Abstract
Ionizable lipid-containing lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) as a non-viral vector with good safety and potency have been considered as an ideal delivery system for gene therapy. The screening of ionizable lipid libraries with common features but diverse structures holds the promise of finding new candidates for LNPs to deliver different nucleic acid drugs such as messenger RNAs (mRNAs). Chemical strategies for the facile construction of ionizable lipid libraries with diverse structure are in high demand. Here, we report on the ionizable lipids containing the triazole moiety prepared by the copper-catalyzed alkyne–azide click reaction (CuAAC). We demonstrated that these lipids served well as the major component of LNPs, in order to encapsulate mRNA using luciferase mRNA as the model system. Thus, this study shows the potential of click chemistry in the preparation of lipid libraries for LNP assembly and mRNA delivery.
1. Introduction
Nucleic acid drugs such as messenger RNA (mRNA) can achieve long-lasting or even curative therapeutic effects through modulating gene expression [1]. However, due to the large size, hydrophilicity, negative charge and nuclease susceptibility, it is still challenging to deliver nucleic acid drugs into target cells. To address this challenge, lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) capable of improving the cellular permeability and cytosolic delivery capacity of nucleic acid drugs have been developed, representing the most clinically advanced delivery platform [2]. The global outbreak of the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic and the rapid approval of two mRNA vaccines have brought the LNPs that lie behind the success of nucleic acid drugs into the spotlight of both the scientific community and the general public [3]. The development of high-performance LNPs to further improve delivery efficiency and promote the clinical translation of diverse nucleic acid drugs is therefore of current research interest [4].
The four-component LNP became a leading non-viral vector for mRNA delivery after its use by Pfizer and Moderna in the development of COVID-19 vaccines [5]. Except for the ionizable lipids in FDA-approved LNP formulations, such as SM-102 and DLin-MC3-DMA, various analogues or derivatives of these known lipids have been prepared and tested for their potential applications in LNP-based mRNA delivery [6]. Some of the chemical modifications on ionizable lipids were reported to endow LNPs with special properties. For example, the introduction of unsaturation into the structure of ionizable lipids greatly improved the mRNA transfection in vivo [7], and the incorporation of piperazine into ionizable lipids preferentially delivered mRNA into immune cells in vivo [8].
For a systematic investigation on the structure–activity relationship of the ionizable lipids in LNPs, different chemical strategies to construct the different libraries of these molecules have been developed in recent years. Michael addition has been applied, in order to prepare the lipid compound libraries by reacting acrylamide tails with different amines [9]. Epoxide ring-opening reactions [10] are used for alkylation modifications to synthesize different anionic lipids. Enzyme-assisted ligation reactions have also been applied to elevate the efficiency of library construction [11]. The azide–alkyne click reaction, catalyzed by a copper catalyst or promoted by an internal strain, has found diverse applications both in chemical–biological studies, and in fast ligation applications, since it features fast reaction rates and high yields of cycloaddition products under mild conditions compatible with bio-active molecules [12,13]. The cycloaddition product of click reactions contains triazole moieties, which is highly compatible with biological systems. We envision that click reactions should be able to serve as a facile method to construct compound libraries of ionizable lipids containing triazole moieties. However, whether the triazole-containing lipid molecules are able to serve as the major component of LNPs for mRNA delivery is unknown. Here, we report our work on the preparation of triazole-containing ionizable lipids based on the copper-catalyzed click reaction (CuAAC) and provide an evaluation of the potential of these lipids in the assembly of LNPs for mRNA delivery.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthesis of Triazole-Containing Ionizable Lipids
Based on the chemical structure of SM-102, which is the major component of the FDA-approved LNP for mRNA vaccines, we designed the framework of Cp1-n, which is made up of a series of ionizable lipids containing triazole moiety (Scheme 1a). The lipid tail in Cp1-n was the same as that in SM-102, while the hydroxyl group in SM-102 was replaced by a series of triazoles with different substitution groups on the 4-position of the triazole structure.
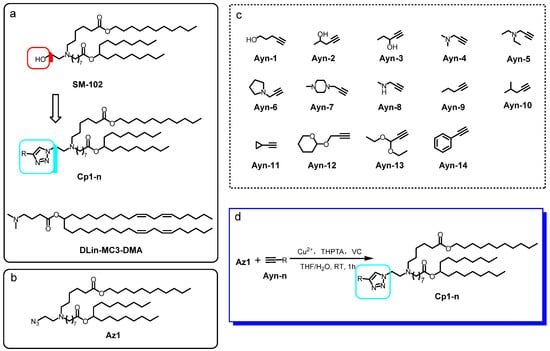
Scheme 1.
