Analytical Techniques for Phytocannabinoid Profiling of Cannabis and Cannabis-Based Products—A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Botany of C. sativa
1.2. Phytocannabinoids
1.3. Use of C. sativa
1.4. Legal Aspect of C. sativa
1.5. Incentive for Investigating Phytocannabinoids in C. sativa and Cannabis-Based Products
2. Analytical Methods for Phytocannabinoid Profiling
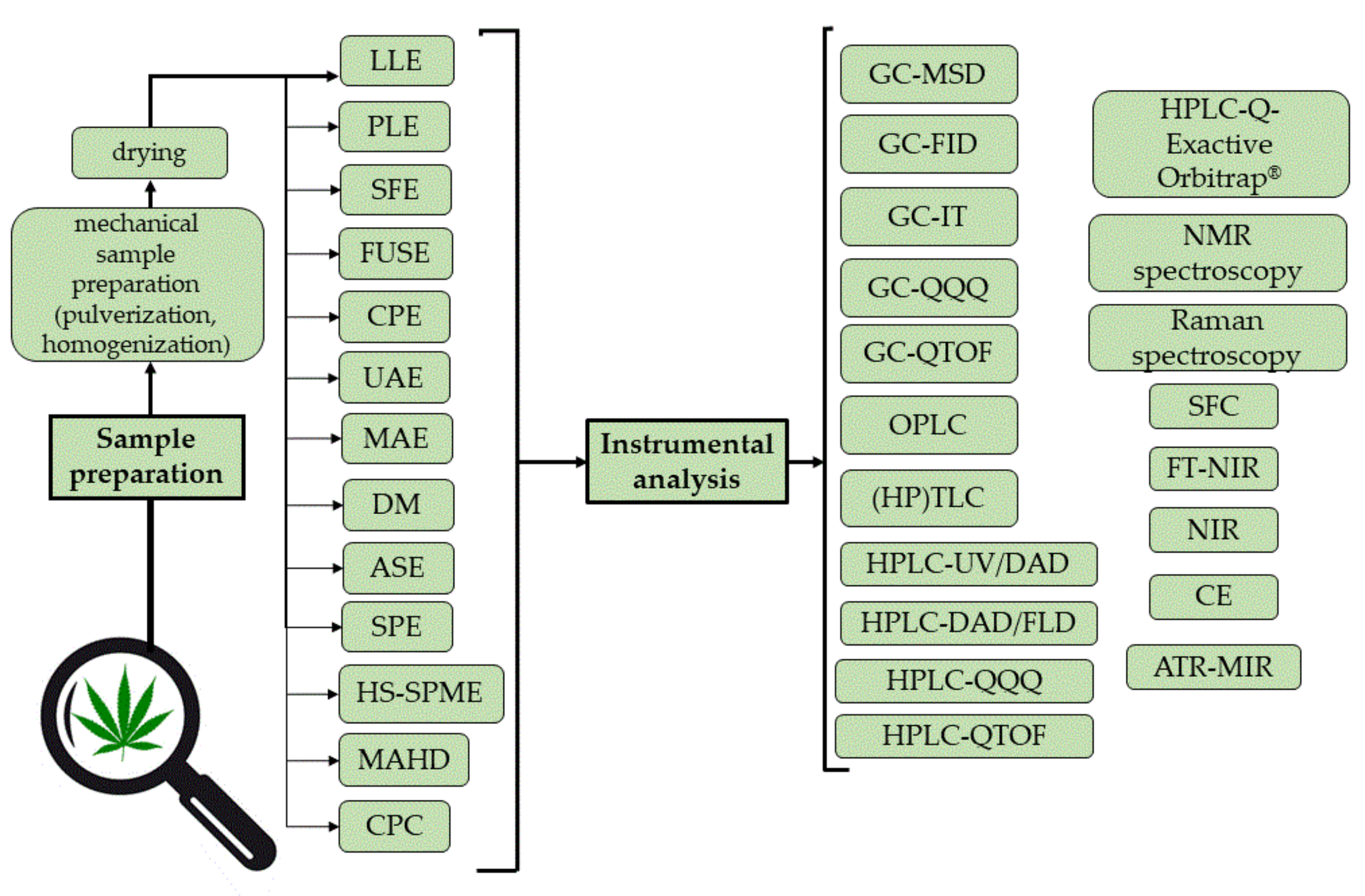
2.1. Sample Preparation Techniques
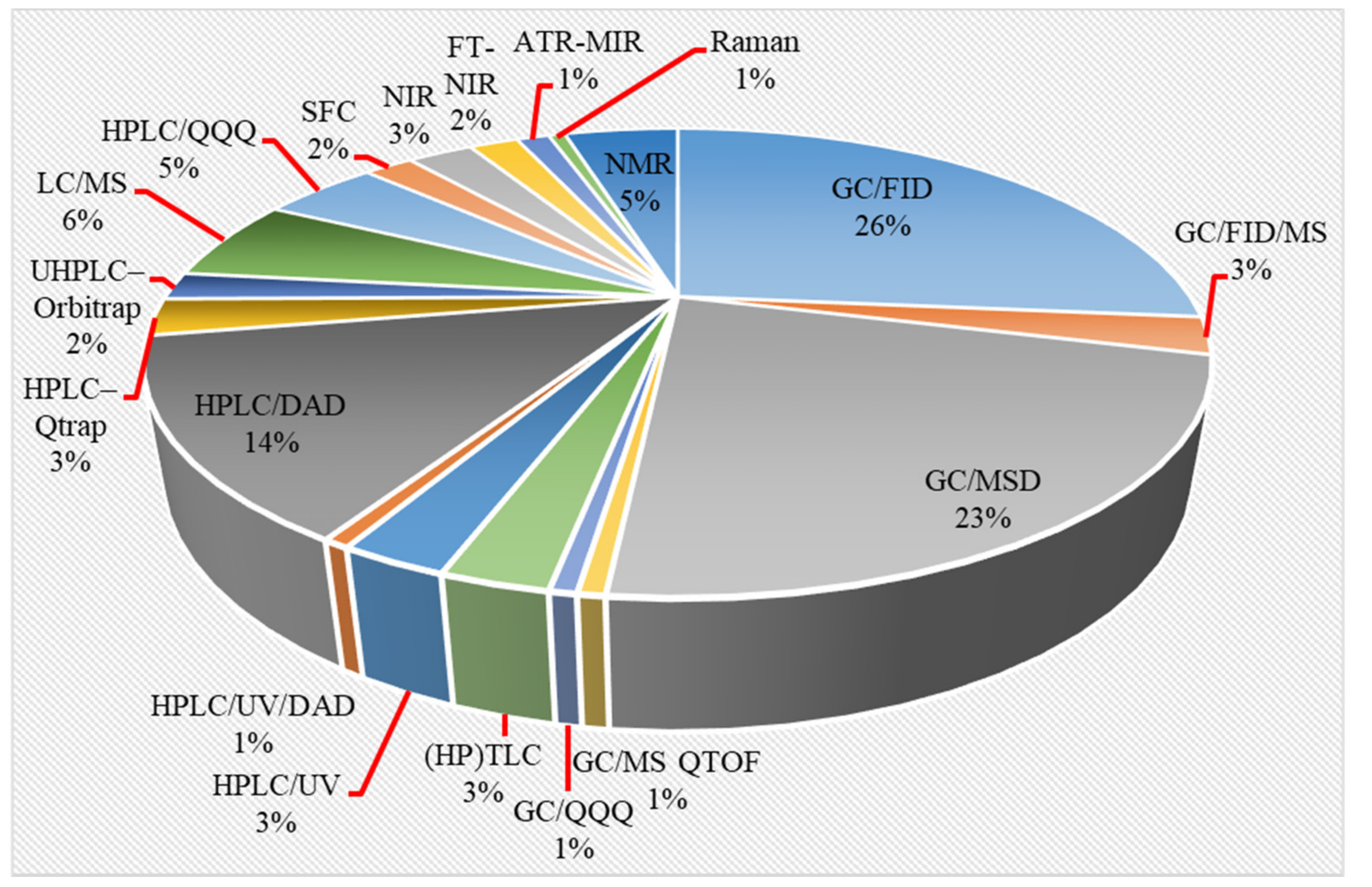
2.2. Instrumental Analysis
2.2.1. GC-Based Methods
- Derivatizationof Phytocannabinoids
- GC Columns
- GC Detectors
2.2.2. LC-Based Methods
- TLC and HPTLC Methods
- HPLC Methods
- HPLC Mobile Phases
- HPLC Columns
- HPLC Detectors
- Matrix Effect
2.2.3. SFC Methods
2.2.4. Vibrational Spectroscopy Methods
2.2.5. Other Analytical Techniques
- CE
- NMR Spectroscopy
3. Conclusions and Future Directions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Citti, C.; Braghiroli, D.; Vandelli, M.A.; Cannazza, G. Pharmaceutical and biomedical analysis of cannabinoids: A critical review. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 147, 565–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borille, B.T.; González, M.; Steffens, L.; Ortiz, R.S.; Limberger, R.P. Cannabis sativa: A systematic review of plant analysis. Drug Anal. Res. 2017, 1, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawler, J.; Stout, J.M.; Gardner, K.M.; Hudson, D.; Vidmar, J.; Butler, L.; Page, J.E.; Myles, S. The Genetic Structure of Marijuana and Hemp. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0133292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez, C.L.; Fanovich, M.A.; Churio, M.S. Cannabinoids: Extraction Methods, Analysis, and Physicochemical Characterization. In Studies in Natural Products Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 143–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime. Recommended Methods for the Identification and Analysis of Cannabis and Cannabis Products Manual for Use by National Drug Analysis Laboratories; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2009; Available online: http://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&scope=site&db=nlebk&db=nlabk&AN=450863 (accessed on 5 July 2020).
