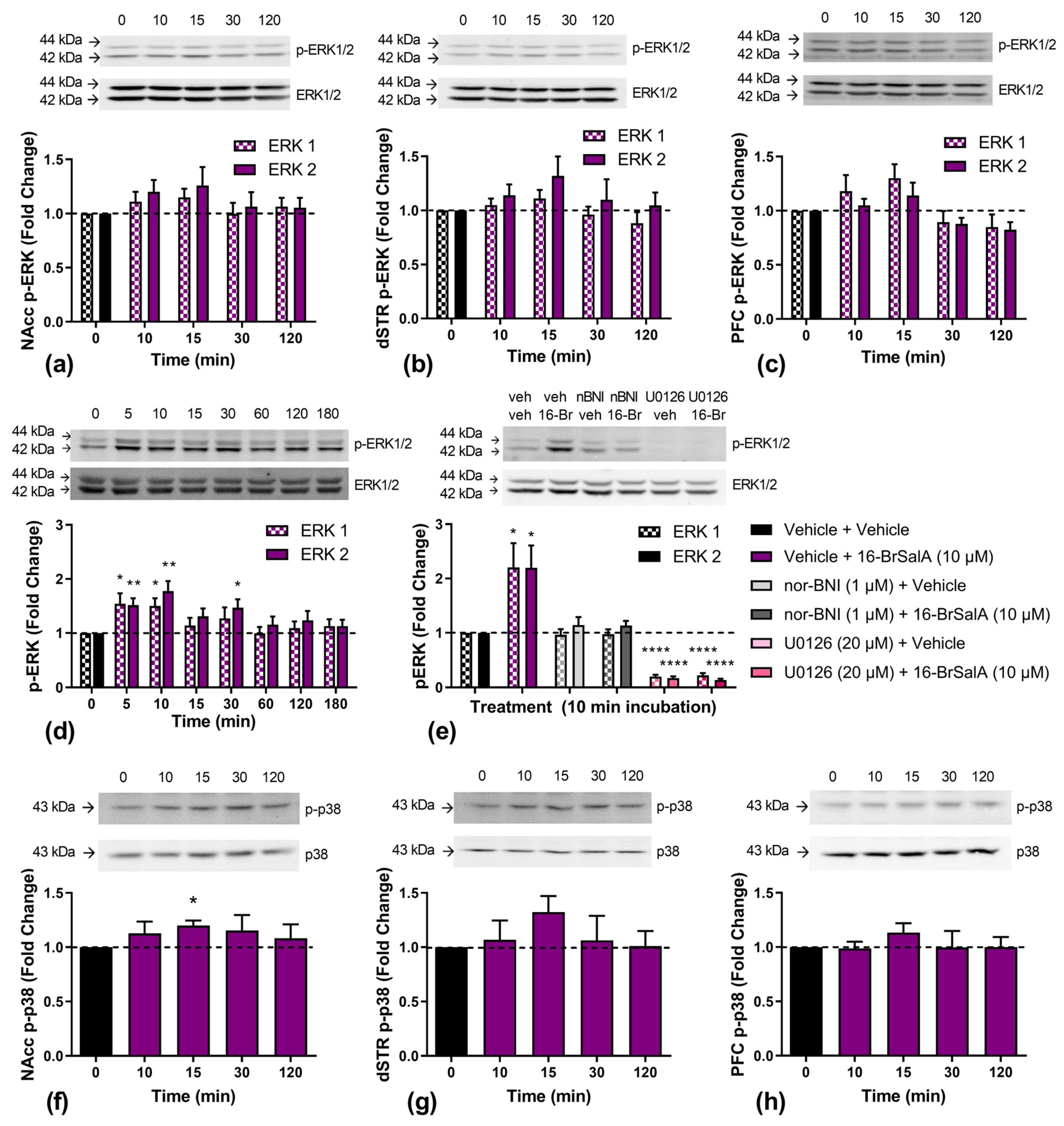
2.3. 16-BrSalA Increases DAT Activity in a KOR- and ERK-Dependant Manner
2.4. 16-BrSalA Has an Improved Side Effect Profile Compared to SalA
2.5. Effect of 16-BrSalA on ERK1/2 and p38
2.6. Effect of 16-BrSalA on Prolactin as a Neuroendocrine Biomarker in Non-Human Primates
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Subjects
3.2. Drugs and Treatment
3.3. Warm Water Tail Withdrawal Assay
3.4. Surgery and Cocaine Self-Administration
3.5. Cocaine-Induced Locomotor Activity
3.6. Light–Dark Test
3.7. Elevated plus Maze
3.8. Forced Swim Test
3.9. Sucrose Self-Administration
3.10. Novel Object Recognition
3.11. Conditioned Place Aversion
3.12. Prolactin Assay
3.13. Rotating Disk Electrode Voltammetry
3.14. Imaging of ASP+ Uptake
3.15. ERK1/2 and p38 Western Blotting
3.16. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Volkow, N.D.; Koob, G.F.; McLellan, A.T. Neurobiologic Advances from the Brain Disease Model of Addiction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nestler, E.J. Cellular Basis of Memory for Addiction. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzmin, A.V.; Semenova, S.; Gerrits, M.A.F.M.; Zvartau, E.E.; van Ree, J.M. κ-Opioid Receptor Agonist U50,488H Modulates Cocaine and Morphine Self-Administration in Drug-Naive Rats and Mice. Eur. J. Pharm. 1997, 321, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glick, S.D.; Visker, K.E.; Maisonneuve, I.M. Effects of Cyclazocine on Cocaine Self-Administration in Rats. Eur. J. Pharm. 1998, 357, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glick, S.D.; Maisonneuve, I.M.; Raucci, J.; Sydney, A. Kappa Opioid Inhibition of Morphine and Cocaine Self-Administration in Rats. Brain Res. 1995, 681, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mello, N.K.; Negus, S.S. Effects of Kappa Opioid Agonists on Cocaine-and Food-Maintained Responding by Rhesus Monkeys. J. Pharm. Exp. 1998, 286, 812–824. [Google Scholar]
- Negus, S.S.; Mello, N.K.; Portoghese, P.S.; Lin, C.E. Effects of Kappa Opioids on Cocaine Self-Administration by Rhesus Monkeys. J. Pharm. Exp. 1997, 282, 44–55. [Google Scholar]
- Wee, S.; Orio, L.; Ghirmai, S.; Cashman, J.R.; Koob, G.F. Inhibition of Kappa Opioid Receptors Attenuated Increased Cocaine Intake in Rats with Extended Access to Cocaine. Psychopharmacology 2009, 205, 565–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schenk, S.; Shippenberg, T.S.; Partridge, B. U69593, a Kappa-Opioid Agonist, Decreases Cocaine Self-Administration and Decreases Cocaine-Produced Drug-Seeking. Psychopharmacology 1999, 144, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schenk, S.; Partridge, B.; Shippenberg, T.S. Effects of the Kappa-Opioid Receptor Agonist, U69593, on the Development of Sensitization and on the Maintenance of Cocaine Self-Administration. Neuropsychopharmacology 2001, 24, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mello, N.K.; Negus, S.S. Interactions between Kappa Opioid Agonists and Cocaine: Preclinical Studies. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2000, 909, 104–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schenk, S.; Partridge, B. Effect of the Kappa-Opioid Receptor Agonist, U69593, on Reinstatement of Extinguished Amphetamine Self-Administration Behavior. Pharm. Biochem. Behav. 2001, 68, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schenk, S.; Partridge, B.; Shippenberg, T.S. Reinstatement of Extinguished Drug-Taking Behavior in Rats: Effect of the Kappa-Opioid Receptor Agonist, U69593. Psychopharmacology 2000, 151, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morani, A.S.; Kivell, B.M.; Prisinzano, T.E.; Schenk, S. Effect of Kappa-Opioid Receptor Agonists U69593, U50488H, Spiradoline and Salvinorin A on Cocaine-Induced Drug-Seeking in Rats. Pharm. Biochem. Behav. 