Dynamic and Static Nature of XH-∗-π and YX-∗-π (X = F, Cl, Br, and I; Y = X and F) in the Distorted π-System of Corannulene Elucidated with QTAIM Dual Functional Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodological Details of the Calculations
3. Results and Discussion
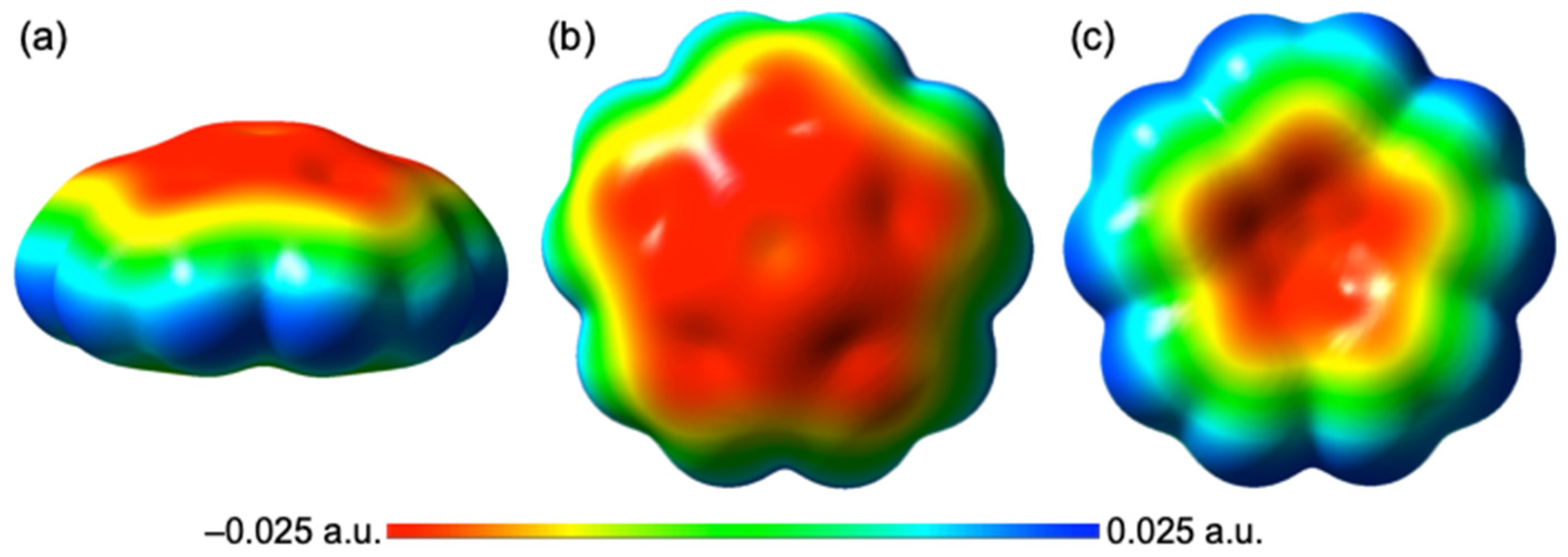
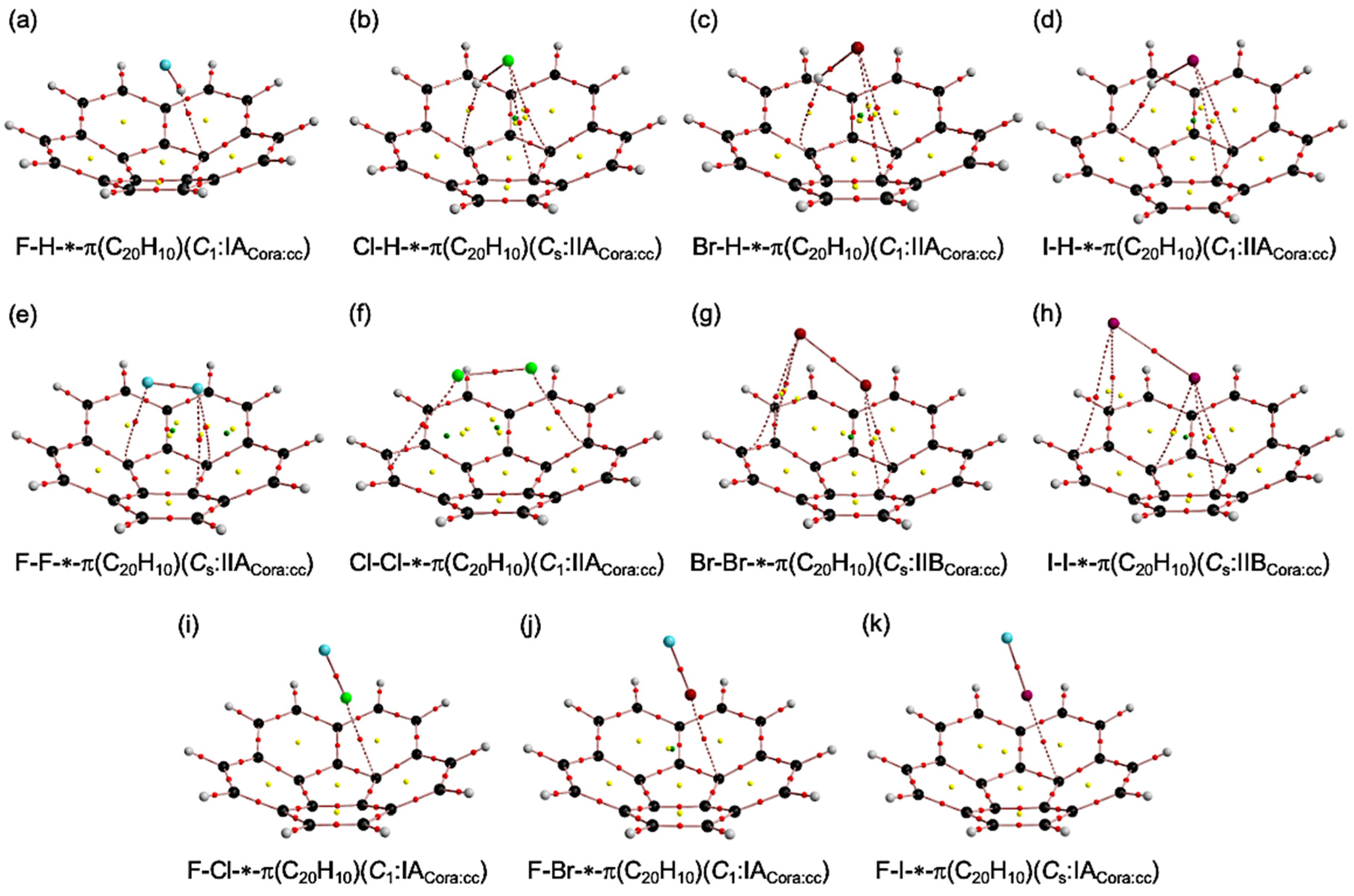
3.1. Optimizations of B–A⋯π(C20H10) (B–A = X–H, X–X, and F–X)
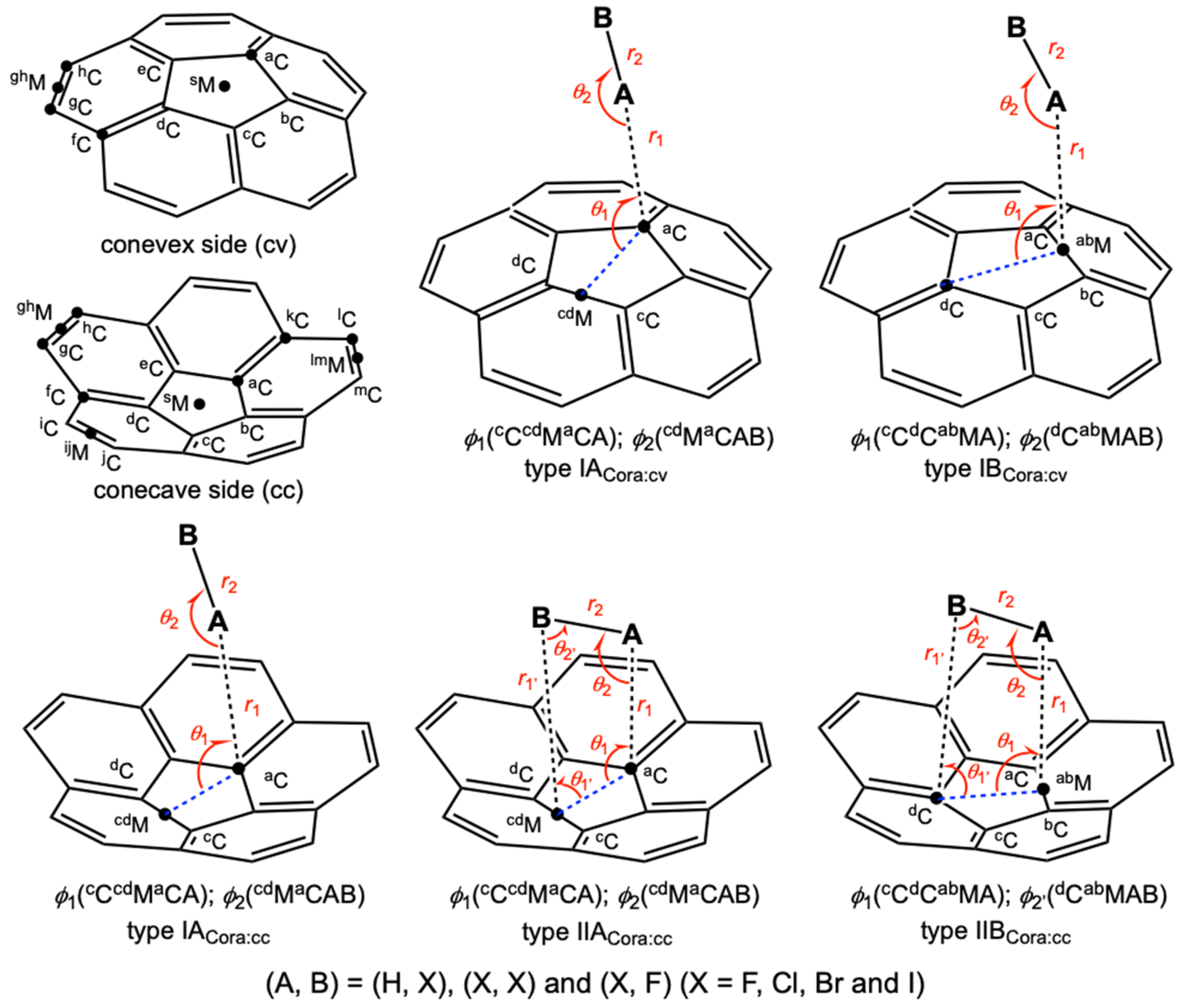
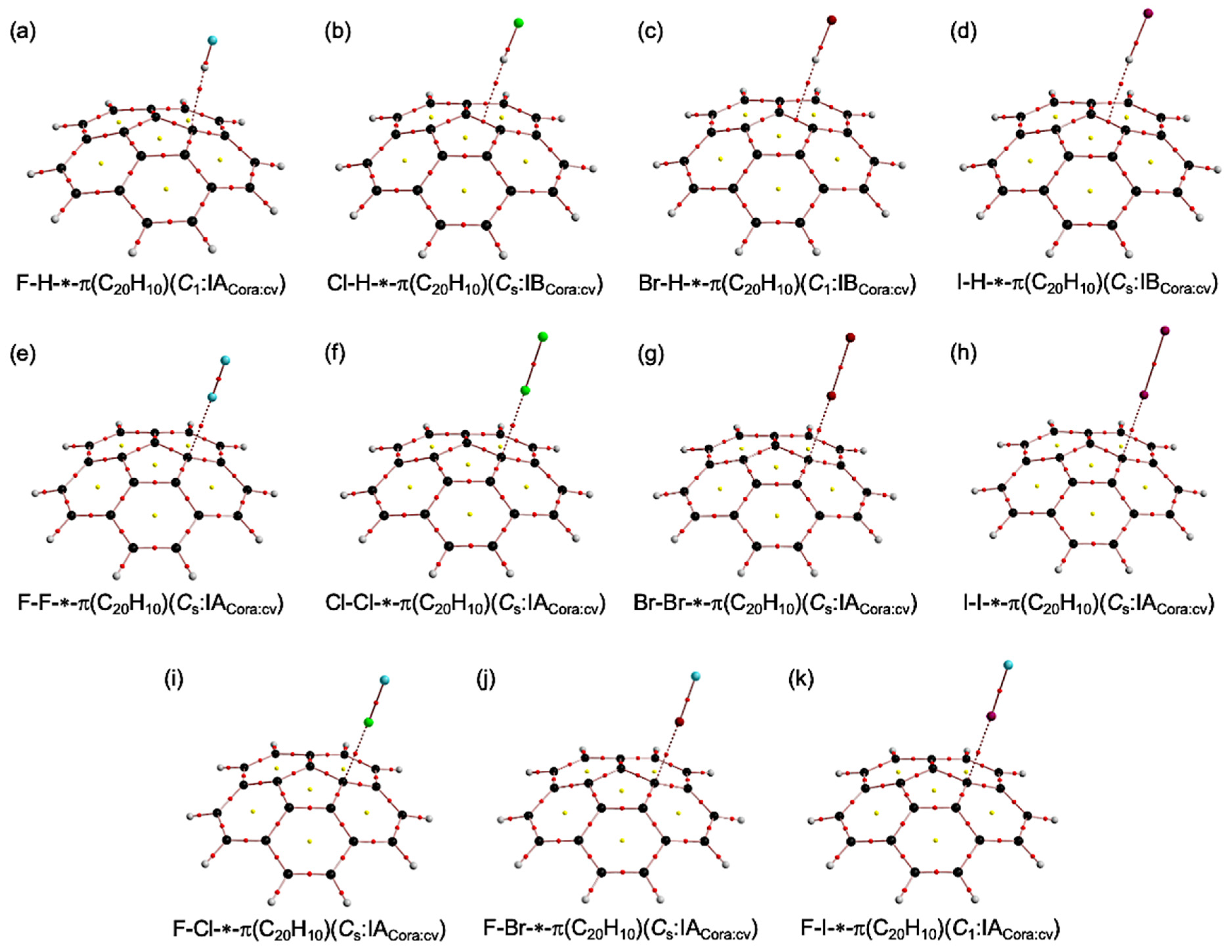
3.2. Molecular Graphs for B–A-∗-π(C20H10) (B–A = X–H, X–X, and F–X)
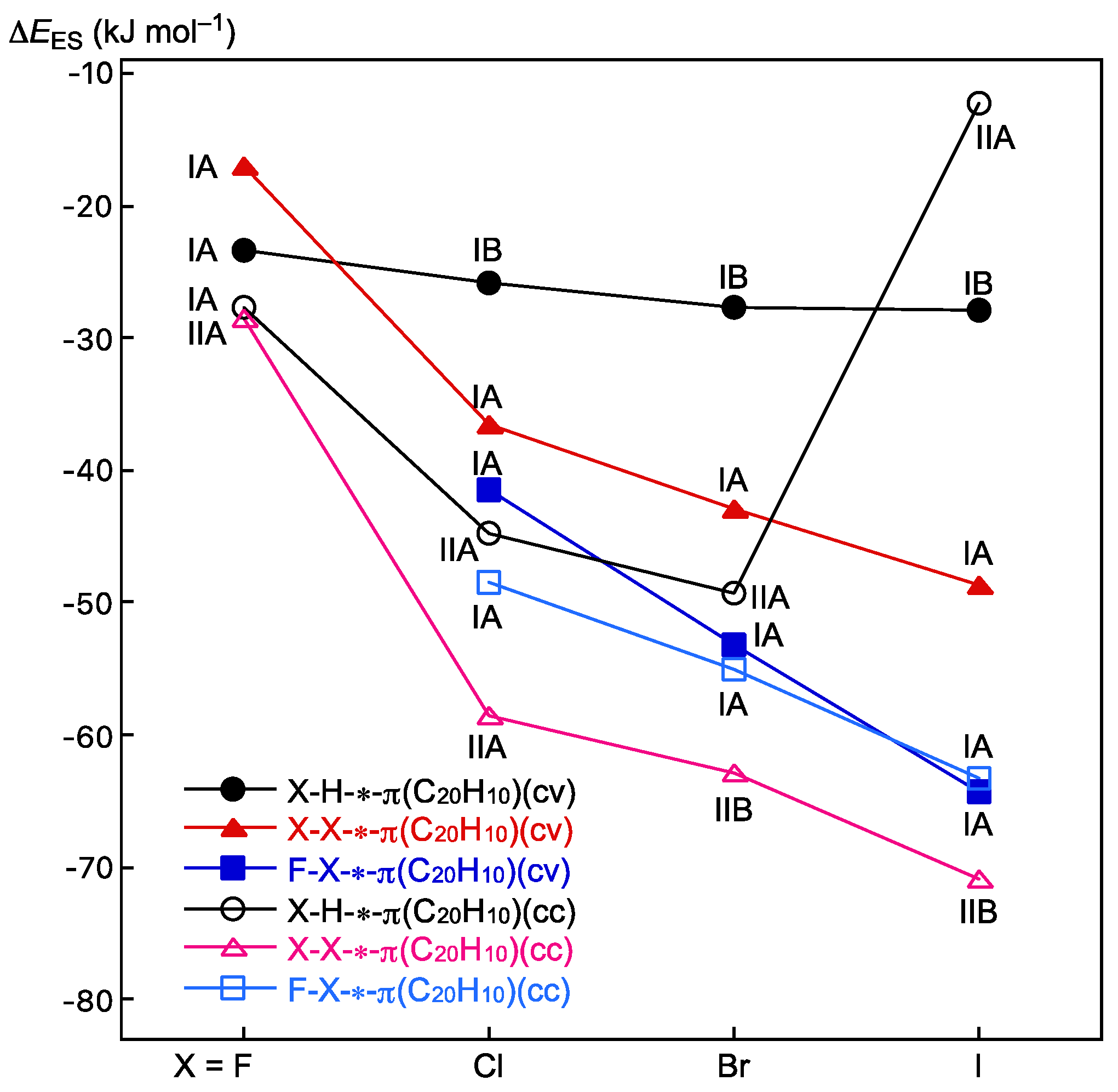
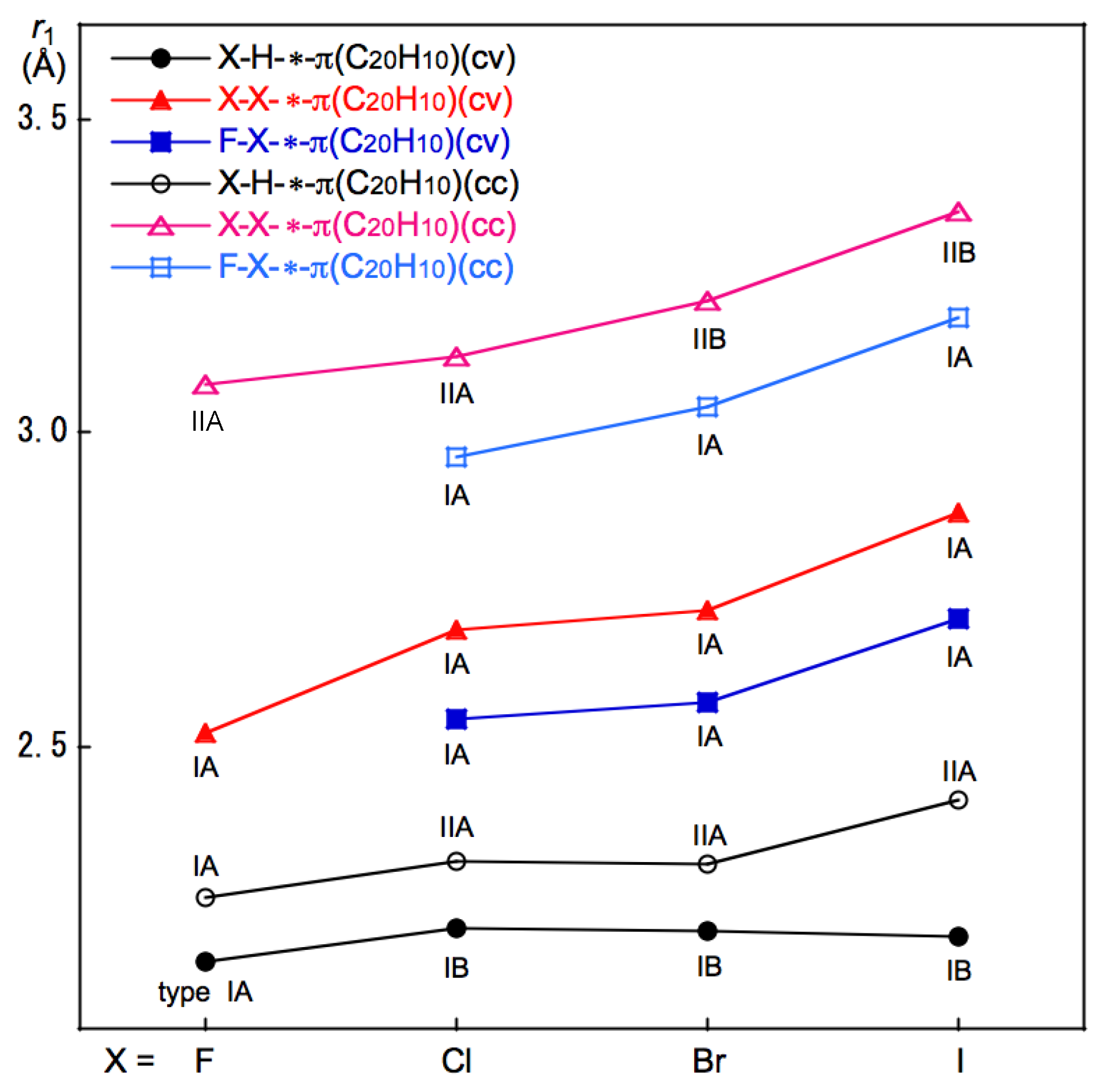
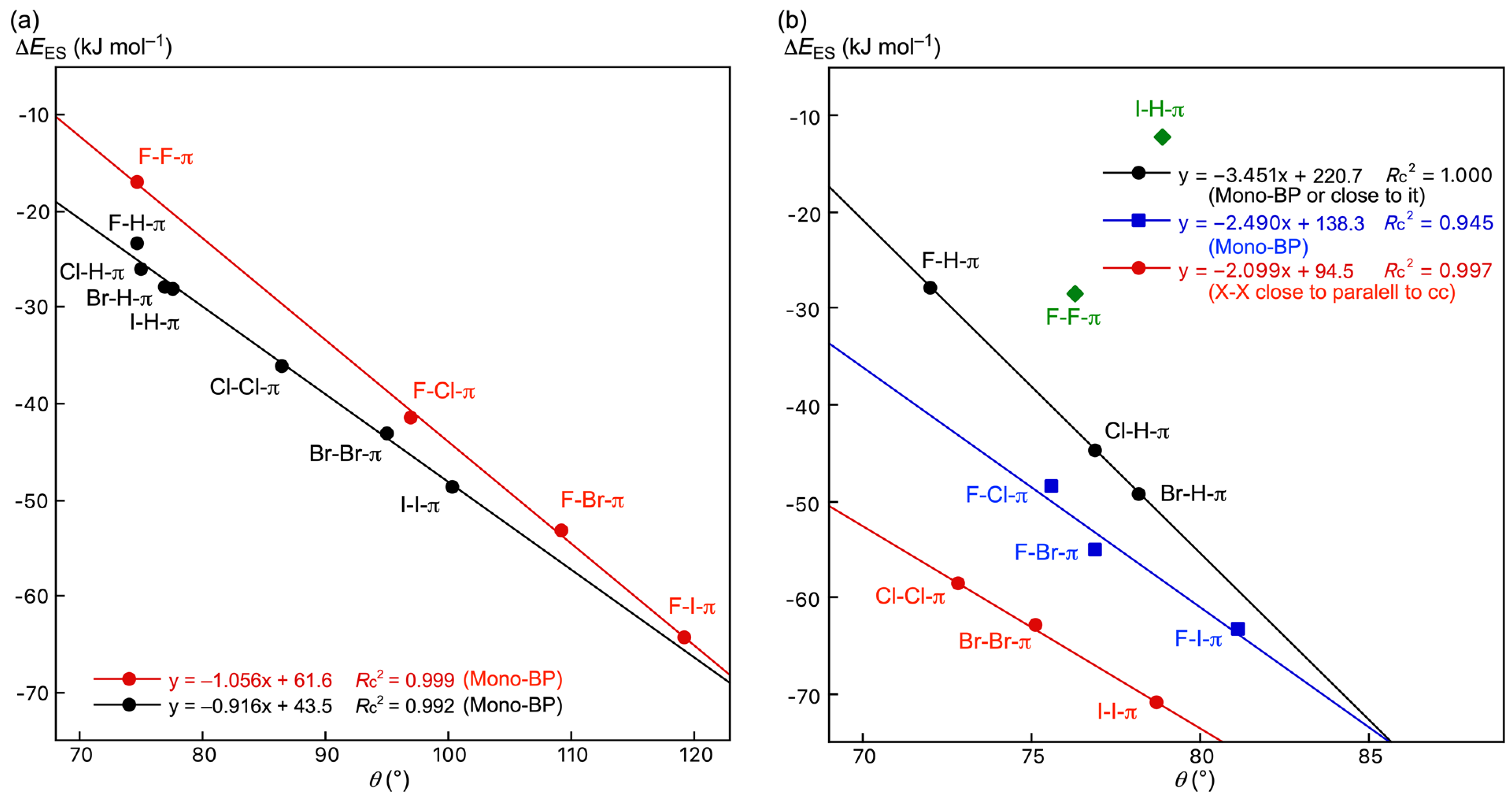
3.3. Survey of B–A-∗-π(C20H10) (B–A = X–H, X–X, and F–X)
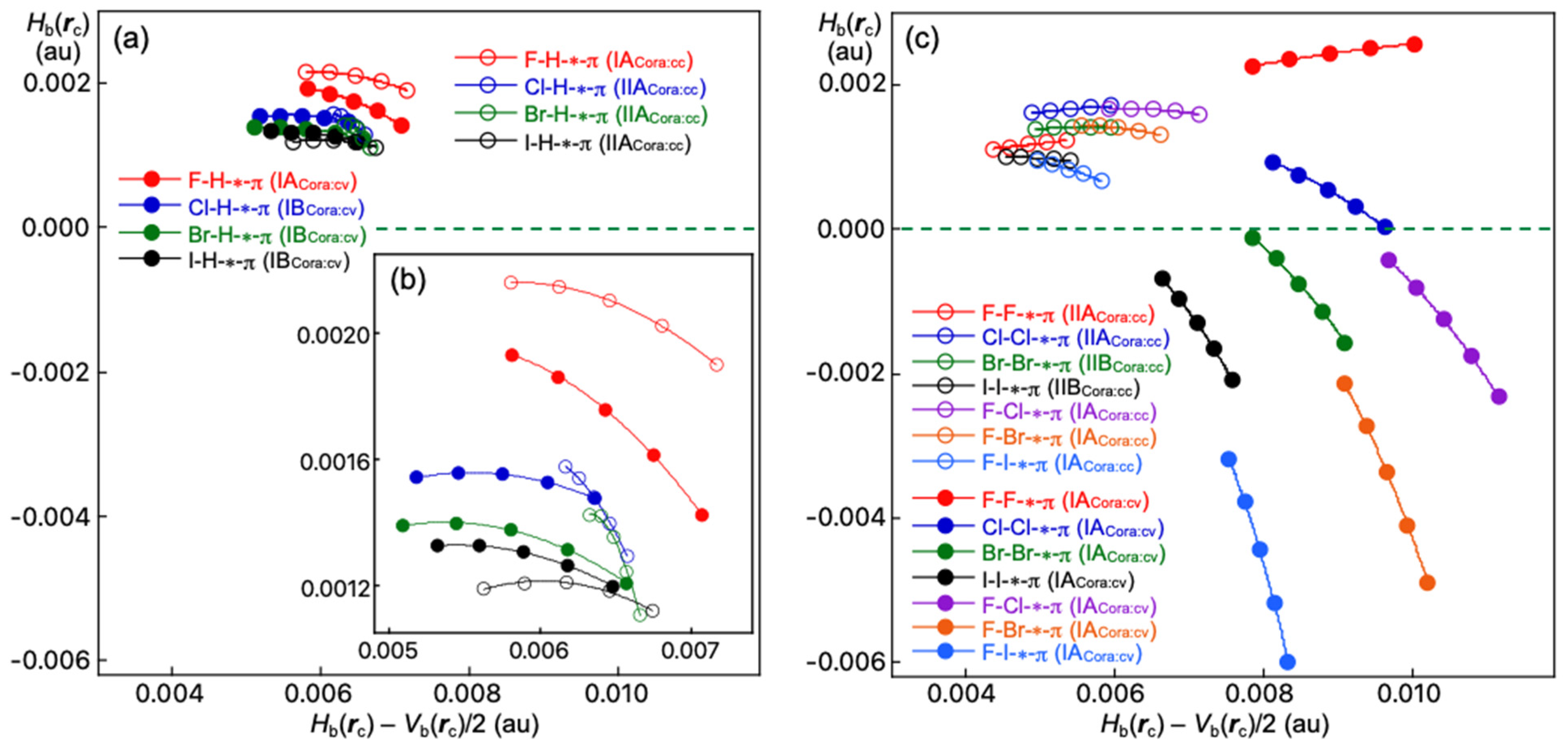
3.4. Nature of B–A-∗-π(C20H10) (B–A = X–H, X–X, and F–X)
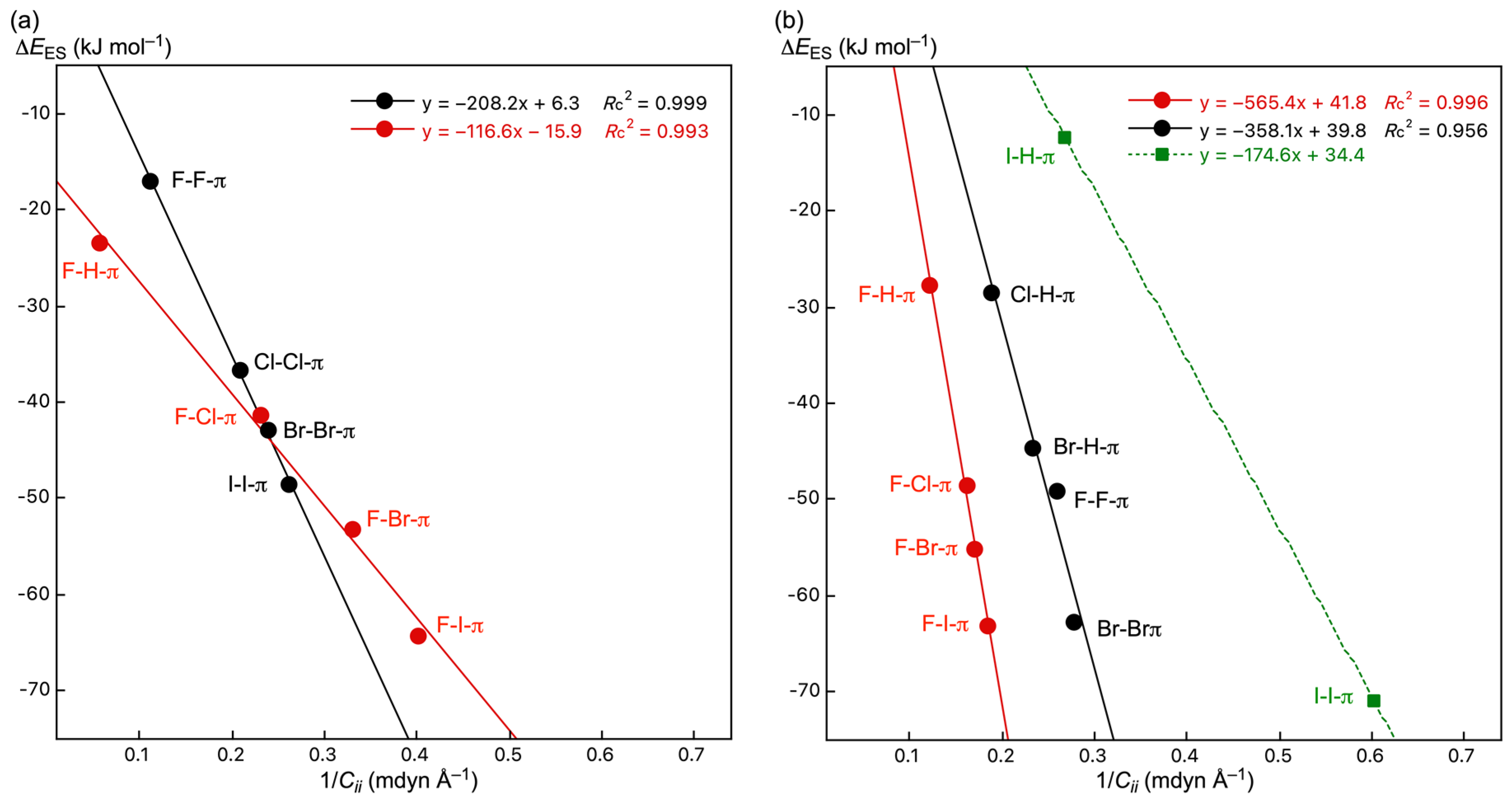
3.5. Factors to Control Structures of B–A-∗-π(C20H10) (B–A = X–H, X–X, and F–X)
3.6. Meaning of the QTAIM-DFA Parameters and the Related Values
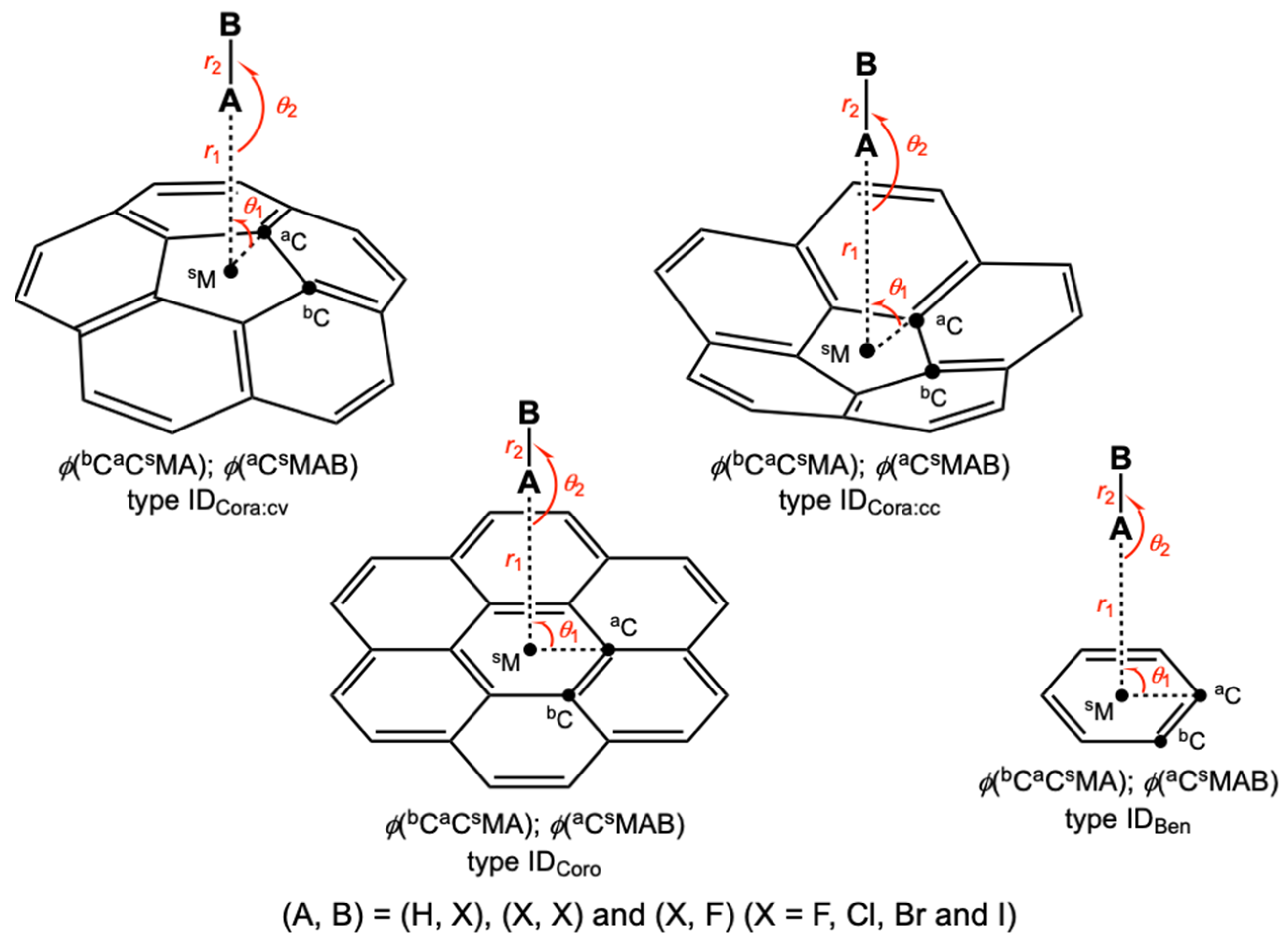
3.7. Differences in the Nature of B–A-∗-π (B–A = X–H and F–X) among π of π(C20H10), π(C24H12) and π(C6H6)
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Jeffrey, G.A. An Introduction to Hydrogen Bonding; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Scheiner, S. Hydrogen Bonding, A Theoretical Perspective; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Desiraju, G.R.; Steiner, T. The Weak Hydrogen Bond in Structural Chemistry and Biology; International Union of Crystallography Monographs on Crystallography; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Gilli, G.; Gilli, P. The Nature of the Hydrogen Bond: Outline of a Comprehensive Hydrogen Bond Theory (IUCr Monographs on Crystallography); Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Han, K.-L.; Zhao, G.-J. Hydrogen Bonding and Transfer in the Excited State; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Meot-Ner, M. The Ionic Hydrogen Bond. Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 213–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabowski, S.J. What Is the Covalency of Hydrogen Bonding? Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 2597–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desiraju, G.R. Reflections on the Hydrogen Bond in Crystal Engineering. Cryst. Growth Des. 2011, 11, 896–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahadevi, A.S.; Sastry, G.N. Cation-p Interaction: Its Role and Relevance in Chemistry, Biology, and Material Science. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 2100–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilday, L.C.; Robinson, S.W.; Barendt, T.A.; Langton, M.J.; Mullaney, B.R.; Beer, P.D. Halogen Bonding in Supramolecular Chemistry. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 7118–7195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, S.; Matsuiwa, K.; Kitamoto, M.; Nakanishi, W. Dynamic Behavior of Hydrogen Bonds from Pure Closed Shell to Shared Shell Interaction Regions Elucidated by AIM Dual Functional Analysis. J. Phys. Chem. A 2013, 117, 1804–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, S.; Nishide, T.; Nakanishi, W. Behavior of Multi-HBs in Acetic Acid Dimer and Related Species: QTAIM Dual Functional Analysis Employing Perturbed Structures Generated Using Coordinates from Compliance Force Constants. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2019, 92, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metrangolo, P.; Resnati, G. (Eds.) Halogen Bonding: Fundamentals and Applications; Series Structure and Bonding; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008; Volume 126. [Google Scholar]
- Gierszal, K.P.; Davis, J.G.; Hands, M.D.; Wilcox, D.S.; Slipchenko, L.V.; Ben-Amotz, D. π-Hydrogen Bonding in Liquid Water. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2011, 2, 2930–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallo, G.; Metrangolo, P.; Milani, R.; Pilati, T.; Priimagi, A.; Resnati, G.; Terraneo, G. The Halogen Bond. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 2478–2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Danovich, D.; Mo, Y.; Shaik, S. On The Nature of the Halogen Bond. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2014, 10, 3726–3737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buemi, G. Intramolecular Hydrogen Bonds. Methodologies and Strategies for Their Strength Evaluation. In Hydrogen Bonding—New Insights; Challenges and Advances in Computational Chemistry and Physics; Grabowski, S.J., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Slater, A.G.; Perdigão, L.M.A.; Beton, P.H.; Champness, N.R. Surface-Based Supramolecular Chemistry Using Hydrogen Bonds. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 3417–3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakanishi, W.; Hayashi, S.; Nishide, T. Intrinsic dynamic and static nature of each HB in the multi-HBs between nucleobase pairs and its behavior, elucidated with QTAIM dual functional analysis and QC calculations. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 24730–24742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Politzer, P.; Murray, J.S.; Clark, T. Halogen bonding and other σ-hole interactions: A perspective. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 11178–11189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, S.; Sugibayashi, Y.; Nakanishi, W. Behaviour of the XH-∗-π and YX-∗- π interactions (X, Y = F, Cl, Br and I) in the coronene π-system, as elucidated by QTAIM dual functional analysis with QC calculations. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 16349–16361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novák, M.; Foroutan-Nejad, C.; Marek, R.J. Modulating electron sharing in ion-π-receptors via substitution and external electric field: A route toward bond strengthening. Chem. Theory Comput. 2016, 12, 3788–3795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, S.; Sugibayashi, Y.; Nakanishi, W. Dynamic and static behavior of the H⋯π and E⋯π interactions in EH2 adducts of benzene π-system (E = O, S, Se and Te), elucidated by QTAIM dual functional analysis. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 9948–9960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugibayashi, Y.; Hayashi, S.; Nakanishi, W. Dynamic and static behavior of hydrogen bonds of the X–H⋯π type (X = F, Cl, Br, I, RO and RR′N.; R, R′ = H or Me) in the benzene π-system, elucidated by QTAIM dual functional analysis. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 28879–28891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugibayashi, Y.; Hayashi, S.; Nakanishi, W. Behavior of Halogen Bonds of the Y−X⋅⋅⋅π Type (X, Y = F, Cl, Br, I) in the Benzene π System, Elucidated by Using a Quantum Theory of Atoms in Molecules Dual-Functional Analysis. Chem. Phys. Chem. 2016, 17, 2579–2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, S.; Sugibayashi, Y.; Nakanishi, W. Quantum chemical calculations with the AIM approach applied to the π-interactions between hydrogen chalcogenides and naphthalene. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 49651–49660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, S.; Sugibayashi, Y.; Nakanishi, W. Behavior of interactions between hydrogen chalcogenides and an anthracene π-system elucidated by QTAIM dual functional analysis with QC calculations. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 31858–31865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, A.K.; Linden, A.; Zoppi, L.; Baldridge, K.K.; Siegel, J.S. Extended Corannulenes: Aromatic Bowl/Sheet Hybridization. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 10792–10796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, D.; Liu, G.; Xiao, C.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, L.; Baldridge, K.K.; Li, Y.; Siegel, J.S.; Wang, Z. Corannurylene Pentapetalae. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 5402–5408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muzammil, E.M.; Halilovic, D.; Stuparu, M.C. Synthesis of corannulene-based nanographenes. Commun. Chem. 2019, 2, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, C.; Steber, A.L.; Rijs, A.M.; Temelso, B.; Shields, G.C.; Lopez, J.C.; Kisiel, Z.; Schnell, M. Corannulene and its complex with water: A tiny cup of water. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 14214–14223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakurai, H.; Daiko, T.; Sakane, H.; Amaya, T.; Hirao, T. Structural Elucidation of Sumanene and Generation of Its Benzylic Anions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 11580–11581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakiyama, Y.; Wang, Y.; Hatano, S.; Abe, M.; Sakurai, H. Generation of “Sumanenylidene”: A Ground-State Triplet Carbene on a Curved π-Conjugated Periphery. Chem. Asian J. 2019, 14, 