Bioguided Phytochemical Study of Ipomoea cairica Extracts with Larvicidal Activity against Aedes aegypti
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material
4.2. Sample Processing
4.3. Monitoring Using TLC and Isolation Using Preparative TLC
4.4. High-Efficiency Liquid Chromatography with a Diode Array Detector and Mass Spectrometry (HPLC-DAD-MS/MS)
4.5. Larval Culture
4.6. Bioassay of Larvicidal Activity
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Kim, S.I.; Ahn, Y.J. Larvicidal activity of lignans and alkaloid identified in Zanthoxylum piperitum bark toward insecticide-susceptible and wild Culex pipiens pallens and Aedes aegypti. Parasites Vectors 2017, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rey, J.; Lounibos, P. Ecología de Aedes aegypti y Aedes albopictus en América y la transmisión de enfermedades. Biomédica 2015, 35, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Patterson, J.; Sammon, M.; Garg, M. Dengue, zika and chikungunya: Emerging arboviruses in the new world. West. J. Emerg. Med. 2016, 17, 671–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministry of Health of Costa Rica Dengue Cases in 2020 Already Exceed All Cases in 2019. Available online: https://www.ministeriodesalud.go.cr/index.php/vigilancia-de-la-salud/analisis-de-situacion-de-salud (accessed on 7 April 2021).
