Protection-Free Strategy for the Synthesis of Boro-Depsipeptides in Aqueous Media under Microwave-Assisted Conditions
Abstract
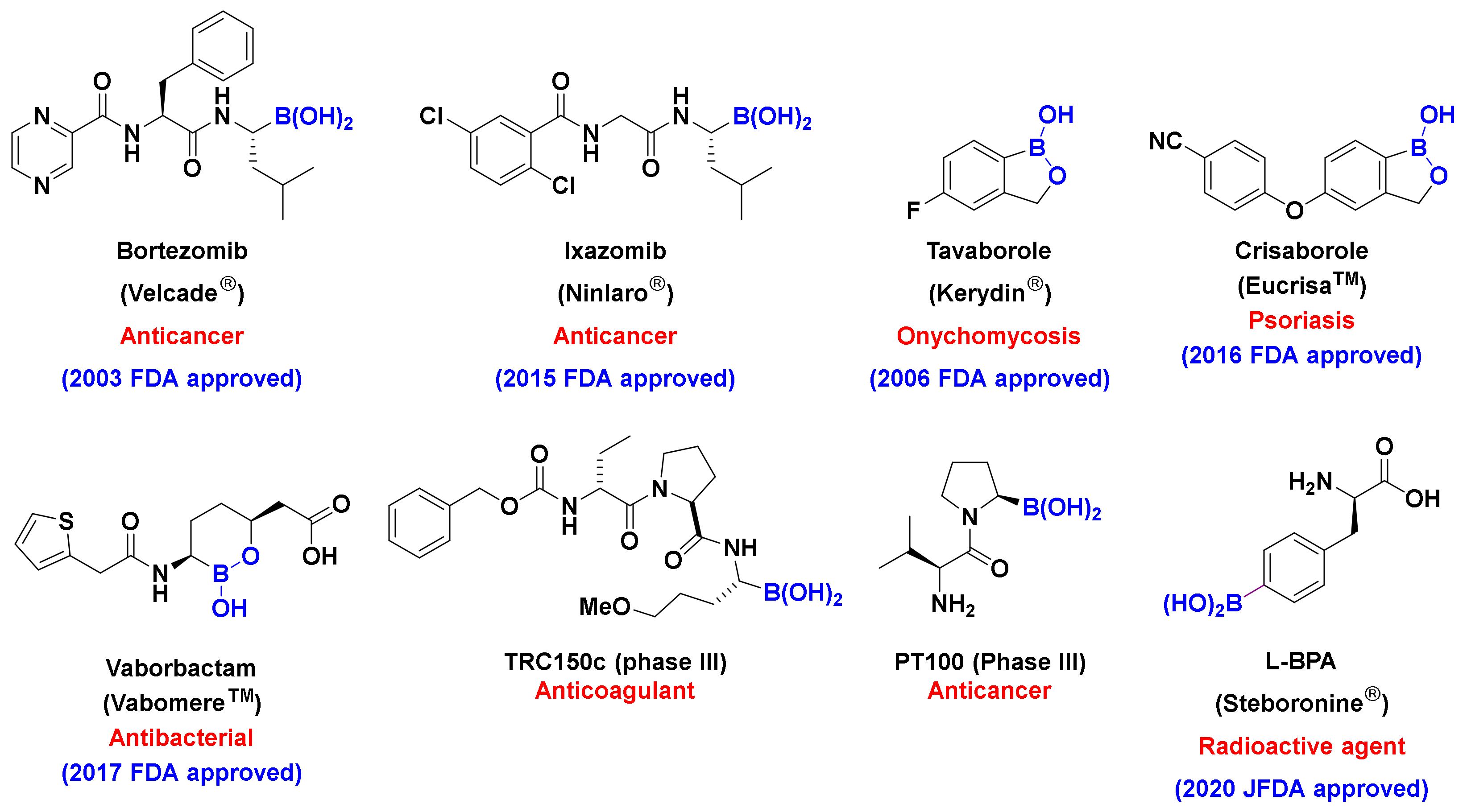
:1. Introduction
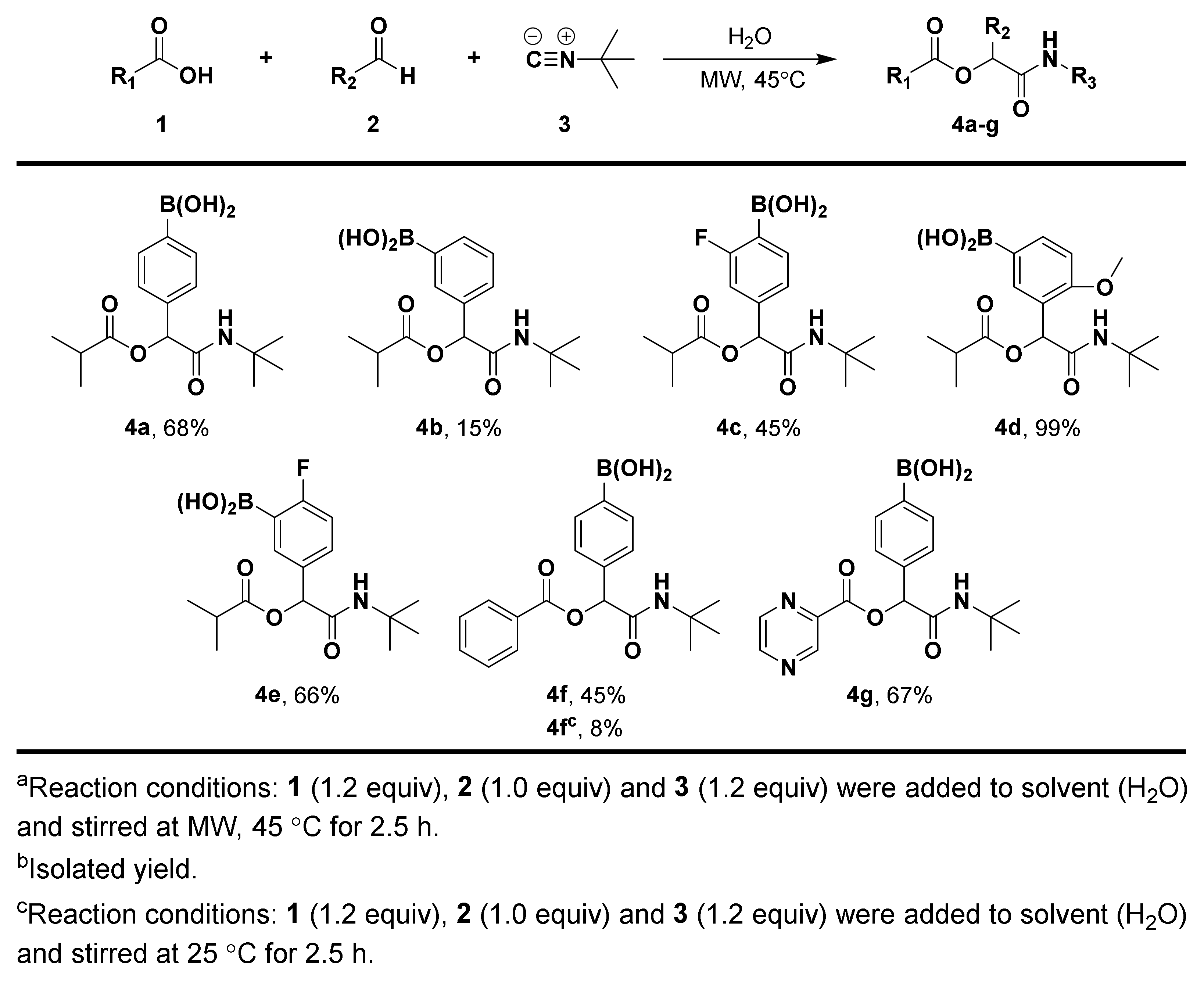
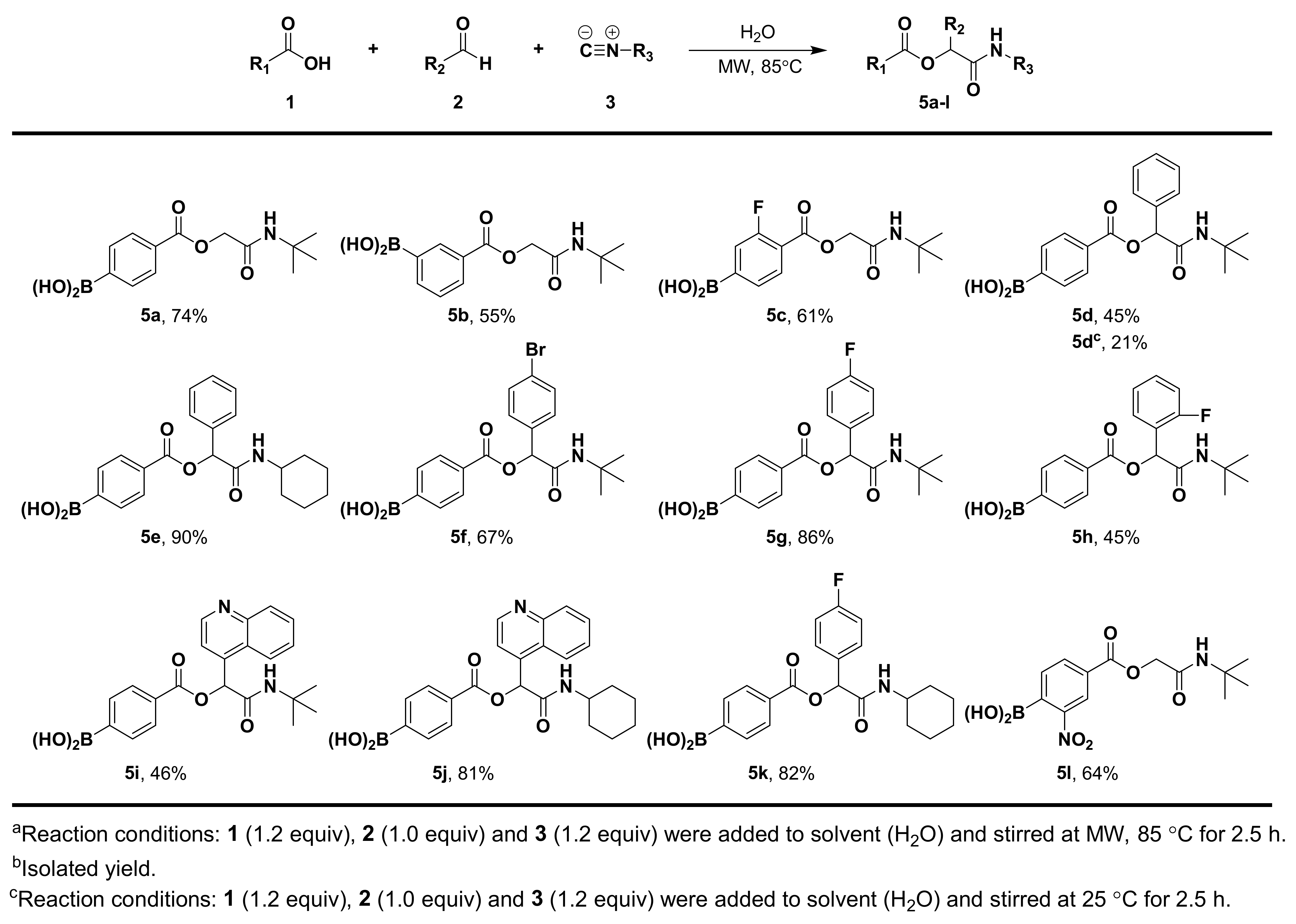
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemistry
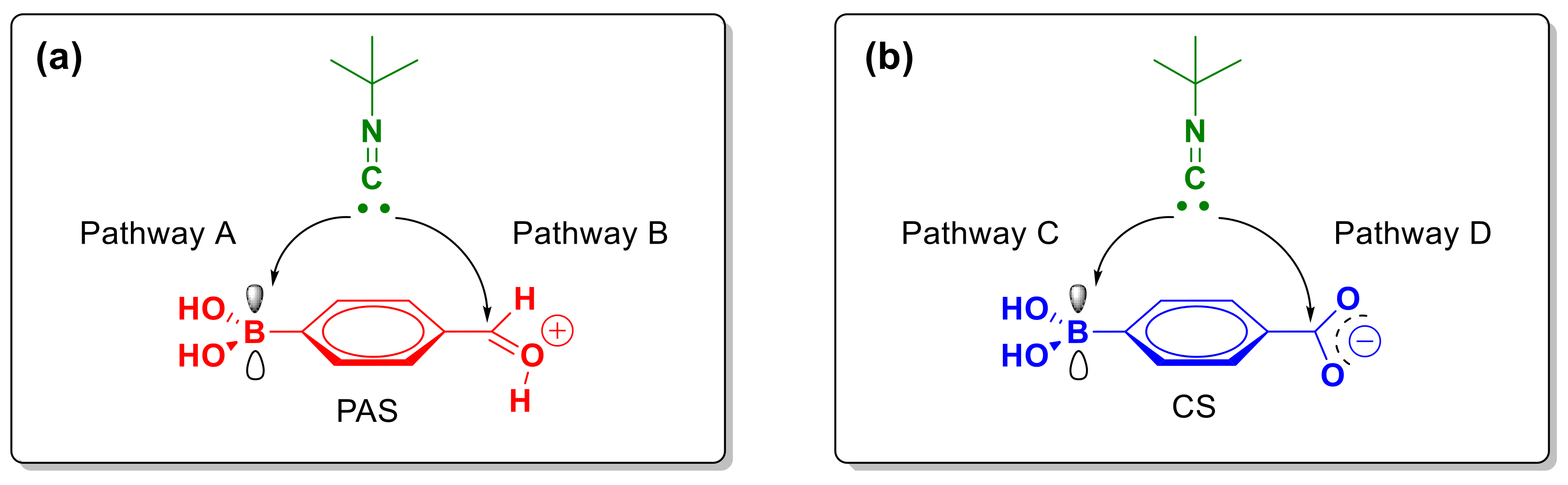
2.2. Theoretical Calculations
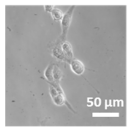
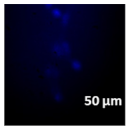
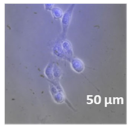
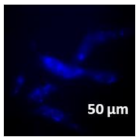
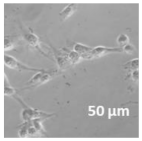
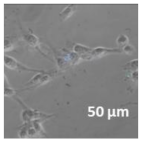
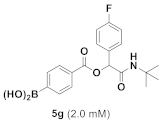
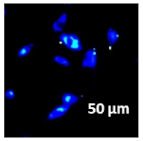
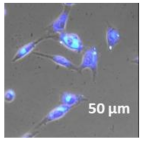
2.3. In Vitro Studies
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemistry
3.1.1. General Information
3.1.2. Spectroscopic Measurements
3.1.3. General Procedure for Compound 4a–g
3.1.4. Synthesis and Characterization of Compound 4a–g
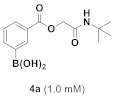
(4-(2-(Tert-Butylamino)-1-(Isobutyryloxy)-2-Oxoethyl)phenyl)boronic Acid (4a)
(3-(2-(Tert-Butylamino)-1-(Isobutyryloxy)-2-Oxoethyl)phenyl)boronic Acid (4b)
(4-(2-(Tert-Butylamino)-1-(Isobutyryloxy)-2-Oxoethyl)-2-Fluorophenyl)boronic Acid (4c)
(3-(2-(Tert-Butylamino)-1-(Isobutyryloxy)-2-Oxoethyl)-4-Methoxyphenyl)boronic Acid (4d)
