Molecular Docking Insight into the Label-Free Fluorescence Aptasensor for Ochratoxin A Detection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
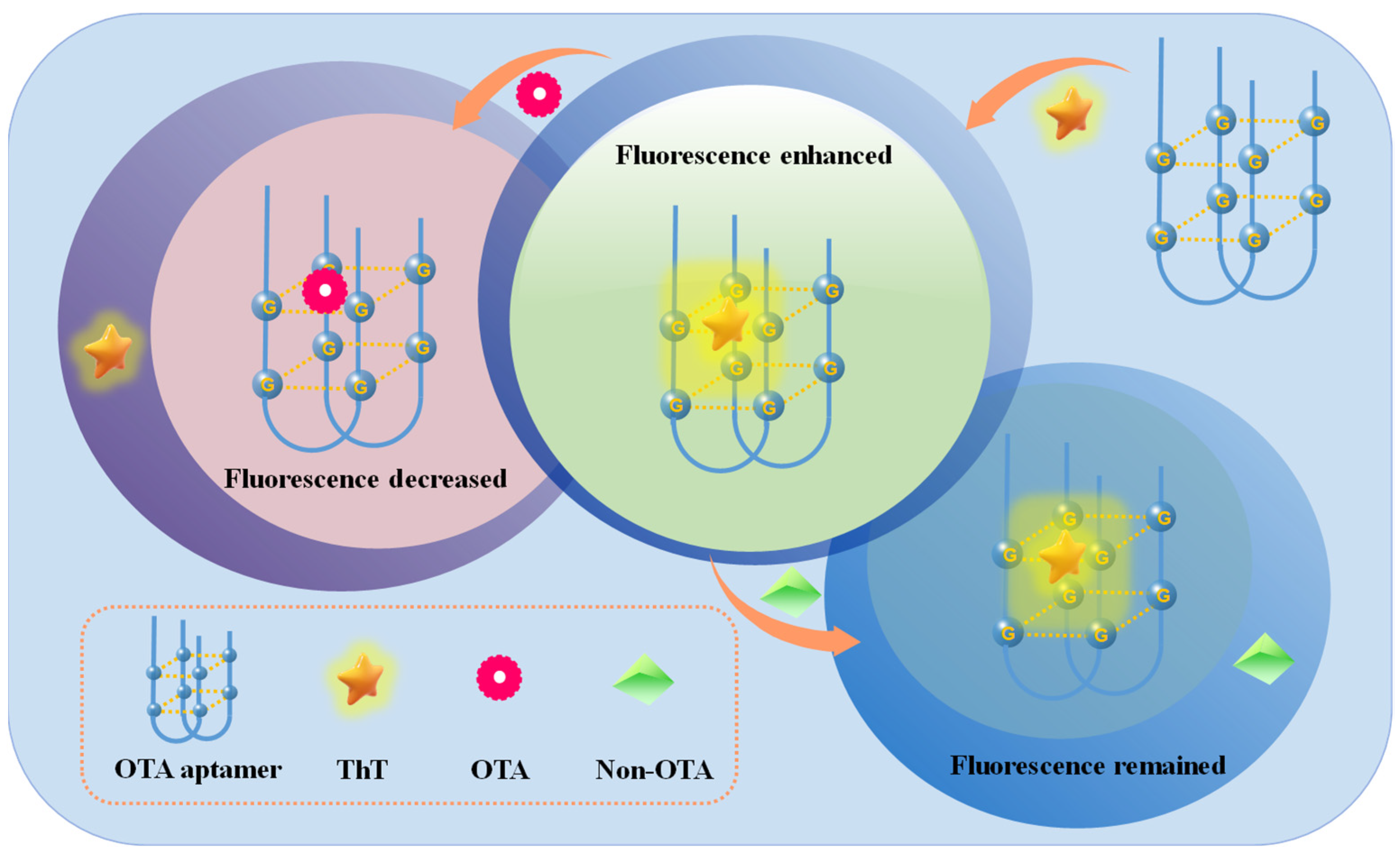
2.1. Scheme of the Proposed Aptasensor for OTA Detection
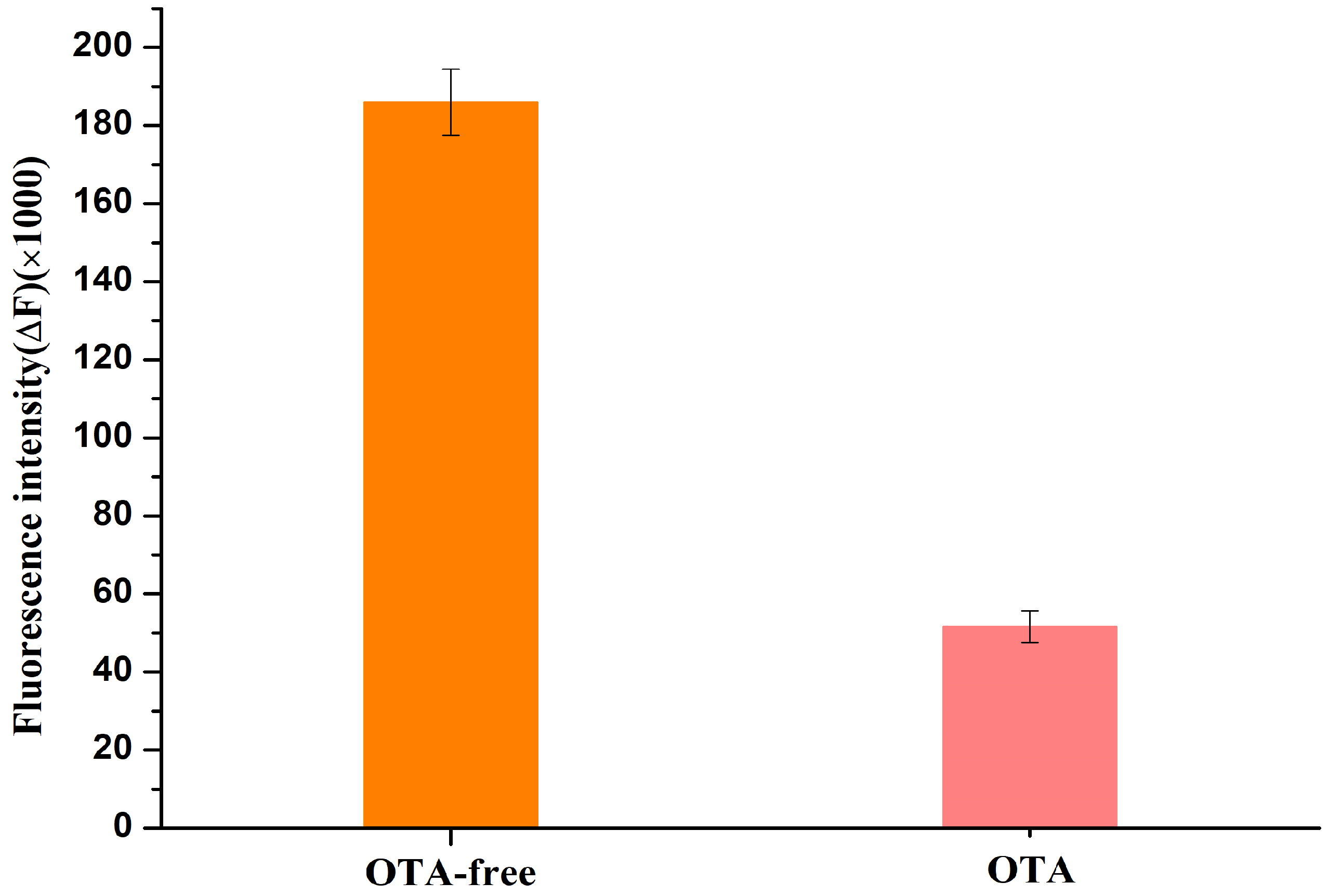
2.2. Feasibility of the Proposed Aptasensor for OTA Detection
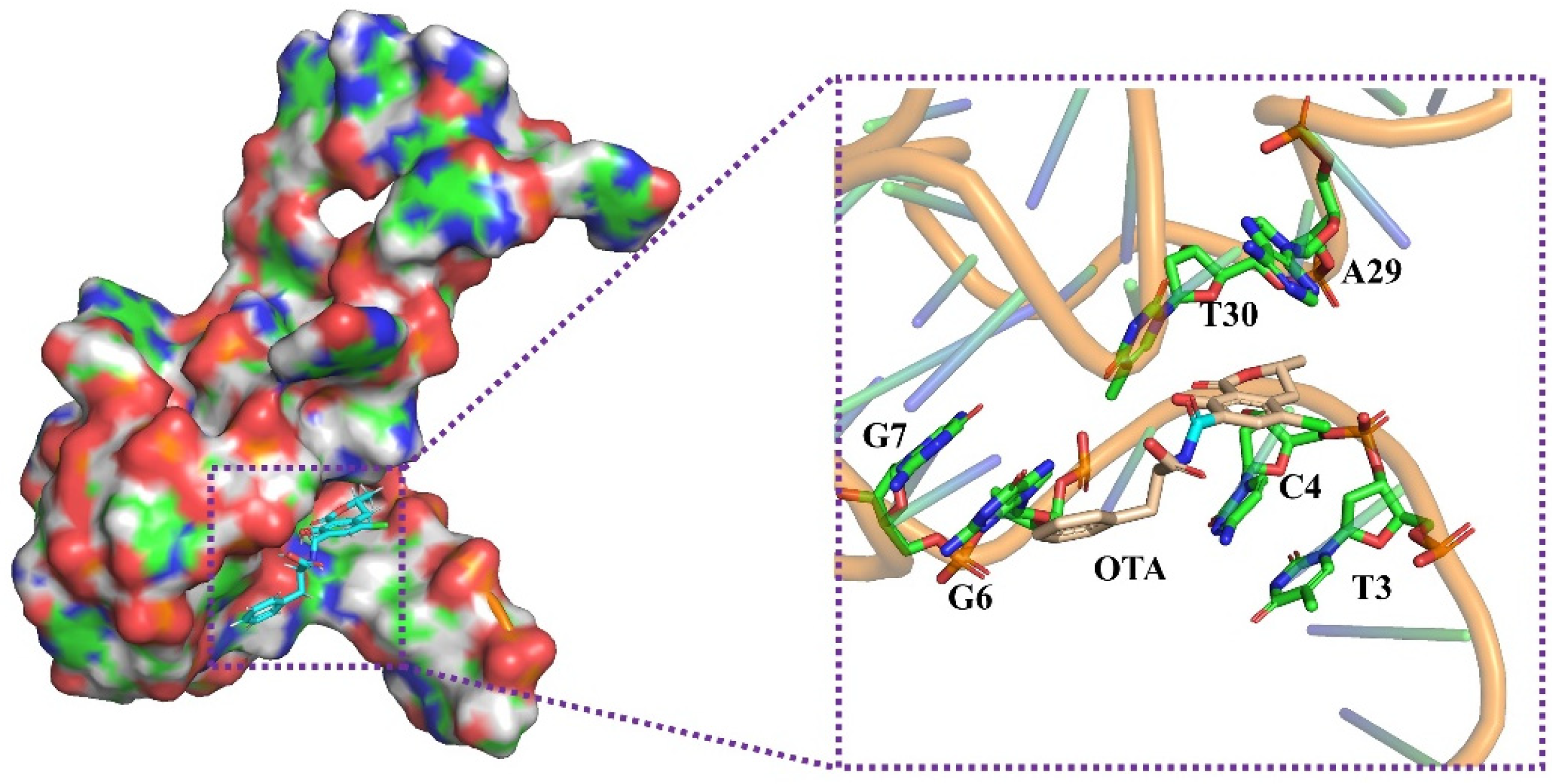
2.3. Molecular Docking between OTA and Its Aptamer
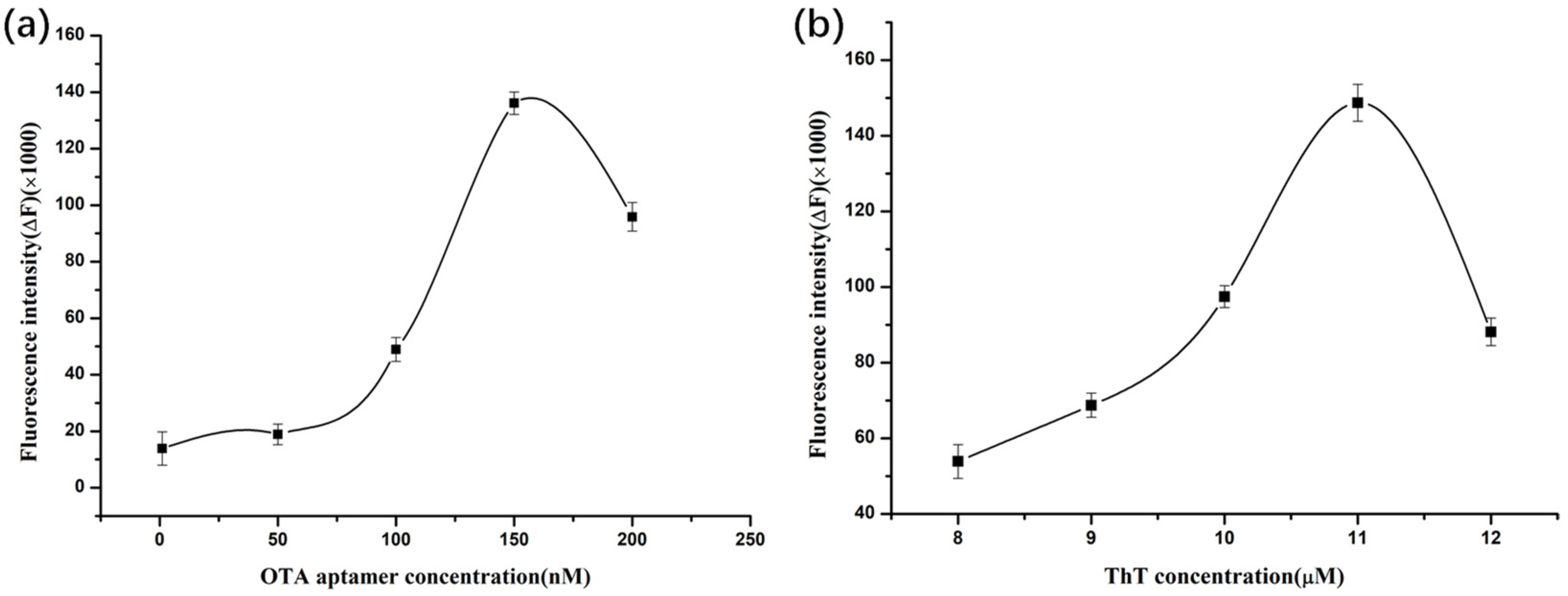
2.4. Optimization of OTA Aptamer Concentration
2.5. Optimization of ThT Dye Concentration
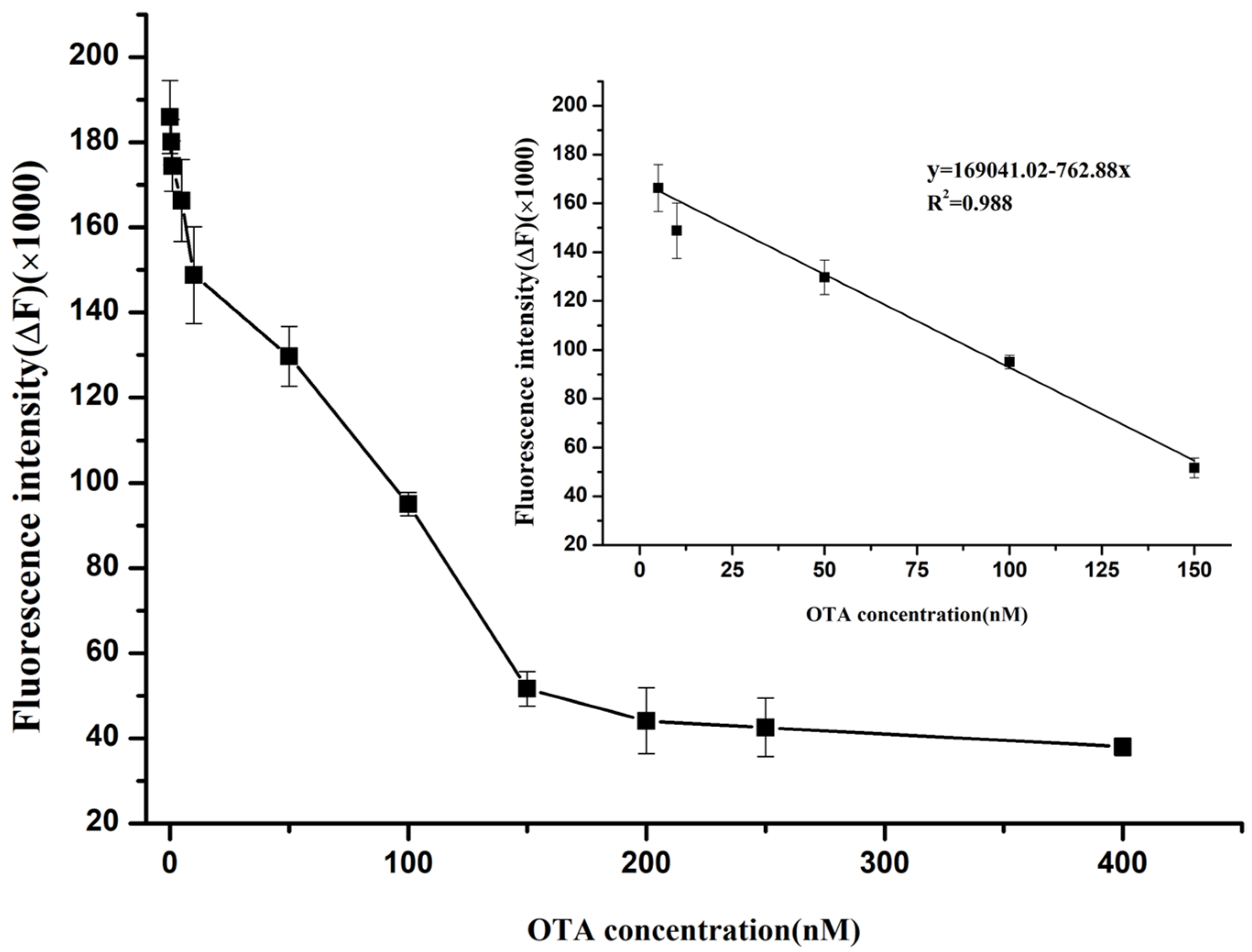
2.6. Sensitivity Performances of the Label-Free Fluorescence Assay
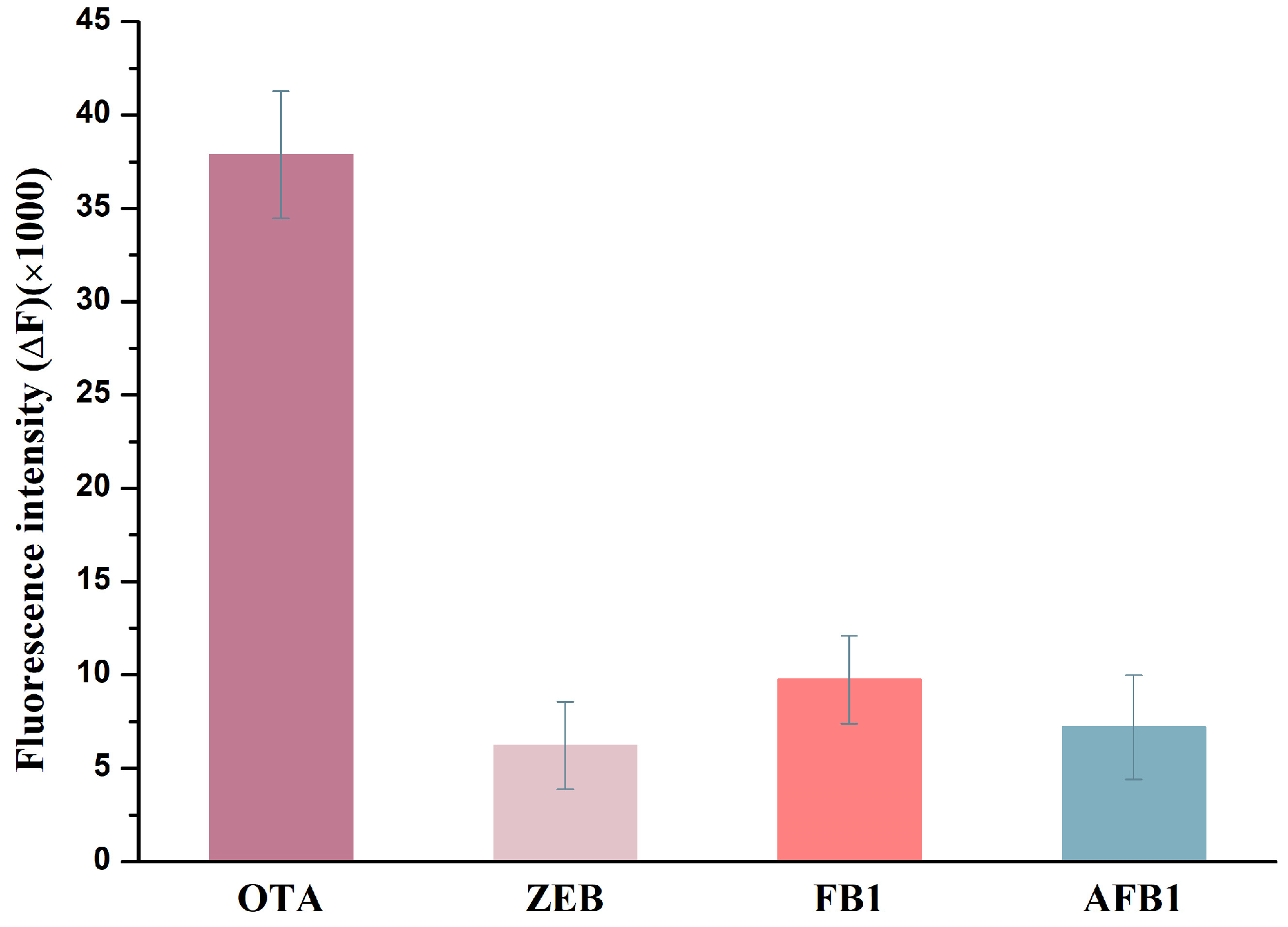
2.7. Selectivity Performances of the Label-Free Fluorescence Assay
2.8. Recovery Analysis in Spiked Wheat Flour Sample
3. Material and Methods
3.1. Materials and Reagents
3.2. Instruments
3.3. Optimization of OTA Aptamer Concentration
3.4. Optimization of ThT Dye Concentration
3.5. Label-Free Fluorescence Analysis of OTA Target
3.6. Selectivity Analysis for OTA Detection
3.7. Determination of OTA in Wheat Flour Sample
3.8. Molecular Docking
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Ropejko, K.; Twarużek, M. The occurrence of ochratoxin A in human body fluids—Review. Toxin Rev. 2019, 40, 347–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrenk, D.; Bodin, L.; Chipman, J.K.; del Mazo, J.; Grasl-Kraupp, B.; Hogstrand, C.; Hoogenboom, L.; Leblanc, J.C.; Nebbia, C.S.; Nielsen, E.; et al. Risk assessment of ochratoxin A in food. EFSA J. 2020, 18, e06113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhai, S.; Xia, Y.; Wang, H.; Ruan, D.; Zhou, T.