- Yu, B.; Luo, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, D.; Yu, S.; Kong, L. Pentasaccharide resin glycosides from Ipomoea cairica and their cytotoxic activities. Phytochemistry 2013, 95, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, A.A.; Amaral, F.A.; Duarte, I.D.G.; Oliveira, P.M.; Alves, R.B.; Silveira, D.; Azevedo, A.O.; Raslan, D.S.; Castro, M.S.A. Antinociceptive effect from Ipomoea cairica extract. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2006, 105, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, S.; Kumar, D. Shiba Phytochemical, antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of methanol extract of leaves and flowers of Ipomoea Cairica. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 5, 198–202. [Google Scholar]
- Ahbirami, R.; Zuharah, W.F.; Thiagaletchumi, M.; Subramaniam, S.; Sundarasekar, J. Larvicidal efficacy of different plant parts of railway creeper, Ipomoea cairica extract against dengue vector mosquitoes, Aedes albopictus (Diptera: Culicidae) and Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae). J. Insect Sci. 2014, 14, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, O.; Braz-Filho, R. Dibenzylbutyrolactone lignans and coumarins from Ipomoea cairica. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 1997, 8, 235–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthil-Nathan, S. A Review of Resistance Mechanisms of Synthetic Insecticides and Botanicals, Phytochemicals, and Essential Oils as Alternative Larvicidal Agents Against Mosquitoes. Front. Physiol. 2020, 10, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, D.; Shukla, K. Ipomoea cairica: A medicinal weed with promising health benefits. Int. J. Inf. Res. Rev. 2015, 2, 687–694. [Google Scholar]