1844–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glendening, E.D.; Landis, C.R.; Weinhold, F. NBO 6.0: Natural bond orbital analysis program. J. Comput. Chem. 2013, 34, 1429–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, W.; Hayashi, S.; Narahara, K. Polar Coordinate Representation of Hb(rc) versus (ℏ2/8m)∇2ρb(rc) at BCP in AIM Analysis: Classification and Evaluation of Weak to Strong Interactions. J. Phys. Chem. A 2009, 113, 10050–10057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, W.; Hayashi, S. Atoms-in-Molecules Dual Functional Analysis of Weak to Strong Interactions. Curr. Org. Chem. 2009, 14, 181–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, W.; Hayashi, S. Role of dG/dw and dV/dw in AIM Analysis: An Approach to the Nature of Weak to Strong Interactions. J. Phys. Chem. A 2013, 117, 1795–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bader, R.F.W. Atoms in Molecules. A Quantum Theory; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1990; Available online: https://global.oup.com/academic/product/atoms-in-molecules-9780198558651?cc=jp&lang=en& (accessed on 18 May 2023).
- Matta, C.F.; Boyd, R.J. An Introduction to the Quantum Theory of Atoms in Molecules. In The Quantum Theory of Atoms in Molecules: From Solid State to DNA and Drug Design; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, W.; Hayashi, S. Perturbed structures generated using coordinates derived from compliance constants in internal vibrations for QTAIM dual functional analysis: Intrinsic dynamic nature of interactions. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 2018, 118, e25590–e25591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandhorst, K.; Grunenberg, J. Compliance 3.0.2. Available online: http://www.oc.tu-bs.de/Grunenberg/compliance.html (accessed on 18 May 2023).
- Brandhorst, K.; Grunenberg, J. Efficient computation of compliance matrices in redundant internal coordinates from Cartesian Hessians for nonstationary points. J. Chem. Phys. 2010, 132, 184101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandhorst, K.; Grunenberg, J. How strong is it? The interpretation of force and compliance constants as bond strength descriptors. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 1558–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grunenberg, J. III-defined concepts in chemistry: Rigid force constants vs. compliance constants as bond strength descriptors for the triple bond in diboryne. Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 4086–4088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakanishi, W.; Hayashi, S. Dynamic Behaviors of Interactions: Application of Normal Coordinates of Internal Vibrations to AIM Dual Functional Analysis. J. Phys. Chem. A 2010, 114, 7423–7430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakanishi, W.; Hayashi, S.; Matsuiwa, K.; Kitamoto, M. Applications of Normal Coordinates of Internal Vibrations to Generate Perturbed Structures: Dynamic Behavior of Weak to Strong Interactions Elucidated by Atoms-in-Molecules Dual Functional Analysis. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2012, 85, 1293–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Petersson, G.A.; et al. Gaussian 09 (Revision D.01); Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Noro, T.; Sekiya, M.; Koga, T. Segmented contracted basis sets for atoms H through Xe: Sapporo-(DK)-nZP sets (n = D, T, Q). Theoret. Chem. Acc. 2012, 131, 1124-1–1124-8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Møller, C.; Plesset, M.S. Note on an Approximation Treatment for Many-Electron Systems. Phys. Rev. 1934, 46, 618–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauss, J. Effects of electron correlation in the calculation of nuclear magnetic resonance chemical shifts. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 99, 3629–3643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauss, J. Accurate Calculation of NMR Chemical Shifts. Ber. Bunsen-Ges. Phys. Chem. 1995, 99, 1001–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biegler-König, F.; Schönbohm, J. The AIM2000 Program (Version 2.0). Available online: http://www.aim2000.de (accessed on 18 May 2023).
- Biegler-König, F. Calculation of atomic integration data. J. Comput. Chem. 2000, 21, 1040–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keith, T.A. AIMAll (Version 17.11.14); TK Gristmill Software: Overland Park, KS, USA, 2017; Available online: http://aim.tkgristmill.com (accessed on 18 May 2023).