2009, 94, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, S.L.; Gerdes, R.M.; D’Addario, C.; Izenwasser, S. Kappa Opioid Agonists Alter Dopamine Markers and Cocaine-Stimulated Locomotor Activity. Behav. Pharmacol. 2001, 12, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidbreder, C.A.; Shoaib, M.; Shippenberg, T.S. Differential Role of δ-Opioid Receptors in the Development and Expression of Behavioral Sensitization to Cocaine. Eur. J. Pharm. 1996, 298, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shippenberg, T.S.; Lefevour, A.; Thompson, A.C. Sensitization to the Conditioned Rewarding Effects of Morphine and Cocaine: Differential Effects of the κ-Opioid Receptor Agonist U69593. Eur. J. Pharm. 1998, 345, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanderschuren, L.J.M.J.; Schoffelmeer, A.N.M.; Wardeh, G.; de Vries, T.J. Dissociable Effects of the κ-Opioid Receptor Agonists Bremazocine, U69593, and U50488H on Locomotor Activity and Long-Term Behavioral Sensitization Induced by Amphetamine and Cocaine. Psychopharmacology 2000, 150, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidbreder, C.A.; Shippenberg, T.S. U-69593 Prevents Cocaine Sensitization by Normalizing Basal Accumbens Dopamine. Neuroreport 1994, 5, 1797–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, A.C.; Zapata, A.; Justice, J.B.; Vaughan, R.A.; Sharpe, L.G.; Shippenberg, T.S. κ-Opioid Receptor Activation Modifies Dopamine Uptake in the Nucleus Accumbens and Opposes the Effects of Cocaine. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 9333–9340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chefer, V.I.; Czyzyk, T.; Bolan, E.A.; Moron, J.; Pintar, J.E.; Shippenberg, T.S. Endogenous κ-Opioid Receptor Systems Regulate Mesoaccumbal Dopamine Dynamics and Vulnerability to Cocaine. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 5029–5037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, A.M.; Rawls, S.M.; Shippenberg, T.S.; McGinty, J.F. The K-Opioid Agonist, U-69593, Decreases Acute Amphetamine-Evoked Behaviors and Calcium-Dependent Dialysate Levels of Dopamine and Glutamate in the Ventral Striatum. J. Neurochem. 1999, 73, 1066–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maisonneuve, I.M.; Archer, S.; Glick, S.D. U50,488, a κ Opioid Receptor Agonist, Attenuates Cocaine-Induced Increases in Extracellular Dopamine in the Nucleus Accumbens of Rats. Neurosci. Lett. 1994, 181, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kivell, B.M.; Uzelac, Z.; Sundaramurthy, S.; Rajamanickam, J.; Ewald, A.; Chefer, V.; Jaligam, V.; Bolan, E.; Simonson, B.; Annamalai, B.; et al. Salvinorin A Regulates Dopamine Transporter Function via a Kappa Opioid Receptor and ERK1/2-Dependent Mechanism. Neuropharmacology 2014, 86, 228–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, A.H.; Collins, R.J. Behavioral Effects of a Novel Kappa Opioid Analgesic, U-50488, in Rats and Rhesus Monkeys. Psychopharmacology 1985, 85, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, Y.; Mori, A.; Yanagita, T. One Year Long-Term Study on Abuse Liability of Nalfurafine in Hemodialysis Patients. Int. J. Clin. Pharm. 2013, 51, 823–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porreca, F.; Mosberg, H.I.; Hurst, R.; Hruby, V.J.; Burks, T.F. Roles of Mu, Delta and Kappa Opioid Receptors in Spinal and Supraspinal Mediation of Gastrointestinal Transit Effects and Hot-Plate Analgesia in the Mouse. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1984, 230. [Google Scholar]