Chemical structure of (a) framework of the triazole-containing ionizable lipids with structural similarity to SM-102 and DLin-MC3-DMA; (b) the azide substrate Az1; (c) different alkynes Ayn-1~15. (d) Reaction scheme between Az1 and Ayn-n to give Cp1-n.
We first prepared the ionizable lipid Az1 with the azide handle at the reaction scale (Scheme 1b), following the protocol described in the Supporting Information, in order to obtain grams of Az1. Then, Az1 was allowed to react with a variety of terminal alkynes under the CuAAC standard condition [14] (Scheme 1d). As shown in Scheme 1c, the Ayn-1~15 with terminal alkynes chosen to react with Az1 were all readily available from a commercial source. The substitution groups on the other end of the terminal alkyne molecules included alkyl, phenyl, alkylhydroxyl, alkylamino and alkyloxyl groups. With the diversity of the substitution groups in the terminal alkyne substrates, we were able to obtain the ionizable molecules with common frameworks and diversity on the substitution groups on the triazole ring linked with the lipid tail. The CuAAC reaction between Az1 and Ayn-n was performed using tris(3-hydroxypropyltriazolylmethyl) amine (THPTA) and copper (I) generated from copper sulfate, together with vitamin C (VC). During the reaction, the azide group in Az1 served as the 1, 3-dipole and underwent a [3+2] cycloaddition reaction with terminal alkynes in Ayn-1~15, in order to generate 1, 2, 3-triazoles Cp1-n. The Cp1-n were then purified and yields of over 80% were obtained, indicating the advantages of CuAAC for the efficient construction of ionizable lipid libraries.
2.2. Biocompatibility of Triazole-Containing Ionizable Lipids
To determine whether the triazole introduced into ionizable lipids was biocompatible, we measured cell viability using the Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) assay. As shown in Figure S1, the relative viabilities of human ovarian cancer HeLa cells treated with Cp1-n were over 80% at concentrations up to 100 μM. This result thus indicates a good biosafety that these triazole-containing ionizable lipids may exist, showing that they are valuable for further research in the preparation of LNPs and delivery of messenger RNA.
2.3. Preparation and Characterization of LNPs with Cp1-n as the Ionizable Lipids
According to the formula for the FDA-approved LNP for the mRNA vaccine against COVID-19 by Moderna [15], the LNP was prepared with the ionizable lipid SM-102, the helper lipid distearoylphosphatidylcholine (DSPC), cholesterol and the PEGylated lipid at a molar ratio of 50:10:38.5:1.5, respectively. We prepared Cp1-n-based LNPs using a similar cocktail protocol, replacing SM-102 with Cp1-n (Figure 1a) [16]. Briefly, the ionizable lipid Cp1-n (or SM-102), DSPC, cholesterol and the PEGylated lipid were mixed, followed by the addition of luciferase mRNA at a 20:1 mass ratio of ionizable lipids to mRNA. These LNPs were then obtained and characterized using dynamic light scattering (DLS) analysis. As shown in Figure 1b, LNPs containing SM-102 had a diameter of 79.96 ± 16.79 nm. Similarly, LNPs containing Cp1-n all formed nanoparticles, with sizes in the range of ~45 nm to ~113 nm (Figure 1c). For example, Cp1-4-based LNP was uniformly distributed, with a mean size of 73.99 ± 3.59 nm. These results thus indicate that the triazole-containing ionizable lipids Cp1-n can readily self-assemble with other components into LNPs. Specifically, the particle size of Cp1-10 is only around 45 nm. This difference is due to the inherent defect of the liposome extruder. In fact, many studies reported that the size of LNPs is related to the mixing flow rate [17,18,19]. In the case of a fast flow rate, LNPs will show a smaller size; while the mixing flow rate cannot be controlled by the liposome extruder, the size of the LNP can be controlled as uniformly as possible and kept below 100 nm by using a polycarbonate membrane. Moreover, all LNPs formed of Cp1-n had positive zeta potentials ranging from +8.64 mV to +25.41 mV (Table 1), suggesting that they can readily cross negatively charged cell membranes.