- Small, E.; Cronquist, A. A Practical and Natural Taxonomy for Cannabis. Taxon 1976, 25, 405–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, E. Evolution and Classification of Cannabis sativa (Marijuana, Hemp) in Relation to Human Utilization. Bot. Rev. 2015, 81, 189–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElSohly, M.A.; Slade, D. Chemical constituents of marijuana: The complex mixture of natural cannabinoids. Life Sci. 2005, 78, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmedic, Z.; Chandra, S.; Slade, D.; Denham, H.; Foster, S.; Patel, A.S.; Ross, S.A.; Khan, I.A.; ElSohly, M.A. Potency Trends of Δ9-THC and Other Cannabinoids in Confiscated Cannabis Preparations from 1993 to 2008*. J. Forensic Sci. 2010, 55, 1209–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Meijer, E.P.M.; Bagatta, M.; Carboni, A.; Crucitiit, P.; Moliterni, C.V.M.; Ranalli, P.; Mandolino, G. The Inheritance of Chemical Phenotype in Cannabis sativa L. Genetics 2003, 163, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aizpurua-Olaizola, O.; Omar, J.; Navarro, P.; Olivares, M.; Etxebarria, N.; Usobiaga, A. Identification and quantification of cannabinoids in Cannabis sativa L. plants by high performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 7549–7560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mechoulam, R.; Shvo, Y. The structure of cannabidiol. Tetrahedron 1963, 19, 2073–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaoni, Y.; Mechoulam, R. Isolation, Structure, and Partial Synthesis of an Active Constituent of Hashish. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1964, 86, 1646–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaoni, Y.; Mechoulam, R. Cannabichromene, a new active principle in hashish. Chem. Commun. 1966, 20–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollner, L.; Bieniek, D.; Korte, F. Cannabidivarin, ein neur Haschisch-Inhalsstoff. Tetrahedron Lett. 1969, 10, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, E.W.; Paton, W.D.M.; Pertwee, R.G. Preliminary Experiments on the Chemistry and Pharmacology of Cannabis. Nature 1970, 228, 134–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tipparat, P.; Kunkaew, W.; Julsrigival, S.; Pinmanee, S.; Natakankitkul, S. Classification of Cannabis Plants Grown in Northern Thailand using physico-chemical properties. J. Nat. Sci. Res. 2014, 10, 46–54. [Google Scholar]
- Hazekamp, A.; Peltenburg, A.; Verpoorte, R.; Giroud, C. Chromatographic and Spectroscopic Data of Cannabinoids from Cannabis sativa L. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2005, 28, 2361–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, P.; Futoran, K.; Lewitus, G.M.; Mukha, D.; Benami, M.; Shlomi, T.; Meiri, D. A new ESI-LC/MS approach for comprehensive metabolic profiling of phytocannabinoids in Cannabis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.H.; Hazekamp, A.; Peltenburg-Looman, A.M.G.; Frédérich, M.; Erkelens, C.; Lefeber, A.W.M.; Verpoorte, R. NMR assignments of the major cannabinoids and cannabiflavonoids isolated from flowers of Cannabis sativa. Phytochem. Anal. 2004, 15, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geskovski, N.; Stefkov, G.; Gigopulu, O.; Stefov, S.; Huck, C.W.; Makreski, P. Mid-infrared spectroscopy as process analytical technology tool for estimation of THC and CBD content in Cannabis flowers and extracts. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2021, 251, 119422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigopulu, O.; Geskovski, N.; Stefkov, G.; Stoilkovska, V.; Spirevska, I.S.; Huck, C.W.; Makreski, P. Synergistic use of FTIR spectroscopy and TG to elucidate the solid state THCA decarboxylation reaction kinetics in THCA standard and cannabis flower. Anal. Chem. 2022, 267, 18. [Google Scholar]
- Russo, E.B. History of Cannabis and Its Preparations in Saga, Science, and Sobriquet. Chem. Biodivers. 2007, 4, 1614–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pertwee, R.G. Handbook of Cannabis. In Oxford Scholarship; Oxford University Press: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Leonard, W.; Zhang, P.; Ying, D.; Fang, Z. Hempseed in food industry: Nutritional value, health benefits, and industrial applications. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 282–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geshtakovska, G.; Stefkov, G. Routes of cannabis administration: A brief review. In Modern Pharmacist-Bridging Science with Practice; Macedonian Pharmaceutical Bulletin; Macedonian Pharmaceutical Association: Ohrid, Macedonia, 2016; pp. 515–516. [Google Scholar]
- Muscarà, C.; Smeriglio, A.; Trombetta, D.; Mandalari, G.; la Camera, E.; Grassi, G.; Circosta, C. Phytochemical characterization and biological properties of two standardized extracts from a non-psychotropic Cannabis sativa L. cannabidiol (CBD)-chemotype. Phytother. Res. 2021, 35, 5269–5281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, R.F.X. Analysis of “Marijuana Edibles”—Food Products Containing Marijuana or Marijuana Extracts—An Overview, Review, and Literature Survey. Microgram J. 2017, 14, 24. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, R. Hemp as an Agricultural Commodity; Congressional Research Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Common Catalogue of Varieties of Agricultural Plant Species. In Official Journal of the European Union; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2012; p. 39. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Commission Regulation (EC) No. 327/2002. In Official Journal of the European Communities; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Vereinte Nationen, Büro für Drogenkontrolle und Verbrechensbekämpfung. World Drug Report; Vereinte Nationen: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Upton, R.; Craker, L.; ElSohly, M.; Romm, A.; Russo, E.; Sexton, M. American Herbal Pharmacopoeia, Cannabis Inflorescence: Cannabis spp.; Standards of Identity, Analysis, and Quality Control; American Herbal Pharmacopoeia: Scotts Valley, CA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Swissmedic Swiss Agency for Therapeutic Products Pharmacopoeia Division. Fleur de Cannabis. In Pharmacopoeia Helvetica, 11th ed.; Supplement 11.3; Swissmedic Swiss Agency for Therapeutic Products Pharmacopoeia Division: Bern, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Council of Europe. Cannabis flos Monograph N°: 3028. In European Pharmacopoeia, 10th ed.; Council of Europe: Strasbourg, France, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Geschäftsstelle der Arzneibuch-Kommissionen. Bundesinstitut fur Arzneimittel und Miedizinprodukte, Monografie Cannabisblüten. In German Pharmacopoeia, 2020th ed.; Geschäftsstelle der Arzneibuch-Kommissionen: Bundesinstitut fur Arzneimittel und Miedizinprodukte: Bonn, German, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez, E.B.; Peterseil, V.; Hackl, G.; Menges, S.; de Meijer, E.; Staginnus, C. Distribution of Chemical Phenotypes (Chemotypes) in European Agricultural Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) Cultivars. J. Forensic Sci. 2020, 65, 715–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geschäftsstelle der Arzneibuch-Kommissionen. Bundesinstitut fur Arzneimittel und Miedizinprodukte, Monografie Cannabis extractum normatum (Eingestellter Cannabis-Extrakt). In German Pharmacopoeia; Geschäftsstelle der Arzneibuch-Kommissionen, Bundesinstitut fur Arzneimittel und Miedizinprodukte: Bern, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Nahar, L.; Guo, M.; Sarker, S.D. Gas chromatographic analysis of naturally occurring cannabinoids: A review of literature published during the past decade. Phytochem. Anal. 2020, 31, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brighenti, V.; Pellati, F.; Steinbach, M.; Maran, D.; Benvenuti, S. Development of a new extraction technique and HPLC method for the analysis of non-psychoactive cannabinoids in fibre-type Cannabis sativa L. (hemp). J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 143, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naviglio, D.; Scarano, P.; Ciaravolo, M.; Gallo, M. Rapid Solid-Liquid Dynamic Extraction (RSLDE): A Powerful and Greener Alternative to the Latest Solid-Liquid Extraction Techniques. Foods 2019, 8, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knezevic, F.; Nikolai, A.; Marchart, R.; Sosa, S.; Tubaro, A.; Novak, J. Residues of herbal hemp leaf teas—How much of the cannabinoids remain? Food Control. 2021, 127, 108146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, J.; Olivares, M.; Alzaga, M.; Etxebarria, N. Optimisation and characterisation of marihuana extracts obtained by supercritical fluid extraction and focused ultrasound extraction and retention time locking GC-MS: Gas Chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2013, 36, 1397–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fairbairn, J.W.; Liebmann, J.A. The extraction and estimation of the cannabinoids in Cannabis sativa L. and its products. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1973, 25, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, R.; Ward, S.; Johnson, R.; Burns, D.T. Distribution of the principal cannabinoids within bars of compressed cannabis resin. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2005, 538, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNODC. Bulletin on Narcotics; Issue 1—005, Office on Drugs and Crime: Vienna, Austria, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Mechtler, K.; Bailer, J.; de Hueber, K. Variations of ∆9-THC Content in Single Plants of Hemp Varieties. Ind. Crops Prod. 2004, 19, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niesink, R.J.M.; Rigter, S.; Koeter, M.W.; Brunt, T.M. Potency trends of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol, cannabidiol and cannabinol in cannabis in the Netherlands: 2005-15: Potency trends of Dutch cannabis. Addiction 2015, 110, 1941–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsumura, Y.; Aoki, R.; Tokieda, Y.; Akutsu, M.; Kawase, Y.; Kataoka, T.; Takagi, T.; Mizuno, T.; Fukada, M.; Fujii, H.; et al. A survey of the potency of Japanese illicit cannabis in fiscal year 2010. Forensic Sci. Int. 2012, 221, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, D.; Dai, K.; Xie, Z.; Chen, J. Secondary Metabolites Profiled in Cannabis Inflorescences, Leaves, Stem Barks, and Roots for Medicinal Purposes. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischedick, J.T.; Hazekamp, A.; Erkelens, T.; Choi, Y.H.; Verpoorte, R. Metabolic fingerprinting of Cannabis sativa L., cannabinoids and terpenoids for chemotaxonomic and drug standardization purposes. Phytochemistry 2010, 71, 2058–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillig, K.W.; Mahlberg, P.G. A chemotaxonomic analysis of cannabinoid variation in Cannabis (Cannabaceae). Am. J. Bot. 2004, 91, 966–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazekamp, A.; Tejkalová, K.; Papadimitriou, S. Cannabis: From Cultivar to Chemovar II—A Metabolomics Approach to Cannabis Classification. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2016, 1, 202–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruci, Z.; Papoutsis, I.; Athanaselis, S.; Nikolaou, P.; Pazari, E.; Spiliopoulou, C.; Vyshka, G. First systematic evaluation of the potency of Cannabis sativa plants grown in Albania. Forensic Sci. Int. 2012, 222, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Béres, T.; Černochová, L.; Zeljković, S.Ć.; Benická, S.; Gucký, T.; Berčák, M.; Tarkowski, P. Intralaboratory comparison of analytical methods for quantification of major phytocannabinoids. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 3069–3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gröger, T.; Schäffer, M.; Pütz, M.; Ahrens, B.; Drew, K.; Eschner, M.; Zimmermann, R. Application of two-dimensional gas chromatography combined with pixel-based chemometric processing for the chemical profiling of illicit drug samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1200, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janatová, A.; Fraňková, A.; Tlustoš, P.; Hamouz, K.; Božik, M.; Klouček, P. Yield and cannabinoids contents in different cannabis (Cannabis sativa L.) genotypes for medical use. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 112, 363–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, B.I.; Arndt, R.R. Cannabinoid compounds in South African Cannabis sativa L. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1980, 32, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilias, Y.; Rudaz, S.; Mathieu, P.; Christen, P.; Veuthey, J.-L. Extraction and analysis of different Cannabis samples by headspace solid-phase microextraction combined with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Sep. Sci. 2005, 28, 2293–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavlovic, R.; Nenna, G.; Calvi, L.; Panseri, S.; Borgonovo, G.; Giupponi, L.; Cannazza, G.; Giorgi, A. Quality Traits of “Cannabidiol Oils”: Cannabinoids Content, Terpene Fingerprint and Oxidation Stability of European Commercially Available Preparations. Molecules 2018, 23, 1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giupponi, L.; Leoni, V.; Pavlovic, R.; Giorgi, A. Influence of Altitude on Phytochemical Composition of Hemp Inflorescence: A Metabolomic Approach. Molecules 2020, 25, 1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlovic, R.; Panseri, S.; Giupponi, L.; Leoni, V.; Citti, C.; Cattaneo, C.; Cavaletto, M.; Giorgi, A. Phytochemical and Ecological Analysis of Two Varieties of Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) Grown in a Mountain Environment of Italian Alps. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvi, L.; Pentimalli, D.; Panseri, S.; Giupponi, L.; Gelmini, F.; Beretta, G.; Vitali, D.; Bruno, M.; Zilio, E.; Pavlovic, R.; et al. Comprehensive quality evaluation of medical Cannabis sativa L. inflorescence and macerated oils based on HS-SPME coupled to GC–MS and LC-HRMS (q-exactive orbitrap®) approach. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 150, 208–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisciottano, I.D.M.; Guadagnuolo, G.; Soprano, V.; Esposito, M.; Gallo, P. A survey of Δ9-THC and relevant cannabinoids in products from the Italian market: A study by LC–MS/MS of food, beverages and feed. Food Chem. 2021, 346, 128898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Garcés, N.; Myers, C. Analysis of the California list of pesticides, mycotoxins, and cannabinoids in chocolate using liquid chromatography and low-pressure gas chromatography-based platforms. J. Sep. Sci. 2021, 44, 2564–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namdar, D.; Mazuz, M.; Ion, A.; Koltai, H. Variation in the compositions of cannabinoid and terpenoids in Cannabis sativa derived from inflorescence position along the stem and extraction methods. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 113, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stambouli, H.; Bouri, A.E.; Bellimam, M.A.; Bouayoun, T.; Karni, N.E. Cultivation of Cannabis sativa L. in northern Morocco. Bull. Narc. 2005, 57, 79–118. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zaripov, E.A.; Lee, T.; Dou, Y.; Harris, C.S.; Egorov, A.; Berezovski, M.V. Single-Run Separation and Quantification of 14 Cannabinoids Using Capillary Electrophoresis. Separations 2021, 8, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinová, J.P.; Vrchotová, N.; Tříska, J.; Hellerová, Š. Industrial hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) as a possible source of cannabidiol. J. Cent. Eur. Agric. 2021, 22, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Union method for the quantitative determination of the Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol content in hemp varieties. Delegated regulation (EU) No 639/2014, Annex III as amended by Regulation (EU) 2017/1155. In Official Journal of the European Communities; 2017; Volume 167, pp. 1–15. Available online: http://data.europa.eu/eli/reg_del/2017/1155/oj (accessed on 8 February 2021).