- Shook, J.E.; Watkins, W.D.; Camporesi, E.M. Differential Roles of Opioid Receptors in Respiration, Respiratory Disease, and Opiate-Induced Respiratory Depression. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 2012, 142, 909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viscusi, E.R.; Torjman, M.C.; Munera, C.L.; Stauffer, J.W.; Setnik, B.S.; Bagal, S.N. Effect of Difelikefalin, a Selective Kappa Opioid Receptor Agonist, on Respiratory Depression: A Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-controlled Trial. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2021, 14, 1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalefield, M.L.; Scouller, B.; Bibi, R.; Kivell, B.M.; Dale, M.L.; Scouller, B.; Bibi, R.; Kivell, B.M. The Kappa Opioid Receptor: A Promising Therapeutic Target for Multiple Pathologies. Front. Pharm. 2022, 13, 837671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.S.; Wang, J.; Chen, J.C.; Tao, Y.M.; Wang, Y.H.; Xu, X.J.; Chen, J.; Xu, Y.G.; Xi, T.; Hu, X.W.; et al. Novel κ-Opioid Receptor Agonist MB-1C-OH Produces Potent Analgesia with Less Depression and Sedation. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2015, 36, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, S.L.; Strain, E.C.; Abreu, M.E.; Bigelow, G.E. Enadoline, a Selective Kappa Opioid Agonist: Comparison with Butorphanol and Hydromorphone in Humans. Psychopharmacology 2001, 157, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vunck, S.A.; Snider, S.E.; van den Oord, E.J.C.G.; Beardsley, P.M. The Kappa Opioid Receptor Agonist, U50,488, Exacerbates Conditioned Fear in Mice. FASEB J. 2011, 25, 617–620. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.J.; Hang, A.; Lu, Y.C.; Long, Y.; Zan, G.Y.; Li, X.P.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, Z.X.; He, L.; Chi, Z.Q.; et al. κ Opioid Receptor Activation in Different Brain Regions Differentially Modulates Anxiety-Related Behaviors in Mice. Neuropharmacology 2016, 110, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mague, S.D.; Pliakas, A.M.; Todtenkopf, M.S.; Tomasiewicz, H.C.; Zhang, Y.; Stevens, W.C.; Jones, R.M.; Portoghese, P.S.; Carlezon, W.A. Antidepressant-Like Effects of κ-Opioid Receptor Antagonists in the Forced Swim Test in Rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2003, 305, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, T.; Shiozaki, Y.; Masukawa, Y.; Misawa, M.; Nagase, H. The Role of Mu- and Kappa-Opioid Receptors in Cocaine-Induced Conditioned Place Preference. Jpn. J. Pharmacol. 1992, 58, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skoubis, P.D.; Matthes, H.W.; Walwyn, W.M.; Kieffer, B.L.; Maidment, N.T. Naloxone Fails to Produce Conditioned Place Aversion in μ-Opioid Receptor Knock-out Mice. Neuroscience 2001, 106, 757–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrich, J.M.; Messinger, D.I.; Knakal, C.R.; Kuhar, J.R.; Schattauer, S.S.; Bruchas, M.R.; Zweifel, L.S.; Kieffer, B.L.; Phillips, P.E.M.; Chavkin, C. Kappa Opioid Receptor-Induced Aversion Requires P38 MAPK Activation in VTA Dopamine Neurons. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 12917–12931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bals-Kubik, R.; Ableitner, A.; Herz, A.; Shippenberg, T.S. Neuroanatomical Sites Mediating the Motivational Effects of Opioids as Mapped by the Conditioned Place Preference Paradigm in Rats. J. Pharm. Exp. 1993, 264, 489–495. [Google Scholar]
- Todtenkopf, M.S.; Marcus, J.F.; Portoghese, P.S.; Carlezon, W.A. Effects of κ-Opioid Receptor Ligands on Intracranial Self-Stimulation in Rats. Psychopharmacology 2004, 172, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, B.L.; Atwater, J.A.; Munemitsu, S.M.; Samuel, C.E.; K Lee, P.W.; Hayes, E.C.; Joklk, W.K.; Lennette, E.H.; John, A.C.; Pfeiffer, A.; et al. Psychotomimesis Mediated by κ Opiate Receptors. Science 1986, 233, 774–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavkin, C. The Therapeutic Potential of κ-Opioids for Treatment of Pain and Addiction. Neuropsychopharmacology 2011, 36, 369–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paton, K.F.; Atigari, D.V.; Kaska, S.; Prisinzano, T.; Kivell, B.M. Strategies for Developing κ Opioid Receptor Agonists for the Treatment of Pain with Fewer Side Effects. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2020, 375, 332–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kivell, B.M.; Ewald, A.W.M.; Prisinzano, T.E. Salvinorin A Analogs and Other Kappa-Opioid Receptor Compounds as Treatments for Cocaine Abuse. Adv. Pharm. 2014, 69, 481–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.I.H.; Sawyer, B.J.; Akins, N.S.; Le, H.v. A Systematic Review on the Kappa Opioid Receptor and Its Ligands: New Directions for the Treatment of Pain, Anxiety, Depression, and Drug Abuse. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 243, 114785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seifert, R. Functional Selectivity of G-Protein-Coupled Receptors: From Recombinant Systems to Native Human Cells. Biochem. Pharm. 2013, 86, 853–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiter, E.; Ahn, S.; Shukla, A.K.; Lefkowitz, R.J. Molecular Mechanism of β-Arrestin-Biased Agonism at Seven-Transmembrane Receptors. Annu. Rev. Pharm. Toxicol. 2012, 52, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruchas, M.R.; Chavkin, C. Kinase Cascades and Ligand-Directed Signaling at the Kappa Opioid Receptor. Psychopharmacology 2010, 210, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mores, K.L.; Cummins, B.R.; Cassell, R.J.; van Rijn, R.M. A Review of the Therapeutic Potential of Recently Developed G Protein-Biased Kappa Agonists. Front. Pharm. 2019, 10, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshidi, R.J.; Jacobs, B.A.; Sullivan, L.C.; Chavera, T.A.; Saylor, R.M.; Prisinzano, T.E.; Clarke, W.P.; Berg, K.A. Functional Selectivity of Kappa Opioid Receptor Agonists in Peripheral Sensory Neurons. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2015, 355, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brust, T.F.; Morgenweck, J.; Kim, S.A.; Rose, J.H.; Locke, J.L.; Schmid, C.L.; Zhou, L.; Stahl, E.L.; Cameron, M.D.; Scarry, S.M.; et al. Biased Agonists of the Kappa Opioid Receptor Suppress Pain and Itch without Causing Sedation or Dysphoria. Sci. Signal. 2016, 9, ra117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, K.L.; Robinson, J.E.; Zhu, H.; DiBerto, J.F.; Polepally, P.R.; Zjawiony, J.K.; Nichols, D.E.; Malanga, C.J.; Roth, B.L. The G Protein–Biased κ-Opioid Receptor Agonist RB-64 Is Analgesic with a Unique Spectrum of Activities In Vivo. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2015, 352, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paton, K.F.; Biggerstaff, A.; Kaska, S.; Crowley, R.S.; la Flamme, A.C.; Prisinzano, T.E.; Kivell, B.M. Evaluation of Biased and Balanced Salvinorin A Analogs in Preclinical Models of Pain. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michel, M.C.; Charlton, S.J. Biased Agonism in Drug Discovery—Is It Too Soon to Choose a Path? Mol. Pharm. 2018, 93, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kivell, B.M.; Paton, K.F.; Kumar, N.; Morani, A.S.; Culverhouse, A.; Shepherd, A.; Welsh, S.A.; Biggerstaff, A.; Crowley, R.S.; Prisinzano, T.E. Kappa Opioid Receptor Agonist Mesyl Sal B Attenuates Behavioral Sensitization to Cocaine with Fewer Aversive Side-Effects than Salvinorin A in Rodents. Molecules 2018, 23, 2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morani, A.S.; Schenk, S.; Prisinzano, T.E.; Kivell, B.M. A Single Injection of a Novel κ Opioid Receptor Agonist Salvinorin A Attenuates the Expression of Cocaine-Induced Behavioral Sensitization in Rats. Behav. Pharmacol. 