(5-(2-(Tert-Butylamino)-1-(Isobutyryloxy)-2-Oxoethyl)-2-Fluorophenyl)boronic Acid (4e)
(4-(1-(Benzoyloxy)-2-(Tert-Butylamino)-2-Oxoethyl)phenyl)boronic Acid (4f)
(4-(2-(Tert-Butylamino)-2-oxo-1-((pyrazine-2-Carbonyl)oxy)ethyl)phenyl)boronic Acid (4g)
3.1.5. General Procedure for Compound 5a–l
3.1.6. Synthesis and Characterization of Compound 5a–l
(4-((2-(Tert-Butylamino)-2-Oxoethoxy)carbonyl)phenyl)boronic Acid (5a)
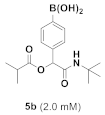
(3-((2-(Tert-Butylamino)-2-Oxoethoxy)carbonyl)phenyl)boronic Acid (5b)
(4-((2-(Tert-Butylamino)-2-Oxoethoxy)carbonyl)-3-Fluorophenyl)boronic Acid (5c)
(4-((2-(Tert-Butylamino)-2-Oxo-1-Phenylethoxy)carbonyl)phenyl)boronic Acid (5d)
(4-((2-(Cyclohexylamino)-2-Oxo-1-Phenylethoxy)carbonyl)phenyl)boronic Acid (5e)
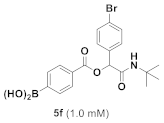
(4-((1-(4-Bromophenyl)-2-(Tert-Butylamino)-2-Oxoethoxy)carbonyl)phenyl)boronic Acid (5f)
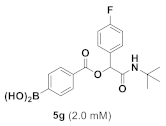
(4-((2-(Tert-Butylamino)-1-(4-Fluorophenyl)-2-Oxoethoxy)carbonyl)phenyl)boronic Acid (5g)
(4-((2-(Tert-Butylamino)-1-(2-Fluorophenyl)-2-Oxoethoxy)carbonyl)phenyl)boronic Acid (5h)
(4-((2-(Tert-Butylamino)-2-Oxo-1-(Quinolin-4-yl)ethoxy)carbonyl)phenyl)boronic Acid (5i)
(4-((2-(Cyclohexylamino)-2-Oxo-1-(Quinolin-4-yl)ethoxy)carbonyl)phenyl)boronic Acid (5j)
(4-((2-(Cyclohexylamino)-1-(4-Fluorophenyl)-2-Oxoethoxy)carbonyl)phenyl)boronic Acid (5k)
