Distinguishing between Decaffeinated and Regular Coffee by HS-SPME-GC×GC-TOFMS, Chemometrics, and Machine Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Targeted Analysis of Aroma-Related Volatile Compounds
2.1.1. Aroma-Related Volatiles
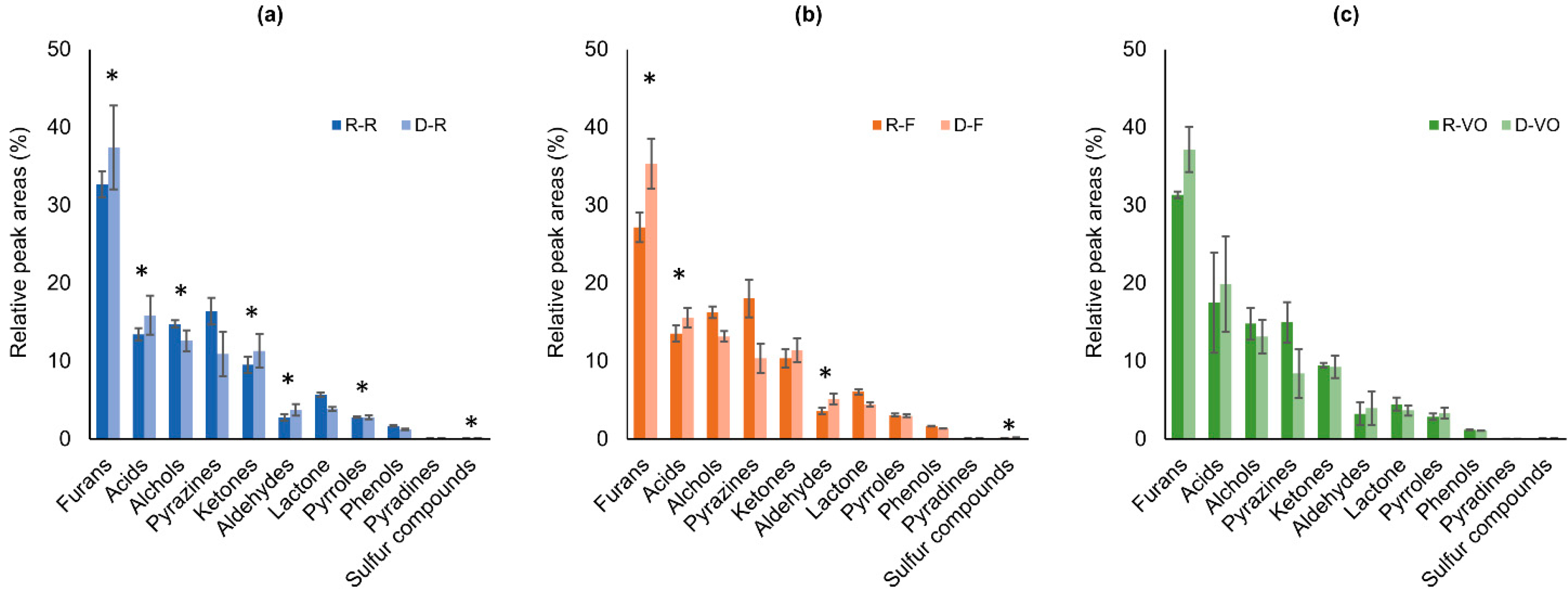
2.1.2. Chemical Families of Aroma-Related Volatiles
2.1.3. Differentiation of Regular and Decaffeinated Coffee by Aroma-Related Volatiles
2.1.4. Predicted Aroma Difference between Regular and Decaffeinated Coffee