2012, 23, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.D.; Schmidt, M.S.; Butelman, E.R.; Harding, W.W.; Tidgewell, K.; Murry, D.J.; Kreek, M.J.; Prisinzano, T.E. Pharmacokinetics of the Plant-Derived κ-Opioid Hallucinogen Salvinorin A in Nonhuman Primates. Synapse 2005, 58, 208–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooker, J.M.; Xu, Y.; Schiffer, W.; Shea, C.; Carter, P.; Fowler, J.S. Pharmacokinetics of the Potent Hallucinogen, Salvinorin A in Primates Parallels the Rapid Onset and Short Duration of Effects in Humans. Neuroimage 2008, 41, 1044–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butelman, E.R.; Prisinzano, T.E.; Deng, H.; Rus, S.; Kreek, M.J. Unconditioned Behavioral Effects of the Powerful κ-Opioid Hallucinogen Salvinorin A in Nonhuman Primates: Fast Onset and Entry into Cerebrospinal Fluid. J. Pharm. Exp. 2009, 328, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, A.P.; Groer, C.E.; Young, D.; Ewald, A.W.; Kivell, B.M.; Prisinzano, T.E. Synthesis and κ-Opioid Receptor Activity of Furan-Substituted Salvinorin A Analogues. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 10464–10475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunningham, C.W.; Rothman, R.B.; Prisinzano, T.E. Neuropharmacology of the Naturally Occurring κ-Opioid Hallucinogen Salvinorin A. Pharm. Rev. 2011, 63, 316–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonson, B.; Morani, A.S.; Ewald, A.W.M.; Walker, L.; Kumar, N.; Simpson, D.; Miller, J.H.; Prisinzano, T.E.; Kivell, B.M. Pharmacology and Anti-Addiction Effects of the Novel κ Opioid Receptor Agonist Mesyl Sal B, a Potent and Long-Acting Analogue of Salvinorin A. Br. J. Pharm. 2015, 172, 515–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prevatt-Smith, K.M.; Lovell, K.M.; Simpson, D.S.; Day, V.W.; Douglas, J.T.; Bosch, P.; Dersch, C.M.; Rothman, R.B.; Kivell, B.M.; Prisinzano, T.E. Potential Drug Abuse Therapeutics Derived from the Hallucinogenic Natural Product Salvinorin A. Medchemcomm 2011, 2, 1217–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morani, A.S.; Ewald, A.; Prevatt-Smith, K.M.; Prisinzano, T.E.; Kivell, B.M. The 2-Methoxy Methyl Analogue of Salvinorin A Attenuates Cocaine-Induced Drug Seeking and Sucrose Reinforcements in Rats. Eur. J. Pharm. 2013, 720, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewald, A.W.M.; Bosch, P.J.; Culverhouse, A.; Crowley, R.S.; Neuenswander, B.; Prisinzano, T.E.; Kivell, B.M. The C-2 Derivatives of Salvinorin A, Ethoxymethyl Ether Sal B and β-Tetrahydropyran Sal B, Have Anti-Cocaine Properties with Minimal Side Effects. Psychopharmacology 2017, 234, 2499–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, A.P.; Day, V.W.; Navarro, H.A.; Prisinzano, T.E. Palladium-Catalyzed Transformations of Salvinorin A, a Neoclerodane Diterpene from Salvia Divinorum. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 5936–5939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Béguin, C.; Duncan, K.K.; Munro, T.A.; Ho, D.M.; Xu, W.; Liu-Chen, L.Y.; Carlezon, W.A.; Cohen, B.M. Modification of the Furan Ring of Salvinorin A: Identification of a Selective Partial Agonist at the Kappa Opioid Receptor. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 1370–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butelman, E.R.; Mandau, M.; Tidgewell, K.; Prisinzano, T.E.; Yuferov, V.; Kreek, M.J. Effects of Salvinorin A, a κ-Opioid Hallucinogen, on a Neuroendocrine Biomarker Assay in Nonhuman Primates with High κ-Receptor Homology to Humans. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2007, 320, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xu, W.; Lee, D.Y.W.; Ma, Z.; Rawls, S.M.; Cowan, A.; Liu-Chen, L.Y. 2-Methoxymethyl-Salvinorin B Is a Potent κ Opioid Receptor Agonist with Longer Lasting Action in Vivo Than Salvinorin A. J. Pharm. Exp. 2008, 324, 1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebner, S.R.; Roitman, M.F.; Potter, D.N.; Rachlin, A.B.; Chartoff, E.H. Depressive-like Effects of the Kappa Opioid Receptor Agonist Salvinorin A Are Associated with Decreased Phasic Dopamine Release in the Nucleus Accumbens. Psychopharmacology 2010, 210, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamarripa, C.A.; Naylor, J.E.; Huskinson, S.L.; Townsend, E.A.; Prisinzano, T.E.; Freeman, K.B. Kappa Opioid Agonists Reduce Oxycodone Self-Administration in Male Rhesus Monkeys. Psychopharmacology 2020, 237, 1471–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkow, N.D.; Michaelides, M.; Baler, R. The Neuroscience of Drug Reward and Addiction. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 2115–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.J.; Kalivas, P.W.; Shaham, Y. Neuroplasticity in the Mesolimbic Dopamine System and Cocaine Addiction. Br. J. Pharm. 2008, 154, 327–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morón, J.A.; Zakharova, I.; Ferrer, J.v.; Merrill, G.A.; Hope, B.; Lafer, E.M.; Lin, Z.C.; Wang, J.B.; Javitch, J.A.; Galli, A.; et al. Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Regulates Dopamine Transporter Surface Expression and Dopamine Transport Capacity. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 8480–8488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estave, P.M.; Spodnick, M.B.; Karkhanis, A.N. KOR Control over Addiction Processing: An Exploration of the Mesolimbic Dopamine Pathway. Handb. Exp. Pharm. 2022, 271, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson-Redmond, A.; Czachowski, C. Effects of Systemic Opioid Receptor Ligands on Ethanol- and Sucrose Seeking and Drinking in Alcohol-Preferring (P) and Long Evans Rats. Psychopharmacology 2014, 231, 4309–4321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallantine, E.L.; Meert, T.F.; Gallantine, E.; Johnson, J. Antinociceptive and Adverse Effects of Μ- and κ-Opioid Receptor Agonists: A Comparison of Morphine and U50488-H. Basic Clin. Pharm. Toxicol. 2008, 103, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muschamp, J.W.; Hollander, J.A.; Thompson, J.L.; Voren, G.; Hassinger, L.C.; Onvani, S.; Kamenecka, T.M.; Borgland, S.L.; Kenny, P.J.; Carlezon, W.A. Hypocretin (Orexin) Facilitates Reward by Attenuating the Antireward Effects of Its Cotransmitter Dynorphin in Ventral Tegmental Area. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E1648–E1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glass, M.J.; Billington, C.J.; Levine, A.S. Opioids and Food Intake: Distributed Functional Neural Pathways? Neuropeptides 1999, 33, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Picó, A.; Vázquez, M.J.; González-Touceda, D.; Folgueira, C.; Skibicka, K.P.; Alvarez-Crespo, M.; van Gestel, M.A.; Velásquez, D.A.; Schwarzer, C.; Herzog, H.; et al. Hypothalamic κ-Opioid Receptor Modulates the Orexigenic Effect of Ghrelin. Neuropsychopharmacology 2013, 38, 1296–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, A.N.; Lyons, A.M.; Shay, C.F.; Dunton, O.; McLaughlin, J.P. Endogenous κ Opioid Activation Mediates Stress-Induced Deficits in Learning and Memory. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 4293–4300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandin, J.; Nylander, I.; Georgieva, J.; Schött, P.A.; Ögren, S.O.; Terenius, L. Hippocampal Dynorphin B Injections Impair Spatial Learning in Rats: A κ-Opioid Receptor-Mediated Effect. Neuroscience 1998, 85, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellano, C.; Libri, V.; Ammassari-Teule, M. The Amygdala Mediates the Impairing Effect of the Selective κ-Opioid Receptor Agonist U-50,488 on Memory in CD1 Mice. Behav. Brain Res. 1988, 30, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paris, J.J.; Reilley, K.J.; McLaughlin, J.P. Kappa Opioid Receptor-Mediated Disruption of Novel Object Recognition: Relevance for Psychostimulant Treatment. J. Addict. Res. Ther. 2011, S4, 1932–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindler, A.G.; Li, S.; Chavkin, C. Behavioral Stress May Increase the Rewarding Valence of Cocaine-Associated Cues Through a Dynorphin/κ-Opioid Receptor-Mediated Mechanism without Affecting Associative Learning or Memory Retrieval Mechanisms. Neuropsychopharmacology 2010, 35, 1932–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braida, D.; Donzelli, A.; Martucci, R.; Capurro, V.; Sala, M. Learning and Memory Impairment Induced by Salvinorin a, the Principal Ingredient of Salvia Divinorum, in Wistar Rats. Int. J. Toxicol. 