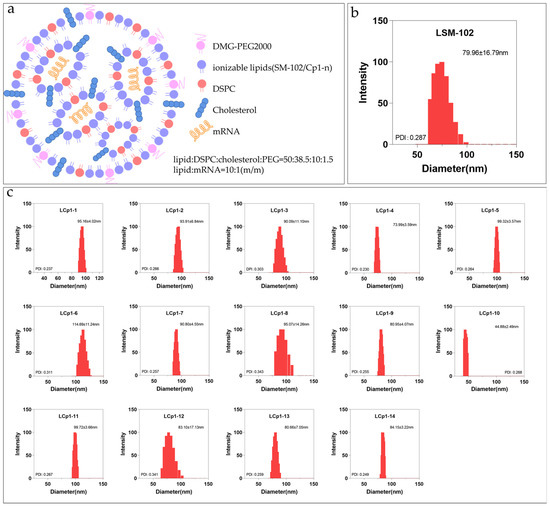
Figure 1.
(a) Schematic illustration of the LNP formulations. (b,c) DLS analysis of LNPs formed of SM-102 or Cp1-n.

Table 1.
Zeta potentials of LNPs formed of SM-102 or Cp1-n.
2.4. Encapsulation Rates of mRNA in the Cp1-n-Based LNPs
To determine whether the triazole in ionizable lipids would affect the encapsulation of mRNA into LNPs, we quantified the encapsulation rates using the RiboGreen fluorescence probe method [20]. The principle behind using a RiboGreen reagent kit to measure encapsulation efficiency is that when RiboGreen binds to mRNA, fluorescence is generated, resulting in the detection of unencapsulated mRNA; after destroying the LNP structure with Triton, the total mRNA can be measured, and the difference is the encapsulated mRNA. As shown in Table 2, LNPs formed of SM-102 had an encapsulation capability of 89.98%, and Cp1-n-based LNPs had comparable encapsulation rates ranging from 84.10% to 91.64%. These results indicate that the presence of triazole linkers would not affect the binding of ionized lipids to mRNA and LNP assembly.

Table 2.
The luciferase mRNA encapsulation rates of LNPs formed of different lipids.
2.5. mRNA Delivery by the Cp1-n-Based LNPs
Next, we measured the transfection efficacies of Cp1-n-based LNPs. Briefly, HeLa cells were treated with SM-102- or Cp1-n-based LNPs containing luciferase mRNA, followed by the quantification of bioluminescence signals from proteins expressed by luciferase mRNA using luciferin substrates. As shown in Figure 2, LNPs formed of Cp1-n had variable mRNA delivery efficiencies. Specifically, compared to LNPs formed of SM-102, LNPs formed of Cp1-1, Cp1-4, Cp1-5, Cp1-6 and Cp1-7 had 0.60, 1.32, 0.18, 0.64 and 0.60-fold bioactivities, respectively whereas others displayed no transfection capabilities. Note that among all these LNPs formed of triazole-containing ionizable lipids, Cp1-4 consisting of dimethylamine was the most effective, even better than SM-102.
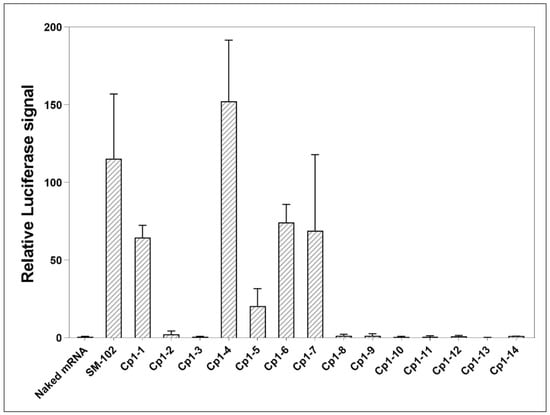
Figure 2.
Relative luciferase signals from HeLa cells treated with naked mRNA, mRNA-encapsulated LNPs formed of SM-102 or Cp1-n for 24 h. Data are shown as mean ± SEM (n = 3).
It has been reported that the proton sponge effect originates from a large number of weakly conjugated bases (which have buffer capacity in the pH range of 4.0–6.0), resulting in the absorption of protons in acidic organelle and the accumulation of osmotic pressure through organelle membranes. This osmotic pressure causes the expansion and rupture of the acidic endosomes and releases the trapped material into the cytoplasm [21].