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, M.; Ye, H.; et al. Ochratoxin A induces liver inflammation: Involvement of intestinal microbiota. Microbiome 2019, 7, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.; Azhar Hayat Nawaz, M.; Akhtar, N.; Raza, R.; Yu, C.; Andreescu, S.; Hayat, A. Morphology controlled NiO nanostructures as fluorescent quenchers for highly sensitive aptamer-based FRET detection of ochratoxin A. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 566, 150647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhamoud, Y.; Yang, D.; Fiati Kenston, S.S.; Liu, G.; Liu, L.; Zhou, H.; Ahmed, F.; Zhao, J. Advances in biosensors for the detection of ochratoxin A: Bio-receptors, nanomaterials, and their applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 141, 111418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, P.T.K.; Jang, C.-H. A Liquid Crystal Sensor Supported on an Aptamer-Immobilized Surface for Specific Detection of Ochratoxin A. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 27414–27421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Li, E.; Gallo, A.; Perrone, G.; Varga, E.; Ma, J.; Yang, B.; Tai, B.; Xing, F. Impact of environmental factors on ochratoxin A: From natural occurrence to control strategy. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 317, 120767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, K.; Vahl, M. Analysis of ochratoxin A in pig kidney and rye flour using liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (LC/MS/MS). Food Addit. Contam. 1999, 16, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupski, L.; Badiale-Furlong, E. Principal components analysis: An innovative approach to establish interferences in ochratoxin A detection. Food Chem. 2015, 177, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Pei, F.; Liu, Q.; Fang, Y. Magnetic Solid-Phase Extraction for the Determination of Ochratoxin A in Wine and Beer by HPLC-FLD. Curr. Anal. Chem. 2018, 14, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, K.; Ikeuchi, R.; Kataoka, H. Determination of ochratoxins in nuts and grain samples by in-tube solid-phase microextraction coupled with liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1220, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Yang, Z.; Khan, I.M.; Niazi, S.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yang, H. Split aptamer acquisition mechanisms and current application in antibiotics detection: A short review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2022, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, S.; Duan, N.; Khan, I.M.; Dong, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, S.; Wang, Z. Strategies to manipulate the performance of aptamers in SELEX, post-SELEX and microenvironment. Biotechnol. Adv. 2022, 55, 107902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.; Zhao, J.; Yu, H.; Wang, C.