- Zhao, Y.; Truhlar, D.G. The M06 Suite of Density Functionals for Main Group Thermochemistry, Thermochemical Kinetics, Noncovalent Interactions, Excited States, and Transition Elements: Two New Functionals and Systematic Testing of Four M06-Class Functionals and 12 Other Functionals. Theor. Chem. Acc. 2008, 120, 215–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bader, R.F.W.; Cremer, T.S.S.D.; Kraka, E. Description of conjugation and hyperconjugation in terms of electron distributions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1983, 105, 5061–5068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bader, R.F.W. A quantum theory of molecular structure and its applications. Chem. Rev. 1991, 91, 893–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bader, R.F.W. A Bond Path: A Universal Indicator of Bonded Interactions. Phys. Chem. A 1998, 102, 7314–7323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biegler-König, F.; Bader, R.F.W.; Tang, T.H. Calculation of the average properties of atoms in molecules. II. J. Comput. Chem. 1982, 3, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bader, R.F.W. Atoms in molecules. Acc. Chem. Res. 1985, 18, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.H.; Bader, R.F.W.; MacDougall, P. Structure and bonding in sulfur-nitrogen compounds. Inorg. Chem. 1985, 24, 2047–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biegler-König, F.; Schönbohm, J.; Bayles, D. AIM2000—A program to Analyze and Visualize Atoms in Molecules. J. Comput. Chem. 2001, 22, 545–559. [Google Scholar]
- Biegler-König, F.; Schönbohm, J. Update of the AIM2000-program for atoms in molecules. J. Comput. Chem. 2002, 23, 1489–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, W.; Nakamoto, T.; Hayashi, S.; Sasamori, T.; Tokitoh, N. Atoms-in-Molecules Analysis of Extended Hypervalent Five-Center, Six-Electron (5c–6e) C2Z2O Interactions at the 1, 8, 9-Positions of Anthraquinone and 9-Methoxyanthracene Systems. Chem. Eur. J. 2007, 13, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakanishi, W.; Hayashi, S.; Narahara, K. Atoms-in-molecules dual parameter analysis of weak to strong interactions: Behaviors of electronic energy densities versus Laplacian of electron densities at bond critical points. J. Phys. Chem. A 2008, 112, 13593–13599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimme, W.; Wortmann, J.; Frowein, D.; Lex, J.; Chen, G.; Gleiter, R. Laticyclic conjugated double bonds within the framework of oligocondensed bicyclo[2.2.2]octenes. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2 1998, 9, 1893–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-T.; Wang, N.-J.; Yeh, Y.-L.; Chou, T.-C. Synthesis, reactions and thermal properties of endo-5, 12: endo-6, 11-dietheno-5, 5a, 6, 11, 11a, 12-hexahydronaphthacene. Tetrahedron 1995, 51, 2907–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa, E.; Alkorta, I.; Elguero, J.; Molins, E. From weak to strong interactions: A comprehensive analysis of the topological and energetic properties of the electron density distribution involving X–H⋯ F–Y systems. J. Chem. Phys. 2002, 117, 5529–5542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, R.; Gervasio, G.; Marabello, D. The experimental charge density in transition metal compounds. C. R. Chim. 2005, 8, 1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Y–X-∗-π(C20H10) (Symmetry: Type) | ρb(rc) | c∇2ρb(rc) 3 | Hb(rc) | R4 | θ 5 | Cii | θp 6 | κp 7 | Predicted Nature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (eao–3) | (au) | (au) | (au) | (°) | (Å mdyn–1) | (°) | (au–1) | ||
| Convex side (with CIV) | |||||||||
| F–H-∗-π(aC) (C1: IACora:cv) | 0.0165 | 0.0064 | 0.0018 | 0.0067 | 74.7 | 17.674 | 123.6 | 362.5 | p-CS/t-HBnc |
| F–F-∗-π(aC) (Cs: IACora:cv) | 0.0167 | 0.0089 | 0.0024 | 0.0092 | 74.7 | 9.004 | 81.9 | 36.3 | p-CS/vdw |
| Cl–Cl-∗-π(aC) (Cs: IACora:cv) | 0.0227 | 0.0089 | 0.0006 | 0.0089 | 86.4 | 4.795 | 122.2 | 198.1 | p-CS/t-HBnc |
| Br–Br-∗-π(aC) (Cs: IACora:cv) | 0.0260 | 0.0085 | −0.0007 | 0.0085 | 95.0 | 4.197 | 141.4 | 127.3 | r-CS/t-HBwc |
| I–I-∗-π(aC) (Cs: IACora:cv) | 0.0251 | 0.0071 | −0.0013 | 0.0072 | 100.3 | 3.828 | 147.9 | 141.2 | r-CS/t-HBwc |
| F–Cl-∗-π(aC) (Cs: IACora:cv) | 0.0302 | 0.0104 | −0.0013 | 0.0105 | 96.9 | 4.321 | 143.2 | 122.1 | r-CS/t-HBwc |
| F–Br-∗-π(aC) (Cs: IACora:cv) | 0.0341 | 0.0097 | −0.0034 | 0.0102 | 109.3 | 3.036 | 159.2 | 75.5 | r-CS/CT-MC |
| F–I-∗-π(aC) (C1: IACora:cv) | 0.0332 | 0.0079 | −0.0044 | 0.0091 | 119.2 | 2.487 | 165.0 | 52.6 | r-CS/CT-MC |
| Convex side (with NIV) | |||||||||
| F–H-∗-π(aC) (C1: IACora:cv) | 0.0165 | 0.0064 | 0.0018 | 0.0067 | 74.7 | 102.1 8 | 111.4 | 307.7 | p-CS/t-HBnc |
| Cl–H-∗-π(abM) (Cs: IBCora:cv) 9 | 0.0160 | 0.0057 | 0.0016 | 0.0060 | 74.9 | 82.0 8 | 88.5 | 117.3 | p-CS/vdW |
| Br–H-∗-π(abM) (C1: IBCora:cv) 9 | 0.0169 | 0.0058 | 0.0014 | 0.0060 | 76.7 | 60.7 8 | 96.2 | 260.9 | p-CS/t-HBnc |
| I–H-∗-π(abM) (Cs: IBCora:cv) | 0.0175 | 0.0059 | 0.0013 | 0.0060 | 77.5 | 52.2 8 | 95.9 | 240.3 | p-CS/t-HBnc |
| F–F-∗-π(aC) (Cs: IACora:cv) | 0.0167 | 0.0089 | 0.0024 | 0.0092 | 74.7 | 75.6 8 | 81.8 | 35.4 | p-CS/vdw |
| Cl–Cl-∗-π(aC) (Cs: IACora:cv) | 0.0227 | 0.0089 | 0.0006 | 0.0089 | 86.4 | 79.2 8 | 120.6 | 136.5 | p-CS/t-HBnc |
| Br–Br-∗-π(aC) (Cs: IACora:cv) | 0.0260 | 0.0085 | −0.0007 | 0.0085 | 95.0 | 65.9 8 | 139.3 | 125.3 | r-CS/t-HBwc |
| I–I-∗-π(aC) (Cs: IACora:cv) | 0.0251 | 0.0071 | −0.0013 | 0.0072 | 100.3 | 60.0 8 | 145.7 | 129.1 | r-CS/t-HBwc |
| F–Cl-∗-π(aC) (Cs: IACora:cv) | 0.0302 | 0.0104 | −0.0013 | 0.0105 | 96.9 | 93.3 8 | 141.8 | 101.6 | r-CS/t-HBwc |
| F–Br-∗-π(aC) (Cs: IACora:cv) | 0.0341 | 0.0097 | −0.0034 | 0.0102 | 109.3 | 86.9 8 | 157.7 | 59.2 | r-CS/CT-MC |
| F–I-∗-π(aC) (C1: IACora:cv) | 0.0332 | 0.0079 | −0.0044 | 0.0091 | 119.2 | 81.6 8 | 164.1 | 49.4 | r-CS/CT-MC |
| Concave side (with CIV) | |||||||||