- Giatropoulos, A.; Kimbaris, A.; Michaelakis, A.; Papachristos, D.P.; Polissiou, M.G.; Emmanouel, N. Chemical composition and assessment of larvicidal and repellent capacity of 14 Lamiaceae essential oils against Aedes albopictus. Parasitol. Res. 2018, 117, 1953–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hari, I.; Mathew, N. Larvicidal activity of selected plant extracts and their combination against the mosquito vectors Culex quinquefasciatus and Aedes aegypti. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 9176–9185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chellappandian, M.; Vasantha-Srinivasan, P.; Senthil-Nathan, S.; Karthi, S.; Thanigaivel, A.; Ponsankar, A.; Kalaivani, K.; Hunter, W.B. Botanical essential oils and uses as mosquitocides and repellents against dengue. Environ. Int. 2018, 113, 214–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez, V.; Rodríguez, G.; Argüello, S. Insecticidal activity of ethanolic plant extracts on Aedes aegypti larvae. 2022; submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Chariandy, C.; Seaforth, C.; Phelps, R.; Pollard, G.; Khambay, B. Screening of medicinal plants from Trinidad and Tobago for antimicrobial and insecticidal properties. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1999, 64, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafabadi, N.S.; Sahari, M.A.; Barzegar, M.; Hamidi Esfahani, Z. Role of Extraction Conditions in the Recovery of Some Phytochemical Compounds of the Jujube Fruit. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2020, 22, 439–451. [Google Scholar]