Tertiary amines have a strong proton absorption capacity in the inner body (pH, 5–6) and lysosomes (pH, 4–5), leading to rapid osmotic expansion and mRNA release [22]. The high transfection efficiencies of Cp1-4, Cp1-5, Cp1-6 and Cp1-7 may be related to this.
These results thus show that the triazole linker in ionizable lipids could allow LNP formation for mRNA delivery. The variable delivery capacities suggest that minor chemical structure alterations to the triazole can also significantly impact the outcomes, which has often been observed during lipid derivatization [23]. However, these results may guide the structural design of ionizable lipid libraries in the future, and therefore, it is advantageous to include one or more tertiary amines at the end of the head structure of the triazole linkers.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General
All chemicals and solvents were purchased from Energy-Chemical or Bidepharm. The Quant-iTTM RiboGreenTM RNA Assay Kit (invitrogen) was purchased from Thermo Fisher Scientific. The Luciferase Reporter Gene Assay Kit was purchased from Yeasen Biotech. The Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) kits were purchased from Coolaber. The liposome supplement was purchased from Avito (Shanghai) Pharmaceutical Technology Co., Ltd. Luciferase mRNA was provided by Vazyme. LC/MS was performed on a LC MS-2020 resolution Mass Spectrometer, and 1H-NMR was performed on a Bruker AVANCE III-400 400 MHz. The particle size and zeta-potential were measured using a BrookHaven 90plus PALS dynamic light diffuser. Luciferase signals were measured using a TECAN Spark 10M multifunctional enzyme spectrometer. A LiposoFast-Basic LF-1 liposome preparation extruder was used for liposome preparation, and Kylin-Bell Lab Instruments ZD-9550 were used for dialysis.
3.2. LNP Formulation
The lipid composition (50% ionizable lipids, 38.5% cholesterol, 10% dsc and 1.5% DMG-PEG2000) was dissolved in 250 μL of anhydrous ethanol, and 20mg of luciferase mRNA was dissolved in 750 μL of 50 mM sodium citrate (pH = 3.0). The ratio of ionizable lipids to mRNA was 20:1 (m/m). After the lipid component was fully mixed with the mRNA component, LNPs were prepared using the extrusion mechanism of liposome. The liposome extruder used a polycarbonate membrane with a pore size of 100 nm, and each sample was extruded 21 times. The prepared LNPs were put into dialysis bags (interception molecular weight 3500) and dialysis was conducted in 1 × PBS (pH = 7.4) for 18 h. The LNPs were collected from the dialysis bags, filtered through a 0.22 μm syringe filter and stored at 4 °C.
3.3. LNP Size Distribution and Zeta Potential
LNPs were equilibrated at room temperature and diluted in water at a ratio of 1:200 for size and zeta potential measurements. Size distribution and zeta potential were measured using a BrookHaven 90plus PALS dynamic light Scatterer.
3.4. mRNA Concentration and Encapsulation Efficiency
The encapsulation rate of LNPs was measured using the RiboGreen fluorescent dye kit (Invitrogen). Its principle is that RiboGreen is a kind of super-sensitive fluorescent nucleic acid dye. RiboGreen fluorescent dye has almost no fluorescent activity in a solution state. When RiboGreen is combined with RNA, its fluorescence is turned on and its activity can be increased by approximately 1000 times. A total of 50 μL of LNP samples were transferred to the centrifuge tube and diluted to 350 μL with 1 × TE buffer solution. The 50 μL dilution of LNPs samples were added into the 96-well plate. A total of 2 μL (100:1 v/v) of Triton X-100 was added, mixed, and incubated at room temperature for 10 min. The RiboGreen reagent was then added to each well, and the fluorescence intensity was measured using a Tecan Spark 10M plate reader (ex, 480 nm; em, 525 nm). If the fluorescence signal value of the sample lysed without Triton X-100 represents the free mRNA content, and the fluorescence signal value of the sample lysed with Triton X-100 represents the total mRNA content, then the encapsulation rate is the ratio of the total mRNA content minus the free mRNA content to the total mRNA content. The raw fluorescence values were subtracted from the background fluorescence, and the total RNA concentration in the LNP formulation was determined according to the standard curve.