(4-((2-(Tert-Butylamino)-2-Oxoethoxy)carbonyl)-2-Nitrophenyl)boronic Acid (5l)
3.2. Cell Line and Cell Culture
3.3. Toxicity Analysis
3.4. Cellular Bio-Distribution
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Bull, S.; Davidson, M.; van den Elsen, J.; Fossey, J.; Jenkins, A.; Jiang, Y.; Kubo, Y.; Marken, F.; Sakurai, K.; Zhao, J.; et al. Exploiting the Reversible Covalent Bonding of Boronic Acids: Recognition, Sensing, and Assembly. Acc. Chem. Res. 2012, 46, 312–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molander, G.A.; Trice, S.L.; Tschaen, B. A modified procedure for the palladium catalyzed borylation/Suzuki-Miyaura cross-coupling of aryl and heteroaryl halides utilizing bis-boronic acid. Tetrahedron 2015, 71, 5758–5764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Bian, C.; Zhong, Y.; Jing, X. The thermal stability and pyrolysis mechanism of boron-containing phenolic resins: The effect of phenyl borates on the char formation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 331, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messersmith, R.E.; Siegler, M.A.; Tovar, J.D. Aromaticity Competition in Differentially Fused Borepin-Containing Polycyclic Aromatics. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 81, 5595–5605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, S.J.; Ding, C.Z.; Akama, T.; Zhang, Y.