- Hewavitharana, A.K.; Golding, G.; Tempany, G.; King, G.; Holling, N. Quantitative GC-MS Analysis of Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol in Fiber Hemp Varieties. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2005, 29, 258–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, S.; Lata, H.; Mehmedic, Z.; Khan, I.; ElSohly, M. Assessment of Cannabinoids Content in Micropropagated Plants of Cannabis sativa and Their Comparison with Conventionally Propagated Plants and Mother Plant during Developmental Stages of Growth. Planta Med. 2010, 76, 743–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delta9-THC determination by the EU official method: Evaluation of Measurement Uncertainty and Compliance Assessment of Hemp Samples|SpringerLink, (n.d.). Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00216-021-03283-x (accessed on 18 July 2021).
- Florian-Ramirez, N.M.; Parada-Alfonso, F.; Garzon-Mendez, W.F. Estudio del contenido de cannabinoids en muestras de marihuana (Cannabis sativa L.) cultivadas en varies regiones de Colombia, Vitae. Rev. De La Faculdad De Quim. Farm. 2009, 16, 237–244. [Google Scholar]
- Pacifico, D.; Miselli, F.; Micheler, M.; Carboni, A.; Ranalli, P.; Mandolino, G. Genetics and Marker-assisted Selection of the Chemotype in Cannabis sativa L. Mol. Breed. 2006, 17, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacifico, D.; Miselli, F.; Carboni, A.; Moschella, A.; Mandolino, G. Time course of cannabinoid accumulation and chemotype development during the growth of Cannabis sativa L. Euphytica 2008, 160, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, J.C.; Hemphill, J.K.; Mahlberg, P.G. Gland distribution and cannabinoid content in clones of Cannabis sativa L. Am. J. Bot. 1977, 64, 687–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Povedano, M.M.; Callado, C.S.; Priego-Capote, F.; Ferreiro-Vera, C. Untargeted characterization of extracts from Cannabis sativa L. cultivars by gas and liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry in high resolution mode. Talanta 2020, 208, 120384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tipparat, P.; Natakankitkul, S.; Chamnivikaipong, P.; Chutiwat, S. Characteristics of cannabinoids composition of Cannabis plants grown in Northern Thailand and its forensic application. Forensic Sci. Int. 2012, 215, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuapia, Y.; Maraba, K.; Tutu, H.; Chimuka, L.; Cukrowska, E. In Situ Decarboxylation-Pressurized Hot Water Extraction for Selective Extraction of Cannabinoids from Cannabis sativa. Chemometric Approach. Molecules 2021, 26, 3343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadola, L.; Broséus, J.; Esseiva, P. Chemical profiling of different hashish seizures by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry and statistical methodology: A case report. Forensic Sci. Int. 2013, 232, e24–e27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamengo, L.; Frison, G.; Bettin, C.; Sciarrone, R. Variability of cannabis potency in the Venice area (Italy): A survey over the period 2010–2012: Variability of cannabis potency in the Venice area (Italy): A survey over the period 2010–2012. Drug Test. Anal. 2014, 6, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Backer, B.; Debrus, B.; Lebrun, P.; Theunis, L.; Dubois, N.; Decock, L.; Verstraete, A.; Hubert, P.; Charlier, C. Innovative development and validation of an HPLC/DAD method for the qualitative and quantitative determination of major cannabinoids in cannabis plant material. J. Chromatogr. B 2009, 877, 4115–4124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardenia, V.; Toschi, T.G.; Scappini, S.; Rubino, R.C.; Rodriguez-Estrada, M.T. Development and validation of a Fast gas chromatography/mass spectrometry method for the determination of cannabinoids in Cannabis sativa L. J. Food Drug Anal. 2018, 26, 1283–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaa, E. Cannabis plants illicitly grown in Jutland (Denmark). Z. Rechtsmed. 1989, 102, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de CássiaMariotti, K.; Marcelo, M.C.A.; Ortiz, R.S.; Borille, B.T.; Reis, M.d.; Fett, M.S.; Ferrão, M.F.; Limberger, R.P. Seized cannabis seeds cultivated in greenhouse: A chemical study by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry and chemometric analysis. Sci. Justice 2016, 56, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazekamp, A.; Simons, R.; Peltenburg-Looman, A.; Sengers, M.; van Zweden, R.; Verpoorte, R. Preparative Isolation of Cannabinoids from Cannabis sativa by Centrifugal Partition Chromatography. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2004, 27, 2421–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fodor, B.; Boldizsár, I.; Molnár-Perl, I. Alkylsilyl speciation and direct sample preparation of plant cannabinoids prior to their analysis by GC-MS. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1021, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, E.; Kim, H.; Jang, S.; Lee, J.; Baeck, S.; In, S.; Kim, E.; Kim, Y.; Han, E. Concentrations of THC, CBD, and CBN in commercial hemp seeds and hempseed oil sold in Korea | Elsevier Enhanced Reader. Forensic Sci. Int. 2020, 306, 110064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciolino, L.A.; Ranieri, T.L.; Taylor, A.M. Commercial cannabis consumer products part 1: GC–MS qualitative analysis of cannabis cannabinoids. Forensic Sci. Int. 2018, 289, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yotoriyama, M.; Ishiharajima, E.; Kato, Y.; Nagato, A.; Sekita, S.; Watanabe, K.; Yamamoto, I. Identification and Determination of Cannabinoids in both Commercially Available and Cannabis Oils Stored Long Term. J. Health Sci. 2005, 51, 483–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheunemann, A.; Elsner, K.; Germerott, T.; Hess, C.; Zörntlein, S.; Röhrich, J. Extensive phytocannabinoid profiles of seized cannabis and cannabis-based medicines—Identification of potential distinguishing markers. Forensic Sci. Int. 2021, 322, 110773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitts, J.E.; O’Neil, P.J.; Leggo, K.P. Variation in the THC Content of Illicitly Imported Cannabis* Products-1984–1989. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1990, 42, 817–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casiraghi, A.; Roda, G.; Casagni, E.; Cristina, C.; Musazzi, U.; Franzè, S.; Rocco, P.; Giuliani, C.; Fico, G.; Minghetti, P.; et al. Extraction Method and Analysis of Cannabinoids in Cannabis Olive Oil Preparations. Planta Med. 2018, 84, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wianowska, D.; Dawidowicz, A.L.; Kowalczyk, M. Transformations of Tetrahydrocannabinol, tetrahydrocannabinolic acid and cannabinol during their extraction from Cannabis sativa L. J. Anal. Chem. 2015, 70, 920–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trofin, I.G.; Vlad, C.C.; Noja, V.V.; Dabija, G. Identification and characterization of special types of herbal Cannabis. UPB Sci. Bull. 2012, 74, 13. [Google Scholar]
- Mölleken, H.; Husmann, H. Cannabinoids in seed extracts of Cannabis sativa cultivars. J. Int. Hemp Assoc. 1997, 4, 76–79. Available online: http://www.druglibrary.org/olsen/hemp/IHA/jiha4201.html (accessed on 5 July 2020).