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Zhou, X.; Li, C.; Liu, M. Structural Insights into the Mechanism of High-Affinity Binding of Ochratoxin A by a DNA Aptamer. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 7731–7740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rode, A.; Endoh, T.; Sugimoto, N. Crowding Shifts the FMN Recognition Mechanism of Riboswitch Aptamer from Conformational Selection to Induced Fit. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2018, 57, 6868–6872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Zhang, F.; Sang, Y.; Katouzian, I.; Jafari, S.M.; Wang, X.; Li, W.; Wang, J.; Mohammadi, Z. Screening, identification, and application of nucleic acid aptamers applied in food safety biosensing. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 123, 355–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Wang, S.; Liu, X.; He, C.; Tang, Y.; Li, Q.; Liu, J.; Su, H.; Tan, T.; Dong, Y. Aptamer-based Colorimetric Biosensing of Ochratoxin A in Fortified White Grape Wine Sample Using Unmodified Gold Nanoparticles. Anal. Sci. 2017, 33, 659–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, K.; Ma, C.; Zhao, H.; Chen, M.; Deng, Z. Sensitive aptamer-based fluorescene assay for ochratoxin A based on RNase H signal amplification. Food Chem. 2019, 277, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.; Jia, B.; Liao, X.; Shi, L.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, M.; Zhou, L.; Li, D.; Kong, W. A CdSe@CdS quantum dots based electrochemiluminescence aptasensor for sensitive detection of ochratoxin A. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 131994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Li, Y. Label-Free Fluorescent Aptamer Sensor Based on Regulation of Malachite Green Fluorescence. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 574–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samokhvalov, A.V.; Safenkova, I.V.; Eremin, S.A.; Bonchuk, A.N.; Maksimenko, O.G.; Sluchanko, N.N.; Zherdev, A.V.; Dzantiev, B.B. Modulation of Aptamer-Ligand-Binding by Complementary Oligonucleotides: A G-Quadruplex Anti-Ochratoxin A Aptamer Case Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, R.; Yang, X.; Jin, P.; Guo, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Yu, H.; Xie, Y.; Qian, H.; Yao, W. G-quadruplex based biosensors for the detection of food contaminants. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Sun, L.; Wang, L.; Li, W.; Hu, G.; Ji, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, X. Engineering DNA G-quadruplex assembly for label-free detection of Ochratoxin A in colorimetric and fluorescent dual modes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 126962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Yu, H.; Alkhamis, O.; Liu, Y.; Lou, X.; Yu, B.; Xiao, Y. Label-Free, Visual Detection of Small Molecules Using Highly Target-Responsive Multimodule Split Aptamer Constructs. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 7199–7207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.L.; Wang, M.; He, B.; Yang, C.; Wang, W.; Leung, C.H. A Luminescent Cocaine Detection Platform Using a Split G-Quadruplex-Selective Iridium(III) Complex and a Three-Way DNA Junction Architecture. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 19060–19067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, L.; Li, F.; Zhao, W.; Luo, L.; Bi, X.; Li, X.; You, T. An ultra-high-sensitivity electrochemiluminescence aptasensor for Pb(2+) detection based on the synergistic signal-amplification strategy of quencher abscission and G-quadruplex generation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, H.; Wan, R.; Khan, M.R.; Wang, N.; Busquets, R.; Deng, R.; He, Q.; Zhao, Z. Ratiometric G-Quadruplex Assay for Robust Lead Detection in Food Samples. Biosensors 2021, 11, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz-Aguado, J.A.; Penner, G. Determination of Ochratoxin A with a DNA Aptamer. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 10456–10461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Gao, S.; Wu, J.; Hu, X. A Fluorescent Aptasensor Based on Assembled G-Quadruplex and Thioflavin T for the Detection of Biomarker VEGF165. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 764123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Ma, P.; Li, K.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, H.; Wang, Z. A novel ratiometric aptasensor based on dual-emission fluorescent signals and the conformation of G-quadruplex for OTA detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 358, 131484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, L.; Li, D.; Liu, R.; Cui, C.; Guo, Z. Label-free aptasensor for ochratoxin A detection using SYBR Gold as a probe. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 246, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, L.; Cui, C.; Xie, W.; Sun, W.; Ji, S.; Tian, J.; Guo, Z. A label-free aptasensor for turn-on fluorescent detection of ochratoxin A based on aggregation-induced emission probe. Methods Appl. Fluoresc. 2019, 8, 015003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Ma, C.; Zhao, H.; He, H.; Chen, H. Label-Free G-Quadruplex Aptamer Fluorescence Assay for Ochratoxin A Using a Thioflavin T Probe. Toxins 2018, 10, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Dong, S.-N.; Abbas, F.; Chu, X.-L.; Fan, A.-Q.; Rhouati, A.; Mao, J.; Liu, Y. Label-free fluorescence aptasensor for ochratoxin A using crystal violet as displacement-type probe. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2021, 49, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Yang, G.; Chen, J.; Wang, S. A signal-on fluorescent aptasensor based on Tb3+ and structure-switching aptamer for label-free detection of Ochratoxin A in wheat. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 41, 704–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Added (nM) | Found (nM) | Recovery (%) | RSD (n = 3) (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | - | - | - |
| 5 | 5.16 ± 6.10 | 103.2 | 6.10 |
| 15 | 14.79 ± 3.14 | 98.60 | 3.14 |
| 100 | 82.89 ± 2.23 | 82.89 | 2.23 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ye, H.; Wang, M.; Yu, X.; Ma, P.; Zhu, P.; Zhong, J.; He, K.; Guo, Y. Molecular Docking Insight into the Label-Free Fluorescence Aptasensor for Ochratoxin A Detection. Molecules 2023, 28, 4841. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28124841
Ye H, Wang M, Yu X, Ma P, Zhu P, Zhong J, He K, Guo Y. Molecular Docking Insight into the Label-Free Fluorescence Aptasensor for Ochratoxin A Detection. Molecules. 2023; 28(12):4841. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28124841
Chicago/Turabian StyleYe, Hua, Mengyuan Wang, Xi Yu, Pengfei Ma, Ping Zhu, Jianjun Zhong, Kuo He, and Yuanxin Guo. 2023. "Molecular Docking Insight into the Label-Free Fluorescence Aptasensor for Ochratoxin A Detection" Molecules 28, no. 12: 4841. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28124841
APA StyleYe, H., Wang, M., Yu, X., Ma, P., Zhu, P., Zhong, J., He, K., & Guo, Y. (2023). Molecular Docking Insight into the Label-Free Fluorescence Aptasensor for Ochratoxin A Detection. Molecules, 28(12), 4841. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28124841