2.2. Non-Targeted Analysis of Two Coffee Groups
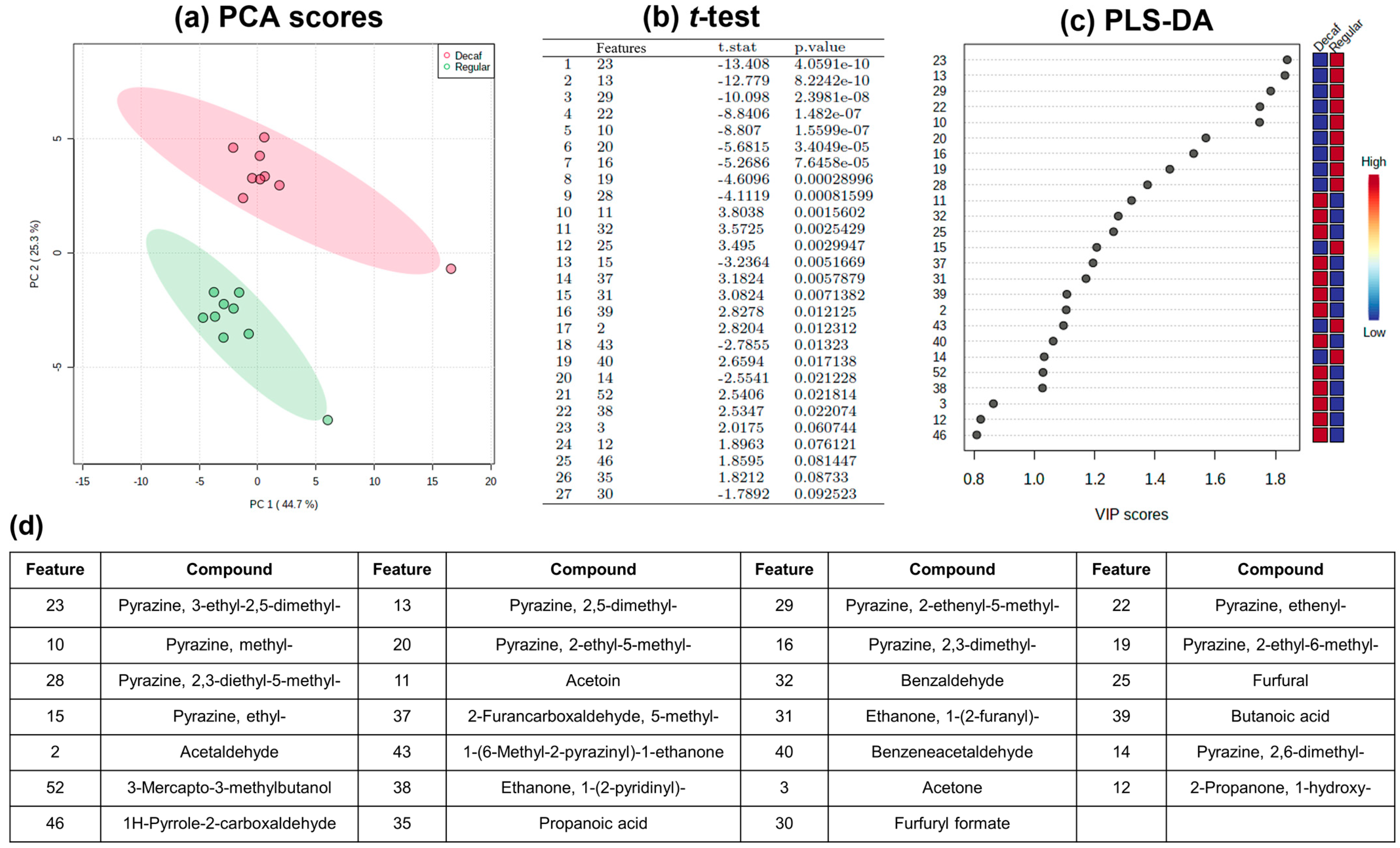
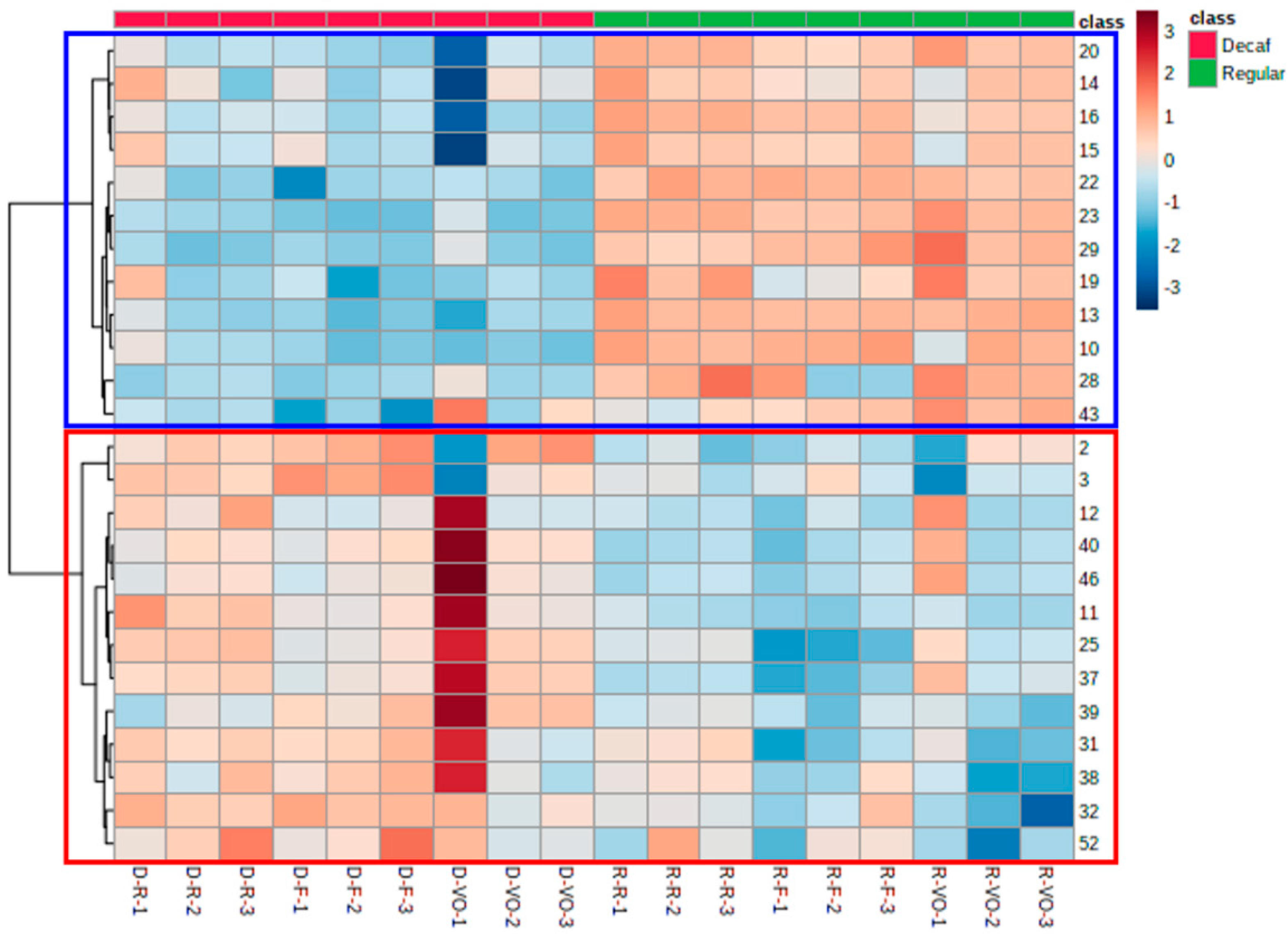
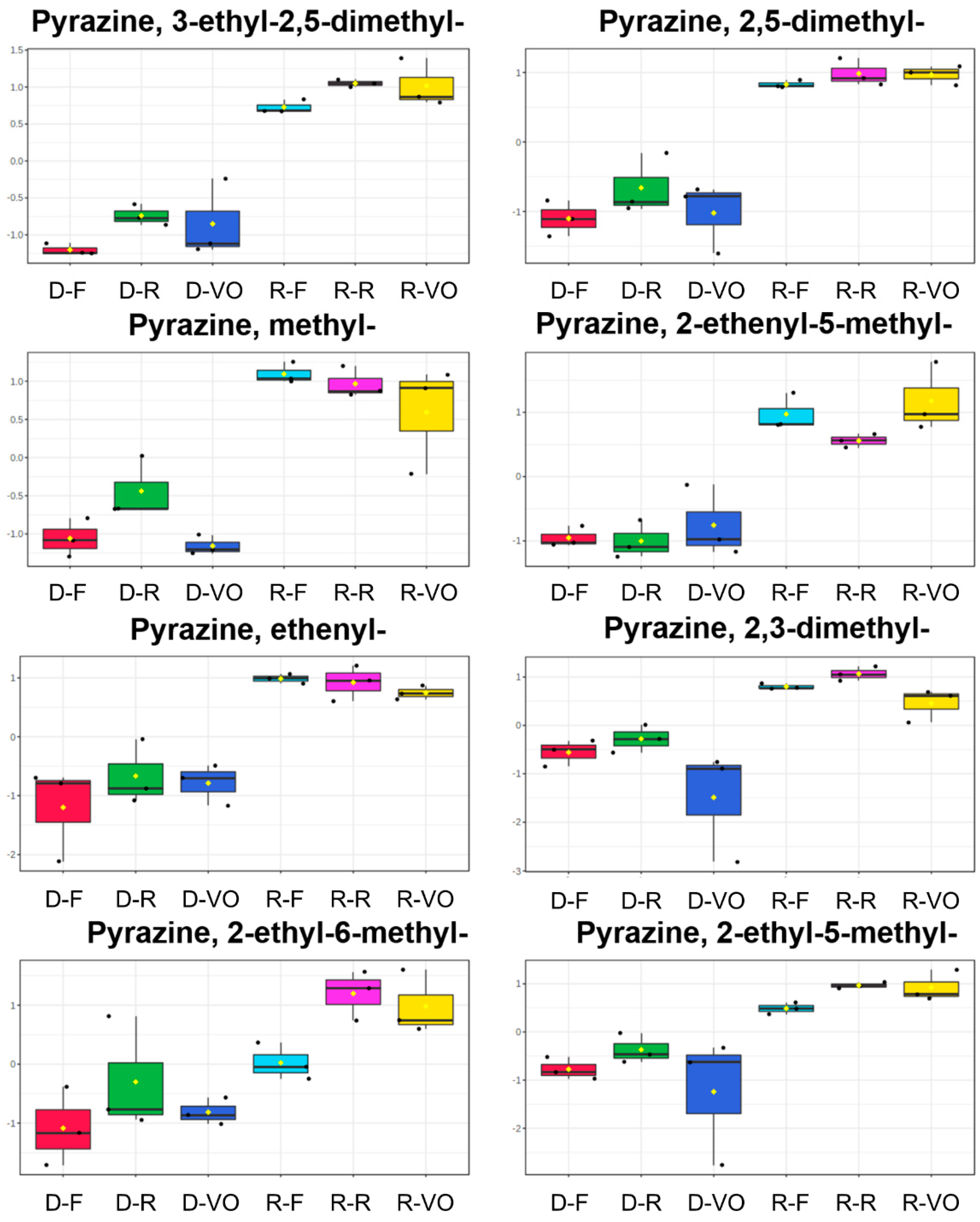
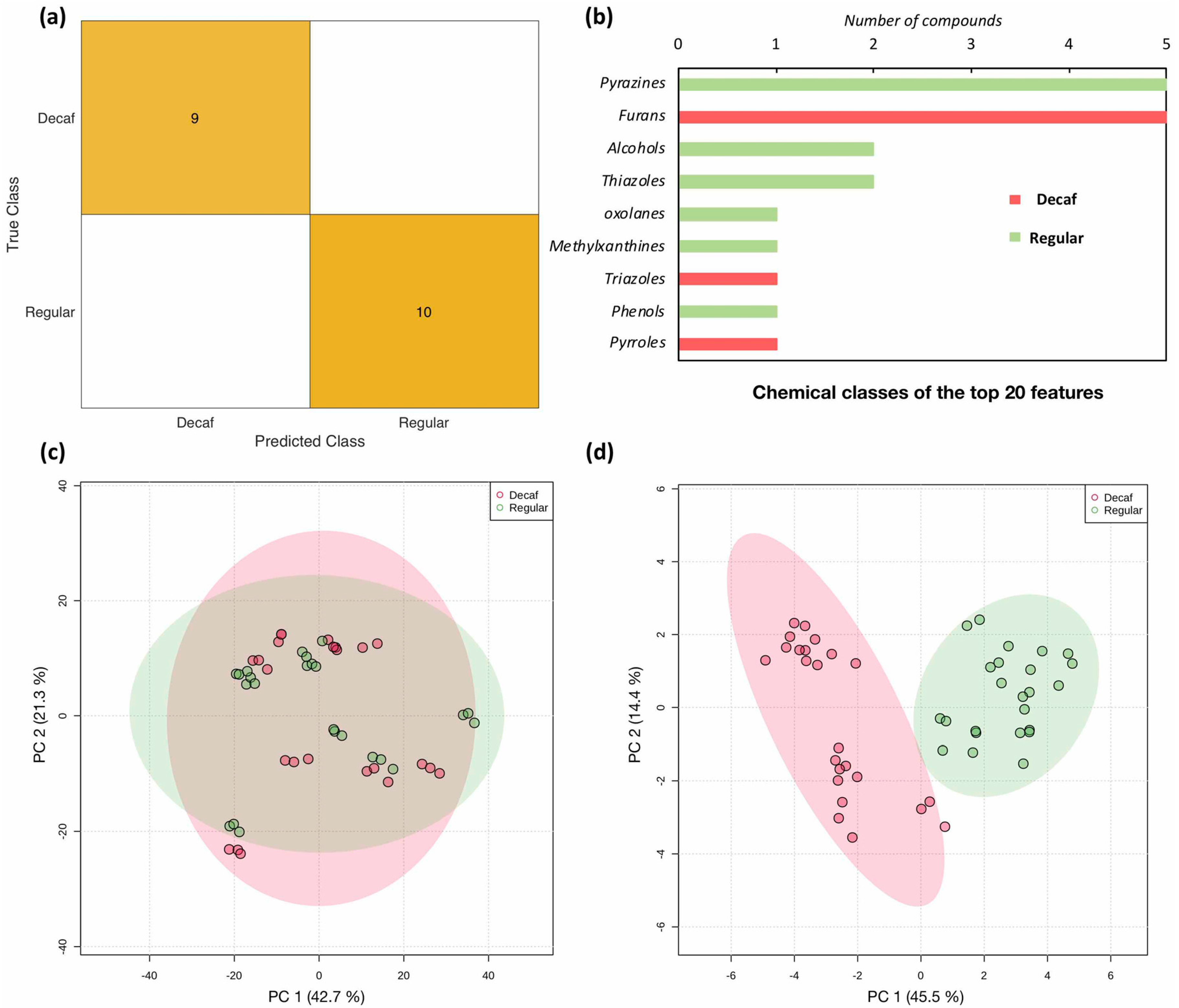
2.2.1. Classification Model and Feature Selection
2.2.2. Prediction Model
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Samples
3.2. HS-SPME-GC×GC-TOFMS Instrumentation
3.3. Data Processing, Chemometrics, and Machine Learning
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Pietsch, A. Decaffeination-Process and Quality. In The Craft and Science of Coffee; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 225–243. ISBN 9780128035580. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y. Coffee Report 2020; Statista: Hamburg, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Folmer, B.; Farah, A.; Jones, L.; Fogliano, V. Human Wellbeing-Sociability, Performance, and Health. In The Craft and Science of Coffee; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 493–520. ISBN 9780128035580. [Google Scholar]
- Kraujalyte, V.; Pelvan, E.; Alasalvar, C. Volatile Compounds and Sensory Characteristics of Various Instant Teas Produced from Black Tea. Food Chem. 2016, 194, 864–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decaffeinated Coffee Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report by Product (Roasted, Raw), by Bean Species (Arabica, Robusta), by Distribution Channel, by Region, and Segment Forecasts, 2020–2027; Grand View Research: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2020.