- Meira, M.; da Silva, E.P.; David, J.M.; David, J.P. Review of the genus Ipomoea: Traditional uses, chemistry and biological activities. Braz. J. Pharmacogn. 2012, 22, 682–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildebert, W.; Sabine, B. Plant Drug Analysis: A Thin Layer Chromatography Atlas; Segunda, Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1996; pp. 125–147. [Google Scholar]
- Mercolini, L.; Mandrioli, R.; Ferranti, A.; Sorella, V.; Protti, M.; Epifano, F.; Curini, M.; Raggi, M.A. Quantitative evaluation of auraptene and umbelliferone, chemopreventive coumarins in citrus fruits, by HPLC-UV-FL-MS. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 1694–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpinella, M.C.; Ferrayoli, C.G.; Palacios, S.M. Antifungal synergistic effect of scopoletin, a hydroxycoumarin isolated from Melia azedarach L. fruits. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 2922–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugan, K.; Mahesh Kumar, P.; Kovendan, K.; Amerasan, D.; Subrmaniam, J.; Hwang, J. Larvicidal, pupicidal, repellent and adulticidal activity of Citrus sinensis orange peel extract against Anopheles stephensi, Aedes aegypti and Culex quinquefasciatus (Diptera: Culicidae). Parasitol. Res. 2012, 111, 1757–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Kim, J.-R.R.; Wang, M.; Shu, S.; Ahn, Y.-J.J. Larvicidal activity of Cnidium monnieri fruit coumarins and structurally related compounds against insecticide-susceptible and insecticide-resistant Culex pipiens pallens and Aedes aegypti. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2012, 68, 1041–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollinger, J.M.; Hornick, A.; Langer, T.; Stuppner, H.; Prast, H. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activity of scopolin and scopoletin discovered by virtual screening of natural products. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 6248–6254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patar, A.A.; Hassan, W.R.M.; Yusof, F.Z.M. Acute toxicity of malathion, dichlorvos and temephos in climbing perch (Anabas testudineus). Malaysian Appl. Biol. 2015, 44, 37–42. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, M.S.; Santana, A.E.G.; Oliveira, L.L.; Zanuncio, J.C.; Serrão, J.E. Toxicity of squamocin on Aedes aegypti larvae, its predators and human cells. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2017, 73, 636–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyoshi, H.; Ohshima, M.; Shimada, H.; Akagi, T.; Iwamura, H.; McLaughlin, J.L. Essential structural factors of annonaceous acetogenins as potent inhibitors of mitochondrial complex I. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Bioenerg. 1998, 1365, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benelli, G.; Pavela, R.; Canale, A.; Cianfaglione, K.; Ciaschetti, G.; Conti, F.; Nicoletti, M.; Senthil-Nathan, S.; Mehlhorn, H.; Maggi, F. Acute larvicidal toxicity of five essential oils (Pinus nigra, Hyssopus officinalis, Satureja montana, Aloysia citrodora and Pelargonium