- Gambaro, V.; Dell’Acqua, L.; Farè, F.; Froldi, R.; Saligari, E.; Tassoni, G. Determination of primary active constituents in Cannabis preparations by high-resolution gas chromatography/flame ionization detection and high-performance liquid chromatography/UV detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 2002, 468, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachenmeier, D.W.; Kroener, L.; Musshoff, F.; Madea, B. Determination of cannabinoids in hemp food products by use of headspace solid-phase microextraction and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2004, 378, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galettis, P.; Williams, M.; Gordon, R.; Martin, J.H. A Simple Isocratic HPLC Method for the Quantitation of 17 Cannabinoids. Aust. J. Chem. 2021, 74, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, G.L.; Voloch, M.H.; Sztulman, G.B.; Neto, O.N.; Yonamine, M. Cannabinoid contents in cannabis products seized in São Paulo, Brazil, 2006–2007. Forensic Toxicol. 2008, 26, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, D.J.; Hammond, K.; Tuffnell, S.; Walker, C.; di Forti, M. Potency of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol and other cannabinoids in cannabis in England in 2016: Implications for public health and pharmacology. Drug Test. Anal. 2018, 10, 628–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazekamp, A.; Fischedick, J.T. Cannabis—From cultivar to chemovar: Towards a better definition of Cannabis potency. Drug Test. Anal. 2012, 4, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potter, D.J.; Clark, P.; Brown, M.B. Potency of Δ9–THC and Other Cannabinoids in Cannabis in England in 2005: Implications for Psychoactivity and Pharmacology. J. Forensic Sci. 2008, 53, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, G.; Hansen, S.; Connor, M.; Poulsen, H.; McGovern, C.; Stacey, J. The results of an experimental indoor hydroponic Cannabis growing study, using the ‘Screen of Green’ (ScrOG) method—Yield, tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and DNA analysis. Forensic Sci. Int. 2010, 202, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Meijer, E.P.M.; Hammond, K.M.; Sutton, A. The inheritance of chemical phenotype in Cannabis sativa L. (IV): Cannabinoid-free plants. Euphytica 2009, 168, 95–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florian-Ramirez, N.M.; Garzon-Mendez, W.F.; Parada-Alfonso, F. Gas Chromatography in Forensic Chemistry: Cannabinoids Content in Marijuana Leaves (Cannabis sativa L.) from Colombia. In Gas Chromatography—Biochemicals Narcotics and Essential Oils; Salih, B., Ed.; InTech: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Poulsen, H.A.; Sutherland, G.J. The potency of cannabis in New Zealand from 1976 to 1996. Sci. Justice 2000, 40, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremlová, B.; Mikulášková, H.K.; Hajduchová, K.; Jancikova, S.; Kaczorová, D.; Zeljković, S.Ć.; Dordevic, D. Influence of Technological Maturity on the Secondary Metabolites of Hemp Concentrate (Cannabis sativa L.). Foods 2021, 10, 1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischedick, J.T.; Glas, R.; Hazekamp, A.; Verpoorte, R. A qualitative and quantitative HPTLC densitometry method for the analysis of cannabinoids in Cannabis sativa L. Phytochem. Anal. 2009, 20, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubrow, G.A.; Pawar, R.S.; Srigley, C.; Sam, J.F.; Talavera, C.; Parker, C.H.; Noonan, G.O. A survey of cannabinoids and toxic elements in hemp-derived products from the United States marketplace. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2021, 97, 103800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glivar, T.; Eržen, J.; Kreft, S.; Zagožen, M.; Čerenak, A.; Čeh, B.; Benković, E.T. Cannabinoid content in industrial hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) varieties grown in Slovenia. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 145, 112082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saloner, A.; Bernstein, N. Nitrogen supply affects cannabinoid and terpenoid profile in medical cannabis (Cannabis sativa L.). Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 167, 113516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamengo, L.; Frison, G.; Bettin, C.; Sciarrone, R. Cannabis potency in the Venice area (Italy): Update 2013: Cannabis potency in the Venice area (Italy): Update 2013. Drug Test. Anal. 2015, 7, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dussy, F.E.; Hamberg, C.; Luginbühl, M.; Schwerzmann, T.; Briellmann, T.A. Isolation of Δ9-THCA-A from hemp and analytical aspects concerning the determination of Δ9-THC in cannabis products. Forensic Sci. Int. 2005, 149, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, D.J. Cyclic alkylboronates as derivatives for the characterization of cannabinolic acids by combined gas chromatography and mass spectrometry. Biol. Mass Spectrom. 1977, 4, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandohee, J.; Holland, B.J.; Li, B.; Tsuzuki, T.; Stevenson, P.G.; Barnett, N.W.; Pearson, J.R.; Jones, O.A.H.; Conlan, X.A. Screening of cannabinoids in industrial-grade hemp using two-dimensional liquid chromatography coupled with acidic potassium permanganate chemiluminescence detection: Liquid Chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2015, 38, 2024–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fetterman, P.S.; Doorenbos, N.J. A simple gas liquid chromatography procedure for determination of cannabinoldlc Acids In Cannabis sativa L. Experimentia 1971, 27, 988–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tucker, R.B.; Graham, B.F. Cannabinoid Content of Colombian Cannabis. Can. Soc. Forensic Sci. J. 1981, 14, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurty, H.G.; Kaushal, R. Analysis of Indian Marihuana. Indian J. Pharmacol. 1974, 36, 152–154. [Google Scholar]
- Stefanidou, M.; Dona, A.; Athanaselis, S.; Papoutsis, I.; Koutselinis, A. The cannabinoid content of marihuana samples seized in Greece and its forensic application. Forensic Sci. Int. 1998, 95, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanidou, M.; Athanaselis, S.; Alevisopolous, G.; Papoutsis, I.; Koutselinis, A. Delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol content in cannabis plants of Greek origin. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2000, 48, 743–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tayyab, M.; Shahwar, D. GCMS analysis of Cannabis sativa L. from four different areas of Pakistan. Egypt. J. Forensic Sci. 2015, 5, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kladar, N.; Čonić, B.S.; Božin, B.; Torović, L. European hemp-based food products—Health concerning cannabinoids exposure assessment. Food Control. 2021, 129, 108233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galand, N.; Ernouf, D.; Montigny, F.; Dollet, J.; Pothier, J. Separation and Identification of Cannabis Components by Different Planar Chromatography Techniques (TLC, AMD, OPLC). J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2004, 42, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, N.A.; Souza, L.M.; Domingos, E.; França, H.S.; Lacerda, V.; Beatriz, A.; Vaz, B.G.; Rodrigues, R.R.T.; Carvalho, V.V.; Merlo, B.B.; et al. Evaluating the selectivity of colorimetric test (Fast Blue BB salt) for the cannabinoids identification in marijuana street samples by UV–Vis, TLC, ESI(+)FT-ICR MS and ESI(+)MS/MS. Forensic Chem. 2016, 1, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Brettell, T.A.; Victoria, J.; Wood, M.R.; Staretz, M.E. High performance thin-layer chromatography (HPTLC) analysis of cannabinoids in cannabis extracts. Forensic Chem. 2020, 19, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caligiani, A.; Palla, G.; Bernardelli, B. GC-MS Analysis of Hashish Samples: A Case of Adulteration with Colophony. J. Forensic Sci. 2006, 51, 1096–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollner, L.; Bieniek, D.; Korte, F. Review of analytical methods for identification and quantification of Cannabis products. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 1986, 6, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsunaga, T.; Nagatomo, H.; Yamamoto, I.; Yoshimura, H. Identification and determination of cannabinoids in commercially available cannabis seeds. Eisei Kagaku 1990, 36, 545–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewari, S.N.; Harpalani, S.P.; Sharma, S.C. Separation and identification of the constituents of hashish (cannabis indica linn.) by thin-layer chromatography and its application in forensic analysis. Mikrochim Acta 1974, 62, 991–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, E.; Gul, W.; Gul, S.; Stamper, B.; Hadad, G.; Salam, R.A.; Ibrahim, A.; Ahmed, S.; Chandra, S.; Lata, H.; et al. Determination of Acid and Neutral Cannabinoids in Extracts of Different Strains of Cannabis sativa Using GC-FID. Planta Med. 2018, 84, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schettino, L.; Prieto, M.; Benedé, J.L.; Chisvert, A.; Salvador, A. A Rapid and Sensitive Method for the Determination of Cannabidiol in Cosmetic Products by Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Cosmetics 2021, 8, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccolella, S.; Formato, M.; Pecoraro, M.T.; Crescente, G.; Pacifico, S. Discrimination of CBD-, THC- and CBC-type acid cannabinoids through diagnostic ions by UHPLC-HR-MS/MS in negative ion mode. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 201, 114125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNODC. Bulletin on Narcotics; Issue 2—008, United Nations, Office on Drugs and Crime: Vienna, Austria, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, P.B.; Taylor, B.J.; Gough, T.A. The tetrahydrocannabinol and tetrahydrocannabinolic acid content of cannabis products. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1981, 33, 369–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ElSohly, M.A.; Mehmedic, Z.; Foster, S.; Gon, C.; Chandra, S.; Church, J.C. Changes in Cannabis Potency Over the Last 2 Decades (1995–2014): Analysis of Current Data in the United States. Biol. Psychiatry 2016, 79, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stambouli, H.; el Bouri, A.; Bouayoun, T. Évolution de la teneur en Δ9-THC dans les saisies de résines de cannabis au Maroc de 2005 à 2014. Toxicol. Anal. Et Clin. 2016, 28, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, S.A.; Mehmedic, Z.; Murphy, T.P.; Elsohly, M.A. GC-MS Analysis of the total delta9-THC content of bBoth drug- and fiber-type cannabis seeds. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2000, 24, 715–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrović, M.; Debeljak, Ž.; Kezić, N.; Džidara, P. Relationship between cannabinoids content and composition of fatty acids in hempseed oils. Food Chem. 2015, 170, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licata, M.; Verri, P.; Beduschi, G. δ9 THC content in illicit cannabis products. Ann. Ist Super Sanita 2005, 41, 483–485. [Google Scholar]
- Swift, W.; Wong, A.; Li, K.M.; Arnold, J.C.; McGregor, I.S. Analysis of Cannabis Seizures in NSW, Australia: Cannabis Potency and Cannabinoid Profile. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rovetto, L.J.; Aieta, N.V. Supercritical carbon dioxide extraction of cannabinoids from Cannabis sativa L. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2017, 129, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christinat, N.; Savoy, M.-C.; Mottier, P. Development, validation and application of a LC-MS/MS method for quantification of 15 cannabinoids in food. Food Chem. 2020, 318, 126469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameur, S.; Haddou, B.; Derriche, Z.; Canselier, J.P.; Gourdon, C. Cloud point extraction of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol from cannabis resin. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 3117–3123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Gunjević, V.; Grillo, G.; Carnaroglio, D.; Binello, A.; Barge, A.; Cravotto, G. Selective recovery of terpenes, polyphenols and cannabinoids from Cannabis sativa L. inflorescences under microwaves. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 162, 113247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poddar, M.K.; Ghosh, J.J.; Datta, J. Micromethod for the estimation of Cannabis components. Sci. Cult. 1975, 41, 492–495. [Google Scholar]