2011, 30, 650–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruchas, M.R.; Macey, T.A.; Lowe, J.D.; Chavkin, C. Kappa Opioid Receptor Activation of P38 MAPK Is GRK3- and Arrestin-Dependent in Neurons and Astrocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 18081–18089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruchas, M.R.; Land, B.B.; Aita, M.; Xu, M.; Barot, S.K.; Li, S.; Chavkin, C. Stress-Induced P38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Activation Mediates κ-Opioid-Dependent Dysphoria. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 11614–11623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chefer, V.I.; Bäckman, C.M.; Gigante, E.D.; Shippenberg, T.S. Kappa Opioid Receptors on Dopaminergic Neurons Are Necessary for Kappa-Mediated Place Aversion. Neuropsychopharmacology 2013, 38, 2623–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Land, B.B.; Bruchas, M.R.; Schattauer, S.; Giardino, W.J.; Aita, M.; Messinger, D.; Hnasko, T.S.; Palmiter, R.D.; Chavkin, C. Activation of the Kappa Opioid Receptor in the Dorsal Raphe Nucleus Mediates the Aversive Effects of Stress and Reinstates Drug Seeking. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 19168–19173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLennan, G.P.; Kiss, A.; Miyatake, M.; Belcheva, M.M.; Chambers, K.T.; Pozek, J.J.; Mohabbat, Y.; Moyer, R.A.; Bohn, L.M.; Coscia, C.J. Kappa Opioids Promote the Proliferation of Astrocytes via Gβγ and β-Arrestin 2-Dependent MAPK-Mediated Pathways. J. Neurochem. 2008, 107, 1753–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belcheva, M.M.; Clark, A.L.; Haas, P.D.; Serna, J.S.; Hahn, J.W.; Kiss, A.; Coscia, C.J. μ and κ Opioid Receptors Activate ERK/MAPK via Different Protein Kinase C Isoforms and Secondary Messengers in Astrocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 27662–27669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruchas, M.R.; Land, B.B.; Chavkin, C. The Dynorphin/Kappa Opioid System as a Modulator of Stress-Induced and pro-Addictive Behaviors. Brain Res. 2010, 1314, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muschamp, J.W.; Van’t Veer, A.; Carlezon, W.A. Tracking Down the Molecular Substrates of Stress: New Roles for P38α MAPK and Kappa-Opioid Receptors. Neuron 2011, 71, 383–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreek, M.J.; Schluger, J.; Borg, L.; Gunduz, M.; Ho, A. Dynorphin A1-13 Causes Elevation of Serum Levels of Prolactin through an Opioid Receptor Mechanism in Humans: Gender Differences and Implications for Modulation of Dopaminergic Tone in the Treatment of Addictions. J. Pharm. Exp. 1999, 288, 260–269. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.; Byon, W.; Lu, Y.; Jacobsen, L.K.; Badura, L.L.; Sawant-Basak, A.; Miller, E.; Liu, J.; Grimwood, S.; Wang, E.Q.; et al. Quantitative PK-PD Model-Based Translational Pharmacology of a Novel Kappa Opioid Receptor Antagonist between Rats and Humans. AAPS J. 2011, 13, 565–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butelman, E.R.; Harris, T.J.; Kreek, M.J. Apparent Efficacy of κ-Opioid Receptor Ligands on Serum Prolactin Levels in Rhesus Monkeys. Eur. J. Pharm. 