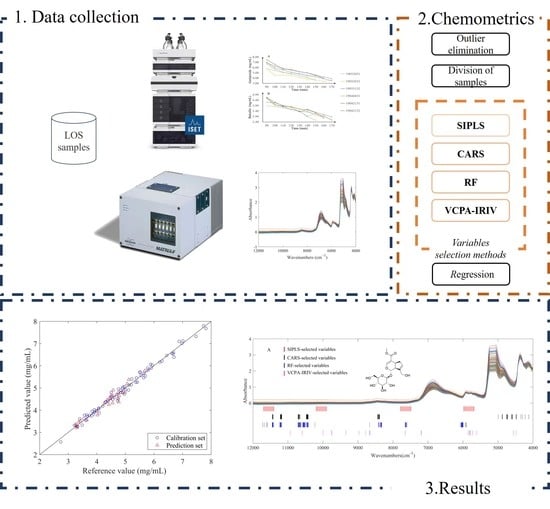
Rapid Determination of Geniposide and Baicalin in Lanqin Oral Solution by Near-Infrared Spectroscopy with Chemometric Algorithms during Alcohol Precipitation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Reference Data Analysis
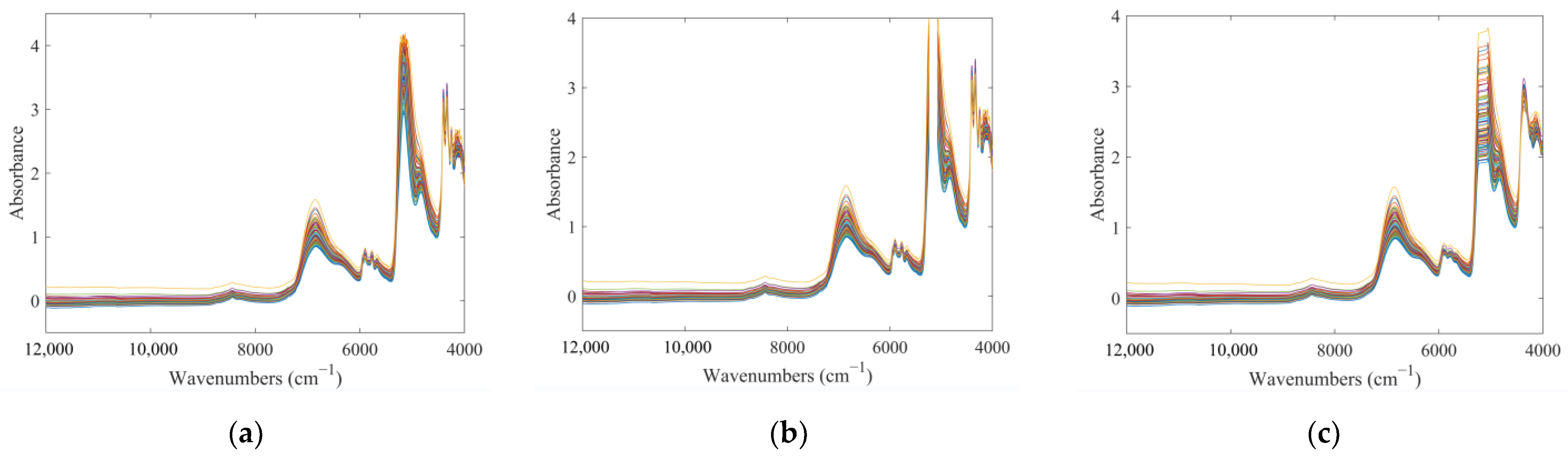
2.2. Raw Spectral Data Analysis
2.3. Division of Samples and Spectral Pre-Treatment
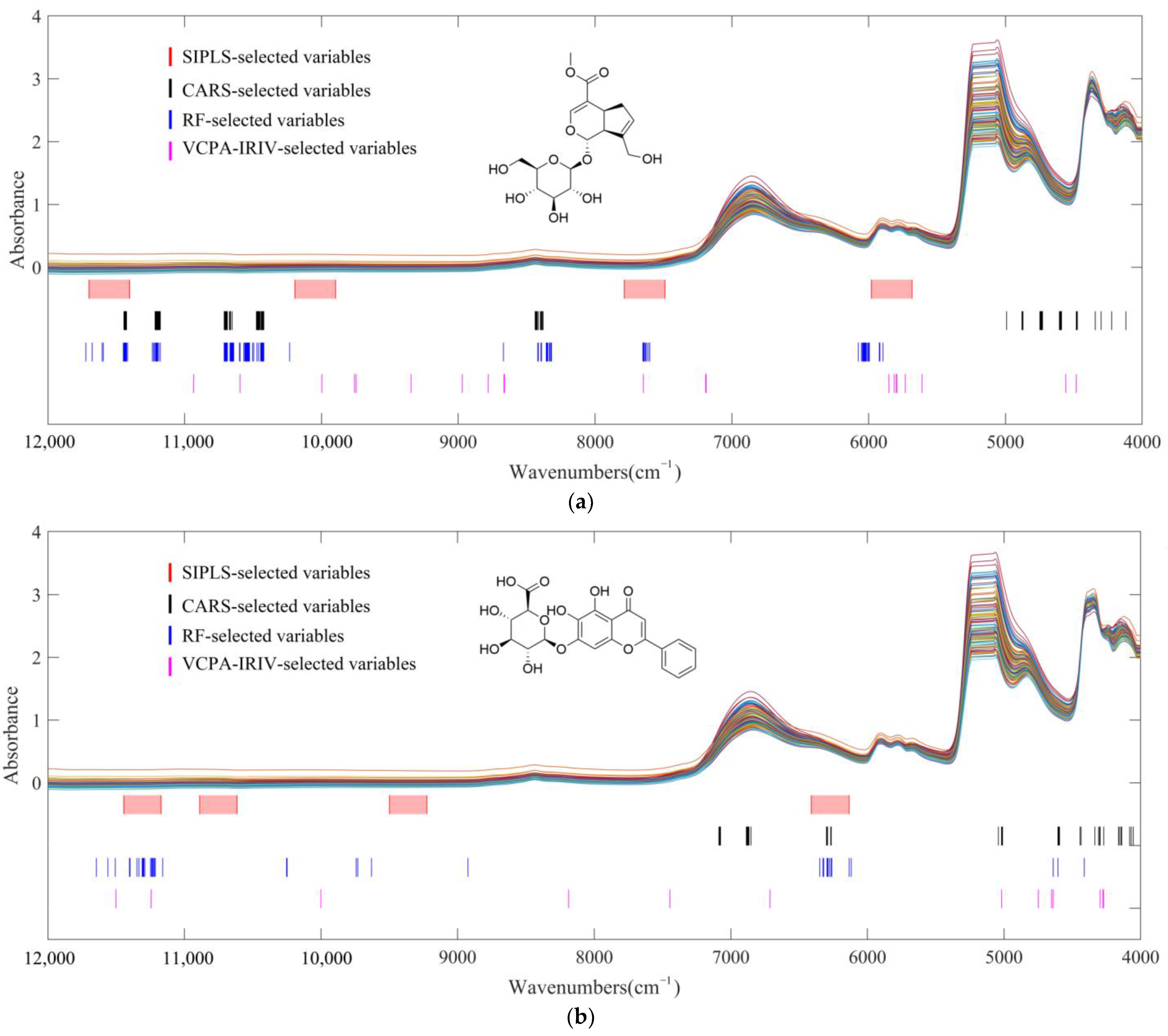
2.4. SIPLS Wavelength Interval Selection Process
2.5. CARS Wavenumber Selection Process
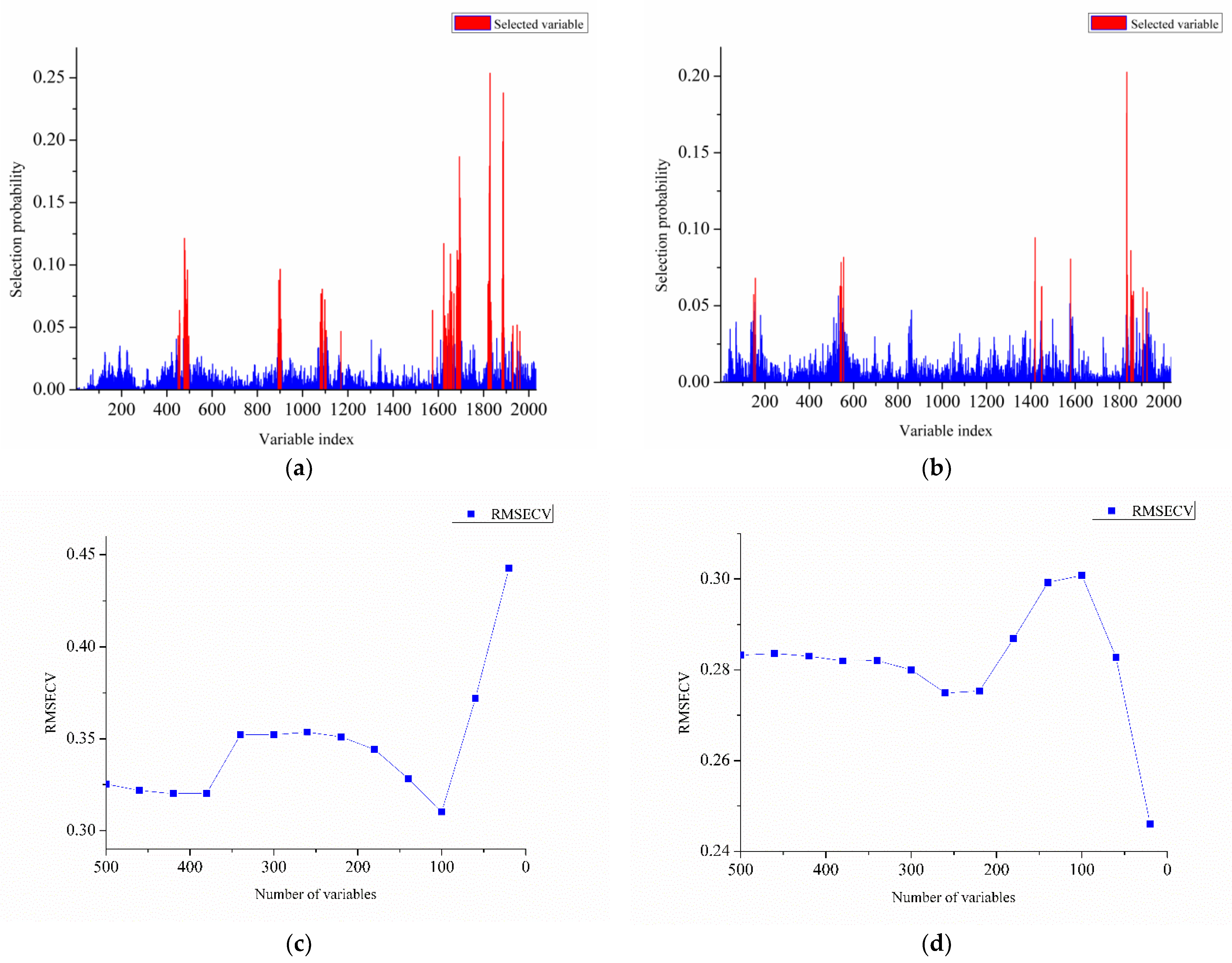
2.6. RF Wavenumber Selection Process
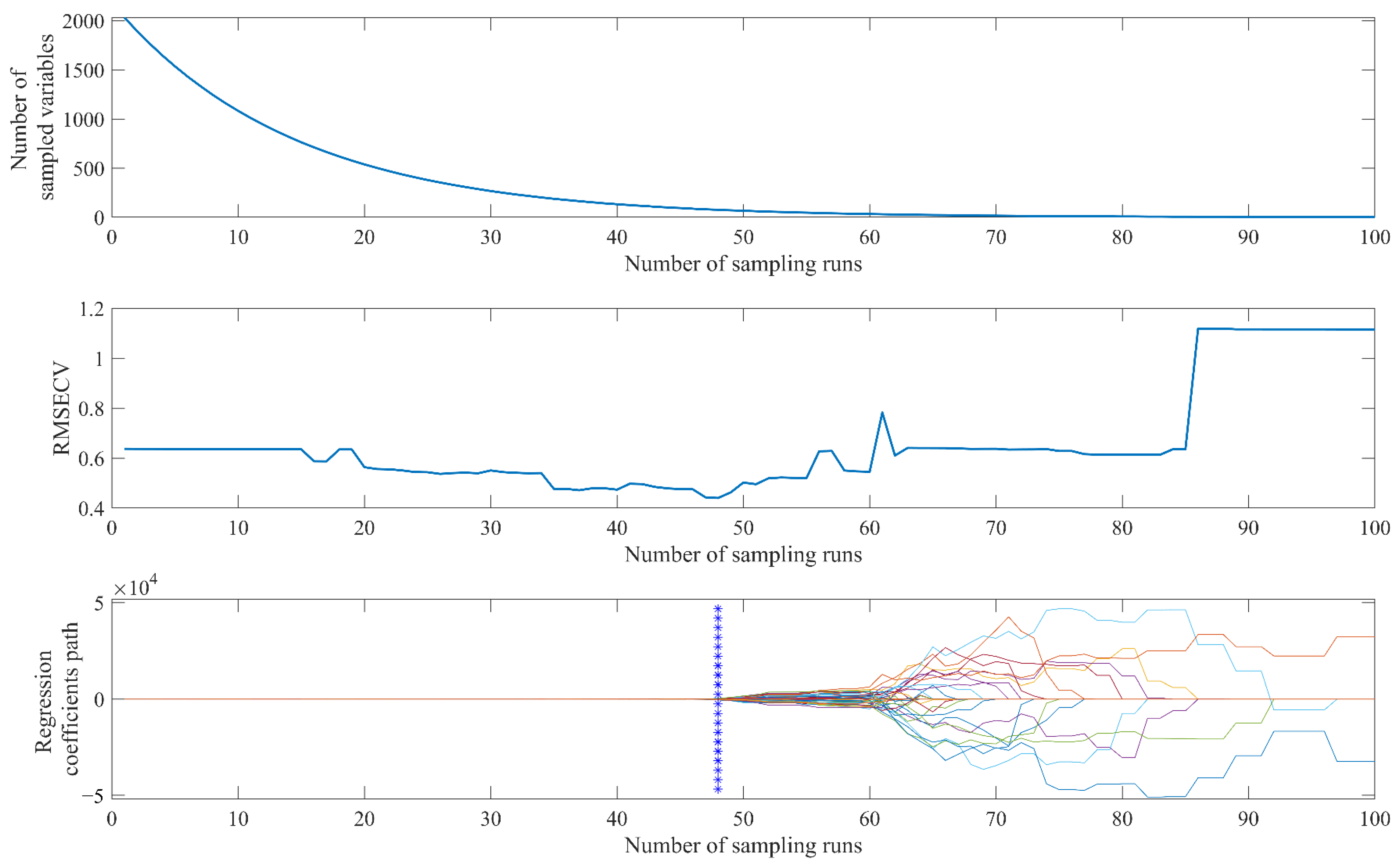
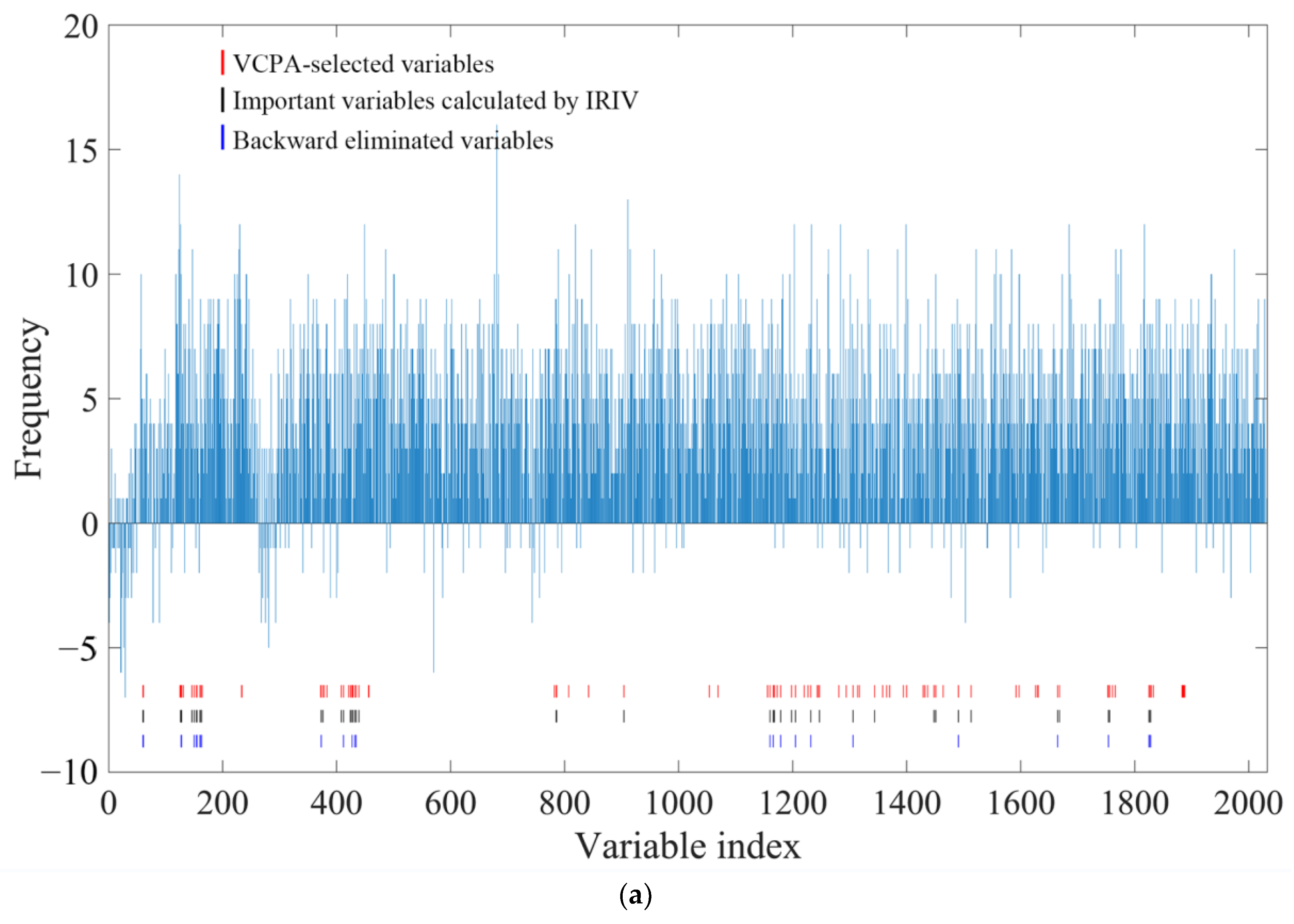
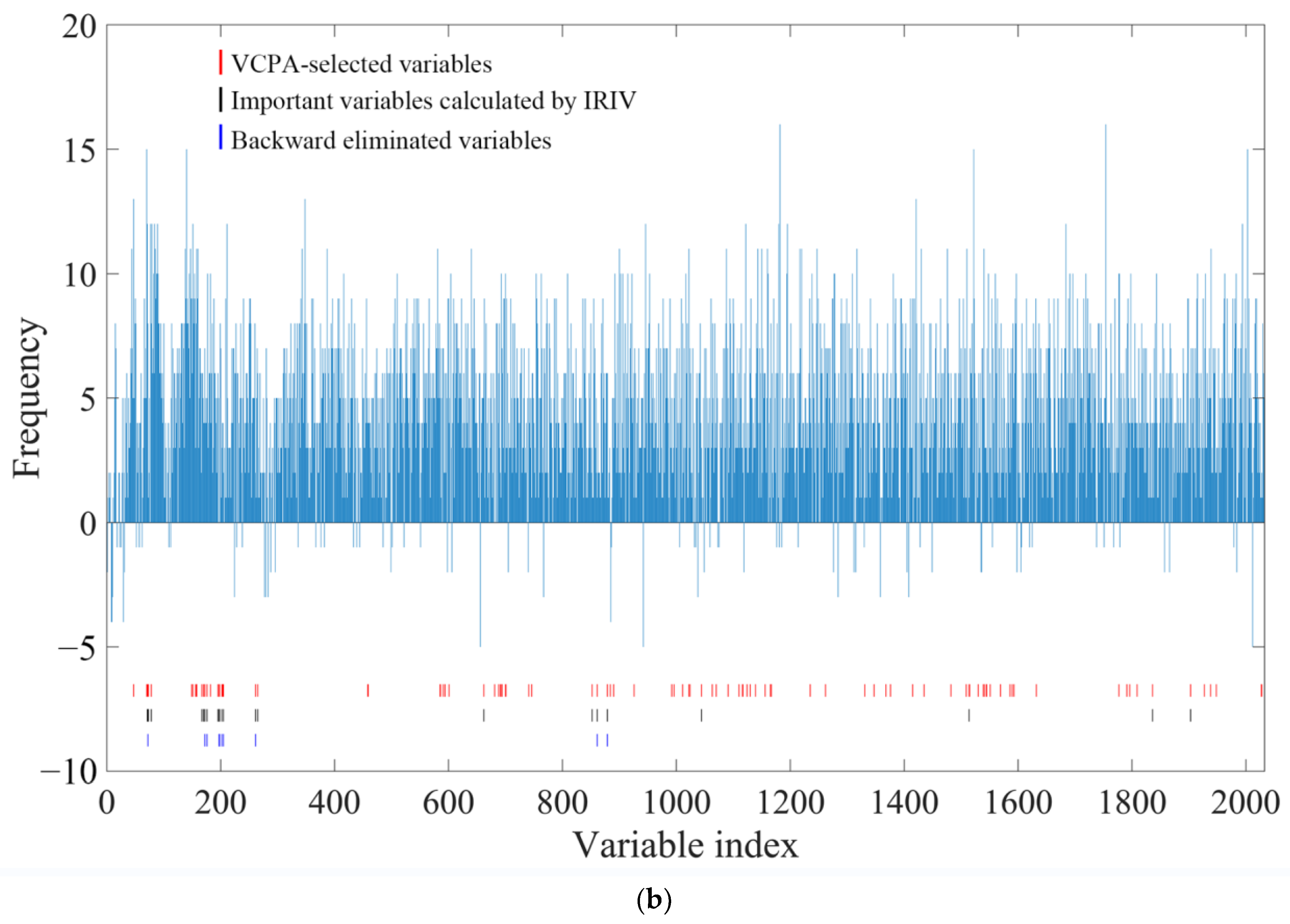
2.7. VCPA-IRIV Wavenumber Selection Process
2.8. Comparison of Different Variable Selection Methods
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Reagents
3.2. Reference Method
3.3. NIR Instrument and Data Acquisition
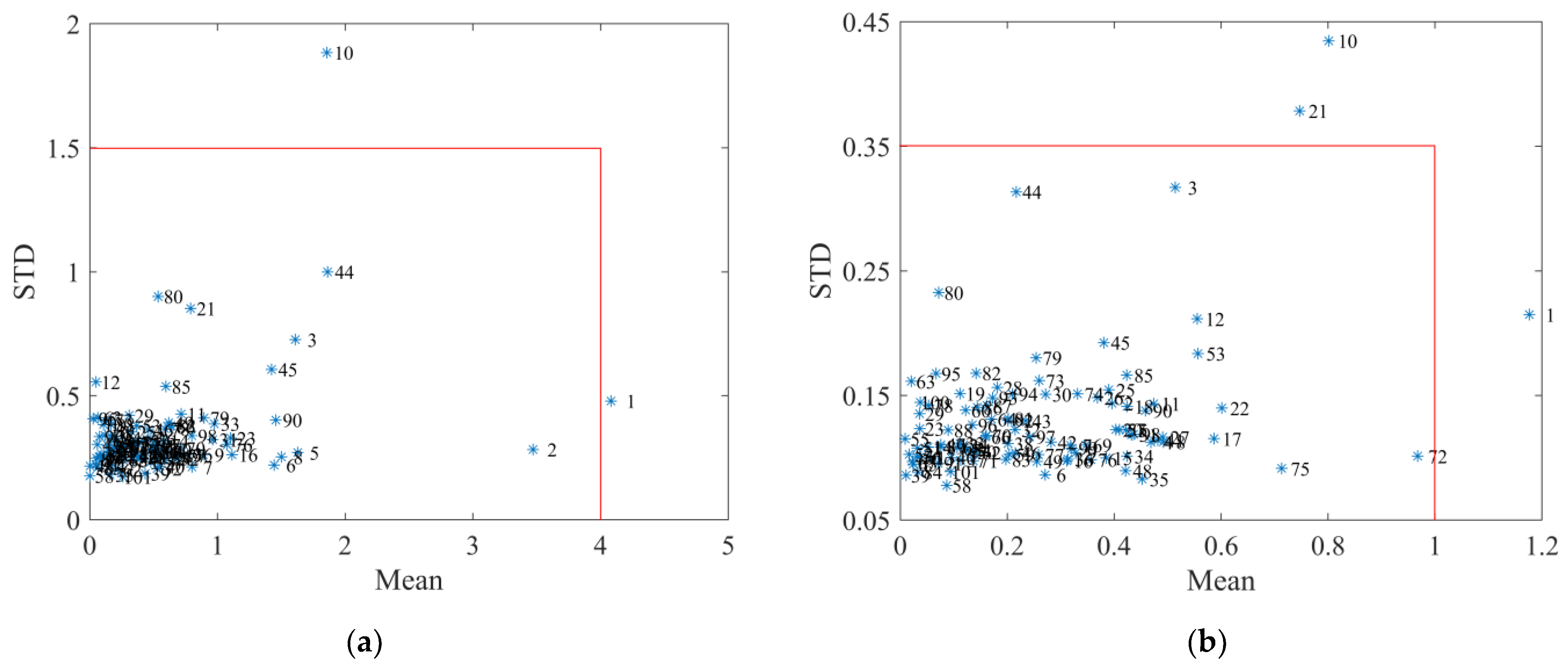
3.4. Outlier Elimination
3.5. Division of Samples and Spectral Preprocessing
3.6. Wavenumber Variables Selection Methods
3.7. PLSR
3.8. Evaluation Criteria of Models
3.9. Software
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Chen, Y.; Chen, M.; Zhang, S.; Ma, H.; Wang, J.; Lu, H.; Wu, Y. Rapid determination of geniposide in the extraction and concentration processes of lanqin oral solution by near-infrared spectroscopy coupled with chemometric algorithms. Vib. Spectrosc. 2020, 107, 103023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Xiao, L.; Xu, D.; Geng, Y.; Liu, X.