- Ilias, Y.; Rudaz, S.; Mathieu, P.; Veuthey, J.-L.; Christen, P. Analysis of Cannabis Material by Headspace Solid-Phase Microextraction Combined with Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. Chim. Int. J. Chem. 2004, 58, 219–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Qamar, S.; Manrique, Y.J.; Parekh, H.S.; Falconer, J.R. Development and Optimization of Supercritical Fluid Extraction Setup Leading to Quantification of 11 Cannabinoids Derived from Medicinal Cannabis. Biology 2021, 10, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, J.; Olivares, M.; Amigo, J.M.; Etxebarria, N. Resolution of co-eluting compounds of Cannabis Sativa in comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography/mass spectrometry detection with Multivariate Curve Resolution-Alternating Least Squares. Talanta 2014, 121, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grijó, D.R.; Osorio, I.A.V.; Cardozo-Filho, L. Supercritical Extraction Strategies Using CO2 and Ethanol to Obtain Cannabinoid Compounds from Cannabis Hybrid Flowers. J. CO2 Util. 2019, 30, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micalizzi, G.; Alibrando, F.; Vento, F.; Trovato, E.; Zoccali, M.; Guarnaccia, P.; Dugo, P.; Mondello, L. Development of a Novel Microwave Distillation Technique for the Isolation of Cannabis sativa L. Essential Oil and Gas Chromatography Analyses for the Comprehensive Characterization of Terpenes and Terpenoids, Including Their Enantio-Distribution. Molecules 2021, 26, 1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrini, M.; Marchei, E.; Pacifici, R.; Pichini, S. A rapid and simple procedure for the determination of cannabinoids in hemp food products by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2005, 36, 939–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broséus, J.; Anglada, F.; Esseiva, P. The differentiation of fibre- and drug type Cannabis seedlings by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry and chemometric tools. Forensic Sci. Int. 2010, 200, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra, S.; Radwan, M.M.; Majumdar, C.G.; Church, J.C.; Freeman, T.P.; ElSohly, M.A. New trends in cannabis potency in USA and Europe during the last decade (2008–2017). Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2019, 269, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qureshi, M.N.; Kanwal, F.; Siddique, M.; Akram, M. Estimation of Biologically Active Cannabinoids in Cannabis indica by Gas Chromatography-mass Spectrometry (GC-MS). World Appl. Sci. J. 2012, 19, 918–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pijlman, F.; Rigter, S.; Hoek, J.; Goldschmidt, H.; Niesink, R. Strong increase in total delta-THC in cannabis preparations sold in Dutch coffee shops. Addict. Biol. 2005, 10, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhove, W.; van Damme, P.; Meert, N. Factors determining yield and quality of illicit indoor cannabis (Cannabis spp.) production. Forensic Sci. Int. 2011, 212, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, K.R.; Lindholst, C.; Thylstrup, B.; Kvamme, S.; Reitzel, L.A.; Worm-Leonhard, M.; Englund, A.; Freeman, T.P.; Hesse, M. Changes in the composition of cannabis from 2000–2017 in Denmark: Analysis of confiscated samples of cannabis resin. Exp. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2019, 27, 402–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, N.; Tose, L.; da Silva, S.; Murgu, M.; Kuster, R.; Ortiz, R.; Camargo, F.; Vaz, B.; Lacerda, V., Jr.; Romão, W. Analysis of Isomeric Cannabinoid Standards and Cannabis Products by UPLC-ESI-TWIM-MS: A Comparison with GC-MS and GC × GC-QMS. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2019, 30, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leghissa, A.; Smuts, J.; Qiu, C.; Hildenbrand, Z.L.; Schug, K.A. Detection of cannabinoids and cannabinoid metabolites using gas chromatography with vacuum ultraviolet spectroscopy. Sep. Sci. Plus. 2018, 1, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giese, M.W.; Lewis, M.A.; Giese, L.; Smith, K.M. Method for the Analysis of Cannabinoids and Terpenes in Cannabis. J. AOAC Int. 2015, 98, 1503–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trigg, S. Development of Gas and Liquid Chromatographic Methods for the Separation and Quantification of 11 Cannabinoids. Bachelor Thesis, Murdoch University, Perth, Australia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sherma, J.; Rabel, F. Thin layer chromatography in the analysis of cannabis and its components and synthetic cannabinoids. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2019, 42, 613–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandrioli, M.; Tura, M.; Scotti, S.; Gallina, T. Fast Detection of 10 Cannabinoids by RP-HPLC-UV Method in Cannabis sativa L. Molecules 2019, 24, 2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirav, A.; Neumark, B.; Eren, K.J.M.; Fialkov, A.B.; Tal, N. Cannabis and its cannabinoids analysis by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry with Cold EI. J. Mass Spectrom. 2021, 6, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalska, T.; Sajewicz, M.; Sherma, J. Planar Chromatography—Mass Spectrometry; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Sherma, J.; Fried, B. (Eds.) Handbook of Thin-Layer Chromatography, 3rd ed.; rev.expanded; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- de Carvalho, T.C.; Tosato, F.; Souza, L.M.; Santos, H.; Merlo, B.B.; Ortiz, R.S.; Rodrigues, R.R.T.; Filgueiras, P.R.; França, H.S.; Augusti, R.; et al. Thin layer chromatography coupled to paper spray ionization mass spectrometry for cocaine and its adulterants analysis. Forensic Sci. Int. 2016, 262, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Research Council (U.S.) (Ed.) Strengthening Forensic Science in the United States: A Path Forward; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Hanus, L. Our Experience with Identification and Separation of Compounds from Marijuana (Cannabis Sativa L.) by Thin Layer Chromatography. Acta Univ. Palacki. Olomuc. Fac. Med. 1987, 116, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mano-Sousa, B.J.; Maia, G.A.S.; Lima, P.L.; Campos, V.A.; Negri, G.; Chequer, F.M.D.; Duarte-Almeida, J.M. Color determination method and evaluation of methods for the detection of cannabinoids by thin-layer chromatography (TLC). J. Forensic Sci. 2021, 66, 854–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Buchanan, B.; Zuccolo, J.; Poulin, M.-M.; Gabriele, J.; Baranowski, D.C. A reliable and validated LC-MS/MS method for the simultaneous quantification of 4 cannabinoids in 40 consumer products. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.-H.; Cheng, Y.-Y.; Ye, Z.-L.; Lin, R.-C.; Qian, Z.-Z. Multiple chromatographic fingerprinting and its application to the quality control of herbal medicines. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 555, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Chen, M.; Tong, W. An Approach to Comparative Analysis of Chromatographic Fingerprints for Assuring the Quality of Botanical Drugs. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 2003, 43, 1068–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, B.; Wene, D.; Fan, Z. Qualitative and quantitative measurement of cannabinoids in cannabis using modified HPLC/DAD method. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 146, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, W.; Gul, S.W.; Radwan, M.M.; Wanas, A.S.; Mehmedic, Z.; Khan, I.I.; Sharaf, M.H.M.; ElSohly, M.A. Determination of 11 Cannabinoids in Biomass and Extracts of Different Varieties of Cannabis Using High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. J. AOAC Int. 2015, 98, 1523–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellati, F.; Brighenti, V.; Sperlea, J.; Marchetti, L.; Bertelli, D.; Benvenuti, S. New Methods for the Comprehensive Analysis of Bioactive Compounds in Cannabis sativa L. (hemp). Molecules 2018, 23, 2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Citti, C.; Pacchetti, B.; Vandelli, M.A.; Forni, F.; Cannazza, G. Analysis of cannabinoids in commercial hemp seed oil and decarboxylation kinetics studies of cannabidiolic acid (CBDA). J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 149, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacifici, R.; Marchei, E.; Salvatore, F.; Guandalini, L.; Busardò, F.P.; Pichini, S. Evaluation of cannabinoids concentration and stability in standardized preparations of cannabis tea and cannabis oil by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2017, 55, 1555–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Lewis, M.M.; Bello, A.M.; Wasilewski, E.; Clarke, H.A.; Kotra, L.P. Cannabis sativa (Hemp) Seeds, Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol, and Potential Overdose. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2017, 2, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citti, C.; Ciccarella, G.; Braghiroli, D.; Parenti, C.; Vandelli, M.A.; Cannazza, G. Medicinal cannabis: Principal cannabinoids concentration and their stability evaluated by a high performance liquid chromatography coupled to diode array and quadrupole time of flight mass spectrometry method. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 128, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palermiti, A.; Cafaro, A.; Barco, S.; Bucchioni, P.; Franceschini, P.; Cusato, J.; de Nicolò, A.; Manca, A.; de Vivo, E.D.; Russo, E.; et al. Analysis of Cannabinoids Concentration in Cannabis Oil Galenic Preparations: Harmonization between Three Laboratories in Northern Italy. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carcieri, C.; Tomasello, C.; Simiele, M.; de Nicolò, A.; Avataneo, V.; Canzoneri, L.; Cusato, J.; di Perri, G.; D’Avolio, A. Cannabinoids concentration variability in cannabis olive oil galenic preparations. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2018, 70, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burnier, C.; Esseiva, P.; Roussel, C. Quantification of THC in Cannabis plants by fast-HPLC-DAD: A promising method for routine analyses. Talanta 2019, 192, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peace, M.R.; Butler, K.E.; Wolf, C.E.; Poklis, J.L.; Poklis, A. Evaluation of Two Commercially Available Cannabidiol Formulations for Use in Electronic Cigarettes. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 7, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yangsud, J.; Santasanasuwan, S.; Ahkkarachinoreh, P.; Maha, A.; Madaka, F.; Suksaeree, J.; Songsak, T.; Vutthipong, A.; Monton, C. Stability of cannabidiol, ∆9-tetrahydrocannabinol, and cannabinol under stress conditions. Adv. Tradit. Med. 2021, 21, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deidda, R.; Schelling, C.; Roussel, J.-M.; Dispas, A.; Bleye, C.D.; Ziemons, É.; Hubert, P.; Veuthey, J.-L. The analysis of cannabinoids in cannabis samples by supercritical fluid chromatography and ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography: A comparison study. Anal. Sci. Adv. 2021, 2, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deidda, R.; Coppey, F.; Damergi, D.; Schelling, C.; Coïc, L.; Veuthey, J.-L.; Sacré, P.-Y.; de Bleye, C.; Hubert, P.; Esseiva, P.; et al. New perspective for the in-field analysis of cannabis samples using handheld near-infrared spectroscopy: A case study focusing on the determination of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 202, 114150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciolino, L.A.; Ranieri, T.L.; Taylor, A.M. Commercial cannabis consumer products part 2: HPLC-DAD quantitative analysis of cannabis cannabinoids. Forensic Sci. Int. 2018, 289, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambach, L.; Penitschka, F.; Broillet, A.; König, S.; Weinmann, W.; Bernhard, W. Simultaneous quantification of delta-9-THC, THC-acid A, CBN and CBD in seized drugs using HPLC-DAD. Forensic Sci. Int. 2014, 243, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakshlag, J.J.; Cital, S.; Eaton, S.J.; Prussin, R.; Hudalla, C. Cannabinoid, Terpene, and Heavy Metal Analysis of 29 Over-the-Counter Commercial Veterinary Hemp Supplements. VMRR 2020, 11, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolomeo, F.; Russo, F.; Vandelli, M.A.; Biagini, G.; Capriotti, A.L.; Laganà, A.; Carbone, L.; Gigli, G.; Cannazza, G.; Citti, C. HPLC-UV-HRMS analysis of cannabigerovarin and cannabigerobutol, the two impurities of cannabigerol extracted from hemp. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 203, 114215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brighenti, V.; Licata, M.; Pedrazzi, T.; Maran, D.; Bertelli, D.; Pellati, F.; Benvenuti, S. Development of a new method for the analysis of cannabinoids in honey by means of high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with electrospray ionisation-tandem mass spectrometry detection. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1597, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Wang, Y.-H.; Avula, B.; Radwan, M.M.; Wanas, A.S.; van Antwerp, J.; Parcher, J.F.; ElSohly, M.A.; Khan, I.A. Decarboxylation Study of Acidic Cannabinoids: A Novel Approach Using Ultra-High-Performance Supercritical Fluid Chromatography/Photodiode Array-Mass Spectrometry. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2016, 1, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- mzCloud—Advanced Mass Spectral Database (n.d.). Available online: https://www.mzcloud.org/ (accessed on 28 October 2020).