graveolens) against the filariasis vector Culex quinquefasciatus: Synergistic and antagonistic effects. Parasitol. Int. 2017, 66, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade-Ochoa, S.; Sánchez-Aldana, D.; Chacón-Vargas, K.F.; Rivera-Chavira, B.E.; Sánchez-Torres, L.E.; Camacho, A.D.; Nogueda-Torres, B.; Nevárez-Moorillón, G.V. Oviposition deterrent and larvicidal and pupaecidal activity of seven essential oils and their major components against Culex quinquefasciatus say (Diptera: Culicidae): Synergism–antagonism effects. Insects 2018, 9, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, C.C.C.; De Menezes, J.E.S.A.; Melo, D.S.; Feitosa, C.R.S. Chemical Composition and larvicidal activity against Aedes aegypti of essential oils from Croton jacobinenesis Baill. Boletín Latinoam. Caribe Plantas Med. Aromáticas 2016, 15, 122–127. [Google Scholar]
- Silvério, M.R.S.; Espindola, L.S.; Lopes, N.P.; Vieira, P.C. Plant natural products for the control of Aedes aegypti: The main vector of important arboviruses. Molecules 2020, 25, 3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza Wuillda, A.C.J.; Martins, R.C.C.; Costa, F.D.N. Larvicidal activity of secondary plant metabolites in aedes aegypti control: An overview of the previous 6 years. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2019, 14, 1934578X19862893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mordue(Luntz), A.J.; Nisbet, A.J. Azadirachtin from the neem tree Azadirachta indica: Its action against insects. An. Soc. Entomol. Bras. 2000, 29, 