-K.; Hernandez, V.; Xia, Y. Therapeutic potential of boron-containing compounds. Future. Med. Chem. 2009, 1, 1275–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smoum, R.; Rubinstein, A.; Dembitsky, V.M.; Srebnik, M. Boron Containing Compounds as Protease Inhibitors. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 4156–4220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correy, G.J.; Zaidman, D.; Harmelin, A.; Carvalho, S.; Mabbitt, P.D.; Calaora, V.; James, P.J.; Kotze, A.C.; Jackson, C.J.; London, N. Overcoming insecticide resistance through computational inhibitor design. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 21012–21021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, Y.; Nair, S. Proteases in cardiometabolic diseases: Pathophysiology, molecular mechanisms and clinical applications. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2015, 1852, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molander, G.A.; Ellis, N. Organotrifluoroborates: Protected Boronic Acids That Expand the Versatility of the Suzuki Coupling Reaction. Acc. Chem. Res. 2007, 40, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, R.-C.; Lin, M.-H.; Liao, P.-H.; Fu, J.-J.; Wu, M.-J.; Wu, Y.-C.; Chang, F.-R.; Wu, C.-C.; Pan, P.-S. Direct synthesis of the arylboronic acid analogues of phenylglycine via microwave-assisted four-component Ugi reaction. Tetrahedron 2014, 70, 1800–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Ornelas, D.E.; Sola-Llano, R.; Bañuelos, J.; Arbeloa, I.L.; Martínez-Álvarez, J.A.; Mora-Montes, H.M.; Franco, B.; PeñaCabrera, E. Synthesis, Photophysical Study, and Biological Application Analysis of Complex Borondipyrromethene Dyes. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 7783–7797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neochoritis, C.G.; Zarganes-Tzitzikas, T.; Novotná, M.; Mitríková, T.; Wang, Z.; Kurpiewska, K.; Kalinowska-Tłuścik, J.; Dömling, A. Isocyanide-Based Multicomponent Reactions of Free Phenylboronic Acids. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2019, 35, 6132–6137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, C.-C.; Liu, P.-Y.; Lin, C.-H.; Chen, H.-C.; Wu, Y.-C.; Chang, F.-R.; Pan, P.-S. Efficient Synthesis of Boron-Containing α-Acyloxyamide Analogs via Microwave Irradiation. Molecules 2013, 18, 9488–9511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barth, R.F.; Coderre, J.A.; Vicente, M.G.H.; Blue, T.E. Boron neutron capture therapy of cancer: Current status and future prospects. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 3987–4002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barth, R.F.; Mi, P.; Yang, W. Boron delivery agents for neutron capture therapy of cancer. Cancer Commun. 