- Pence, H.E.; Williams, A. ChemSpider: An Online Chemical Information Resource. J. Chem. Educ. 2010, 87, 1123–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, D.S.; Feunang, Y.D.; Marcu, A.; Guo, A.C.; Liang, K.; Vázquez-Fresno, R.; Sajed, T.; Johnson, D.; Li, C.; Karu, N.; et al. HMDB 4.0: The human metabolome database for 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D608–D617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bäckström, B.; Cole, M.D.; Carrott, M.J.; Jones, D.C.; Davidson, G.; Coleman, K. A preliminary study of the analysis of Cannabis by supercritical fluid chromatography with atmospheric pressure chemical ionisation mass spectroscopic detection. Sci. Justice 1997, 37, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wang, Y.-H.; Avula, B.; Radwan, M.M.; Wanas, A.S.; Mehmedic, Z.; van Antwerp, J.; ElSohly, M.A.; Khan, I.A. Quantitative Determination of Cannabinoids in Cannabis and Cannabis Products Using Ultra-High-Performance Supercritical Fluid Chromatography and Diode Array/Mass Spectrometric Detection. J. Forensic Sci. 2017, 62, 602–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Food and Drug Administration. Guidance for Industry PAT—A Framework for Innovative Pharmaceutical Development, Manufacturing, and Quality Assurance; Food and Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths, P.R.; de Haseth, J.A. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectrometry, 2nd ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Borille, B.T.; Marcelo, M.C.A.; Ortiz, R.S.; Mariotti, K.d.; Ferrão, M.F.; Limberger, R.P. Near infrared spectroscopy combined with chemometrics for growth stage classification of cannabis cultivated in a greenhouse from seized seeds. Spectrochim. Acta Part A: Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2017, 173, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez, J.; Francisco, S. Optimization of Cannabis Grows Using Introduction Fourier Transform Mid-Infrared Spectroscopy; Perkin Elmer Inc.: Waltham, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Callado, C.S.; Núñez-Sánchez, N.; Casano, S.; Ferreiro-Vera, C. The potential of near infrared spectroscopy to estimate the content of cannabinoids in Cannabis sativa L.: A comparative study. Talanta 2018, 190, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grekopoulos, J.E. Construction and Validation of Quantification Methods for Determining the Cannabidiol Content in Liquid Pharma-Grade Formulations by Means of Near-Infrared Spectroscopy and Partial Least Squares Regression. Med. Cannabis Cannabinoids 2019, 2, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchateau, C.; Kauffmann, J.; Canfyn, M.; Stévigny, C.; de Braekeleer, K.; Deconinck, E. Discrimination of legal and illegal Cannabis spp. according to European legislation using near infrared spectroscopy and chemometrics. Drug Test. Anal. 2020, 12, 1309–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Fei, B. Medical hyperspectral imaging: A review. J. Biomed. Opt. 2014, 19, 010901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Politi, M.; Peschel, W.; Wilson, N.; Zloh, M.; Prieto, J.M.; Heinrich, M. Direct NMR analysis of cannabis water extracts and tinctures and semi-quantitative data on Δ9-THC and Δ9-THC-acid. Phytochemistry 2008, 69, 562–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, F.L. Shining a new light into molecular workings. Nat. Methods 2011, 8, 385–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, L.; Baltensperger, D.; Kurouski, D. Raman-Based Differentiation of Hemp, Cannabidiol-Rich Hemp, and Cannabis. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 7733–7737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, L.; Filter, C.; Baltensperger, D.; Kurouski, D. Confirmatory non-invasive and non-destructive differentiation between hemp and cannabis using a hand-held Raman spectrometer. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 3212–3216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebersbach, P.; Stehle, F.; Kayser, O.; Freier, E. Chemical fingerprinting of single glandular trichomes of Cannabis sativa by Coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering (CARS) microscopy. BMC Plant Biol. 2018, 18, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lurie, I.S.; Meyers, R.P.; Conver, T.S. Capillary Electrochromatography of Cannabinoids. Anal. Chem. 1998, 70, 3255–3260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peschel, W.; Politi, M. 1 H NMR and HPLC/DAD for Cannabis sativa L. chemotype distinction, extract profiling and specification. Talanta 2015, 140, 150–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isahq, M.S.; Afridi, M.S.; Ali, J.; Hussain, M.M.; Ahmad, S.; Kanwal, F. Proximate composition, phytochemical screening, GC-MS studies of biologically active cannabinoids and antimicrobial activities of Cannabis indica. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Dis. 2015, 5, 897–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uziel, A.; Gelfand, A.; Amsalem, K.; Berman, P.; Lewitus, G.M.; Meiri, D.; Lewitus, D.Y. Full-Spectrum Cannabis Extract Microdepots Support Controlled Release of Multiple Phytocannabinoids for Extended Therapeutic Effect. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 23707–23716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risoluti, R.; Gullifa, G.; Battistini, A.; Materazzi, S. The Detection of Cannabinoids in Veterinary Feeds by MicroNIR/Chemometrics: A New Analytical Platform. Analyst 2020, 145, 1777–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazekamp, A.; Choi, Y.H.; Verpoorte, R. Quantitative Analysis of Cannabinoids from Cannabis sativa Using 1H-NMR. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2004, 52, 718–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Happyana, N.; Agnolet, S.; Muntendam, R.; van Dam, A.; Schneider, B.; Kayser, O. Analysis of cannabinoids in laser-microdissected trichomes of medicinal Cannabis sativa using LCMS and cryogenic NMR. Phytochemistry 2013, 87, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.H.; Kim, H.K.; Hazekamp, A.; Erkelens, C.; Lefeber, A.W.M.; Verpoorte, R. Metabolomic Differentiation of Cannabis sativa Cultivars Using 1H NMR Spectroscopy and Principal Component Analysis. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 953–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Pol, P.; Liebregts, N.; de Graaf, R.; Korf, D.J.; van den Brink, W.; van Laar, M. Validation of Self-Reported Cannabis Dose and Potency: An Ecological Study: Self-Reported Cannabis Dose and Potency. Addiction 2013, 108, 1801–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Pol, P.; Liebregts, N.; Brunt, T.; van Amsterdam, J.; de Graaf, R.; Korf, D.J.; van den Brink, W.; van Laar, M. Cross-Sectional and Prospective Relation of Cannabis Potency, Dosing and Smoking Behaviour with Cannabis Dependence: An Ecological Study: Cannabis Potency, Titration and Dependence. Addiction 2014, 109, 1101–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leghissa, A. Method Development for Qualification and Quantification of Cannabinoids and Terpenes in Extracts by Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. 91. Available online: https://rc.library.uta.edu/uta-ir/handle/10106/26115?show=full (accessed on 8 January 2022).
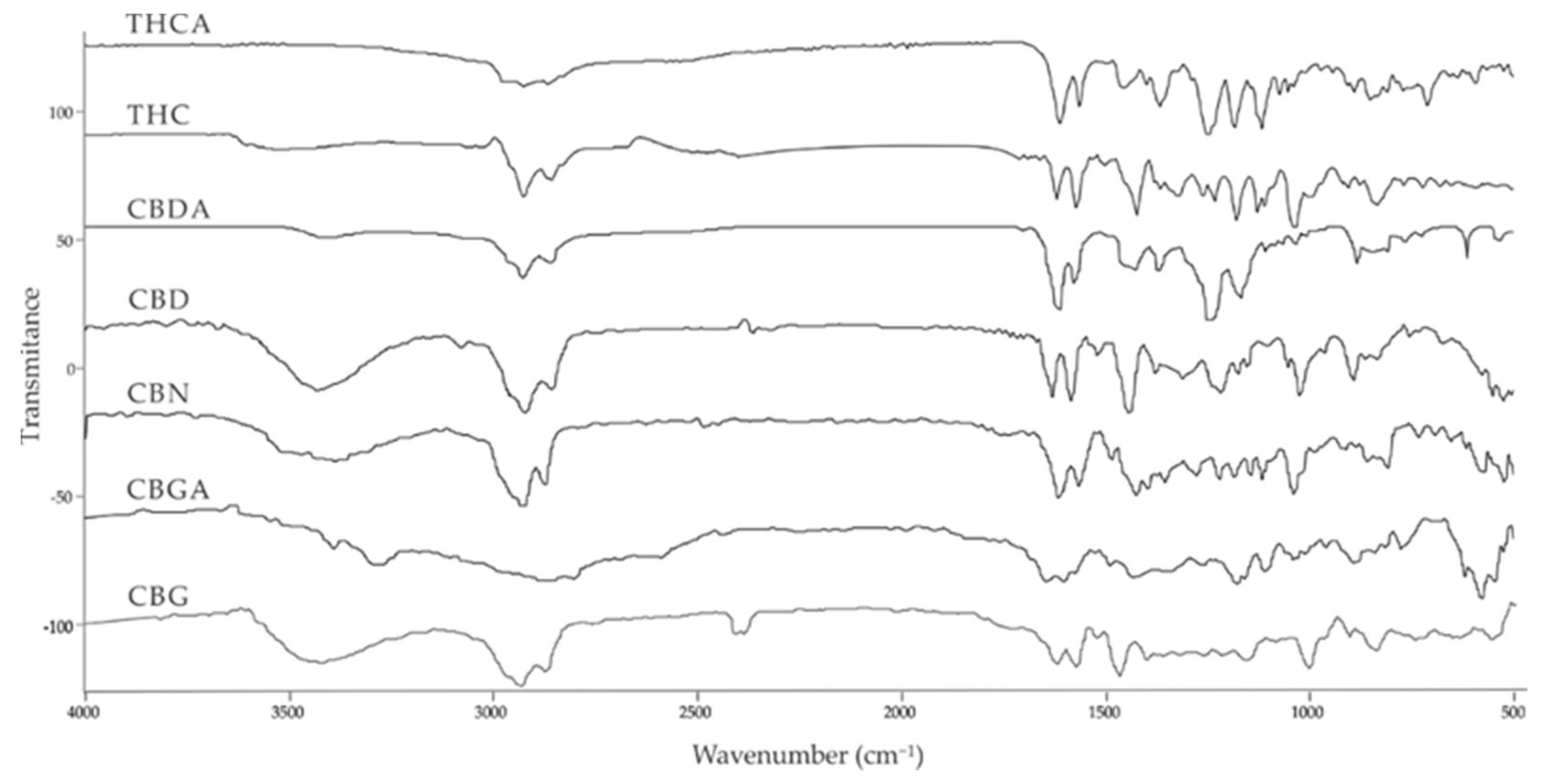
| Compound [18] | Molecular Formula and Mr [18] | [M-H]− [MF1-H]− [MF2-H]− [MF3-H]− [19] | Structure [19] | UV-VIS Spectra [18] Acidic HPLC Systems/ Basic HPLC Systems | 1H NMR in Deuterated Chloroform [4,20] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Δ9-THC | C21H30O2 314.472 | C21H29O2, 313.2173 C16H21O2, 245.1547 C12H15O2, 191.1078 C11H15O22, 179.1067 | 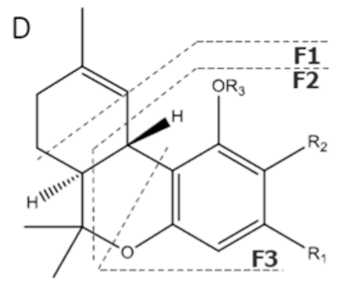 R1-C5H11, R2-H, R3-H | 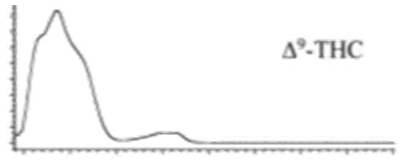 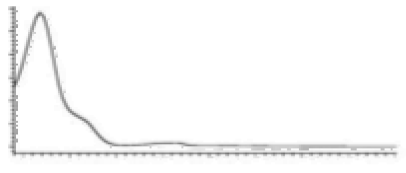 | 3.20 (1H, dm, 10.9 Hz) 6.31 (1H, q, 1.6 Hz) 1.68 (3H, s) 2.16 (2H, m) 1.90 (1H, m), 1.40 (m) 1.69 (m) 1.41 (3H, s) 1.09 (3H, s) 6.14 (1H, d, 1.6Hz) 6.27 (1H, d, 1.6 Hz) 2.42 (2H, t, 7.3 Hz, 1.6 Hz), 1.55 (2H, q, 7.8 Hz) 1.29 (m) 1.29 (m) d 0.87 (3H, t, 7.0 Hz) 4.87 (1H, s) |
| Δ8-THC | C21H30O2 314.472 | C21H29O2, 313.2173 C16H21O2, 245.1547 C12H15O2, 191.1078 C11H15O2, 179.1067 |  - |   | |
| THV | C19H26O2 286.418 | C19H25O2, 285.1860 C14H17O2, 217.1234 C10H11O2, 163.0765 C9H11O2, 151.0765 | 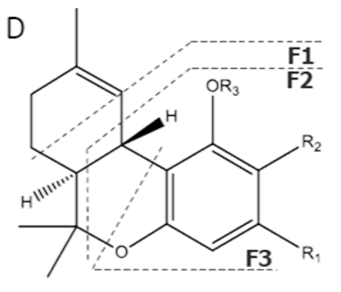 R1-C3H17, R2-H, R3-H | - - | |
| CBD | C21H30O2 314.472 | C21H29O2, 313.2173 C16H21O2, 245.1547 C12H15O2, 191.1078 C11H15O2, 179.1067 | 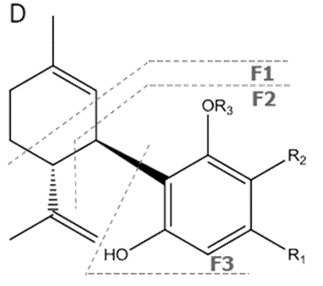 R1-C5H11, R2-H, R3-H | 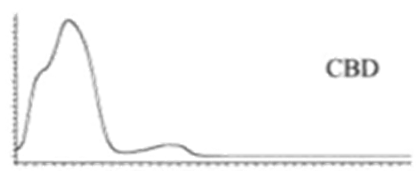 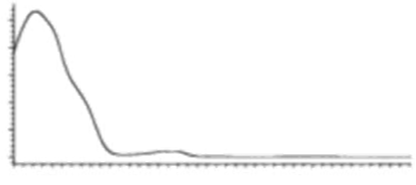 | 3.90 (1H, dm, 11.8Hz) 5.57 (1H, s) 2.21 (1H, m), 2.09 (1H, m) 1.84 (m) 2.40 (m) 1.79 (3H, s) 4.64 (trans, 1H, m), 4.54 (cis, 1H, m) 1.66 (3H, s) 6.26 (1H, brs) 6.16 (1H, brs) 2.43 (2H, t, 7.5Hz) 1.55 (2H, q, 7.6Hz) 1.29 (m) 1.29 (m) 0.88 (3H, t, 6.8Hz) 5.99 (1H, s) 5.02 (1H, s) |
| CBN | C21H26O2 310.440 | C21H25O2, 309.1860 C19H19O2, 279.1391 C12H11O2, 171.0815 | 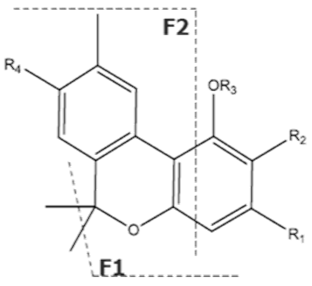 R1-C5H11, R2-H, R3-H, R4-H | 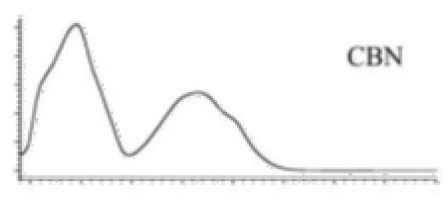 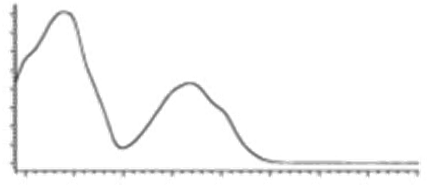 | 8.16 (1H, s) 2.38 (3H, s) 7.07 (1H, d, 7.9Hz) 7.14 (1H, d, 7.9Hz) 1.60 (6H, s) 1.60 (6H, s) 6.29 (1H, d, 1.1Hz) 6.44 (1H, d, 1.1Hz) 2.50 (2H, t, 7.5Hz) 1.63 (m) 1.32 (m) g 1.32 (m) g 0.89 (3H, t, 6.8Hz)5.13 (1H, s) |
| CBG | C21H32O2 316.488 | C21H31O2, 315.2329 C16H21O2, 245.1547 C12H15O2, 191.1078 C11H15O2, 179.1067 | 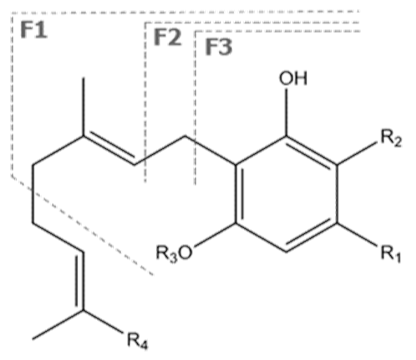 R1-C5H11, R2-H, R3-H, R4-H | 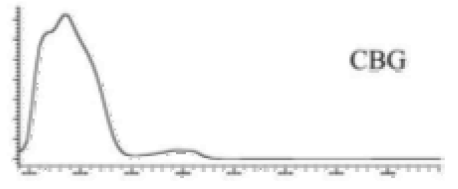 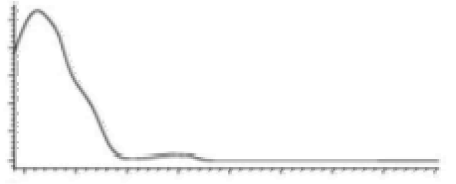 | 6.26 (2H, s) d 6. (2H, s) d 3.41 (2H, d, 7.0 Hz) 5.29 (1H, m) 1.82 (3H, s) 2.09 (4H, m) 2.09 (4H, m) 5.07 (1H, m) 1.60 (3H, s) 1.69 (3H, s) 2.45 (2H, t, 7.5 Hz) 1.56 (2H, q, 7.8 Hz) 1.33 (4H, m) 1.33 (4H, m) 0.90 (3H, t, 6.9 Hz) 5.36 (2H, s) |
| CBC | C21H30O2 314.172 | C12H29O2, 313.2173 C16H19O2, 243.1391 C12H15O2, 191.1078 C11H15O2, 179.1067 | 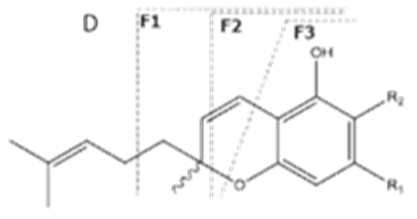 R1-C5H11, R2-H | 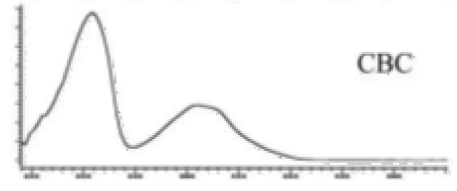  | N/A |
| CBL | C21H30O2 314.472 | C21H29O2, 313.2173 C16H19O2, 243.1391 C12H15O2, 191.1078 C11H15O2, 179.1067 | 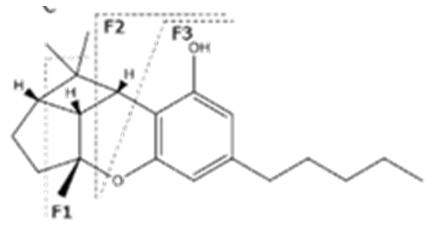 | N/A | N/A |
| Δ9-THCA | C22H30O24 358.482 | C22H29O4, 357.2071 C21H30O2, 245.1547 C12H15O2, 191.1078 C11H15O22, 179.1067 |  R1-C5H11, R2-COOH, R3-H | 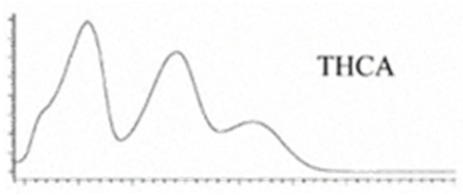 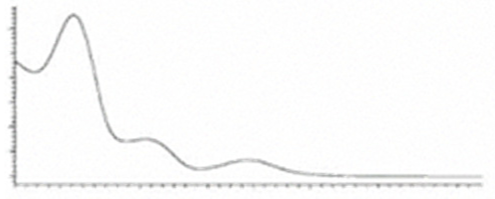 | 3.23 (1H, dm, 7.0 Hz), 6.39(1H, brs), 1.68 (3H, s), 2.17 (2H, m) 1.92 (1H, m) 1.35 (m) 1.67 (m) 1.44 (3H, s) 1.11 (3H, s) 6.26 (1H, s) 2.94 (1H, m) 2.78 (1H, m) 1.57 (2H, 1.35 (m) 1.35 (m) 0.90 (3H, t, 6.9 Hz) 12.19 (1H, s) |