- Illy, A.; Viani, R. Espresso Coffee the Science of Quality, 2nd ed.; Illy, A., Viani, R., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; ISBN 0-12-370371-9. [Google Scholar]
- Pickard, S.; Becker, I.; Merz, K.H.; Richling, E. Determination of the Alkylpyrazine Composition of Coffee Using Stable Isotope Dilution-Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (SIDA-GC-MS). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 6274–6281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angeloni, S.; Mustafa, A.M.; Abouelenein, D.; Alessandroni, L.; Acquaticci, L.; Nzekoue, F.K.; Petrelli, R.; Sagratini, G.; Vittori, S.; Torregiani, E.; et al. Characterization of the Aroma Profile and Main Key Odorants of Espresso Coffee. Molecules 2021, 26, 3856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Park, M.K.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, Y.S. Effect of Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Decaffeination on Volatile Components of Green Teas. J. Food Sci. 2007, 72, S497–S502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, R.; Babu, G.D.K.; Gulati, A. Effect of Decaffeination Conditions on Quality Parameters of Kangra Orthodox Black Tea. Food Res. Int. 2013, 53, 693–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, S.; Perestrelo, R.; Silva, P.; Pereira, J.A.M.; Câmara, J.S. Current Trends and Recent Advances on Food Authenticity Technologies and Chemometric Approaches. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 85, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, G.R.; Petronilho, S.; Ferreira, A.S.; Pinto, M.; Passos, C.P.; Coelho, E.; Rodrigues, C.; Figueira, C.; Rocha, S.M.; Coimbra, M.A. Insights on Single-dose Espresso Coffee Capsules’ Volatile Profile: From Ground Powder Volatiles to Prediction of Espresso Brew Aroma Properties. Foods 2021, 10, 2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, J.S.; Augusto, F.; Salva, T.J.G.; Ferreira, M.M.C. Prediction Models for Arabica Coffee Beverage Quality Based on Aroma Analyses and Chemometrics. Talanta 2012, 101, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelwareth, A.; Zayed, A.; Farag, M.A. Chemometrics-Based Aroma Profiling for Revealing Origin, Roasting Indices, and Brewing Method in Coffee Seeds and Its Commercial Blends in the Middle East. Food Chem. 2021, 349, 129162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez-Carvelo, A.M.; González-Casado, A.; Bagur-González, M.G.; Cuadros-Rodríguez, L. Alternative Data Mining/Machine Learning Methods for the Analytical Evaluation of Food Quality and Authenticity–A Review. Food Res. Int. 2019, 122, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Zhan, Y.; Xu, Z.; John Nduwamungu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Powers, R.; Xu, C. The Application of Machine-Learning and Raman Spectroscopy for the Rapid Detection of Edible Oils Type and Adulteration. Food Chem. 2022, 373, 131471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gazeli, O.; Bellou, E.; Stefas, D.; Couris, S. Laser-Based Classification of Olive Oils Assisted by Machine Learning. Food Chem. 2020, 302, 125329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Wang, J. The Prediction of Food Additives in the Fruit Juice Based on Electronic Nose with Chemometrics. Food Chem. 2017, 230, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poisson, L.; Blank, I.; Dunkel, A.; Hofmann, T. The Chemistry of Roasting-Decoding Flavor Formation. In The Craft and Science of Coffee; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 273–309. ISBN 9780128035580. [Google Scholar]