| F–H-∗-π(aC) (C1: IACora:cc) | 0.0144 | 0.0065 | 0.0021 | 0.0068 | 72.0 | 8.175 | 95.9 | 273.2 | p-CS/t-HBnc |
| Cl–H-∗-π(aC) (Cs: IIACora:cc) | 0.0162 | 0.0064 | 0.0015 | 0.0065 | 76.9 | 31.667 | 108.6 | 409.5 | p-CS/t-HBnc |
| Br–H-∗-π(aC) (C1: IIACora:cc) | 0.0174 | 0.0065 | 0.0014 | 0.0066 | 78.2 | 34.149 | 117.2 | 736.5 | p-CS/t-HBnc |
| I–H-∗-π(fC) (C1: IIACora:cc) | 0.0172 | 0.0062 | 0.0012 | 0.0063 | 78.9 | 57.414 | 93.5 | 200.2 | p-CS/t-HBnc |
| F–F-∗-π(aC) (Cs: IIACora:cc) | 0.0093 | 0.0048 | 0.0012 | 0.0050 | 76.3 | 12.665 | 84.6 | 6.4 | p-CS/vdw |
| Br–Br-∗-π(aC) (Cs: IIBCora:cc) | 0.0124 | 0.0054 | 0.0014 | 0.0056 | 75.4 | 9.442 | 86.3 | 85.5 | p-CS/vdw |
| I–I-∗-π(aC) (Cs: IIBCora:cc) | 0.0130 | 0.0049 | 0.0010 | 0.0050 | 78.7 | 4.975 | 91.2 | 117.9 | p-CS/t-HBnc |
| F–Cl-∗-π(aC) (C1: IACora:cc) | 0.0137 | 0.0065 | 0.0017 | 0.0067 | 75.6 | 6.162 | 95.0 | 140.9 | p-CS/t-HBnc |
| F–Br-∗-π(aC) (C1: IACora:cc) | 0.0139 | 0.0061 | 0.0014 | 0.0062 | 76.9 | 5.875 | 99.9 | 204.6 | p-CS/t-HBnc |
| F–I-∗-π(aC) (Cs: IACora:cc) | 0.0141 | 0.0054 | 0.0008 | 0.0054 | 81.1 | 5.412 | 109.2 | 324.3 | p-CS/t-HBnc |
| Concave side (with NIV) | |||||||||
| F–H-∗-π(aC) (C1: IACora:cc) | 0.0144 | 0.0065 | 0.0021 | 0.0068 | 72.0 | 100.0 8 | 100.2 | 282.2 | p-CS/t-HBnc |
| Cl–H-∗-π(aC) (Cs: IIACora:cc) | 0.0162 | 0.0064 | 0.0015 | 0.0065 | 76.9 | 77.7 8 | 125.4 | 955.4 | p-CS/t-HBnc |
| Br–H-∗-π(aC) (C1: IIACora:cc) | 0.0174 | 0.0065 | 0.0014 | 0.0066 | 78.2 | 59.0 8 | 137.7 | 1830 | p-CS/t-HBnc |
| I–H-∗-π(fC) (C1: IIACora:cc) | 0.0172 | 0.0062 | 0.0012 | 0.0063 | 78.9 | 53.5 8 | 92.2 | 344.1 | p-CS/t-HBnc |
| F–F-∗-π(aC) (Cs: IIACora:cc) | 0.0093 | 0.0048 | 0.0012 | 0.0050 | 76.3 | 76.2 8 | 89.3 | 305.2 | p-CS/vdw |
| Cl–Cl-∗-π(fC) (C1: IIACora:cc) | 0.0118 | 0.0054 | 0.0017 | 0.0056 | 72.8 | 97.0 8 | 84.5 | 94.5 | p-CS/vdw |
| Br–Br-∗-π(aC) (Cs: IIBCora:cc) | 0.0124 | 0.0054 | 0.0014 | 0.0056 | 75.4 | 76.0 8 | 88.5 | 98.1 | p-CS/vdw |
| I–I-∗-π(aC) (Cs: IIBCora:cc) | 0.0130 | 0.0049 | 0.0010 | 0.0050 | 78.7 | 70.9 8 | 94.1 | 136.2 | p-CS/t-HBnc |
| F–Cl-∗-π(aC) (C1: IACora:cc) | 0.0137 | 0.0065 | 0.0017 | 0.0067 | 75.6 | 95.4 8 | 93.8 | 131.4 | p-CS/t-HBnc |
| F–Br-∗-π(aC) (C1: IACora:cc) | 0.0139 | 0.0061 | 0.0014 | 0.0062 | 76.9 | 79.2 8 | 97.1 | 168.1 | p-CS/t-HBnc |
| F–I-∗-π(aC) (Cs: IACora:cc) | 0.0141 | 0.0054 | 0.0008 | 0.0054 | 81.1 | 76.0 8 | 107.7 | 228.9 | p-CS/t-HBnc |
| Y–X-∗-π(C20H10) (Symmetry: Type) | θ 2 | θp3 | Δθ 4 | Δθp5 | Y–X-∗-π(C24H12/C6H6) (Symmetry: Type) | θ 2 | θp 3 | Δθ 4 | Δθp 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (°) | (°) | (°) | (°) | (°) | (°) | (°) | (°) | ||
| Convex side of π(C20H10) | Y–X-∗-π(C24H12) | ||||||||
| F–H-∗-π(aC) (C5v: IDCora:cv) 6,7 | 66.1 | 68.9 | −1.3 | −0.6 | F–H-∗-π(aC) (C6v: IDCor) 6,7 | 67.0 | 68.8 | −0.4 | −0.7 |
| Cl–H-∗-π(aC) (C5v: IDCora:cv) 6,7 | 71.5 | 74.4 | −0.7 | 2.3 | Cl–H-∗-π(aC) (C6v: IDCor) 6,7 | 72.0 | 73.7 | −0.2 | 1.6 |
| Br–H-∗-π(aC) (C5v: IDCora:cv) 6,7 | 72.5 | 75.8 | −0.3 | 3.1 | Br–H-∗-π(aC) (C6v: IDCor) 6,7 | 72.7 | 75.2 | −0.1 | 2.5 |
| I–H-∗-π(aC) (C5v: IDCora:cv) 6,7 | 73.6 | 77.7 | 0.1 | 3.6 | I–H-∗-π(aC) (C6v: IDCor) 6,7 | 73.7 | 77.6 | 0.2 | 3.5 |
| F–F-∗-π(aC) (C5v: IDCora:cv) 6,7 | 70.5 | 73.5 | −1.4 | −1.9 | F–F-∗-π(aC) (C6v: IDCor) 6,7 | 71.3 | 74.9 | −0.6 | −0.5 |
| F–Cl-∗-π(aC) (C5v: IDCora:cv) 6,7 | 69.6 | 77.6 | 1.2 | 5.4 | F–Cl-∗-π(aC) (C6v: IDCor) 6,7 | 69.1 | 75.8 | 0.7 | 3.6 |
| F–Br-∗-π(aC) (C5v: IDCora:cv) 6,7 | 71.7 | 81.3 | 2.1 | 7.2 | F–Br-∗-π(aC) (C6v: IDCo) 6,7 | 70.8 | 78.8 | 1.2 | 4.7 |
| F–I-∗-π(aC) (C5v: IDCora:cv) 7,8 | 76.5 | 90.8 | 3.5 | 11.6 | F–I-∗-π(aC) (C6v: IDCor) 6,7 | 75.1 | 86.8 | 2.1 | 7.6 |
| Concave side of π(C20H10) | Y–X-∗-π(C6H6) | ||||||||
| F–H-∗-π(aC) (C5v: IDCora:cc) 6,7 | 68.2 | 76.0 | 0.8 | 6.5 | F–H-∗-π(aC) (C6v: IDBzn) 6,7 | 67.4 | 69.5 | – | – |
| Cl–H-∗-π(aC) (C5v: IDCora:cc) 6,7 | 74.8 | 84.8 | 2.6 | 12.7 | Cl–H-∗-π(aC) (C6v: IDBzn) 6,7 | 72.2 | 72.1 | – | – |
| Br–H-∗-π(aC) (C5v: IDCora:cc) 6,7 | 75.9 | 86.8 | 3.1 | 14.1 | Br–H-∗-π(aC) (C6v: IDBzn) 6,7 | 72.8 | 72.7 | – | – |
| I–H-∗-π(aC) (C5v: IDCora:cc) 6,7 | 77.8 | 88.1 | 4.3 | 14.0 | I–H-∗-π(aC) (C6v: IDBzn) 6,7 | 73.5 | 74.1 | – | – |
| F–F-∗-π(aC) (C5v: IDCora:cc) 6,7 | 72.7 | 75.7 | 0.8 | 0.3 | F–F-∗-π(aC) (C6v: IDBzn) 6,7 | 71.9 | 75.4 | – | – |
| F–Cl-∗-π(aC) (C5v: IDCora:cc) 6,7 | 73.1 | 83.8 | 4.7 | 11.6 | F–Cl-∗-π(aC) (C6v: IDBzn) 6,7 | 68.4 | 72.2 | – | – |
| F–Br-∗-π(aC) (C5v: IDCora:cc) 6,7 | 74.5 | 86.4 | 4.9 | 12.3 | F–Br-∗-π(aC) (C6v: IDBzn) 6,7 | 69.6 | 74.1 | – | – |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hayashi, S.; Kato, T.; Sugibayashi, Y.; Nakanishi, W. Dynamic and Static Nature of XH-∗-π and YX-∗-π (X = F, Cl, Br, and I; Y = X and F) in the Distorted π-System of Corannulene Elucidated with QTAIM Dual Functional Analysis. Molecules 2023, 28, 4219. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28104219
Hayashi S, Kato T, Sugibayashi Y, Nakanishi W. Dynamic and Static Nature of XH-∗-π and YX-∗-π (X = F, Cl, Br, and I; Y = X and F) in the Distorted π-System of Corannulene Elucidated with QTAIM Dual Functional Analysis. Molecules. 2023; 28(10):4219. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28104219
Chicago/Turabian StyleHayashi, Satoko, Takahiro Kato, Yuji Sugibayashi, and Waro Nakanishi. 2023. "Dynamic and Static Nature of XH-∗-π and YX-∗-π (X = F, Cl, Br, and I; Y = X and F) in the Distorted π-System of Corannulene Elucidated with QTAIM Dual Functional Analysis" Molecules 28, no. 10: 4219. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28104219
APA StyleHayashi, S., Kato, T., Sugibayashi, Y., & Nakanishi, W. (2023). Dynamic and Static Nature of XH-∗-π and YX-∗-π (X = F, Cl, Br, and I; Y = X and F) in the Distorted π-System of Corannulene Elucidated with QTAIM Dual Functional Analysis. Molecules, 28(10), 4219. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28104219