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Y. Non-Invasive Detection of Anti-Inflammatory Bioactivity and Key Chemical Indicators of the Commercial Lanqin Oral Solution by Near Infrared Spectroscopy. Molecules 2022, 27, 2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, Y.; Shen, J.; Luo, Y.; Qu, H.; Gong, X. Research progress on the ethanol precipitation process of traditional Chinese medicine. Chin. Med. 2020, 15, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henriques, J.; Sousa, J.; Veiga, F.; Cardoso, C.; Vitorino, C. Process analytical technologies and injectable drug products: Is there a future? Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 554, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, X.; Li, L.; Li, H.; Gao, L.; Yuan, X.; Du, H.; Guan, Y.; Zang, H. Multi critical quality attributes monitoring of Chinese oral liquid extraction process with a spectral sensor fusion strategy. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2022, 278, 121317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Han, H.; Cheng, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Qu, H. A feasibility research on the monitoring of traditional Chinese medicine production process using NIR-based multivariate process trajectories. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 231, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, L.; Ni, H.; Pan, D.; Zhang, X.; Xu, F.; Wu, Y.; Bao, L.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, W.; Wu, Y. Nondestructive qualitative and quantitative analysis of Yaobitong capsule using near-infrared spectroscopy in tandem with chemometrics. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2021, 252, 119517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parhizkar, E.; Ghazali, M.; Ahmadi, F.; Sakhteman, A. PLS-LS-SVM based modeling of ATR-IR as a robust method in detection and qualification of alprazolam. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2017, 173, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Huang, Q.; Lin, Z.; Tan, C. Detection of adulterants in medicinal products by infrared spectroscopy and ensemble of window extreme learning machine. Microchem. J. 2022, 173, 107009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boido, E.; Fariña, L.; Carrau, F.; Cozzolino, D.; Dellacassa, E. Application of near-infrared spectroscopy/artificial neural network to quantify glycosylated norisoprenoids in Tannat grapes. Food Chem. 2022, 387, 132927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Fernández, J.; Moya, D.; Dolors Benaiges, M.; Valero, F.; Alcalà, M. Near Infrared Spectroscopy: A useful technique for inline monitoring of the enzyme catalyzed biosynthesis of third-generation biodiesel from waste cooking oil. Fuel 2022, 319, 123794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scappaticci, C.; Spera, S.; Biancolillo, A.; Marini, F. Detection and Quantification of Alprazolam Added to Long Drinks by Near Infrared Spectroscopy and Chemometrics. Molecules 2022, 27, 6420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahir, S.; Omar, A.; Jamlos, M.; Azmi, M.; Muncan, J. A review of visible and near-infrared (Vis-NIR) spectroscopy application in plant stress detection. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2022, 338, 113468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, R.; Ribeiro, D.; Santos, J.; Páscoa, R. Comparison of near infrared spectroscopy and Raman spectroscopy for the identification and quantification through MCR-ALS and PLS of peanut oil adulterants. Talanta 2021, 230, 122373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, L.; Lin, Z.; Chen, J.; Wu, Y.; Liu, X. Mid-infrared and near-infrared spectroscopy for rapid detection of Gardeniae Fructus by a liquid-liquid extraction process. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 145, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, N.; Chen, J.; Pan, T.; Yao, L.; Han, Y.; Yu, J. Near-infrared spectroscopy combined with equidistant combination partial least squares applied to multi-index analysis of corn. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2016, 76, 648–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosas, J.G.; Blanco, M.; González, J.M.; Alcalà, M. Real-time determination of critical quality attributes using near-infrared spectroscopy: A contribution for Process Analytical Technology (PAT). Talanta 2012, 97, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Li, W.; Liu, X.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, W.; Chen, Y. Determination of geographical origin and icariin content of Herba Epimedii using near infrared spectroscopy and chemometrics. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2018, 191, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, Y.; Li, H.; Deng, B.; Cao, D. An overview of variable selection methods in multivariate analysis of near-infrared spectra. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 113, 102–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.; Ning, J.; Zhang, Z. Intelligent assessment of tea quality employing visible-near infrared spectra combined with a hybrid variable selection strategy. Microchem. J. 2020, 157, 105085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Peng, Y.; Pei, Y.; Zeng, J.; Shen, H.; Cao, J.; Qiao, Y.; Wu, Z. Systematic discovery about NIR spectral assignment from chemical structural property to natural chemical compounds. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, D.; Sun, L.; Zou, B.; Zhang, Q.; Tan, W.; Che, W. Non-destructive prediction of protein content in wheat using NIRS. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2018, 189, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, C.; Sun, L.; Bai, H.; Liu, Y.; Yang, J.; Wang, X. Quantitative detection of azodicarbonamide in wheat flour by near-infrared spectroscopy based on two-step feature selection. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2021, 219, 104445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Sun, S.; Tan, Z.; Liu, Y. Nondestructive detection of sunset yellow in cream based on near-infrared spectroscopy and interval random forest. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2020, 242, 118718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leardi, R.; Nørgaard, L. Sequential application of backward interval partial least squares and genetic algorithms for the selection of relevant spectral regions. J. Chemom. 2004, 18, 486–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liang, Y.; Xu, Q.; Cao, D. Key wavelengths screening using competitive adaptive reweighted sampling method for multivariate calibration. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 648, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xu, Q.; Liang, Y. Random frog: An efficient reversible jump Markov Chain Monte Carlo-like approach for variable selection with applications to gene selection and disease classification. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 740, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, Y.; Wang, W.; Tan, M.; Liang, Y.; Li, H.; Cao, D.; Lu, H.; Xu, Q. A strategy that iteratively retains informative variables for selecting optimal variable subset in multivariate calibration. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 807, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, Y.; Bin, J.; Liu, D.; Xu, L.; Yan, T.; Cao, D.; Xu, Q. A hybrid variable selection strategy based on continuous shrinkage of variable space in multivariate calibration. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1058, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Han, X.; Yu, J.; Feng, Y.; Chu, G. Rapid prediction method of α-Glycosidase inhibitory activity of Coreopsis tinctoria extract from different habitats by near infrared spectroscopy. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2022, 268, 120601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
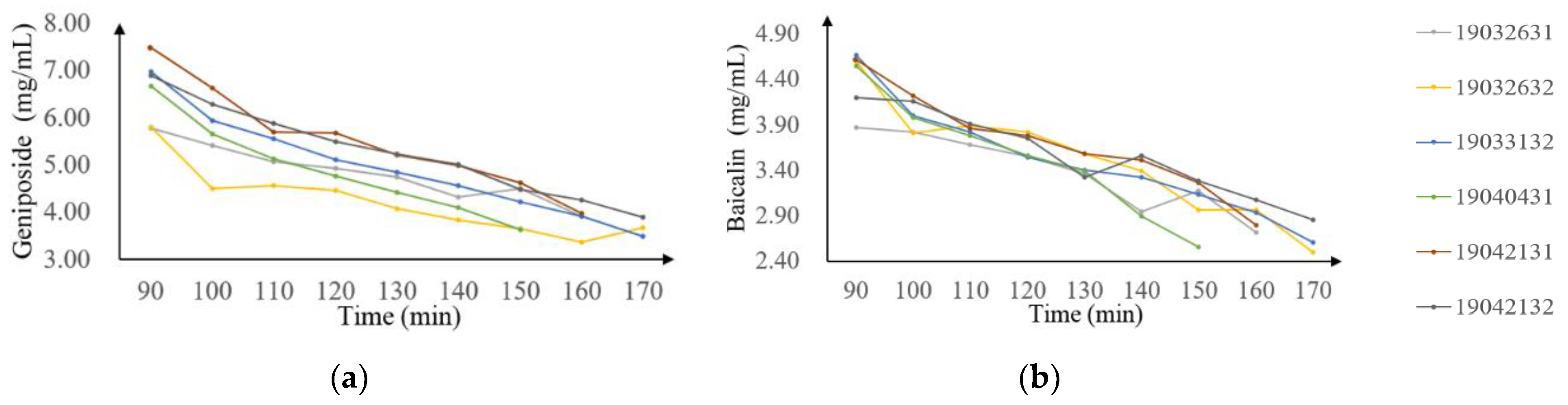
| Data Sets | Sample Number | Minimum Concentration (mg/mL) | Maximum Concentration (mg/mL) | Mean | STD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Geniposide | Calibration set | 74 | 2.738 | 7.819 | 4.965 | 1.183 |
| Prediction set | 25 | 3.265 | 5.675 | 4.352 | 0.6560 | |
| Baicalin | Calibration set | 74 | 1.763 | 4.722 | 3.339 | 0.7525 |
| Prediction set | 25 | 2.017 | 4.610 | 3.167 | 0.6825 | |
| Pretreatment | LVs 1 | Rcv | RMSECV 2 | RPDCV |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. Models for geniposide | ||||
| Raw | 6 | 0.9032 | 0.5045 | 2.33 |
| Normalization | 7 | 0.9020 | 0.5074 | 2.32 |
| SNV | 9 | 0.8962 | 0.5213 | 2.25 |
| SG smoothing | 10 | 0.9151 | 0.4740 | 2.48 |
| MSC | 9 | 0.8902 | 0.5354 | 2.20 |
| B. Models for baicalin | ||||
| Raw | 5 | 0.8847 | 0.3484 | 2.15 |
| Normalization | 6 | 0.9121 | 0.3064 | 2.44 |
| SNV | 7 | 0.8990 | 0.3273 | 2.28 |
| SG smoothing | 10 | 0.9187 | 0.2951 | 2.53 |
| MSC | 4 | 0.8960 | 0.3319 | 2.25 |
| NI 1 | NV 2 | LVs | Rcv | RMSECV | RPDCV | NV | LVs | Rcv | RMSECV | RPDCV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. models for geniposide | B. models for baicalin | |||||||||
| 10 | 812 | 10 | 0.9630 | 0.3169 | 3.71 | 812 | 9 | 0.9208 | 0.2916 | 2.56 |
| 11 | 739 | 10 | 0.9638 | 0.3134 | 3.75 | 739 | 8 | 0.9140 | 0.3031 | 2.47 |
| 12 | 676 | 10 | 0.9692 | 0.2896 | 4.06 | 677 | 10 | 0.9119 | 0.3067 | 2.44 |
| 13 | 624 | 10 | 0.9667 | 0.3008 | 3.91 | 625 | 10 | 0.9264 | 0.2815 | 2.66 |