2018, 38, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hattori, Y.; Ishimura, M.; Ohta, Y.; Takenaka, H.; Watanabe, T.; Tanaka, H.; Ono, K.; Kirihata, M. Detection of boronic acid derivatives in cells using a fluorescent sensor. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2015, 13, 6927–6930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, H.; Sakurai, Y.; Suzuki, M.; Masunaga, S.-I.; Takamiya, K.; Maruhashi, A.; Ono, K. Development of a simple and rapid method of precisely identifying the position of 10B atoms in tissue: An improvement in standard alpha autoradiography. J. Radiat. Res. 2013, 55, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hattori, Y.; Kusaka, S.; Mukumoto, M.; Uehara, K.; Asano, T.; Suzuki, M.; Masunaga, S.-I.; Ono, K.; Tanimori, S.; Kirihata, M. Biological Evaluation of Dodecaborate-Containing l-Amino Acids for Boron Neutron Capture Therapy. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 6980–6984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
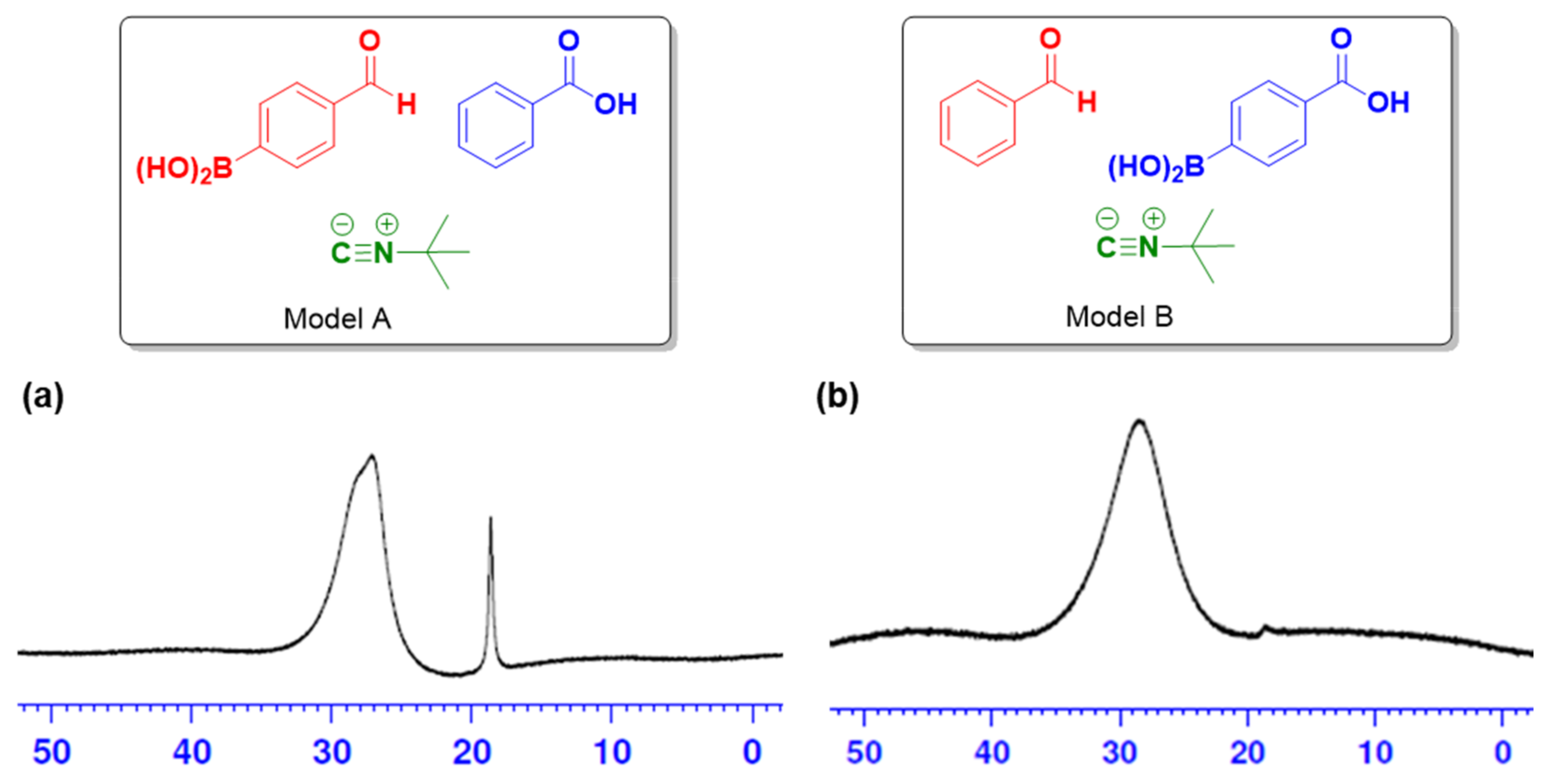
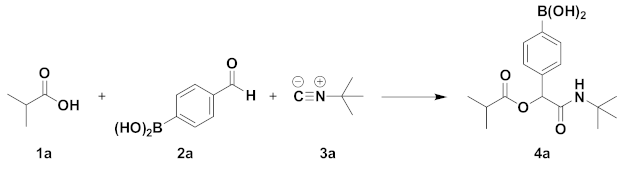
| Entry | Solvent | t (°C) | Time (h) | Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ether | 25 | 2.5 | ND |
| 2 | DCM | 25 | 2.5 | ND |
| 3 | MeOH | 25 | 2.5 | ND |
| 4 | H2O | 25 | 2.5 | 5 |
| 5 | H2O | 25 | 24 | 57 |
| 6 | H2O | 45 | 2.5 | 56 |
| 7 | H2O | MW, 45 | 1.0 | 55 |
| 8 | H2O | MW, 45 | 2.5 | 68 |