615–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishore, N.; Mishra, B.; Tiwari, V.; Tripathi, V. A review on natural products with mosquitosidal potentials. Res. Signpost Chall. Scope Nat. Prod. Med. Chem. 2011, 37661, 335–365. [Google Scholar]
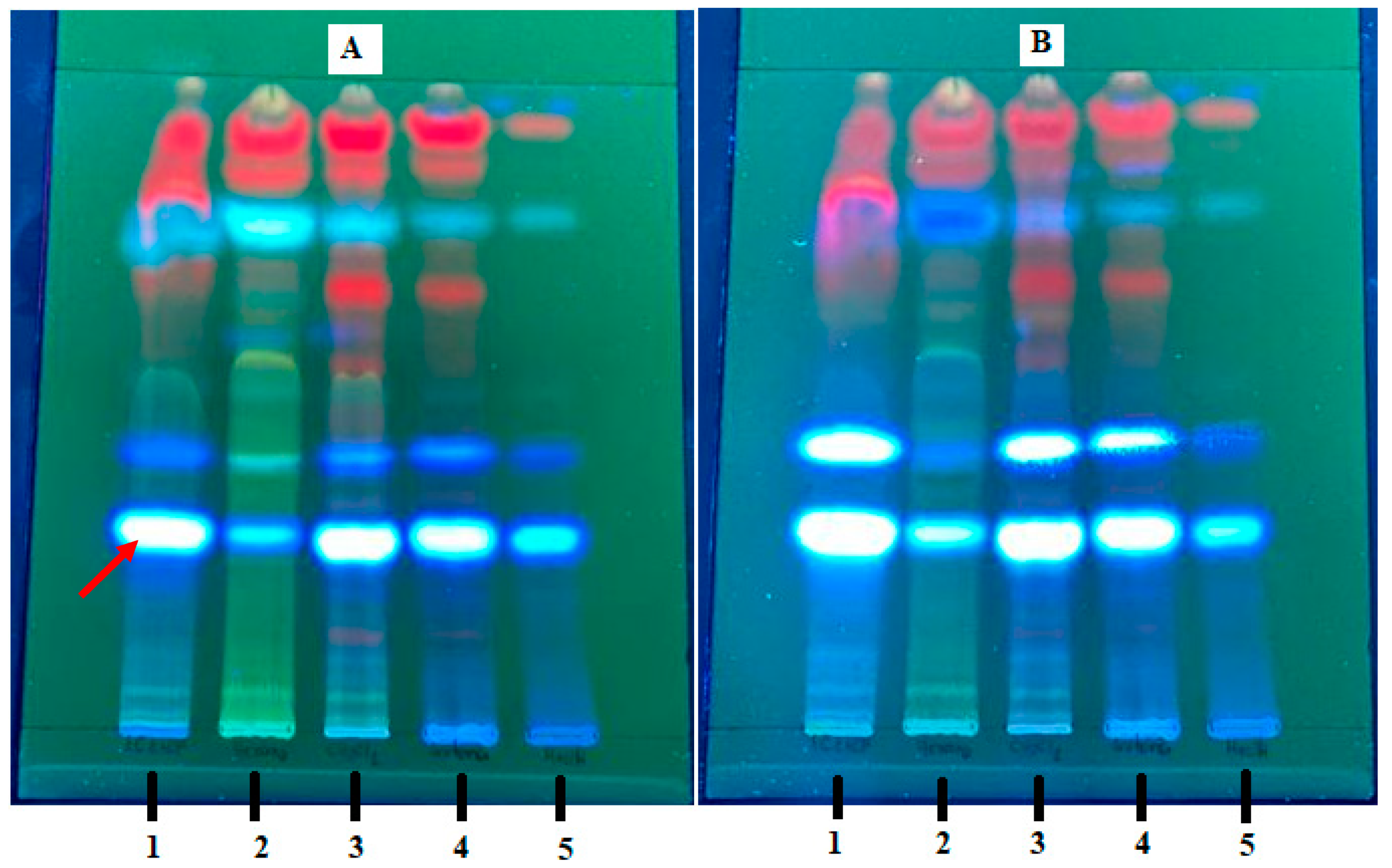
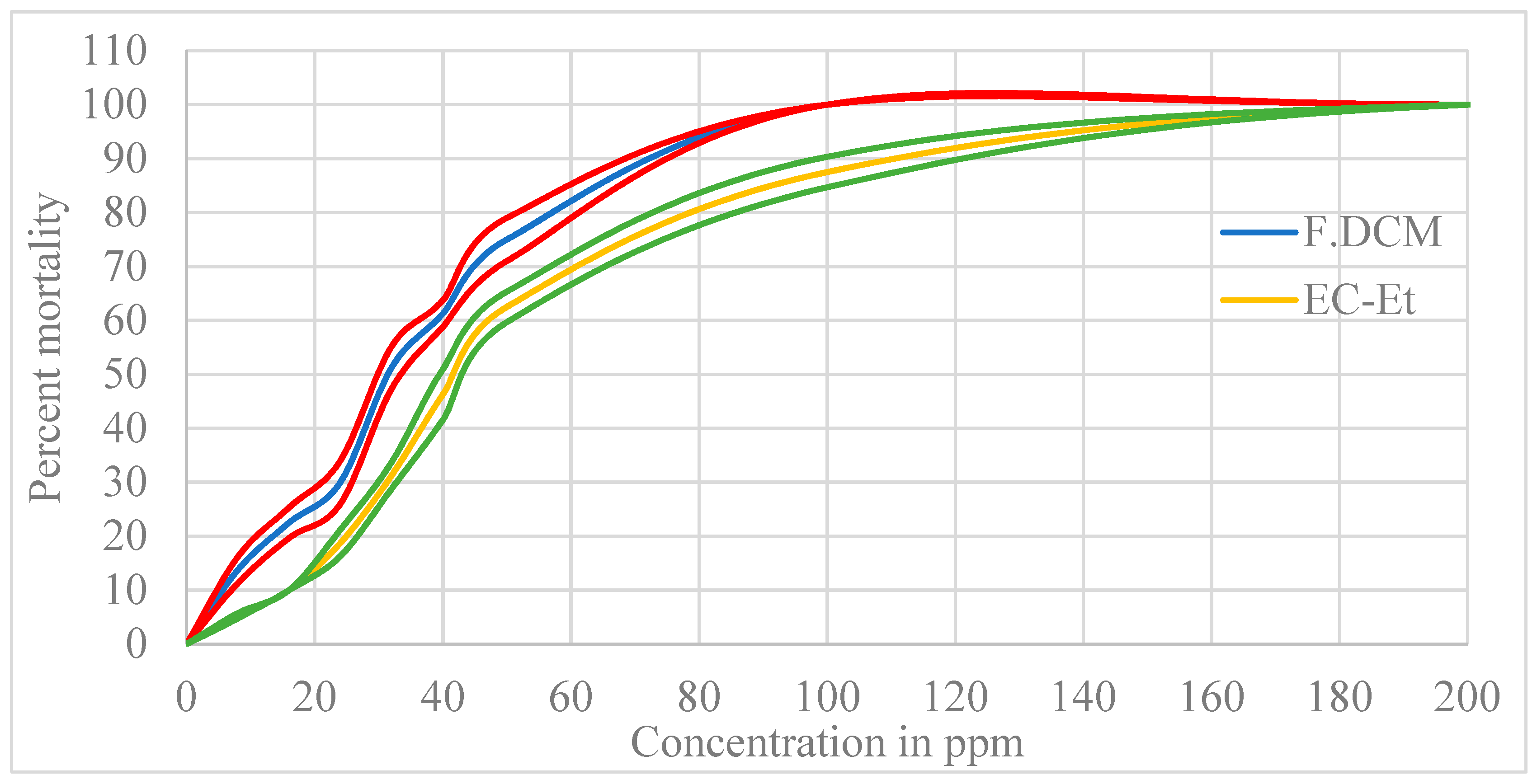
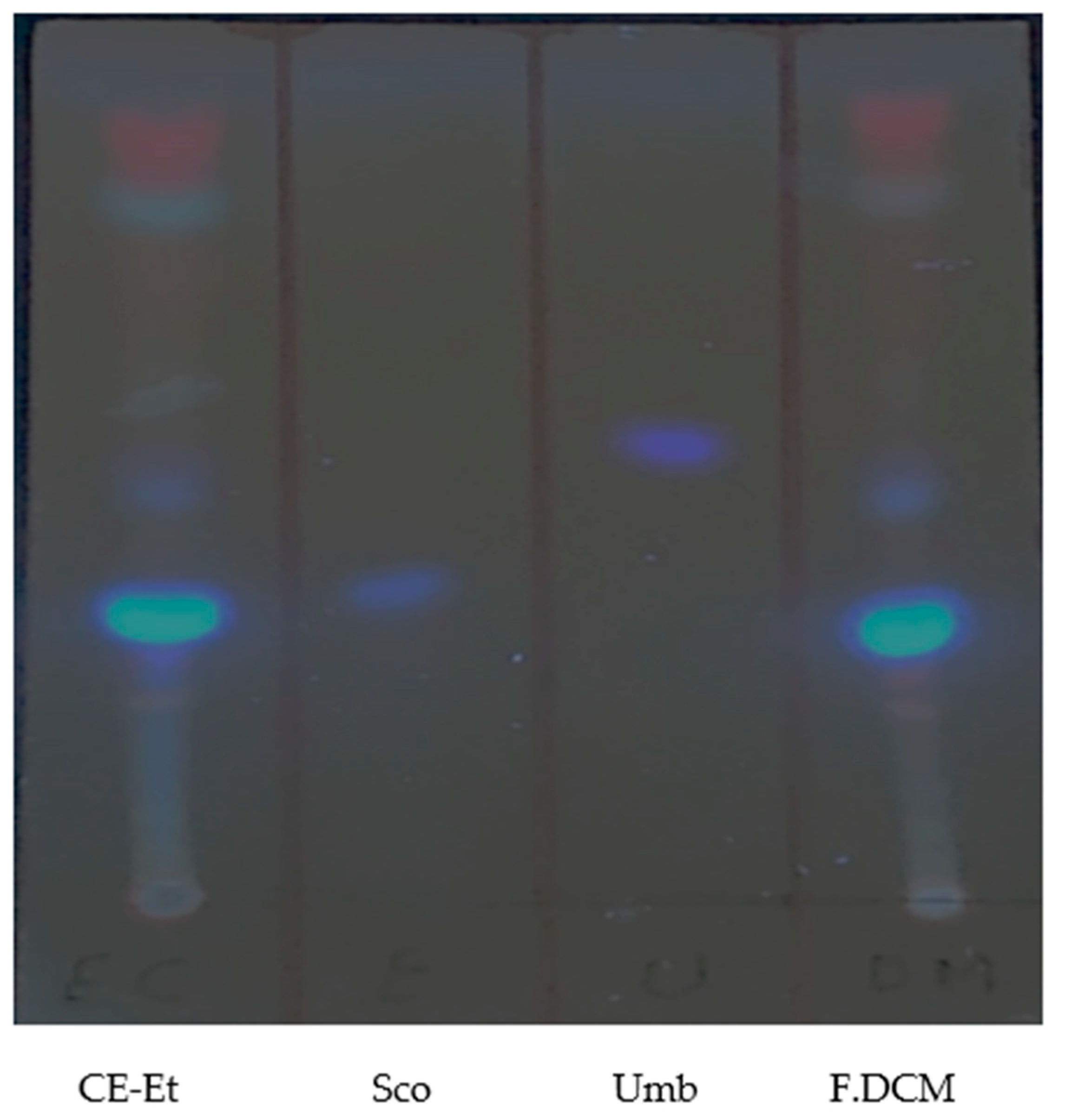
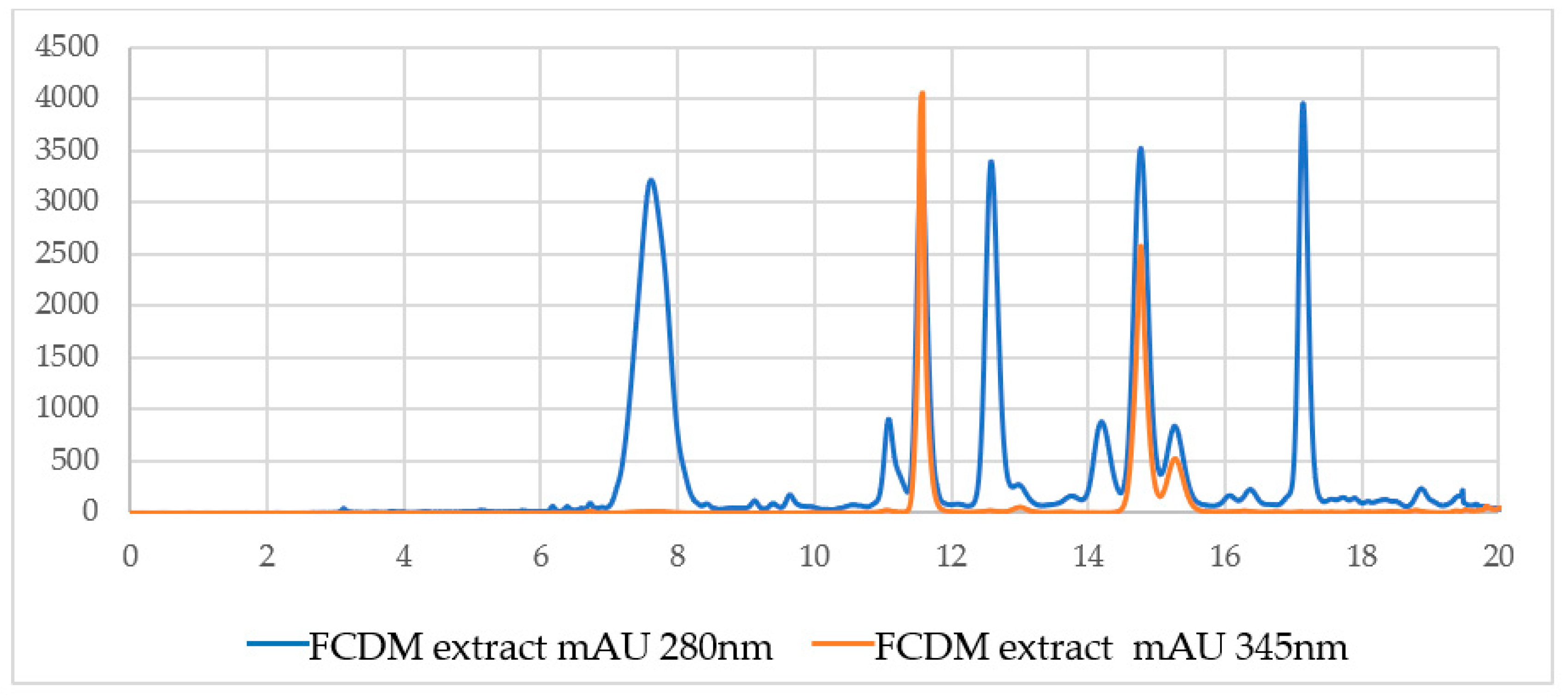
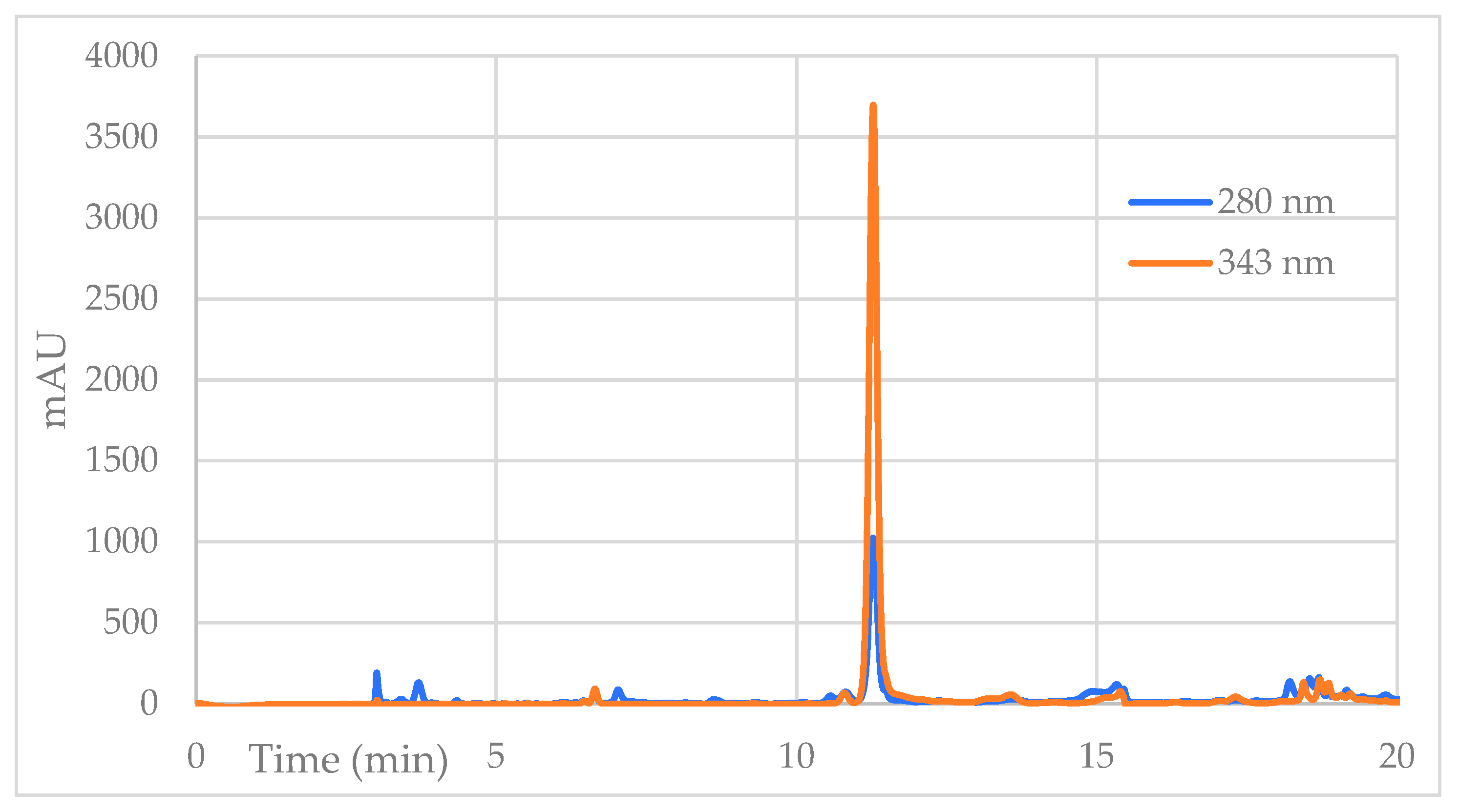
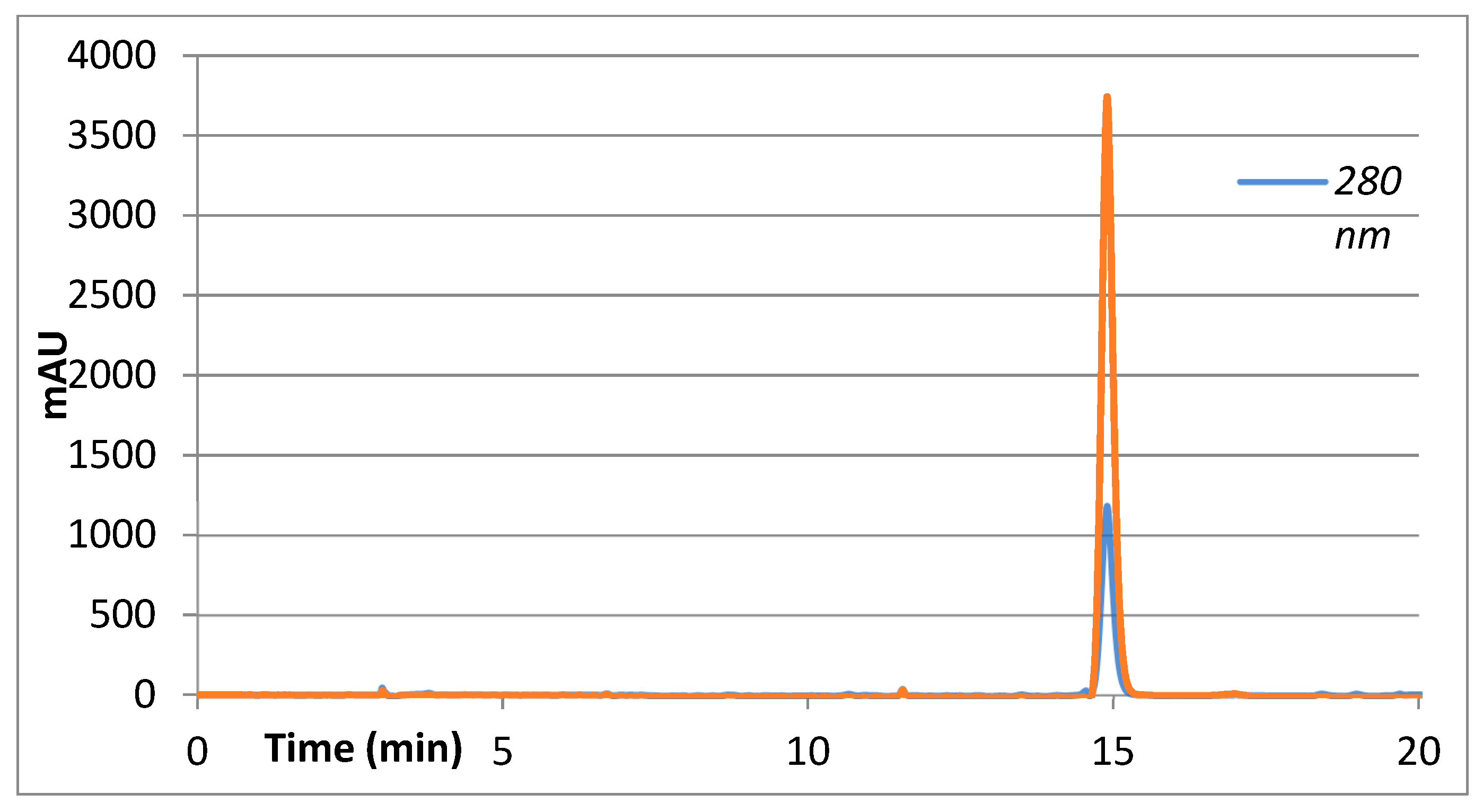

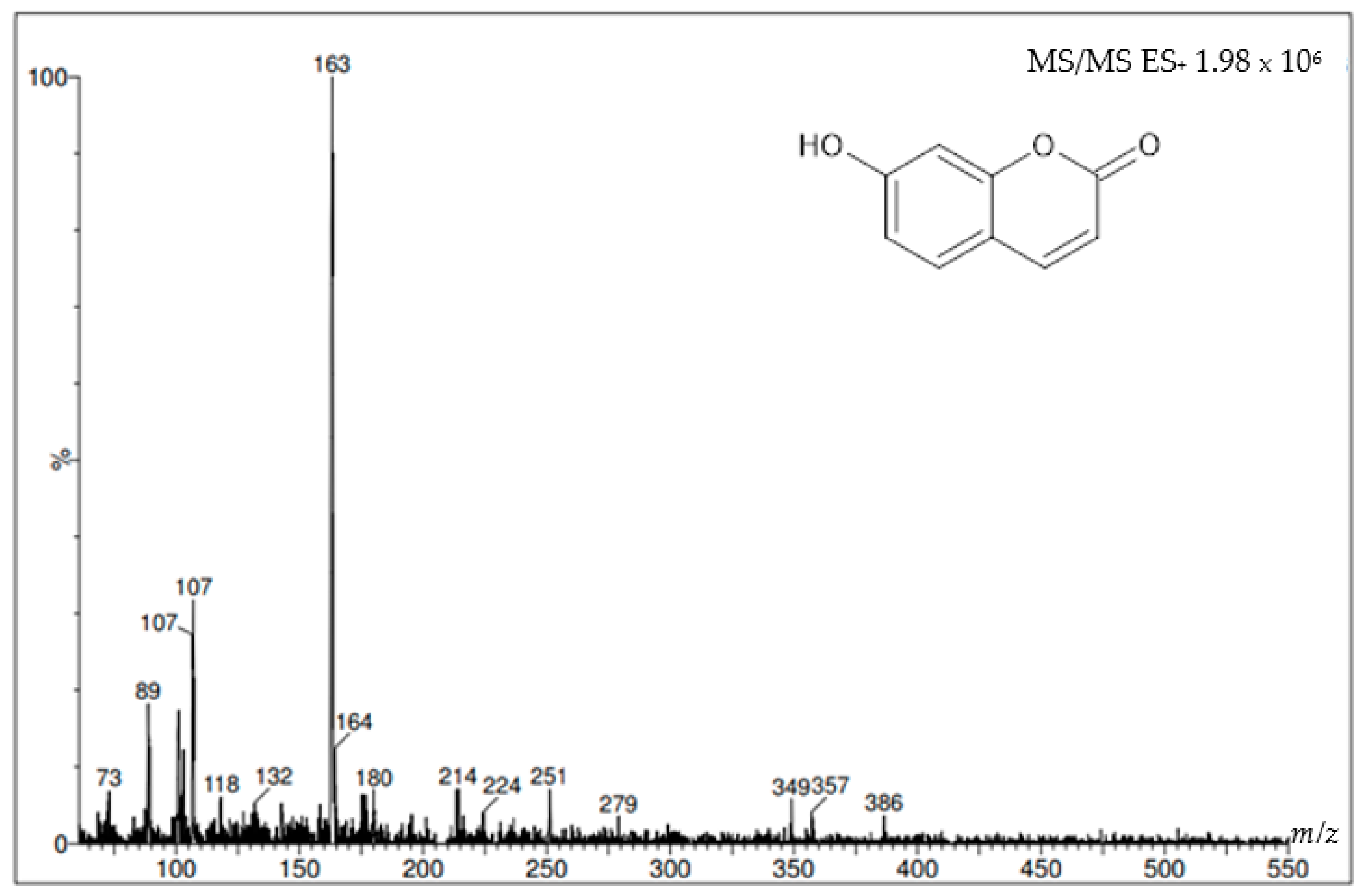

| Sample | Percent Mortality at 24 h |
|---|---|
| Stems | 71.3 ± 4.8% |
| Leaves | 40.0 ± 0.0% |
| Positive control | 100 ± 0% |
| Negative control | 0 ± 0% |
| Sample | Percent Mortality at 24 h |
|---|---|
| Crude ethanolic extract | 71.3 ± 4.8% |
| F.He | 0 ± 0% |
| F.DCM | 100 ± 0% |
| F.Ac | 18.8 ± 2.9% |
| F.Me | 0 ± 0% |
| Positive control | 100 ± 0% |
| Negative control | 0 ± 0% |
| Sample | Percent Mortality at 24 h * |
|---|---|
| F.DCM | 100 ± 0% |
| F.DCM (1) | 0 ± 0% |
| F.DCM (2) | 0 ± 0% |
| F.DCM (3) | 0 ± 0% |
| Positive control | 100 ± 0% |
| Negative control | 0 ± 0% |
| Fraction | LC50 in mg/L (95% CI *) | LC90 in mg/L (95% CI *) | Diagnostic Dose in mg/L (95% CI *) |
|---|---|---|---|
| F.DCM | 30.608 (23.9–39.1) | 79.875 (62.5–98.1) | 349.2 (273.1–446.4) |
| Crude ethanolic extract | 42.1 (32.1–55.0) | 131 (100.0–172.0) | 664 (507–870) |
| Sample | Percent Mortality |
|---|---|
| Scopoletin | 0 |
| Umbelliferone | 0 |
| Scopoletin + Umbelliferone | 0 |
| CONTROL+ | 100.00 |
| CONTROL− | 0.00 |