| Δ9-THCA-C4 | C21H28O4 344.455 | C21H27O4, 343.1915 C15H19O2, 231.1391 C11H13O2, 177.0921 C10H13O2, 165.0921 | 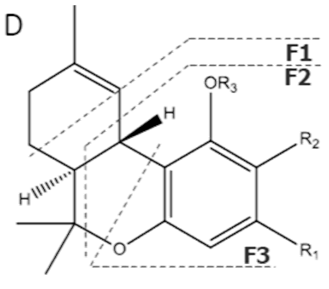 R1-C4H9, R2-COOH, R3-H | 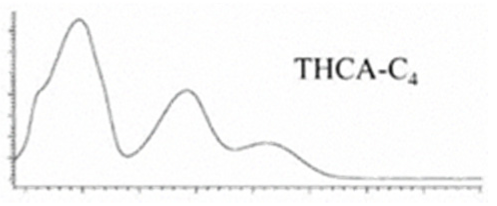 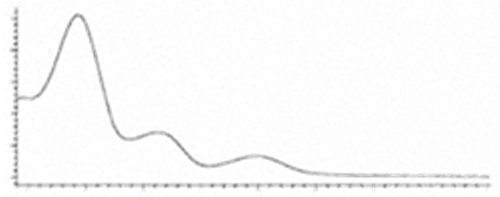 | N/A |
| THVA | C20H26O4 330.428 | C20H25O4, 329.1758 C14H17O2, 217.1234 C10H11O2, 163.0765 C9H11O2, 151.0765 | 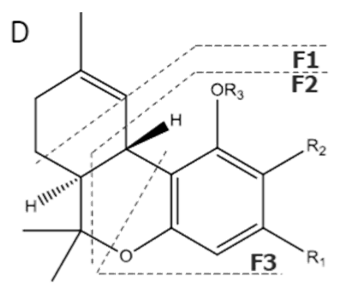 R1-C3H7, R2-COOH, R3-H |   | N/A |
| CBDA | C22H30O4 358.482 | C22H29O4, 357.2071 C16H2102, 245.1547 C12H1502, 191.1078 C11H1502, 179.1067 | 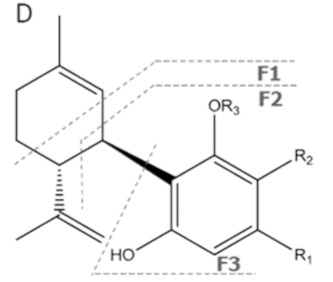 R1-C5H11, R2-COOH, R3-H |  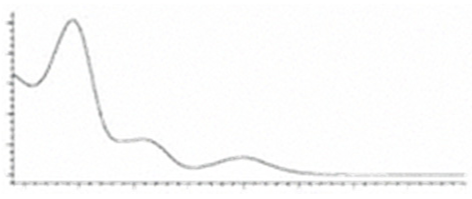 | N/A |
| CBNA | C22H26O4 354.450 | C22H25O4, 353.175 C19H1902, 279.1391 C12H1102, 171.0815 C21H2502, 309.1860 | 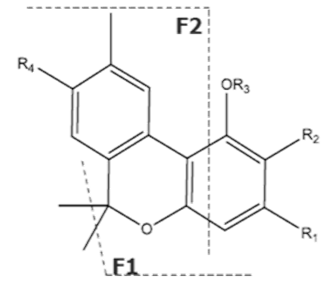 R1-C5H11, R2-COOH, R3-H, R4-H | 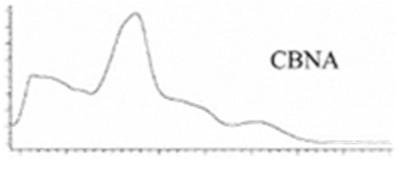 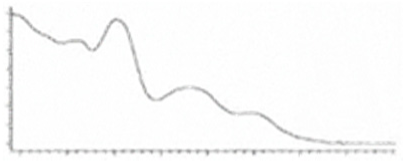 | N/A |
| CBGA | C22H32O4 360.498 | C22H31O4, 359.2228 C16H21O2, 245.1547 C12H15O2, 191.1078 C11H15O2, 179.1067 | 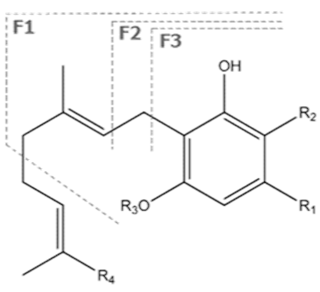 R1-C5H11, R2-COOH, R3-H, R4-H | 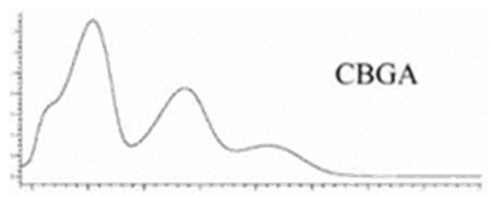 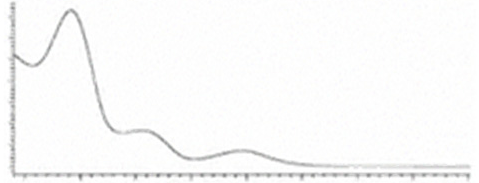 | N/A |
| CBCA | C22H30O4 358.482 | C22H29O4, 357.2071 C16H19O2, 243.1391 C12H15O2, 191.1078 C11H15O2, 179.1067 | R1-C5H11, R2-COOH,  | 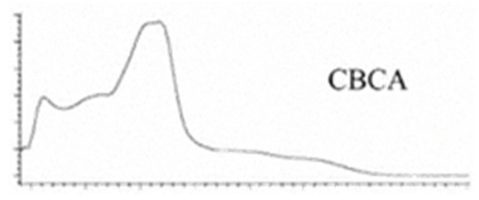 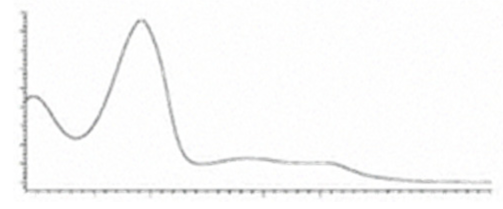 | N/A |
| CBLA | C22H30O4 358.482 | - - - - | 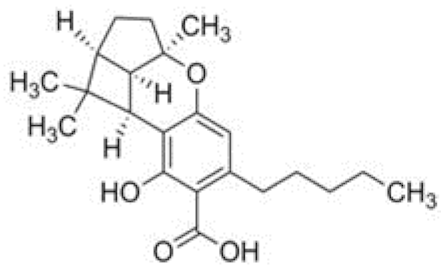 |  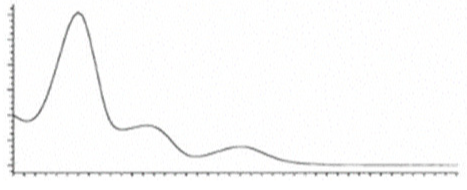 | N/A |
| Sample Preparation Technique | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| LLE |
|
|
| PLE |
|
|
| HS-SPME |
|
|
| SFE |
|
|
| FUSE, UAE |
|
|
| SPE |
|
|
| MHD |
|
|
| CPE |
|
|
| CPC |
|
|
| Solvent/Solvent Mixture | References |
|---|---|
| MeCN | [89,90] |
| MeCN + 1% acetic acid | [65] |
| MeCN saturated with n-hexane | [91] |
| MeOH | [38,42,50,54,56,68,78,79,85,89,92,93,94,95,96,97,98,99,100,101] |
| absolute ethanol (99.7%, v/v) | [10,49,51,53,66,90,102,103,104,105,106,107,108] |
| EtOH(96%, v/v) | [40,54,55,66,90,92,100,109,110,111,112,113] |
| isopropanol | [63,108] |
| cyclohexane | [82,114] |
| EtAc | [69,89,115,116,117] |
| CHCl3 | [44,52,58,77,118,119,120] |
| n-hexane | [40,47,54,66,75,76,78,86,87,101,121,122,123,124,125] |
| light petroleum | [46] |
| petroleum ether | [126,127,128] |
| toluene | [129] |
| benzene | [130] |
| CCl4 (later evaporated and extracts reconstituted in chloroform) | [131] |
| MeCN/MeOH (8:2, v/v) | [132] |
| hexane/isopropanol (9:1, v/v) | [57,94,106,133] |
| hexane/EtAc (9:1, v/v), (7:3, v/v), (6:4, v/v) | [54,57,66,94,104] |
| hexane/CHCl3 (1:1, v/v) | [134,135] |
| MeOH/CHCl3 (4:1, v/v) | [48,136] |
| MeOH/CHCl3 (9:1, v/v), (99:1, v/v) | [57,67,86,106,137] |
| MeOH/hexane (9:1, v/v) | [138] |
| petroleum ether/MeOH (9:1, v/v) | [45] |
| EtOH/H2O (1:1, v/v) | [133] |
| KOH in MeOH and hexane/EtAc (9:1, v/v) | [139] |
| IS (tribenzylamine) in 96% EtOH | [57] |
| IS (tribenzylamine) in MeCN | [140] |
| IS (nonadecane) in EtOH | [138] |
| IS (diphenylhydramine) in EtOH | [74] |
| IS (4-androstene-3,17-dione) in EtOH | [9,137] |
| IS (docosane) in petroleum ether | [128,141] |
| IS (nonadecane) in MeOH/CHCl3 (9:1, v/v) | [67] |
| IS (squalane) in hexane | [76,89,142] |
| IS (chrysene-d12) in hexane | [71] |
| IS (ketamine hydrochloride) in MeCN | [124] |
| IS (4-androstene-3,17-dione) in MeOH/CHCl3 (9:1, v/v) | [9,75,86,87,143,144,145] |
| Analytical Techniques | Advantages | Disadvantages | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| GC-FID |
|
|
|
| GC-MSD |
|
| / |
| GC-QQQ/QTOF |
| / | / |
| (HP)TLC |
|
|
|
| HPLC-UV/DAD |
|
| / |
| HPLC-QQQ |
|
|
|
| HPLC-Q-Exactive Orbitrap® |
| ||
| SFC |
|
| / |
| NMR |
|
| / |
| RAMAN |
| / | / |
| FTIR, NIR, MIR |
|
| / |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stefkov, G.; Cvetkovikj Karanfilova, I.; Stoilkovska Gjorgievska, V.; Trajkovska, A.; Geskovski, N.; Karapandzova, M.; Kulevanova, S. Analytical Techniques for Phytocannabinoid Profiling of Cannabis and Cannabis-Based Products—A Comprehensive Review. Molecules 2022, 27, 975. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27030975
Stefkov G, Cvetkovikj Karanfilova I, Stoilkovska Gjorgievska V, Trajkovska A, Geskovski N, Karapandzova M, Kulevanova S. Analytical Techniques for Phytocannabinoid Profiling of Cannabis and Cannabis-Based Products—A Comprehensive Review. Molecules. 2022; 27(3):975. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27030975
Chicago/Turabian StyleStefkov, Gjoshe, Ivana Cvetkovikj Karanfilova, Veronika Stoilkovska Gjorgievska, Ana Trajkovska, Nikola Geskovski, Marija Karapandzova, and Svetlana Kulevanova. 2022. "Analytical Techniques for Phytocannabinoid Profiling of Cannabis and Cannabis-Based Products—A Comprehensive Review" Molecules 27, no. 3: 975. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27030975
APA StyleStefkov, G., Cvetkovikj Karanfilova, I., Stoilkovska Gjorgievska, V., Trajkovska, A., Geskovski, N., Karapandzova, M., & Kulevanova, S. (2022). Analytical Techniques for Phytocannabinoid Profiling of Cannabis and Cannabis-Based Products—A Comprehensive Review. Molecules, 27(3), 975. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27030975