| 9 | H2O | MW, 45 | 4.0 | 33 |
| 10 | H2O | MW, 65 | 2.5 | 63 |
| 11 | H2O | MW, 85 | 2.5 | 53 |
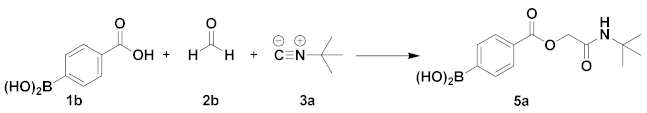
| Entry | Solvent | t (°C) | Time (h) | Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | H2O | 25 | 2.5 | 63 |
| 2 | H2O | 25 | 24 | 62 |
| 3 | H2O | 85 | 2.5 | 53 |
| 4 | H2O | MW, 45 | 2.5 | 55 |
| 5 | H2O | MW, 65 | 2.5 | 74 |
| 6 | H2O | MW, 85 | 2.5 | 89 |
| 7 | H2O | MW, 95 | 2.5 | 53 |
| Entry | Dihedral Angle | HOMO-Side | LUMO-Side | HOMO-Top | LUMO-Top |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.00069° |  |  |  | 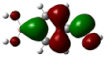 |
| 2 | −0.01869° |  | 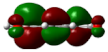 |  | 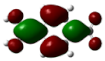 |
| Entry | Dihedral Angle | HOMO | LUMO | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | PAS 0.00069° | OO 1.14 | B 0.00 | Ph 98.69 | COHH 0.17 | OO 2.16 | B 0.73 | Ph 39.08 | COHH 58.03 |
| 2 | CS −0.01869° | OO 0.02 | B 0.00 | Ph 14.18 | COHH 85.80 | OO 11.42 | B 19.85 | Ph 64.04 | COHH 4.70 |
| Compound | Bright Field | DAHMI Stain b | Merged Image |
|---|---|---|---|
 |  |  |  |
 | 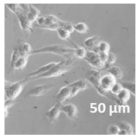 |  | 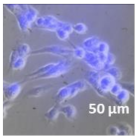 |
 | 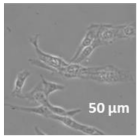 |  |  |
 |  |  |  |