- Cordero, C.; Liberto, E.; Bicchi, C.; Rubiolo, P.; Reichenbach, S.E.; Tian, X.; Tao, Q. Targeted and Non-Targeted Approaches for Complex Natural Sample Profiling by GC×GC-QMS. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2010, 48, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seninde, D.R.; Chambers, E., IV. Co Ff Ee Flavor: A Review. Beverages 2020, 6, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, J.S.; Teófilo, R.F.; Salva, T.D.J.G.; Augusto, F.; Ferreira, M.M.C. Exploratory and Discriminative Studies of Commercial Processed Brazilian Coffees with Different Degrees of Roasting and Decaffeinated. Braz. J. Food Technol. 2013, 16, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Toci, A.; Farah, A.; Trugo, L.C. Effect of Decaffeination Using Dichloromethane on the Chemical Composition of Arabica and Robusta Raw and Roasted Coffees. Quim. Nova 2006, 29, 965–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzi, G.P. The Strecker Degradation and Its Contribution to Food Flavor. In Flavor Chemistry: 30 Years of Progress; Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1999; pp. 335–343. [Google Scholar]
- Rannou, C.; Laroque, D.; Renault, E.; Prost, C.; Sérot, T. Mitigation Strategies of Acrylamide, Furans, Heterocyclic Amines and Browning during the Maillard Reaction in Foods. Food Res. Int. 2016, 90, 154–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Galilea, I.; Fournier, N.; Cid, C.; Guichard, E. Changes in Headspace Volatile Concentrations of Coffee Brews Caused by the Roasting Process and the Brewing Procedure. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 8560–8566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Rios, O.; Suarez-Quiroz, M.L.; Boulanger, R.; Barel, M.; Guyot, B.; Guiraud, J.P.; Schorr-Galindo, S. Impact of “Ecological” Post-Harvest Processing on Coffee Aroma: II. Roasted Coffee. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2007, 20, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burdock, G.A. Fenaroli’s Handbook of Flavor Ingredients, 5th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Zapata, J.; Londoño, V.; Naranjo, M.; Osorio, J.; Lopez, C.; Quintero, M. Characterization of Aroma Compounds Present in an Industrial Recovery Concentrate of Coffee Flavor. CYTA-J. Food 2018, 16, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutler, D.R.; Edwards, T.C.; Beard, K.H.; Cutler, A.; Hess, K.T.; Gibson, J.; Lawler, J.J. Random Forests for Classification in Ecology. Ecology 2007, 88, 2783–2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Ishwaran, H. Random Forests for Genomic Data Analysis. Genomics 2012, 99, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eskin, N.A.M.; Ho, C.T.; Shahidi, F. Browning Reactions in Foods. In Biochemistry of Foods; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 245–289. ISBN 9780080918099. [Google Scholar]
- Fisk, I.D.; Kettle, A.; Hofmeister, S.; Virdie, A.; Kenny, J.S. Discrimination of Roast and Ground Coffee Aroma. Flavour 2012, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaya-Farfan, J.; Rodriguez-Amaya, D.B. The Maillard Reactions. In Chemical Changes During Processing and Storage of Foods; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 215–263. ISBN 9780128173800. [Google Scholar]
- Rahn, A.; Yeretzian, C. Impact of Consumer Behavior on Furan and Furan-Derivative Exposure during Coffee Consumption. A Comparison between Brewing Methods and Drinking Preferences. Food Chem. 2019, 272, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franklin, L.M.; Mitchell, A.E. Review of the Sensory and Chemical Characteristics of Almond (Prunus dulcis) Flavor. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 2743–2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berk, E.; Hamzalloglu, A.; Gökmen, V. Investigations on the Maillard Reaction in Sesame (Sesamum Indicum L.) Seeds Induced by Roasting. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 4923–4930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruszewski, B.; Obiedziński, M.W. Impact of Raw Materials and Production Processes on Furan and Acrylamide Contents in Dark Chocolate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 2562–2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wailzer, B.; Klocker, J.; Wolschann, P.; Buchbauer, G. Structural Features for Furan-Derived Fruity and Meaty Aroma Impressions. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2016, 11, 1475–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zambolim, L. Current Status and Management of Coffee Leaf Rust in Brazil. Trop. Plant Pathol. 2016, 41, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieterle, F.; Ross, A.; Schlotterbeck, G.; Senn, H. Probabilistic Quotient Normalization as Robust Method to Account for Dilution of Complex Biological Mixtures. Application In1H NMR Metabonomics. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 4281–4290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

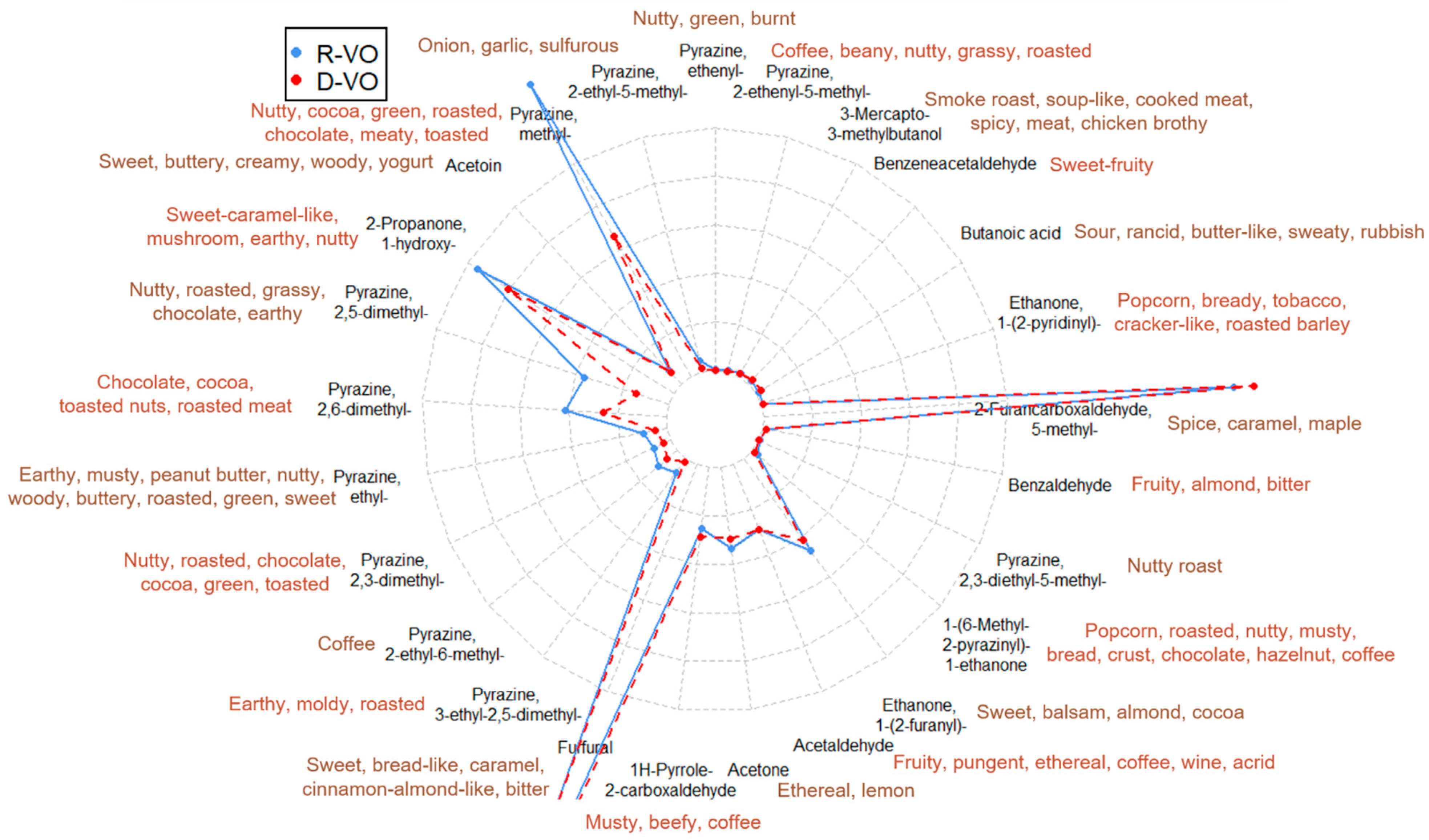
| Chemical Family | Compound | Aroma Description | CAS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acids | Acetic acid | Pungent, sour, acidic, vinegar | 64-19-7 |
| Propanoic acid | Pungent, acidic, cheesy, vinegar, sour milk, butter-like | 79-09-4 | |
| Butanoic acid | Sour, rancid, butter-like, sweaty, rubbish | 107-92-6 | |
| Butanoic acid, 3-methyl- | Acidic, sweaty, rancid, cheese, herbaceous | 503-74-2 | |
| Alcohols | 2,3-Butanediol (isomer) | Fruity, creamy, buttery | 513-85-9 |
| 2,3-Butanediol (isomer) | Fruity, creamy, buttery | 513-85-9 | |
| 2-Furanmethanol | Caramellic, burnt, smoky, sweet, coffee | 98-00-0 | |
| Aldehydes | Acetaldehyde | Fruity, pungent, ethereal, coffee, wine, acrid | 75-07-0 |
| Butanal, 2-methyl- | Malty, fermented, buttery-oily | 96-17-3 | |
| Butanal, 3-methyl- | Almond, fruity, buttery-oily, malty, pungent, acrid, apple-like, sweaty | 590-86-3 | |
| Benzaldehyde | Fruity, almond, bitter | 100-52-7 | |
| Benzeneacetaldehyde | Sweet-fruity | 122-78-1 | |
| Propanal, 2-methyl- | Grassy, fermented, buttery-oily | 78-84-2 | |
| Furans | Furan, 2-methyl- | Pungent, fruity | 534-22-5 |
| 2-Furfurylthiol 1 | Smoke roast, caramel, burned matter, fresh coffee | 98-02-2 | |
| Furfural | Sweet, bread-like, caramel, cinnamon-almond-like, bitter | 98-01-1 | |
| Furan, 2-[(methylthio)methyl]- 1 | Smoke roast | 1438-91-1 | |
| Furfuryl formate | Floral | 13493-97-5 | |
| Ethanone, 1-(2-furanyl)- | Sweet, balsam, almond, cocoa | 1192-62-7 | |
| 2-Furanmethanol, acetate | Ethereal-floral, herbal-spicy, green | 623-17-6 | |
| 2-Furancarboxaldehyde, 5-methyl- | Spice, caramel, maple | 620-02-0 | |
| Furaneol | Sweet, caramel | 3658-77-3 | |
| Ketones | Acetone | Ethereal, lemon | 67-64-1 |
| 2,3-Butanedione | Buttery-oily, fruity, caramel | 431-03-8 | |
| 2,3-Pentanedione | Buttery-oily, caramel-like | 600-14-6 | |
| Acetoin | Sweet, buttery, creamy, woody, yogurt | 513-86-0 | |
| 2-Propanone, 1-hydroxy- | Sweet-caramel-like, mushroom, earthy, nutty | 116-09-6 | |
| 1-Hydroxy-2-butanone | Sweet, coffee, toasted | 5077-67-8 | |
| Lactones | Butyrolactone | Caramel, fatty, creamy, oily, sweet | 96-48-0 |
| Phenols | Phenol, 2-methoxy- | Phenolic, spicy, burnt, smoky | 8021-39-4 |
| Phenol, 4-ethyl-2-methoxy- | Phenolic, spicy, sweet | 2785-89-9 | |
| 2-Methoxy-4-vinylphenol | Phenolic, clove, spicy | 7786-61-0 | |
| Pyridines | Pyridine, 3-ethyl- | Rotten fish, smoky, leather, tobacco, caramel, burnt, coffee-like, toasted | 536-78-7 |
| Ethanone, 1-(2-pyridinyl)- | Popcorn, bready, tobacco, cracker-like, roasted barley | 1122-62-9 | |