| Time (min) | Concentration of A | Concentration of B | Flow Rate (mL/min) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.01 | 85 | 15 | 1.00 |
| 3.00 | 65 | 35 | 1.00 |
| 7.00 | 60 | 40 | 1.00 |
| 10.00 | 55 | 45 | 1.00 |
| 13.00 | 50 | 50 | 1.00 |
| 15.00 | 50 | 50 | 0.50 |
| 16.00 | 50 | 50 | 0.50 |
| 18.00 | 15 | 85 | 0.50 |
| 18.00 | 15 | 85 | 1.25 |
| 19.00 | 0 | 100 | 1.25 |
| 20.00 | 85 | 15 | 1.00 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Álvarez Valverde, V.; Rodríguez Rodríguez, G.; Argüello Vargas, S. Bioguided Phytochemical Study of Ipomoea cairica Extracts with Larvicidal Activity against Aedes aegypti. Molecules 2022, 27, 1348. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27041348
Álvarez Valverde V, Rodríguez Rodríguez G, Argüello Vargas S. Bioguided Phytochemical Study of Ipomoea cairica Extracts with Larvicidal Activity against Aedes aegypti. Molecules. 2022; 27(4):1348. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27041348
Chicago/Turabian StyleÁlvarez Valverde, Víctor, Gerardo Rodríguez Rodríguez, and Silvia Argüello Vargas. 2022. "Bioguided Phytochemical Study of Ipomoea cairica Extracts with Larvicidal Activity against Aedes aegypti" Molecules 27, no. 4: 1348. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27041348
APA StyleÁlvarez Valverde, V., Rodríguez Rodríguez, G., & Argüello Vargas, S. (2022). Bioguided Phytochemical Study of Ipomoea cairica Extracts with Larvicidal Activity against Aedes aegypti. Molecules, 27(4), 1348. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27041348