 |  |  |  |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qiu, S.-B.; Liu, P.-Y.; Wang, B.-C.; Chen, P.-R.; Xiao, J.-H.; Hsu, T.-Y.; Pan, K.-L.; Lai, Z.-Y.; Chen, Y.-W.; Chen, Y.-C.; et al. Protection-Free Strategy for the Synthesis of Boro-Depsipeptides in Aqueous Media under Microwave-Assisted Conditions. Molecules 2022, 27, 2325. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27072325
Qiu S-B, Liu P-Y, Wang B-C, Chen P-R, Xiao J-H, Hsu T-Y, Pan K-L, Lai Z-Y, Chen Y-W, Chen Y-C, et al. Protection-Free Strategy for the Synthesis of Boro-Depsipeptides in Aqueous Media under Microwave-Assisted Conditions. Molecules. 2022; 27(7):2325. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27072325
Chicago/Turabian StyleQiu, Shuo-Bei, Pei-Yao Liu, Bo-Cheng Wang, Pin-Rui Chen, Jing-Han Xiao, Ting-Yu Hsu, Kuan-Lin Pan, Zhi-Yin Lai, Yi-Wei Chen, Ying-Chuan Chen, and et al. 2022. "Protection-Free Strategy for the Synthesis of Boro-Depsipeptides in Aqueous Media under Microwave-Assisted Conditions" Molecules 27, no. 7: 2325. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27072325
APA StyleQiu, S.-B., Liu, P.-Y., Wang, B.-C., Chen, P.-R., Xiao, J.-H., Hsu, T.-Y., Pan, K.-L., Lai, Z.-Y., Chen, Y.-W., Chen, Y.-C., Chen, J.-K., & Pan, P.-S. (2022). Protection-Free Strategy for the Synthesis of Boro-Depsipeptides in Aqueous Media under Microwave-Assisted Conditions. Molecules, 27(7), 2325. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27072325