1999, 383, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, N.R.; Roberts, D.C.S. Progressive Ratio Schedules in Drug Self-Administration Studies in Rats: A Method to Evaluate Reinforcing Efficacy. J. Neurosci. Methods 1996, 66, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slattery, D.A.; Cryan, J.F. Using the Rat Forced Swim Test to Assess Antidepressant-like Activity in Rodents. Nat. Protoc. 2012, 7, 1009–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tejeda, H.A.; Counotte, D.S.; Oh, E.; Ramamoorthy, S.; Schultz-Kuszak, K.N.; Bäckman, C.M.; Chefer, V.; O’Donnell, P.; Shippenberg, T.S. Prefrontal Cortical Kappa-Opioid Receptor Modulation of Local Neurotransmission and Conditioned Place Aversion. Neuropsychopharmacology 2013, 38, 1770–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, C.A.; Stevens Negus, S.; Kelly, M.; Mello, N.K. The Effects of Heroin on Prolactin Levels in Male Rhesus Monkeys: Use of Cumulative-Dosing Procedures. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2002, 27, 319–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zapata, A.; Kivell, B.M.; Han, Y.; Javitch, J.A.; Bolan, E.A.; Kuraguntla, D.; Jaligam, V.; Oz, M.; Jayanthi, L.D.; Samuvel, D.J.; et al. Regulation of Dopamine Transporter Function and Cell Surface Expression by D3 Dopamine Receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 35842–35854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolan, E.A.; Kivell, B.M.; Jaligam, V.; Oz, M.; Jayanthi, L.D.; Han, Y.; Sen, N.; Urizar, E.; Gomes, I.; Devi, L.A.; et al. D2 Receptors Regulate Dopamine Transporter Function via an Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinases 1 and 2-Dependent and Phosphoinositide 3 Kinase-Independent Mechanism. Mol. Pharm. 2007, 71, 1222–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
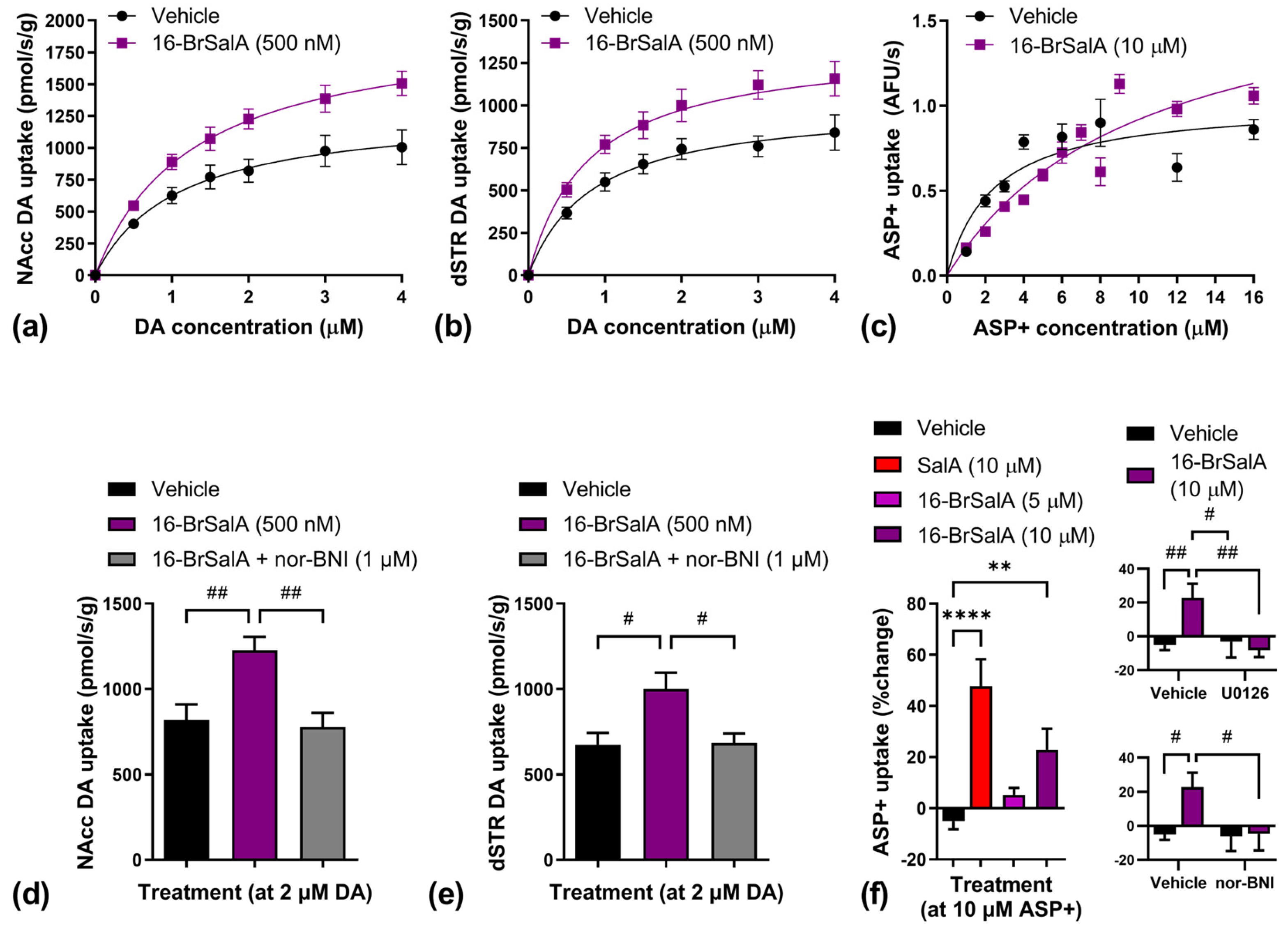
| Region | Treatment | Vmax | Km |
|---|---|---|---|
| NAcc | Vehicle | 1356.16 ± 215.36 | 1.17 ± 0.28 |
| 16-BrSalA | 1965.33 ± 131.65 * | 1.28 ± 0.15 | |
| dSTR | Vehicle | 1034.36 ± 126.44 | 0.90 ± 0.18 |
| 16-BrSalA | 1433.44 ± 24.00 * | 0.94 ± 0.14 | |
| In vitro | Vehicle | 1.02 ± 0.08 | 2.41 ± 0.51 |
| 16-BrSalA | 1.84 ± 0.19 **** | 10.05 ± 1.89 **** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
van de Wetering, R.; Ewald, A.; Welsh, S.; Kornberger, L.; Williamson, S.E.; McElroy, B.D.; Butelman, E.R.; Prisinzano, T.E.; Kivell, B.M. The Kappa Opioid Receptor Agonist 16-Bromo Salvinorin A Has Anti-Cocaine Effects without Significant Effects on Locomotion, Food Reward, Learning and Memory, or Anxiety and Depressive-like Behaviors. Molecules 2023, 28, 4848. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28124848
van de Wetering R, Ewald A, Welsh S, Kornberger L, Williamson SE, McElroy BD, Butelman ER, Prisinzano TE, Kivell BM. The Kappa Opioid Receptor Agonist 16-Bromo Salvinorin A Has Anti-Cocaine Effects without Significant Effects on Locomotion, Food Reward, Learning and Memory, or Anxiety and Depressive-like Behaviors. Molecules. 2023; 28(12):4848. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28124848
Chicago/Turabian Stylevan de Wetering, Ross, Amy Ewald, Susan Welsh, Lindsay Kornberger, Samuel E. Williamson, Bryan D. McElroy, Eduardo R. Butelman, Thomas E. Prisinzano, and Bronwyn M. Kivell. 2023. "The Kappa Opioid Receptor Agonist 16-Bromo Salvinorin A Has Anti-Cocaine Effects without Significant Effects on Locomotion, Food Reward, Learning and Memory, or Anxiety and Depressive-like Behaviors" Molecules 28, no. 12: 4848. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28124848
APA Stylevan de Wetering, R., Ewald, A., Welsh, S., Kornberger, L., Williamson, S. E., McElroy, B. D., Butelman, E. R., Prisinzano, T. E., & Kivell, B. M. (2023). The Kappa Opioid Receptor Agonist 16-Bromo Salvinorin A Has Anti-Cocaine Effects without Significant Effects on Locomotion, Food Reward, Learning and Memory, or Anxiety and Depressive-like Behaviors. Molecules, 28(12), 4848. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28124848