| 14 | 580 | 10 | 0.9656 | 0.3055 | 3.85 | 580 | 10 | 0.9219 | 0.2896 | 2.58 |
| 15 | 541 | 10 | 0.9652 | 0.3074 | 3.82 | 540 | 8 | 0.9174 | 0.2974 | 2.51 |
| 16 | 508 | 10 | 0.9762 | 0.2549 | 4.61 | 508 | 10 | 0.9212 | 0.2908 | 2.57 |
| 17 | 478 | 10 | 0.9657 | 0.3053 | 3.85 | 477 | 10 | 0.9261 | 0.2820 | 2.65 |
| 18 | 451 | 10 | 0.9702 | 0.2846 | 4.13 | 451 | 10 | 0.9317 | 0.2714 | 2.75 |
| 19 | 427 | 10 | 0.9673 | 0.2982 | 3.94 | 428 | 10 | 0.9299 | 0.2748 | 2.72 |
| 20 | 407 | 10 | 0.9670 | 0.2993 | 3.93 | 406 | 10 | 0.9199 | 0.2931 | 2.55 |
| 21 | 388 | 10 | 0.9697 | 0.2869 | 4.10 | 386 | 8 | 0.9324 | 0.2701 | 2.77 |
| 22 | 369 | 10 | 0.9687 | 0.2916 | 4.03 | 369 | 9 | 0.9293 | 0.2761 | 2.71 |
| 23 | 353 | 10 | 0.9681 | 0.2945 | 3.99 | 353 | 9 | 0.9322 | 0.2706 | 2.76 |
| 24 | 338 | 10 | 0.9740 | 0.2664 | 4.41 | 339 | 9 | 0.9299 | 0.2748 | 2.72 |
| 25 | 324 | 10 | 0.9715 | 0.2786 | 4.22 | 325 | 9 | 0.9390 | 0.2570 | 2.91 |
| 26 | 312 | 10 | 0.9783 | 0.2436 | 4.83 | 312 | 9 | 0.9350 | 0.2651 | 2.82 |
| 27 | 300 | 10 | 0.9717 | 0.2775 | 4.24 | 300 | 9 | 0.9401 | 0.2548 | 2.93 |
| 28 | 291 | 10 | 0.9755 | 0.2588 | 4.54 | 289 | 9 | 0.9402 | 0.2546 | 2.93 |
| 29 | 280 | 10 | 0.9700 | 0.2857 | 4.11 | 280 | 8 | 0.9380 | 0.2591 | 2.88 |
| 30 | 271 | 10 | 0.9708 | 0.2817 | 4.17 | 270 | 10 | 0.9353 | 0.2644 | 2.83 |
| Variables Selection Methods | Number of Variables | LVs | Rcv | RMSECV | RPDCV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. Models for geniposide | |||||
| Global | 2032 | 10 | 0.9151 | 0.4740 | 2.48 |
| SIPLS | 312 | 10 | 0.9783 | 0.2436 | 4.83 |
| CARS | 76 | 9 | 0.9729 | 0.2716 | 4.33 |
| RF | 100 | 10 | 0.9645 | 0.3103 | 3.79 |
| VCPA-IRIV | 21 | 10 | 0.9883 | 0.1793 | 6.56 |
| B. Models for baicalin | |||||
| Global | 2032 | 10 | 0.9187 | 0.2951 | 2.53 |