| Pyrazines | Pyrazine, methyl- | Nutty, cocoa, green, roasted, chocolate, meaty, toasted | 109-08-0 |
| Pyrazine, 2,5-dimethyl- | Nutty, roasted, grassy, chocolate, earthy | 123-32-0 | |
| Pyrazine, 2,6-dimethyl- | Chocolate, cocoa, toasted nuts, roasted meat | 108-50-9 | |
| Pyrazine, ethyl- | Earthy, musty, peanut butter, nutty, woody, buttery, roasted, green, sweet | 13925-00-3 | |
| Pyrazine, 2,3-dimethyl- | Nutty, roasted, chocolate, cocoa, green, toasted | 5910-89-4 | |
| Pyrazine, 2-ethyl-6-methyl- | Earthy, musty, mold, flowery, fruity, hazelnut-like, toasted | 13925-03-6 | |
| Pyrazine, 2-ethyl-5-methyl- | Onion, garlic, sulfurous | 13360-64-0 | |
| Pyrazine, ethenyl- | Nutty, green, burnt | 4177-16-6 | |
| Pyrazine, 3-ethyl-2,5-dimethyl- | Earthy, moldy, roasted | 13360-65-1 | |
| Pyrazine, 2-ethenyl-6-methyl- | Coffee | 13925-09-2 | |
| Pyrazine, 2,3-diethyl-5-methyl- | Nutty roast | 18138-04-0 | |
| Pyrazine, 2-ethenyl-5-methyl- | Coffee, beany, nutty, grassy, roasted | 13925-08-1 | |
| 1-(6-Methyl-2-pyrazinyl)-ethanone | Popcorn, roasted, nutty, musty, bread, crust, chocolate, hazelnut, coffee | 22047-26-3 | |
| Pyrroles | 1H-Pyrrole, 1-methyl- | Smoky, woody, herbal, sweet, animal, coffee | 96-54-8 |
| Ethanone, 1-(1H-pyrrol-2-yl)- | Nutty, bread, walnut, licorice, cracker, popcorn-like | 1072-83-9 | |
| 1H-Pyrrole-2-carboxaldehyde | Musty, beefy, coffee | 1003-29-8 | |
| Sulfur-containing compounds | Methanethiol | Freshness, sulfurous, fresh coffee | 74-93-1 |
| 3-Mercapto-3-methylbutanol | Smoke roast, soup-like, cooked meat, spicy, meat, chicken brothy | 34300-94-2 |
| Group | Sample | Bean Species | Bean Origin | Decaffeination Process 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Regular | R-R | Arabica | Latin America/India/Eastern Africa | - |
| Decaf | D-R | Arabica | Latin America/India/Eastern Africa | LiCO2/water 2 |
| Regular | R-F | Arabica | Latin America | - |
| Decaf | D-F | Arabica | Latin America | LiCO2/water |
| Regular | R-VO | Arabica | Brazil/Colombia | - |
| Decaf | D-VO | Arabica | Brazil/Colombia | LiCO2/water |
| Regular | R-VI | Arabica | Ethiopia/Mexico | - |
| Decaf | D-VI | Arabica | Colombia/Ethiopia | LiCO2/water |
| Regular | R-S | Arabica | - | |
| Decaf | D-S | Arabica | Unknown | |
| Regular | R-DE | Arabica, Robusta | - | |
| Decaf | D-DE | Arabica, Robusta | DCM/water 3 | |
| Regular | R-I | Arabica | - | |
| Decaf | D-I | Arabica | LiCO2 | |
| Regular | R-L | Arabica | - | |
| Decaf | D-L | Arabica, Robusta | scCO2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zou, Y.; Gaida, M.; Franchina, F.A.; Stefanuto, P.-H.; Focant, J.-F. Distinguishing between Decaffeinated and Regular Coffee by HS-SPME-GC×GC-TOFMS, Chemometrics, and Machine Learning. Molecules 2022, 27, 1806. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27061806
Zou Y, Gaida M, Franchina FA, Stefanuto P-H, Focant J-F. Distinguishing between Decaffeinated and Regular Coffee by HS-SPME-GC×GC-TOFMS, Chemometrics, and Machine Learning. Molecules. 2022; 27(6):1806. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27061806
Chicago/Turabian StyleZou, Yun, Meriem Gaida, Flavio A. Franchina, Pierre-Hugues Stefanuto, and Jean-François Focant. 2022. "Distinguishing between Decaffeinated and Regular Coffee by HS-SPME-GC×GC-TOFMS, Chemometrics, and Machine Learning" Molecules 27, no. 6: 1806. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27061806
APA StyleZou, Y., Gaida, M., Franchina, F. A., Stefanuto, P.-H., & Focant, J.-F. (2022). Distinguishing between Decaffeinated and Regular Coffee by HS-SPME-GC×GC-TOFMS, Chemometrics, and Machine Learning. Molecules, 27(6), 1806. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27061806