3.5. Cell Transfection and Luciferase Expression
HeLa cells were cultured in a DMEM high sugar medium at 37 ℃ in an incubator with 5% CO2. The cells were then seeded into 96-well plates, with a density of 15,000 cells/well. After 24 h, 1 μg of mRNA or LNPs with 1 μg of mRNA were added into each well. The cells were further cultured for 24 h. After lysis using the cell lysis buffer, the cell lysate was transferred into 96-well plates. A total of 20 μL of luciferase substrate was then added, and the bioluminescence signals were further measured. The luciferase intensity data were normalized and compared.
4. Conclusions
In summary, we have used the biorthogonal CuAAC to synthesize a library of triazole-containing ionizable lipids Cp1-n. A cell viability assay demonstrated that the introduction of triazole into ionizable lipid structures was biocompatible. Cp1-n were then further applied in order to prepare LNPs for luciferase mRNA delivery. We showed that LNPs could be easily formed using these triazole-containing ionizable lipids, which had an average size of ~100 nm and a surface potential of +15 mV. Moreover, LNPs formed of Cp1-n could efficiently package luciferase mRNA, with encapsulation rates of ~85%. The mRNA delivery efficacy of Cp1-4-based LNPs was found to be 1.32 times higher than that of SM-102-based LNPs.
Overall, our work provides a facile chemical approach to rapidly prepare triazole-containing ionizable lipids, which are also suitable for LNP preparation and mRNA delivery. Similar bioorthgonal chemistries could also be employed to quickly diversify the ionizable lipid libraries with distinct chemical structures and properties. In the future, we will continue to explore chemical strategies to expand the library of triazole-containing ionizable lipids and elucidate their structure–activity relationships for mRNA delivery.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/molecules28104046/s1, Chemical synthesis and characterization. Figure S1: cytotoxicity of Cp1-n. Table S1: The ratio of reactant. Table S2: The yield of CuAAC reaction.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.X. and Y.Z.; methodology, Y.W.; validation, X.S., Y.F. and D.F.; investigation, Y.W.; data curation, Y.W.; writing—original draft preparation, X.X. and Y.Z.; writing—review and editing, X.X. and Y.Z.; supervision, Y.Z.; project administration, Y.Z.; funding acquisition, X.X. and Y.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20202004, BE2022835), National Natural Science Foundation of China (22225703, 22137003, 21977043).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Sample Availability
Samples of the compounds Cp1-n and SM-102 are available from the authors.
References
- Barbier, A.J.; Jiang, A.Y.; Zhang, P.; Wooster, R.; Anderson, D.G. The clinical progress of mRNA vaccines and immunotherapies. Nat. Biotechnol. 2022, 40, 840–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Zaks, T.; Langer, R.; Dong, Y. Lipid nanoparticles for mRNA delivery. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2021, 6, 1078–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, Y. Lipid Nanoparticle-mRNA Formulations for Therapeutic Applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 2021, 54, 4283–4293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.L.; Wang, Z.G.; Liu, S.L. Lipid Nanoparticles for mRNA Delivery to Enhance Cancer Immunotherapy. Molecules 2022, 27, 5607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eygeris, Y.; Gupta, M.; Kim, J.; Sahay, G. Chemistry of Lipid Nanoparticles for RNA Delivery. Acc. Chem. Res. 2022, 55, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semple, S.C.; Akinc, A.; Chen, J.; Sandhu, A.P.; Mui, B.L.; Cho, C.K.; Sah, D.W.; Stebbing, D.; Crosley, E.J.; Yaworski, E.; et al. Rational design of cationic lipids for siRNA delivery. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.M.; Cheng, Q.; Yu, X.; Liu, S.; Johnson, L.T.; Siegwart, D.J. A Systematic Study of Unsaturation in Lipid Nanoparticles Leads to Improved mRNA Transfection In Vivo. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2021, 60, 5848–5853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, H.; Hatit, M.Z.C.; Zhao, K.; Loughrey, D.; Lokugamage, M.P.; Peck, H.E.; Cid, A.D.; Muralidharan, A.; Kim, Y.; Santangelo, P.J.; et al. Piperazine-derived lipid nanoparticles deliver mRNA to immune cells in vivo. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, M.; Tang, Y.; Chen, J.; Muriph, R.; Ye, Z.; Huang, C.; Evans, J.; Henske, E.P.; Xu, Q. Lung-selective mRNA delivery of synthetic lipid nanoparticles for the treatment of pulmonary lymphangioleiomyomatosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2116271119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilstra, G.; Couture-Senecal, J.; Lau, Y.M.A.; Manning, A.M.; Wong, D.S.M.; Janaeska, W.W.; Wuraola, T.A.; Pang, J.; Khan, O.F. Iterative Design of Ionizable Lipids for Intramuscular mRNA Delivery. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 2294–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, X.Q.; Ho, W.; Li, F.; Gao, M.; Bai, X.; Xu, X. Enzyme-Catalyzed One-Step Synthesis of Ionizable Cationic Lipids for Lipid Nanoparticle-Based mRNA COVID-19 Vaccines. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 18936–18950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prescher, J.A.; Bertozzi, C.R. Chemistry in living systems. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2005, 1, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Favalli, N.; Bassi, G.; Zanetti, T.; Scheuermann, J.; Neri, D. Screening of copper and palladium-mediated reactions compatible with DNA-encoded chemical libraries. Helv. Chim. Acta 2019, 102, e1900033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, W.G.; Green, L.G.; Grynszpan, F.; Radic, Z.; Carlier, P.R.; Taylor, P.; Finn, M.G.; Sharpless, K.B. Click chemistry in situ: Acetylcholinesterase as a reaction vessel for the selective assembly of a femtomolar inhibitor from an array of building blocks. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2002, 41, 1053–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassett, K.J.; Benenato, K.E.; Jacquinet, E.; Lee, A.; Woods, A.; Yuzhakov, O.; Himansu, S.; Deterling, J.; Geilich, B.M.; Ketova, T.; et al. Optimization of Lipid Nanoparticles for Intramuscular Administration of mRNA Vaccines. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2019, 15, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahl, K.; Senn, J.J.; Yuzhakov, O.; Bulychev, A.; Brito, L.A.; Hassett, K.J.; Laska, M.E.; Smith, M.; Almarsson, O.; Thompson, J.; et al. Preclinical and Clinical Demonstration of Immunogenicity by mRNA Vaccines against H10N8 and H7N9 Influenza Viruses. Mol. Ther. 2017, 25, 1316–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belliveau, N.M.; Huft, J.; Lin, P.J.C.; Chen, S.; Leung, A.K.K.; Leaver, T.J.; Wild, A.W.; Lee, J.B.; Taylor, R.J.; Tam, Y.K.; et al. Microfluidic Synthesis of Highly Potent Limit-size Lipid Nanoparticles for In Vivo Delivery of siRNA. Mol. Ther.-Nucleic Acids 2012, 1, e37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Love, K.T.; Chen, Y.; Eltoukhy, A.A.; Kastrup, C.; Sahay, G.; Jeon, A.; Dong, Y.; Whitehead, K.A.; Anderson, D.G. Rapid Discovery of Potent siRNA-Containing Lipid Nanoparticles Enabled by Controlled Microfluidic Formulation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 6948–6951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terada, T.; Kulkarni, J.A.; Huynh, A.; Chen, S.; van der Meel, R.; Tam, Y.Y.C.; Cullis, P.R. Characterization of Lipid Nanoparticles Containing Ionizable Cationic Lipids Using Design-of-Experiments Approach. Langmuir 2021, 37, 1120–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, R.K.; Mattern-Schain, S.I.; Best, M.D.; Kirkpatrick, S.S.; Freeman, M.B.; Grandas, O.H.; Mountain, D.J.H. Improving the efficacy of liposome-mediated vascular gene therapy via lipid surface modifications. J. Surg. Res. 2017, 219, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yezhelyev, M.V.; Qi, L.; O’Regan, R.M.; Nie, S.; Gao, X. Proton-Sponge Coated Quantum Dots for siRNA Delivery and Intracellular Imaging. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 9006–9012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, S.M.; Barman, S.; Basu, A.; Ghatak, T.; Pore, S.K.; Ghosh, S.K.; Mukherjee, R.; Maity, A.R. Amine as a bottom-line functionality on DDS surface for efficient endosomal escape and further subcellular targets. J. Drug. Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 71, 103303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolbers, F.; ter Braak, P.; Le Gac, S.; Luttge, R.; Andersson, H.; Vermes, I.; van den Berg, A. Viability study of HL60 cells in contact with commonly used microchip materials. Electrophoresis 2006, 27, 5073–5080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).