| SIPLS | 289 | 9 | 0.9402 | 0.2546 | 2.93 |
| CARS | 38 | 10 | 0.9382 | 0.2586 | 2.89 |
| RF | 20 | 9 | 0.9452 | 0.2441 | 3.06 |
| VCPA-IRIV | 13 | 10 | 0.9502 | 0.2329 | 3.21 |
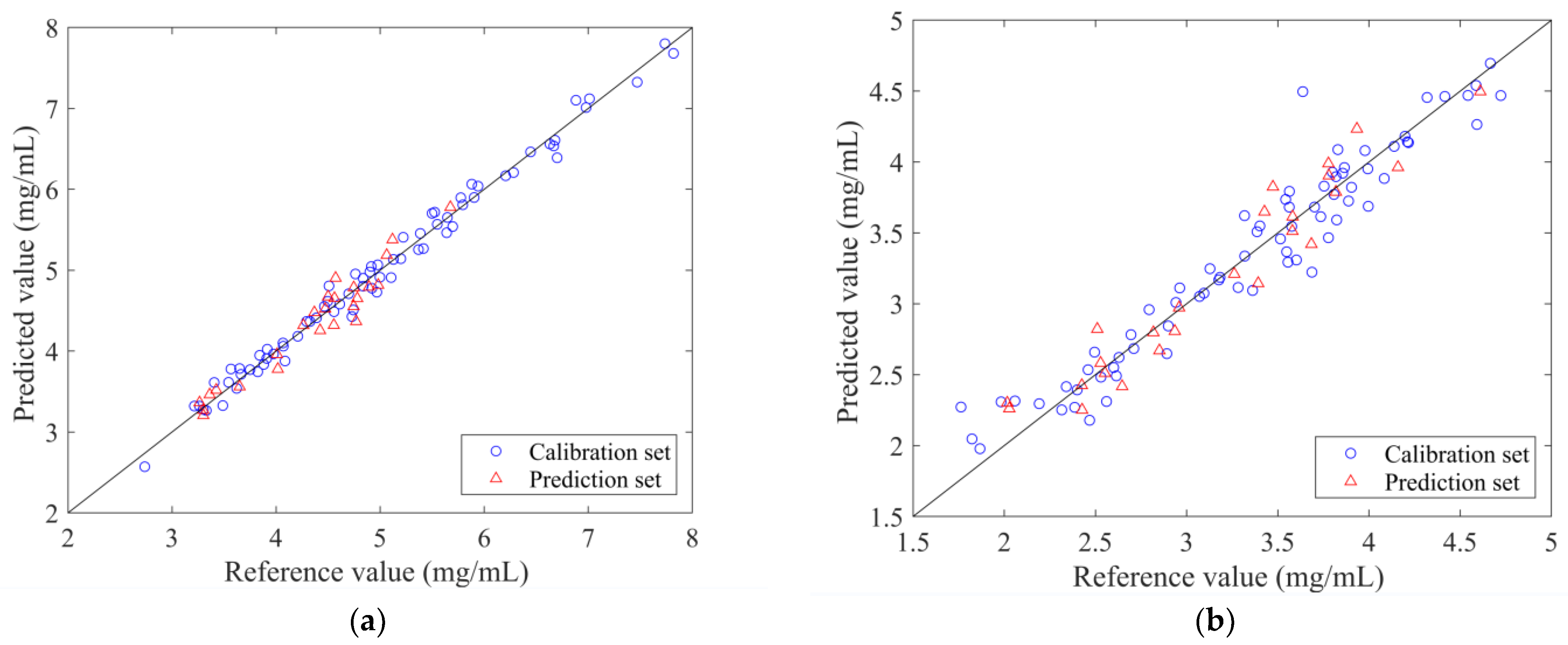
| Analytes | LVs | Rc 1 | RMSEC | RSEC 2 | RPDC 3 | Rp 4 | RMSEP | RSEP 5 | RPDP 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Geniposide | 10 | 0.9939 | 0.1297 | 2.54% | 9.06 | 0.9654 | 0.1676 | 3.81% | 3.84 |
| Baicalin | 10 | 0.9629 | 0.2018 | 5.90% | 3.70 | 0.9597 | 0.1880 | 5.81% | 3.57 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, H.; Chen, M.; Zhang, S.; Pan, H.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Y. Rapid Determination of Geniposide and Baicalin in Lanqin Oral Solution by Near-Infrared Spectroscopy with Chemometric Algorithms during Alcohol Precipitation. Molecules 2023, 28, 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010004
Ma H, Chen M, Zhang S, Pan H, Chen Y, Wu Y. Rapid Determination of Geniposide and Baicalin in Lanqin Oral Solution by Near-Infrared Spectroscopy with Chemometric Algorithms during Alcohol Precipitation. Molecules. 2023; 28(1):4. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010004
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Hui, Ming Chen, Siyu Zhang, Hongye Pan, Yong Chen, and Yongjiang Wu. 2023. "Rapid Determination of Geniposide and Baicalin in Lanqin Oral Solution by Near-Infrared Spectroscopy with Chemometric Algorithms during Alcohol Precipitation" Molecules 28, no. 1: 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010004
APA StyleMa, H., Chen, M., Zhang, S., Pan, H., Chen, Y., & Wu, Y. (2023). Rapid Determination of Geniposide and Baicalin in Lanqin Oral Solution by Near-Infrared Spectroscopy with Chemometric Algorithms during Alcohol Precipitation. Molecules, 28(1), 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010004